fuse box OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 545 of 6000
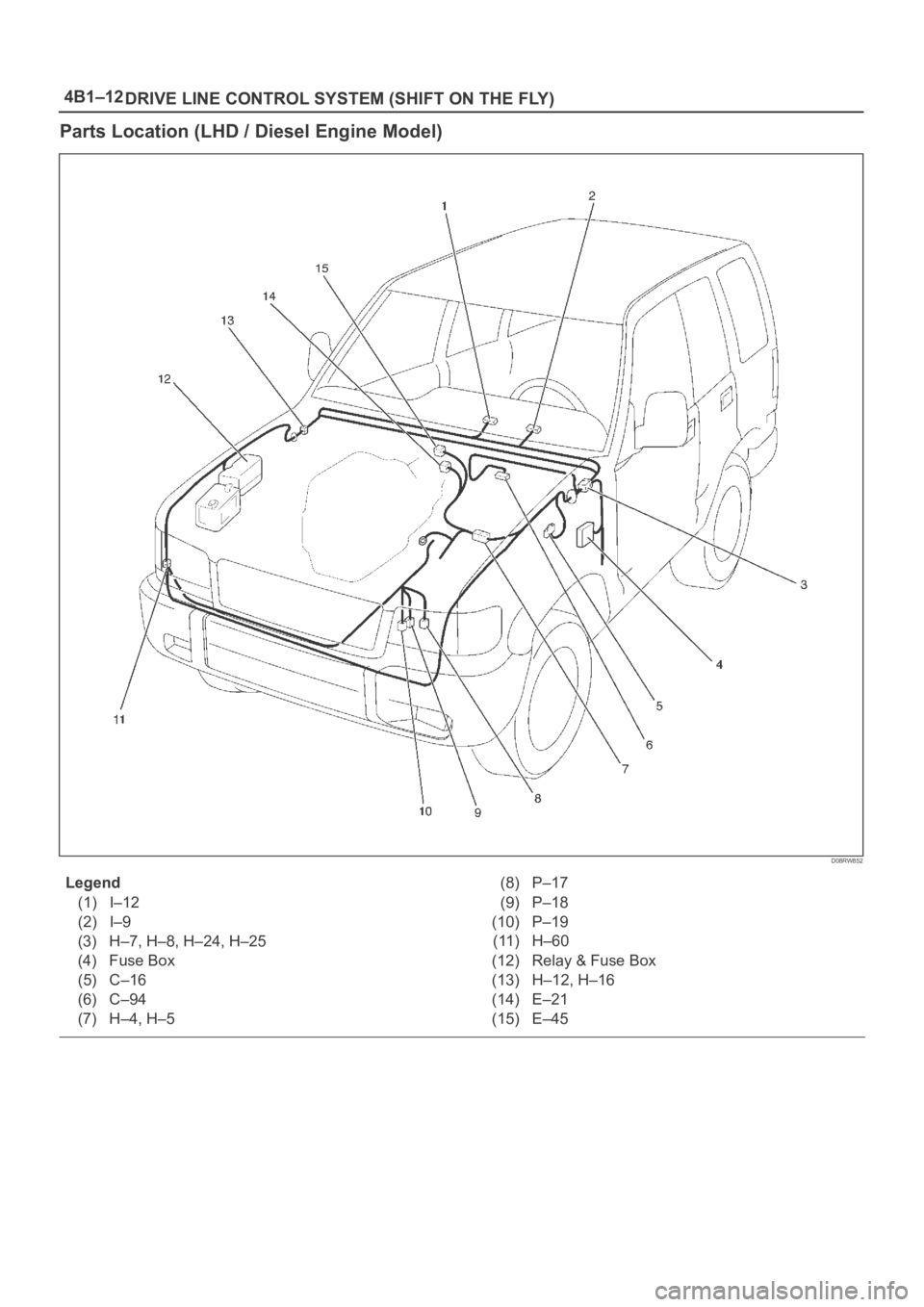
4B1–12
DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Parts Location (LHD / Diesel Engine Model)
D08RW852
Legend
(1) I–12
(2) I–9
(3) H–7, H–8, H–24, H–25
(4) Fuse Box
(5) C–16
(6) C–94
(7) H–4, H–5(8) P–17
(9) P–18
(10) P–19
(11) H–60
(12) Relay & Fuse Box
(13) H–12, H–16
(14) E–21
(15) E–45
Page 546 of 6000

4B1–13 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Parts Location (LHD / Gasoline Engine Model)
D08RW854
Legend
(1) I–12
(2) I–9
(3) H–7, H–8, H–24, H–25
(4) Fuse Box
(5) C–16
(6) C–94
(7) H–5
(8) M–11, M–12(9) M–22
(10) M–23
(11) M–24
(12) H–10
(13) M–26
(14) Relay & Fuse Box
(15) H–12, H–16
(16) E–30
Page 547 of 6000
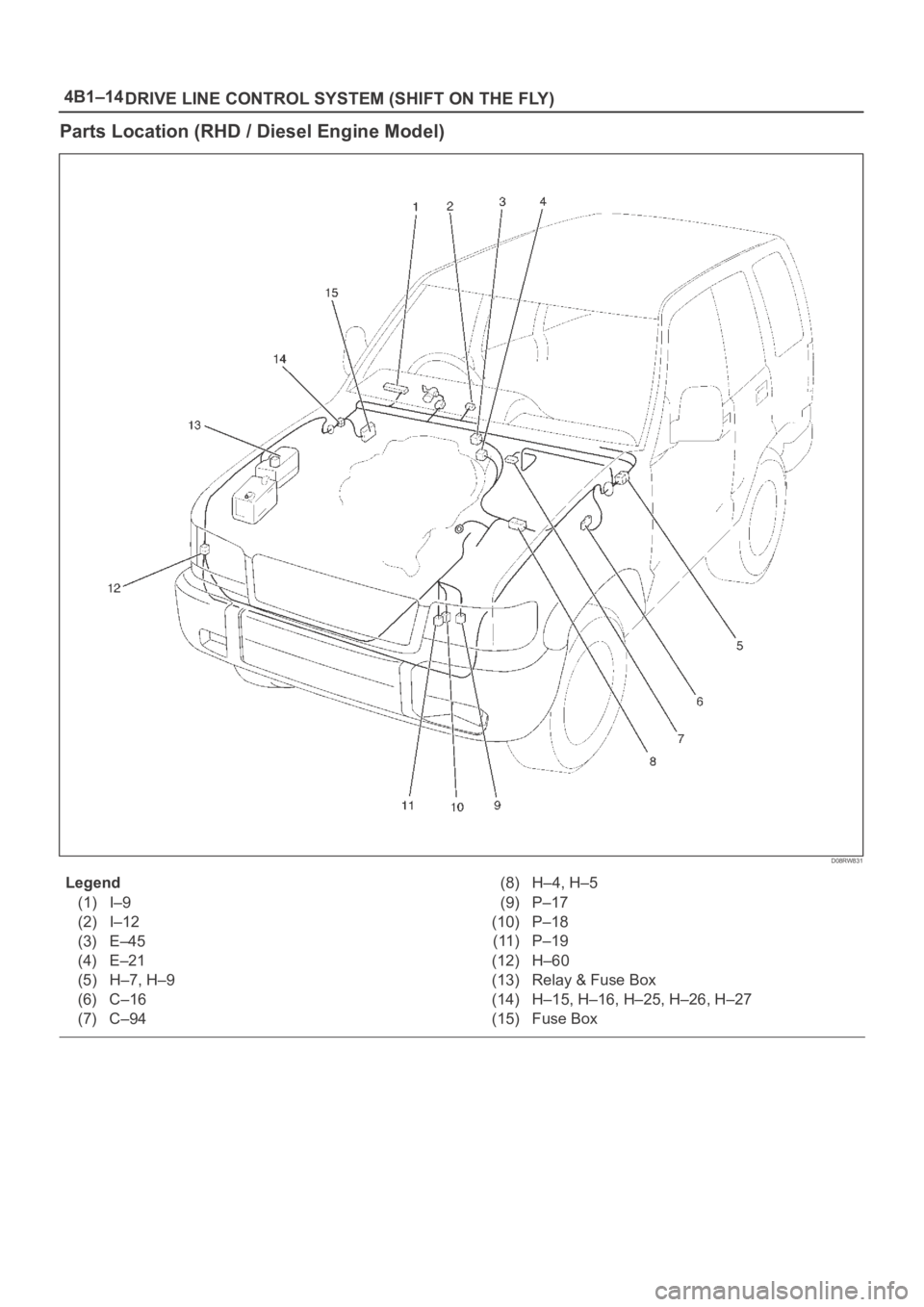
4B1–14
DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Parts Location (RHD / Diesel Engine Model)
D08RW831
Legend
(1) I–9
(2) I–12
(3) E–45
(4) E–21
(5) H–7, H–9
(6) C–16
(7) C–94(8) H–4, H–5
(9) P–17
(10) P–18
(11) P–19
(12) H–60
(13) Relay & Fuse Box
(14) H–15, H–16, H–25, H–26, H–27
(15) Fuse Box
Page 548 of 6000

4B1–15 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (SHIFT ON THE FLY)
