change wheel Seat Alhambra 2015 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SEAT, Model Year: 2015, Model line: Alhambra, Model: Seat Alhambra 2015Pages: 305, PDF Size: 5.46 MB
Page 151 of 305
Driving
● Use of CFC-free coolants.
Ban on heavy metals, with the exceptions
dictated by law (Annex II of ELV Directive
2000/53/EC): cadmium, lead, mercury, hexa-
v al
ent chromium.
Manufacturing methods ● Reduction of the quantity of thinner in the
protective wax for cavities.
● Use of plastic film as protection during ve-
hicle transport.
● Use of solvent-free adhesives.
● Use of CFC-free coolants in cooling sys-
tems.
● Recycling and energy recovery from resi-
dues (RDF).
● Improvement in the quality of waste water.
● Use of systems for the recovery of residual
heat (thermal recovery, enthalpy wheels,
etc.).
● The use of water-soluble paints. Correct economical and ecological
driving
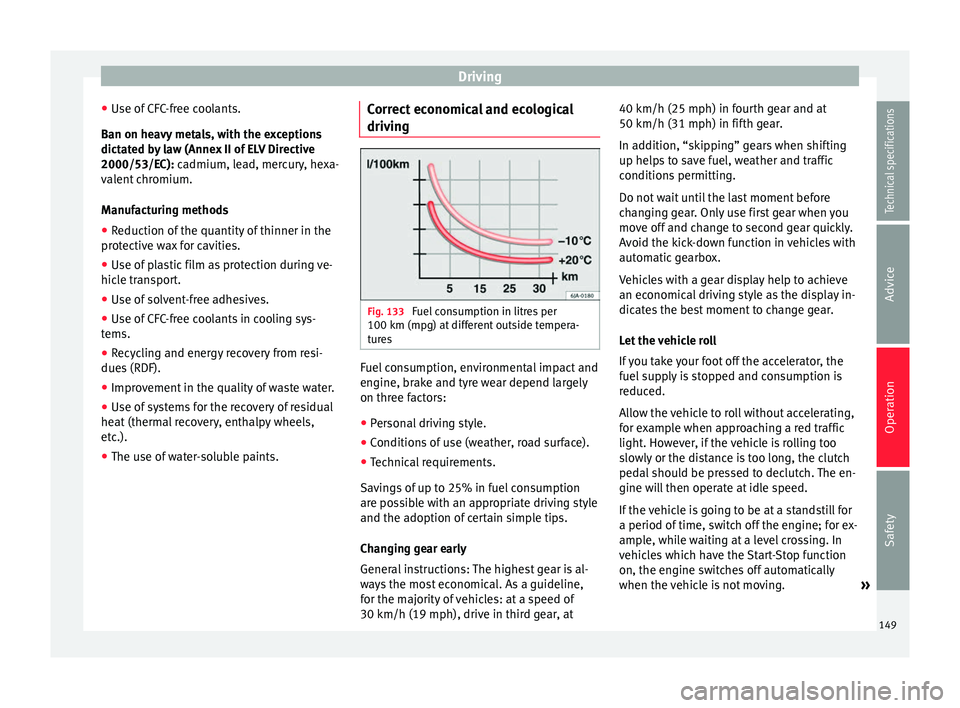
Fig. 133
Fuel consumption in litres per
100 km (mpg) at different outside tempera-
tures Fuel consumption, environmental impact and
engine, brake and tyre wear depend largely
on three factors:
● Personal driving style.
● Conditions of use (weather, road surface).
● Technical requirements.
Savings of up to 25% in fuel consumption
are possible with an appropriate driving style
and the adoption of certain simple tips.
Changing gear early
General instructions: The highest gear is al-
ways the most economical. As a guideline,
for the majority of vehicles: at a speed of
30 km/h (19 mph), drive in third gear, at 40 km/h (25 mph) in fourth gear and at
50 km/h (31 mph) in fifth gear.
In addition, “skipping” gears when shifting
up helps to save fuel, weather and traffic
conditions permitting.
Do not wait until the last moment before
changing gear. Only use first gear when you
move off and change to second gear quickly.
Avoid the kick-down function in vehicles with
automatic gearbox.
