belt SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.GPages: 698, PDF Size: 16.01 MB
Page 48 of 698

MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION 0B-19
ALL LATCHES, HINGES AND LOCKS
INSPECTION
DOORS
Check that each door of front, rear and back doors opens and
closes smoothly and locks securely when closed.
If any malfunction is found, lubricate hinge and latch or repair
door lock system.
ENGINE HOOD
Check that secondary latch operates properly (check that sec-
ondary latch keeps hood from opening all the way even when
pulling hood release handle inside vehicle.) Also check that hood
opens and closes smoothly and properly and hood locks securely
when closed.
If any malfunction is found, lubricate hinge and latch, or repair
hood lock system.
FINAL INSPECTION
SEATS
Check that seat slides smoothly and locks securely at any position. Also check that reclining mechanism of front
seat back allows it to be locked at any angle.
SEAT BELT
Inspect belt system including webbing, buckles, latch plates, retractors and anchors for damage or wear.
Check that seat belt is securely locked. If “REPLACE BELT” label on front seat belt is visible, replace belt.
BATTERY ELECTROLYTE LEVEL CHECK
Check that the electrolyte level of all battery cells is between the upper and lower level lines on the case. If bat-
tery is equipped with built-in indicator, check battery condition by the indicator.
ACCELERATOR PEDAL OPERATION
Check that pedal operates smoothly without getting caught or interfered by any other part.
WARNING:
When carrying out road tests, select a safe place where no man or no running vehicle is seen so as to
prevent any accident.
Page 66 of 698

AIR CONDITIONING (OPTIONAL) 1B-1
6F1
6F2
6G
1B
7A
7A1
7B1
7C1
7D
7E
7F
8A
8B
8C
8D
8E
9
10
10A
10B
SECTION 1B
AIR CONDITIONING (OPTIONAL)
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION .............................. 1B-3
REFRIGERANT CIRCULATION .................. 1B-3
REFRIGERANT TYPE ................................. 1B-3
MAJOR COMPONENTS AND
LOCATION ................................................... 1B-4
DIAGNOSIS ..................................................... 1B-5
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS TABLE ................... 1B-5
ABNORMAL NOISE DIAGNOSIS ................ 1B-7
QUICKLY CHECKING OF REFRIGERANT
CHARGE ...................................................... 1B-9
PERFORMANCE DIAGNOSIS .................. 1B-10
PERFORMANCE DIAGNOSIS TABLE .. 1B-12
DETAIL DIAGNOSIS TABLE (AMBIENT
TEMPERATURE AT 30°C (86°F)) ......... 1B-13
COMPRESSOR DRIVE BELT ................... 1B-15ELECTRICAL DIAGNOSIS ........................... 1B-16
WIRING DIAGRAM .................................... 1B-16
A/C SYSTEM INSPECTION OF ECM AND
ITS CIRCUITS ........................................... 1B-17
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY, EVACUATING
AND CHARGING........................................... 1B-20
OPERATION PROCEDURE FOR
REFRIGERANT CHARGING ..................... 1B-20
RECOVERY ............................................... 1B-21
REPLENISHING COMPRESSOR OIL ...... 1B-21
EVACUATING............................................ 1B-22
EVACUATING PROCEDURE ................ 1B-22
CHECKING SYSTEM FOR PRESSURE
LEAKS.................................................... 1B-23
CHARGING................................................ 1B-24
CHARGING PROCEDURE .................... 1B-24 WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System :
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
CAUTION:
The air conditioning system of this vehicle uses refrigerant HFC-134a (R-134a).
None of refrigerant, compressor oil and component parts is interchangeable between two types of
A/C : one using refrigerant HFC-134a (R-134a) and the other using refrigerant CFC-12 (R-12).
Be sure to check which refrigerant is used before any service work including inspection and mainte-
nance. For identification between these two types, refer to “REFRIGERANT TYPE” in this section.
When replenishing or changing refrigerant and compressor oil and when replacing parts, make sure
that the material or the part to be used is appropriate to the A/C installed in the vehicle being serviced.
Use of incorrect one will result in leakage of refrigerant, damage in parts or other faulty condition.
NOTE:
For basic servicing method of the air conditioning system that is not described in this section, refer to
“AIR CONDITIONING BASIC MANUAL (Part number : 99520-02130)”.