Parts Location (RHD / Gasoline Engine Model)
D08RW853
Legend
(1) I–9
(2) I–12
(3) H–7, H–9
(4) C–16
(5) H–5
(6) C–94
(7) M–26
(8) M–11, M–12(9) M–22
(10) M–23
(11) M–24
(12) H–10
(13) H–12
(14) Relay & Fuse Box
(15) E–30
(16) H–15, H–16, H–25, H–26, H–27
(17) Fuse Box
Page 588 of 6000
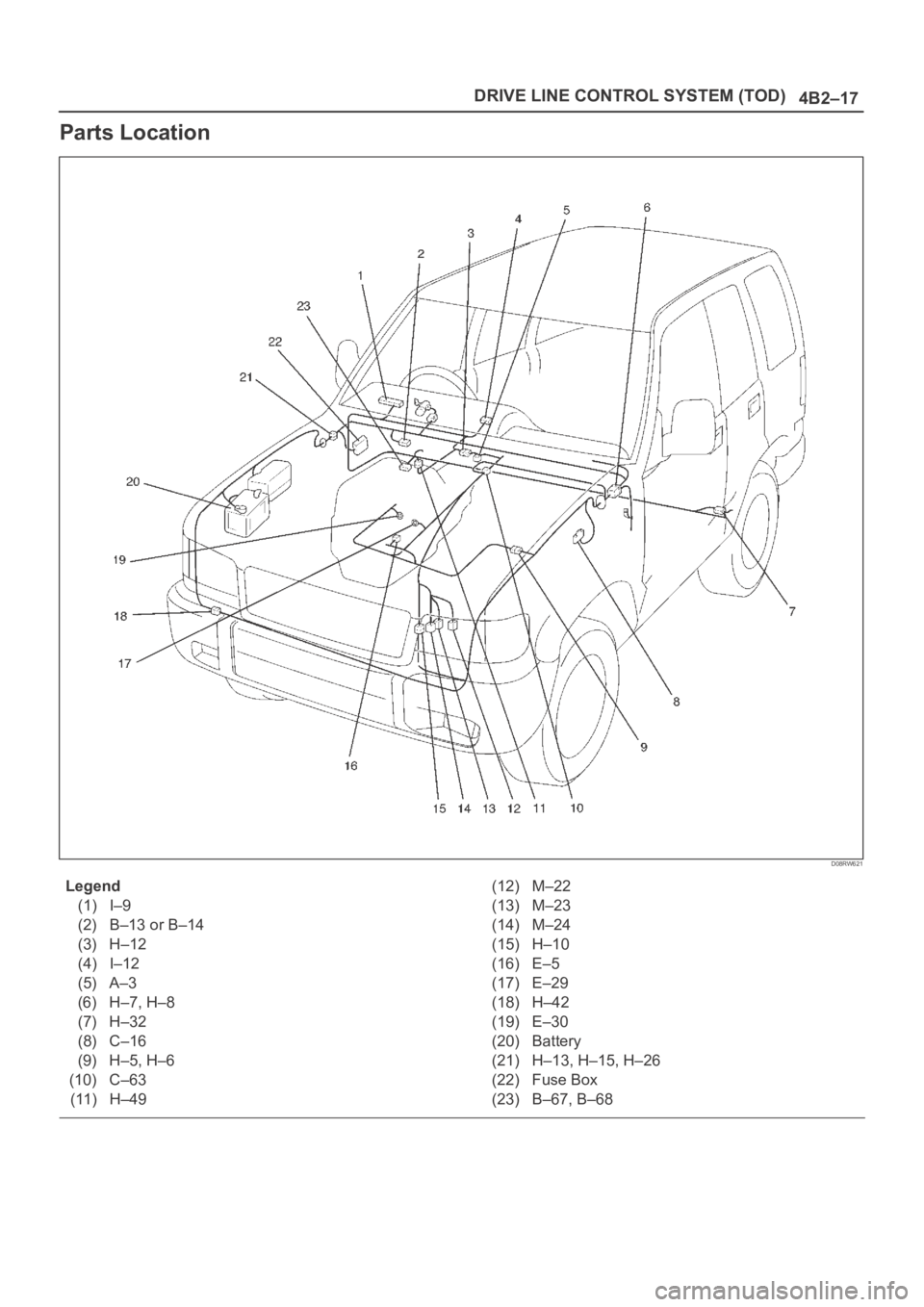
4B2–17 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD)
Parts Location
D08RW621
Legend
(1) I–9
(2) B–13 or B–14
(3) H–12
(4) I–12
(5) A–3
(6) H–7, H–8
(7) H–32
(8) C–16
(9) H–5, H–6
(10) C–63
(11) H–49(12) M–22
(13) M–23
(14) M–24
(15) H–10
(16) E–5
(17) E–29
(18) H–42
(19) E–30
(20) Battery
(21) H–13, H–15, H–26
(22) Fuse Box
(23) B–67, B–68
Page 815 of 6000

5A–5 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
FR
Front Right
GEN
Generator
MV
Millivolts
RL
Rear Left
RR
Rear RightRPS
Revolution per Second
VDC
Vo l t s D C
VA C
Vo l t s A C
W/L
Warning Light
WSS
Wheel Speed Sensor
General Diagnosis
General Information
ABS malfunction can be classified into two types, those
which can be detected by the ABS warning light and those
which can be detected as a vehicle abnormality by the
driver.
In either case, locate the fault in accordance with the
“BASIC DIAGNOSTIC FLOWCHART” and repair.