Vehicles with a gear display help to achieve
an economical driving style as the display in-
dicates the best moment to change gear.
Let the vehicle roll
If you take your foot off the accelerator, the
fuel supply is stopped and consumption is
reduced.
Allow the vehicle to roll without accelerating,
for example when approaching a red traffic
light. However, if the vehicle is rolling too
slowly or the distance is too long, the clutch
pedal should be pressed to declutch. The en-
gine will then operate at idle speed.
If the vehicle is going to be at a standstill for
a period of time, switch off the engine; for ex-
ample, while waiting at a level crossing. In
vehicles which have the Start-Stop function
on, the engine switches off automatically
when the vehicle is not moving.
»
149
Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 156 of 305

Operation
Driver assistance systems
Braking and stability systems Brake assist systems The brake assist systems ESC, ABS, BAS, ASR
and EDL only operate when the ignition is
switched on. They contribute significantly to
increasing active safety.
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
ESC reduces the risk of skidding and increa-
ses the vehicle stability by braking individual
wheels under specific driving conditions. ESC
detects critical handling situations, such as
understeer, oversteer and wheelspin on the
driven wheels. The system stabilises the ve-
hicle by braking individual wheels or by re-
ducing the engine torque.
The ESC has limits. It is important to realise
that the ESC is also subject to the laws of
physics. ESC will not be able to deal with all
situations with which drivers may be faced.
For example, if the road surface changes sud-
denly then ESC will not be useful in all cases.
If the vehicle suddenly enters a section cov-
ered by water, mud or snow then ESC will not
provide assistance in the same way as on dry
ground. If the vehicle loses its grip on the
ground and moves on a film of water (“aqua-
planing”), the ESC will not be able to assist the driver to control the vehicle as the loss of
adherence with the road surface will prevent-
ing braking and steering. If the vehicle is
driven through series of bends at high
speed, the ESC will not always be as effec-
tive: the vehicle reaction to aggressive driv-
ing is not the same as at reduced speeds.
When driving with a trailer, ESC does not pro-
vide the same amount of vehicle control as
without a trailer.
Adjust your speed and driving style to road,
traffic and weather conditions. ESC cannot
push the limits of the laws of physics; im-
prove the transmission available or maintain
the vehicle on the road if a lack of driver at-
tention creates an inevitable situation. Other-
wise, ESC assists in maintaining vehicle con-
trol in extreme situations and uses the move-
ments of the steering made by the driver to
maintain the vehicle moving in the desired
direction. If the vehicle is driven at such a
speed that it will leave the road before ESC
can intervene then the system cannot pro-
vide assistance.
The ABS, BAS, ASR and EDL systems are in-
corporated into the ESC. The ESC is always
on. The ESC should only be turned off using
the ASR button
›››
Fig. 134 when traction is
in s
ufficient. Always remember to turn on the
ASR once more when the vehicle has traction
again. Anti-lock brake system (ABS)
ABS can prevent the wheels from locking dur-
ing braking until just before the vehicle stops
thus helping the driver to steer the vehicle
and maintain control. This means that, even
during full braking, the risk of skidding is re-
duced:
● Press and hold the brake pedal fully. Do not
remove your foot from the brake pedal or re-
duce braking force!
● Do not “pump” the brake pedal, or reduce
braking force!
● Maintain vehicle direction when braking
fully.
● When the brake pedal is released or when
the brake force is reduced, ABS is turned off.
ABS control can be observed by vibration of
the brake pedal and noise. You should never
expect
the ABS to reduce the braking dis-
tance under
any circumstances. This distance
will increase when driving on gravel, recent
snow or on icy and slippery ground.
When driving on loose ground, the all-terrain
configuration of the ABS is automatically
turned on. When ABS is activated, the front
wheels may lock briefly. This shortens the
braking distance in off-road situations as the
wheels are prevented from digging into loose
surfaces. All-terrain ABS only intervenes
when driving in a straight line. When the
154
Page 157 of 305
Driver assistance systems
front wheels are turned, the normal ABS is
activated.
Brake assist system (BAS)
The brake assist system may reduce the re-
quired braking distance. The brake assist
system boosts the braking force if you press
the brake pedal quickly in an emergency. As
a result, the braking pressure increases rap-
idly, the braking force is multiplied and the
braking distance is reduced. This enables the
ABS to be activated more quickly and effec-
tively.
