engine OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 5703 of 6000

7A–14
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 2: No Forward Gears In Any Range/No Reverse
StepActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?
Go to Step 2
Use Chart 15a:
Possible Causes
of Low Line
Pressure in this
section
21. Check internal linkage:
– Manual linkage (58) not moving manual valve (326).
2. Check for internal mechanical damage:
– Turbine shaft (506) broken loose.
– Overrun roller clutch (516) broken loose.
Was the problem found?
Repair or replace—
Chart 3: No Engine Brake In Any Range
StepActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?
Go to Step 2
Use Chart 15a:
Possible Causes
of Low Line
Pressure in this
section
21. Check for overrun clutch leaks caused by:
– Damaged piston lip (513)
– Check ball defective (504)
2. Check for overrun lockout valve (705) stuck by foreign
material.
3. Check for leaks at turbine shaft (506) caused by:
– Teflon seal rings damaged (508)
– Excessive wear of turbine shaft bearing surfaces.
Was the problem found?
Repair or replace—
Page 5704 of 6000

7A–15 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 4: Poor Shifting In All Gears (All Harsh Or All Soft)
StepActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?
Go to Step 2Go to Step 3
21. Check for these conditions which could affect clutch apply
time:
– Defective band apply solenoid (323).
– Defective servo or/and accumulator piston.
– Excessive clutch piston travel.
2. Check of possible causes of internal leaks:
– Cut or damaged sealing ring(s)
– Damaged sealing gasket(s)
– Check ball missing or out of location in 2nd and 3rd clutch
pistons.
3. Check for caused of burned clutch plates or band.
Was the problem found?
Repair or replace—
3Was the line pressure high?
Go to Step 4
Use Chart 15a:
Possible Causes
of Low Line
Pressure in this
section
4Were DTCs P0560 and P0705 set?
Diagnose those
DTC(s) first
Use Chart 15b:
Possible Causes
of High Line
Pressure in this
section
Chart 5a: Delays In Drive And Reverse
NOTE: A short delay (less than 3 seconds) when first
engaging drive or reverse after allowing vehicle to sit
overnight is normal.
Step
ActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?More than 3
second delay in
drive and reverse
with engine off 1
hour or less.
Teflon seals (508)
on turbine shaft
damaged. Repair
Use Chart 15a:
Possible Causes
of Low Line
Pressure in this
section.
Chart 5b: Delays In Reverse Only
StepActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?
Go to Step 2
Use Chart 15a:
Possible Causes
of Low Line
Pressure in this
section.
2Main case valve body gasket (88) damaged.
– Reverse check ball (85) in valve body (84) missing or out of
location.
– Check for restrictions at valve body transfer plate orifice.
Was the problem found?
Repair—
Page 5705 of 6000

