OBD port OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1986 of 6000

6E–93 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Circuit Description
The rail pressure control valve (RPCV) is built in the high
pressure oil circuit.
RPCV is an important device which is used to control oil
pressure in the HEUI system.
The circuit receives current through Engine 15A fuse from
the battery, current flowing in the order of RPCV.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1196 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
Rail Pressure Control display on the Tech 2 while
moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the
Rail Pressure Control. A change in the Rail Pressure
Control display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P1196 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. Verifies that the fault is present.
DTC P1196 – RP System High Warning
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Engine is running.
2. Observe the “Rail Pressure Control” display on the
Te c h 2 .
Is the action correct?
—Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
3Replace the RPCV.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repairGo to Step 4
41. Engine is running.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor “ DTC” info for DTC P1196.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P1196 failed this
ignition?
—Go to Step 5—
51. Check the 2 way valve.
2. Observe the “RP Control” display on the Tech 2.
Is the action correct?
—Go to Step 4Go to Step 6
6Replace the 2 way valve.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 2069 of 6000

6E–176
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Symptom Diagnosis
Preliminary Checks
Before using this section, perform the “On–Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” and verify all of the
following items:
The powertrain control module (ECM) and
malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (CHECK ENGINE
lamp) are operating correctly.
There are no DTC(s) stored.
Tech–2 data is within normal operating range. Refer
to
Typical Scan Data Values.
Verify the customer complaint and locate the correct
symptom in the table of contents. Perform the
procedure included in the symptom chart.
Visual/Physical Check
Several of the symptom procedures call for a careful
visual/physical check. This can lead to correcting a
problem without further checks and can save valuable
time.
This check should include the following items:
ECM grounds for cleanliness, tightness and proper
location.
Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections, as shown on the “Vehicle Emission
Control Information” label. Check thoroughly for any
type of leak or restriction.
Air intake ducts for collapsed or damaged areas.
Injector wires for cracking, hardness, and carbon
tracking.
Wiring for proper connections, pinches and cuts.
Intermittents
IMPORTANT:An intermittent problem may or may not
turn on the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) or store a
DTC. DO NOT use the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
charts for intermittent problems. The fault must be
present to locate the problem.
Most intermittent problems are caused by faulty electrical
connections or wiring. Perform a careful visual/physical
check for the following conditions:
Poor mating of the connector halves or a terminal not
fully seated in the connector (backed out).
Improperly formed or damaged terminal.
All connector terminals in the problem circuit should
be carefully checked for proper contact tension.
Poor terminal–to–wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body to
check.
Road test the vehicle with a Digital Multimeter
(5-8840-0285-0) connected to a suspected circuit. An
abnormal voltage when the malfunction occurs is a good
indication that there is a fault in the circuit being
monitored.
Use a scan tool to help detect intermittent conditions. The
scan tools have several features that can be used to
locate an intermittent condition. Use the following feature
to find intermittent faults:
Using a Tech–2 “Freeze Frame” buffer or “Failure
Records” buffer can aid in locating an intermittent
condition. Review and record the information in the
freeze frame or failure record associated with the
intermittent DTC being diagnosed. The vehicle can
be driven within the conditions that were present
when the DTC originally set.
To check for loss of diagnostic code memory, disconnect
the MAP sensor and idle the engine until the MIL (CHECK
ENGINE lamp) comes on. DTC P0107 should be stored
and kept in memory when the ignition is turned “OFF.” If
not, the ECM is faulty. When this test is completed, make
sure that you clear the DTC P0107 from memory.
An intermittent MIL (CHECK ENGINE lamp) with no
stored DTC may be caused by the following:
MIL (CHECK ENGINE lamp) wire to ECM shorted to
ground.
Poor ECM grounds. Refer to the ECM wiring
diagrams.
Check for improper installation of electrical options such
as lights, cellular phones, etc.
Check for an open diode across the A/C compressor
clutch and check for other open diodes (refer to wiring
diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis).
If problem has not been found, refer to
ECM Connector
Symptom
tables.