Page 70 of 698
AIR CONDITIONING (OPTIONAL) 1B-5
DIAGNOSIS
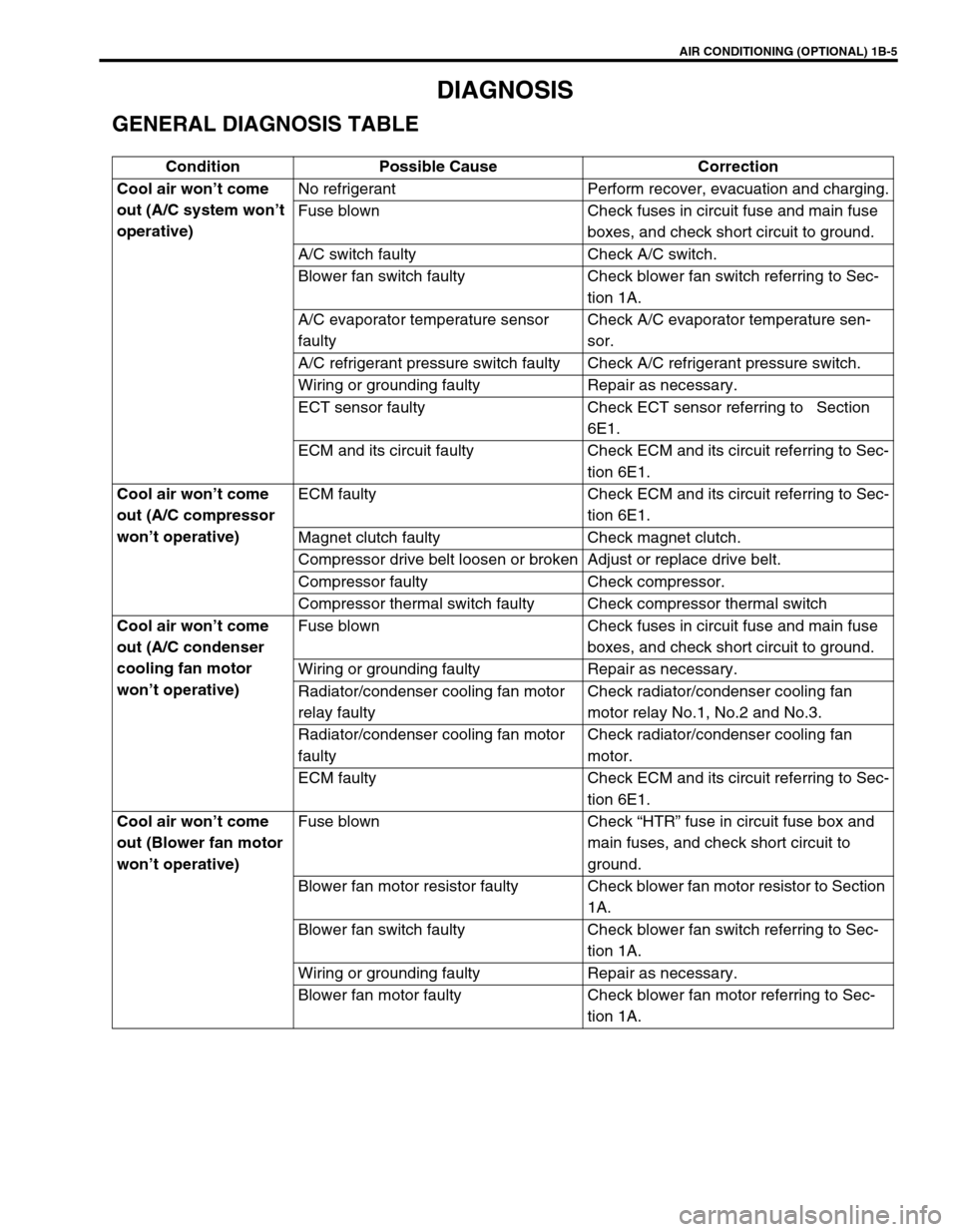
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS TABLE
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Cool air won’t come
out (A/C system won’t
operative)No refrigerant Perform recover, evacuation and charging.
Fuse blown Check fuses in circuit fuse and main fuse
boxes, and check short circuit to ground.
A/C switch faulty Check A/C switch.
Blower fan switch faulty Check blower fan switch referring to Sec-
tion 1A.
A/C evaporator temperature sensor
faultyCheck A/C evaporator temperature sen-
sor.
A/C refrigerant pressure switch faulty Check A/C refrigerant pressure switch.
Wiring or grounding faulty Repair as necessary.
ECT sensor faulty Check ECT sensor referring to Section
6E1.
ECM and its circuit faulty Check ECM and its circuit referring to Sec-
tion 6E1.
Cool air won’t come
out (A/C compressor
won’t operative)ECM faulty Check ECM and its circuit referring to Sec-
tion 6E1.
Magnet clutch faulty Check magnet clutch.
Compressor drive belt loosen or broken Adjust or replace drive belt.
Compressor faulty Check compressor.
Compressor thermal switch faulty Check compressor thermal switch
Cool air won’t come
out (A/C condenser
cooling fan motor
won’t operative)Fuse blown Check fuses in circuit fuse and main fuse
boxes, and check short circuit to ground.
Wiring or grounding faulty Repair as necessary.
Radiator/condenser cooling fan motor
relay faultyCheck radiator/condenser cooling fan
motor relay No.1, No.2 and No.3.
Radiator/condenser cooling fan motor
faultyCheck radiator/condenser cooling fan
motor.
ECM faulty Check ECM and its circuit referring to Sec-
tion 6E1.
