differential OPEL GT-R 1973 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1973, Model line: GT-R, Model: OPEL GT-R 1973Pages: 625, PDF Size: 17.22 MB
Page 5 of 625

The 1973 Opel Chassis Service MayI has been completely revised with respect to layout, format and information content
in a” attempt
to provide you “The Technician” with a tiore logical and usable publication. An example of the new grouping
layout 6 exhibited on the preceding
page. Each wow is rubdivided as follows:
Grouo 1
_. _
Subiect IIContents.
0
General InformationIGeneral InformationLifting
Maintenance and Lubrication
1ElectricalBattery
Starting System
lgriition System
Charging System
Washers and Wipers
Lighting Systems
Signal SystemI
Instrument Panel
Gauges
Wiring Diagrams
2
Body and Bumpers:General Body InformationI
Frame & Body Mountings
Windows
& Window Moldings
DONS
Rear Compartment LidRoof &Sun Roof
Seat?., Interior Trim & Headlining
Bumpers.
3Suspension and Steering
Front Suspension
Steering Linkages1Front End Alignment
Steering Gear
Steering Column
Rear Suspension
Wheels and Tires
4
Propelley Shaft & Rear AxlePropeller Shaft & Central Joint
Differential
5Brakes ~Power Booster and Master Cylinder
Front Disc BrakeI
Rear Drum Brake
6EngineEngine Mechanical and Mounts
Cooling System
Fuel System
Exhaust Systems
Carburetor and Throttle Linkage
Emission Control Systems
Tune-up
7TransmissionClutch
Manual Transmission
Automatic Transmission
BChassis Sheet MetalHood, Fenders and Grille
9
Accessol;iesHeaterAirConditioning
Radio
Page 218 of 625

REAR SUSPENSION3F- 51
REAR SUSPENSION
CONTENTS
Subject
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION:
Description and Operation of Rear Suspension. . . . . .DIAGNOSIS: (Not Applicable)
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS: (Not
Applicable)
MAJOR REPAIR:
Rear Shock Absorber Removal and Replacement . .
Rear
SpringRemovalandInstallation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .LowerControlArmReplacement
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Stabilizer
RodReplacement. . . . . . . . . . . ~ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..-....Track Rod Replacement
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .SPECIFICATIONS:
Rear
SuspensionSpecifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Page No.3F-5
13F-513F-523F-533F-533F-533F-53
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONDESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OF REAR
SUSPENSIONAll Opels utilize the three link rear suspension ar-
rangement. This rear suspension consists of coil
springs, track rod, shock absorbers and lower control
arms.The coil springs set between two seats which arc
situated ahead of the rear axle housing.
The track rod is utilized on all models to control the
lateral stability of the rear axle assembly. It is of
tubular design. A stabilizer rod is used on all Wagons
as well as Fast Backs and Sedans. The GT is not
equipped with a stabilizer rod.
The lower control arms are of tubular design and
function as two links of the three link suspension
system. They are attached to the underbody through
brackets welded to the side rails and to the rear axle
assembly through the front portion of the spring seat
bracket. The lower control arms control the fore and
aft movement of the rear axle assembly.
The third link in this suspension system is the torque
tube which is connected to the differential carrier
and also to the underbody through rubber bushings
in the central joint support bracket.The torque tube in conjunction with the lower con-
trol arms absorb all acceleration and braking torque.
MAJOR REPAIR
REAR SHOCK ABSORBER REMOVALAND INSTALLATION
RemovalNOTE: The trim panel under the spare tire must be
removed on the GT to gain access to attaching nuts.
1. Remove upper attaching nut, retainer and rubber
grommet.
2. Remove lower attaching nut and rubber grommet
retainer, compress shock absorber and remove from
lower mounting pin.
Installation1. Replace upper and lower rubber grommets, if
necessary, before installing shock absorber.