Page 2070 of 6000
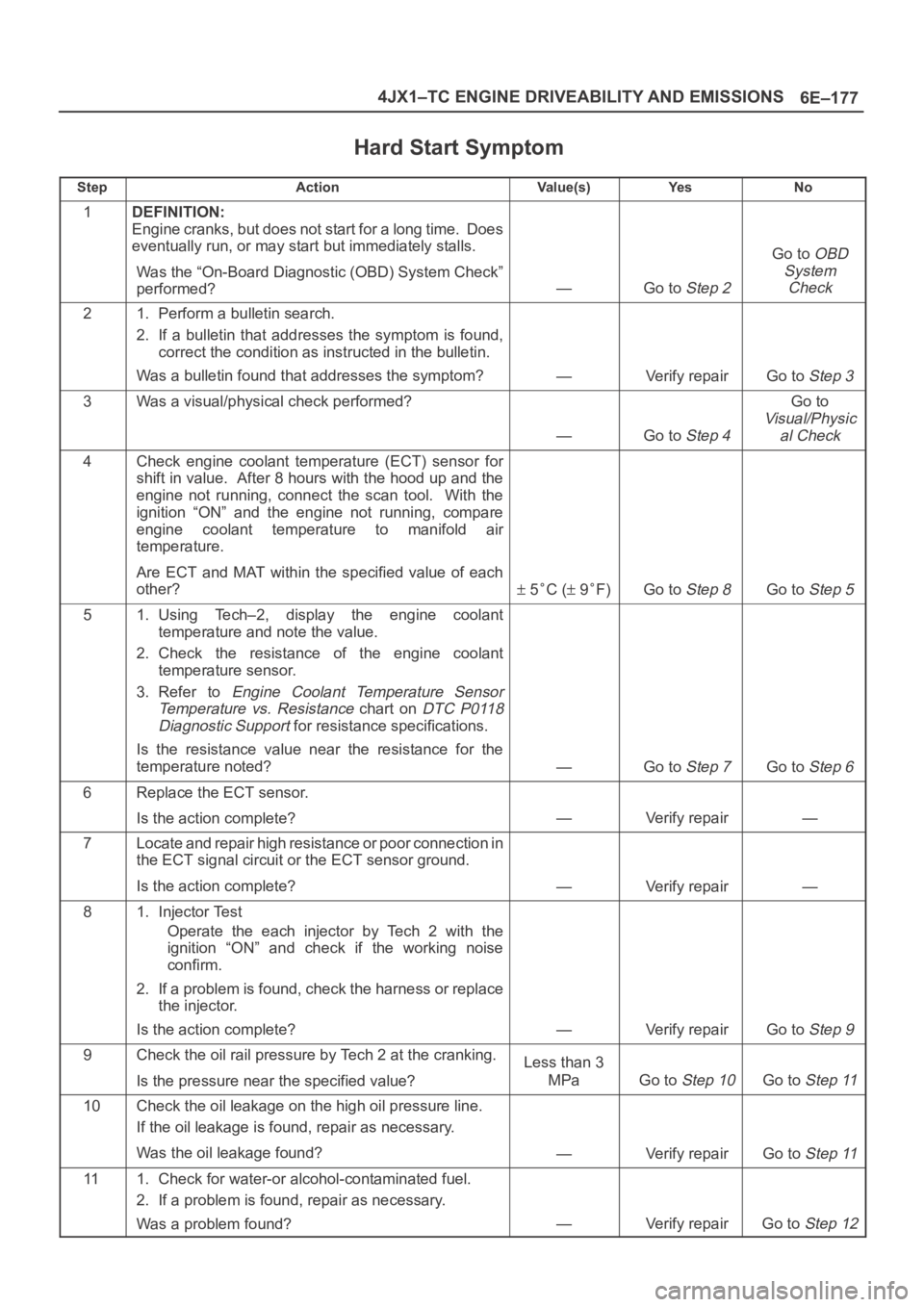
6E–177 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Hard Start Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Engine cranks, but does not start for a long time. Does
eventually run, or may start but immediately stalls.
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to
Visual/Physic
al Check
4Check engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor for
shift in value. After 8 hours with the hood up and the
engine not running, connect the scan tool. With the
ignition “ON” and the engine not running, compare
engine coolant temperature to manifold air
temperature.
Are ECT and MAT within the specified value of each
other?
5C ( 9F)Go to Step 8Go to Step 5
51. Using Tech–2, display the engine coolant
temperature and note the value.
2. Check the resistance of the engine coolant
temperature sensor.
3. Refer to
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Temperature vs. Resistance
chart on DTC P0118
Diagnostic Support
for resistance specifications.
Is the resistance value near the resistance for the
temperature noted?
—Go to Step 7Go to Step 6
6Replace the ECT sensor.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
7Locate and repair high resistance or poor connection in
the ECT signal circuit or the ECT sensor ground.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
81. Injector Test
Operate the each injector by Tech 2 with the
ignition “ON” and check if the working noise
confirm.
2. If a problem is found, check the harness or replace
the injector.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
9Check the oil rail pressure by Tech 2 at the cranking.
Is the pressure near the specified value?Less than 3
MPa
Go to Step 10Go to Step 11
10Check the oil leakage on the high oil pressure line.
If the oil leakage is found, repair as necessary.
