ignition RENAULT SCENIC 2011 J95 / 3.G Engine And Peripherals Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: RENAULT, Model Year: 2011, Model line: SCENIC, Model: RENAULT SCENIC 2011 J95 / 3.GPages: 198, PDF Size: 0.85 MB
Page 2 of 198

13B-2V4 MR-372-J84-13B000$010.mif
13B
DDCR INJECTION
Vdiag No.: 44, 48
1. APPLICABILITY OF THE DOCUMENT
This document presents the fault finding procedure applicable to all computers with the following specifications:
Following the introduction of the Pump repriming function on K9K engines, a new Vdiag was issued to cover this
function.
When replacing a high pressure pump on vehicles fitted with a computer with Vdiag 44, it is essential to reprogram
the injection computer to activate the Pump repriming function.
After reprogramming, Vdiag 44 is replaced by Vdiag 48.
2. PREREQUISITES FOR FAULT FINDING:
Documentation type:
Fault finding procedures (this document):
– Assisted fault finding (integrated into the diagnostic tool), Dialogys.
Wiring Diagrams:
– Visu-Schéma (CD-ROM), paper.
Type of diagnostic tools:
–CLIP
Special tooling required:
3. REMINDERS
Procedure
To run fault finding on the vehicle's computers, switch on the ignition in fault finding mode (forced + after ignition
feed).
Proceed as follows:
– Vehicle card in card reader.
– Press and hold the start button (longer than 5 seconds) with the start-up conditions not fulfilled.
– Then connect the diagnostic tool and perform the required operations.Vehicle(s): MEGANE II, SCENIC II
for engines K9K 722, 728, 729
Function concerned: DELPHI K9 DIESEL
DIRECT COMMON RAIL INJECTION (DDCR)Computer name: DDCR INJECTION
Program No.: BE
Vdiag No.: 44, 48
SPECIAL TOOLING REQUIRED
Multimeter.
Elé. 1590 112-track computer bornier.
Elé. 1681 Universal bornier.
Mot. 1711 Injector flow measuring kit.
DDCR_V44_PRELI/DDCR_V48_PRELI
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Introduction
Page 3 of 198

13B-3V4 MR-372-J84-13B000$010.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Introduction13B
DDCR INJECTION
Vdiag No.: 44, 48
To cut off + after ignition, proceed as follows:
– disconnect the diagnostic tool,
– press the start button twice briefly (less than 3 seconds),
– check that the + after ignition feed has been cut off by checking that the computer warning lights on the instrument
panel have gone out.
Fault
Faults are declared present or stored (depending on whether they appeared in a certain context and have
disappeared since, or whether they remain present but are not diagnosed within the current context).
The present or stored status of the faults should be taken into consideration when the diagnostic tool is used after
the + after ignition feed has been connected (with no system components activated).
For a present fault,apply the procedure described in the Interpretation of faults section.
For a stored fault, note the faults displayed and apply the Notes paragraph.
If the fault is confirmed when the notes are applied, the fault is present. Deal with the fault.
If the fault is not confirmed, check:
– the electrical lines which correspond to the fault,
– the connectors on these lines (corrosion, bent pins, etc.),
– the resistance of the faulty component,
– the condition of the wires (melted or cut insulation, wear).
Or use diagnostics to check the circuit of the suspect component.
Conformity check
The conformity check is designed to check the statuses and parameters that do not display any faults on
the diagnostic tool when inconsistent. Therefore, this stage is used to:
Run fault finding on faults that do not have a fault display, and which may correspond to a customer complaint,
– Check that the system is operating correctly and that there is no risk of a fault recurring after repair.
– This section features the fault finding procedures for statuses and parameters, and the conditions for checking
them.
If a status is not operating normally or a parameter is outside permitted tolerance values, you should consult
the corresponding fault finding page.