2. Extend shock absorber and position in car. Attach
at lower end first, torque nut to 15 lb.ft. on the GT,
and torque to 47 lb.ft. on the Opel 1900
- Manta.
Page 219 of 625

3F. 521973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
3. Install rubber grommet, retainer and self-locking
nut at top of shock absorber. Torque to 10 lb. ft.
Always use new self-locking nuts.
REAR SPRING REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Rear Spring Removal1. Raise rear of car with floor jack under differential
carrier and support with jack stands positioned un-
der side jack brackets. See Figure
3F-2.Figure 3F-3 Removing Coil
SpringFigure 3F-2 Raising Rear of Car
2. Remove rear wheels.3. Disconnect shock absorbers from rear axle.
4. Disconnect stabilizer and shackles, if equipped,
from frame.
5. Lower rear axle assembly as far as possible withoutputting the brake hose under stress.
6. If necessary, tilt the rear axle assembly to remove
springs. See Figure
3F-3. Note the upper and lower
rubber damper rings.
Rear Spring Installation
1. Make certain the lower damper rings are properly
positioned in the spring seats and position the springsin their respective position in the damper rings. See
Figure
3F-4.2. Properly install upper damper rings on springs.
CAUTION: Fasteners are important attaching parts in
that they could affect the performance of vital corn-
ponents and systems, and/or could result in major
repair expense. They must be replaced with one of
the same part number or with an equivalent part if
replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a
re-
placement part of lesser
qua/ity or substitute designFigure 3F-4 Installing Coil Spring
Torque values must be used as specitied during reas-
sembly to assure proper retention of these parts.3. Raise rear axle assembly to compress springs in
their seats.
4. Attach shock absorbers and tighten retaining nuts
to 15 Ib.ft. For the GT and 47 lb.ft. for the Opel 1900
- Manta.
5. Attach stabilizer shackles, if equipped, to axle
brackets and tighten bolts to 25 lb. ft. with vehicle at
curb weight.
6. Install rear wheels torquing lug nuts to 65 lb.ft.
Page 222 of 625

WHEELS AND TIRES3G- 55
WHEELS AND TIRES
CONTENTS
Subject
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION: (Not Applicable)
DIAGNOSIS:
Car
RoughnessandVibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .AbnormalTireWear
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS:
Demounting and Mounting Tubeless Tires
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .Wheel
andTireBalance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .MAJOR REPAIR: (Not Applicable)
SPECIFICATIONS:
Specifications
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Page No.
3G-55
3G-58
3G-6136-6236-62
DIAGNOSIS
CAR ROUGHNESS AND VIBRATIONinflation pressures and perform tire inspection, in-
cluding removal of any foreign material on tire tread
or wheel large enough to upset balance.
Possible Causes
To assist in the diagnosis and correction of some of
the more stubborn cases of tire vibration and rough-
ness conditions that may be encountered, the follow-
ing information is offered:Tire inflation pressure recommendations are very
important at all times and particularly so on all ride
complaints. Raising or lowering tire pressures to
“improve” mileage or traction should not be at-
tempted.
VIBRATION, or a quivering motion condition, no-
ticeable by feel through the steering column, steering
wheel, floor
p&n, or by hood and fender shake, usu-
ally originates from the front wheels and tires. Front
end vibration, when caused by unbalanced front
wheels, can be generally felt as steering wheel “nib-ble”.Next, road-test the car with the owner, if possible,
and have the owner explain the specific ride disturb-
ance.After road-testing, raise car on hoist and proceed to
isolate the offending tire/wheel assembly.
Reproducing the Disturbance
A vibration felt through the seats as a side-to-side
disturbance can usually be attributed to the rearIn an attempt to reproduce the disturbance ex-
wheels and tires.perienced in the ride, a wheel spinner can be used on
the front wheels of the car.
Both front and rear vibration can be noticed mainly
at highway speeds, usually over 60 mph.The rear wheels may be spun by placing car in
“Drive” with engine running.