Was the oil leakage found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 11
111. Check for water-or alcohol-contaminated fuel.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
Page 2165 of 6000
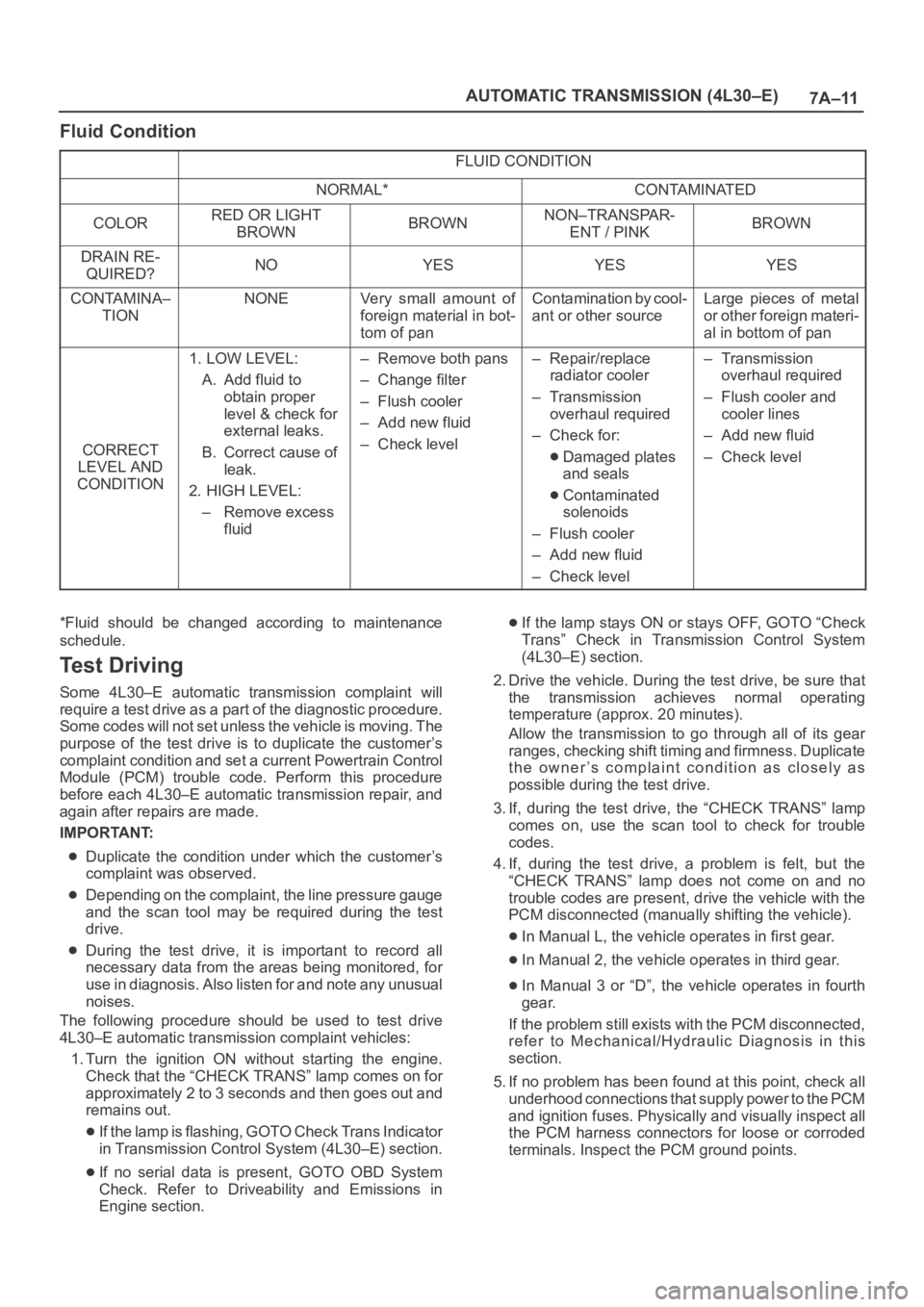
7A–11 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Fluid Condition
FLUID CONDITION
NORMAL*CONTAMINATED
COLORRED OR LIGHT
BROWNBROWNNON–TRANSPAR-
ENT / PINKBROWN
DRAIN RE-
QUIRED?NOYESYESYES
CONTAMINA–
TIONNONEVery small amount of
foreign material in bot-
tom of panContamination by cool-
ant or other sourceLarge pieces of metal
or other foreign materi-
al in bottom of pan
CORRECT
LEVEL AND
CONDITION
1. LOW LEVEL:
A. Add fluid to
obtain proper
level & check for
external leaks.
B. Correct cause of
leak.
2. HIGH LEVEL:
– Remove excess
fluid– Remove both pans
– Change filter
– Flush cooler
– Add new fluid
– Check level– Repair/replace
radiator cooler
–Transmission
overhaul required
– Check for:
Damaged plates
and seals
Contaminated
solenoids
– Flush cooler
– Add new fluid
– Check level
–Transmission
overhaul required
– Flush cooler and
cooler lines
– Add new fluid
– Check level
*Fluid should be changed according to maintenance
schedule.
Te s t D r i v i n g
Some 4L30–E automatic transmission complaint will
require a test drive as a part of the diagnostic procedure.
