battery replacement OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 2120 of 6000

6E–227 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
QOS
Diagnostics
– Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Service Engine
Soon lamp)
– Data Link Connector (DLC)
– Data Output
ECM Service Precautions
The ECM is designed to withstand normal current draws
associated with vehicle operation. Avoid overloading any
circuit. When testing for opens and shorts, do not ground
or apply voltage to any of the ECM’s circuits unless
instructed to do so. These circuits should only be tested
using digital voltmeter. The ECM should remain
connected to the ECM or to a recommended breakout
box.
Intake Throttle Position (ITP) Sensor
ITP sensor is a potentiometer type and installed to the
intake throttle valve body. A voltage of 5V is applied
constantly from ECM to ITP sensor thereby to determine
by change in voltage the opening of the intake throttle
valve during warming up.
Transmission Range Switch
IMPORTANT:The vehicle should not be driven with the
transmission range switch disconnected; idle quality will
be affected.
The four inputs from the transmission range switch
indicate to the ECM which position is selected by the
transmission selector lever.
For more information on the transmission on the
transmission range switch, refer to
Automatic
Tr a n s m i s s i o n
.
Accelerator Position Sensor (AP)
AP sensor is a potentiometer type and installed to
accelerator pedal bracket. A voltage of 5V constantly
applied from ECM to the sensor thereby to determine the
accelerator pedaling angle by change in voltage. Further,
this sensor is provided with an accelerator switch, which
is set off only when the accelerator pedal is stepped on.
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum
Equipment
Aftermarket (add-on) electrical and vacuum equipment is
defined as any equipment which connects to the vehicle’s
electrical or vacuum systems that is installed on a vehicle
after it leaves the factory. No allowances have been
made in the vehicle design for this type of equipment.
NOTE: No add-on vacuum equipment should be added
to this vehicle.
NOTE: Add-on electrical equipment must only be
connected to the vehicle’s electrical system at the battery
(power and ground).
Add-on electrical equipment, even when installed to
these guidelines, may still cause the powertrain system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such asportable telephones and radios. Therefore, the first step
in diagnosing any powertrain problem is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. After
this is done, if the problem still exists, it may be diagnosed
in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the ECM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
TS23793
There are several ways for a person to become statically
charged. The most common methods of charging are by