Customer complaints - Fault-finding chart
If the diagnostic tool check is correct, but the customer complaint is still present, it should be dealt with using
Customer complaints.NOTE:
The right-hand and left-hand xenon bulb computers are powered when the dipped headlights are lit. Fault finding
can only be carried out on them after the ignition has been switched on in fault finding mode (forced + after ignition
feed) and the dipped headlights are on.
A summary of the overall procedure to follow is provided on the following page in the form of a flow chart.
Page 8 of 198

13B-8V4 MR-372-J84-13B000$020.mif
13B
DDCR INJECTION
Vdiag No.: 44, 48
System outline
The DDCR injection system used on the K9 engine is an electronically managed high pressure injection system.
The fuel is compressed by a high pressure pump then stored in a rail that feeds the injectors. Injection occurs when
a current pulse is applied to the injector holders. The injected flow is proportional to the rail pressure and to
the applied pulse length, and the start of injection is phased with the start of the pulse.
The circuit comprises two subsystems, which are distinguished by the fuel pressure level.
– The low pressure system includes the tank, diesel fuel filter, transfer pump and injector holder return pipes.
– The high pressure circuit contains the high pressure pump, the rail, the injector holders and the high pressure tubes.
Finally, there are a certain number of sensors and regulating actuators for controlling and monitoring the entire
system.
Functions provided
Function: Fuel supply management (timing, flow and pressure).
Quantity of fuel injected and injection timing adjustment
The injection checking parameters are the quantities to be injected and their respective timing. These are calculated
by the computer using signals from the following sensors:
• Engine speed (Crankshaft + Cam for synchronisation)
• Accelerator pedal
• Turbocharging pressure and air temperature (Turbocharger pressure)
• Coolant temperature
• Air temperature
• Air load (Flow and Pressure)
• Rail pressure
• Flowmeter
• Turbocharging solenoid valve
The quantities to be injected and their respective timing are converted into:
• a reference tooth
• the time between this tooth and the start of the pulse
• the time for which the supply to the injector holder is on
An electrical current (pulse) is sent to each injector holder according to previously calculated data. The system
makes one or two injections (1 pilot injection, 1 main injection). The general principle is to calculate an overall
injected flow which will then be divided into a main injection flow and a pilot injection flow, to help the combustion
process work properly and to reduce pollutant emissions.
An accelerometer is used to monitor some of the fuel injection deviation. This has several roles:
• Protecting the engine by detecting injection leaks (disabled on the basic vehicle).
• Checking the pilot quantity by measuring deviation and dispersion
• By changing both the duration and timing of the injection, the quantity of fuel injected and the mixture ignition timing
can be adjusted.
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – System operation
Page 11 of 198

13B-11V4 MR-372-J84-13B000$020.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – System operation13B
DDCR INJECTION
Vdiag No.: 44, 48
WITH FLOWMETER (K9K 728)
The flow of fresh air entering the engine is given by a hot wire ratiometric sensor. This flow sensor is used to
manage the amount of exhaust gas to be recirculated to ensure optimum recirculation rates. A fresh air temperature
sensor is built into the flowmeter.
Air flow measurement allows closed-loop control via the EGR valve.
Besides electrical faults with the sensor, there is a consistency test between the measured air flow and an estimated
air flow without EGR.
This flow evaluates the amount of fresh inlet air, based on the values supplied by the surrounding systems:
– the inlet air temperature measured by a sensor located after the turbocharger and/or after the intercooler (if fitted),
– the turbocharging pressure,
– the engine speed.
Pre-postheating actuation
Pre-postheating actuation consists of controlling the heater plugs and preheating warning light on the instrument
panel. The heater plugs are activated by relays, and the power is supplied from the battery. After the ignition is
switched on. Preheating is activated for a period of time. The warning light is illuminated for an activation period that
depends on the battery voltage, the atmospheric pressure, and the coolant temperature. When the temperature is
below a certain threshold, a postheating function can be used to improve the combustion stability, and consequently
engine operation (reducing unburnt particles and pollutant emissions).