Please refer to Section 5C for the diagnosis of
mechanical troubles such as brake noise, brake judder
(brake pedal or vehicle vibration felt when braking),
uneven braking, and parking brake trouble.
ABS Service Precautions
Required Tools and Items:
Box Wrench
Brake Fluid
Special Tool
Some diagnosis procedures in this section require the
installation of a special tool.
J-39200 High Impedance Multimeter
When circuit measurements are requested, use a circuit
tester with high impedance.
Computer System Service Precautions
The Anti-lock Brake System interfaces directly with the
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU) which is a
control computer that is similar in some regards to the
Powertrain Control Module. These modules are designed
to withstand normal current draws associated with
vehicle operation. However, care must be taken to avoid
overloading any of the EHCU circuits. In testing for opens
or shorts, do not ground or apply voltage to any of the
circuits unless instructed to do so by the appropriate
diagnostic procedure. These circuits should only be
tested with a high impedance multimeter (J-39200) or
special tools as described in this section. Power should
never be removed or applied to any control module with
the ignition in the “ON” position.
Before removing or connecting battery cables, fuses or
connectors, always turn the ignition switch to the “OFF”
position.
General Service Precautions
The following are general precautions which should be
observed when servicing and diagnosing the Anti-lock
Brake System and/or other vehicle systems. Failure toobserve these precautions may result in Anti-lock Brake
System damage.
If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle using
an electric arc welder, the EHCU and valve block
connectors should be disconnected before the
welding operation begins.
The EHCU and valve block connectors should never
be connected or disconnected with the ignition “ON” .
EHCU of the Anti-lock Brake System are not
separately serviceable and must be replaced as
assemblies. Do not disassemble any component
which is designated as non-serviceable in this
Section.
If only rear wheels are rotated using jacks or drum
tester, the system will diagnose a speed sensor
malfunction and the “ABS” warning light will
illuminate. But actually no trouble exists. After
inspection stop the engine once and re-start it, then
make sure that the “ABS” warning light does not
illuminate.
