NISSAN TERRANO 2002 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2002, Model line: TERRANO, Model: NISSAN TERRANO 2002Pages: 1767, PDF Size: 41.51 MB
Page 671 of 1767
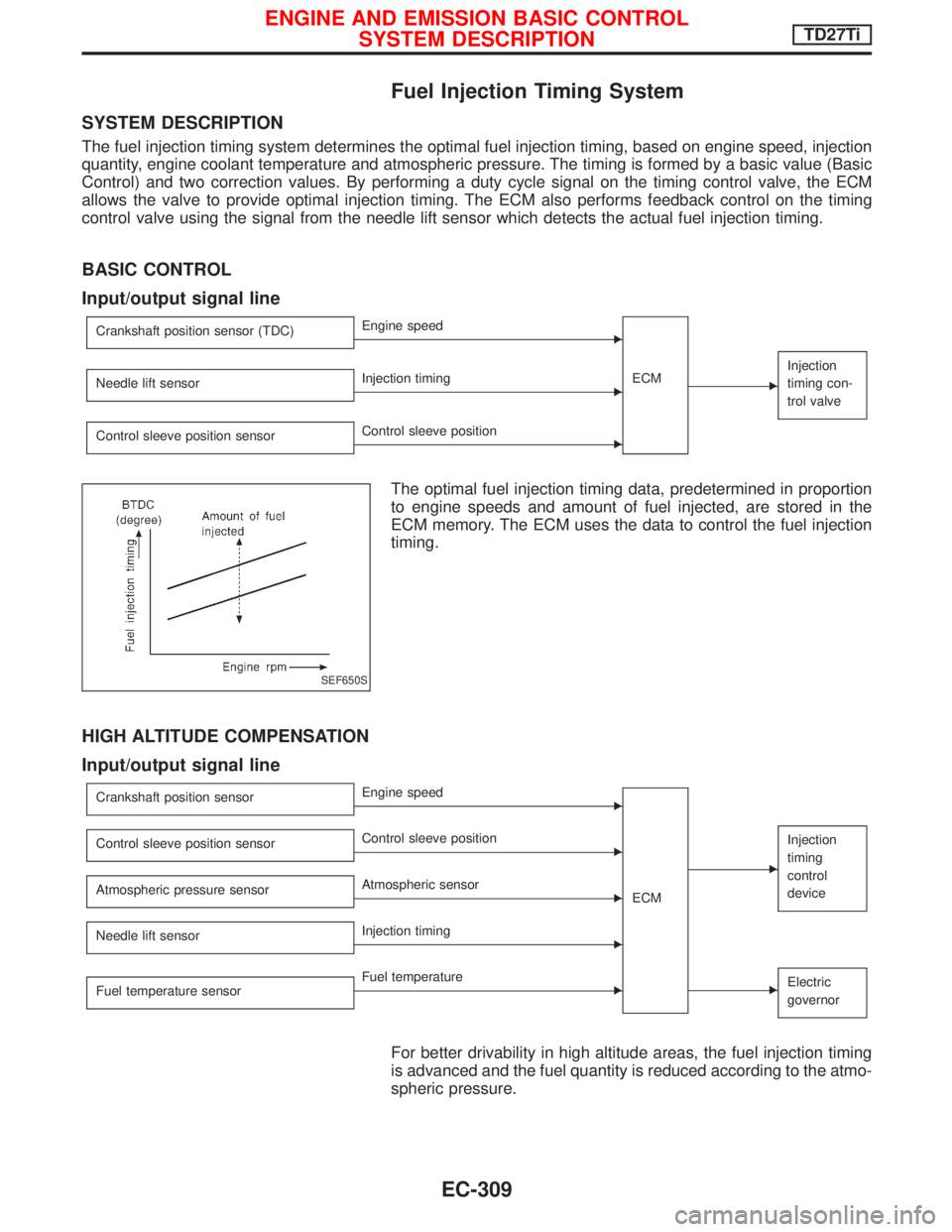
Fuel Injection Timing System
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The fuel injection timing system determines the optimal fuel injection timing, based on engine speed, injection
quantity, engine coolant temperature and atmospheric pressure. The timing is formed by a basic value (Basic
Control) and two correction values. By performing a duty cycle signal on the timing control valve, the ECM
allows the valve to provide optimal injection timing. The ECM also performs feedback control on the timing
control valve using the signal from the needle lift sensor which detects the actual fuel injection timing.
