check engine OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1072 of 6000
6C–5
ENGINE FUEL
Installation
1. Install the fuel filter in the proper direction.
2. Install fuel filter holder fixing bolt.
3. Connect fuel hoses on engine side(1) and fuel tank
side(2).
041RW001
4. Install fuel filler cap
5. Connect the battery ground cable.
Inspection
After installation, start engine and check for fuel leakage.
In–Tank Fuel Filter
The filter is located on the lower end of fuel pickup tube in
the fuel tank. It prevents dirt from entering the fuel pipe
and also stops water unless the filter is completely
submerged in the water. It is a self cleaning type, not
requiring scheduled maintenance. Excess water and
sediment in the tank restricts fuel supply to the engine,
resulting in engine stoppage. In such a case, the tank
must be cleaned thoroughly.
Fuel Pump Flow Test
If reduction of fuel supply is suspected, perform the
following checks:
1. Make sure that there is fuel in the tank.
2. With the engine running, check the fuel feed pipe and
hose from fuel tank to injector for evidence of
leakage. Retighten, if pipe or hose connection is
loose. Also, check pipes and hoses for squashing or
clogging.
3. Insert the hose from fuel feed pipe into a clean
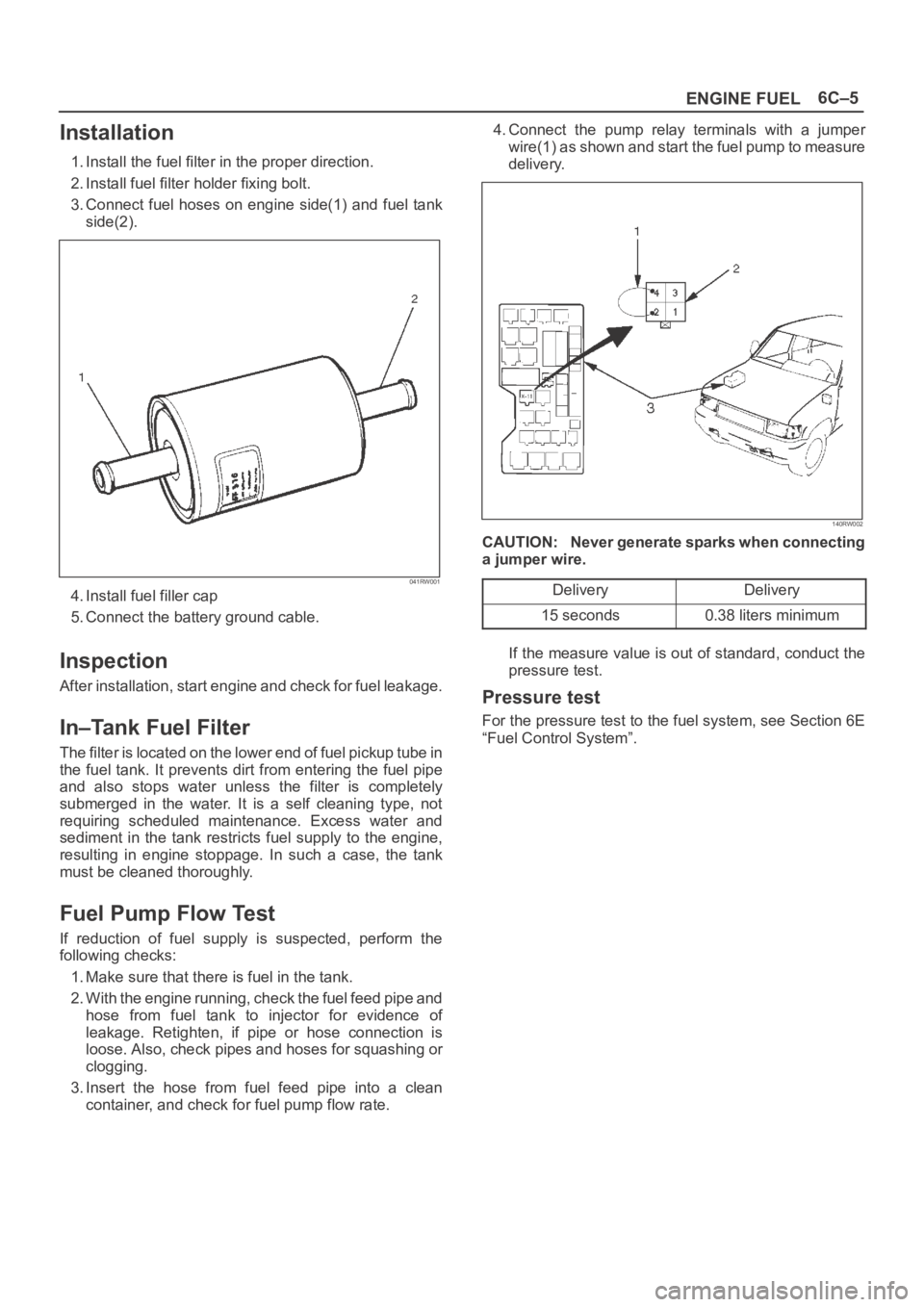
container, and check for fuel pump flow rate.4. Connect the pump relay terminals with a jumper
wire(1) as shown and start the fuel pump to measure
delivery.
140RW002
CAUTION: Never generate sparks when connecting
a jumper wire.
Delivery
Delivery
15 seconds0.38 liters minimum
If the measure value is out of standard, conduct the
pressure test.
Pressure test
For the pressure test to the fuel system, see Section 6E
“Fuel Control System”.