friction and induction.
An example of charging by friction is a person sliding
across a vehicle seat.
Charge by induction occurs when a person with well
insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object
and momentary touches ground. Charges of the
same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components.
NOTE: To prevent possible electrostatic discharge
damage, follow these guidelines:
Do not touch the ECM connector pins or soldered
components on the ECM circuit board.
Do not open the replacement part package until the
part is ready to be installed.
Before removing the part from the package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
If the part has been handled while sliding across the
seat, while sitting down from a standing position, or
while walking a distance, touch a known good ground
before installing the part.
Page 2137 of 6000
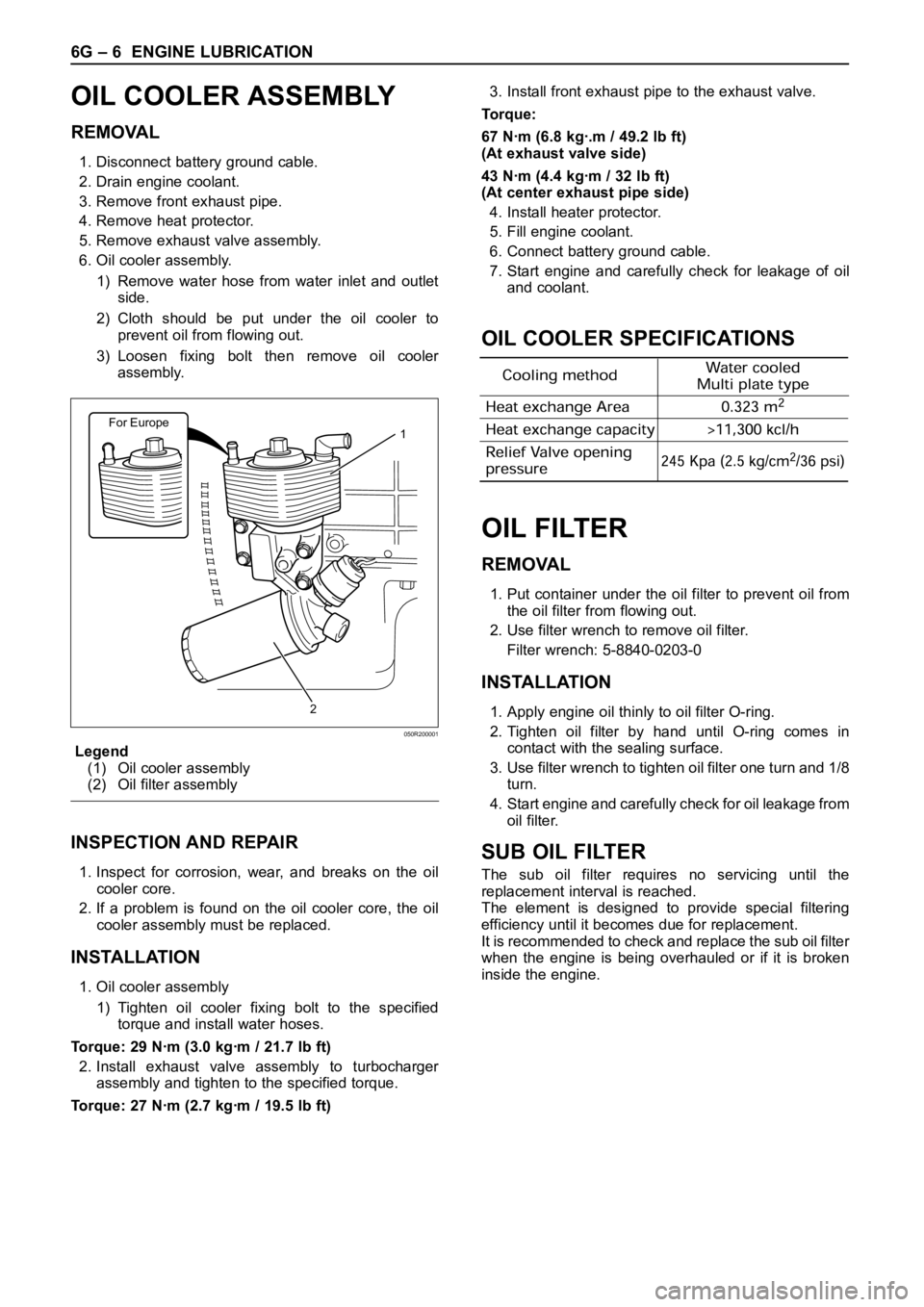
6G – 6 ENGINE LUBRICATION
OIL COOLER ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Drain engine coolant.
3. Remove front exhaust pipe.
4. Remove heat protector.
5. Remove exhaust valve assembly.
6. Oil cooler assembly.
1) Remove water hose from water inlet and outlet
side.
2) Cloth should be put under the oil cooler to
prevent oil from flowing out.
3) Loosen fixing bolt then remove oil cooler
assembly.
Legend
(1) Oil cooler assembly
(2) Oil filter assembly
INSPECTION AND REPAIR
1. Inspect for corrosion, wear, and breaks on the oil
cooler core.
2. If a problem is found on the oil cooler core, the oil
cooler assembly must be replaced.
INSTALLATION
1. Oil cooler assembly
1) Tighten oil cooler fixing bolt to the specified
torque and install water hoses.
Torque: 29 Nꞏm (3.0 kgꞏm / 21.7 lb ft)
2. Install exhaust valve assembly to turbocharger
assembly and tighten to the specified torque.
Torque: 27 Nꞏm (2.7 kgꞏm / 19.5 lb ft)3. Install front exhaust pipe to the exhaust valve.
Torque:
67 Nꞏm (6.8 kgꞏ.m / 49.2 lb ft)
(At exhaust valve side)
43 Nꞏm (4.4 kgꞏm / 32 lb ft)
(At center exhaust pipe side)
4. Install heater protector.
5. Fill engine coolant.
6. Connect battery ground cable.
7. Start engine and carefully check for leakage of oil
and coolant.
OIL COOLER SPECIFICATIONS
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL
1. Put container under the oil filter to prevent oil from
the oil filter from flowing out.
2. Use filter wrench to remove oil filter.
Filter wrench: 5-8840-0203-0
INSTALLATION
1. Apply engine oil thinly to oil filter O-ring.
2. Tighten oil filter by hand until O-ring comes in
contact with the sealing surface.
3. Use filter wrench to tighten oil filter one turn and 1/8
turn.
4. Start engine and carefully check for oil leakage from
oil filter.
SUB OIL FILTER
The sub oil filter requires no servicing until the
replacement interval is reached.
The element is designed to provide special filtering
efficiency until it becomes due for replacement.