BASIC CONTROL
Input/output signal line
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
ECM
E
Injection
timing con-
trol valve
Needle lift sensorEInjection timing
Control sleeve position sensor
EControl sleeve position
The optimal fuel injection timing data, predetermined in proportion
to engine speeds and amount of fuel injected, are stored in the
ECM memory. The ECM uses the data to control the fuel injection
timing.
HIGH ALTITUDE COMPENSATION
Input/output signal line
Crankshaft position sensorEEngine speed
ECM
E
Injection
timing
control
deviceControl sleeve position sensorEControl sleeve position
Atmospheric pressure sensor
EAtmospheric sensor
Needle lift sensor
EInjection timing
Fuel temperature sensor
EFuel temperatureEElectric
governor
For better drivability in high altitude areas, the fuel injection timing
is advanced and the fuel quantity is reduced according to the atmo-
spheric pressure.
SEF650S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
EC-309
Page 672 of 1767
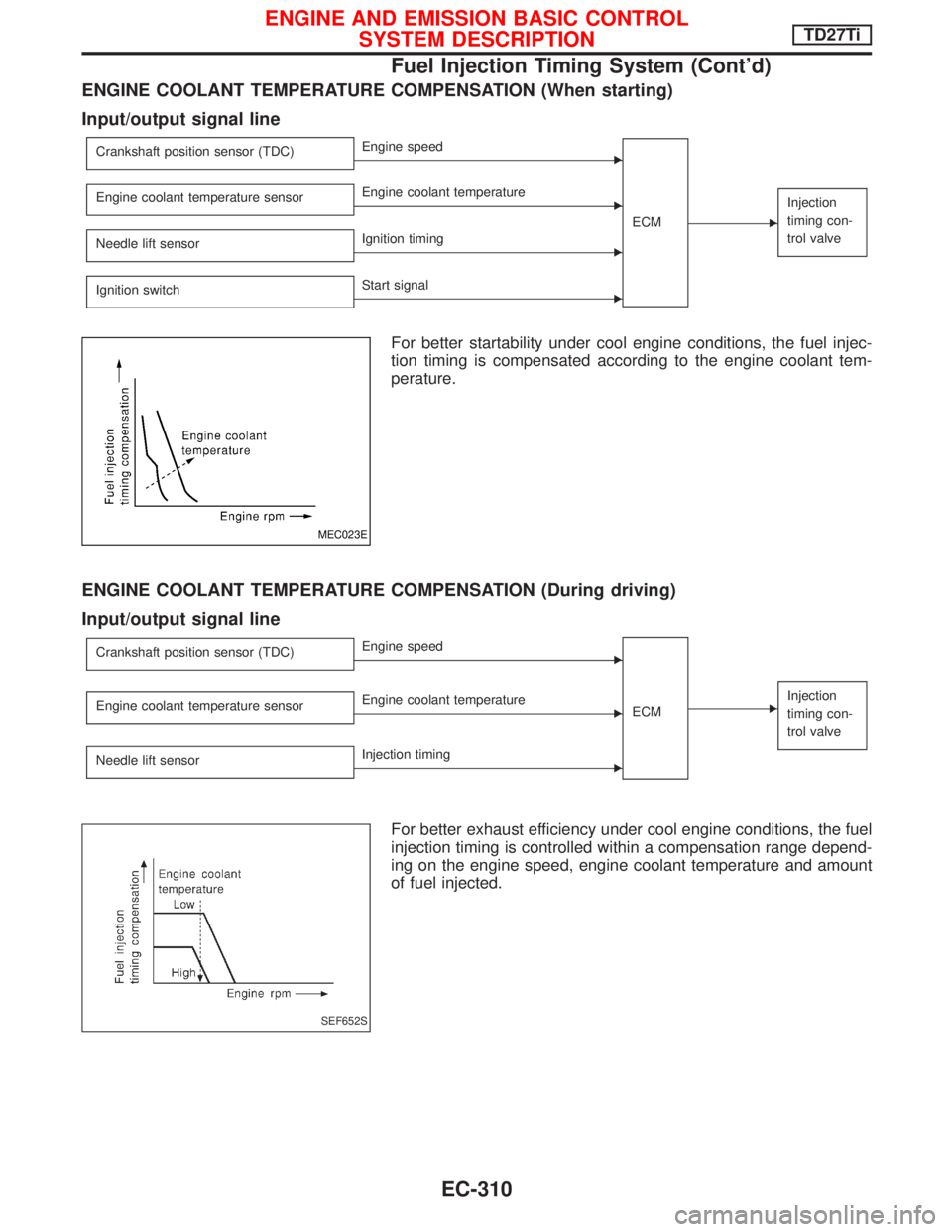
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION (When starting)
Input/output signal line
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
ECM
E
Injection
timing con-
trol valveEngine coolant temperature sensorEEngine coolant temperature
Needle lift sensor
EIgnition timing
Ignition switch
EStart signal
For better startability under cool engine conditions, the fuel injec-
tion timing is compensated according to the engine coolant tem-
perature.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION (During driving)
Input/output signal line
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
ECM
EInjection
timing con-
trol valveEngine coolant temperature sensorEEngine coolant temperature
Needle lift sensor
EInjection timing
For better exhaust efficiency under cool engine conditions, the fuel
injection timing is controlled within a compensation range depend-
ing on the engine speed, engine coolant temperature and amount
of fuel injected.