Page 1073 of 6000
6C–6
ENGINE FUEL
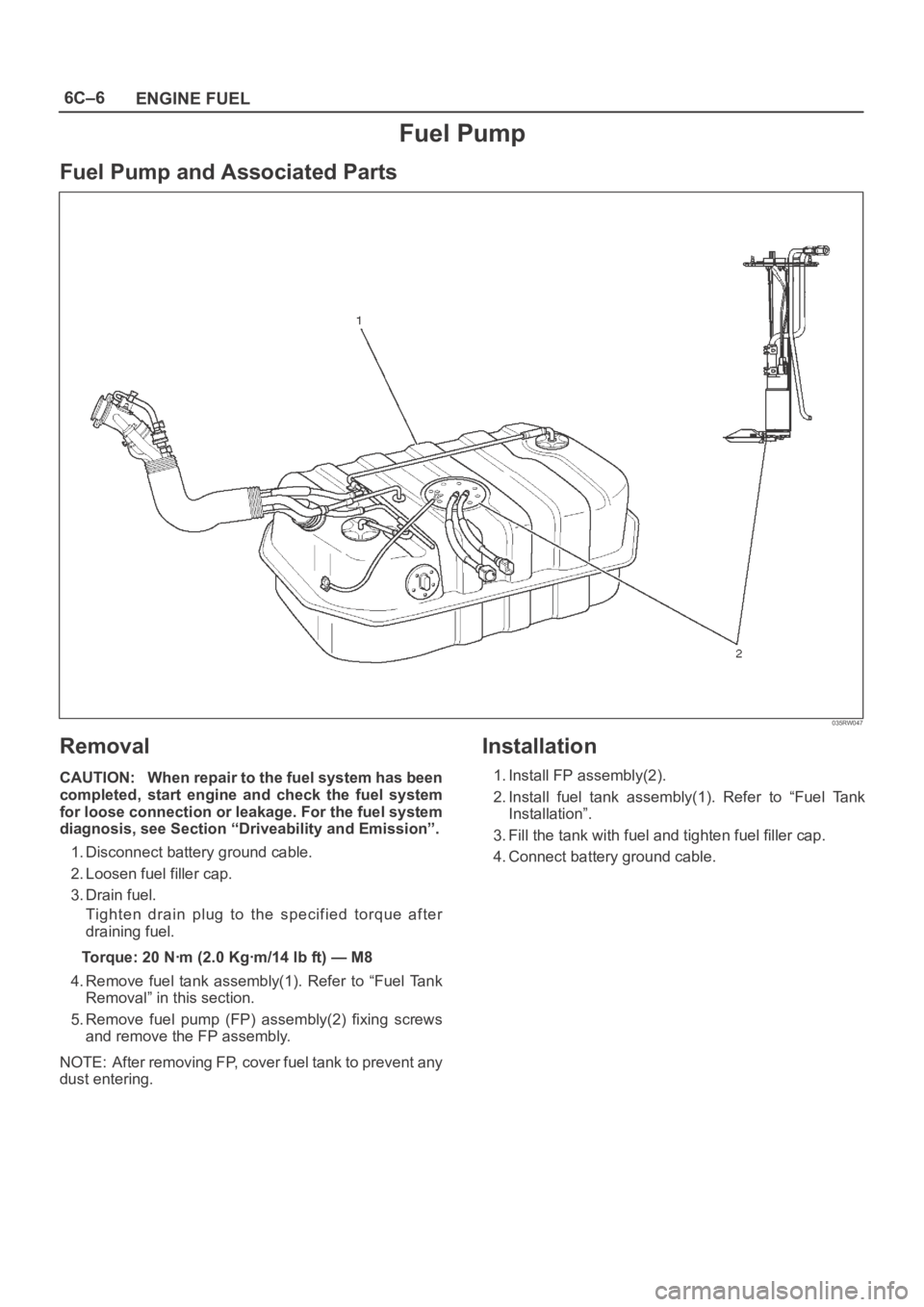
Fuel Pump
Fuel Pump and Associated Parts
035RW047
Removal
CAUTION: When repair to the fuel system has been
completed, start engine and check the fuel system
for loose connection or leakage. For the fuel system
diagnosis, see Section “Driveability and Emission”.
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Loosen fuel filler cap.
3. Drain fuel.
Tighten drain plug to the specified torque after
draining fuel.
Torque: 20 Nꞏm (2.0 Kgꞏm/14 lb ft) — M8
4. Remove fuel tank assembly(1). Refer to “Fuel Tank
Removal” in this section.
5. Remove fuel pump (FP) assembly(2) fixing screws
and remove the FP assembly.
NOTE: After removing FP, cover fuel tank to prevent any
dust entering.
Installation
1. Install FP assembly(2).
2. Install fuel tank assembly(1). Refer to “Fuel Tank
Installation”.
3. Fill the tank with fuel and tighten fuel filler cap.
4. Connect battery ground cable.
Page 1074 of 6000
6C–7
ENGINE FUEL
Fuel Pump Relay
General Description
In order to control the FP operation, the FP relay is
provided. When the starter switch is turned to “ON”
position, the FP relay operates the FP for 2 seconds.When it is turned to “START” position, the Power Train
Control Module (PCM) receives the reference pulse from
the Ignition Control Module and it operates the relay,
again causing the FP to feed fuel.
