sensor SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1997, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997Pages: 2053, PDF Size: 88.33 MB
Page 986 of 2053

EBCM Connection Fact View.............................4E-95
EBCM Connector...............................................4E-95
Hydraulic Modulator Connector..........................4E-96
Repair Instructions..............................................4E-99
On-Vehicle Service...............................................4E-99
Service Precautions...........................................4E-99
ABS 5.3 Assembly..........................................4E-100
ABS/TCS Unit..................................................4E-100
Front Wheel Speed Sensor..............................4E-101Rear Wheel Speed Sensor...............................4E-101
Acceleration Sensor .........................................4E-102
System Fuse...................................................4E-102
Indicators........................................................4E-102
Unit Repair........................................................4E-103
ABS Front Tooth Wheel....................................4E-103
Special Tools and Equipment..........................4E-104
Special Tools Table..........................................4E-104
Page 987 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-3
SSANGYONG MY2002
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM OPERATION
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
Before using this section, it is important that you have
a basic knowledge of the following items. Without this
knowledge, it will be difficult to use the diagnostic
procedures contained in this section.
•Basic Electrical Circuits - You should understand
the basic theory of electricity and know the meaning
of voltage, current (amps), and resistance (ohms).
You should understand what happens in a circuit
with an open or shorted wire. You should be able to
read and understand a wiring diagram.
Use of Circuit Testing Tools - You should know
how to use a test light and how to bypass
components to test circuits using fused jumper
wires. You should be familiar with a digital
multimeter. You should be able to measure voltage,
resistance, and current, and be familiar with the
controls and how to use them correctly.
ABS SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The ABS 5.3 Antilock Braking System (ABS) consists
of a conventional hydraulic brake system plus antilock
components. The conventional brake system includes
a vacuum booster, master cylinder, front disc brakes,
rear disc brakes, interconnecting hydraulic brake pipes
and hoses, brake fluid level switch and the BRAKE
indicator.
The ABS components include a hydraulic unit, an elec-
tronic brake control module (EBCM), two system fuses,
four wheel speed sensors (one at each wheel), intercon-
necting wiring, the ABS indicator, the EBD indicator
and the TCS indicator. See “ABS Component Locator”
in this section for the general layout of this system.
The hydraulic unit with the attached EBCM is located
between the surge tank and the bulkhead on the left
side of the vehicle.
The basic hydraulic unit configuration consists of hy-
draulic check valves, two solenoid valves for each
wheel, a hydraulic pump, and two accumulators. The
hydraulic unit controls hydraulic pressure to the front
calipers and rear calipers by modulating hydraulic
pressure to prevent wheel lockup.
Units equipped with TCS add two more valves for each
drive wheel for the purpose of applying the brake to a
wheel that is slipping. This is done with pressure from
the hydraulic pump in the unit. There is also a TCS
indicator lamp on the instrument panel to alert the driver
to the fact that the TCS system is active. The
components identified in the drawing are those added
to the basic ABS 5.3 system to provide traction control.
Nothing in the hydraulic unit or the EBCM is serviceable.
In the event of any failure, the entire ABS unit withattached EBCM must be replaced. For more
information, refer to “Base Braking Mode” and
“Antilock Braking Mode” in this section.
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
(TCS) DESCRIPTION
General Information
The traction control system (TCS) is a traction system
by means of brake intervention only, available in a low
speed range (< 60kph).
It workes on µ - split roads with sidewise different friction
coefficients.
The spinning driven wheel is braked and the drive
torque can be transferred to the wheel on the high-µ
side. During TCS active, the TCS information lamp is
blinking.
The temperature of the brakes is calculated by a mathe-
matical model and TCS is switched passive if the calcu-
lated temperature is greater than a threshold value (500
°C).
TCS is permitted again, when the calculated tempera-
ture is less than 350 °C.
Control Algorithm
The input signals for the control algorithm are the
filtered wheel speed signals from the ABS speed
processing.
With the speed difference of the driven wheels, the
control deviation is calculated.
If the control deviation exceeds a certain threshold
value, the wheel with the greater slip is braked actively.
The threshold value depends on the vehicle speed:
It is reduced with increasing vehicle speed down to a
constant value.