ROUGHNESS, noticeable primarily at speeds be-
tween 40 and 65 mph, can be felt (and occasionally
heard), and is due to certain irregularities in the tire.
Roughness usually sets up a “trembling” feel or a
shuddering effect.When spinning rear wheels, never exceed a speedom-
eter speed of 35 mph with a standard rear axle assem-
bly, or 75 mph on one with a positive traction rear
axle. Excessive speeds may cause damage to the rear
axle assembly.
Road-Test With Owner
When a ride complaint is encountered, first checkJack up both rear wheels by placing the jack under
the differential housing. Spin one wheel and tire with
the opposite wheel held from rotating by holding the
Page 232 of 625
GROUP 4
PROPELLER SHAFT
AND DIFFERENTIALTitlePage No.Propeller Shaft and
CentralJoint. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4A-2
RearAxle. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4B-7
Page 233 of 625
4A- 21973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
PROPELLER SHAFT AND CENTRAL JOINT
CONTENTS
Subject
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION:
PropellerShaftandCentralJoint. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .DIAGNOSIS: (Not Applicable)
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS: (Not
Applicable)
MAJOR REPAIR:
’Propeller Shaft Removal andInstallation
. . . . . . . ..-....Disassembly andAssembly of CentralJoint
. . . . . . . . . . . .SPECIFICATIONS:
Propeller Shaft and Central Joint Specifications . .
DESCRIPTION AND OPEqATlON
PROPELLER SHAFT AND CENTRAL JOINTDue to the use of both automatic and manual trans-
missions, propeller shafts of various lengths are re-
quired depending upon vehicle, engine, and
transmission (manual or automatic) application. The
propeller shaft is of a strong design due to increased
engine torque. It is also a one piece tubular shaft, but
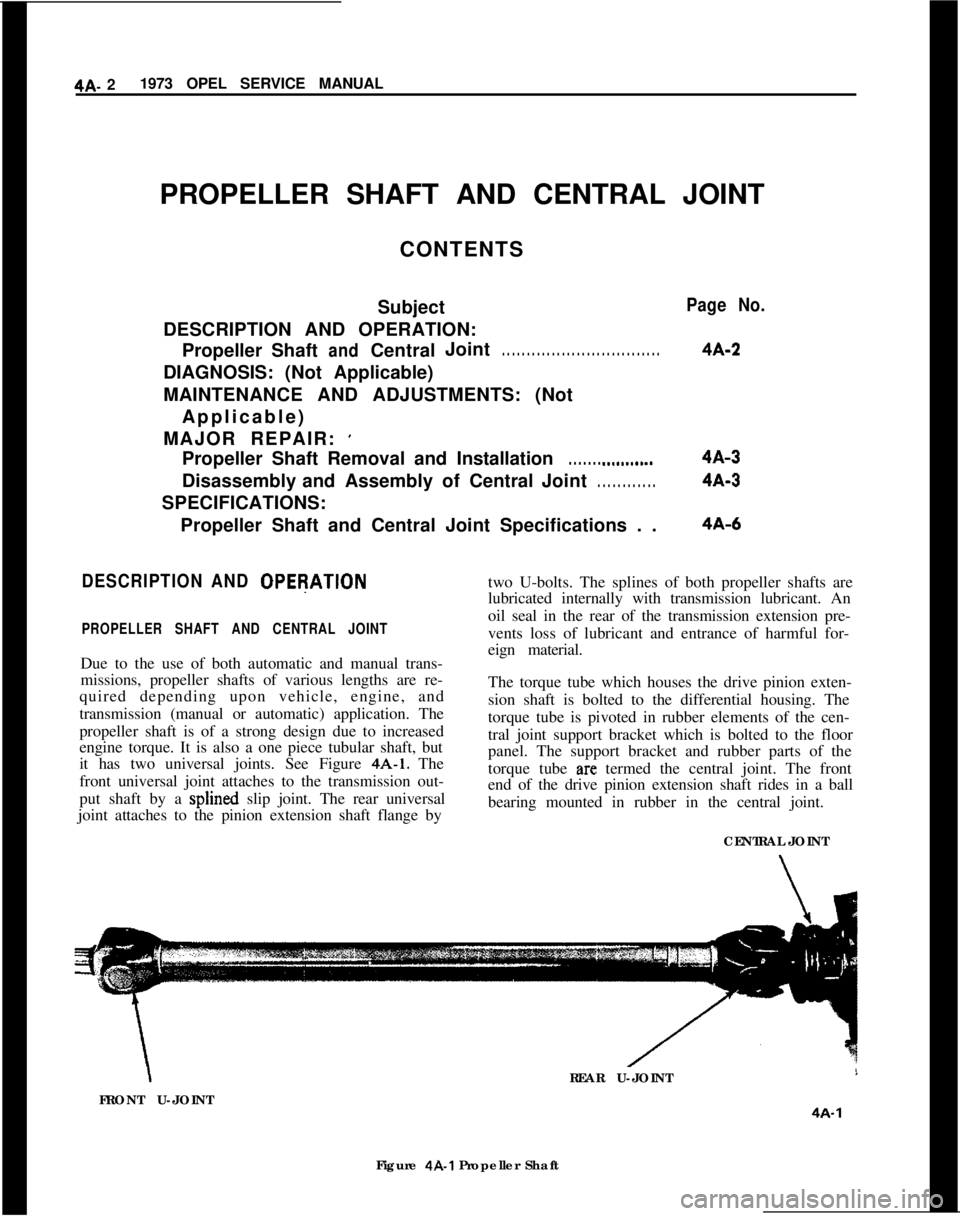
it has two universal joints. See Figure 4A-1. The
front universal joint attaches to the transmission out-
