ignition switch SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1997, Model line: KORANDO, Model: SSANGYONG KORANDO 1997Pages: 2053, PDF Size: 88.33 MB
Page 485 of 2053
M161 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F2 -- 67
D AEW OO M Y_2000
3. Turn the ignition switch to “OFF” position.
4. Disconnect the ECT sensor connector.
5. Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
6. Measure the resistance between the ECT sensor terminal pin No. 1 and No. 4.
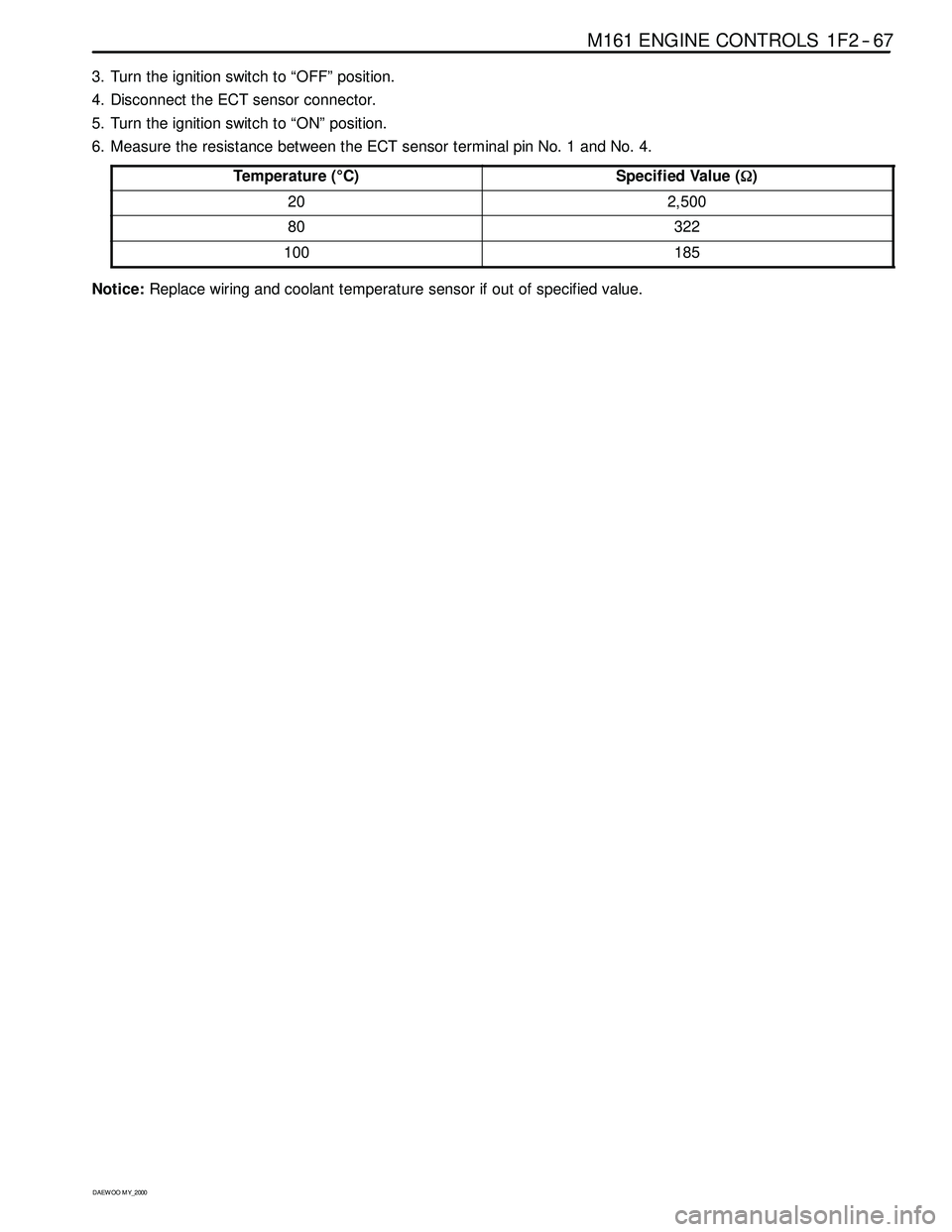
Temperature (°C)
Specified Value (Ω)
202,500
80322
100185
Notice:Replace wiring and coolant temperature sensor if out of specified value.