KAA4F010
Page 989 of 2053
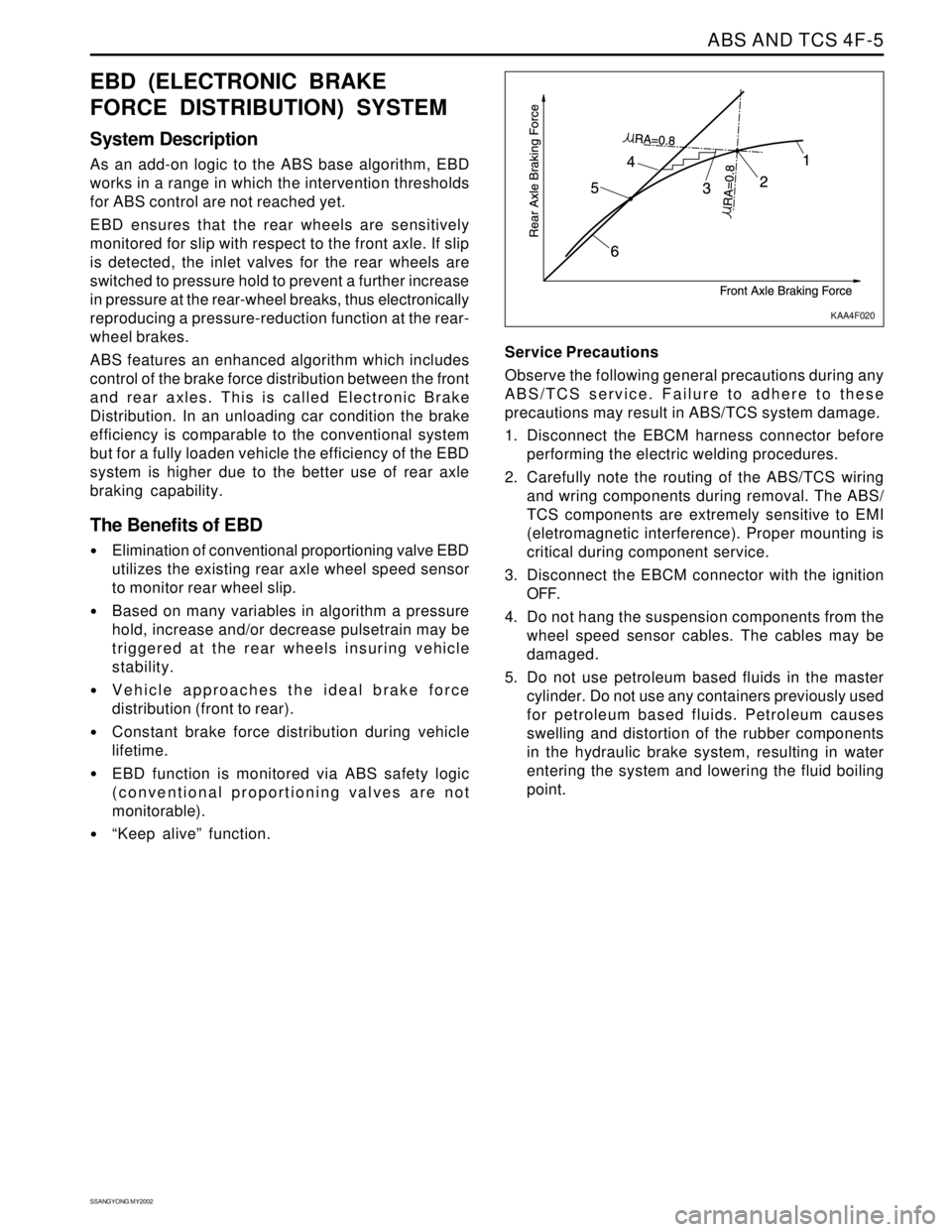
ABS AND TCS 4F-5
SSANGYONG MY2002
EBD (ELECTRONIC BRAKE
FORCE DISTRIBUTION) SYSTEM
System Description
As an add-on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD
works in a range in which the intervention thresholds
for ABS control are not reached yet.
EBD ensures that the rear wheels are sensitively
monitored for slip with respect to the front axle. If slip
is detected, the inlet valves for the rear wheels are
switched to pressure hold to prevent a further increase
in pressure at the rear-wheel breaks, thus electronically
reproducing a pressure-reduction function at the rear-
wheel brakes.
ABS features an enhanced algorithm which includes
control of the brake force distribution between the front
and rear axles. This is called Electronic Brake
Distribution. In an unloading car condition the brake
efficiency is comparable to the conventional system
but for a fully loaden vehicle the efficiency of the EBD
system is higher due to the better use of rear axle
braking capability.
The Benefits of EBD
Elimination of conventional proportioning valve EBD
utilizes the existing rear axle wheel speed sensor
to monitor rear wheel slip.
Based on many variables in algorithm a pressure
hold, increase and/or decrease pulsetrain may be
triggered at the rear wheels insuring vehicle
stability.
Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force
distribution (front to rear).
Constant brake force distribution during vehicle
lifetime.
EBD function is monitored via ABS safety logic
(conventional proportioning valves are not
monitorable).
“Keep alive” function.Service Precautions
Observe the following general precautions during any
ABS/TCS service. Failure to adhere to these
precautions may result in ABS/TCS system damage.