7A–16
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 6: Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0730
StepActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?
Go to Step 2
Use Chart 15b:
Possible Causes
of High Line
Pressure in this
section
21. 1st and 2nd gear missing or 3rd and 4th gear missing.
Check appropriate shift valve. If OK replace solenoid.
2. No engine brake in any range (All ranges in Drive and Reverse
are OK).
Check for suspected conditions modifying delays to clutch
apply:
– Overrun clutch seal damaged.
– Excessive overrun clutch piston travel.
– Defective 3–4 accumulator piston.
– Causes of internal leaks.
– Causes of burned clutch plates.
3. 1st and 4th gear missing or 2nd and 3rd gear missing.
Shift solenoid A stuck. Replace shift solenoid A.
4. DTC P0730 is set in D range 1st gear above 3500 rpm.
Go to Step 3.
5. DTC P0730 is set in D range 3rd gear between 55-80 mph.
NOTE: Perform this test within safe and legal limits.
Check for suspected conditions modifying delays to clutch
apply:
– 4th clutch seal damaged.
– Excessive 4th clutch piston travel.
– Defective 3–4 accumulator piston.
– Causes of internal leaks.
– Causes of burned clutch plates.
Was the problem found?
Repair or replace—
3Check 3rd gear in “D” in winter mode.
Does vehicle move?Shift solenoid A
stuck. Replace
shift solenoid A.
Go to Step 4
4Check for suspected conditions modifying delays to clutch apply:
– 2nd clutch seal damaged.
– Excessive 2nd clutch piston travel.
– Defective accumulator piston.
– Causes of internal leaks.
– Check ball missing or out of location in 2nd clutch.
– Seals cut, damaged or missing.
– Gaskets defective.
– Causes of burned clutch plates.
Was the problem found?
Repair or replace—
Page 5707 of 6000
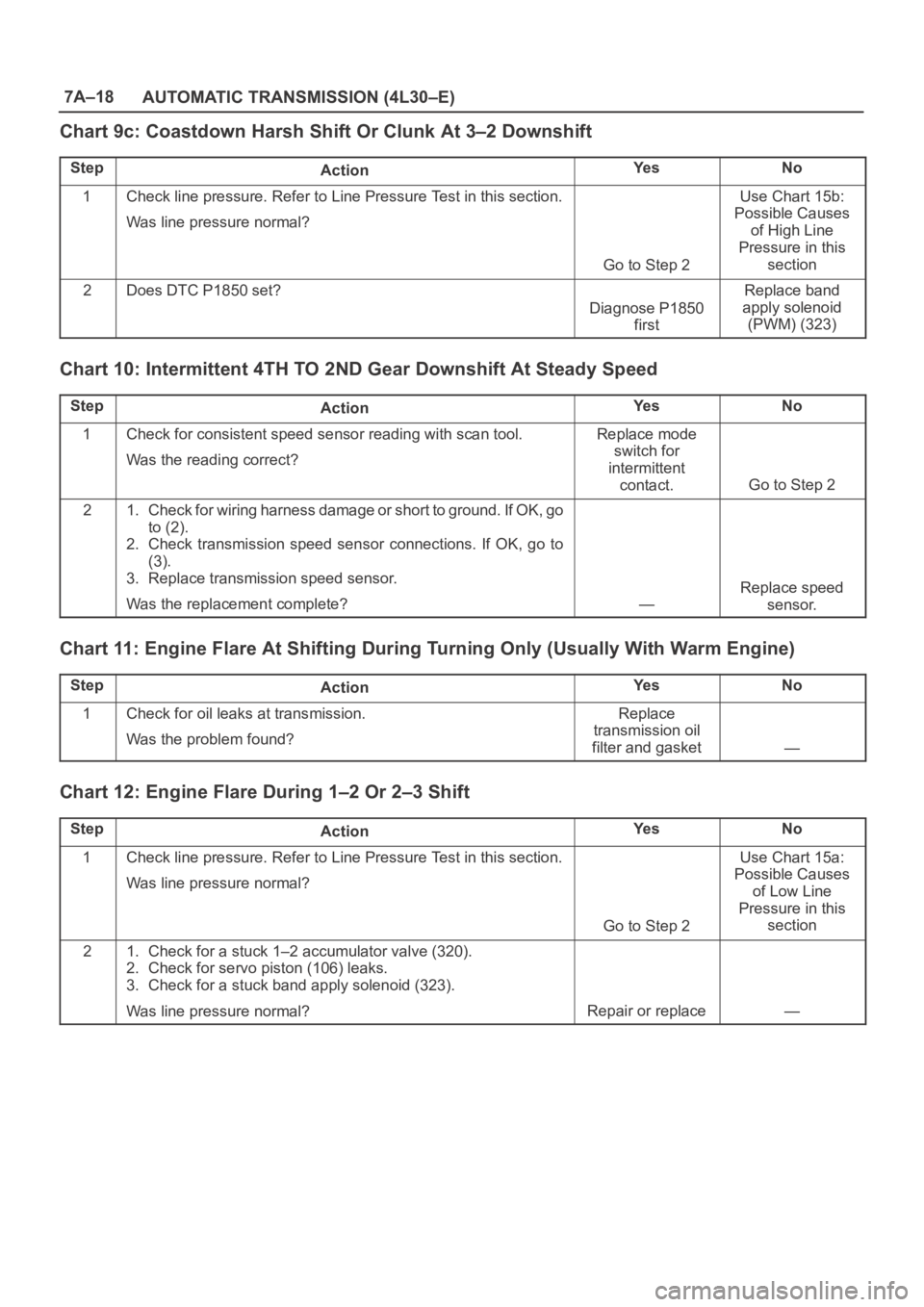
7A–18
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 9c: Coastdown Harsh Shift Or Clunk At 3–2 Downshift
StepActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?
Go to Step 2
Use Chart 15b:
Possible Causes
of High Line
Pressure in this
section
2Does DTC P1850 set?
Diagnose P1850
first
Replace band
apply solenoid
(PWM) (323)
Chart 10: Intermittent 4TH TO 2ND Gear Downshift At Steady Speed
StepActionYe sNo
1Check for consistent speed sensor reading with scan tool.
Was the reading correct?Replace mode
switch for
intermittent
contact.
Go to Step 2
21. Check for wiring harness damage or short to ground. If OK, go
to (2).
2. Check transmission speed sensor connections. If OK, go to
(3).
3. Replace transmission speed sensor.
Was the replacement complete?
—
Replace speed
sensor.
Chart 11: Engine Flare At Shifting During Turning Only (Usually With Warm Engine)
StepActionYe sNo
1Check for oil leaks at transmission.
Was the problem found?Replace
transmission oil
filter and gasket
—
Chart 12: Engine Flare During 1–2 Or 2–3 Shift
StepActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?
Go to Step 2
Use Chart 15a:
Possible Causes
of Low Line
Pressure in this
section
21. Check for a stuck 1–2 accumulator valve (320).
2. Check for servo piston (106) leaks.
3. Check for a stuck band apply solenoid (323).
Was line pressure normal?
Repair or replace—
Page 5711 of 6000