Page 488 of 2053

1F2 -- 70 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Acceleration Pedal Position Sensor 1 Inspection
1. Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
2. Measure the signal voltage between the ECM pin No. 47 and No. 31 while operating the accelerator pedal as follow-
ing conditions.
DNot depress the pedal (closed throttle position)
DFully depress the pedal (full throttle with kick down)
Condition of Throttle Valve
Specified Value (V)
Closed Throttle Valve0.3 ~ 0.7
Fully Depressed Throttle Valve4.3 ~ 4.8
Notice:If measured value is not within the specified value, check the pedal valve sensor and the supply voltage to
APP 1 sensor.
Acceleration Pedal Position Sensor 2 Inspection
1. Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
2. Measure the signal voltage between the ECM pin No. 48 and No. 50 while operating the accelerator pedal as follow-
ing conditions.
DNot depress the pedal (closed throttle position)
DFully depress the pedal (full throttle with kick down)
Condition of Throttle Valve
Specified Value (V)
Closed Throttle Valve0.1 ~ 0.4
Fully Depressed Throttle Valve2.1 ~ 2.5
Notice:If measured value is not within the specified value, check the pedal valve sensor and the supply voltage to
APP sensor 2.
Page 494 of 2053

1F2 -- 76 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
STOP LAMP SWITCH
KAB1F320
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
135Stop lamp switch failure
When malfunction of stop
lamp switch – implausible
condition of stop lamp signal
input
DMonitoring the actual operational
status and vehicle speed signal
through scan tool
DInspection the Engine Control Module
(ECM) pin 49 about short circuit or
open with bad contact
DInspection the contact condition of
stop lamp switch
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
The stop lamp switch is normally opened. When the ignition switch ON and brake ON, the battery voltage is supplied to
the ECM. A scan tool should display ON when brake pedal is depressed and should read OFF with brake pedal rele-
ased.
Page 502 of 2053

1F2 -- 84 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Oxygen Sensor Signal Voltage Inspection
1. Maintain the engine speed is at idle while the coolant temperature is over 80°C.
2. Measure the oxygen sensor signal voltage between the ECM terminal No. 16 and No. 17.
Specified Value
-- 0.2 ~ 1.0 v
Notice:If the measured value is not within the specified value, the possible cause may be in cable, oxygen sensor or
ECM
Oxygen Sensor Heating Voltage Inspection
1. Maintain the engine speed is at idle while the coolant temperature is over 80°C.
2. Measure the oxygen sensor signal voltage between the ECM terminal No. 11 and No. 9.
Specified Value
11 ~ 14 v
Notice:If the measured value is not within the specified value, the possible cause may be in cable, oxygen sensor or
ECM
Oxygen sensor Heating Current Consumption Inspection
1. Turn the ignition switch to “ON” position.
2. Measure the oxygen sensor heating current consumption between the ECM terminal No. 9 and No. 5.
Specified Value
0.2~2.0A
Notice:If the measured value is not within the specified value, the possible cause may be in cable, oxygen sensor or
ECM
Page 504 of 2053

1F2 -- 86 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE
YAA1F830
The Engine Control Module (ECM), located inside the right side kick panel, is the control center of the fuel injection
system. It constantly looks at the information from various sensors and controls the systems that affect the vehicle’s
performance. Engine rpm and air mass are used to measure the air intake quantity resulting in fuel injection metering.
The ECM also performs the diagnostic functions of the system. It can recognize operational problems, store failure
code(s) which identify the problem areas to aid the technician in making repairs.
There are no serviceable parts in the ECM. The calibrations are stored in the ECM in the Programmable Read Only
Memory (PROM).
The ECM supplies either 5 or 12 volts to power the sensors or switches. This is done through resistance in the ECM
which are so high in value that a test light will not come ON when connected to the circuit. In some cases, even an
ordinary shop voltmeter will not give and accurate reading because its resistance is too low. You must use a digital
voltmeter with a 10 Mohm input impedance to get accurate voltage readings. The ECM controls output circuits such as
the ignition coils, the fuel injectors, the fuel pump relay, the camshaft actuator, the canister purge valve, etc., by con-
trolling the ground circuit.