¡Do not lift your foot off the brake pedal!
When the br ak
e pedal is released or when
the brake force is reduced, braking assist au-
tomatically turns off the brake servo.
Traction control when accelerating (ASR)
In the event of wheelspin, the traction control
system reduces the engine torque to match
the amount of grip available. The ASR makes
some situations easier, for example, when
starting, accelerating or going uphill, even in
unfavourable road conditions.
The ASR can be switched on or off manually
››› page 156.
Electr
onic differential lock system (EDL and
XDS)
EDL is available when driving in straight lines
under normal conditions. When the EDL de- tects wheelspin, it brakes the spinning wheel
and directs the power to the other drive
wheels. To prevent the disc brake of the
braked wheel from overheating, the EDL cuts
out automatically if subjected to excessive
loads. The EDL will switch on again automati-
cally when the brake has cooled down.
The XDS function is an extension of the elec-
tronic differential lock. The XDS does not re-
act to the traction of the driving wheels, but
to the adherence of the front wheel on the in-
side of the curve whilst gripping rapidly in
corners. The XDS gives pressure to the brakes
of the wheel on the interior of the corner to
prevent skidding. This improves traction,
which assists the vehicle in continuing the
required line.
WARNING
Driving at high speed on icy, slippery wet
ground can result in loss of vehicle control
and serious injury to the driver and passen-
gers.
● Adjust your speed and driving style to visi-
bility, road, traffic and weather conditions.
Even though the brake assist systems, ABS,
BAS, EDL, ASR and ESC, provide more securi-
ty, do not take unnecessary risks while driv-
ing.
● Brake assist systems can not overcome the
laws of physics. Even with ESC and other sys-
tems, slippery and wet roads will always be
dangerous. ●
Driving to quickly on wet ground can result
in the wheels losing contact with the ground
in an effect known as “aquaplaning”. Without
adherence, it is impossible to brake, steer or
control the vehicle.
● Brake assist systems cannot avoid acci-
dents if, for example, the driver does not re-
spect safety distances or drives to quickly in
difficult conditions.
● Even though brake assist systems are ex-
tremely effective and help control the vehicle
in difficult situations, remember that the ve-
hicle stability depends on tyre grip.
● When accelerating on a slippery surface,
for example on ice or snow, press the acceler-
ator carefully. The wheels can still slip even
with brake assist systems resulting in loss of
vehicle control. WARNING
The effectiveness of the ESC can be consider-
ably reduced if other components and sys-
tems affecting driving dynamics are not main-
tained or are not functioning correctly. This
includes, among others, brakes, tyres and
other systems already mentioned.
● Remember that changing and fitting other
components to the vehicle can affect opera-
tion of the ABS, BAS, ASL EDL and ESC.
● Changes to the vehicle suspension or using
unapproved wheel/tyre combinations can af-
fect operation of the ABS, BAS, ASL EDL and
ESC, as well as their effectiveness. » 155
Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 158 of 305
Operation
●
Likewise, the effectiveness of ESC depends
on the use of suitable tyres ››› page 231. Note
● To ensure that the ESC and ASR work prop-
erly, all four wheels must be fitted with iden-
tical tyres. Any differences in the rolling radi-
us of the tyres can cause the system to re-
duce engine power when this is not desired.
● If a malfunction should occur in the ABS,
the ESC, EDL and ASR will also be out of ac-
tion.
● Noises may be heard while any of the
above systems are operating. Turning on and off the ASR
Fig. 134
Detailed view of the centre console:
button used to switch ASR on and off (vehi-
cles with ESC) The electronic stability control ESC consists
of ABS, EDL and ASR and only works when
the engine is running.
The ASR can be switched off while the engine
is running by pressing the
OFF
››› Fig. 134
button. The ASR (and similar) is only switch-
ed off when the required traction is not ob-
tained:
● When driving through deep snow or on
loose ground (gravel, etc.).
● When “freeing” a trapped vehicle.
Turn the ASR back on by pressing the but-
ton OFF
››› Fig. 134 .
St ar
t assist systems
Introduction WARNING
The intelligent technology in the start assist
systems cannot change the laws of physics.