Some codes will not set unless the vehicle is moving. The
purpose of the test drive is to duplicate the customer’s
complaint condition and set a current Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) trouble code. Perform this procedure
before each 4L30–E automatic transmission repair, and
again after repairs are made.
IMPORTANT:
Duplicate the condition under which the customer’s
complaint was observed.
Depending on the complaint, the line pressure gauge
and the scan tool may be required during the test
drive.
During the test drive, it is important to record all
necessary data from the areas being monitored, for
use in diagnosis. Also listen for and note any unusual
noises.
The following procedure should be used to test drive
4L30–E automatic transmission complaint vehicles:
1. Turn the ignition ON without starting the engine.
Check that the “CHECK TRANS” lamp comes on for
approximately 2 to 3 seconds and then goes out and
remains out.
If the lamp is flashing, GOTO Check Trans Indicator
in Transmission Control System (4L30–E) section.
If no serial data is present, GOTO OBD System
Check. Refer to Driveability and Emissions in
Engine section.
If the lamp stays ON or stays OFF, GOTO “Check
Trans” Check in Transmission Control System
(4L30–E) section.
2. Drive the vehicle. During the test drive, be sure that
the transmission achieves normal operating
temperature (approx. 20 minutes).
Allow the transmission to go through all of its gear
ranges, checking shift timing and firmness. Duplicate
the owner’s complaint condition as closely as
possible during the test drive.
3. If, during the test drive, the “CHECK TRANS” lamp
comes on, use the scan tool to check for trouble
codes.
4. If, during the test drive, a problem is felt, but the
“CHECK TRANS” lamp does not come on and no
trouble codes are present, drive the vehicle with the
PCM disconnected (manually shifting the vehicle).
In Manual L, the vehicle operates in first gear.
In Manual 2, the vehicle operates in third gear.
In Manual 3 or “D”, the vehicle operates in fourth
gear.
If the problem still exists with the PCM disconnected,
refer to Mechanical/Hydraulic Diagnosis in this
section.
5. If no problem has been found at this point, check all
underhood connections that supply power to the PCM
and ignition fuses. Physically and visually inspect all
the PCM harness connectors for loose or corroded
terminals. Inspect the PCM ground points.
Page 2265 of 6000
7A1–20
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
821RW263
810RT022
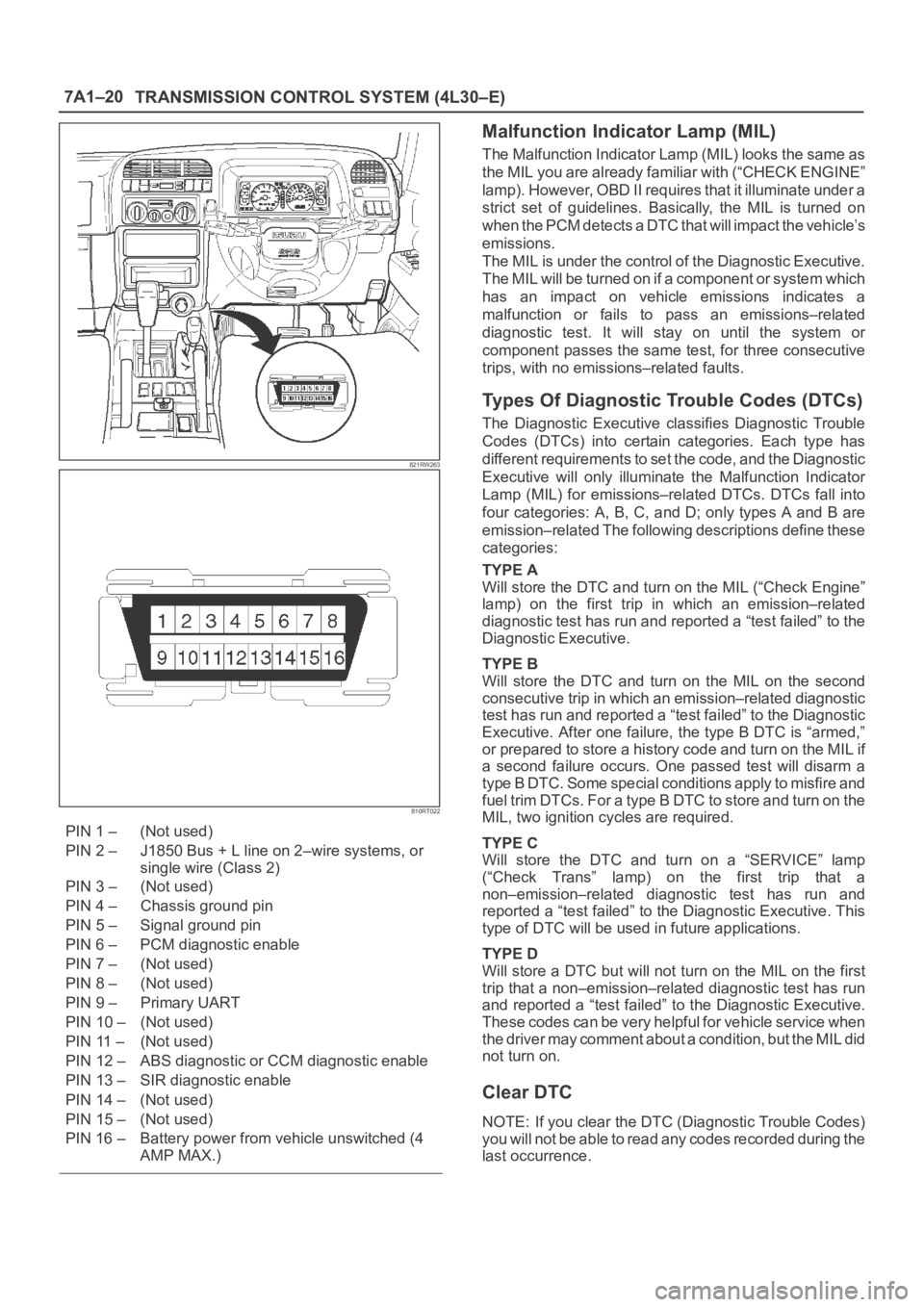
PIN 1 – (Not used)
PIN 2 – J1850 Bus + L line on 2–wire systems, or
single wire (Class 2)
PIN 3 – (Not used)
PIN 4 – Chassis ground pin
PIN 5 – Signal ground pin
PIN 6 – PCM diagnostic enable
PIN 7 – (Not used)
PIN 8 – (Not used)
PIN 9 – Primary UART
PIN 10 – (Not used)
PIN 11 – (Not used)
PIN 12 – ABS diagnostic or CCM diagnostic enable
PIN 13 – SIR diagnostic enable
PIN 14 – (Not used)
PIN 15 – (Not used)
PIN 16 – Battery power from vehicle unswitched (4
AMP MAX.)
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) looks the same as
the MIL you are already familiar with (“CHECK ENGINE”
lamp). However, OBD II requires that it illuminate under a