Fuel Tank
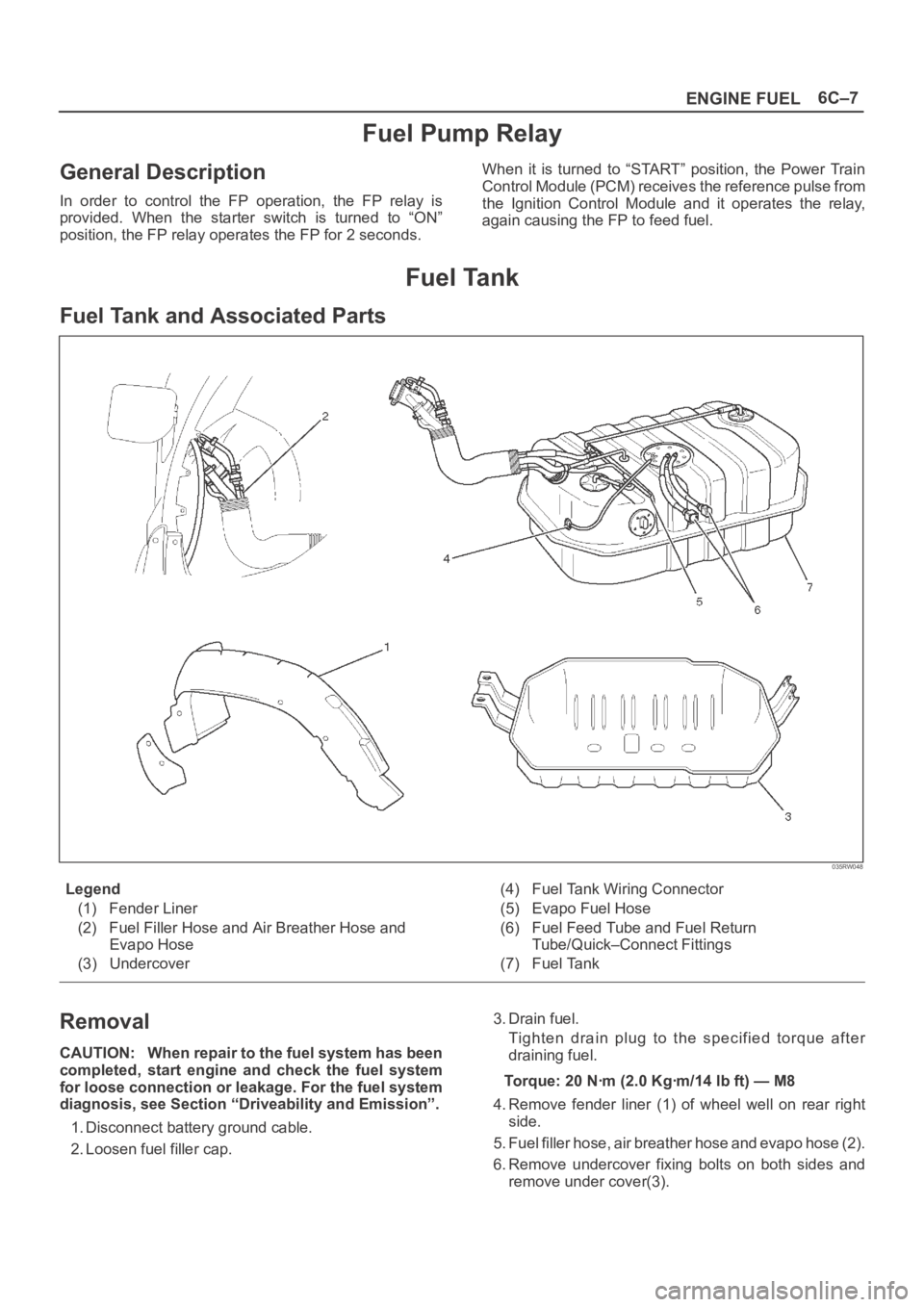
Fuel Tank and Associated Parts
035RW048
Legend
(1) Fender Liner
(2) Fuel Filler Hose and Air Breather Hose and
Evapo Hose
(3) Undercover(4) Fuel Tank Wiring Connector
(5) Evapo Fuel Hose
(6) Fuel Feed Tube and Fuel Return
Tube/Quick–Connect Fittings
(7) Fuel Tank
Removal
CAUTION: When repair to the fuel system has been
completed, start engine and check the fuel system
for loose connection or leakage. For the fuel system
diagnosis, see Section “Driveability and Emission”.
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Loosen fuel filler cap.3. Drain fuel.
Tighten drain plug to the specified torque after
draining fuel.
Torque: 20 Nꞏm (2.0 Kgꞏm/14 lb ft) — M8
4. Remove fender liner (1) of wheel well on rear right
side.
5. Fuel filler hose, air breather hose and evapo hose (2).
6. Remove undercover fixing bolts on both sides and
remove under cover(3).
Page 1077 of 6000

6C–10
ENGINE FUEL
Reuse of Quick–Connector
(Delivery Pipe)
Replace the pipe and connector if scratch, dent or
crack is found.
Remove mud and dust from the pipe and make sure
that the end including spool is free of defects, such as
scratch, rust, and dent, which may cause poor
sealability. If defective, replace with a new pipe.
If the retainer removed according to the removal step
above is attached to the pipe, clean and insert it
straight into the quick-connector till it clicks. After it
clicks, try pulling it out to make sure that it is not drawn
and is securely locked.
NOTE: The retainer, once removed from the pipe, cannot
be reused. Just replace with a new retainer. Insert the
new retainer into the connector side until it clicks, and
connect the pipe as inserting it into the retainer until it
clicks.
141RW018
(Return Pipe)
Replace the pipe and connector if scratch, dent or
crack is found.
Remove mud or dust from the pipe and make sure
that the end including spool is free from defects, such
as scratch, rust, and dent, which may cause poor
sealability. If defective, replace with a new pipe.
