Back OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 2243 of 6000

7A–89 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Overdrive Internal Components
252RW003
Legend
(501) Retainer, 4th Clutch
(502) Plate, 4th Clutch (Steel)
(503) Plate Assembly, 4th Clutch (Lined)
(504) Retainer And Ball Assembly, Check Valve
(505) Seal, O–Ring/Turbine Shaft
(506) Shaft, Turbine
(508) Ring, Oil Seal/Turbine Shaft
(510) Housing, Overrun Clutch
(513) Piston, Overrun Clutch
(514) Spring, Overrun Clutch Release
(515) Retainer, Release Spring/Overrun Clutch
(516) Roller Assembly, Overdrive Clutch
(517) Cam, Overdrive Roller Clutch
(518) Ring, Snap/Overrun Clutch Hub
(519) Gear, Overdrive Sun(520) Plate, Waved/Overrun Clutch
(521) Plate, Overrun Clutch (Steel)
(522) Plate Assembly, Overrun Clutch (Lined)
(523) Plate, Backing/Overrun Clutch
(524) Ring, Snap/Overrun Clutch Housing
(525) Carrier Assembly, Overdrive Complete
(526) Ring, Snap/Turbine Shaft/Carrier
(527) Bearing Assembly, Thrust
(528) Gear, Overdrive Internal
(529) Washer, Thrust/Internal Gear/Support
(530) Ring, Snap/Adapter/4th Clutch Spring
(531) Retainer and spring assembly, 4th clutch
(532) Piston, 4th Clutch
(533) Seal, 4th Clutch Piston (Inner)
(534) Seal, 4th Clutch Piston (outer)
Page 2246 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–1
TRANSMISSION
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
CONTENTS
Service Precaution 7A1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description 7A1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shift Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Band Apply Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Torque Converter Clutch Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . .
Line Pressure Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
On–Board Diagnostic System 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . .
Fail Safe Mechanism 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Torque Management Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . .
ATF Warning Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ABS Control (If equipped) 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Winter Drive Mode 7A1–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Backup Mode 7A1–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functions of Input / Output Components 7A1–10. .
Diagnosis 7A1–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Check Trans Indicator 7A1–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Check 7A1–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
“Check Trans” Check 7A1–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tech2 OBD II Connection 7A1–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OBD II Diagnostic Management System 7A1–18. .
16 – Terminal Data Link Connector (DLC) 7A1–19.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) 7A1–20. . . . . . . .
Types Of Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(DTCs) 7A1–20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clear DTC 7A1–20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Check 7A1–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Precaution 7A1–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Information On PCM 7A1–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intermittent Conditions 7A1–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission And PCM Identification 7A1–22. . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
Identification 7A1–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0218 Transmission Fluid Over
Temperature 7A1–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Conditions For Setting The DTC 7A1–25. . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When The DTC Sets 7A1–25. . . . . . .
Conditions For Clearing The DTC 7A1–25. . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 7A1–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Description 7A1–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0560 System Voltage Malfunction 7A1–27. . .
DTC P0705 Transmission Range Switch
(Mode Switch) Illegal Position 7A1–30. . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0706 Transmission Range Switch
(Mode Switch) Performance 7A1–33. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0712 Transmission Fluid Temperature
(TFT) Sensor Circuit Low Input 7A1–36. . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0713 Transmission Fluid Temperature
(TFT) Sensor Circuit High Input 7A1–39. . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0719 TCC Brake Switch Circuit High
(Stuck On) 7A1–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0722 Transmission Output Speed
Sensor (OSS) Low Input 7A1–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0723 Transmission Output Speed
Sensor (OSS) Intermittent 7A1–48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0730 Transmission Incorrect
Gear Ratio 7A1–51. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0748 Pressure Control Solenoid
(PCS) (Force Motor) Circuit Electrical 7A1–54. . . . .
DTC P0753 Shift Solenoid A Electrical 7A1–56. . . . .
DTC P0758 Shift Solenoid B Electrical 7A1–59. . . . .
DTC P1790 ROM Transmission Side Bad
Check Sum 7A1–63. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1792 EEPROM Transmission Side
Bad Check Sum 7A1–64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1835 Kickdown Switch Always On 7A1–65. . .
DTC P1850 Brake Band Apply Solenoid
Malfunction 7A1–67. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1860 TCC Solenoid Electrical 7A1–71. . . . . . .