Turbocharger control solenoid valve actuation
The turbocharger system comprises a solenoid valve that is used to actuate the vanes (or wastegate) to create an
overpressure or a vacuum in the inlet circuit.
Page 13 of 198

13B-13V4 MR-372-J84-13B000$020.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – System operation13B
DDCR INJECTION
Vdiag No.: 44, 48
Cruise control/speed limiter management:
When activated, the cruise control function maintains the vehicle at a preselected speed, regardless of the driving
conditions encountered. Using the control buttons, the driver can increase or decrease the vehicle speed.
The cruise control function can be deactivated either by using the control buttons or by switching off the cruise
control function selection switch, or when system events are detected such as depressing the brake or clutch
pedals, or when system errors are detected such as an inconsistent vehicle speed or excessive vehicle
deceleration. The cruise control function can also be temporarily suspended when the driver wants to resume
control of the vehicle and exceed the selected cruising speed by depressing the accelerator pedal which then
exceeds the selected fuel flow. The cruising speed is resumed when the driver releases the accelerator pedal.
The cruise control function can be reactivated and the last cruising speed can be resumed after deactivating
the function for whatever reason until the vehicle ignition is switched off (i.e. for as long as computer supply not cut
off). The vehicle will then attempt to return to the cruising speed using a controlled vehicle acceleration rate.
When switched on (using the selection switch), the vehicle speed limiter function limits the vehicle speed to a preset
value. The driver controls the vehicle in the normal way using the accelerator pedal until the limit speed is reached.
If an attempt is made to exceed this speed, the system will ignore the pedal request and will control the vehicle
speed as the cruise control function would do, provided that the driver continues to press the accelerator pedal.
As with the cruise control function, the set speed can be altered by adjusting the control buttons, with single touches
or holding down.
For safety reasons, the cruising speed can be exceeded by depressing the accelerator pedal beyond the pedal
position limiting value. Vehicle speed is then controlled using the accelerator pedal until the vehicle speed is
decreased to below the cruising speed, when the limiter function is activated again.
The driver has the following controls for the cruise control/speed limiter function:
– accelerator pedal,
– brake pedal,
– clutch pedal,
– function selector switch, used to select cruise control or speed limiter operating mode.
Instrument panel display
The computer displays certain information on the instrument panel relating to engine operation. This concerns 5
functions: the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp) of the EOBD (European On Board Diagnostic), pre-postheating,
the coolant temperature, and engine faults: Level 1 (non-critical fault) and Level 2 (emergency stop). These five
functions are represented by 3 warning lights or messages displayed by the on-board computer.
Pre-postheating warning light
This light is used both as an in-operation indicator light and as a system fault indicator:
– permanently lit during + after ignition feed: indicates preheating of the heater plugs.
After preheating and an automatic timed 3 second off period, the warning light will come on if a Level 1 fault occurs
(leading to reduced operation and reduced safety levels. The driver should have repairs carried out as soon as
possible.)
Page 14 of 198
13B-14V4 MR-372-J84-13B000$020.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – System operation13B
DDCR INJECTION
Vdiag No.: 44, 48
Temperature / emergency stop warning light
This indicator light is used both as an in-operation indicator light and as a system fault warning light. It illuminates for
3 seconds when the power is switched on (automatic test procedure controlled by the instrument panel)
Continuously lit: indicates engine overheating or a Level 2 fault.
– if the fault reaches a critical level, the injection cuts off automatically after several seconds.
– in the event of engine overheating, it is the driver's choice to stop the car or continue driving.
ACTIVATION PROGRAMMING OF THE INSTRUMENT PANEL WARNING LIGHTS
Orange SERVICE warning light (level 1)
This warning light comes on, accompanied by the faulty injection message.
The driver should have the repairs carried out as soon as possible.
Red STOP warning light (level 2)
This warning light comes on, accompanied by the faulty injection message.
The driver should have the repairs carried out as soon as possible.