Page 808 of 2053
OM600 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F3 -- 5
D AEW OO M Y_2000
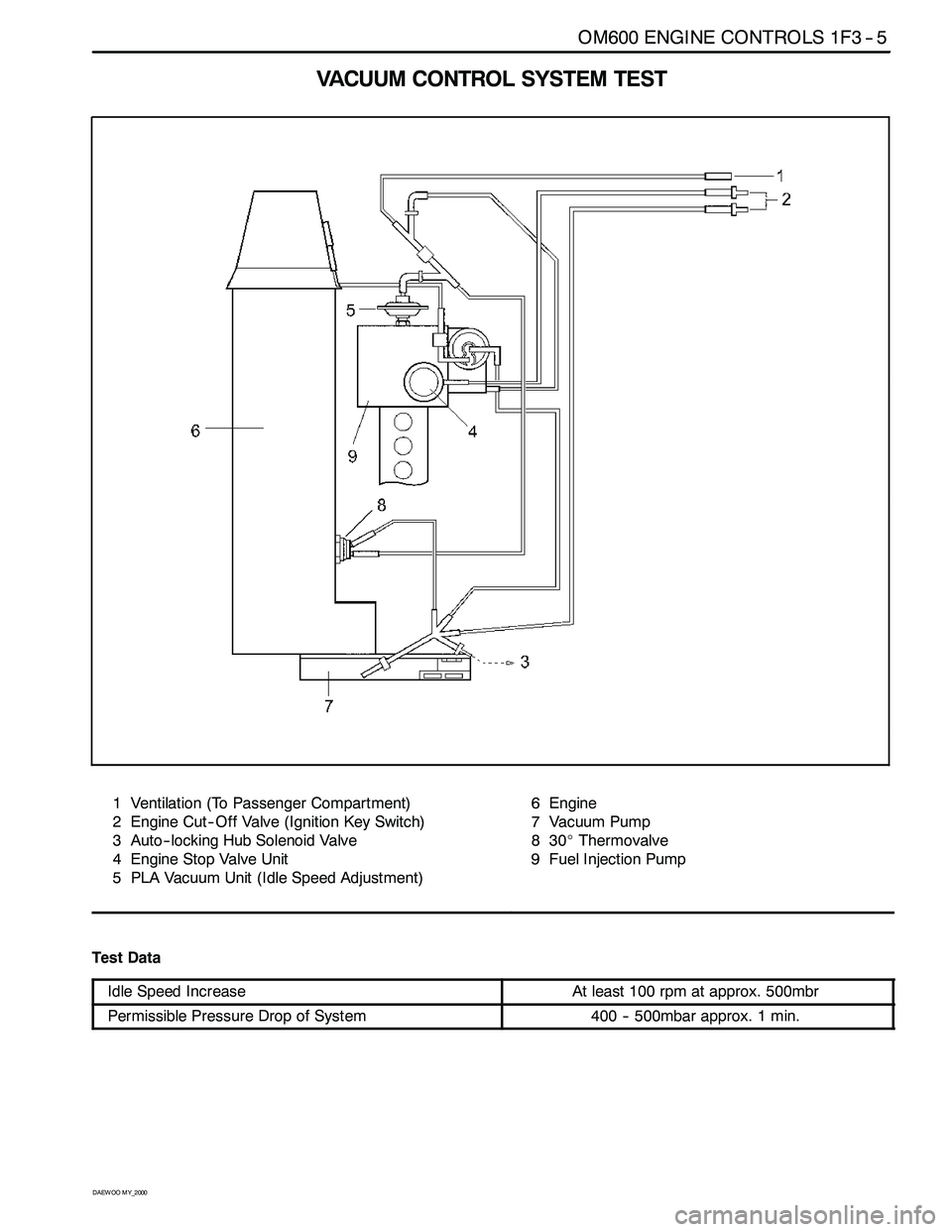
VACUUM CONTROLSYSTEM TEST
1 Ventilation (To Passenger Compartment)
2 Engine Cut -- Off Valve (Ignition Key Switch)
3 Auto-- locking Hub Solenoid Valve
4 Engine Stop Valve Unit
5 PLA Vacuum Unit (Idle Speed Adjustment)6Engine
7 Vacuum Pump
830_Thermovalve
9 Fuel Injection Pump
Test Data
Idle Speed IncreaseAt least 100 rpm at approx. 500mbr
Permissible Pressure Drop of System400 -- 500mbar approx. 1 min.