put shaft by a splined slip joint. The rear universal
joint attaches to the pinion extension shaft flange by
Page No.
4A-2
4A-3
4A-3
4A-6two U-bolts. The splines of both propeller shafts are
lubricated internally with transmission lubricant. An
oil seal in the rear of the transmission extension pre-
vents loss of lubricant and entrance of harmful for-
eign material.
The torque tube which houses the drive pinion exten-
sion shaft is bolted to the differential housing. The
torque tube is pivoted in rubber elements of the cen-
tral joint support bracket which is bolted to the floor
panel. The support bracket and rubber parts of the
torque tube
arc termed the central joint. The front
end of the drive pinion extension shaft rides in a ball
bearing mounted in rubber in the central joint.
CENTRAL JOINT\REAR U-JOINT
FRONT U-JOINT
4A-1Figure 4R1 Propeller Shaft
Page 234 of 625
PROPELLER SHAFT AND CENTRAL JOINT4A- 3MAJOR REPAIR
PROPELLER SHAFT REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION
Removal
1. Raise rear of car and support on jack stands at rear
jack brackets.
2. Disconnect parking brake cable equalizer from
rod.3. On the Opel
1900 and Manta, unhook parking
brake cable from floor panel.
4. On the Opel 1900 and Manta, unhook exhaust
system and let it down.
5. Mark the mating parts of the U-joint and the drive
pinion extension shaft flange.
6. Loosen bolt locks and remove bolts or nuts.
7. Work propeller shaft slightly forward, lower rear
end of shaft and slide assembly rearward. Remove
thrust spring from front of propeller shaft.
S. Install plug in transmission extension housing to
prevent loss of lubricant.
installation
CAUTION:
Fasteners in the foJlowing steps are impor-
tant attaching parts in that they could affect the
performance of
vital components and systems, and-
/or could
result in major repair expense. They must
be replaced with one of the
samepart number or with
an equivalent part
ifreplacement becomes oecessary.