The improved comfort provided by start as-
sist systems should not prompt you to take
risks.
● Unintentional movements of the vehicle
could cause serious injury.
● The start assist systems are not a replace-
ment for driver awareness. ●
Always try to adapt the speed of the vehi-
cle and your style of driving to the condition
of the ground or the road and to weather and
traffic conditions.
● The start assist system cannot keep the ve-
hicle stationary in all conditions on a gradi-
ent or cause it to brake on steep downhill
gradients, e.g. if the road is slippery or icy. Auto Hold function*
Fig. 135
Detailed view of the centre console:
Auto Hold button The control lamp on the button switches on
when the Auto Hold function is on.
When the Auto Hold function is on, this helps
the driver if they must regularly stop the vehi-
cle or if they must stop with the engine run-
ning for prolonged periods, for example, on
hills, before a traffic light or in traffic jams
with continuous stopping and starting.
156
Page 159 of 305

Driver assistance systems
The Auto Hold function automatically pre-
vents the vehicle from rolling away acciden-
tally when at a standstill, without the driver
having to keep his/her foot on the brake ped-
al.
When the system that detects that the vehi-
cle has stopped, the Auto Hold keeps the ve-
hicle at a standstill. The brake pedal can be
released.
If the driver presses the brake pedal briefly or
the accelerator to start off, the Auto Hold
function releases the brake once more. The
vehicle moves according to the gradient.
If any of the conditions necessary for the Au-
to Hold function change while the vehicle
stopped, the system is turned off as is the in-
dicator on the button ››› Fig. 135 . The elec-
tr onic
parking brake engages where necessa-
ry to park the vehicle safely ››› .
Conditions for keeping the vehicle at a
standstill with Auto Hold:
● The driver door must be closed.
● The driver seat belt must be buckled.
● The engine must be running.
● The ASR system is switched on
››› page 137 . Sw
it
ching Auto Hold on and off manually
Press the AUTO HOLD button
››› . The control
lamp on the button switches off when the Au-
to Hold function is switched off.
Permanent Auto Hold connection
The Auto Hold function must be switched on
every time the engine is started. However, to
switch the Auto Hold function on permanent-
ly, the mark must be switched on in the
Set
-
tin
gs menu, “Autohold” submenu ››› page 47.
Auto Hold works automatically under the
following conditions:
All points must be fulfilled simultaneously
››› :
Manual gearboxAutomatic gearbox
1.If the vehicle is stopped using the brake pedal on a
flat or slope.
2.The engine must be “running smoothly”.
3.On a slope, the 1st gear
is engaged uphill or the
reverse gear is engaged
for a downhill. The
clutch must be held
down.A gear for driving is se-
lected from R, D or S.
Upon accelerating and
pressing in the clutch
simultaneously, the
brake releases gradual-
ly.Upon accelerating, the
brake releases gradual-
ly. Auto Hold turns off automatically under the
following conditions:
Manual gearboxAutomatic gearbox
1.If one of the conditions mentioned in
table on
page 157 changes.
2.If the engine is “not running regularly” or if there is a malfunction.
3.When changing to idle
speed.If the selector lever is
placed in neutral (N).
4.If the engine is turned
off or stalls.If the engine is switch-
ed off.
5.If the driver accelerates
while pressing the
clutch in.If the vehicle is acceler-
ated.
6. When one of the wheels
has minimal contact
with the ground (e.g. on
uneven ground). WARNING
The Auto Hold technology is limited by the
laws of physics. The improved comfort provi-
ded by Auto Hold should never prompt you to
take risks.
● Never leave the vehicle running and with
the Auto Hold function switched on.
● Auto Hold cannot always stop the vehicle
uphill and downhill (e.g. if the ground is slip-
pery or frozen). » 157
Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 166 of 305

Operation
● Perpendicular parking: press the button at speeds up to 50 km/h (31 mph) twice.
When the function is enabled, the button
››› Fig. 141 will light up.
● If nec
essary, press the button once
more to change parking mode.
● Apply the turn signal for the side on which
a gap is to be detected for parking. The in-
strument panel displays the side correspond-
ing to the road.
Parking
● Parking parallel to the road: drive next to
the gap at a speed of no more than 40 km/h
(25 mph) and
at a distance of between 0.5 m
and 2 m.