After cleaning the pipe, insert it straight into the
connector until it clicks. After it clicks, try pulling it out
to make sure that it is not drawn and is securely
locked.
141RW017
Assembling Advice
Application of engine oil or light oil to the pipe facilitates
connecting work. The work should be started immediately
after lubrication, since dust may stick to the pipe surface
to cause poor sealability if a long time passes after
lubrication.
Test/Inspection After Assembling
1. Reconnect the battery negative cable.
2. Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position and check
pump startup sound. As the pump is actuated to raise
fuel pressure, check and see fuel leak from the piping
system.
3. Make sure of no fuel leakage by conducting the above
fuel leak check a few times.
4. Start the engine and make sure of stable idling speed
and normal vehicle run.The entry of dust during the
work may sometimes affect the fuel injection system.
Page 1078 of 6000
6C–11
ENGINE FUEL
Fuel Gauge Unit
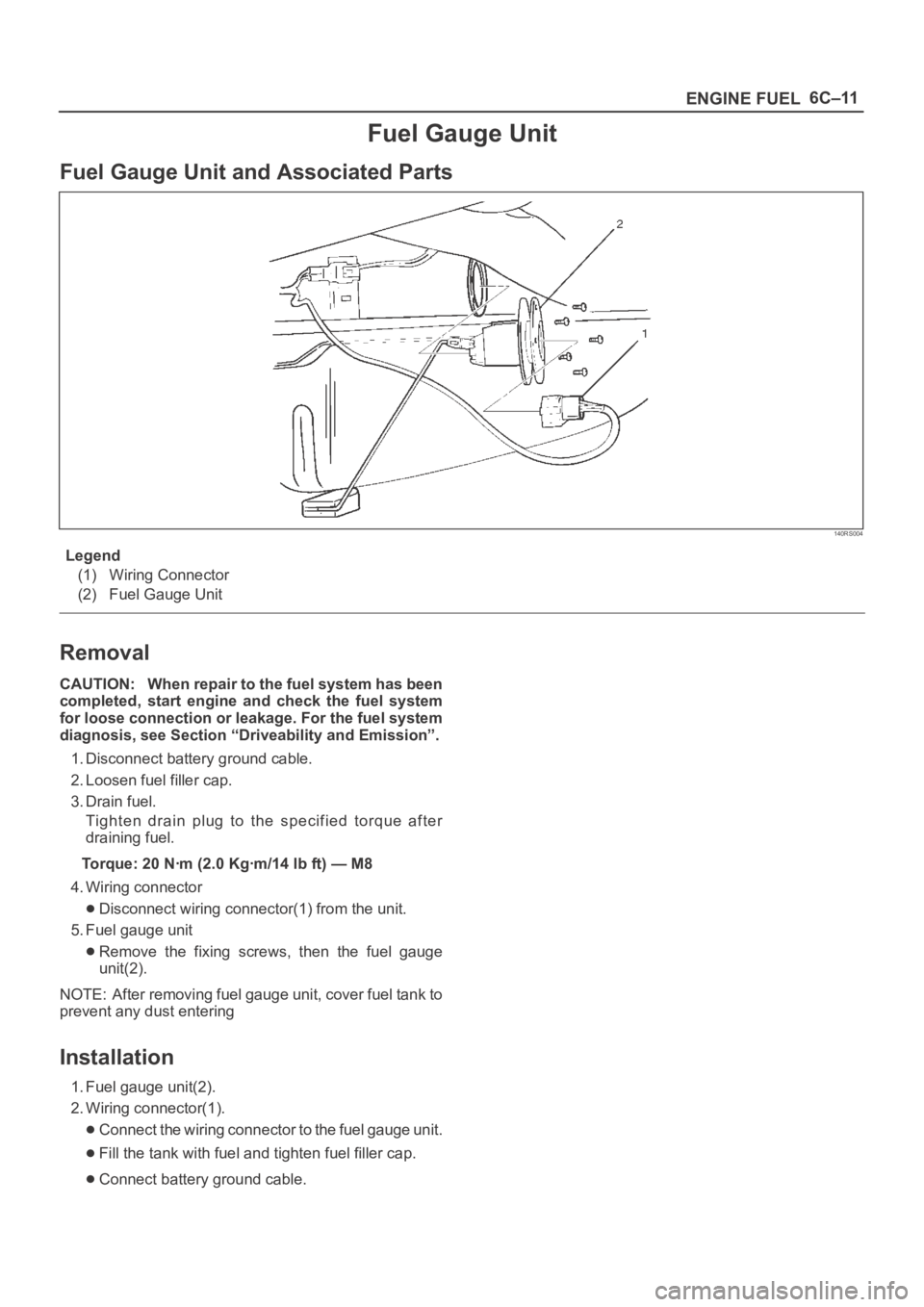
Fuel Gauge Unit and Associated Parts
140RS004
Legend
(1) Wiring Connector
(2) Fuel Gauge Unit
Removal
CAUTION: When repair to the fuel system has been
completed, start engine and check the fuel system
for loose connection or leakage. For the fuel system
diagnosis, see Section “Driveability and Emission”.
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Loosen fuel filler cap.
3. Drain fuel.
Tighten drain plug to the specified torque after
draining fuel.
Torque: 20 Nꞏm (2.0 Kgꞏm/14 lb ft) — M8
4. Wiring connector
Disconnect wiring connector(1) from the unit.
5. Fuel gauge unit
Remove the fixing screws, then the fuel gauge
unit(2).
