NISSAN TERRANO 2002 Service Repair Manual
TERRANO 2002
NISSAN
NISSAN
https://www.carmanualsonline.info/img/5/57393/w960_57393-0.png
NISSAN TERRANO 2002 Service Repair Manual
Trending: manual radio set, fuel cap release, key, door lock, radiator, oil filter, check engine light
Page 661 of 1767
IIf MI illuminates or flashes irregularly while the engine is
running, water may have accumulated in fuel filter. Drain
water from fuel filter. If this does not correct the problem,
perform specified trouble diagnostic procedures.
IAfter performing each TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS, perform
ªOVERALL FUNCTION CHECKº or ªDTC (Diagnostic
Trouble Code) CONFIRMATION PROCEDUREº.
The DTC should not be displayed in the ªDTC CONFIRMA-
TION PROCEDUREº if the repair is successful. The ªOVER-
ALL FUNCTION CHECKº should indicate a good result if
the repair is completed successfully.
IWhen measuring ECM signals with a circuit tester, never
allow the two tester probes to contact.
Accidental contact of probes will cause a short circuit and
damage the ECM power transistor.
SAT652J
SEF348N
PRECAUTIONS AND PREPARATIONTD27Ti
Precautions (Cont'd)
EC-299
Page 662 of 1767
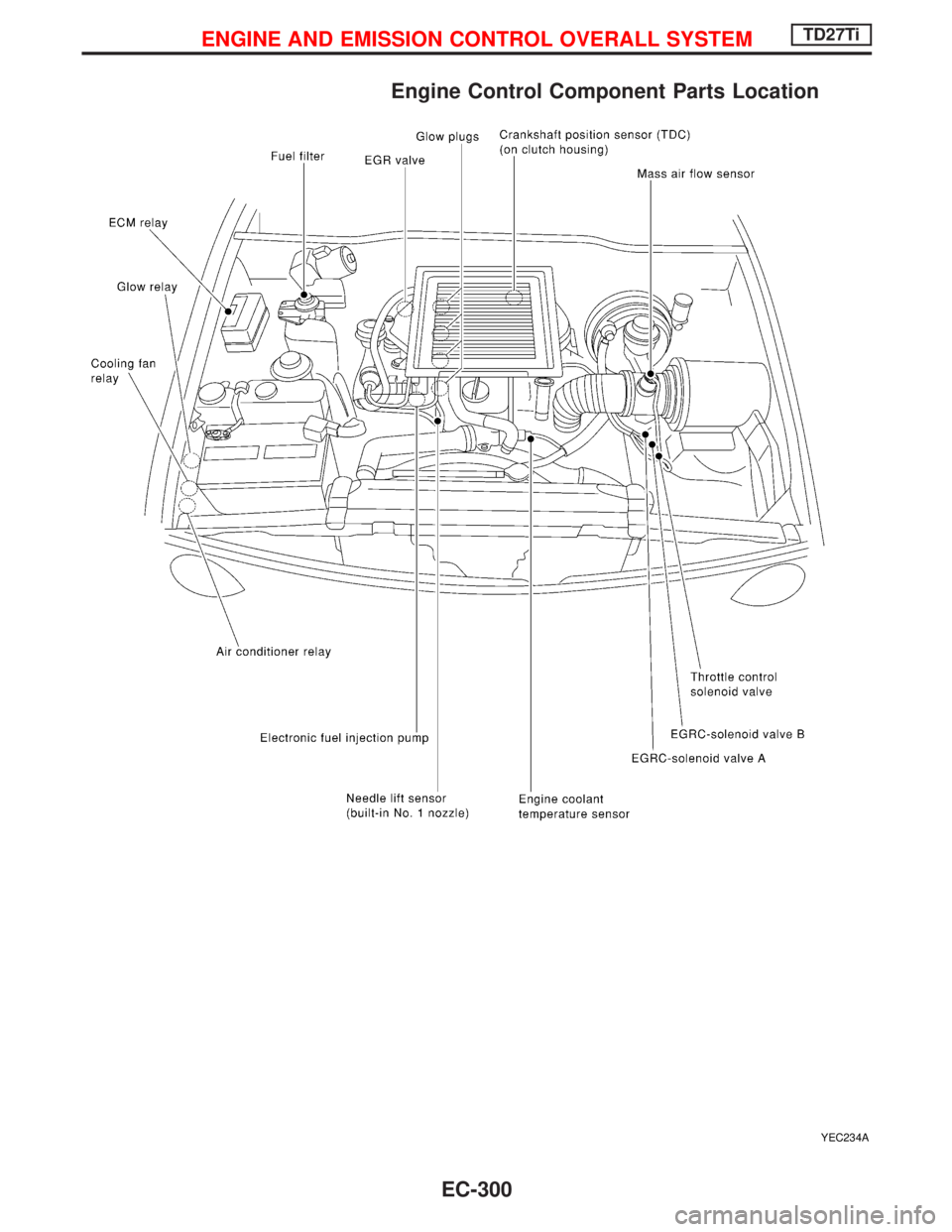
Engine Control Component Parts Location
YEC234A
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMTD27Ti
EC-300
Page 663 of 1767
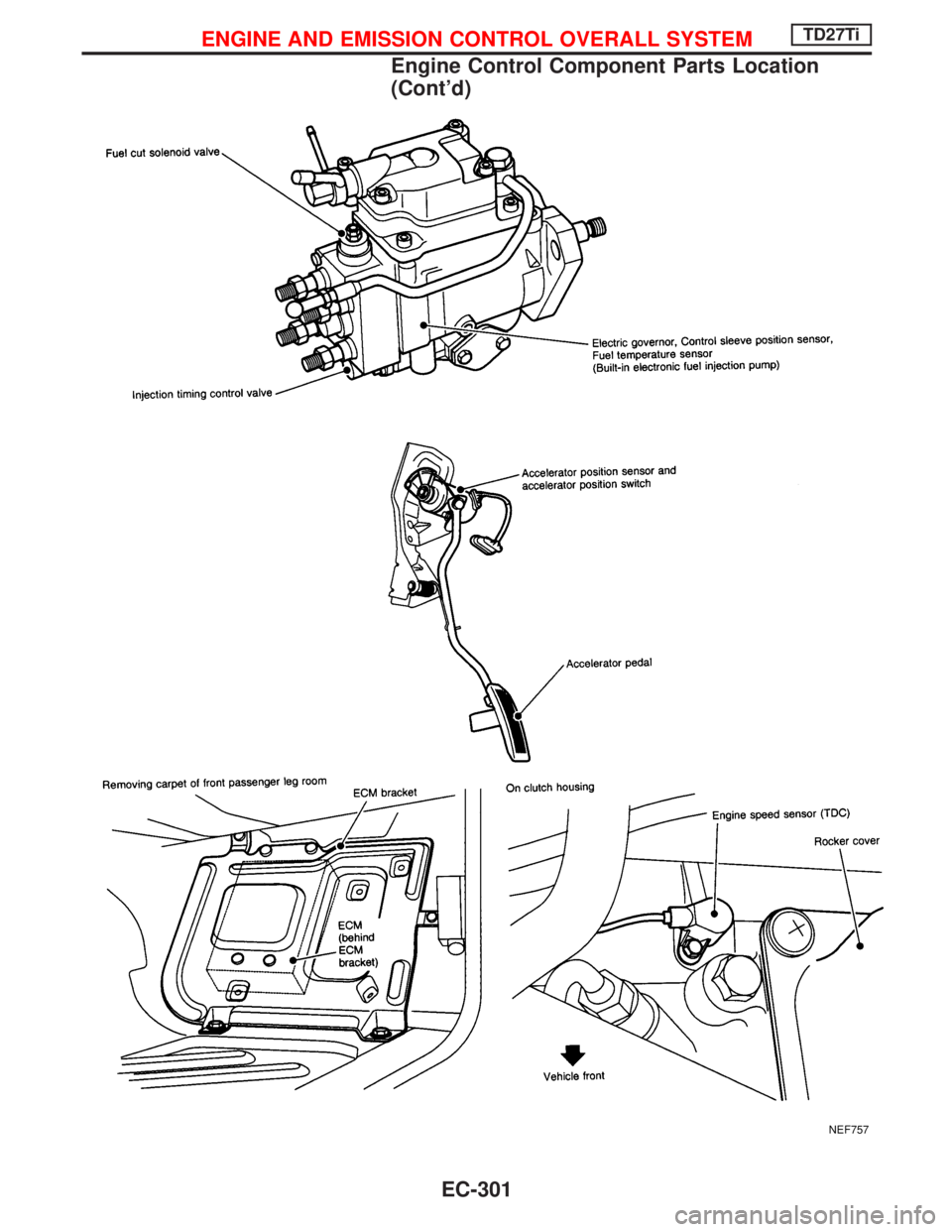
NEF757
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMTD27Ti
Engine Control Component Parts Location
(Cont'd)
EC-301
Page 664 of 1767
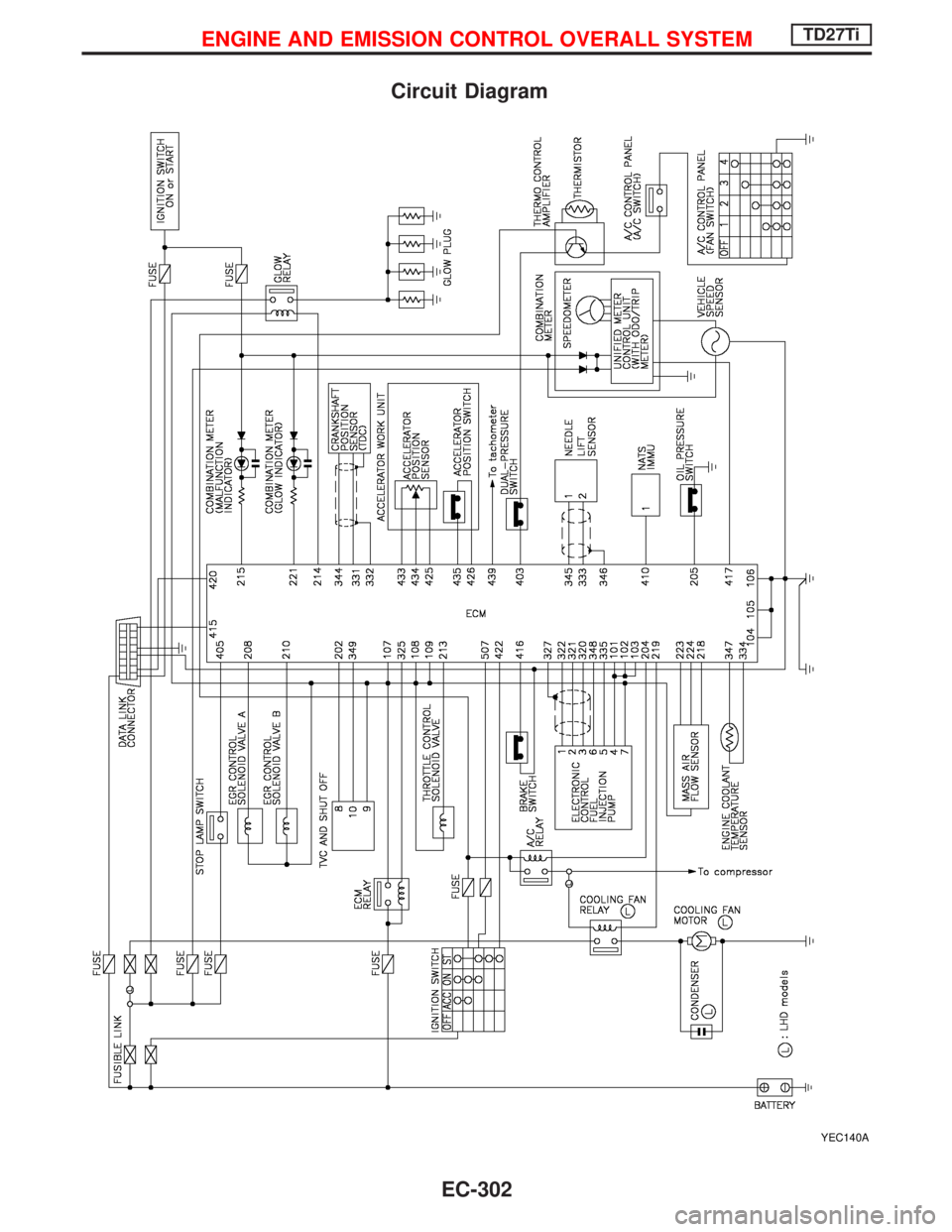
Circuit Diagram
YEC140A
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMTD27Ti
EC-302
Page 665 of 1767
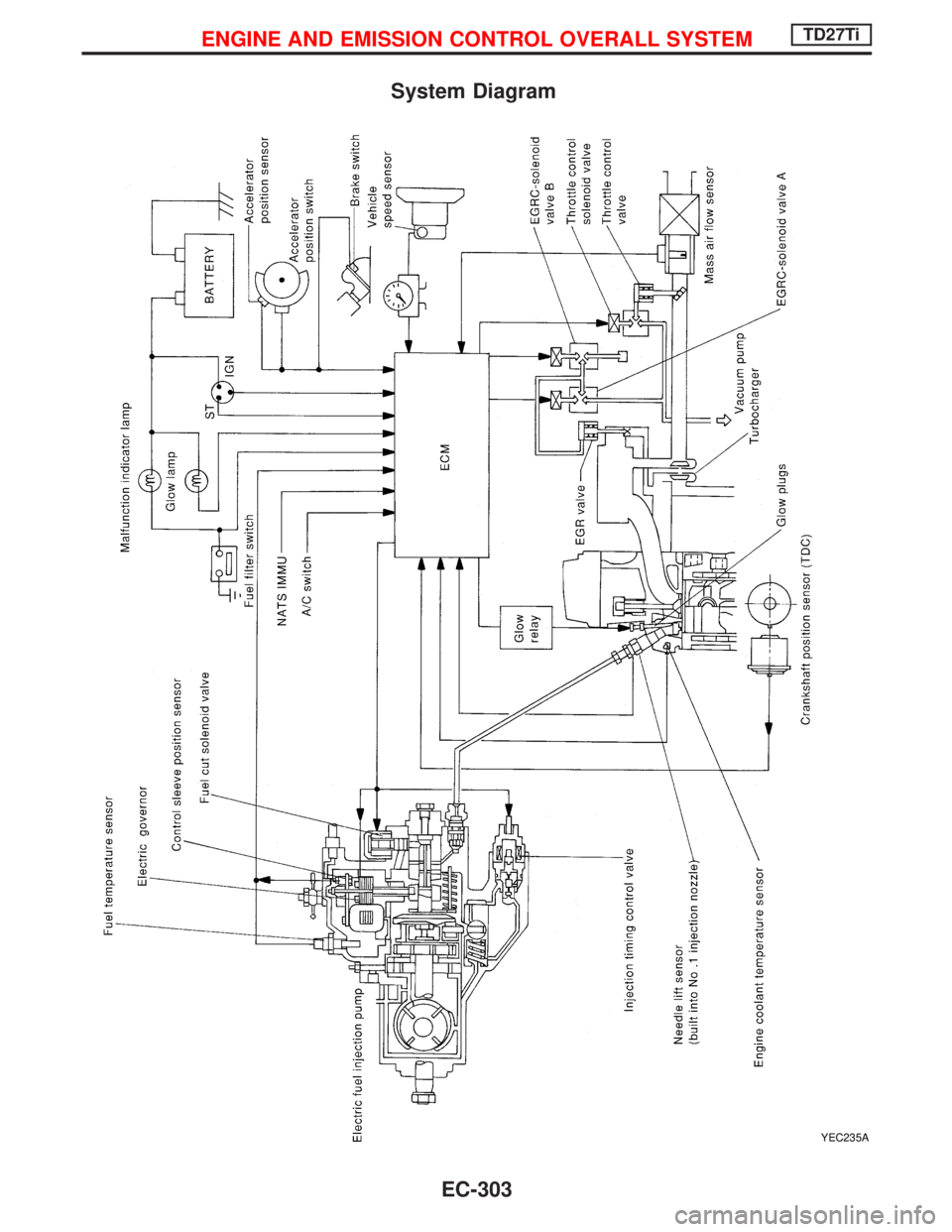
System Diagram
YEC235A
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMTD27Ti
EC-303
Page 666 of 1767
Vacuum Hose Drawing
q1Throttle body control valve actuator
to throttle body control solenoid
valve
q
2EGR valve to 3-way connector
q
3EGRC-solenoid valve A to 3-way
connector-1q
4EGRC-solenoid valve B to 3-way
connector-1
q
5Throttle body control solenoid
valve to 2-way connector-2
q
6EGRC-solenoid valve A to 3-way
connector-2q
7Tube to 3-way connector-2
q
8Tube to vacuum pump
q