● P
arking perpendicular to the road: drive
next to the gap at a speed of no more than
20 km/h (12 mph)
and at a distance of be-
tween 0.5 m and 2 m.
● The best parking results will be achieved if
you position the vehicle as parallel as possi-
ble to the line of parked cars or the kerb.
● When a suitable parking place is displayed
on the instrument panel, stop and select re-
verse gear.
● Follow the instructions given on the instru-
ment panel display
● Then, release the steering wheel when the
warning signal sounds ››› : The system will
move the steering wheel! Observe the sur-
rounding area. ●
Observe the surrounding area and acceler-
ate carefully at a maximum of 7 km/h
(4 mph).
● The park assist system is only responsible
f or mo
ving the steering wheel during the ma-
noeuvre.
The driver applies the accelerator,
the clutch, the gears and the brake.
● Follow the instructions given by the park
assist system until the manoeuvre is comple-
ted.
● The park assist system steers the vehicle
forwards and backwards until it is in a
straight position in the parking space.
● The manoeuvre is complete when the corre-
sponding indication is given on the instru-
ment panel display.
Stopping the parking manoeuvre
The park assist system stops the manoeuvre
in the event of one of the following:
● Press button .
● Driving faster than 7 km/h (4 mph).
● The driver moves the steering wheel.
● The parking manoeuvre has not been com-
pleted after 6 minutes since the park assist
system was activated.
● A sliding door is opened. To restart the ma-
noeuvre, close the sliding door and press the
button again.●
There is a system malfunction (system tem-
porarily unavailable).
● The ASR system is switched off or the ASR
or ESC is working. WARNING
The steering wheel turns quickly by itself
when parking using the park assist system.
Placing your hand between the steering
wheel spokes could lead to injuries. Note
● The park assist system has its limitations.
For example, it is not possible to park on
tight bends using the park assist system.
● Even if the park assist system recognises
that there is not enough space for parking
the vehicle, the instrument panel display will
still show this place. In this case, the parking
manoeuvre should not be requested.
● Changing gears between forward and re-
verse gears before indicated (that is, before
the signal from the parking sensor system)
the parking results may not be ideal.
● For parallel parking (parallel to the road), a
sound will tell the driver when they must
change from forward gears to reverse; the
signal from the parking sensor system does
not indicate changes of direction.
● The park assist can also be activated after-
wards, if you pass close to a parallel parking
space at a maximum of 40 km an hour 164
Page 170 of 305
Operation1) Do not use the rear assist system in the fol-
lowing cases:
– If the position and installation angle of the camera
have been changed, e.g. in a rear-end collision. Have a
specialised workshop check the system.
2) Optical illusions of the camera (examples)
The rear assist camera produces two-dimensional im-
ages. Any cracks in or objects protruding from the
ground or from other vehicles are more difficult to spot
or cannot be seen due to a lack of depth in the image
displayed.
Objects or other vehicles may seem to be closer or fur-
ther away than what they really are:
– On changing from a flat surface to a slope or gradient.
– On changing from a slope or gradient to a flat surface.
– If the vehicle has been overloaded at the rear.
– On approaching protruding objects. These objects
may be outside the angle of vision of the camera when
reversing. Cleaning the camera lens
Keep the camera lens clean and clear of snow
and ice:
● Moisten the lens using a commercially
available, alcohol-based glass cleaning
agent and clean the lens with a dry cloth
››› .
● Remove snow using a small brush.
● Use de-icing spray to remove any ice ››› . CAUTION
● Never use abrasive cleaners to clean the
camera lens.
● Never remove snow or ice from the camera
lens using warm or hot water. This could
damage the lens. Note
● SEAT recommends that you practise park-
ing with the rear assist system in a quiet lo-
cation or in a car park to become familiar with
the system, including the orientation lines
and their function.