NOTE: After removing fuel gauge unit, cover fuel tank to
prevent any dust entering
Installation
1. Fuel gauge unit(2).
2. Wiring connector(1).
Connect the wiring connector to the fuel gauge unit.
Fill the tank with fuel and tighten fuel filler cap.
Connect battery ground cable.
Page 1079 of 6000
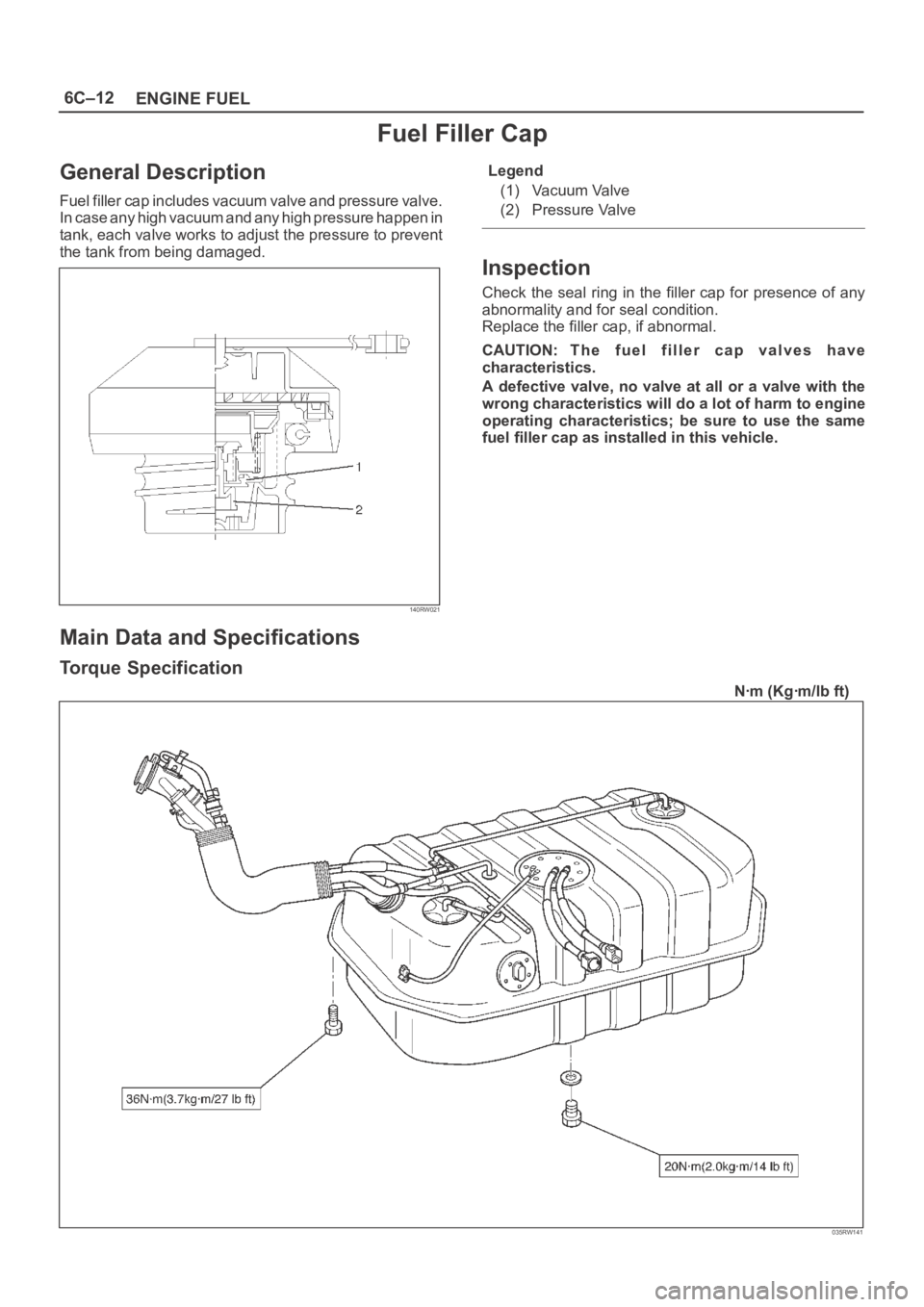
6C–12
ENGINE FUEL
Fuel Filler Cap
General Description
Fuel filler cap includes vacuum valve and pressure valve.
In case any high vacuum and any high pressure happen in
tank, each valve works to adjust the pressure to prevent
the tank from being damaged.
140RW021
Legend
(1) Vacuum Valve
(2) Pressure Valve
Inspection
Check the seal ring in the filler cap for presence of any
abnormality and for seal condition.
Replace the filler cap, if abnormal.
CAUTION: The fuel filler cap valves have
characteristics.
A defective valve, no valve at all or a valve with the
wrong characteristics will do a lot of harm to engine
operating characteristics; be sure to use the same
fuel filler cap as installed in this vehicle.