9Tube to brake booster
Refer to ªSystem Diagramº, on previous page for vacuum control system
NEF759
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMTD27Ti
EC-304
Page 667 of 1767
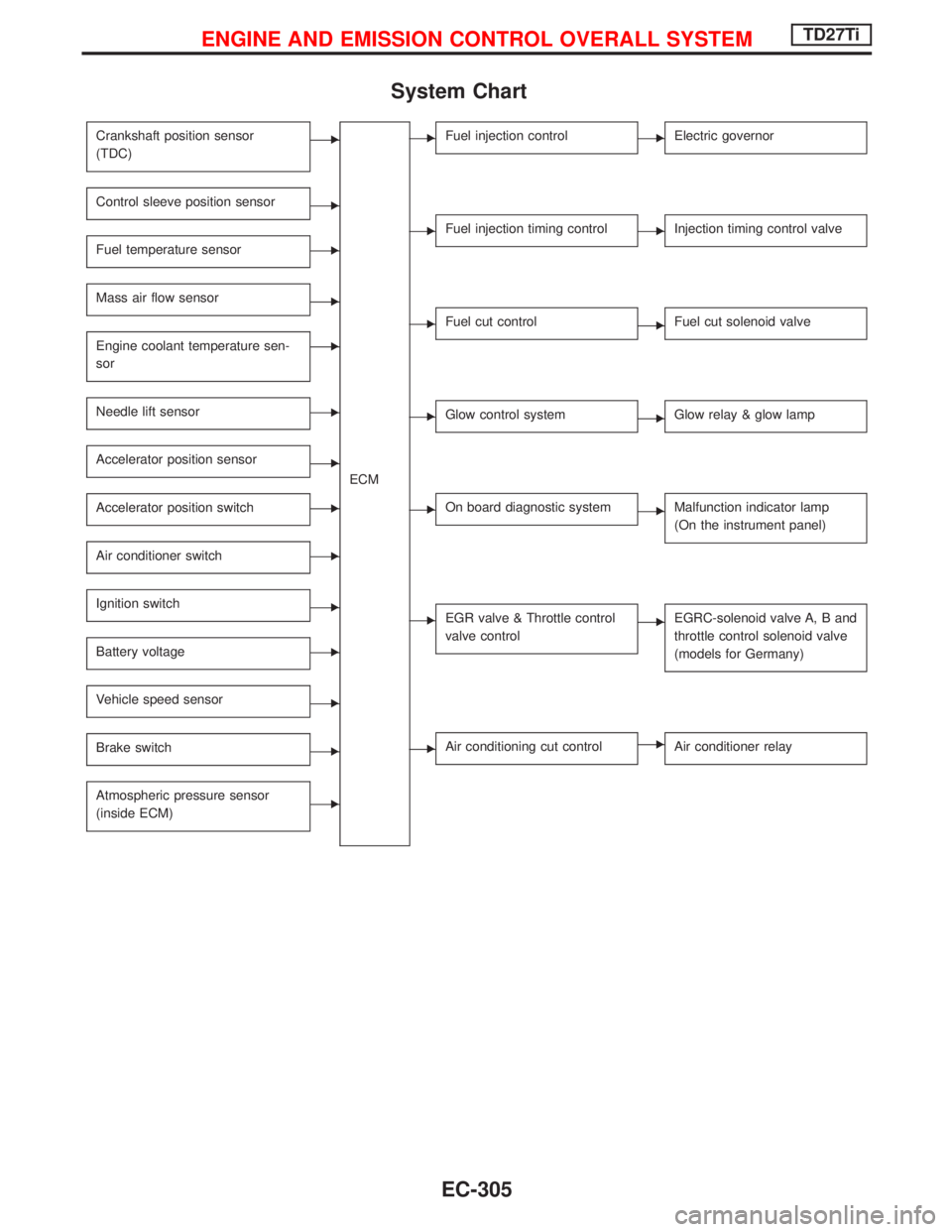
System Chart
Crankshaft position sensor
(TDC)E
ECM
Control sleeve position sensorE
Fuel temperature sensorE
Mass air flow sensorE
Engine coolant temperature sen-
sorE
Needle lift sensorE
Accelerator position sensorE
Accelerator position switchE
Air conditioner switchE
Ignition switchE
Battery voltageE
Vehicle speed sensorE
Brake switchE
Atmospheric pressure sensor
(inside ECM)E
EFuel injection controlEElectric governor
EFuel injection timing controlEInjection timing control valve
EFuel cut controlEFuel cut solenoid valve
EGlow control systemEGlow relay & glow lamp
EOn board diagnostic systemEMalfunction indicator lamp
(On the instrument panel)
EEGR valve & Throttle control
valve controlEEGRC-solenoid valve A, B and
throttle control solenoid valve
(models for Germany)
EAir conditioning cut controlEAir conditioner relay
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMTD27Ti