It is recommended to check and replace the sub oil filter
when the engine is being overhauled or if it is broken
inside the engine.
For Europe1
2
050R200001
Page 2288 of 6000
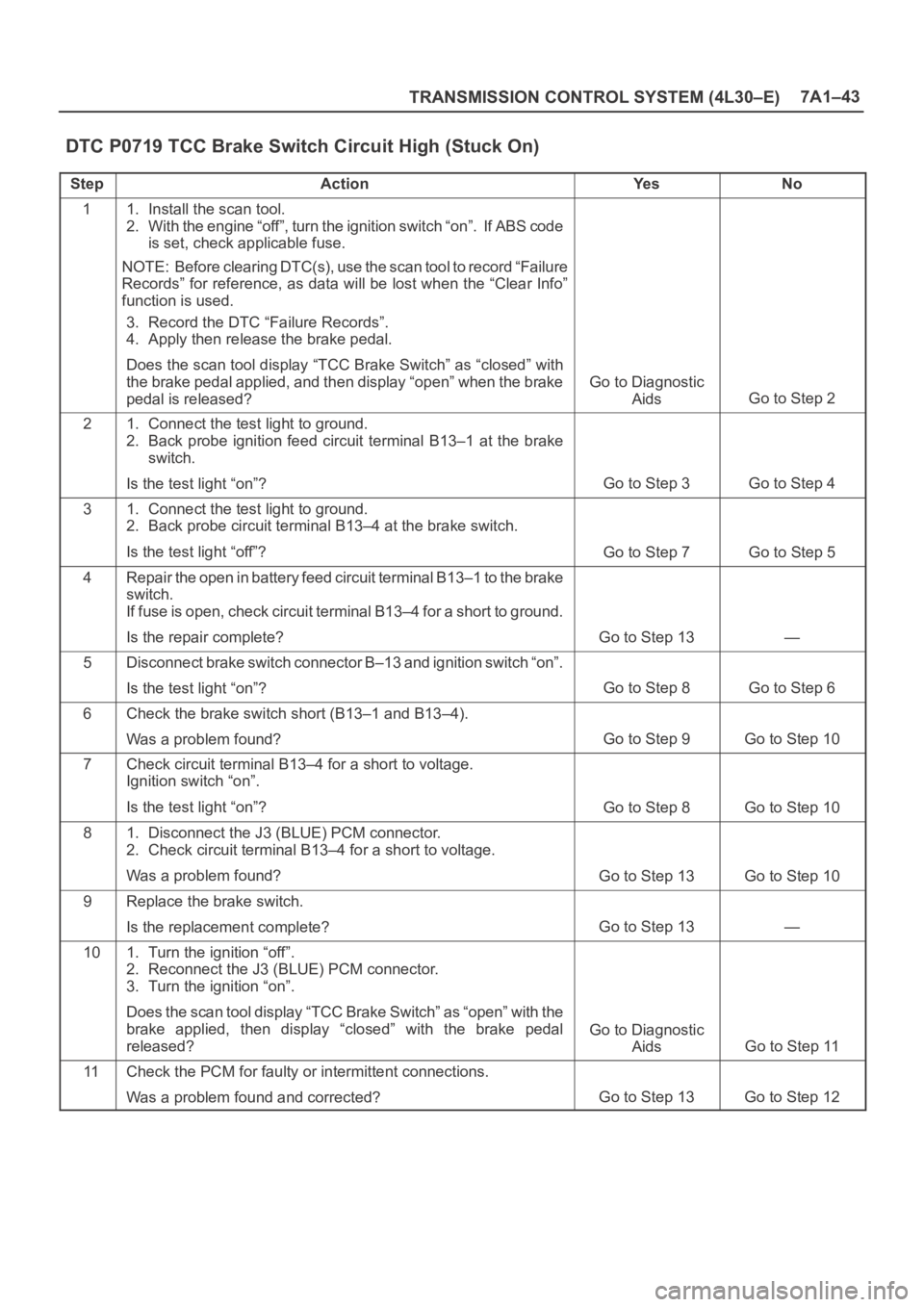
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–43
DTC P0719 TCC Brake Switch Circuit High (Stuck On)
StepActionYe sNo
11. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”. If ABS code
is set, check applicable fuse.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Failure
Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the “Clear Info”
function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Failure Records”.
4. Apply then release the brake pedal.
Does the scan tool display “TCC Brake Switch” as “closed” with
the brake pedal applied, and then display “open” when the brake
pedal is released?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 2
21. Connect the test light to ground.
2. Back probe ignition feed circuit terminal B13–1 at the brake
switch.