If the battery has been discharged
The engine may stall if the battery has been completely
discharged and the engine is started via jumper cables.
This is because the Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
requires a large quantity of electricity. In this case, wait
until the battery is recharged, or set the ABS to a
non-operative state by removing the fuse for the ABS
(40A). After the battery has been recharged, stop the
engine and install the ABS fuse. Start the engine again,
and confirm that the ABS warning light does not light.
Note on Intermittents
As with virtually any electronic system, it is difficult to
identify an intermittent failure. In such a case duplicating
the system malfunction during a test drive or a good
description of vehicle behavior from the customer may be
helpful in locating a “most likely” failed component or
circuit. The symptom diagnosis chart may also be useful
in isolating the failure. Most intermittent problems are
caused by faulty electrical connections or wiring. When
an intermittent failure is encountered, check suspect
circuits for:
Suspected harness damage.
Poor mating of connector halves or terminals not fully
seated in the connector body (backed out).
Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Page 830 of 6000
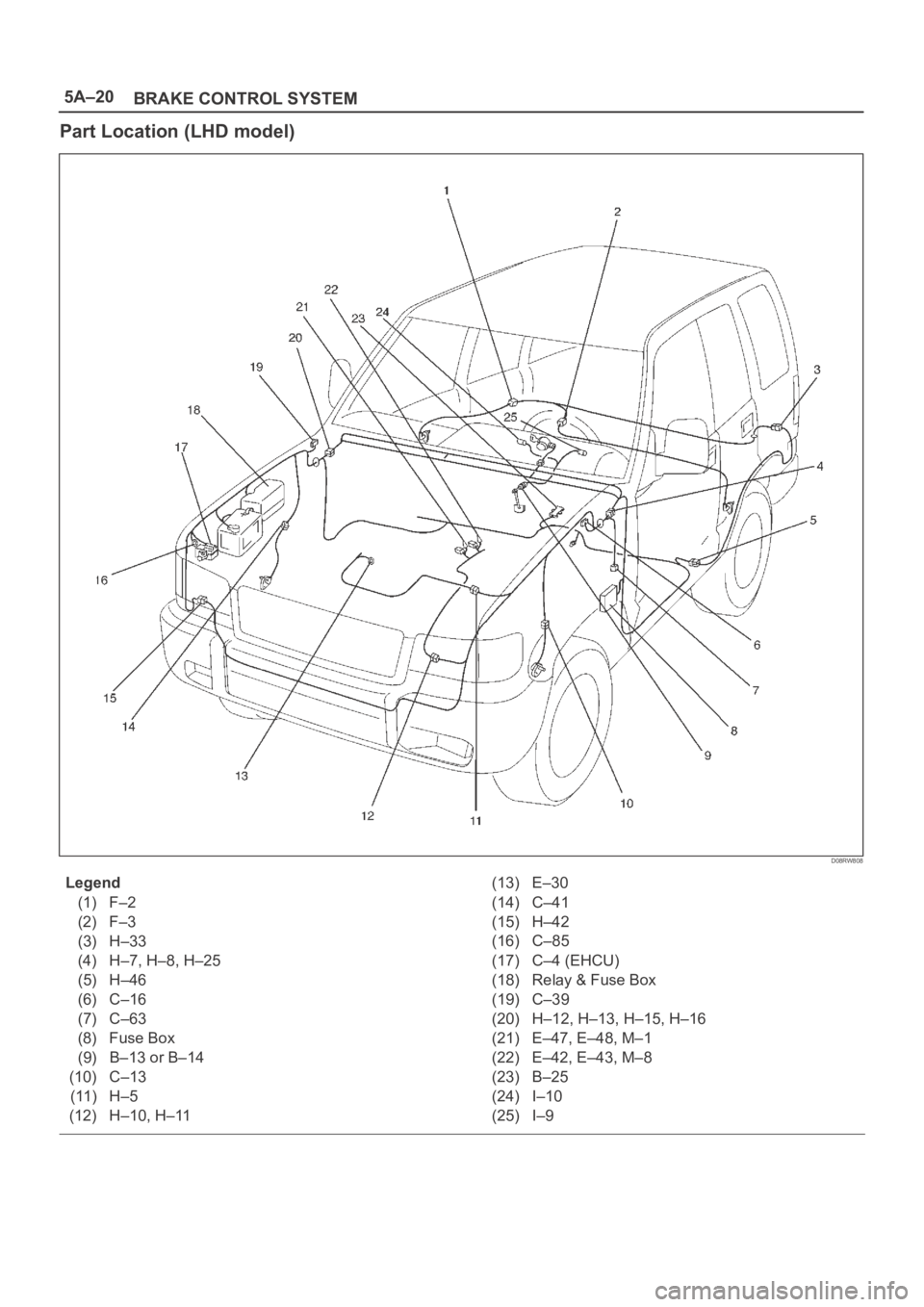
5A–20
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Part Location (LHD model)
D08RW808
Legend
(1) F–2
(2) F–3
(3) H–33
(4) H–7, H–8, H–25
(5) H–46
(6) C–16
(7) C–63
(8) Fuse Box
(9) B–13 or B–14
(10) C–13
(11) H–5
(12) H–10, H–11(13) E–30
(14) C–41