MEC023E
SEF652S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
Fuel Injection Timing System (Cont'd)
EC-310
Page 673 of 1767
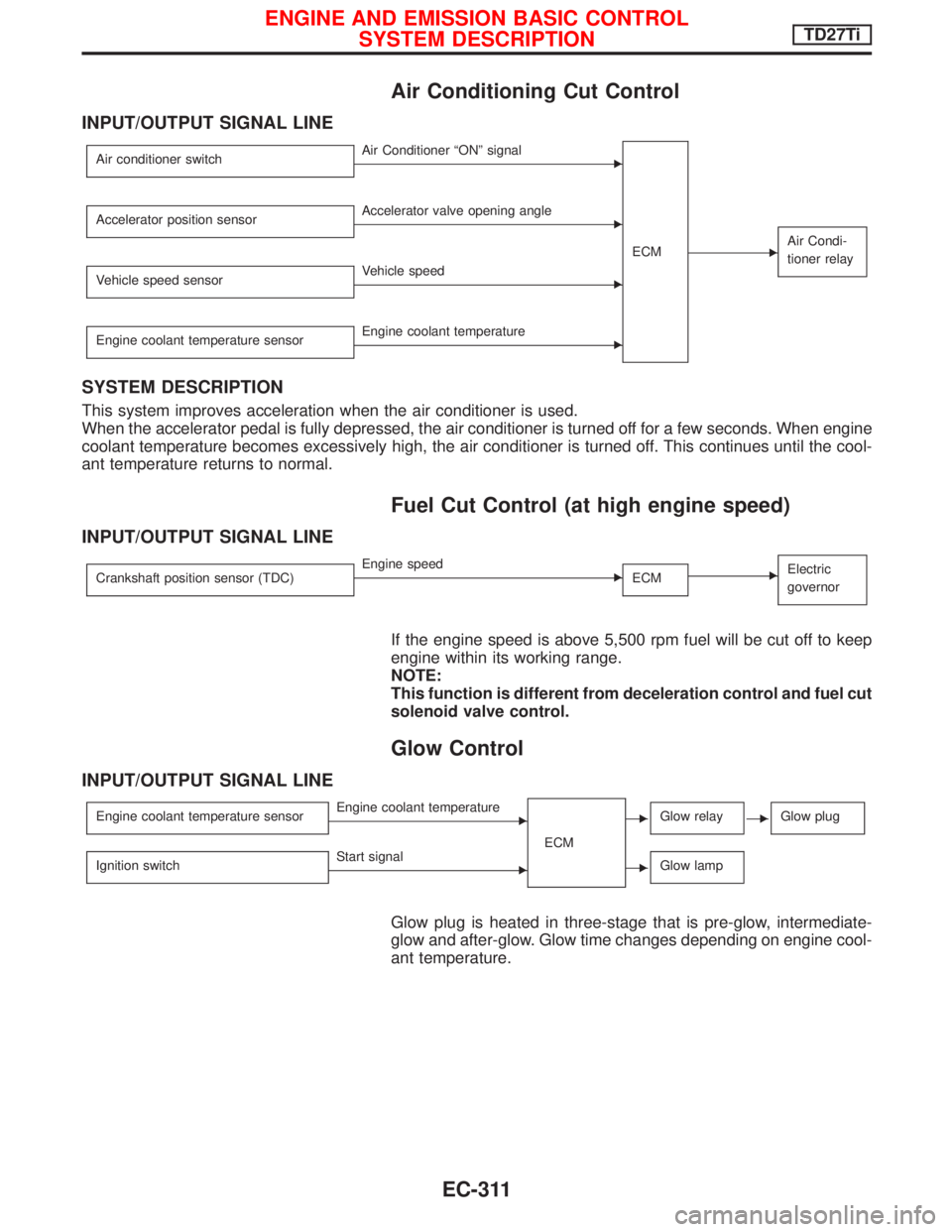
Air Conditioning Cut Control
INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
Air conditioner switchEAir Conditioner ªONº signal
ECM
EAir Condi-
tioner relay
Accelerator position sensorEAccelerator valve opening angle
Vehicle speed sensor
EVehicle speed
Engine coolant temperature sensor
EEngine coolant temperature
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
This system improves acceleration when the air conditioner is used.