Excess pollution OBD ORANGE warning light:
This warning light is used to alert the driver of any injection faults that could lead to excessive pollution, or if
the EOBD system has been deactivated. The injection computer requests illumination of the OBD warning light for
a present fault only after three consecutive driving cycles.
The 3 second visual inspection when the ignition is switched on (automatic test procedure managed by
the instrument panel) is carried out by the injection computer.
Faults that activate the OBD warning light
Associated
faultTitle Specification
DF010 EGR position sensor circuit CC.1 - CO.0
DF016 EGR control circuit CC.1
DF026 Cylinder 1 injector control circuit CO – CC
DF027 Cylinder 2 injector control circuit CO – CC
DF028 Cylinder 3 injector control circuit CO – CC
DF029 Cylinder 4 injector control circuit CO – CC
DF038 Computer 3. DEF
DF114 EGR solenoid valve circuit 4. DEF
Page 15 of 198
13B-15V4 MR-372-J84-13B000$020.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – System operation13B
DDCR INJECTION
Vdiag No.: 44, 48
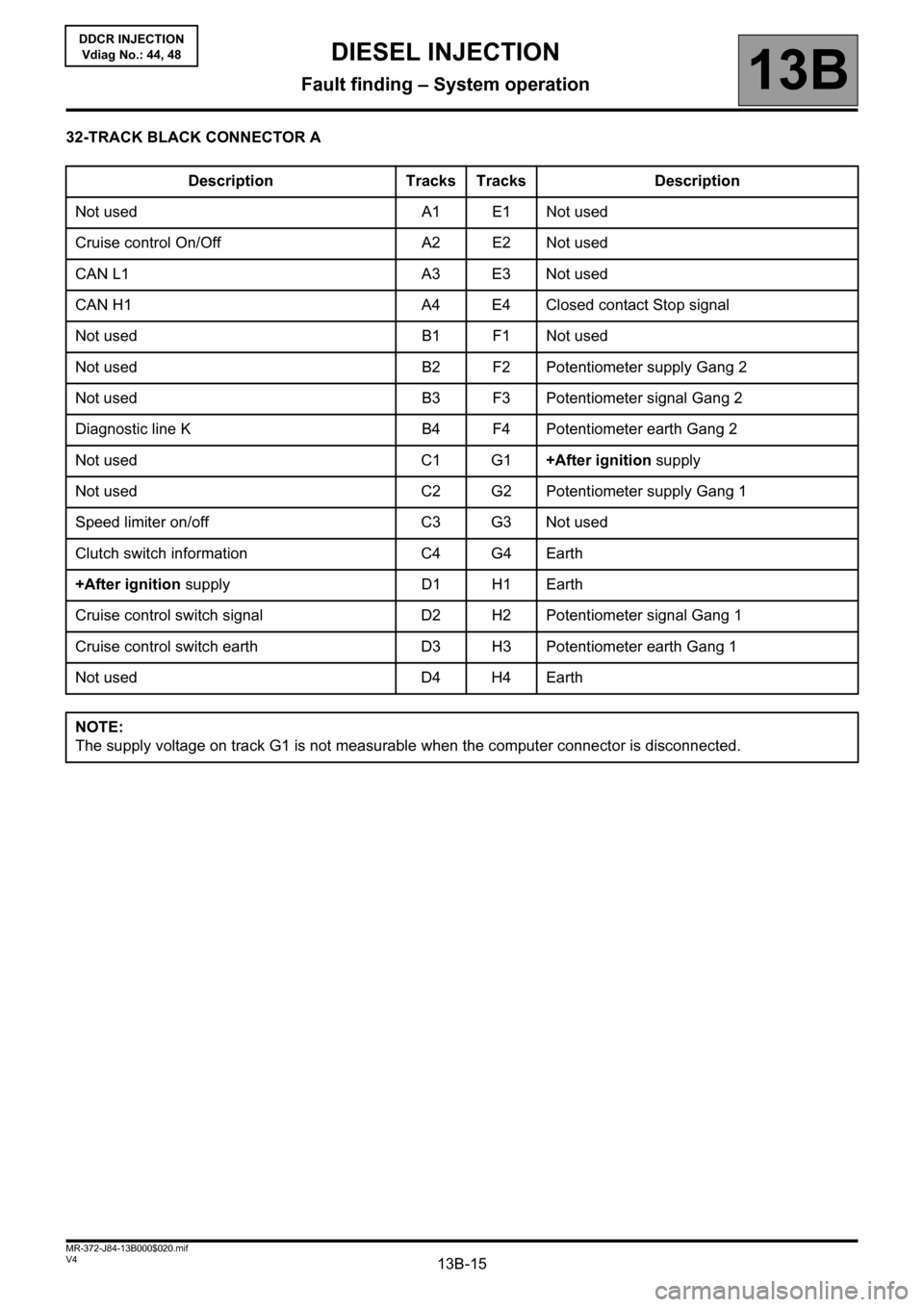
32-TRACK BLACK CONNECTOR A
Description Tracks Tracks Description
Not used A1 E1 Not used
Cruise control On/Off A2 E2 Not used
CAN L1 A3 E3 Not used
CAN H1 A4 E4 Closed contact Stop signal
Not used B1 F1 Not used
Not used B2 F2 Potentiometer supply Gang 2
Not used B3 F3 Potentiometer signal Gang 2
Diagnostic line K B4 F4 Potentiometer earth Gang 2
Not used C1 G1+After ignition supply
Not used C2 G2 Potentiometer supply Gang 1
Speed limiter on/off C3 G3 Not used
Clutch switch information C4 G4 Earth
+After ignition supply D1 H1 Earth
Cruise control switch signal D2H2 Potentiometer signal Gang 1
Cruise control switch earth D3H3 Potentiometer earth Gang 1
Not used D4 H4 Earth
NOTE:
The supply voltage on track G1 is not measurable when the computer connector is disconnected.
Page 18 of 198

13B-18V4 MR-372-J84-13B000$030.mif
13B
DDCR INJECTION
Vdiag No.: 44, 48
COMPUTER REPLACEMENT, PROGRAMMING AND REPROGRAMMING OPERATIONS
Before reprogramming or removing the computer in After-Sales operations, save the following data to the