(15) H–42
(16) C–85
(17) C–4 (EHCU)
(18) Relay & Fuse Box
(19) C–39
(20) H–12, H–13, H–15, H–16
(21) E–47, E–48, M–1
(22) E–42, E–43, M–8
(23) B–25
(24) I–10
(25) I–9
Page 844 of 6000
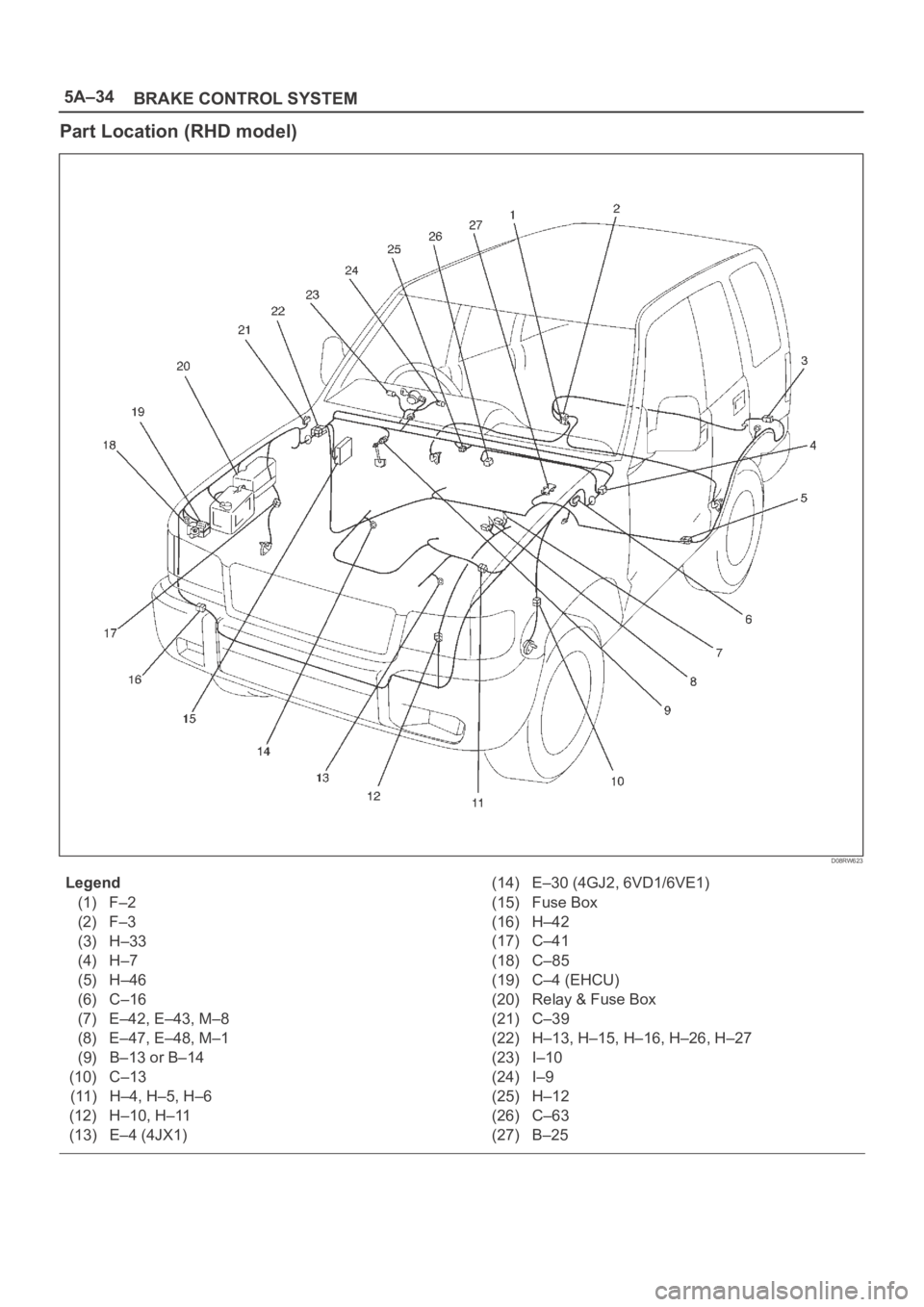
5A–34
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Part Location (RHD model)
D08RW623
Legend
(1) F–2
(2) F–3
(3) H–33
(4) H–7
(5) H–46
(6) C–16
(7) E–42, E–43, M–8
(8) E–47, E–48, M–1
(9) B–13 or B–14
(10) C–13
(11) H–4, H–5, H–6
(12) H–10, H–11
(13) E–4 (4JX1)(14) E–30 (4GJ2, 6VD1/6VE1)
(15) Fuse Box
(16) H–42
(17) C–41
(18) C–85
(19) C–4 (EHCU)
(20) Relay & Fuse Box
(21) C–39
(22) H–13, H–15, H–16, H–26, H–27
(23) I–10
(24) I–9
(25) H–12
(26) C–63
(27) B–25
Page 961 of 6000

6A–5
ENGINE MECHANICAL
4. Engine Lacks Compression
Condition
Possible causeCorrection
Engine lacks compressionSpark plug loosely fitted or spark
plug gasket defectiveTighten to specified torque or replace
gasket
Valve timing incorrectAdjust
Cylinder head gasket defectiveReplace gasket
Valve incorrectly seatedLap valve
Valve stem seizedReplace valve and valve guide
Valve spring weakened or brokenReplace
Cylinder or piston rings wornOverhaul engine
Piston ring seizedOverhaul engine.
Engine Compression Test Procedure
1. Start and run the engine until the engine reaches
normal operating temperature.
2. Turn the engine off.
3. Remove all the spark plugs.
4. Remove ignition coil fuse (15A) and disable the
ignition system.
5. Remove the fuel pump relay from the relay and fuse
box.
6. Engage the starter and check that the cranking speed