When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, the air conditioner is turned off for a few seconds. When engine
coolant temperature becomes excessively high, the air conditioner is turned off. This continues until the cool-
ant temperature returns to normal.
Fuel Cut Control (at high engine speed)
INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
ECMEElectric
governor
If the engine speed is above 5,500 rpm fuel will be cut off to keep
engine within its working range.
NOTE:
This function is different from deceleration control and fuel cut
solenoid valve control.
Glow Control
INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
Engine coolant temperature sensorEEngine coolant temperature
ECMEGlow relayEGlow plug
Ignition switchEStart signalEGlow lamp
Glow plug is heated in three-stage that is pre-glow, intermediate-
glow and after-glow. Glow time changes depending on engine cool-
ant temperature.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
EC-311
Page 674 of 1767

Description
IIn this system blow-by gas is sucked into the air inlet pipe
through the control valve after oil separation by oil separator.
Blow-by Control Valve
ICheck control valve for clogging and abnormalities.
Ventilation Hose
1. Check hoses and hose connections for leaks.
2. Disconnect all hoses and clean with compressed air. If any
hose cannot be freed of obstructions, replace.
NEF760
MEC971D
NEF762
SEC692
CRANKCASE VENTILATION SYSTEMTD27Ti
EC-312
Page 675 of 1767

CAUTION:
IDo not disassemble No. 1 nozzle (with needle lift sensor).
Entrust disassembly or adjustment to BOSCH service
shop.
Plug flare nut with a cap or rag so that no dust enters the
nozzle. Cover nozzle tip for protection of needle.
Removal and Installation
1. Remove fuel injection tube and spill tube.
2. Remove injection nozzle assembly.
Also remove washers from nozzle end.
3. Install injection nozzle in the reverse order of removal.
Injection nozzle to engine:
:54-64N×m (5.5 - 6.5 kg-m, 40 - 47 ft-lb)
Injection nozzle to tube:
:20-25N×m (2.0 - 2.5 kg-m, 14 - 18 ft-lb)
a. Always clean the nozzle holes.
b. Always use new injection nozzle gasket.
c. Note that small washer should be installed in specified
direction.
d. Bleed air from fuel system.
Disassembly (No.2-4nozzle)
1. Loosen nozzle nut while preventing nozzle top from turning.
2. Arrange all disassembled parts in the order shown at left.
SEM621B
NEM244
NEF459
SEF785
MEC996D
INJECTION NOZZLETD27Ti
EC-313
Page 676 of 1767

Inspection (No.2-4nozzle)
Thoroughly clean all disassembled parts with fresh kerosene or
solvent.
IIf nozzle needle is damaged or fused, replace nozzle assem-
bly with a new one.
IIf end of nozzle needle is seized or excessively discolored,
replace nozzle assembly.
ICheck nozzle body and distance piece for proper contact. If
excessively worn or damaged, replace nozzle assembly or dis-
tance piece.
ICheck nozzle spring for excessive wear or damage. If exces-
sively worn or damaged, replace it with a new spring.
ICheck distance piece and nozzle holder for proper contact. If
excessively worn or damaged, replace nozzle holder assembly.