● The orientation lines will not be displayed
on the screen if the rear lid is open or the fac-
tory-fitted towing bracket is electrically con-
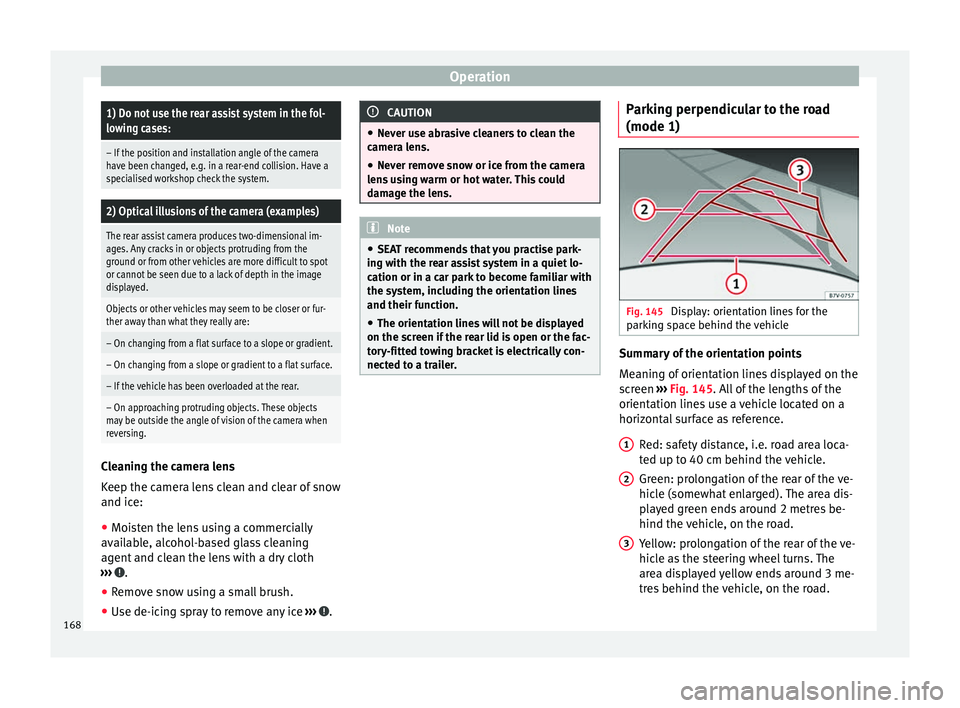
nected to a trailer. Parking perpendicular to the road
(mode 1)
Fig. 145
Display: orientation lines for the
parking space behind the vehicle Summary of the orientation points
Meaning of orientation lines displayed on the
screen
››› Fig. 145 . All of the lengths of the
orient ation line
s use a vehicle located on a
horizontal surface as reference.
Red: safety distance, i.e. road area loca-
ted up to 40 cm behind the vehicle.
Green: prolongation of the rear of the ve-
hicle (somewhat enlarged). The area dis-
played green ends around 2 metres be-
hind the vehicle, on the road.
Yellow: prolongation of the rear of the ve-
hicle as the steering wheel turns. The
area displayed yellow ends around 3 me-
tres behind the vehicle, on the road.
1 2
3
168
Page 174 of 305
Operation
Travelling down hills with the CCS
When travelling down hills the CCS cannot
maintain a constant speed. Slow the vehicle
down using the brake pedal and reduce
gears if required.
Automatic off
The cruise control system (CCS) is switched
off automatically or temporarily:
● If the system detects a fault that could af-
fect the working order of the CCS.
● If you increase the stored speed by using
the accelerator for a certain time.
● if the brake or clutch pedal is depressed.
● If you change gears.
● If the airbag is triggered.
Lane Assist system* Introduction WARNING
The intelligent technology in the lane assist
system cannot change the limits imposed by
the laws of physics and by the system itself.
Careless or uncontrolled use of the Lane As-
sist system may cause accidents and injury.
The system is not a replacement for driver
awareness. ●
Always adapt your speed and the distance
to the vehicles ahead in line with visibility,
weather conditions, the condition of the road
and the traffic situation.
● Always keep your hands on the steering
wheel so you can turn it at any time.
● The lane assist system does not detect all
road markings. In some circumstances, the
poor state of the road, structures located on
it or certain objects may be mistakenly recog-
nised as road markings by the lane assist
system. In such situations, switch the lane
assist system off immediately.
● Pay attention to the instructions on the in-
strument panel display and act accordingly to
its requests.