Do not use a replacement part of lesser quality or
substitute design. Torque values must be used as
specirid during reassembly to assure proper reten-
tion of these parts.1. Remove plug from rear of transmission.
2. Slide thrust spring onto transmission output shaft
and slide propeller shaft through the oil seal and onto
the transmission output shaft. Make certain trans-
mission rear seal is not damaged.
3. Align rear universal joint and pinion flange locat-
ing marks and secure with respective bolts and lock
plates. Torque bolts to 11
lb.ft. Bend lock plate tangs
to secure bolts or nuts.
4. Connect parking brake cable equalizer to brake
rod and adjust to specifications.
5. On the Opel 1900 and Manta connect parking
brake cable to floor panel.DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY OF THE
CENTRAL JOINT
Disassembly of Central Joint1. Raise and support rear of car under axle tubes.
2. Release brake line bracket from rear of torque
tube.3. Disconnect parking brake cable equalizer and re-
turn spring from brake rod.
4. On the Opel 1900 and Manta, unhook exhaust
system and let it down.
5. Mark universal joint and flange. Disconnect pro-
peller shaft from flange and support it out of the way.
6. Support torque tube with floor jack using mini-
mum pressure.
7. Remove the central joint bracket to underbody
attaching bolts.
8. Allow floor jack to lower the torque tube.
9. Disconnect torque tube from differential carrier by
removing the attaching bolts.
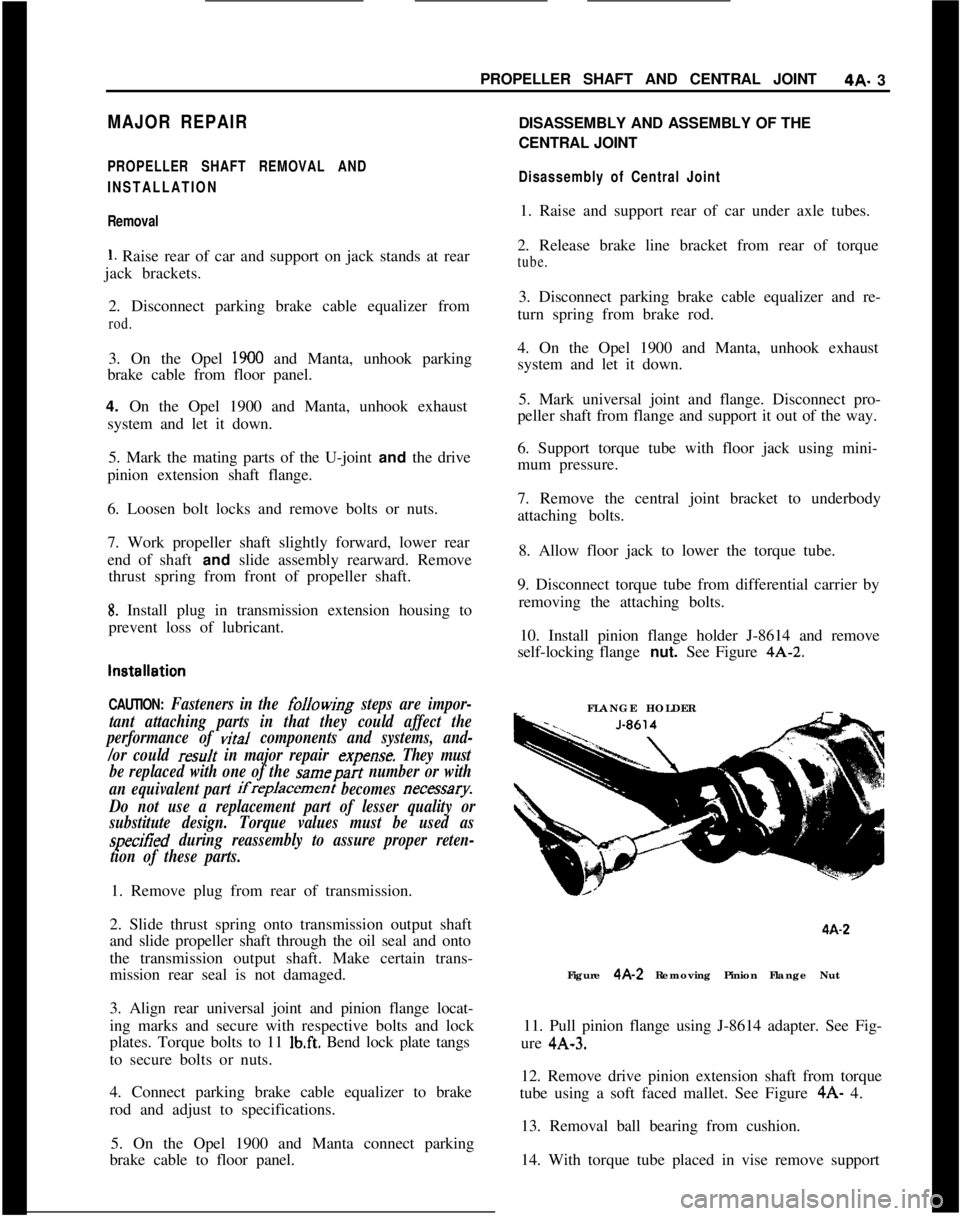
10. Install pinion flange holder J-8614 and remove
self-locking flange nut. See Figure 4A-2.
FLANGE HOLDER4A-2
Figure 4A-2 Removing Pinion Flange Nut
11. Pull pinion flange using J-8614 adapter. See Fig-
ure 4A-3.
12. Remove drive pinion extension shaft from torque
tube using a soft faced mallet. See Figure 4A- 4.
13. Removal ball bearing from cushion.
14. With torque tube placed in vise remove support
Page 236 of 625
PROPELLER SHAFT AND CENTRAL JOINT4A- 5
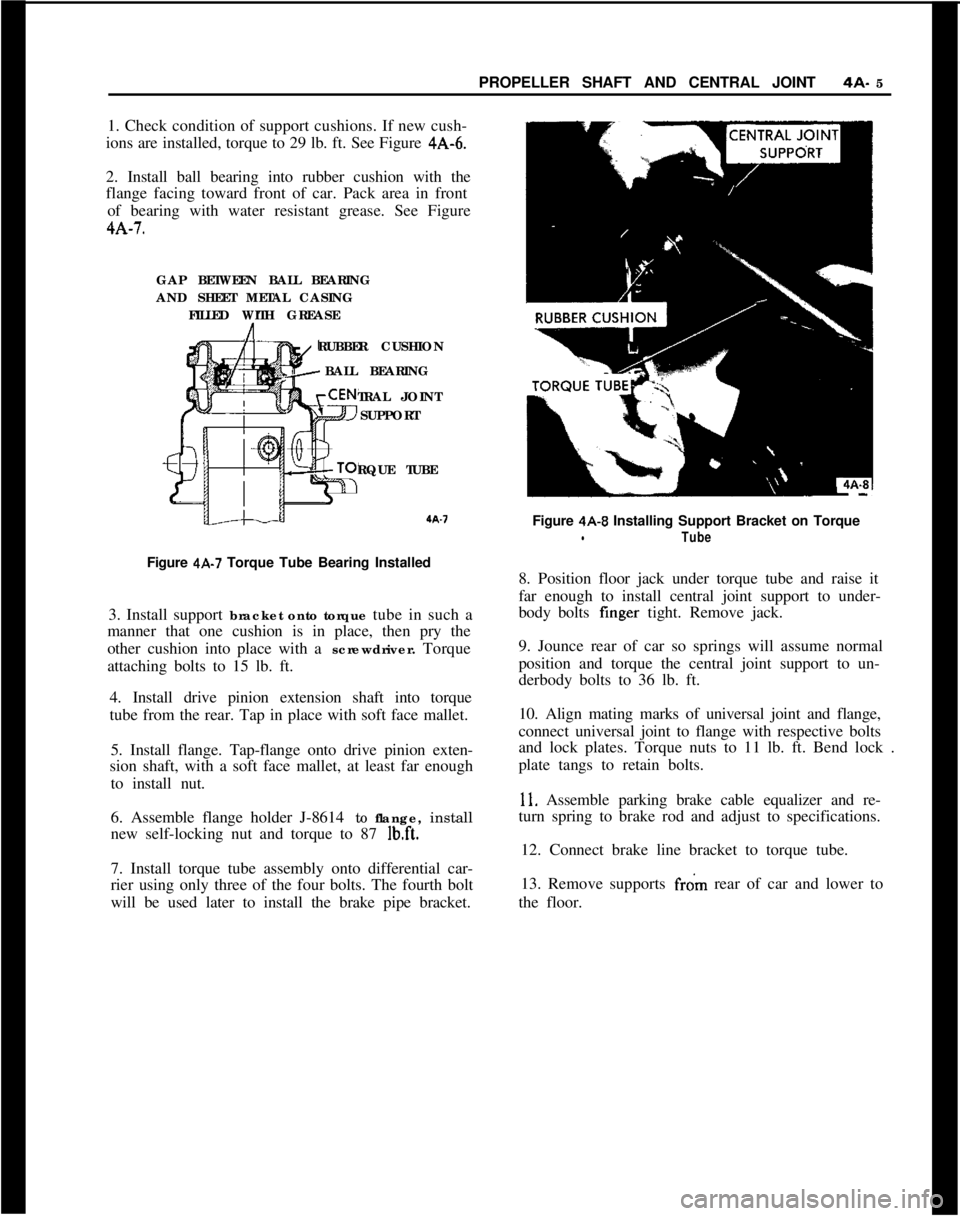
1. Check condition of support cushions. If new cush-
ions are installed, torque to 29 lb. ft. See Figure 4A-6.
2. Install ball bearing into rubber cushion with the
flange facing toward front of car. Pack area in front
of bearing with water resistant grease. See Figure4A-7.
GAP BETWEEN BALL BEARING
AND SHEET METAL CASING
FILLED WITH GREASE
RUBBER CUSHION
BALL BEARING
TRAL JOINT
SUPPORT
RQUE TUBEa.7
Figure 4A-7 Torque Tube Bearing Installed
3. Install support bracket onto torque tube in such a
manner that one cushion is in place, then pry the
other cushion into place with a screwdriver. Torque
attaching bolts to 15 lb. ft.
4. Install drive pinion extension shaft into torque
tube from the rear. Tap in place with soft face mallet.
5. Install flange. Tap-flange onto drive pinion exten-
sion shaft, with a soft face mallet, at least far enough
to install nut.
6. Assemble flange holder J-8614 to flange, install
new self-locking nut and torque to 87
lb.ft.7. Install torque tube assembly onto differential car-
rier using only three of the four bolts. The fourth bolt
will be used later to install the brake pipe bracket.Figure
4A-8 Installing Support Bracket on TorquelTube8. Position floor jack under torque tube and raise it
far enough to install central joint support to under-
body bolts finger tight. Remove jack.
9. Jounce rear of car so springs will assume normal
position and torque the central joint support to un-
derbody bolts to 36 lb. ft.
10. Align mating marks of universal joint and flange,
connect universal joint to flange with respective bolts
and lock plates. Torque nuts to 11 lb. ft. Bend lock .
plate tangs to retain bolts.
11. Assemble parking brake cable equalizer and re-
turn spring to brake rod and adjust to specifications.
12. Connect brake line bracket to torque tube.
13. Remove supports
f&n rear of car and lower to
the floor.