diagnostic tool:
– The C2I parameters (individual injector correction) and the engine adaptives using command SC003 Save
computer data.
The system can be reprogrammed with the diagnostic socket using the RENAULT CLIP diagnostic tool
(Consult Technical Note 3585A, Computer programming and reprogramming procedure, and follow the
instructions given by the diagnostic tool).
Any time the computer has been reprogrammed
– Use the diagnostic tool command SC001 Enter saved data to restore the C2I and the engine adaptives.
– Use command AC028 Static test to reinitialise the computer (fan assembly, etc.).
– When changing the pump, refer to the high pressure pump replacement procedure (consult Technical Note 5011A,
Repriming Delphi high pressure pumps on K9K engines).
– Switch the ignition off and then on again.
–Activate the starter without releasing the key until the engine starts (the engine start time can be up to 20
seconds).
– Stop the engine (to initialise the computer) and wait 30 seconds.
– Switch the ignition on again and use the diagnostic tool to carry out the following steps:
– Run command VP010 Enter VIN.
– After injection system programming, stored faults may appear on other computers. Clear the memory of these
computers. IMPORTANT:
Before reprogramming the injection computer, move the main Cruise control/Speed limiter switch to the rest
position. The information about the cruise control or the speed limiter displayed on the instrument panel
disappears.
Otherwise, if the main switch remains in the cruise control or speed limiter position during and after reprogramming,
the Cruise control/Speed limiter function will not be operational.
The procedure for resetting the function is as follows:
Vehicle ignition on.
Main switch in rest position (the computer then detects the rest position).
Switch in Cruise control position to activate the Cruise control function.
Switch in Speed limiter position to activate the Speed limiter function.
IMPORTANT
– Switch on the diagnostic tool (mains or cigarette lighter supply).