Is the test light “on”?
Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Connect the test light to ground.
2. Back probe circuit terminal B13–4 at the brake switch.
Is the test light “off”?
Go to Step 7Go to Step 5
4Repair the open in battery feed circuit terminal B13–1 to the brake
switch.
If fuse is open, check circuit terminal B13–4 for a short to ground.
Is the repair complete?
Go to Step 13—
5Disconnect brake switch connector B–13 and ignition switch “on”.
Is the test light “on”?
Go to Step 8Go to Step 6
6Check the brake switch short (B13–1 and B13–4).
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 9Go to Step 10
7Check circuit terminal B13–4 for a short to voltage.
Ignition switch “on”.
Is the test light “on”?
Go to Step 8Go to Step 10
81. Disconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
2. Check circuit terminal B13–4 for a short to voltage.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 13Go to Step 10
9Replace the brake switch.
Is the replacement complete?
Go to Step 13—
101. Turn the ignition “off”.
2. Reconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
3. Turn the ignition “on”.
Does the scan tool display “TCC Brake Switch” as “open” with the
brake applied, then display “closed” with the brake pedal
released?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 11
11Check the PCM for faulty or intermittent connections.
Was a problem found and corrected?
Go to Step 13Go to Step 12
Page 2571 of 6000

8B–2WIPER/WASHER SYSTEM
Service Precaution
WARNING: IF SO EQUIPPED WITH A
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS),
REFER TO THE SRS COMPONENT AND WIRING
LOCATION VIEW IN ORDER TO DETERMINE
WHETHER YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING. WHEN YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE
ON OR NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING, REFER TO THE SRS SERVICE
INFORMATION. FAILURE TO FOLLOW WARNINGS
COULD RESULT IN POSSIBLE AIR BAG
DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY, OR
OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS SYSTEM REPAIRS.CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
ISUZU will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. ISUZU will also call out
the fasteners that require thread lockers or thread
sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED, do not
use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases, or other
corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners or
fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings
adversely affect the fastener torque and the joint
clamping force, and may damage the fastener. When
you install fasteners, use the correct tightening
sequence and specifications. Following these
instructions can help you avoid damage to parts and
systems.
Windshield Wiper/Washer System
General Description
The circuit consists of the starter switch, windshield wiper
& washer switch, windshield wiper motor, windshield
washer motor and windshield intermittent relay.When the wiper & washer switch is turned on with the
starter switch on, the battery voltage is applied to the
wiper motor to activate the wiper.
The washer motor squirts glass cleaning fluid while the
washer switch is being pushed. The intermittent relay is
used to control motion of the wiper.
Windshield Wiper And Washer Switch
Removal and Installation
Refer to the Lighting Switch (Combination Switch) in
Lighting System section.
Windshield Wiper Motor
Removal
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
2. Disconnect the connector.
3. Remove 4 mounting bolts.
4. Remove the windshield wiper motor(1).
880RW007
Installation
To install, follow the removal steps in the reverse order.
Page 3341 of 6000

8H–2SECURITY AND LOCKS
Service Precaution
WARNING: IF SO EQUIPPED WITH A
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS),
REFER TO THE SRS COMPONENT AND WIRING
LOCATION VIEW IN ORDER TO DETERMINE
WHETHER YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING. WHEN YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE
ON OR NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING, REFER TO THE SRS SERVICE
INFORMATION. FAILURE TO FOLLOW WARNINGS
COULD RESULT IN POSSIBLE AIR BAG
DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY, OR
OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS SYSTEM REPAIRS.CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
ISUZU will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. ISUZU will also call out
the fasteners that require thread lockers or thread
sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED, do not
use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases, or other
corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners or
fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings
adversely affect the fastener torque and the joint
clamping force, and may damage the fastener. When
you install fasteners, use the correct tightening
sequence and specifications. Following these
instructions can help you avoid damage to parts and
systems.
Front Door Lock Assembly
Front Door Lock Assembly and Associated Parts
632RS003
Legend
(1) Door Trim Panel
(2) Waterproof Sheet
(3) To Outside Handle(4) Rear Guide Rail
(5) Door Lock Assembly
(6) Door Lock Switch Connector (W/Power Door
Lock)
Removal
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
2. Remove the door trim panel.3. Remove the waterproof sheet.
Refer to the Window Regulator removal procedure in
Body Structure section.