strict set of guidelines. Basically, the MIL is turned on
when the PCM detects a DTC that will impact the vehicle’s
emissions.
The MIL is under the control of the Diagnostic Executive.
The MIL will be turned on if a component or system which
has an impact on vehicle emissions indicates a
malfunction or fails to pass an emissions–related
diagnostic test. It will stay on until the system or
component passes the same test, for three consecutive
trips, with no emissions–related faults.
Types Of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
The Diagnostic Executive classifies Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTCs) into certain categories. Each type has
different requirements to set the code, and the Diagnostic
Executive will only illuminate the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) for emissions–related DTCs. DTCs fall into
four categories: A, B, C, and D; only types A and B are
emission–related The following descriptions define these
categories:
TYPE A
Will store the DTC and turn on the MIL (“Check Engine”
lamp) on the first trip in which an emission–related
diagnostic test has run and reported a “test failed” to the
Diagnostic Executive.
TYPE B
Will store the DTC and turn on the MIL on the second
consecutive trip in which an emission–related diagnostic
test has run and reported a “test failed” to the Diagnostic
Executive. After one failure, the type B DTC is “armed,”
or prepared to store a history code and turn on the MIL if
a second failure occurs. One passed test will disarm a
type B DTC. Some special conditions apply to misfire and
fuel trim DTCs. For a type B DTC to store and turn on the
MIL, two ignition cycles are required.
TYPE C
Will store the DTC and turn on a “SERVICE” lamp
(“Check Trans” lamp) on the first trip that a
non–emission–related diagnostic test has run and
reported a “test failed” to the Diagnostic Executive. This
type of DTC will be used in future applications.
TYPE D
Will store a DTC but will not turn on the MIL on the first
trip that a non–emission–related diagnostic test has run
and reported a “test failed” to the Diagnostic Executive.
These codes can be very helpful for vehicle service when
the driver may comment about a condition, but the MIL did
not turn on.
Clear DTC
NOTE: If you clear the DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Codes)
you will not be able to read any codes recorded during the
last occurrence.
Page 2266 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–21
NOTE: To use the DTC again to identify a problem, you
will need to reproduce the fault or the problem. This may
require a new test drive or just turning the ignition on (this
depends on the nature of the fault).
1. IF you have a Tech2:
1. Connect the Tech2 if it is still not connected
GOTHROUGH Tech2 OBD II CONNECTION.
2. Push “F4” and answer “Yes” to the question “Do
you really want to clear the codes?”
a. When a malfunction remains as it is the Tech2
displays “4L30E CODES NOT CLEARED”. This
means that the problem is still there or that the
recovery was not done. Please GOTO DTC
CHECK.
b. When a malfunction has been repaired and the
recovery is done. The Tech2 displays “4L30E
CODES CLEARED”.