7A–22
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 16: Possible Causes Of
Transmission Fluid Leaks
Before attempting to correct an oil leak, the actual source
of the leak must be determined. In many cases, the
source of the leak may be difficult to determine due to
“wind flow” around the engine and transmission.
The suspected area should be wiped clean before in-
specting for the source of the leak.Oil leaks around the engine and transmission are gener-
ally carried toward the rear of the vehicle by the air
stream. In determining the source of an leak, the following
two checks should be made:
1. With the engine running, check for external line
pressure leaks.
2. With the engine off, check for oil leaks due to the
raised oil level caused by drainback of converter oil
into the transmission.
Possible Causes Of Fluid Leaks Due To Sealing Malfunction
240RX008
Legend
(1) Electrical Connector (Main Case) Seal
(2) Transmission Vent (Breather)
(3) Speed Sensor O–Ring
(4) Extension (Adapter) Lip Seal
(5) Extension (Adapter) to Main Case Gasket
(6) Overfill and Oil Drain Screws Gasket
(7) Oil Pan Gasket (Main Case)
(8) Selector Shaft Seal(9) Oil Cooler Connectors (2)
(10) Oil Pan Gasket (Adapter Case)
(11) Converter housing attaching bolts not correctly
torqued
(12) Converter Housing Lip Seal
(13) Line Pressure Tap Plug
(14) Electrical Connector (Adapter Case) Seal
(15) Adapter Case Seal Rings (2)
Page 5712 of 6000

7A–23 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Stall Test
The stall test allows you to check the transmission for
internal abrasion and the one way clutch for slippage.
Torque converter performance can also be evaluated.
The stall test results together with the road test results will
identify transmission components requiring servicing or
adjustment.
Stall Test Procedure:
1. Check the level of the engine coolant, the engine oil,
and the automatic transmission fluid. Replenish if
necessary.
2. Block the wheels and set the parking brake.
3. Connect a tachometer to the engine.
4. Start the engine and allow it to idle until the engine
coolant temperature reaches 70 – 80
C (158 –
176
F).
5. Hold the brake pedal down as far as it will go.
6. Place the selector in the “D” range.
7. Gradually push the accelerator pedal to the floor.
The throttle valve will be fully open.
Note the engine speed at which the tachometer
needle stabilizes.
Stall Speed : 2,100
150 rpm
NOTE: Do not continuously run this test longer than 5
seconds.
8. Release the accelerator pedal.
9. Place the selector in the “N” range.
10. Run the engine at 1,200 rpm for one minute.
This will cool the transmission fluid.
11. Repeat Steps 7 – 10 for the “3”, “2”, “L” and “R”
ranges.
Line Pressure Test
The line pressure test checks oil pump and control valve
pressure regulator valve function. It will also detect oil
leakage.
Line Pressure Test Procedure:
1. Check the level of the engine coolant, the engine oil,
and the automatic transmission fluid.
Replenish if required.
2. Block the wheels and set the parking brake.
3. Remove the pressure detection plug at the left side of
the transmission case.
Set 5–8840–0004–0 pressure gauge and adapter to
the pressure detection plug hole.
241RS001
4. Start the engine and allow it to idle until the engine
coolant temperature reaches 70 – 80
C (158 –
176
F).
5. Hold the brake pedal down as far as it will go.
6. Place the selector in the “D” range.
7. Note the pressure gauge reading with the engine
idling.
8. Gradually push the accelerator pedal to the floor. The
throttle valve will be fully open.
Note the pressure gauge reading with the accelerator
pedal fully depressed.
NOTE: Do not continuously run this test longer than 5
seconds.
9. Release the accelerator pedal.
10. Place the selector in the “N” range.
11. Run the engine at 1,200 rpm for one minute.
This will cool the transmission fluid.
12. Repeat Steps 7 – 11 for the “3”, “2”, “L”, and “R”
ranges.
13. Install a pressure detection plug to the transmission
case, applying recommended thread locking agent
(LOCTITE 242) or its equivalent to thread of plug.
Make sure that thread is cleaned before applying
locking agents.
14. Tighten the pressure detection plug to the specified
torque.
Torque:9–14Nꞏm(0.9–1.4kgꞏm/7–10lbft)
Page 5713 of 6000