Main Data and Specifications
Torque Specification
Nꞏm (Kgꞏm/lb ft)
035RW141
Page 1081 of 6000
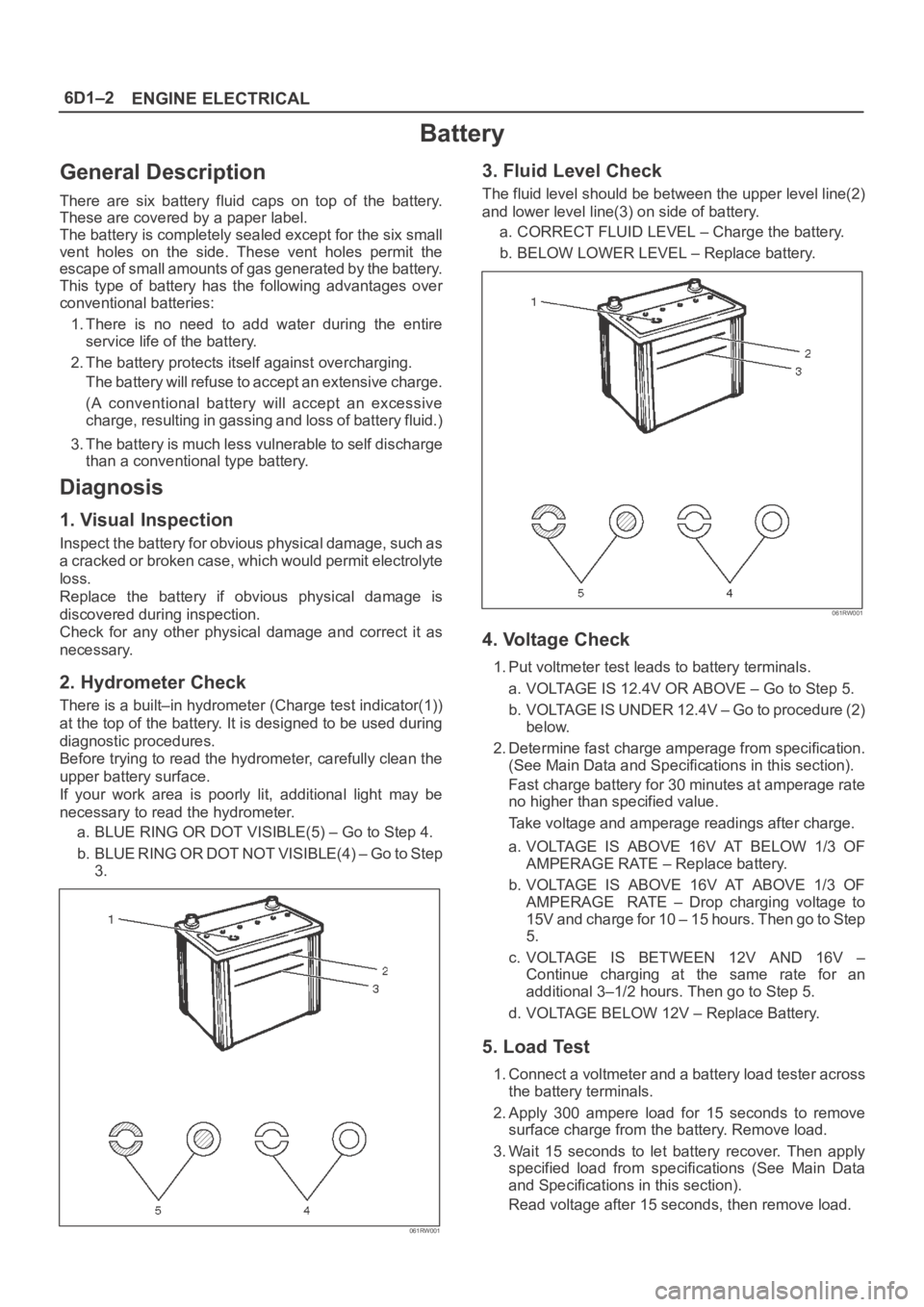
6D1–2
ENGINE ELECTRICAL
Battery
General Description
There are six battery fluid caps on top of the battery.
These are covered by a paper label.
The battery is completely sealed except for the six small
vent holes on the side. These vent holes permit the
escape of small amounts of gas generated by the battery.
This type of battery has the following advantages over
conventional batteries:
1. There is no need to add water during the entire
service life of the battery.
2. The battery protects itself against overcharging.
The battery will refuse to accept an extensive charge.
(A conventional battery will accept an excessive
charge, resulting in gassing and loss of battery fluid.)
3. The battery is much less vulnerable to self discharge
than a conventional type battery.
Diagnosis
1. Visual Inspection
Inspect the battery for obvious physical damage, such as
a cracked or broken case, which would permit electrolyte
loss.
Replace the battery if obvious physical damage is
discovered during inspection.
Check for any other physical damage and correct it as
necessary.
2. Hydrometer Check
There is a built–in hydrometer (Charge test indicator(1))
at the top of the battery. It is designed to be used during
diagnostic procedures.
Before trying to read the hydrometer, carefully clean the
upper battery surface.
If your work area is poorly lit, additional light may be
necessary to read the hydrometer.
a. BLUE RING OR DOT VISIBLE(5) – Go to Step 4.
b . B L U E R I N G O R D O T N O T V I S I B L E ( 4 ) – G o t o S t e p
3.
061RW001
3. Fluid Level Check
The fluid level should be between the upper level line(2)
and lower level line(3) on side of battery.
a. CORRECT FLUID LEVEL – Charge the battery.
b. BELOW LOWER LEVEL – Replace battery.
061RW001
4. Voltage Check
1. Put voltmeter test leads to battery terminals.
a. VOLTAGE IS 12.4V OR ABOVE – Go to Step 5.
b. VOLTAGE IS UNDER 12.4V – Go to procedure (2)
below.
2. Determine fast charge amperage from specification.
(See Main Data and Specifications in this section).
Fast charge battery for 30 minutes at amperage rate
no higher than specified value.