EC-305
Page 668 of 1767

Fuel Injection System
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Three types of fuel injection control are provided to accommodate engine operating conditions; normal control,
idle control and start control. The ECM determines the appropriate fuel injection control. Under each control,
the amount of fuel injected is compensated to improve engine performance. The ECM performs duty cycle
control on the electric governor (built into the fuel injection pump) according to sensor signals to compensate
the amount of fuel injected to the preset value.
START CONTROL
Input/output signal line
Engine coolant temperature sensorEEngine coolant temperature
ECM
EElectric
governorCrankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
Control sleeve position sensor
EControl sleeve position
When the ECM receives a start signal from the ignition switch, the
ECM adapts the fuel injection system for the start control. The
amount of fuel injected at engine starting is a preset program value
in the ECM. The program is determined by the engine speed and
engine coolant temperature.
For better startability under cool engine conditions, the lower the
coolant temperature becomes, the greater the amount of fuel
injected. The ECM ends the start control when the engine speed
reaches a value between 800 rpm and 1,200 rpm, which is deter-
mined by the engine coolant temperature and shifts the control to
the normal or idle control.
SEF648S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
EC-306
Page 669 of 1767
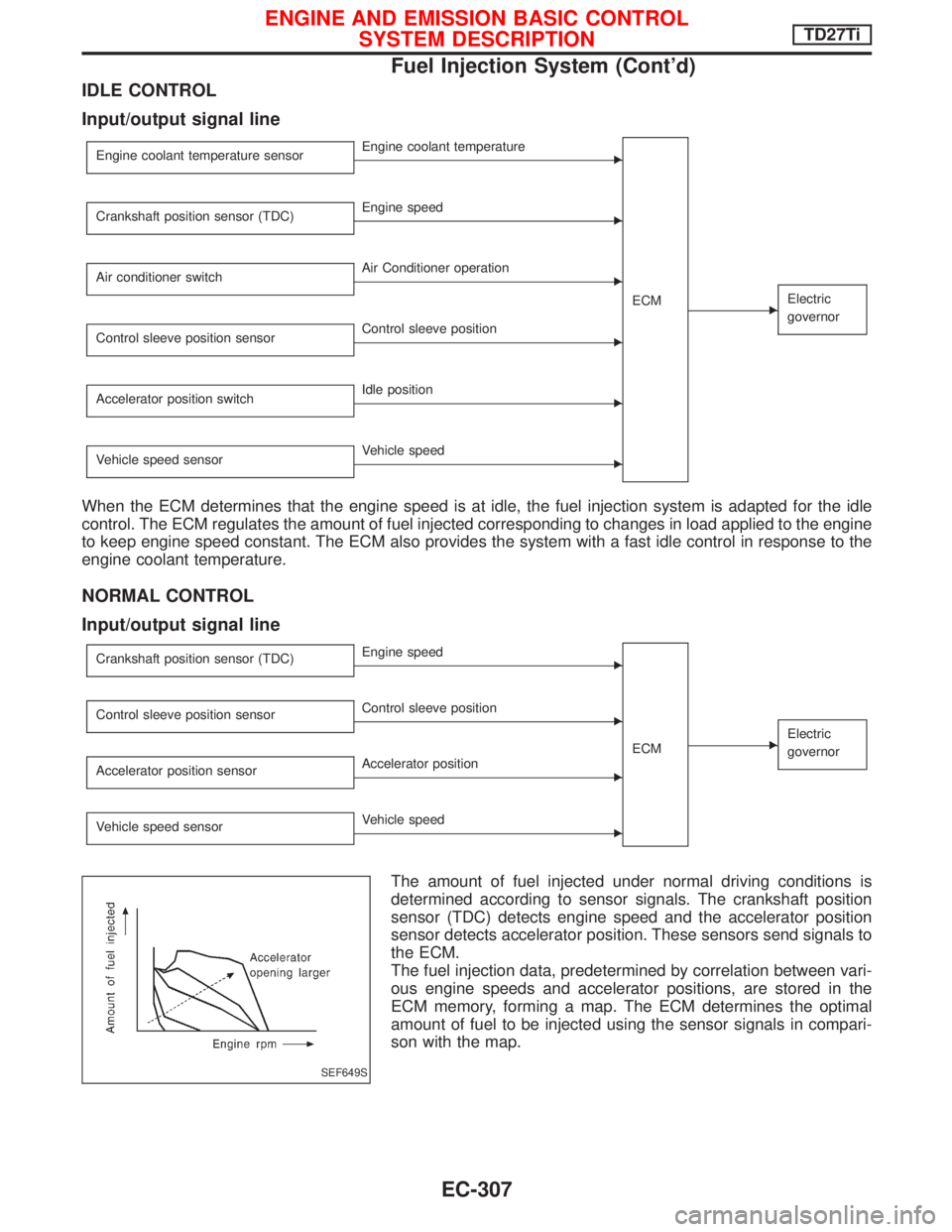
IDLE CONTROL
Input/output signal line
Engine coolant temperature sensorEEngine coolant temperature
ECM
EElectric
governor
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
Air conditioner switch
EAir Conditioner operation
Control sleeve position sensor
EControl sleeve position
Accelerator position switch
EIdle position
Vehicle speed sensor
EVehicle speed
When the ECM determines that the engine speed is at idle, the fuel injection system is adapted for the idle
control. The ECM regulates the amount of fuel injected corresponding to changes in load applied to the engine