1. Disconnect the EBCM harness connector before
performing the electric welding procedures.
2. Carefully note the routing of the ABS/TCS wiring
and wring components during removal. The ABS/
TCS components are extremely sensitive to EMI
(eletromagnetic interference). Proper mounting is
critical during component service.
3. Disconnect the EBCM connector with the ignition
OFF.
4. Do not hang the suspension components from the
wheel speed sensor cables. The cables may be
damaged.
5. Do not use petroleum based fluids in the master
cylinder. Do not use any containers previously used
for petroleum based fluids. Petroleum causes
swelling and distortion of the rubber components
in the hydraulic brake system, resulting in water
entering the system and lowering the fluid boiling
point.
KAA4F020
Page 997 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-14 ABS AND TCS
COMPONENT LOCATOR
ABS, ABS/TCS 5.3
1 ABS/TCS Hydraulic Unit
(with EBCM in case of ABS only)
2 ABS/TCS EBCM Unit (in case of TCS)
3 Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
KAA4F100
4 ABS Warning Indicator Light
5 Diagnosis Connector
6 Front Wheel Speed Sensor
7 Acceleration Sensor
Page 1021 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-38 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 03
LEFT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR FAULT
KAA4F140
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
8. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
10. This step tests for an open or a high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Use the scan tool to monitor wheel speeds during a
road test. Watch the wheel speeds being displayed on
the scan tool to see if any of the readings are unusual,
such as one sensor varying in speed from the other
three, a signal going intermittently high or low, etc. If
this does not identify the intermittent, wet the speed
sensor harness on the underside of the vehicle and
perform a road test, monitoring wheel speeds with the
scan tool.
Step
1
DTC 03 - Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Fault
Action Yes
Go to Step 3No
Go to Step 2 Value(s)
-
Examine the wheel speed sensor.
Are there any signs of physical damage?
Page 1022 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-39
SSANGYONG MY2002
Step
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
DTC 03 - Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Fault (Cont’d)
Action
Go to Step 4
System OK
Go to Step 6
System OK
Go to Step 7
System OK
Go to Step 9
System OK
Go to Step 11
System OK
System OKGo to Step 3
-
Go to Step 5
-
Go to Step 8
-
Go to Step 10
-
Go to Step 12
-
- 1280 - 1920 Ω
-
≈ 70 mv
-
>1v
-
∞
-
>5 Ω
-
-
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the left rear wheel speed sensor
connector.
3. Use a digital voltmeter (DVM) to measure resis-
tance between the sensor terminals.
Is the resistance within the specified value at approxi-
mately 25-C (77-F)?
Replace the wheel speed sensor.
Is the repair complete?
1. Switch the DVM to the ac millivolt range.
2. Measure the voltage output between the wheel
speed sensor terminals while rotating the wheel
about 1 revolution per second.
Is the output within the specified value?
Replace the speed sensor or the toothed wheel, as
required.
Is the repair complete?
1. Disconnect the harness from the EBCM.
2. Connect a DVM between ground and one terminal of
the wheel speed connector.
3. Turn the ignition to ON.
4. Repeat the above test for the other terminal of the
wheel speed connector.
Is the voltage for either of these terminals within the
specified value?
Repair the short to voltage in the affected circuit.
Is the repair complete?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Measure the resistance to ground from terminal at
the harness EBCM connector.
3. Measure the resistance to ground from terminal 36
at the harness EBCM connector.
Is the resistance at either circuit less than the speci-
fied value?
Repair the short to ground in the affected circuit.
Is the repair complete?
1. Measure the resistance between terminal 10 at the
harness EBCM connector and the harness wheel
speed sensor connector.
2. Measure the resistance between terminal 36 at the
harness EBCM connector and the harness wheel
speed sensor connector.
Is the resistance on either circuit within the specified
value?
Repair the open or the high resistance in the affected
circuit, as required. Be sure to check terminals 2 and 8
of connector C113 and junction J101 and J102.
Is the repair complete?
Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?
Value(s) Yes No
Page 1023 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-40 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 07
LEFT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONTINUITY FAULT
KAA4F140
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
4. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
8. This step tests for an open or high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Page 1024 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-41
SSANGYONG MY2002
Step
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
DTC 07 - Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Continuity Fault
Action
Go to Step 3
Go to Step 4
System OK
Go to Step 5
System OK
Go to Step 7
System OK
Go to Step 9
System OK
System OKGo to Step 2
Go to Step 3
-
Go to Step 6
-
Go to Step 8
-
Go to Step 10
-
- -
1280 - 1920 Ω
-
>1v
-
∞
-
>5 Ω
-
-
Examine the wheel speed sensor.
Are there any signs of physical damage?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the left rear wheel speed sensor
connector.