is approximately 300 rpm.7. Install cylinder compression gauge into spark plug
hole.
8. With the throttle valve opened fully, keep the starter
engaged until the compression gage needle reaches
the maximum level. Note the reading.
9. Repeat the test with each cylinder.
If the compression pressure obtained falls below the
limit, engine overhaul is necessary.
Limit; 1000 kPa (145 psi)
Page 1146 of 6000
6E–29 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Engine Component Locator Table
Number
NameLocation
1Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) ValveRear right side of the engine
2Throttle Position (TP) SensorOn the rear of the throttle body
3Intake Air Temperature (IAT) SensorOn the intake air duct near the throttle body
4Check Engine (MIL) LightOn the instrument panel beneath the
tachometer
5Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) ValveOn the left of the cylinder head cover
6Air CleanerLeft front of the engine bay
7Mass Air Flow (MAF) SensorAttached to the air filter box
8Camshaft Position (CMP) SensorOn the rear right side at the left of the cylinder
head cover
9Fuel Pressure RegulatorRear right side of the engine
10Idle Air Control (IAC) ValveOn the left of the throttle body
11Upper Intake ManifoldTop of the engine
12Fuse/Relay BoxAlong the inside of the right fender
13Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorBolted to the top of the upper intake manifold
14Throttle BodyBetween the intake air duct and the upper
intake manifold
15Engine Coolant Temperature SensorOn the coolant crossover pipe at the front of
the engine, near the throttle body