Page 2247 of 6000

7A1–2
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
Service Precaution
WARNING: IF SO EQUIPPED WITH A
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS),
REFER TO THE SRS COMPONENT AND WIRING
LOCATION VIEW IN ORDER TO DETERMINE
WHETHER YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING. WHEN YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE
ON OR NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING, REFER TO THE SRS SERVICE
INFORMATION. FAILURE TO FOLLOW WARNINGS
COULD RESULT IN POSSIBLE AIR BAG
DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY, OR
OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS SYSTEM REPAIRS.
CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
ISUZU will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. ISUZU will also call out
the fasteners that require thread lockers or thread
sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED, do not
use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases, or other
corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners or
fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings
adversely affect the fastener torque and the joint
clamping force, and may damage the fastener. When
you install fasteners, use the correct tightening
sequence and specifications. Following these
instructions can help you avoid damage to parts and
systems.
General Description
The 4L30–E is a 4–speed fully automatic transmission. It
uses a microcomputer as a control unit to judge running
conditions including throttle opening rate and vehicle
speed, then it sets the shifting point in the optimum timing
so that best driving performance can be achieved.
In addition, the built–in shift mode select function can
select three shift modes according to the driver’s
preference:
Normal mode –Normal shift pattern.
Winter mode –Starts in 3rd gear to reduce slippage on
ice or snow.
Power mode has a delayed upshift for when more
powerful acceleration is required.
Also, the built–in fail safe function (“backup mode”)
assures driving performance even if the vehicle speed
sensor, throttle signal or any solenoid fails.
Further, the self–diagnostic function conducts diagnosis
in a short time when the control system fails, thus
improving serviceability.
The major features of 4L30–E are as follows:
A compact structure consisting of 2 sets of planetary
gears and flat torque converter.
Electronic control selects the optimum shift mode
according to the driving conditions.
Electronic control maintains the optimum hydraulic
pressure for clutch, band brake as well as
transmission so that shift feeling is improved.
Two sets of planetary gears reduce friction of power
train.
Also, a lockup mechanism in the torque converter
reduces fuel consumption.
Wide gear ratio and high torque rate of torque
converter provide excellent starting performance.
Page 2251 of 6000

7A1–6
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
Shift Control
The transmission gear is shifted according to the shift
pattern selected by the driver. In shifting gears, the gear
ratio is controlled by the ON/ OFF signal using the shift
solenoid A and the shift solenoid B.
Band Apply Control
The band apply is controlled when in the 3–2 downshift
(engine overrun prevention) and the garage shift (shock
control).
The band apply solenoid is controlled by the signal from
the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to regulate the flow of
the oil.
Torque Converter Clutch Control
The clutch ON/OFF is controlled by moving the converter
clutch valve through shifting Torque Converter Clutch
(TCC) solenoid using the ON/OFF signal.
Line Pressure Control
The throttle signal allows the current signal to be sent to
the force motor. After receiving the current signal, the
force motor activates the pressure regulator valve to
regulate the line pressure.
On–Board Diagnostic System
Several malfunction displays can be stored in the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) memory, and read out
of it afterward.The serial data lines, which are required for the testing of
the final assembly and the coupling to other electronic
modules, can be regulated by this function.
Fail Safe Mechanism
If there is a problem in the transmission system, the PCM
will go into a “backup” mode.
The vehicle can still be driven, but the driver must use the
select lever to shift gears.
Torque Management Control
The transmission control side sends the absolute spark
advance signal to the engine control side while the
transmission is being shifted. This controls the engine
spark timing in compliance with the vehicle running
condition to reduce the shocks caused by the change of
speed.
ATF Warning Control
The oil temperature sensor detects the ATF oil
temperature to control the oil temperature warning, TCC,
and the winter mode.
ABS Control (If equipped)
When the select lever is at “L” or “R” range, a signal is sent
to the ABS controller as one of the ABS control
conditions.
Page 2254 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–9
Winter Drive Mode
1.Operation
The winter switch will operate when switched on after
all of the following conditions are present:
a. The gear select position is “D”, “N”, “R” and “P”
range.
b. Vehicle speed is 7 mph (11 km/h) or less.
c. Transmission oil temperature is 120
C (248F) or
less.
d. Kickdown switch is off.
e. Accelerator opening is at 8% or less.
2.Cancel Release
1. Cancellation by driver
a. Turning off the winter drive mode switch
b. Shifting select position to “3”, “2”, or “L” (Winter
drive mode is not canceled by selecting “D”, “N”,
“R”, or “P”)
c. Ignition key is turned off.