Page 3366 of 6000

SECURITY AND LOCKS8H–27
StepNo Ye s Action
41. Lock the door and unlock it three times.
2. Close the door and then open it.
NOTE: This step must be performed within ten seconds after step
3.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 5Finished
5Answer back mode changes.
Is this step complete?
Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
6The control unit makes lock/unlock response once with interval of
one second.
Is the response complete?
Finished—
7The control unit makes lock/unlock response three times with
interval of one second.
Is the response complete?
Finished—
Anti–theft & Keyless Entry Control
Unit/Transmitter Replacement
Anti–theft & Keyless Entry Control Unit
Replacement
1. Remove and install the control unit.
Refer to Anti–theft & Keyless Entry Control Unit
Removal and Installation in this section.
2. Register ID code.
Refer to ID Code Registration in this section.
3. Check that the keyless entry system works normally.
Transmitter Replacement
1. Prepare a new transmitter.
2. Regiter ID code.
Refer to ID Code Registration in this section.
3. Check that the keyless entry system works normally.
Transmitter Battery Replacement
1. Remove a screw to remove the cover.
2. Remove the batteries.
3. Set the new batteries into the transmitter.
4. Install the cover to the transmitter.
5. Check that the keyless entry system works normally.
Page 3447 of 6000

SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM 9J–10
Accident With Deployment – Component
Replacement And Inspections
Certain SRS components must be replaced or inspected
for damage after a frontal crash involving air bag
deployment. Those components are:
Air bag assembly
SDM
CAUTION: Refer to “SDM Replacement Guidelines”
below for important information on SDM
replacement in both deployment and non
deployment crashes.
SRS coil assembly — Inspect wiring and connector
for any signs of scorching, melting, or damage due to
excessive heat. Replace if damaged. Refer to
section “SRS Coil Assembly” in this manual.
Accident With or Without Deployment –
Component Inspection
Certain SRS system components and rotation parts must
be inspected after any crash, whether the air bag
deployed or not. Those components are:
Steering column — Refer to Inspection Required
“After an Accident” in this manual.
Knee bolsters and mounting points — Inspect for any
distortion, bending, cracking, or other damage.
I/P steering column reinforcement plate — Inspect for
any distortion, bending, cracking, or other damage.
I/P braces — Inspect for any distortion, bending,
cracking, or other damage.
Seat belts and mounting points — Refer to “Seat
Belts” in Section “Seat Belt” of this workshop manual.
SDM Replacement Guidelines
SDM replacement policy requires replacement of SDM,
after crash involving air bag deployment when “SRS
Warning Lamp” turn “ON”, “SRS Diagnosis” should be
done according to Section “Restraint Control System.”
If accident without deployment air bag, it is not necessary
replacement of SDM when do not indicate to replace the
SDM by scan tool after SRS system check.
Wiring Damage
If any SRS wire harness is damaged, it should be
replaced. Don’t repair SRS harness. It is replace only.
SRS Connector (Plastic Body And
Terminal Metal Pin) Damage
If any connector or terminal in the SRS wire harness
(except pigtails) is damaged, it should be replaced.
SRS Wire Pigtail Damage
If the wiring pigtail (a wire or wires attached directly to the
device, not by a connector) is damaged, the entire
component (with pigtail) must be replaced. Examples of
“pigtail” components are the driver air bag assembly, the
passenger air bag assembly, and the SRS coil assembly.
On–Vehicle Service
Service Precaution
WARNING: WHEN PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
AROUND SRS COMPONENTS OR SRS WIRING,
FOLLOW THE PROCEDURES LISTED BELOW TO
TEMPORARILY DISABLE THE SRS. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW PROCEDURES COULD RESULT IN
POSSIBLE AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL
INJURY OR OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS REPAIRS.
The SDM in Driver–Passenger SRS can maintain
sufficient voltage to cause a deployment for up to 15
seconds after the ignition switch is turned “OFF,” the
battery is disconnected, or the fuse powering the SDM is
removed.
Many of the service procedures require removal of the
“C–21” fuse, and disconnection of the air bag assembly
from the deployment loop to avoid an accidental
deployment. If the air bag assembly is disconnected from
the deployment loop as noted in the “Disabling the SRS”
procedure that follows, service can begin immediately
without waiting for the 15 second time period to expire.
Disabling The SRS
Removal
Turn the ignition switch to “LOCK” and remove key.
1. Remove SRS fuse C–21, from left dash side lower
fuse block or disconnect battery.
2. Disconnect yellow 2–pin connector at the base of
steering column.