– Connect a battery charger.
– Switch off all electrical consumers (lights, interior lights, air conditioning, radio/CD, etc.).
– Wait for the engine to cool (engine coolant temperature below 60°C and air temperature below 50°C).
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Replacement of components
Page 19 of 198

13B-19V4 MR-372-J84-13B000$030.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Replacement of components13B
DDCR INJECTION
Vdiag No.: 44, 48
REPLACING THE INJECTORS:
The system may be configured via the diagnostic socket using the RENAULT CLIP diagnostic tool.
The C2I parameters must be replaced after replacing an injector/injectors.
To do this, reprogram the C2I into the computer using the following commands:
Cylinder 1 injector: command VP001 Cylinder 1 injector code (cylinder at flywheel end).
Cylinder 2 injector: command VP002 Cylinder 2 injector code.
Cylinder 3 injector: command VP003 Cylinder 3 injector code.
Cylinder 4 injector: command VP004 Cylinder 4 injector code.
It is also possible to enter the four C2I using command SC002 Enter injector codes.
The technician can use the appropriate command to re-enter the new C2I for the replaced injector and to erase the
old C2I.
–Only after simultaneously replacing at least three injectors, reset the injector programming adaptives, using
command RZ004 Pressure regulation programming adaptives. IMPORTANT
AFTER A PROGRAMMING OPERATION, DO NOT CONNECT THE BATTERY FOR AT LEAST 30 minutes (to
carry out other work on the vehicle).
Note:
If commands SC001 and SC003 have been lost or if they are not operating after programming the computer:
– Enter the C2I for each injector manually, by reading the C2I on each injector (see Replacement of
components, Injector replacement).
– Use command AC028 Static test to reinitialise the computer (fan assembly, etc.).
– Switch the ignition off and then on again.
– Clear the engine management computer faults.
IMPORTANT
It is not possible to try an injection computer from the Parts Department as it will not be possible to fit it on another
vehicle afterwards.
Note:
C2I (individual injector correction) is a calibration carried out in the factory on each injector to adjust the flow
of each injector precisely.
The correction values are written on a label affixed to each injector, then entered in the computer which can then
actuate each injector by taking account of their manufacturing variation.
Page 25 of 198

13B-25
AFTER REPAIRDeal with any faults displayed by the diagnostic tool. Clear the computer fault memory.
Carry out a road test followed by another check with the diagnostic tool.
V4 MR-372-J84-13B000$061.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Interpretation of faults13B
DDCR INJECTION
Vdiag No.: 44, 48
DF002
PRESENTAIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUITCO.1: Open circuit or short circuit to + 12 volts.
CC.0: Short circuit to earth.
1.DEF: inconsistency.
NOTESNone.
Check the connection and condition of the 4-track connector of the air temperature sensor.
Repair if necessary.
Check the connection and condition of the computer 48-track brown connector B.
Repair if necessary.
Check for the +5 V after ignition feed between track 3 and track 1 earth on the air temperature sensor
connector.
Repair if necessary.
Measure the resistance of the air temperature sensor between tracks 2 and 3.
Replace the air temperature sensor if the resistance is not:
7419 Ω ± 365 Ω at -5°C.
5887 Ω ± 282 Ω at 0°C.
4707 Ω ± 220 Ω at 5°C.
3791 Ω ± 173 Ω at 10°C.
3075 Ω ± 137 Ω at 15°C.
2510 Ω ± 113 Ω at 20°C.
2063 Ω ± 87 Ω at 25°C.
1716 Ω ± 71 Ω at 30°C.
Check the insulation, continuity and the absence of interference resistance on the following connections:
Sensor connector track 2 Track J1 computer connector B
Sensor connector track 3 Track C1 computer connector B
Sensor connector track 4 Track C2 computer connector B
Sensor connector track 1 Track C3 computer connector B
Repair if necessary.
If the fault is still present, replace the air temperature sensor.
DDCR_V44_DF002P/DDCR_V48_DF002P