2. Automatic cancellation
a. When vehicle runs at 21mph (34 km/h) or more
for 1 second or more
b. When transmission oil temperature reaches
140
C (284F) or above
NOTE: The mode returns to normal drive mode or power
drive mode after the winter drive mode is canceled.
Backup Mode
If a major system failure occurs which could affect safety
or damage the transmission under normal vehicle
operation, the diagnostic system detects the fault and
overrides the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The “CHECK TRANS” light flashes to alert the driver, and
the transmission must be manually shifted as follows:
Select lever position
Gear Ratio Selected
D4 (Fourth)
Manual 34 (Fourth)
Manual 23 (Third)
Manual L1 (First)
RReverse
Shifts are firmer to prevent clutch slip and consequent
wear. The fault should be corrected as soon as possible.
Page 2256 of 6000
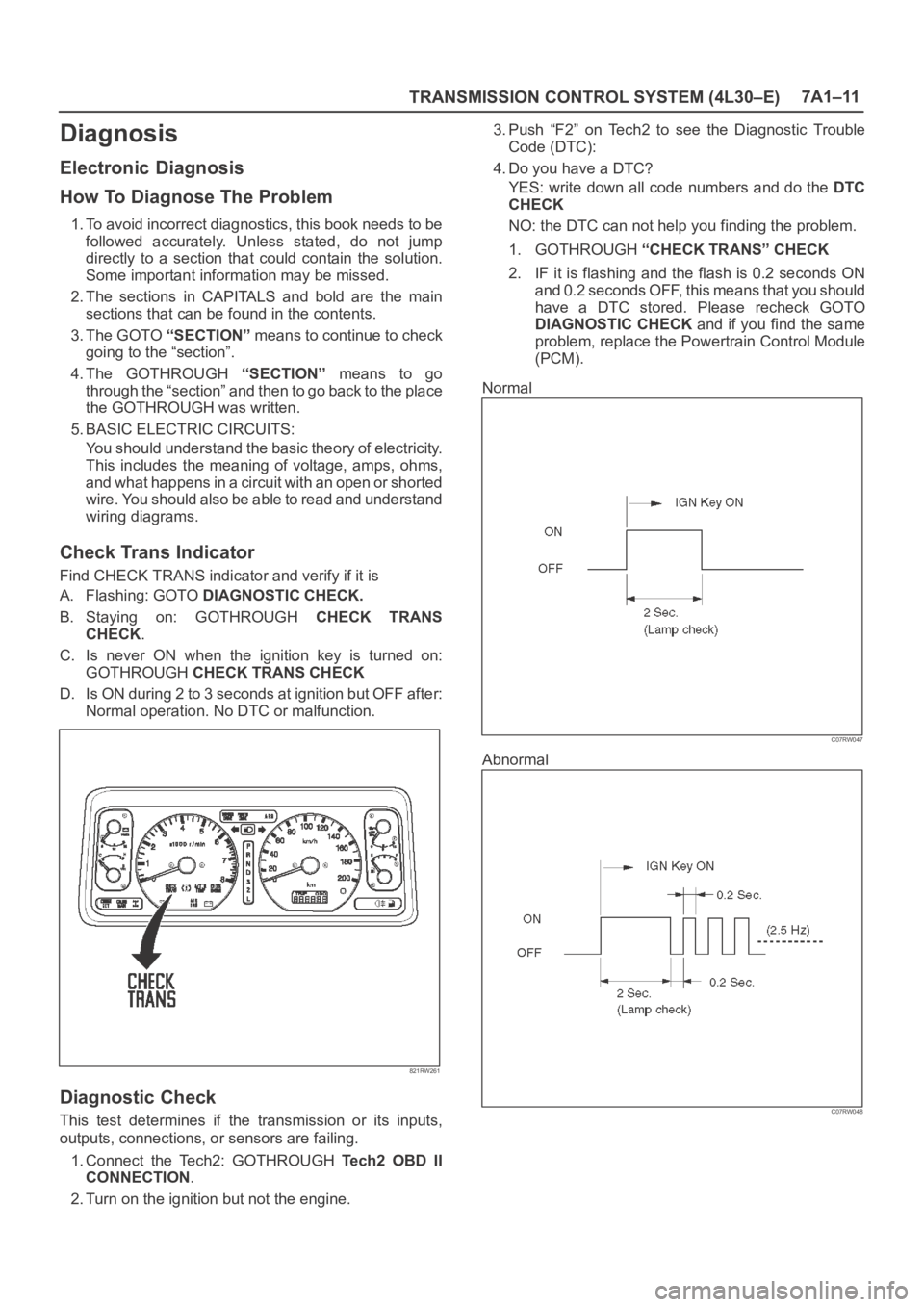
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–11
Diagnosis
Electronic Diagnosis
How To Diagnose The Problem
1. To avoid incorrect diagnostics, this book needs to be
followed accurately. Unless stated, do not jump
directly to a section that could contain the solution.