Cleaning (No.2-4nozzle)
a. Do not touch the nozzle mating surface with your fingers.
b. To wash the nozzles, use a wooden stick and brass brush
with clean diesel fuel.
1. Remove any carbon from exterior of nozzle body (except wrap-
ping angle portion) by using Tool.
2. Clean oil sump of nozzle body using Tool.
3. Clean nozzle seat by using Tool.
Take extra precautions when performing this job, since nozzle
efficiency depends greatly on a good nozzle seat.
SEF830
YEC231A
SEF832
INJECTION NOZZLETD27Ti
EC-314
Page 677 of 1767
4. Clean spray hole of nozzle body by using Tool.
To prevent spray hole from canting, always clean it by start-
ing with inner side and working towards the outside.
5. Decarbonate nozzle needle tip by using Tool.
6. Check needle sink.
(1) Pull needle about halfway out from body and then release it.
(2) Needle should sink into body very smoothly from just its own
weight.
(3) Repeat this test and rotate needle slightly each time.
If needle fails to sink smoothly from any position, replace both
needle and body as a unit.
Assembly (No.2-4nozzle)
Assembly is in the reverse order of disassembly.
Holder to nozzle nut:
:29-49N×m (3.0 - 5.0 kg-m, 22 - 36 ft-lb)
SEF833
SEF834
SEF835
SEF967
INJECTION NOZZLETD27Ti
Cleaning (No.2-4nozzle) (Cont'd)
EC-315
Page 678 of 1767

Test and Adjustment
WARNING:
When using nozzle tester, be careful not to allow diesel fuel
sprayed from nozzle to contact your hands or body, and make
sure your eyes are properly protected with goggles.
INJECTION PRESSURE TEST
1. Install nozzle to injection nozzle tester and bleed air from flare
nut.
2. Pump the tester handle slowly (once per second) and watch the
pressure gauge.
3. Read the pressure gauge when the injection pressure just
starts dropping.
Initial injection pressure:
Used
12,259 - 12,749 kPa (122.6 - 127.5 bar,
120 - 130 kg/cm
2, 1,706 - 1,849 psi)
New
12,749 - 13,730 kPa (127.5 - 137.3 bar,
130 - 140 kg/cm
2, 1,849 - 1,991 psi)
Always check initial injection pressure using a new nozzle.
4. To adjust injection pressure, change adjusting shims. (No. 2 -
4 nozzle)
a. Increasing the thickness of adjusting shims increases ini-
tial injection pressure. Decreasing thickness reduces ini-
tial pressure.
b. A shim thickness of 0.04 mm (0.0016 in) corresponds
approximately to a difference of 471 kPa (4.71 bar, 4.8
kg/cm
2, 68 psi) in initial injection pressure.
Refer to SDS for adjusting shim.
EF791A
SEF672A
SEF427F
INJECTION NOZZLETD27Ti
EC-316
Page 679 of 1767

LEAKAGE TEST
1. Maintain the pressure at about 981 to 1,961 kPa (9.8 to 19.6
bar, 10 to 20 kg/cm2, 142 to 284 psi) below initial injection
pressure.
2. Check that there is no dripping from the nozzle tip or around the
body.
3. If there is leakage, replace nozzle assembly.
SPRAY PATTERN TEST
1. Check spray pattern by pumping tester handle one full stroke
per second.
a. If main spray angle is within 30 degrees as shown, injec-
tion nozzle is good.
b. It is still normal even if a thin stream of spray deviates from
the main spray (pattern B).
2. If the spray pattern is not correct, disassemble and clean
nozzle.
3. Test again and if spray pattern is not corrected, replace nozzle.
SEF674A
SEF079S
INJECTION NOZZLETD27Ti
Test and Adjustment (Cont'd)
EC-317
Page 680 of 1767

q1Electric fuel injection pump
q
2Key
q
3Bracketq
4Injection pump drive gear
q
5Dust cover
q
6Bracketq
7Gasket
q
8Gasket
Removal
1. Remove battery.
Disconnect electronic injection pump harness connectors.
2. Set No. 1 piston at TDC on its compression stroke.
3. Remove fuel hoses (supply, return and spill) and injection
tubes.
NEF460
EEF181
ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION PUMPTD27Ti
EC-318