2. IF you have no Tech2:
To clear the DTC, remove Fuse “Stop, A/T CONT”
(C–14, 15A) for at least 10 seconds.
DTC Check
1. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) have been identified
by Tech2.
2. You have written the list of the DTCs. The order of the
malfunctions has no meanings for this PCM. Usually
only one or two malfunctions should be set for a given
problem.
3. Check directly the DTCs you identified. The DTCs are
sorted by number. Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) Identification in this section.
PCM Precaution
The PCM can be damaged by:
1. Electrostatic discharge
2. The short circuit of some terminals to voltage or to
ground.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage Description:
1. Electronic components used to control systems are
often designed to carry very low voltage, and are very
susceptible to damage caused by electrostatic
discharge. It is possible for less than 100 volts of
static electricity to cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as
4,000 volts for a person to even feel the zap of a static
discharge.2. There are several ways for a person to become
statically charged. The most common methods of
charging are by friction and induction. An example of
charging by friction is a person sliding across a car
seat, in which a charge of as much as 25,000 volts
can build up. Charging by induction occurs when a
person with well insulated shoes stands near a highly
charged object and momentarily touches ground.
Charges for the same polarity are drained off, leaving
the person highly charged with the opposite polarity.
Static charges of either type can cause damage,
therefore, it is important to use care when handling
and testing electronic components.
NOTICE: To prevent possible electrostatic
discharge damage:
1. Do not touch the PCM connector pins or soldered
components on the PCM circuit board.
2. Be sure to follow the guidelines listed below if
servicing any of these electronic components:
3. Do not open the replacement part package until it is
time to install the part.
4. Avoid touching electrical terminals of the part.
5. Before removing the part from its package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
6. Always touch a known good ground before handling
the part. This step should be repeated before
installing the part if the part has been handled while
sliding across the seat, while sitting down from a
standing position or while walking some distance.
Information On PCM
1. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is located in
the center console and is the control center of the
electronic transmission control system.
2. The PCM must be maintained at a temperature below
185
F (85C) at all times. This is most essential if the
vehicle is put through a paint baking process. The
PCM will become inoperative if its temperature
exceeds 85
C (185F). Therefore, it is
recommended that the PCM be removed or that
temporary insulation be placed around the PCM
during the time the vehicle is in a paint oven or other
high temperature process.
3. The PCM is designed to process the various inputs
and then respond by sending the appropriate
electrical signals to control transmission upshift,
downshift, shift feel and torque converter clutch
engagement.
4. The PCM constantly interprets information from the
various sensors, and controls the systems that affect
transmission and vehicle performance. By analyzing
operational problems, the PCM is able to perform a
diagnostic function by displaying DTC(s) and aid the
technician in making repairs.
Intermittent Conditions
If the Tech2 displays a diagnostic trouble code as
intermittent, or if after a test drive a DTC does not
reappear though the detection conditions for this DTC are
present, the problem is most likely a faulty electrical
Page 4658 of 6000

6E–1 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
ENGINE
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CONTENTS
Specifications 6E–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tightening Specifications 6E–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle Type Specifications 6E–5. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagrams and Schematics 6E–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (1 of 11) 6E–6. . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (2 of 11) For EC,
THAILAND, SOUTH EAST ASIA, LATIN
AMERICA, GULF, SAUDI, CHINA. 6E–7. . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (3 of 11) For SOUTH
AFRICA and EXP. 6E–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (4 of 11) 6E–9. . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (5 of 11) 6E–10. . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (6 of 11) For
AUSTRALIA, THAILAND, SOUTH EAST
ASIA, LATIN AMERICA, GULF, SAUDI,
LATIN AMERICA. 6E–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (7 of 11) For EC. 6E–12. . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (8 of 11) For EXPORT
and SOUTH AFRICA. 6E–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (9 of 11) Except EXP
and SOUTH AFRICA 6E–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (10 of 11) For
EXPORT and SOUTH AFRICA 6E–15. . . . . . . . .
PCM Wiring Diagram (11 of 11) 6E–16. . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinouts 6E–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Red
Connector – Row “A” 6E–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Red
Connector – Row “B” 6E–19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White
Connector – Row “C” (For EC) 6E–20. . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White
Connector – Row “C” (For except EC) 6E–21. . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White
Connector – Row “D”
(For except EXPORT and SOUTH
AFRICA) 6E–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way White
Connector – Row “D”
(For EXPORT and SOUTH AFRICA) 6E–23. . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Blue
Connector – Row “E”
(For except EXPORT and SOUTH
AFRICA) 6E–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Blue
Connector – Row “E”
(For EXPORT and SOUTH AFRICA) 6E–26. . . . .
PCM Pinout Table, 32-Way Blue
Connector – Row “F” 6E–27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Component Locators 6E–28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Component Locator (This illustration
is based on RHD model.) 6E–28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . Engine Component Locator Table 6E–29. . . . . . . .