Some important information may be missed.
2. The sections in CAPITALS and bold are the main
sections that can be found in the contents.
3. The GOTO “SECTION” means to continue to check
going to the “section”.
4. The GOTHROUGH “SECTION” means to go
through the “section” and then to go back to the place
the GOTHROUGH was written.
5. BASIC ELECTRIC CIRCUITS:
You should understand the basic theory of electricity.
This includes the meaning of voltage, amps, ohms,
and what happens in a circuit with an open or shorted
wire. You should also be able to read and understand
wiring diagrams.
Check Trans Indicator
Find CHECK TRANS indicator and verify if it is
A. Flashing: GOTO DIAGNOSTIC CHECK.
B. Staying on: GOTHROUGH CHECK TRANS
CHECK.
C. Is never ON when the ignition key is turned on:
GOTHROUGH CHECK TRANS CHECK
D. Is ON during 2 to 3 seconds at ignition but OFF after:
Normal operation. No DTC or malfunction.
821RW261
Diagnostic Check
This test determines if the transmission or its inputs,
outputs, connections, or sensors are failing.
1. Connect the Tech2: GOTHROUGH Te c h 2 O B D I I
CONNECTION.
2. Turn on the ignition but not the engine.3. Push “F2” on Tech2 to see the Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC):
4. Do you have a DTC?
YES: write down all code numbers and do the DTC
CHECK
NO: the DTC can not help you finding the problem.
1. GOTHROUGH “CHECK TRANS” CHECK
2. IF it is flashing and the flash is 0.2 seconds ON
and 0.2 seconds OFF, this means that you should
have a DTC stored. Please recheck GOTO
DIAGNOSTIC CHECK and if you find the same
problem, replace the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM).
Normal
C07RW047
Abnormal
C07RW048
Page 2258 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–13