Page 238 of 625

REAR AXLE
CONTENTS
SubjectPage No.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION:
Rear Axle Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4B- 7
DIAGNOSIS:
RearAxleTroubleDiagnosis. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4B- 8
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS: (Not Applicale)
MAJOR REPAIR:
Removal and Installation of Rear Axle Assembly
Removal and Installation of Axle Shaft Assembly
Disassembly and Assembly of Differential
.* . . . . . . . . . . . .SPECIFICATIONS:
DifferentialSpecifications
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4B- 94B-10
48-l 1
4B-22
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
REAR AXLE DESCRIPTIONThe Opel rear axle is a semi-floating type that carries
car weight through the axle shafts by way of ball
bearings which are located on the outer ends of each
axle shaft. The rear axle assembly is attached to the
under body by way of the shock absorbers, track rod,
central joint support, and lower control arms. A sta-
bilizer rod is used on all Wagons, as well as Fast
Backs and Sedans. The GT is not equipped with a
stabilizer rod. The rear springs have a progressive
spring rate which is attained by a gradual reduction
of coil thickness. The springs are arranged between
the spring seats welded onto the rear axle tubes and
the under body side members. The upper and lower
ends are seated in profiled rubber dampening rings.
The differential housing is a malleable iron casting
with tubular axle housings pressed into the sides to
form a complete assembly. An oil feed passage to the
pinion bearings and an oil return hole are provided
to allow lubricant to circulate. A removable steel
cover is bolted on the rear of the differential housing
to permit service of the differential without removing
the rear axle assembly from the vehicle. A breather
fitting is located on top of the right axle tube.Within the differential carrier, the differential case is
supported by two tapered roller side bearings. These
side bearings are preloaded by shims located between
the bearing inner races and differential case. During
installation, varying the shim thickness from side to
side also determines the ring gear to pinion backlash.
The differential case houses two side gears meshed
with two pinions. The pinions and side gears are
backed by thrust washers. The pinion gears are held
in place by a pinion shaft which is anchored in the
differential case by a lock pin.
The inner end of the axle shafts engage and extend
through the splines of the side gears with a floating
tit.
The axle shafts have an enlarged diameter from mid-
shaft to the flange end.
A ball bearing and oil seal are used on all models, and
are pressed onto the outer end of the axle shaft as an
assembly.The drive pinion is mounted in two roller bearings in
the rear axle housing. Pinion setting is established by
shims located between the differential carrier and therear’pinion bearing outer race.
Page 239 of 625

4S- 91973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
DIAGNOSIS
DIFFERENTIAL TROUBLE DIAGNOSISConditionPossible Cause
1. Noise is the same in1. a) Road noise.
“Drive” or “Coast”.b) Tire noise.
c) Front wheel bearing noise.
d) Front or rear U-joint angle
too great.
2. Noise changes on a2. a) Road noise.
different type of road.b) Tire noise.
3. Noise lowers tone as3. Tire noise.
car speed is lowered.
4. Similar noise is pro-4. a) Engine noise.duced with car standingb) Transmission noise.
and driving.c) Driveline angle.
5. Vibration5. a) Rough rear wheel bearing.
b) Tire unbalance.
c) Worn universal joint in
propeller shaft.
d) Front or rear U-joint angle
too great.
e) Mis-indexed, propeller shaft
at companion flange.
tJ Companion flange runout too
6. A knock or click6. A brinelled rear wheel bearing
approximately every two (2)
revolutions of rear wheel.
7. Noise most pronounced on7. Differential side gear and pin
turns.
8. A continuous low pitch8. Pinion bearing.
whirring or scraping noise
starting at relatively low
speed.9. Drive noise, coast9. Ring and pinion gear.
noise or float noise.
10. Clunk on accelera-
10. a) Worn differential cross sha
tion or deceleration.in case.
11. Groan in “Forward” or11. Wrong lube in differential.
“Reverse”.
12. Clunk or knock on12. a) Excessive end play of axle
rough road operation.to differential cross shaft
b) Excessive differential gear
clearance.