Page 921 of 2053

SECTION 4A
HYDRAULIC BRAKES
CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when
a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this
cable will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK
unless otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Description and Operation...................................4A-2
General Description.............................................4A-2
Diagnostic Information and Procedures..............4A-3
Brake System Testing ..........................................4A-3
Brake Hose Inspection.........................................4A-3
Brake Warning Lamp Circuit Description..............4A-4
Brake Warning Lamp Diagnosis...........................4A-5
LCRV (Load Conscious Reducing Valve)..............4A-8
Repair Instructions..............................................4A-10On-Vehicle Service...............................................4A-10
Manual Bleeding The Brakes.............................4A-10
Front Brake Hose...............................................4A-13
Rear Brake Hose...............................................4A-13
Stoplamp Switch................................................4A-14
Brake Pedal.......................................................4A-14
Specifications.....................................................4A-15
General Specification .........................................4A-15
Fastener Tightening Specifications.....................4A-16
Page 924 of 2053

SSAMGYONG MY2002
4A-4 HYDRAULIC BRAKES
KAA4A010
BRAKE WARNING LAMP CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Diagnostic Aids
The BRAKE lamp glows brightly when the ignition is
ON and either the parking brake lever switch or the
brake fluid level switch is closed.
If neither switch is closed, the BRAKE lamp receives
a ground through the generator, and it glows dimly
when the ignition is ON and the engine is off. When
the engine starts, the generator creates voltage. With
voltage on both sides of the lamp, the lamp turns off.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic
table.
1. This step begins the test sequence for a BRAKE
warning lamp that stays on when the engine is run-
ning.
2. This step begins the test sequence for a BRAKE
warning lamp that never turns on.