D07RW028
Tech2 OBD II Connection
In order to access OBD II Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) data, use of the Tech2 scan tool is required.
1. The electronic diagnosis equipment is composed of:
1. Tech2 (3000094) hand–held scan tool, and DLC
cable (3000095).
901RW176
2. SAE 16/19 adapter (3000098) (1), RS 232 loop
back connector (3000112) (2), and PCMCIA card
(3000117) (3).
F07RW033
Page 2259 of 6000
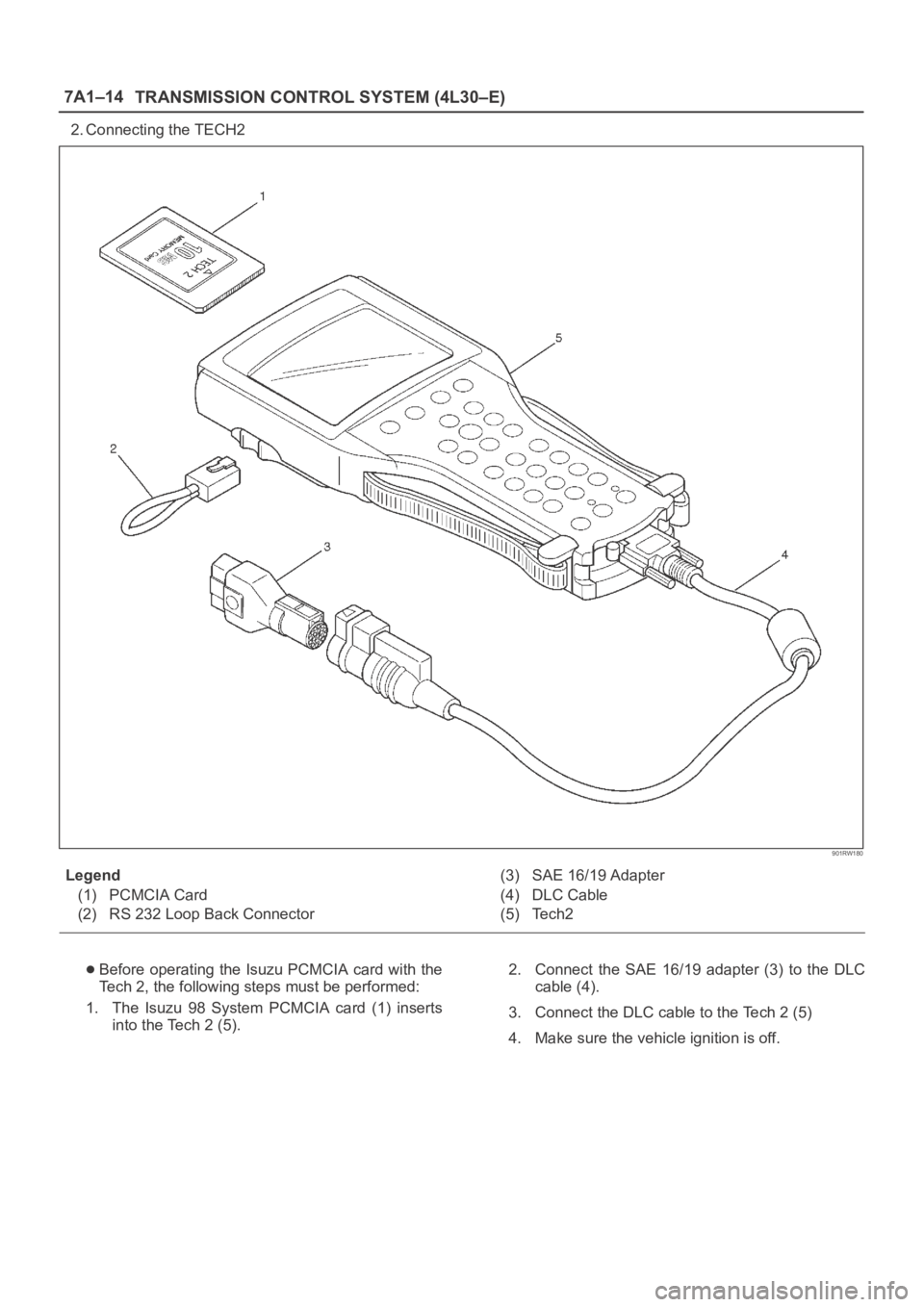
7A1–14
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
2. Connecting the TECH2
901RW180
Legend
(1) PCMCIA Card
(2) RS 232 Loop Back Connector(3) SAE 16/19 Adapter
(4) DLC Cable
(5) Tech2
Before operating the Isuzu PCMCIA card with the
Tech 2, the following steps must be performed:
1. The Isuzu 98 System PCMCIA card (1) inserts
into the Tech 2 (5).2. Connect the SAE 16/19 adapter (3) to the DLC
cable (4).
3. Connect the DLC cable to the Tech 2 (5)
4. Make sure the vehicle ignition is off.
Page 2260 of 6000
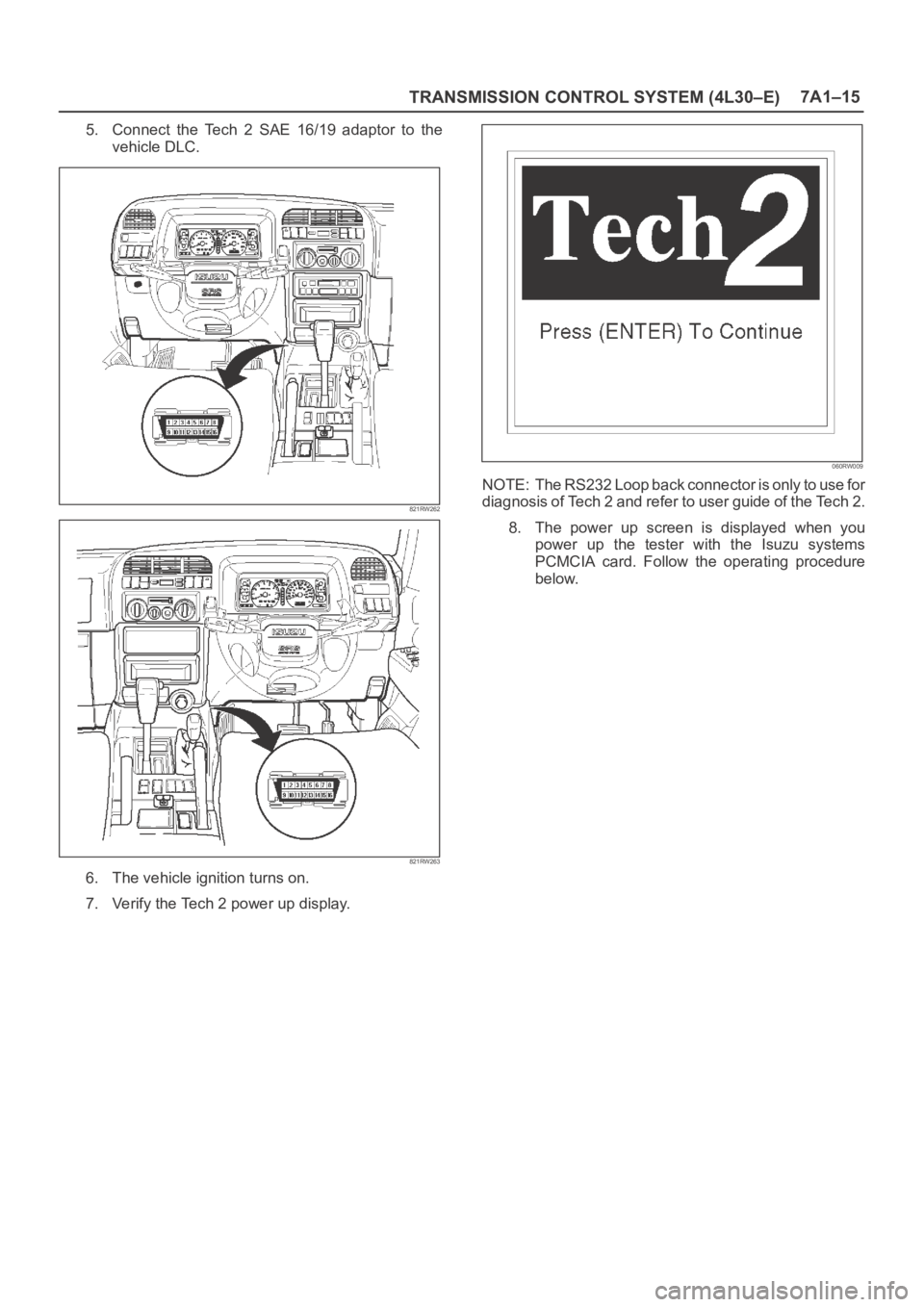
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–15
5. Connect the Tech 2 SAE 16/19 adaptor to the
vehicle DLC.
821RW262
821RW263
6. The vehicle ignition turns on.
7. Verify the Tech 2 power up display.
060RW009
NOTE: The RS232 Loop back connector is only to use for
diagnosis of Tech 2 and refer to user guide of the Tech 2.
8. The power up screen is displayed when you
power up the tester with the Isuzu systems
PCMCIA card. Follow the operating procedure
below.
Page 2267 of 6000

7A1–22
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
connection or loose wiring. Terminals and grounds should
always be the prime suspect. Intermittents rarely occur
inside sophisticated electronic components such as the