3. Remove glove box assembly, refer to “Passenger Air
Bag Assembly Replacement” in this manual.
4. Disconnect yellow 2–pin connector behind the glove
box assembly.
CAUTION: With the “C–21” fuse removed and
ignition switch “ON”, the “AIR BAG” warning lamp
will be “ON”. This is normal operation and does not
indicate an SRS malfunction.
Enabling The SRS
Installation
CAUTION: Never use the air bag assembly from
another vehicle. Use only the air bag assembly for
Trooper.
Turn ignition switch to “LOCK” and remove key.
1. Connect yellow 2–pin connector passenger air bag
assembly.
2. Install glove box assembly. Refer to “Passenger air
bag assembly replacement” in this manual.
3. Connect yellow 2–pin connector at the base of
steering column.
4. Install “AIR BAG” fuse C–21 to left dash side lower
fuse block or connect battery.
Turn ignition switch to “ON” and verify that the “AIR BAG”
warning lamp turn on 3.5 seconds and then turns “OFF.” If
it does not operate as described, perform the “SRS
Diagnostic System Check” in this manual.
Page 3454 of 6000

SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM9J–17
COOL BEFORE HANDLING ANY METAL PORTION
OF IT. DO NOT PLACE THE DEPLOYED INFLATOR
MODULE NEAR ANY FLAMMABLE OBJECTS.
FAILURE TO FOLLOW PROCEDURES MAY RESULT
IN FIRE OR PERSONAL INJURY. AFTER AN AIR BAG
ASSEMBLY HAS BEEN DEPLOYED, THE METAL
CANISTER AND SURROUNDING AREAS OF THE AIR
BAG ASSEMBLY WILL BE HOT. DO NOT TOUCH THE
METAL AREAS OF THE AIR BAG ASSEMBLY FOR
ABOUT THIRTY MINUTES AFTER DEPLOYMENT. IF
THE DEPLOYED AIR BAG ASSEMBLY MUST BE
MOVED BEFORE IT IS COOL, WEAR GLOVES AND
HANDLE BY THE AIR BAG ITSELF.
21. Disconnect the pigtail adapter from the air bag
assembly as soon after deployment as possible to
avoid damage to the pigtail adapter or SRS
deployment harness from contacting the hot air bag
assembly canister. The pigtail adapter and SRS
deployment harness are designed to be reused.
They should, however, be inspected for damage after
each deployment and replaced if necessary.
22. Dispose of the deployed air bag assembly through
normal refuse channels after it has cooled for at least
30 minutes.
23. Wash your hands with mild soap and water afterward.
NOTE: The remaining steps are to be followed in the
unlikely event that the air bag assembly did not deploy
after following the above procedures.
24. Ensure that the SRS deployment harness has been
disconnected from the power source and that its two
banana plugs have been shorted together by fully
seating one banana plug into the other.
25. Disconnect the pigtail adapter from the air bag
assembly.
WARNING: WHEN STORING A LIVE AIR BAG
ASSEMBLY OR WHEN LEAVING A LIVE AIR BAG
ASSEMBLY UNATTENDED ON A BENCH OR OTHER
SURFACE, ALWAYS FACE THE BAG UP AND AWAY
FROM THE SURFACE. THIS IS NECESSARY SO
THAT A FREE SPACE IS PROVIDED TO ALLOW THE
AIR BAG TO EXPAND IN THE UNLIKELY EVENT OF
ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT. FAILURE TO FOLLOW
PROCEDURES MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
26. Temporarily store the air bag assembly with the bag
facing up, away from the surface upon which it rests.
Deployment Outside Vehicle (Fixing Air
Bag on Tire)
Read and understand the items of “CAUTIONS ABOUT
AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT AND DISPOSAL
PROCEDURES” and “Usage of Deployment Tool” for
safe deployment of air bag.
1. Remove air bag assembly from vehicle. Refer to air
bag assembly Removal “in this section”.2. Inspect J–41434 Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS) Deployment Harness and appropriate pigtail
adapter for damage. If harness or pigtail is damaged,
discard and obtain a replacement.
3. Extend double pole extension cord to a position far
away 10 m (33 feet) from the air bag assembly.
4. Place a power source near the extended end of SRS
air bag deployment harness. (Use of 12V battery is
recommended).
827RW057
Legend
(A) 10 m (33 feet) or more
5. Insert one of the banana plugs into the other banana
plug to short the two SRS air bag deployment
harness. Do not the harness to a power source until
deployment.