Take voltage and amperage readings after charge.
a. VOLTAGE IS ABOVE 16V AT BELOW 1/3 OF
AMPERAGE RATE – Replace battery.
b. VOLTAGE IS ABOVE 16V AT ABOVE 1/3 OF
AMPERAGE RATE – Drop charging voltage to
15V and charge for 10 – 15 hours. Then go to Step
5.
c. VOLTAGE IS BETWEEN 12V AND 16V –
Continue charging at the same rate for an
additional 3–1/2 hours. Then go to Step 5.
d. VOLTAGE BELOW 12V – Replace Battery.
5. Load Test
1. Connect a voltmeter and a battery load tester across
the battery terminals.
2. Apply 300 ampere load for 15 seconds to remove
surface charge from the battery. Remove load.
3. Wait 15 seconds to let battery recover. Then apply
specified load from specifications (See Main Data
and Specifications in this section).
Read voltage after 15 seconds, then remove load.
Page 1089 of 6000

6D2–4
IGNITION SYSTEM
Spark Plug
Removal
1. Remove spark plugs.
Inspection and Repair
The spark plug affects entire engine performance and
therefore its inspection is very important.
Check electrode and insulator for presence of cracks,
and replace if any.
Check electrode for wear, and replace if necessary.
Check gasket for damage, and replace if necessary.
Measure insulation resistance with an ohmmeter, and
replace if faulty.
Adjust spark plug gap to 1.0 mm (0.04 in) 1.1 mm
(0.043 in).
Check fuel and electrical systems if spark plug is
extremely dirty.
Use spark plugs having low heat value (hot type plug)
if fuel and electrical systems are normal.
Use spark plugs having high heat value (cold type
plug) if insulator and electrode are extremely burned.
Sooty Spark Plugs
Much deposit of carbon or oil on the electrode and
insulator of spark plug reduces the engine performance.
Possible causes:
Too rich mixture
Presence of oil in combustion chamber
Incorrectly adjusted spark plug gap
Burning Electrodes
This fault is characterized by scorched or heavily oxidized
electrode or blistered insulator nose.
Possible causes:
Too lean mixture
Improper heat value
Measuring Insulation Resistance
Measure insulation resistance using a 500 volt
megaohm meter.
Replace spark plugs if measured value is out of
standard.
Insulation resistance: 50 M
or more
011RS010
Cleaning Spark Plugs
Clean spark plugs with a spark plug cleaner.
Raise the ground electrode to an angle of 45 to 60
degrees. If electrode is wet, dry it before cleaning.
After spark plug is thoroughly cleaned, check
insulator for presence of cracks.
Clean threads and metal body with a wire brush.
File the electrode tip if electrode is extremely worn.
Bend the ground electrode to adjust the spark plug
gap.
011RS011
Installation
1. Spark plugs
Tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Torque: 18 Nꞏm (1.8 Kgꞏm/13 lb ft)
Page 1109 of 6000
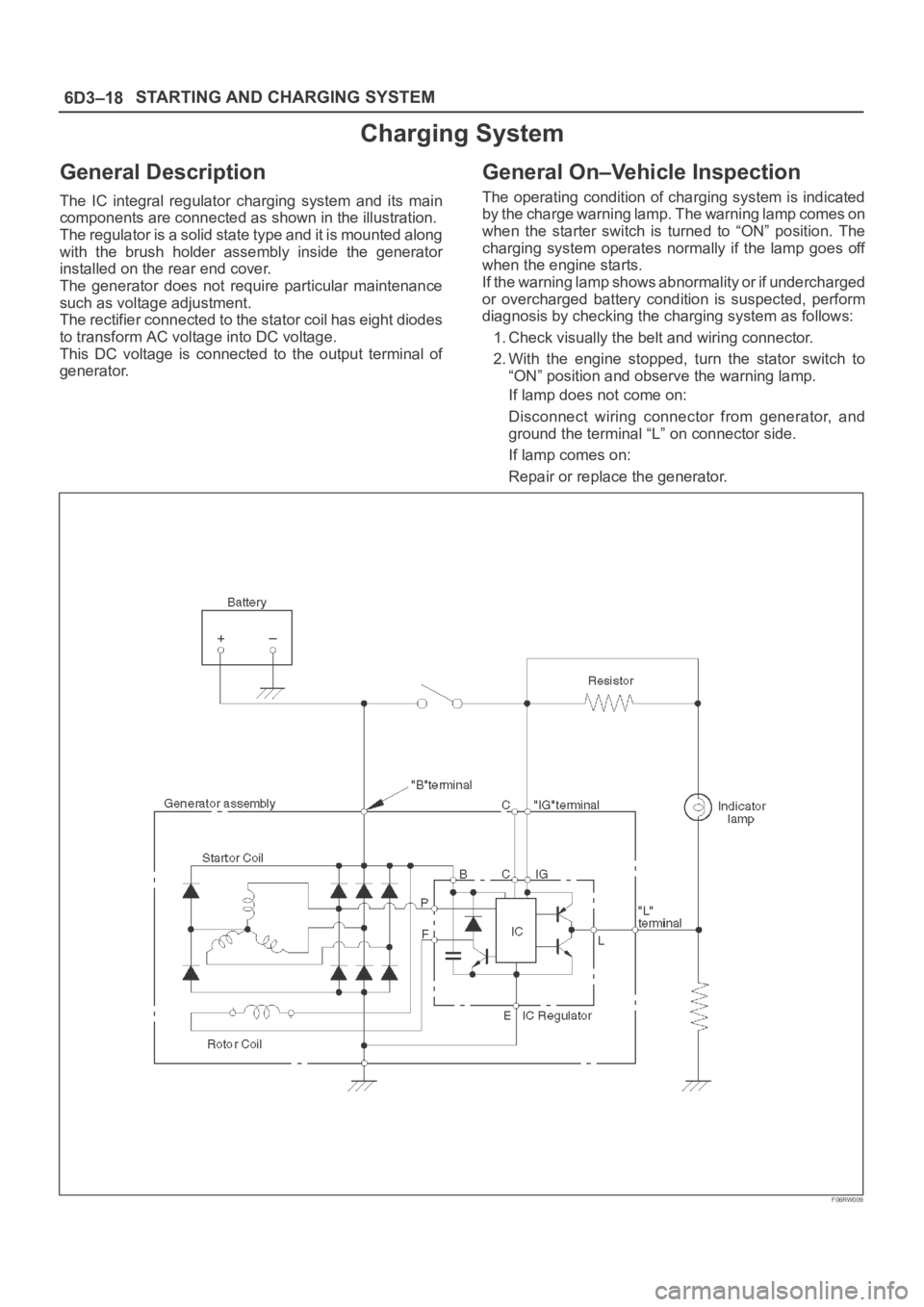
6D3–18STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
Charging System
General Description
The IC integral regulator charging system and its main
components are connected as shown in the illustration.