Engine Component Locator Table 6E–31. . . . . . . .
Undercarriage Component Locator 6E–32. . . . . .
Undercarriage Component Locator Table
(Automatic Transmission) 6E–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Undercarriage Component Locator Table
(Manual Transmission) 6E–33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuse and Relay Panel (Underhood
Electrical Center) 6E–33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Sensors and Miscellaneous Component
Locators 6E–34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnosis 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Strategy-Based Diagnostics 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Strategy-Based Diagnostics 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Stored 6E–37
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No DTC 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Matching Symptom 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intermittents 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Trouble Found 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Vehicle Repair 6E–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Service Information 6E–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OBD Serviceablity Issues 6E–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maintenance Schedule 6E–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Visual / Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection 6E–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required 6E–38. . . . . .
Serial Data Communications 6E–38. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Class II Serial Data Communications 6E–38. . . . .
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) 6E–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
On-Board Diagnostic Tests 6E–39. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Comprehensive Component Monitor
Diagnostic Operation 6E–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Common OBD Terms 6E–40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
The Diagnostic Executive 6E–40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Types 6E–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Verifying Vehicle Repair 6E–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes Using
A Tech 2 6E–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tech 2 Tech 2 6E–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tech 2 Features 6E–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Getting Started 6E–44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating Procedure (For Example) 6E–44. . . . .
DTC Modes 6E–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Information Mode 6E–46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Injector Balance Test 6E–46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EGR Control Test 6E–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control System Test 6E–48. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 4659 of 6000

6E–2
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Primary System-Based Diagnostic 6E–50. . . . . . . . .
Primary System-Based Diagnostic 6E–50. . . . . . .
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensor 6E–50. . . . .
HO2S Heater 6E–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Trim System Monitor Diagnostic
Operation 6E–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Trim System Monitor Diagnostic
Operation 6E–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Trim Cell Diagnostic Weights 6E–50. . . . . . .
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check 6E–51.
A/C Clutch Control Circuit Diagnosis 6E–54. . . . . . .
Electronic Ignition System Diagnosis 6E–60. . . . . . .
Fuel Metering System Check 6E–60. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve 6E–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel System Pressure Test 6E–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure and Fuel
Injector Balance Test Procedure 6E–60. . . . . . . . . .
Knock Sensor Diagnosis 6E–65. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Diagnosis 6E–65
Multiple PCM Information Sensor DTCS Set 6E–65
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Diagnosis
(For except EXPORT and
SOUTH AFRICA) 6E–68. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Tech 2 Data Definitions and Ranges 6E–68
Typical Scan Data Values 6E–70. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) 6E–74. . . . . . .
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) “ON”
Steady 6E–77. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Cranks But Will Not Run 6E–79. . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel System Electrical Test 6E–85. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel System Diagnosis 6E–88. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control (IAC) System Check 6E–93. . . . . . .
Knock Sensor (KS) System Check
(Engine Knock, Poor Performance, or Poor
Economy) 6E–95. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
Check 6E–97. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Output
Check 6E–99. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes 6E–101. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0101
MAF System Performance 6E–104. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0102
MAF Sensor Circuit Low Frequency 6E–107. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0103
MAF Sensor Circuit High Frequency 6E–110. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0107
MAP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–112. . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0108
MAP Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–115. . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0112
IAT Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–118. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0113
IAT Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–121. . . . . . . . . . Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0117
ECT Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–124. . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0118
ECT Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–127. . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0121
TP System Performance 6E–130. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0122
TP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–133. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0123
TP Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–136. . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0131
HO2S Circuit Low Voltage Bank 1
Sensor 1 6E–139. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0132
HO2S Circuit High Voltage Bank 1
Sensor 1 6E–142. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0134
HO2S Circuit Insufficient Activity Bank 1
Sensor 1 6E–145. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0151
HO2S Circuit Low Voltage Bank 2
Sensor 1 6E–148. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0152
HO2S Circuit HIGH Voltage Bank 2
Sensor 1 6E–151. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0171
Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 1 6E–154. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0172
Fuel Trim System Rich Bank 1 6E–158. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0174
Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2 6E–162. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0175
Fuel Trim System Rich Bank 2 6E–166. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0201
Injector 1 Control Circuit 6E–170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0202
Injector 2 Control Circuit 6E–173. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0203
Injector 3 Control Circuit 6E–176. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0204
Injector 4 Control Circuit 6E–179. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0205
Injector 5 Control Circuit 6E–182. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0206
Injector 6 Control Circuit 6E–185. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0325
KS Module Circuit 6E–188. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0327
KS Sensor Circuit 6E–190. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0336
58X Reference Signal Circuit 6E–193. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0337
CKP Sensor Circuit Low Frequency 6E–195. . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0341
CMP Sensor Circuit Performance 6E–198. . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0342
CMP Sensor Circuit Low 6E–202. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 4662 of 6000

6E–5 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Specifications
Tightening Specifications
ApplicationNꞏmLb Ft.Lb In.