827RW055
Page 3467 of 6000

SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM 9J–30
Service Precautions for SRS
Component Service
CAUTION: When fasteners are removed, always
reinstall them at the same location from which they
were removed. If a fastener needs to be replaced, use
the correct part number fastener for that application.
If the correct part number fastener is not available, a
fastener of equal size and strength (or stronger) may
be used. fasteners that are not reused, and those
requiring thread locking compound will be called
out. The correct torque value must be used when
installing fasteners that require it. If the above
conditions are not followed, parts or system damage
could result.
WARNING: WHEN PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
AROUND SRS COMPONENTS OR SRS WIRING,
FOLLOW THE PROCEDURES LISTED BELOW TO
TEMPORARILY DISABLE THE SRS. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW PROCEDURES COULD RESULT IN
POSSIBLE AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL
INJURY OR OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS REPAIRS.
The SDM in Driver–Passenger SRS can maintain
sufficient voltage to cause a deployment for up to 15
seconds after the ignition switch is turned “OFF,” the
battery is disconnected, or the fuse powering the SDM is
removed.
Many of the service procedures require removal of the
“C–21” fuse, and disconnection of the air bag assembly
from the deployment loop to avoid an accidental
deployment. If the air bag assembly is disconnected from
the deployment loop as noted in the “Disabling the SRS”
procedure that follows, service can begin immediately
without waiting for the 15 second time period to expire.
Disabling The SRS
Removal
Turn the ignition switch to “OFF” and turn the steering
wheel so that the vehicle’s wheels are pointing straight
ahead.
1. Remove SRS fuse “C–21” from left dash side lower
fuse block or disconnect battery.
2. Disconnect yellow 2–pin connector at the base of
steering column.
3 . R e m o v e g l o v e b o x a s s e m b l y ; R e f e r t o “ P a s s e n g e r a i r
bag assembly replacement” in this section.
4. Disconnect passenger air bag assembly yellow 2–pin
connector behind the glove box assembly.
CAUTION: W i t h t h e “ C – 2 1 ” f u s e r e m o v e d a n d
ignition switch “ON,” the “AIR BAG” warning lamp
will be “ON.” This is normal operation and does not
indicate an SRS malfunction.
Enabling The SRS
Installation
Turn ignition switch to “LOCK” and remove key.
1. Connect yellow 2–pin connector passenger air bag
assembly.2. Install glove box assembly. Refer to “Passenger Air
Bag Assembly Replacement” in this section.
3. Connect yellow 2–pin connector at the base of the
steering column.
4. Install “AIR BAG” fuse “C–21” to left dash side lower
fuse block or connect battery.
Turn ignition switch to “ON” and verify that the “AIR BAG”
warning lamp turn on 3.5 seconds and then turns “OFF.” If
it does not operate as described, perform the “SRS
Diagnostic System Check” in this section.
Handling / Installation / Diagnosis
1. Air bag assembly should not be subjected to
temperatures above 93
C (200F).
2. Air bag assembly, and SDM should not be used if they
have been dropped from a height of 100 centimeters
(3.28 feet) or more.
3. When a SDM is replaced, it must be oriented with the
arrow on the SDM pointing toward the front of the
vehicle. It is very important for the SDM to be located
flat on the mounting surface, parallel to the vehicle
datum line. It is important that the SDM mounting
surface is free of any dirt or other foreign material.
4. Do not apply power to the SRS unless all components
are connected or a diagnostic chart requests it, as
this will set a diagnostic trouble code.
5. The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” must be the
starting point of any SRS diagnostics. The “SRS
Diagnostic System Check” will verify proper “AIR
BAG” warning lamp operation and will lead you to the
correct chart to diagnose any SRS malfunctions.
Bypassing these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis, and incorrect
parts replacements.
Inspections Required After An Accident
CAUTION: C e r t a i n S R S c o m p o n e n t s m u s t b e
replaced after a frontal crash involving air bag
deployment.
In all types of accidents regardless of “Air Bag”
deployment, visually inspect all of the following
components and replace as required:
— Driver air bag assembly
— Passenger air bag assembly
— Driver pretensioner assembly
— Passenger pretensioner assembly
— Steering wheel
— SRS coil assembly
— Steering column
— Knee bolster and instrument panel mounting
attachments
— Driver seat and belt
— Passenger seat and belt
—SDM
SDM always should be checked according to “SDM
Replacement Guidelines.”