● Always pay attention to the vehicle's sur-
roundings. Note
The lane assist system has been exclusively
developed for driving on asphalted roads. Note
If the lane assist system does not work as de-
scribed in this chapter, do not use it and con-
tact a specialised workshop. Note
If you observe any system malfunction, have
the system checked by a specialised work-
shop. Control lampsBlinks
or
lights up
Possible causeSolution
(yellow)
Lane assist system
connected but in-
active.
The system cannot
clearly detect the
lane. See
page 173,
The lane assist sys-
tem is inactive (con-
trol lamp lit in yel-
low).
(green)
Lane assist system
connected and ac-
tive.–
Several warning and control lamps light up
for a few seconds when the ignition is switch-
ed on, signalling that the function is being
verified. They will switch off after a few sec-
onds.
WARNING
Observe the safety warnings ››› in Control
and warning lamps on page 47. 172
Page 175 of 305
Driver assistance systems
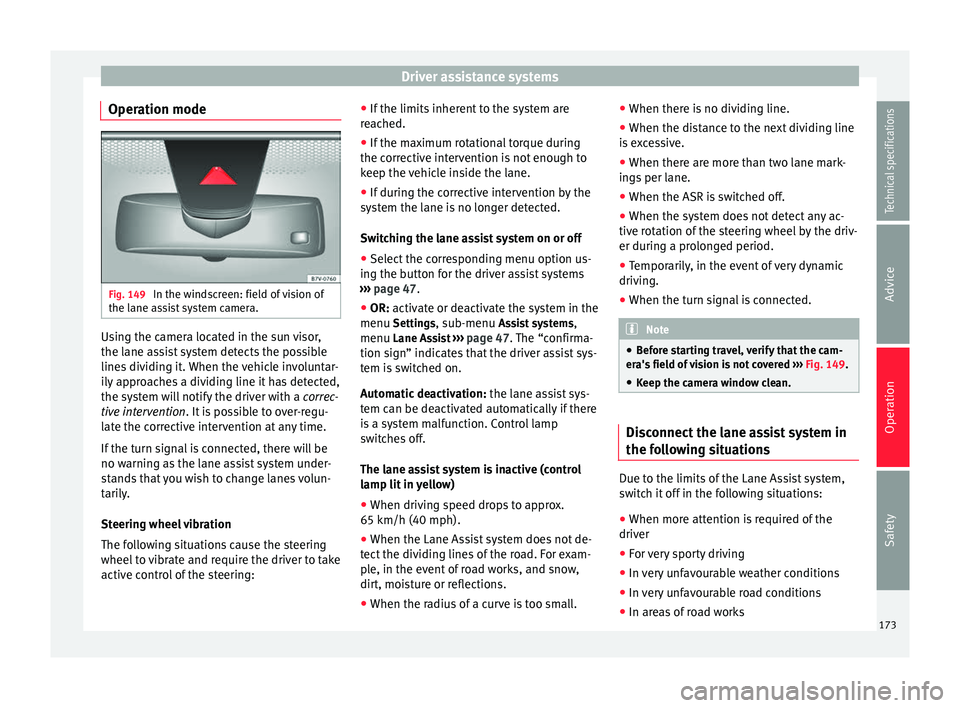
Operation mode Fig. 149
In the windscreen: field of vision of
the lane assist system camera. Using the camera located in the sun visor,
the lane assist system detects the possible
lines dividing it. When the vehicle involuntar-
ily approaches a dividing line it has detected,
the system will notify the driver with a
correc-
tive intervention . It is possible to over-regu-
l at
e the corrective intervention at any time.
If the turn signal is connected, there will be
no warning as the lane assist system under-
stands that you wish to change lanes volun-
tarily.
Steering wheel vibration
The following situations cause the steering
wheel to vibrate and require the driver to take
active control of the steering: ●
If the limits inherent to the system are
reached.
● If the maximum rotational torque during
the corrective intervention is not enough to
keep the vehicle inside the lane.
● If during the corrective intervention by the
system the lane is no longer detected.
Switching the lane assist system on or off
● Select the corresponding menu option us-
ing the button for the driver assist systems
››› page 47.
● OR: activate or deactivate the system in the
menu Setting
s, sub-menu Assist systems ,
menu Lane Assist ››› page 47. The “confirma-
tion sign” indic
ates that the driver assist sys-
tem is switched on.