3. Use a digital voltmeter (DVM) to measure resis-
tance between the sensor terminals.
Is the resistance within the specified value at ap-
proximately 25-C (77-F)?
Replace the wheel speed sensor.
Is the repair complete?
1. Disconnect the harness from the EBCM.
2. Connect a DVM between ground and one terminal
of the wheel speed connector.
3. Turn the ignition to ON.
4. Repeat the above test for the other terminal of the
wheel speed connector.
Is the voltage for either of these terminals within the
specified value?
Repair the short to voltage in the affected circuit.
Is the repair complete?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Measure the resistance to ground from terminal 10
at the harness EBCM connector.
3. Measure the resistance to ground from terminal 36
at the harness EBCM connector.
Is the resistance at either circuit less than the speci-
fied value?
Repair the short to ground in the affected circuit.
Is the repair complete?
1. Measure the resistance between terminal 10 at the
harness EBCM connector and the harness wheel
speed sensor connector.
2. Measure the resistance between terminal 36 at the
harness EBCM connector and the harness wheel
speed sensor connector.
Is the resistance on either circuit within the specified
value?
Repair the open or high resistance in the affected
circuit as required. Be sure to check terminals 2 and
8 of connector C113 and junction J101 and J102.
Is the repair complete?
Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?
Value(s) Yes No
Page 1025 of 2053

SSANGYONG MY2002
4F-42 ABS AND TCS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 04
RIGHT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR FAULT
KAA4F150
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it
moves past the sensor. Each tooth-gap-tooth series
on the wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake
control module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these
pulses to determine the wheel speed. The voltage gen-
erated depends on the air gap between the sensor and
the toothed wheel, and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or
a contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
The wheel speed sensor is defective.
There is a problem in the wiring.
There is a problem with a connector.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is
ON.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
8. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
10. This step tests for an open or high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed
and retained. This will help to prevent false signals due
to the pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of
the wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the
wiring and the connectors carefully and completely may
result in misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with
the reappearance of the malfunction.
Use the scan tool to monitor wheel speeds during a
road test. Watch the wheel speeds being displayed on
the scan tool to see if any of the readings are unusual,
such as one sensor varying in speed from the other
three, a signal going intermittently high or low, etc. If
this does not identify the intermittent, wet the speed
sensor harness on the underside of the vehicle and
perform a road test, monitoring wheel speeds with the
scan tool.
Step
1
DTC 04 - Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Fault
Action Yes
Go to Step 3No
Go to Step 2 Value(s)
-
Examine the wheel speed sensor.
Are there any signs of physical damage?
Page 1026 of 2053

ABS AND TCS 4F-43
SSANGYONG MY2002
Step
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
DTC 04 - Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Fault (Cont’d)
Action
Go to Step 4
System OK
Go to Step 6
System OK
Go to Step 7
System OK
Go to Step 9
System OK
Go to Step 11
System OK
System OKGo to Step 3
-
Go to Step 5
-
Go to Step 8
-
Go to Step 10
-
Go to Step 12
-
- 1280 - 1920 Ω
-
≈ 70 mv
-
>1v
-
∞
-
>5 Ω
-
-
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the left rear wheel speed sensor
connector.
3. Use a digital voltmeter (DVM) to measure resis-
tance between the sensor terminals.
Is the resistance within the specified value at approxi-
mately 25-C (77-F)?
Replace the wheel speed sensor.
Is the repair complete?
1. Switch the DVM to the ac millivolt range.
2. Measure the voltage output between the wheel
speed sensor terminals while rotating the wheel
about 1 revolution per second.
Is the output within the specified value?
Replace the speed sensor or the toothed wheel, as
required.
Is the repair complete?
1. Disconnect the harness from the EBCM.
2. Connect a DVM between ground and one terminal of
the wheel speed connector.
3. Turn the ignition to ON.
4. Repeat the above test for the other terminal of the
wheel speed connector.
Is the voltage for either of these terminals within the
specified value?
Repair the short to voltage in the affected circuit.
Is the repair complete?
1. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
2. Measure the resistance to ground from terminal 14
at the harness EBCM connector.
3. Measure the resistance to ground from terminal 15
at the harness EBCM connector.
Is the resistance at either circuit less than the speci-
fied value?
Repair the short to ground in the affected circuit.
Is the repair complete?
1. Measure the resistance between terminal 14 at the
harness EBCM connector and the harness wheel
speed sensor connector.
2. Measure the resistance between terminal 15 at the
harness EBCM connector and the harness wheel
speed sensor connector.
Is the resistance on either circuit within the specified
value?
Repair the open or the high resistance in the affected
circuit, as required. Be sure to check terminals 7 and 1
of connector C113 and junction J103 and J104.
Is the repair complete?
Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?
Value(s) Yes No