to keep engine speed constant. The ECM also provides the system with a fast idle control in response to the
engine coolant temperature.
NORMAL CONTROL
Input/output signal line
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
ECM
EElectric
governor
Control sleeve position sensorEControl sleeve position
Accelerator position sensor
EAccelerator position
Vehicle speed sensor
EVehicle speed
The amount of fuel injected under normal driving conditions is
determined according to sensor signals. The crankshaft position
sensor (TDC) detects engine speed and the accelerator position
sensor detects accelerator position. These sensors send signals to
the ECM.
The fuel injection data, predetermined by correlation between vari-
ous engine speeds and accelerator positions, are stored in the
ECM memory, forming a map. The ECM determines the optimal
amount of fuel to be injected using the sensor signals in compari-
son with the map.
SEF649S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
Fuel Injection System (Cont'd)
EC-307
Page 670 of 1767

FUEL TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION
Input/output signal line
Fuel temperature sensorEFuel temperature
ECM
EElectric
governorCrankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
Control sleeve position sensor
EControl sleeve position
The amount of fuel leaking at or around high-pressure parts inside the fuel injection pump varies with the fuel
temperature and engine speed. This will result in a difference between the target amount of fuel injected and
the actual amount. The ECM compensates for the actual amount depending on the signal obtained from the
fuel temperature sensor.
DECELERATION CONTROL
Input/output signal line
Accelerator position sensorEAccelerator position
ECM
EElectric
governor
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
The ECM cuts power supply delivery to the electric governor during deceleration for better fuel efficiency. The
ECM determines the time of deceleration according to signals from the accelerator position sensor and crank-
shaft position sensor (TDC).
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
Fuel Injection System (Cont'd)
EC-308
Trending: cruise control, fuse box, heater, steering wheel, low beam, fog light, Full system