Automatic deactivation: the lane assist sys-
tem can be deactivated automatically if there
is a system malfunction. Control lamp
switches off.
The lane assist system is inactive (control
lamp lit in yellow)
● When driving speed drops to approx.
65 km/h (40 mph).
● When the Lane Assist system does not de-
tect the dividing lines of the road. For exam-
ple, in the event of road works, and snow,
dirt, moisture or reflections.
● When the radius of a curve is too small. ●
When there is no dividing line.
● When the distance to the next dividing line
is excessive.
● When there are more than two lane mark-
ings per lane.
● When the ASR is switched off.
● When the system does not detect any ac-
tive rotation of the steering wheel by the driv-
er during a prolonged period.
● Temporarily, in the event of very dynamic
driving.
● When the turn signal is connected. Note
● Before starting travel, verify that the cam-
era's field of vision is not covered ››› Fig. 149.
● Keep the c
amera window clean. Disconnect the lane assist system in
the following situations
Due to the limits of the Lane Assist system,
switch it off in the following situations:
● When more attention is required of the
driver
● For very sporty driving
● In very unfavourable weather conditions
● In very unfavourable road conditions
● In areas of road works
173
Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety
Page 179 of 305
Driver assistance systems
● when a sporty driving style is employed,
● in the event of a major distraction for the
driver,
The tiredness detection function switches off
when the ignition is switched off or when the
driver unbuckles their seat belt and opens
the door. If driving for a long time under 65
km/h (40 mph), the system ceases to assess
tiredness automatically. If driving speed is
then increased, the behaviour at the wheel
will again be evaluated.
Tyre monitoring systems
Introduction The tyre monitor indicator monitors the tyre
pressure of each wheel during driving using
the ABS sensors. The ABS sensors monitor
the tyre tread perimeter and vibrations of
each tire. The tyre monitor indicator warns
the driver if it detects a considerable drop in
tyre pressure of one or several tyres while
driving. Loss of tyre pressure will be indica-
ted by the indicator
as well as an audible
warning and sometimes a text message on
the dash panel display. When you open the
driver door, you will find a label indicating
the tyre pressure recommended by the manu-
facturer for the maximum vehicle load for
each tyre approved for the vehicle in ques-
tion. By pressing the adjustment button on the tyre monitoring indicator, you may
change the reference pressure for the tyres
so that the tyre pressure coincides with ac-
tual pressure
››› page 179 .
S uit
able use of the adjustment button
››› page 179. WARNING
Unsuitable handling of the wheels and tyres
may lead to sudden tyre pressure losses, to
tread separation or even to a blow-out.
● Check tyre pressures regularly and ensure
they are maintained at the pressures indica-
ted. If the tyre pressure is too low, the tyres
could overheat, resulting in tread detachment
or even burst tyres.
● Tyre pressure should be that indicated on
the label when the tyres are cold at all times
››› page 235.
● Re
gularly check the cold inflation pressure
of the tyres. If necessary, change the tyre
pressure of the vehicle tyres while they are
cold.
● Regularly check your tyres for damage and
wear.
● Never exceed the maximum permitted
speed or loads specified for the type of tyre
fitted on your vehicle. WARNING
Incorrect use of the tyre monitoring indicator
button could result in the indicator giving er- roneous messages or prevented from indicat-
ing the danger caused by a defective tyre
››› page 179. CAUTION
● The tyre valves may be damaged if the cap
is not in place. Check that the caps are identi-
cal to the standard caps and have been cor-
rectly tightened. Do not use metal caps
››› page 179.
● Do not damage the valves when changing
the tyres ››› page 179
. For the sake of the environment
Under-inflated tyres lead to increased fuel
consumption and tyre wear. Note
● Do not only rely on the tyre monitoring sys-
tem. Regularly check your tyres to ensure
that the tyre pressure is correct and that the
tyres are not damaged due to puncture, cuts,
tears and impacts/dents. Remove objects
from the tyres only when the tyres have not
been pierced by these.
● The tyre monitoring system is set to the
tyre pressure recommended by the manufac-
turer and indicated on the label ››› Fig. 175. 177
Technical specifications
Advice
Operation
Safety