Page 926 of 2053
SSAMGYONG MY2002
4A-6 HYDRAULIC BRAKES
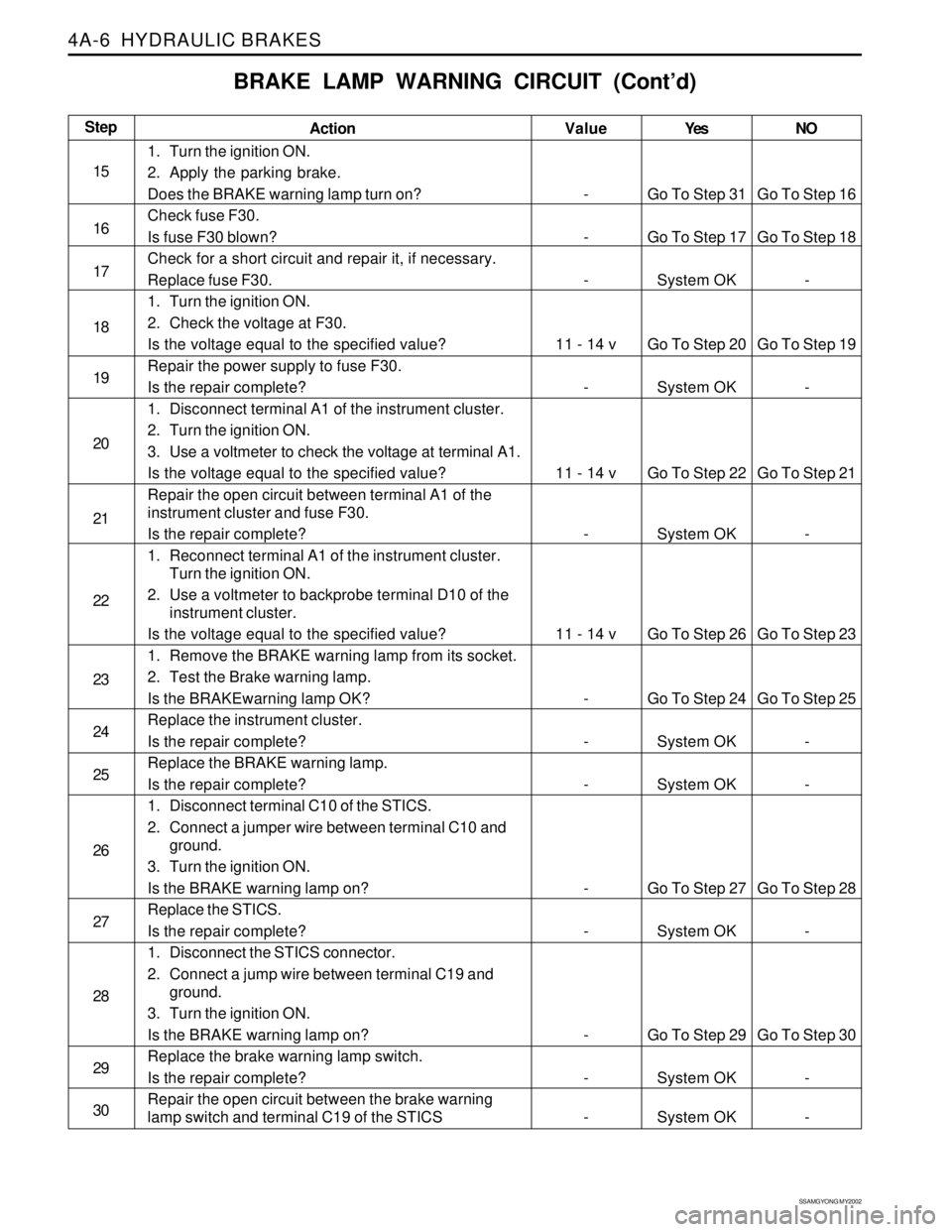
Action
1. Turn the ignition ON.
2. Apply the parking brake.
Does the BRAKE warning lamp turn on?
Check fuse F30.
Is fuse F30 blown?
Check for a short circuit and repair it, if necessary.
Replace fuse F30.
1. Turn the ignition ON.
2. Check the voltage at F30.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?
Repair the power supply to fuse F30.
Is the repair complete?
1. Disconnect terminal A1 of the instrument cluster.
2. Turn the ignition ON.
3. Use a voltmeter to check the voltage at terminal A1.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?
Repair the open circuit between terminal A1 of the
instrument cluster and fuse F30.
Is the repair complete?
1. Reconnect terminal A1 of the instrument cluster.
Turn the ignition ON.
2. Use a voltmeter to backprobe terminal D10 of the
instrument cluster.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?
1. Remove the BRAKE warning lamp from its socket.
2. Test the Brake warning lamp.
Is the BRAKEwarning lamp OK?
Replace the instrument cluster.
Is the repair complete?
Replace the BRAKE warning lamp.
Is the repair complete?
1. Disconnect terminal C10 of the STICS.
2. Connect a jumper wire between terminal C10 and
ground.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the BRAKE warning lamp on?
Replace the STICS.
Is the repair complete?
1. Disconnect the STICS connector.
2. Connect a jump wire between terminal C19 and
ground.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the BRAKE warning lamp on?
Replace the brake warning lamp switch.
Is the repair complete?
Repair the open circuit between the brake warning
lamp switch and terminal C19 of the STICS
BRAKE LAMP WARNING CIRCUIT (Cont’d)
Yes
Go To Step 31
Go To Step 17
System OK
Go To Step 20
System OK
Go To Step 22
System OK
Go To Step 26
Go To Step 24
System OK
System OK
Go To Step 27
System OK
Go To Step 29
System OK
System OKNO
Go To Step 16
Go To Step 18
-
Go To Step 19
-
Go To Step 21
-
Go To Step 23
Go To Step 25
-
-
Go To Step 28
-
Go To Step 30
-
-Step
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30Value
-
-
-
11 - 14 v
-
11 - 14 v
-
11 - 14 v
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Page 989 of 2053
ABS AND TCS 4F-5
SSANGYONG MY2002
EBD (ELECTRONIC BRAKE
FORCE DISTRIBUTION) SYSTEM
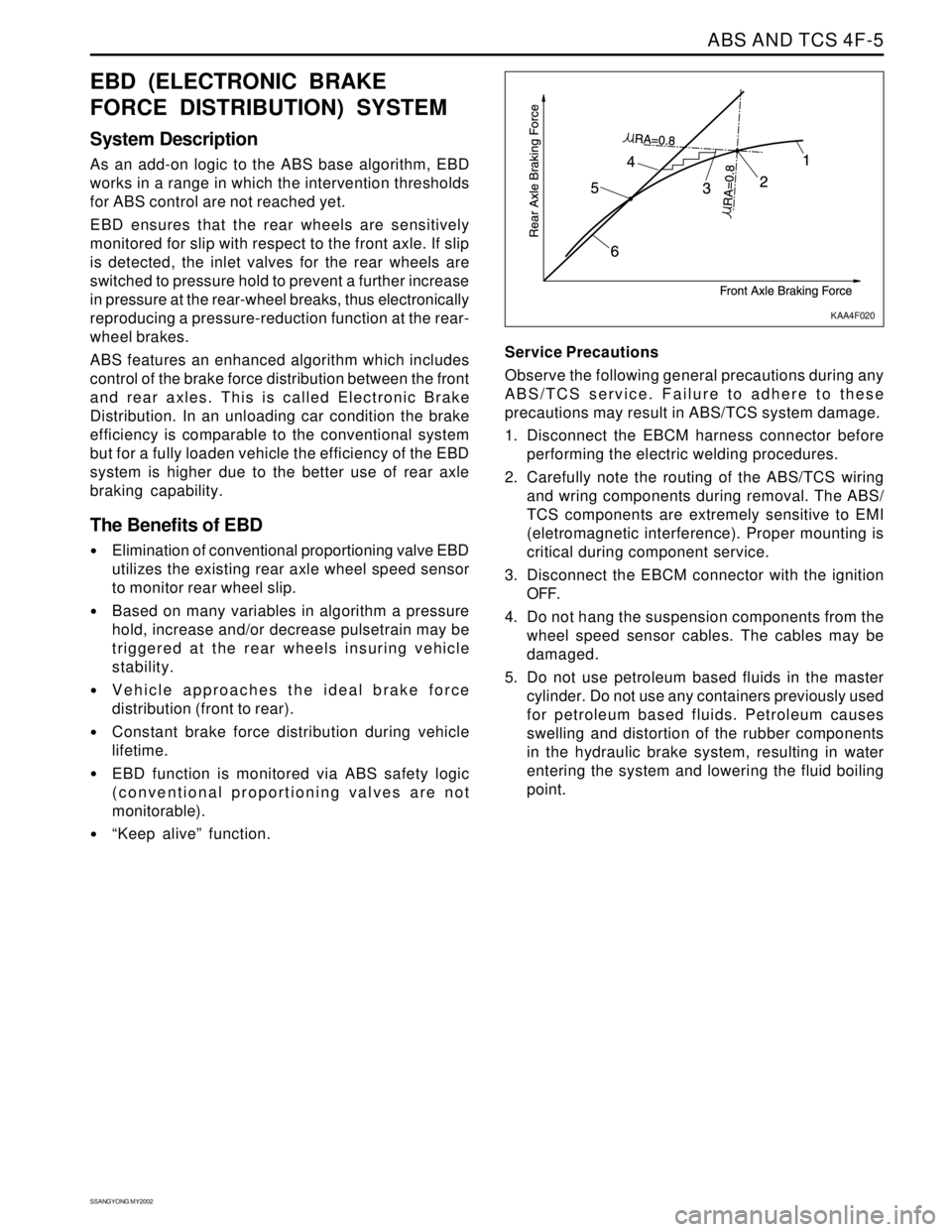
System Description
As an add-on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD
works in a range in which the intervention thresholds
for ABS control are not reached yet.
EBD ensures that the rear wheels are sensitively
monitored for slip with respect to the front axle. If slip
is detected, the inlet valves for the rear wheels are
switched to pressure hold to prevent a further increase
in pressure at the rear-wheel breaks, thus electronically
reproducing a pressure-reduction function at the rear-
wheel brakes.
ABS features an enhanced algorithm which includes
control of the brake force distribution between the front
and rear axles. This is called Electronic Brake
Distribution. In an unloading car condition the brake
efficiency is comparable to the conventional system
but for a fully loaden vehicle the efficiency of the EBD
system is higher due to the better use of rear axle
braking capability.
The Benefits of EBD
Elimination of conventional proportioning valve EBD
utilizes the existing rear axle wheel speed sensor
to monitor rear wheel slip.
Based on many variables in algorithm a pressure
hold, increase and/or decrease pulsetrain may be
triggered at the rear wheels insuring vehicle
stability.
Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force
distribution (front to rear).
Constant brake force distribution during vehicle
lifetime.
EBD function is monitored via ABS safety logic
(conventional proportioning valves are not
monitorable).
“Keep alive” function.Service Precautions
Observe the following general precautions during any
ABS/TCS service. Failure to adhere to these
precautions may result in ABS/TCS system damage.
1. Disconnect the EBCM harness connector before
performing the electric welding procedures.
2. Carefully note the routing of the ABS/TCS wiring
and wring components during removal. The ABS/
TCS components are extremely sensitive to EMI
(eletromagnetic interference). Proper mounting is
critical during component service.
3. Disconnect the EBCM connector with the ignition
OFF.
4. Do not hang the suspension components from the
wheel speed sensor cables. The cables may be
damaged.
5. Do not use petroleum based fluids in the master
cylinder. Do not use any containers previously used
for petroleum based fluids. Petroleum causes
swelling and distortion of the rubber components
in the hydraulic brake system, resulting in water
entering the system and lowering the fluid boiling
point.
KAA4F020