7A–24
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
MODELEVERENGINE SPEEDLINE PRESSUREFORCE MOTORMODEPOSITIONENGINE SPEEDkPaPSICURRENT
NORMAL/POWERD,3,2,LIDLE312–36345.2–52.6VA R I A B L E
WINTERDIDLE312 – 36345.2 – 52.60.9 – 1.0A
NORMAL/POWER
WINTERREVERSEIDLE419 – 48660.7 – 70.50.9 – 1.0A
NORMAL/POWERD, 3, 2, LSTALL SPEED1,236 – 1,320179.3 – 191.40.1 – 0.2A
WINTERDSTALL SPEED1,236 – 1,320179.3 – 191.40.1 – 0.2A
NORMAL/POWER
WINTERREVERSESTALL SPEED1,634 – 1,743236.9 – 252.80.1 – 0.2A
Shift Speed Chart (V6 3.2L 6VD1 Model)
Transfer gear ratio:High: 1.000
Rear axle ratio:4.555
“Normal mode”
Upshift
Range
Throttle
opening1 2
(First Gear) (Second Gear)
Km/h (mph)2 3
(Second Gear) (Third Gear)
Km/h (mph)3 4
(Third Gear) (Fourth Gear)
Km/h (mph)
DFully opened37 43 (23 27)76 82 (47 51)125 131 (78 81)
(Drive)Half throttle29 35 (18 22)54 60 (34 37)107 113 (66 70)
3Fully opened37 43 (23 27)76 82 (47 51)—
(Third)Half throttle29 35 (18 22)54 60 (34 37)—
2Fully opened37 43 (23 27)——
(Second)Half throttle29 35 (18 22)——
Downshift
Range
Throttle
opening1 2
(First Gear) (Second Gear)
Km/h (mph)2 3
(Second Gear) (Third Gear)
Km/h (mph)3 4
(Third Gear) (Fourth Gear)
Km/h (mph)
D
Fully opened14 20 (9 12)69 75 (43 47)107 113 (66 70)
D
(Drive)Half throttle13 19 (8 12)30 36 (19 22)61 67 (38 42)(Drive)
Fully closed12 18 (7 11)20 26 (12 16)27 33 (17 20)
3
Fully opened14 20 (9 12)69 75 (43 47)—
3
(Third)Half throttle13 19 (8 12)30 36 (19 22)—(Third)
Fully closed12 18 (7 11)20 26 (12 16)—
2
Fully opened14 20 (9 12)82 88 (51 55)—
2
(Second)Half throttle13 19 (8 12)82 88 (51 55)—(Second)
Fully closed12 18 (7 11)82 88 (51 55)—
L
(First)—36 42 (22 26)——
Page 5718 of 6000