Page 3489 of 6000

RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM 9J1–2
Diagnostic Information
CAUTION: When fasteners are removed, always
reinstall them at the same location from which they
were removed. if a fastener needs to be replaced, use
the correct part number fastener for that application.
if the correct part number fastener is not available, a
fastener of equal size and strength (or stronger) may
be used. fasteners that are not reused, and those
requiring thread locking compound will be called
out. the correct torque value must be used when
installing fasteners that require it. if the above
conditions are not followed, parts or system damage
could result.
Diagnostic Procedures
WARNING: TO AVOID DEPLOYMENT WHEN
TROUBLESHOOTING THE SRS, DO NOT USE
ELECTRICAL TEST EQUIPMENT SUCH AS A
BATTERY–POWERED OR AC–POWERED
VOLTMETER, OHMMETER, ETC., OR ANY TYPE OF
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT OTHER THAN THAT
SPECIFIED IN THIS MANUAL. DO NOT USE A NON
POWERED, PROBE–TYPE TESTER.
INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS MANUAL MUST BE
FOLLOWED CAREFULLY, OTHERWISE PERSONAL
INJURY MAY RESULT.
The diagnostic procedures used in this section are
designed to aid in finding and repairing SRS problems.
Outlined below are the steps to find and repair SRS
problems quickly and effectively. Failure to carefully
follow these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and incorrect parts
replacement.
1.Perform The “SRS Diagnostic System Check”.
The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” should always
be the starting point of any SRS diagnostics. The
“SRS Diagnostic System Check” checks for proper
“AIR BAG” warning lamp operation and checks for
SRS trouble codes using both “Flash Code” and
“Scan Tool” Methods.
2.Refer To The Proper Diagnostic Chart As Directed
By The “SRS Diagnostic System Check”.
The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” will lead you to
the correct chart to diagnose any SRS problems.
Bypassing these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and incorrect
parts replacement.
3.Repeat The “SRS Diagnostic System Check”
After Any Repair Or Diagnostic Procedures Have
Been Performed.
Preforming the “SRS Diagnostic System Check” after
all repair or diagnostic procedures will assure that the
repair has been made correctly and that no other
conditions exist.
Diagnostic Codes
The Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM) maintains a
history record of all diagnostic codes that have beendetected since the SRS codes were last cleared during
service.
1. Active Codes — Faults that are presently detected
this ignition cycle. Active codes are stored in RAM
(Random Access Memory).
2. History Codes — All faults detected since the last
time the history fault memory was cleared. History
codes are stored in EEPROM. (Electronically
Erasable Programmable Read only Memory)
How To Read Trouble Codes
All codes (Active and history) can be read (or cleared) by
using a scan tool or equivalent.
If a PDT is not available, have the vehicle serviced by
ISUZU dealer.
How To Clear Trouble Codes
Trouble codes can only be cleared by using a Scan Tool.
If a “scan tool” is not available then inform the owner of the
stored codes and suggest that the codes are cleared
upon the next visit to an Isuzu dealership.
Scan Tool Diagnostics
A scan tool can be used to read current and history codes
and to clear all history codes after a repair is complete.
The scan tool must be updated to communicate with the
SRS through a memory card or a manufacturer’s update
before it can be used for SRS diagnostics. To use the
scan tool, connect it to the DLC connector and turn the
ignition switch “ON”. Then follow the manufacturer’s
directions for communication with the SRS. The scan tool
reads serial data from the SDM “Serial Data” output
(terminal 24) to the DLC connector (terminal 9).
Basic Knowledge Required
Before using this section of the Service Manual, there is
some basic knowledge which will be required. Without
this knowledge, you will have trouble using the diagnostic
procedures in this section. Use care to prevent harm or
unwanted deployment. Read all cautions in the service
manual and on warning labels attached to SRS
components.
Basic Electrical Circuits
You should understand the basic theory of electricity
including series and parallel circuits, and understand the
voltage drops across series resistors. You should know
the meaning of voltage (volts), current (amps), and
resistance (ohms). You should understand what happens
in a circuit with an open or a shorted wire. You should be
able to read and understand a wiring diagram.
“Flash Code” Diagnostics
Flash code diagnostics can be used to read active codes
and to determine if history codes are present but cannot
be used to clear codes or read history codes. Flash code
diagnostics is enabled by grounding by terminal 4
shorting to terminal 13 of the DLC connector with the
ignition switch “ON”. Grounding terminal 4 of the DLC
connector pulls the “Diagnostics Request” input (Terminal
1) of the SDM low and signals the SDM to enter the flash
code diagnostic display mode.