PCM.
Use the DTC information to understand which wires and
sensors are involved.
When an intermittent problem is encountered, check
suspect circuits for:
1. Poor terminal to wire connection.
2. Terminals not fully seated in the connector body
(backed out).
3. Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
4. Loose, dirty, or corroded ground connections:
HINT: Any time you have an intermittent in more than
one circuit, check whether the circuits share a
common ground connection.
5. Pinched or damaged wires.
6. Electro–Magnetic Interference (EMI):
HINT: Check that all wires are properly routed away
from spark plug wires, distributor wires, coil, and
generator. Also check for improperly installed
electrical options, such as lights, 2–way radios, etc.Use the F3 SNAPSHOT mode of the Tech2 to help isolate
the cause of an intermittent fault. The snapshot mode will
record information before and after the problem occurs.
Set the snapshot to “trigger” on the suspect DTC. If you
notice the reported symptom during the test drive, trigger
the snapshot manually.
After the snapshot has been triggered, command the
Tech2 to play back the flow of data recorded from each of
the various sensors. Signs of an intermittent fault in a
sensor circuit are sudden unexplainable jump in data
values out of the normal range.
Transmission And PCM Identification
The chart below contains a list of all important information
concerning rear axle ratio, Powertrain Control Module
(PCM), and transmission identification.
VEHICLE
Rr axlePCMTRANSMISSION
Ty p eEngine
Rr axle
RatioISUZU Parts No.Calibration
CodeIsuzu Part No.Model Code
Isuzu /
Trooper3.2L V64.555
8–16254–949–0
8–16254–749–0
8–16253–989–0
G208–96018–272–3FP (4X4)