7A–29 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Changing Transmission Fluid
There is no need to change the transmission fluid unless
the transmission is used under one or more of the
following heavy duty conditions.
A. Repeated short trips
B. Driving on rough roads
C. Driving on dusty roads
D. Towing a trailer
If the vehicle is used under these conditions, change the
fluid every 20,000 miles (32,000 km).
More over, the remaining life percentage of ATF can be
estimated by using Tech 2 as an auxiliary tool to judge the
right time for ATF replacement.
The remaining life percentage is calculated from ATF’S
heat history. When it is close to 0%, ATF replacement is
recommended.
1. Place a large drain pan under the oil pan.
2. Remove the transmission oil drain screw (2) and drain
fluid.
3. Tighten drain screw (2).
Torque: 38 N
m (3.9 kgꞏm/28 lb ft)
4. Remove the transmission overfill screw (1) and fill
transmission through overfill screw opening, using
DEXRON
–III ATF.
NOTE: Add transmission fluid until it flows out over the
overfill screw opening.
5. Let engine idle until a fluid temperature between 32
C
(90
F) and 57C (135F) is reached.
6. Add transmission fluid until it flows out over the overfill
screw opening, then close the overfill screw (1).
Torque: 38 N
m (3.9 kgꞏm/28 lb ft)NOTE: To prevent fluid leaks, the overfill screw and oil
drain screws gasket must be replaced each time these
screws are removed.
NOTE: Check transmission fluid temperature with
service scan tool.
7. Reset “Oil Life Monitor” data by using Tech 2.
Refer to Tech 2 OBD II Connector in Transmission
Control System (4L30-E) Section.
242RW003
Selector Lever
Inspection
1. Make sure that when the selector lever is shifted from
“P” to “L”, a “clicking” can be felt at each shift position.
Make sure that the gear corresponds to that of the
position plate indicator.
2. Check to see if the selector lever can be shifted as
shown in illustration.
C07RW009
Page 5719 of 6000

7A–30
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Removal
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Remove transfer control lever knob.
3. Remove front console.
Disconnect wiring harness connectors from front
console.
4. Disconnect shift lock cable (1) from the selector lever
assembly side.
256RW012
5. Disconnect shift control rod (2) from the selector lever
assembly side.
256RW013
6. Disconnect wiring harness connectors from the
selector lever assembly.
7. Remove selector lever assembly.
Installation
To install, follow the removal steps in the reverse order,
noting the following points:
Adjustment of select lever and control rod
1. Place the vehicle on a level surface.
NOTE: If the vehicle is not on level surface, the shift
select cable set positions will vary with the movement of
engine. To prevent possible misadjustment of the cable,
the vehicle must be placed on a level surface.
2. Install the shift control rod (1) to the transmission
select lever (2), and then place the lever in the “N”
position.
3. Set select lever in the “N” position.
4. Push select lever forward (“R” position side) and
s e c u r e i t ( u s i n g a r u b b e r b a n d ( 3 ) , e t c . ) s o t h a t t h e p i n
comes into contact with the wall of the detent plate.
5. Install the shift control rod (1) to the selector lever arm
(4).
To r q u e : 3 2 N
m (3.3 kgꞏm/24 lb ft)
NOTE: Do not apply oil to the threaded portions.
256RW014
6. After adjustment, make sure that the selector lever
operates normally, and that each selector position is
properly indicated. (The red mark shows through the
window.)
Adjustment of shift lock cable
1. Set ignition key in “LOCK” position and selector lever
in “P” position.
2. Adjust cable screw cap on selector lever side to
provide a gap (slack for cable) of 1 – 2 mm between
rod on steering lock side and stopper.
Adjust cap as follows:
a. Pull screw cap (1) in arrow direction to remove
inner cable slack.
b. With cable kept as (a), adjust gap between nut (2)
and bracket to 5 mm (0.2 in).
c. Lock inner cable by turning nut (3) while holding nut
(2) in place.
Torque : 3.7 N
m (38 kgꞏcm/33 lb in)
Page 5722 of 6000

7A–33 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Transmission (With Transfer Case)
Transmission And Associated Parts
240RW027
Legend
(1) Transfer Control Lever Knob
(2) Front Console
(3) Selector Lever Assembly
(4) Transfer Control Lever
(5) Transfer and Exhaust Protector
(6) Rear Propeller Shaft
(7) Front Propeller Shaft
(8) Harness Protector
(9) Rear Mount Nut(10) Third Crossmember
(11) Exhaust Pipe
(12) Transmission Oil Cooler Pipe
(13) Starter
(14) Transmission Harness Connector
(15) Under Cover
(16) Torque Converter Bolt
(17) Engine Transmission Bolt
(18) Transmission Assembly
Removal
NOTE: Before remove transmission and transfer
assembly from vehicle, change the tansfer mode to 2WD
using push button on dash panel.1. Remove engine hood.
2. Disconnect battery ground cable.
3. Remove transfer control lever knob (1) and
disconnect wiring harness connectors, then remove
front console (2).