Camshaft Position Sensor Retaining Screw9—78
Crankshaft Position Sensor Mounting Bolt10—87
EGR Bolt2821—
EGR Nut2821—
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor207.7—
Fuel Drain Plug2922—
Fuel Pressure Regulator Attaching Screw6.5—60
Fuel Rail Bolts2518—
Fuel Tank Undercover Retaining Bolts3627—
Heated Oxygen Sensor4231—
Lower Intake Manifold to Engine Block Bolts2518—
Lower Intake Manifold to Engine Block Nuts2518—
Spark Plugs1813—
Throttle Body Mounting Bolts2518—
Upper Intake Manifold to Lower Intake Manifold Bolts2518—
VSS Retaining Bolt13—120
Vehicle Type Specifications
ECAUSTRALIA
THAILAND
SOUTH-EA
ST-ASIA
LATIN
AMERICAGULF
CONTRIES
SAUDI
CHINASOU
TH
AFRI
CA
EXPORTSpecifications
UBSUBSUBSUBSUBSUBS
OBD
O2
SENCATEGRMTATMTATMTATMTATMTMTATOBDSEN
SORAEGR
I21
I21
11
11
11
11
1
1
I
Page 4694 of 6000

6E–37 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnosis
Strategy-Based Diagnostics
Strategy-Based Diagnostics
The strategy-based diagnostic is a uniform approach to
repair all Electrical/Electronic (E/E) systems. The
diagnostic flow can always be used to resolve an E/E
system problem and is a starting point when repairs are
necessary. The following steps will instruct the technician
how to proceed with a diagnosis:
1. Verify the customer complaint.
To verify the customer complaint, the technician
should know the normal operation of the system.
2. Perform preliminary checks.
Conduct a thorough visual inspection.
Review the service history.
Detect unusual sounds or odors.
Gather diagnostic trouble code information to
achieve an effective repair.
3. Check bulletins and other service information.
This includes videos, newsletters, etc.
4. Refer to service information (manual) system
check(s).
“System checks” contain information on a system
that may not be supported by one or more DTCs.
System checks verify proper operation of the
system. This will lead the technician in an
organized approach to diagnostics.
5. Refer to service diagnostics.
DTC Stored
Follow the designated DTC chart exactly to make an
effective repair.
No DTC
Select the symptom from the symptom tables. Follow the
diagnostic paths or suggestions to complete the repair.
You may refer to the applicable component/system check
in the system checks.
No Matching Symptom
1. Analyze the complaint.
2. Develop a plan for diagnostics.
3. Utilize the wiring diagrams and the theory of
operation.
Call technical assistance for similar cases where repair
history may be available. Combine technician knowledge
with efficient use of the available service information.
Intermittents
Conditions that are not always present are called
intermittents. To resolve intermittents, perform the
following steps:
1. Observe history DTCs, DTC modes, and freezeframe
data.
2. Evaluate the symptoms and the conditions described
by the customer.3. Use a check sheet or other method to identify the
circuit or electrical system component.
4. Follow the suggestions for intermittent diagnosis
found in the service documentation.
Most Tech 2s, such as the Tech II and the
5–8840–0285–0 (Fluke model 87 DVOM), have
data-capturing capabilities that can assist in detecting
intermittents.
No Trouble Found
This condition exists when the vehicle is found to operate
normally. The condition described by the customer may
be normal. Verify the customer complaint against another
vehicle that is operating normally. The condition may be
intermittent. Verify the complaint under the conditions
described by the customer before releasing the vehicle.
1. Re-examine the complaint.
When the Complaint cannot be successfully found or
isolated, a re-evaluation is necessary. The complaint
should be re-verified and could be intermittent as
defined in
Intermittents, or could be normal.
2. Repair and verify.
After isolating the cause, the repairs should be made.
Validate for proper operation and verify that the
symptom has been corrected. This may involve road
testing or other methods to verify that the complaint
has been resolved under the following conditions:
Conditions noted by the customer.
If a DTC was diagnosed, verify a repair by
duplicating conditions present when the DTC was
set as noted in the Failure Records or Freeze
Frame data.
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of the vehicle repair will be more
comprehensive for vehicles with OBD system
diagnostics. Following a repair, the technician should
perform the following steps:
IMPORTANT:Follow the steps below when you verify
repairs on OBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
1. Review and record the Failure Records and the
Freeze Frame data for the DTC which has been
diagnosed (Freeze Frame data will only be stored for
an A or B type diagnostic and only if the MIL(”Check
Engine” lamp) has been requested).
2. Clear the DTC(S).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the
Failure Records and Freeze Frame data.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the specific
DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic
test associated with that DTC runs.