The regulator is a solid state type and it is mounted along
with the brush holder assembly inside the generator
installed on the rear end cover.
The generator does not require particular maintenance
such as voltage adjustment.
The rectifier connected to the stator coil has eight diodes
to transform AC voltage into DC voltage.
This DC voltage is connected to the output terminal of
generator.
General On–Vehicle Inspection
The operating condition of charging system is indicated
by the charge warning lamp. The warning lamp comes on
when the starter switch is turned to “ON” position. The
charging system operates normally if the lamp goes off
when the engine starts.
If the warning lamp shows abnormality or if undercharged
or overcharged battery condition is suspected, perform
diagnosis by checking the charging system as follows:
1. Check visually the belt and wiring connector.
2. With the engine stopped, turn the stator switch to
“ON” position and observe the warning lamp.
If lamp does not come on:
Disconnect wiring connector from generator, and
ground the terminal “L” on connector side.
If lamp comes on:
Repair or replace the generator.
F06RW009
Page 1119 of 6000
6E–2
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Primary System-Based Diagnostic 6E–50. . . . . . . . .
Primary System-Based Diagnostic 6E–50. . . . . . .
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensor 6E–50. . . . .
HO2S Heater 6E–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Trim System Monitor Diagnostic
Operation 6E–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Trim System Monitor Diagnostic
Operation 6E–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Trim Cell Diagnostic Weights 6E–50. . . . . . .
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check 6E–51.
A/C Clutch Control Circuit Diagnosis 6E–54. . . . . . .
Electronic Ignition System Diagnosis 6E–60. . . . . . .
Fuel Metering System Check 6E–60. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve 6E–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel System Pressure Test 6E–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure and Fuel
Injector Balance Test Procedure 6E–60. . . . . . . . . .
Knock Sensor Diagnosis 6E–65. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Diagnosis 6E–65
Multiple PCM Information Sensor DTCS Set 6E–65
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Diagnosis
(For except EXPORT and
SOUTH AFRICA) 6E–68. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Tech 2 Data Definitions and Ranges 6E–68
Typical Scan Data Values 6E–70. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) 6E–74. . . . . . .
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) “ON”
Steady 6E–77. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Cranks But Will Not Run 6E–79. . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel System Electrical Test 6E–85. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel System Diagnosis 6E–88. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control (IAC) System Check 6E–93. . . . . . .
Knock Sensor (KS) System Check
(Engine Knock, Poor Performance, or Poor
Economy) 6E–95. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
Check 6E–97. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Output
Check 6E–99. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes 6E–101. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0101
MAF System Performance 6E–104. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0102
MAF Sensor Circuit Low Frequency 6E–107. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0103
MAF Sensor Circuit High Frequency 6E–110. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0107
MAP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–112. . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0108
MAP Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–115. . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0112
IAT Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–118. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0113
IAT Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–121. . . . . . . . . . Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0117
ECT Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–124. . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0118
ECT Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–127. . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0121
TP System Performance 6E–130. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0122
TP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 6E–133. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0123
TP Sensor Circuit High Voltage 6E–136. . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0131
HO2S Circuit Low Voltage Bank 1
Sensor 1 6E–139. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0132
HO2S Circuit High Voltage Bank 1
Sensor 1 6E–142. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0134
HO2S Circuit Insufficient Activity Bank 1
Sensor 1 6E–145. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0151
HO2S Circuit Low Voltage Bank 2
Sensor 1 6E–148. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0152
HO2S Circuit HIGH Voltage Bank 2
Sensor 1 6E–151. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0171
Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 1 6E–154. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0172
Fuel Trim System Rich Bank 1 6E–158. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0174
Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2 6E–162. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0175
Fuel Trim System Rich Bank 2 6E–166. . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0201
Injector 1 Control Circuit 6E–170. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0202
Injector 2 Control Circuit 6E–173. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0203
Injector 3 Control Circuit 6E–176. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0204
Injector 4 Control Circuit 6E–179. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0205
Injector 5 Control Circuit 6E–182. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0206
Injector 6 Control Circuit 6E–185. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0325
KS Module Circuit 6E–188. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0327
KS Sensor Circuit 6E–190. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0336
58X Reference Signal Circuit 6E–193. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0337
CKP Sensor Circuit Low Frequency 6E–195. . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0341
CMP Sensor Circuit Performance 6E–198. . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0342
CMP Sensor Circuit Low 6E–202. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .