ECU SSANGYONG MUSSO 1998 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SSANGYONG, Model Year: 1998, Model line: MUSSO, Model: SSANGYONG MUSSO 1998Pages: 1463, PDF Size: 19.88 MB
Page 967 of 1463
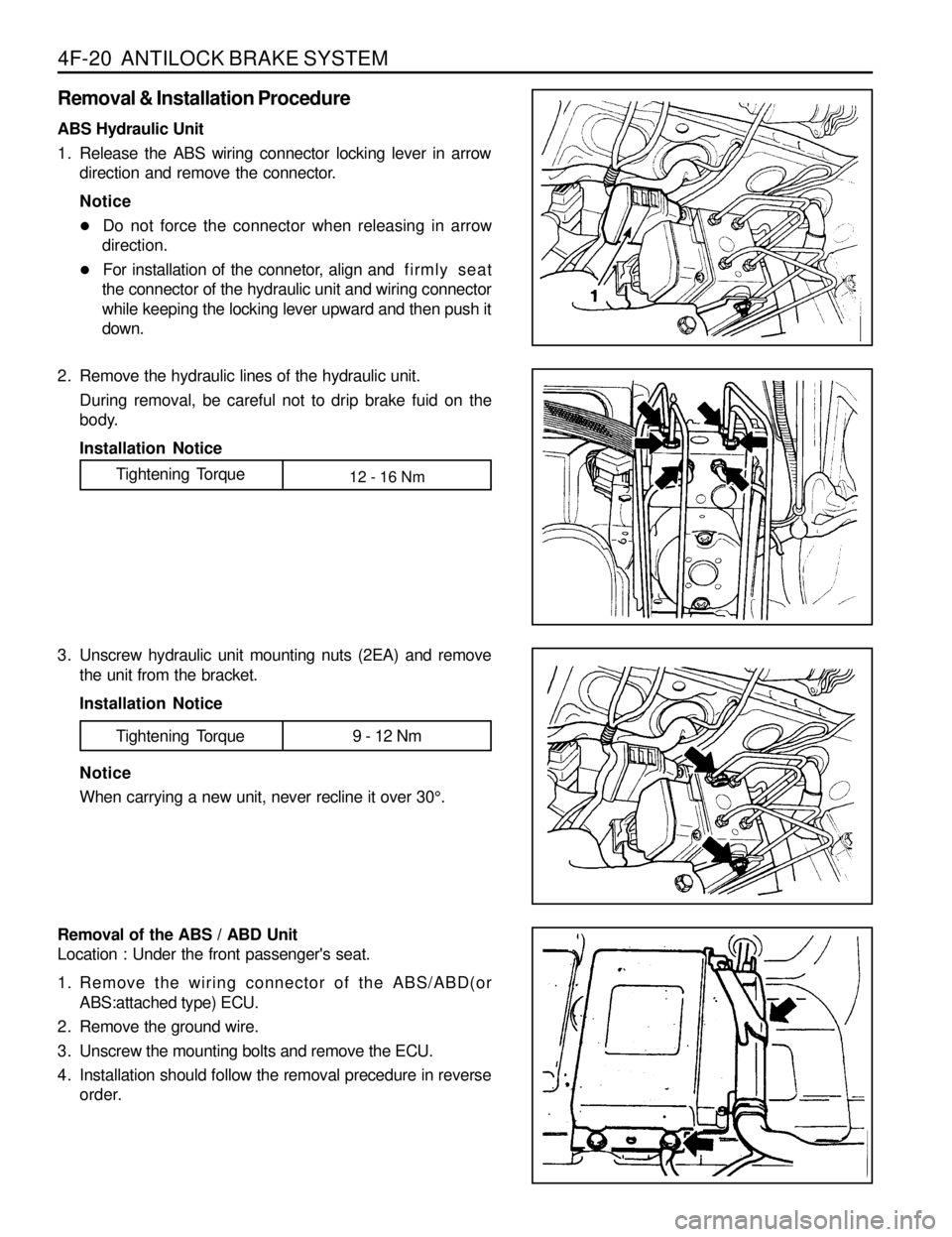
4F-20 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
Removal & Installation Procedure
ABS Hydraulic Unit
1. Release the ABS wiring connector locking lever in arrow
direction and remove the connector.
Notice
lDo not force the connector when releasing in arrow
direction.
lFor installation of the connetor, align and firmly seat
the connector of the hydraulic unit and wiring connector
while keeping the locking lever upward and then push it
down.
2. Remove the hydraulic lines of the hydraulic unit.
During removal, be careful not to drip brake fuid on the
body.
Installation Notice
3. Unscrew hydraulic unit mounting nuts (2EA) and remove
the unit from the bracket.
Installation Notice
Tightening Torque 9 - 12 Nm
Removal of the ABS / ABD Unit
Location : Under the front passenger's seat.
1. Remove the wiring connector of the ABS/ABD(or
ABS:attached type) ECU.
2. Remove the ground wire.
3. Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove the ECU.
4. Installation should follow the removal precedure in reverse
order.
Tightening Torque12 - 16 Nm
Notice
When carrying a new unit, never recline it over 30°.
Page 1001 of 1463

5A-24 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Transmission Control Unit(TCU)
The TCU is an in-vehicle micro-processor based transmission management system. It is usually mounted in the
vehicle cabin, under the instrument panel, under the seat, behind the side kick panels or under the floor in the
footwell on the passenger side. Different control units are supplied for different vehicle applications.
The TCU contains:
lProcessing logic circuits which include a central microcontroller and a back-up memory system.
lInput circuits.
lOutput circuits which control external devices such as the variable pressure solenoid (VPS), on/off solenoid
drivers, a diagnostics output and the driving mode indicator light.
The various items which make up the TCU are discussed below.
Processing Logic
Shift schedule and calibration information is stored in an erasable programmable read only memory (EEPROM).
Throttle input calibration constants and the diagnostics information are stored in electrically erasable programmable
read only memory (EEPROM) that retains the memory even when power to the TCU is disconnected.
In operation the software continuously monitors the input values and uses these, via the shift schedule, to determine
the required gear state, At the same time it monitors, via the solenoid outputs, the current gear state. Whenever the
input conditions change such that the required gear state is different to the current gear state, the TCU initiates a
gear shift to bring the two states back into line.
Once the TCU has determined the type of gear shift required the software accesses the shift logic, estimates the
engine torque output, adjusts the variable pressure solenoid ramp pressure then executes the shift.
The TCU continuously monitors every input and output circuit for short or open circuits and operating range. When
a failure or abnormal operation is detected the TCU records the condition code in the diagnostics memory and
implements a limp mode, The actual limp mode used depends upon the failure detected with the object to maintain
maximum driveability without damaging the transmission. In general input failures are handled by providing a default
value. Output failures, which are capable of damaging the transmission, result in full limp mode giving only third or
fourth gear and reverse. For further details of limp modes and memory retention refer to the Diagnostic Section.
The TCU is designed to operate at ambient temperatures between -40 and 85°C . It is also protected against
electrical noise and voltage spikes, however all the usual precautions should be observed, for example when arc
welding or jump starting.
TCU Inputs
To function correctly, the TCU requires engine speed, road speed, transmission sump temperature, throttle position
and gear position inputs to determine the variable pressure solenoid current ramp and on/off solenoid states. This
ensures the correct gear selection and shift feel for all driving conditions.
The inputs required by the TCU are as follows:
lEngine Speed
The engine speed signal is derived from the tachometer signal line, a dedicated sensor or a Controlled Area
Network (CAN).
lRoad Speed
4WD (Diesel) - The shaft speed signal is derived from the speedo sensor located on the transfer case. This signal
is transmitted directly to the TCU.
4WD (Gasoline) - The speedo sensor sends the shaft speed signal to the engine control module (ECM). The
information is then transferred to the TCU via the CAN.
lTransmission Sump Temperature
The transmission sump temperature sensor is a thermistor located in the solenoid wiring loom within the transmission.
This sensor is a typical NTC resistor with low temperatures producing a high resistance and high temperatures
Page 1003 of 1463

5A-26 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
Inhibitor
Switch Throttle Position Sensor
The throttle position sensor(TPS) is a resistance potentiometer
mounted on the throttle body of the engine.
It transmits a signal to the TCU proportional to the throttle plate
opening.
The potentiometer is connected to the TCU by three wires:
5 volts positive supply, earth and variable wiper voltage.
Throttle voltage adjustments are as follows:
lClosed throttle voltage is 0.2V to 1.0V.
lWide open throttle voltage is 3V -4.7V.
These measurements are taken between pins 29 and 27 of
the TCU.
Maintaining good shift feel through the transmission life span
is dependant on having an accurate measure of
the engine throttle position. To achieve this the TCU
continuously monitors the maximum and minimum throttle
potentiometer voltages and, if a change occurs, stores the new
voltage values.
However these limits will be lost and will require relearning
should a new TCU be installed, or the throttle calibration data
is cleared by the execution of a particular sequence, This last
instance depends on the installation, and reference should be
made to the Diagnostics Section of this manual. The relearning
will happen automaticallyNotice
Above figure of T.P.S. is for the diesel engine
which is installed on the injection pump.
Gear Position Sensor
The gear position sensor is incorporated in the inhibitor switch
mounted on the side of the transmission case.
(Refer to figure 3.5.) The gear position sensor is a multi-function
switch providing three functions:
lInhibit starting of the vehicle when the shift lever is in a
position other than Park or Neutral
lIlluminate the reversing lamps when Reverse is
selected indicate to the TCU which lever position has
been selected by way of a varying resistance (Refer to
table 3.3.)
Figure 3.5 - Inhibitor Switch
Page 1063 of 1463
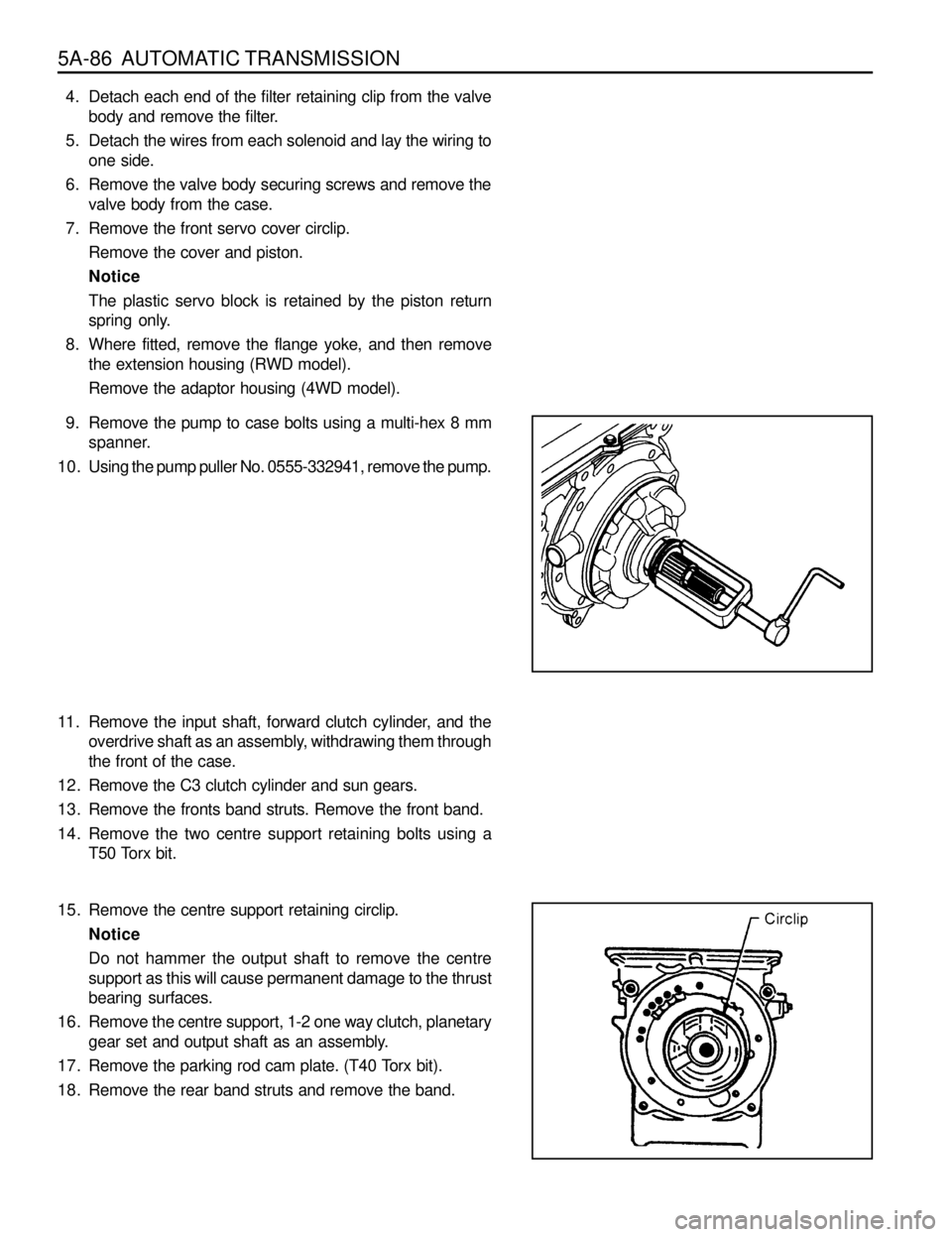
5A-86 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
9. Remove the pump to case bolts using a multi-hex 8 mm
spanner.
10. Using the pump puller No. 0555-332941, remove the pump.
11. Remove the input shaft, forward clutch cylinder, and the
overdrive shaft as an assembly, withdrawing them through
the front of the case.
12. Remove the C3 clutch cylinder and sun gears.
13. Remove the fronts band struts. Remove the front band.
14. Remove the two centre support retaining bolts using a
T50 Torx bit.
15. Remove the centre support retaining circlip.
Notice
Do not hammer the output shaft to remove the centre
support as this will cause permanent damage to the thrust
bearing surfaces.
16. Remove the centre support, 1-2 one way clutch, planetary
gear set and output shaft as an assembly.
17. Remove the parking rod cam plate. (T40 Torx bit).
18. Remove the rear band struts and remove the band.4. Detach each end of the filter retaining clip from the valve
body and remove the filter.
5. Detach the wires from each solenoid and lay the wiring to
one side.
6. Remove the valve body securing screws and remove the
valve body from the case.
7. Remove the front servo cover circlip.
Remove the cover and piston.
Notice
The plastic servo block is retained by the piston return
spring only.
8. Where fitted, remove the flange yoke, and then remove
the extension housing (RWD model).
Remove the adaptor housing (4WD model).
Page 1071 of 1463
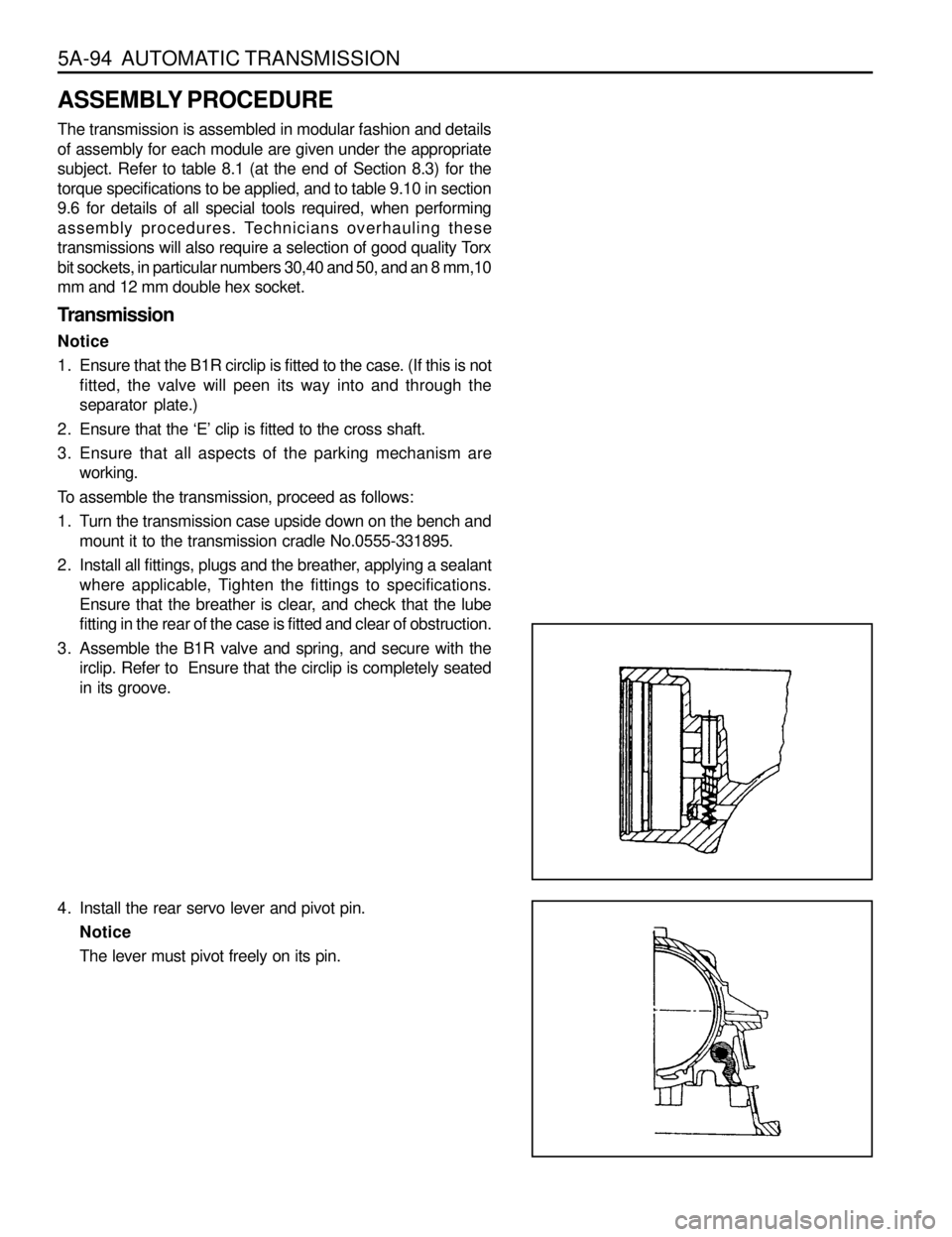
5A-94 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
ASSEMBLY PROCEDURE
The transmission is assembled in modular fashion and details
of assembly for each module are given under the appropriate
subject. Refer to table 8.1 (at the end of Section 8.3) for the
torque specifications to be applied, and to table 9.10 in section
9.6 for details of all special tools required, when performing
assembly procedures. Technicians overhauling these
transmissions will also require a selection of good quality Torx
bit sockets, in particular numbers 30,40 and 50, and an 8 mm,10
mm and 12 mm double hex socket.
Transmission
Notice
1. Ensure that the B1R circlip is fitted to the case. (If this is not
fitted, the valve will peen its way into and through the
separator plate.)
2. Ensure that the ‘E’ clip is fitted to the cross shaft.
3. Ensure that all aspects of the parking mechanism are
working.
To assemble the transmission, proceed as follows:
1. Turn the transmission case upside down on the bench and
mount it to the transmission cradle No.0555-331895.
2. Install all fittings, plugs and the breather, applying a sealant
where applicable, Tighten the fittings to specifications.
Ensure that the breather is clear, and check that the lube
fitting in the rear of the case is fitted and clear of obstruction.
3. Assemble the B1R valve and spring, and secure with the
irclip. Refer to Ensure that the circlip is completely seated
in its groove.
4. Install the rear servo lever and pivot pin.
Notice
The lever must pivot freely on its pin.
Page 1072 of 1463
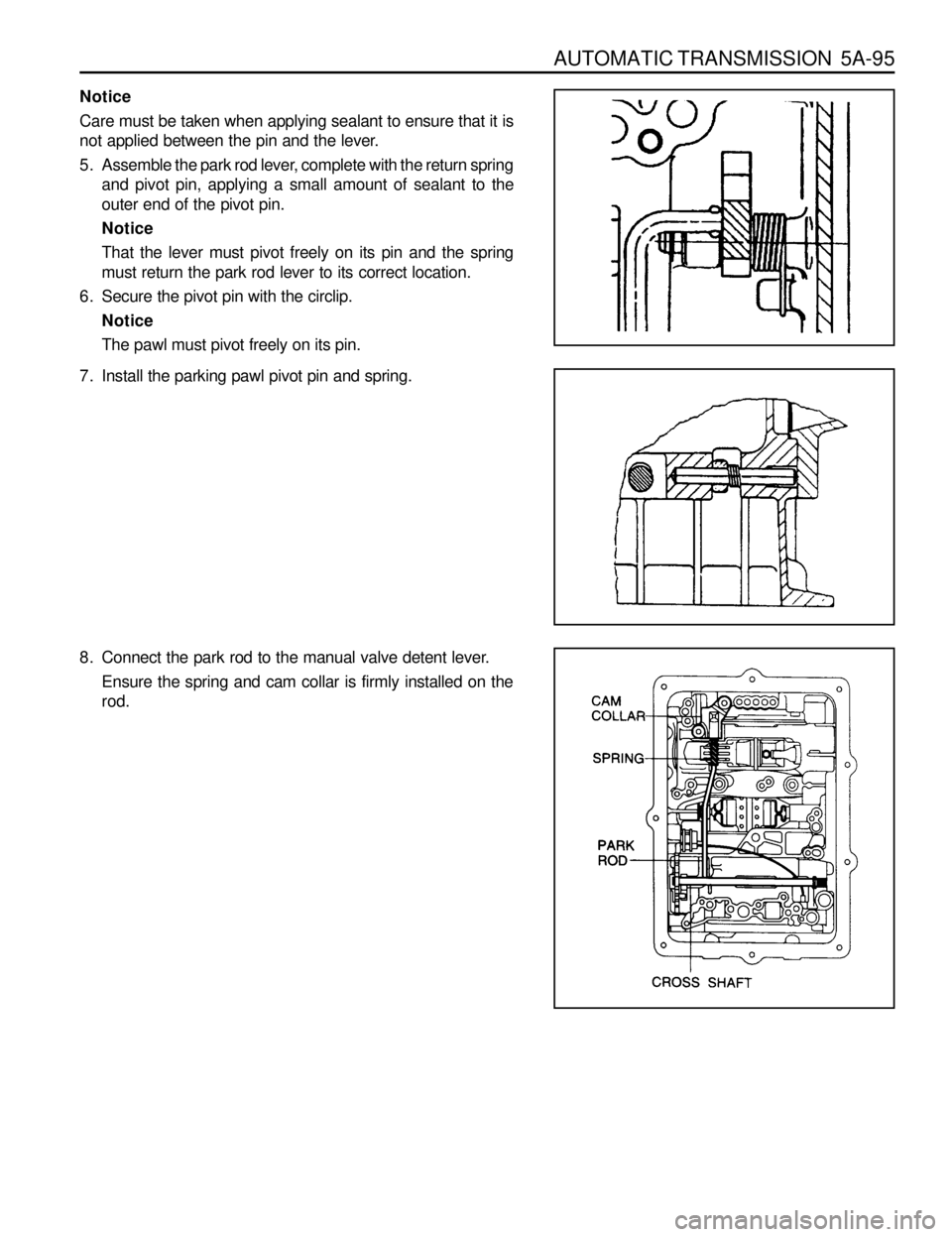
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-95
Notice
Care must be taken when applying sealant to ensure that it is
not applied between the pin and the lever.
5. Assemble the park rod lever, complete with the return spring
and pivot pin, applying a small amount of sealant to the
outer end of the pivot pin.
Notice
That the lever must pivot freely on its pin and the spring
must return the park rod lever to its correct location.
6. Secure the pivot pin with the circlip.
Notice
The pawl must pivot freely on its pin.
7. Install the parking pawl pivot pin and spring.
8. Connect the park rod to the manual valve detent lever.
Ensure the spring and cam collar is firmly installed on the
rod.
Page 1076 of 1463

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-99
Output Shaft and Gear Assembly
To assemble the output shaft and gear assembly (refer to
(figure 8.19), proceed as follows:
1. Check that the output shaft bush is not won or damaged.
Replace if necessary.
2. Check for damage to parking pawl teeth on the ring gear.
Replace if necessary.
3. Check that the sealing ring grooves have not been
damaged.
4. Lubricate the sealing rings with automatic transmission fluid.
5. Assemble the sealing rings to the output shaft with the scat
cut uppermost.
6. If previously dismantled, assemble the ring gear to the output
shaft and secure with circlip. Ensure that the circlip is firmly
seated in its groove.
7. Fit the thrust bearing assembly No. 10 onto the output shaft
using petroleum jelly.
8. Carefully install the output shaft assembly in the case to
prevent damage to the sealing rings.
Rear Servo Assembly
To assemble the rear servo assembly (refer to figure 8.18),
proceed as follows.
1. Check the servo piston ‘O’ rings and gasket for any damage.
2. Lubricate the servo piston ‘O’ rings with automatic
transmission fluid, and fit the ‘O’ rings to the piston grooves.
3. Assemble the piston to the cover, ensuring that ‘O’ ring
compression is adequate but not excessive.
4. Align the spring on the piston spigot, then position the rear
servo rod into the spigot.
Notice
Do not use petroleum jelly on the gasket.
5. Assemble the gasket to the cover and fit the assembly to
the case.
6. Apply Loctite 567 sealant to the bolts. Install the bolts and
tighten to specification.
Page 1083 of 1463
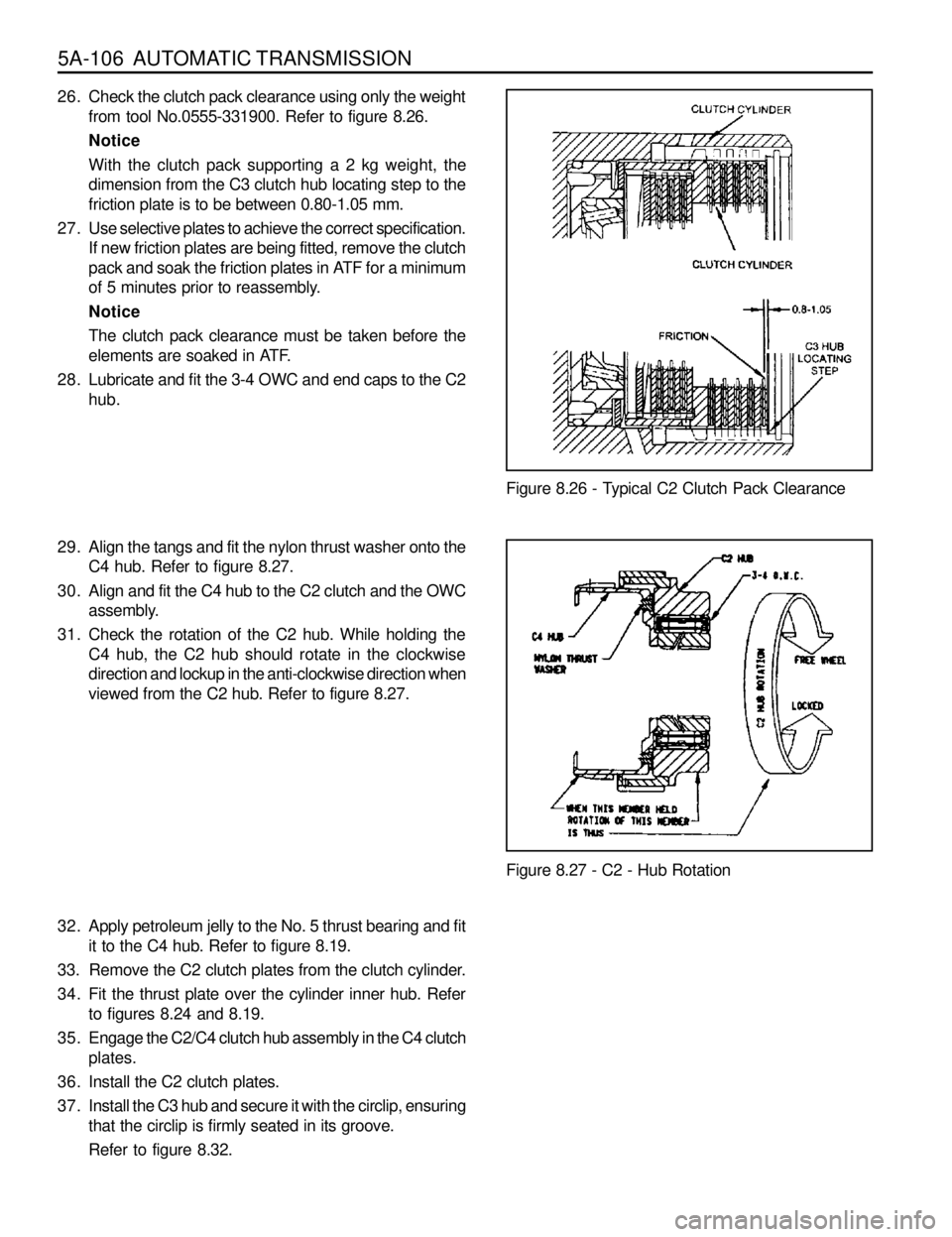
5A-106 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
29. Align the tangs and fit the nylon thrust washer onto the
C4 hub. Refer to figure 8.27.
30. Align and fit the C4 hub to the C2 clutch and the OWC
assembly.
31. Check the rotation of the C2 hub. While holding the
C4 hub, the C2 hub should rotate in the clockwise
direction and lockup in the anti-clockwise direction when
viewed from the C2 hub. Refer to figure 8.27.
Figure 8.27 - C2 - Hub Rotation
32. Apply petroleum jelly to the No. 5 thrust bearing and fit
it to the C4 hub. Refer to figure 8.19.
33. Remove the C2 clutch plates from the clutch cylinder.
34. Fit the thrust plate over the cylinder inner hub. Refer
to figures 8.24 and 8.19.
35. Engage the C2/C4 clutch hub assembly in the C4 clutch
plates.
36. Install the C2 clutch plates.
37. Install the C3 hub and secure it with the circlip, ensuring
that the circlip is firmly seated in its groove.
Refer to figure 8.32.Figure 8.26 - Typical C2 Clutch Pack Clearance 26. Check the clutch pack clearance using only the weight
from tool No.0555-331900. Refer to figure 8.26.
Notice
With the clutch pack supporting a 2 kg weight, the
dimension from the C3 clutch hub locating step to the
friction plate is to be between 0.80-1.05 mm.
27. Use selective plates to achieve the correct specification.
If new friction plates are being fitted, remove the clutch
pack and soak the friction plates in ATF for a minimum
of 5 minutes prior to reassembly.
Notice
The clutch pack clearance must be taken before the
elements are soaked in ATF.
28. Lubricate and fit the 3-4 OWC and end caps to the C2
hub.
Page 1088 of 1463
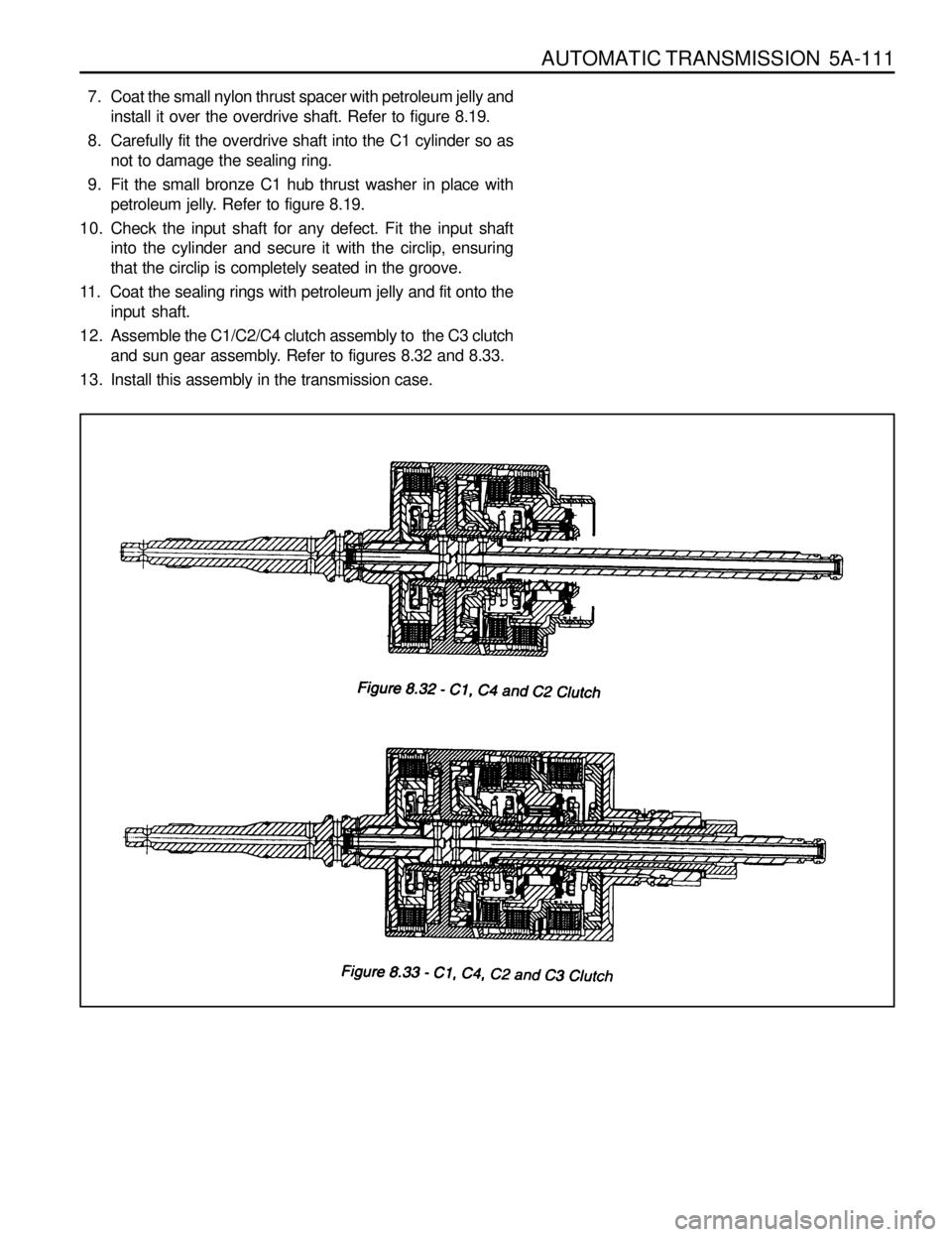
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-111
7. Coat the small nylon thrust spacer with petroleum jelly and
install it over the overdrive shaft. Refer to figure 8.19.
8. Carefully fit the overdrive shaft into the C1 cylinder so as
not to damage the sealing ring.
9. Fit the small bronze C1 hub thrust washer in place with
petroleum jelly. Refer to figure 8.19.
10. Check the input shaft for any defect. Fit the input shaft
into the cylinder and secure it with the circlip, ensuring
that the circlip is completely seated in the groove.
11. Coat the sealing rings with petroleum jelly and fit onto the
input shaft.
12. Assemble the C1/C2/C4 clutch assembly to the C3 clutch
and sun gear assembly. Refer to figures 8.32 and 8.33.
13. Install this assembly in the transmission case.
Page 1100 of 1463
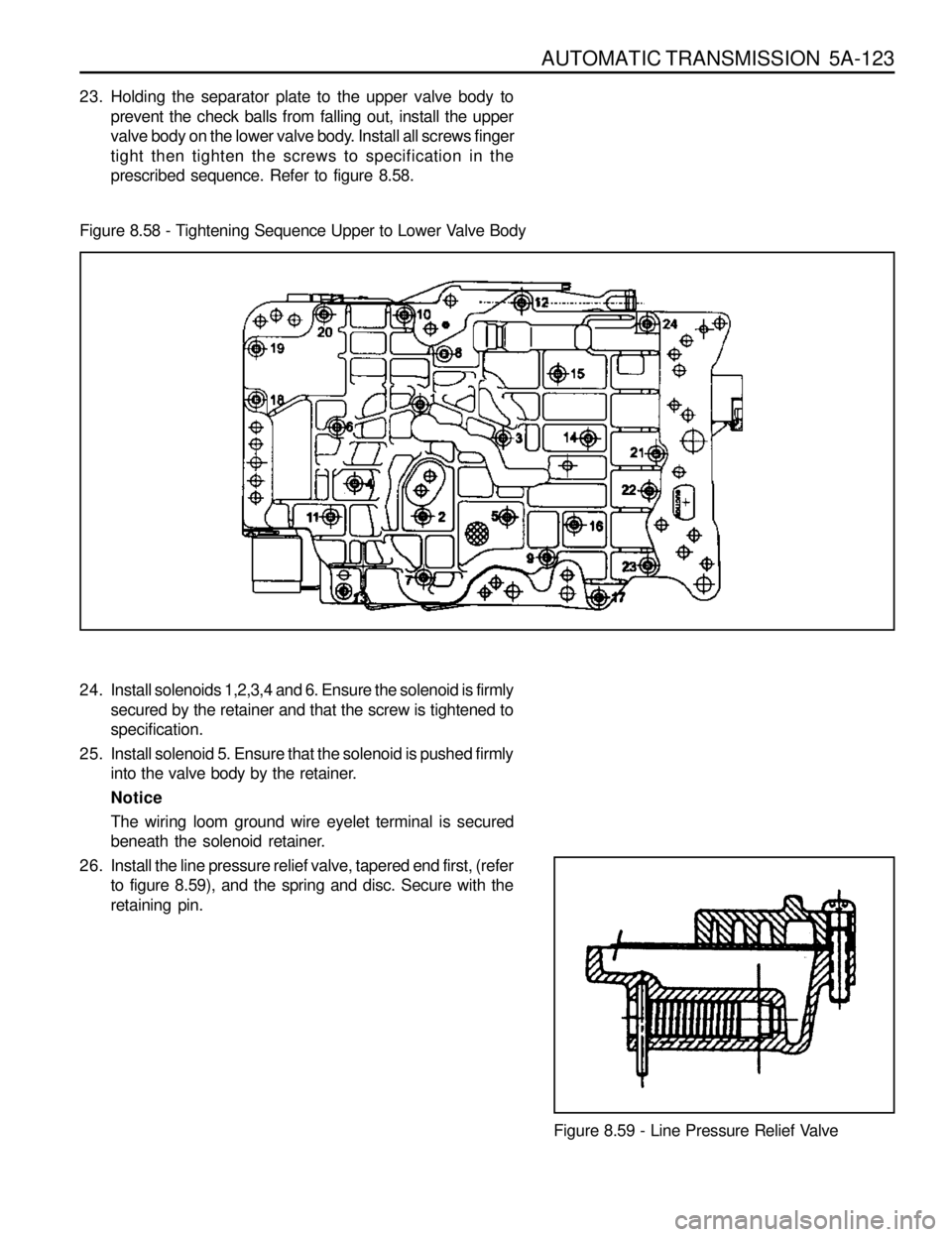
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-123
23. Holding the separator plate to the upper valve body to
prevent the check balls from falling out, install the upper
valve body on the lower valve body. Install all screws finger
tight then tighten the screws to specification in the
prescribed sequence. Refer to figure 8.58.
24. Install solenoids 1,2,3,4 and 6. Ensure the solenoid is firmly
secured by the retainer and that the screw is tightened to
specification.
25. Install solenoid 5. Ensure that the solenoid is pushed firmly
into the valve body by the retainer.
Notice
The wiring loom ground wire eyelet terminal is secured
beneath the solenoid retainer.
26. Install the line pressure relief valve, tapered end first, (refer
to figure 8.59), and the spring and disc. Secure with the
retaining pin. Figure 8.58 - Tightening Sequence Upper to Lower Valve Body
Figure 8.59 - Line Pressure Relief Valve