Cool air won’t come
out (Blower fan motor
won’t operative)Fuse blown Check “HTR” fuse in circuit fuse box and
main fuses, and check short circuit to
ground.
Blower fan motor resistor faulty Check blower fan motor resistor to Section
1A.
Blower fan switch faulty Check blower fan switch referring to Sec-
tion 1A.
Wiring or grounding faulty Repair as necessary.
Blower fan motor faulty Check blower fan motor referring to Sec-
tion 1A.
Page 71 of 698
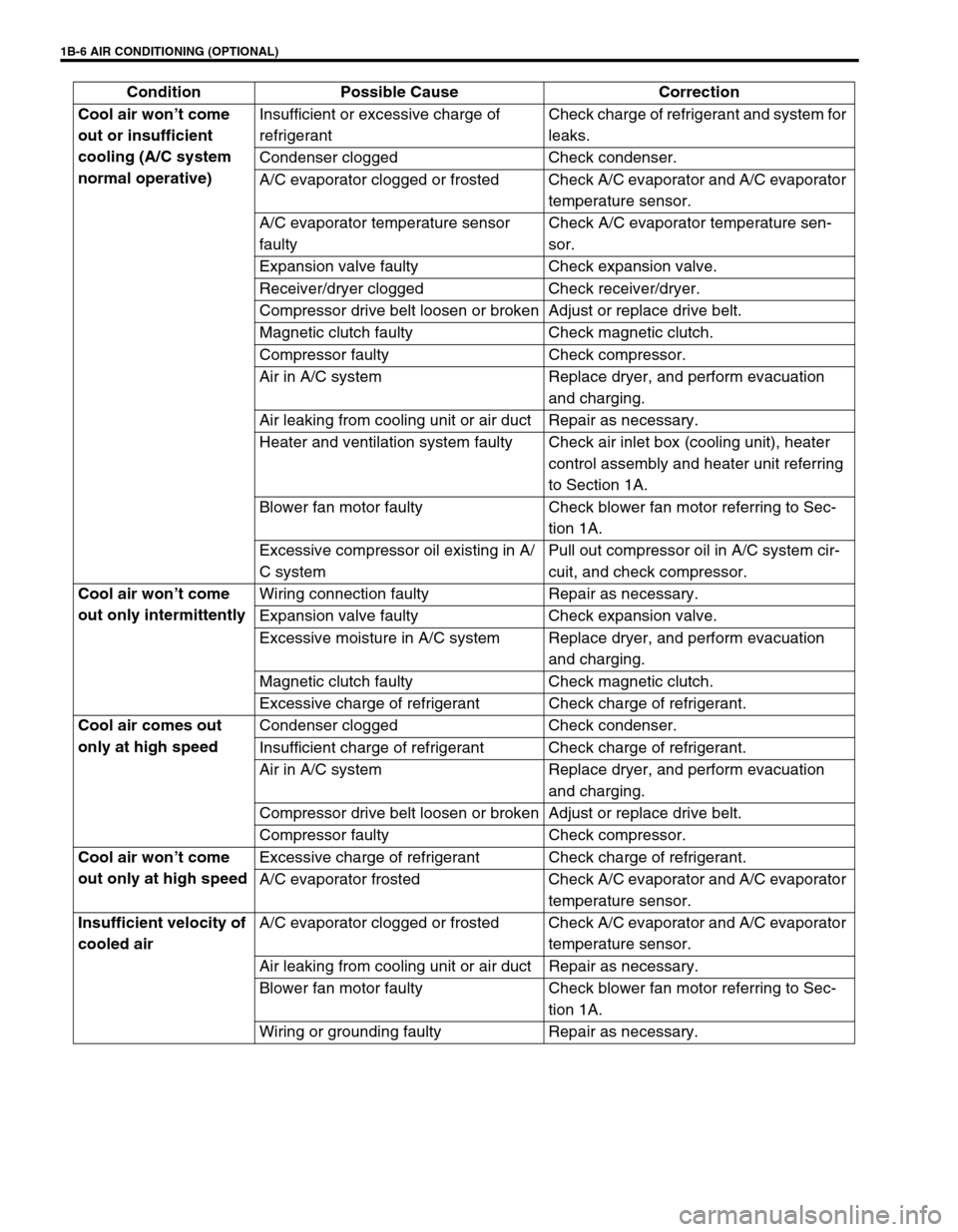
1B-6 AIR CONDITIONING (OPTIONAL)
Cool air won’t come
out or insufficient
cooling (A/C system
normal operative)Insufficient or excessive charge of
refrigerantCheck charge of refrigerant and system for
leaks.
Condenser clogged Check condenser.
A/C evaporator clogged or frosted Check A/C evaporator and A/C evaporator
temperature sensor.
A/C evaporator temperature sensor
faultyCheck A/C evaporator temperature sen-
sor.
Expansion valve faulty Check expansion valve.
Receiver/dryer clogged Check receiver/dryer.
Compressor drive belt loosen or broken Adjust or replace drive belt.
Magnetic clutch faulty Check magnetic clutch.
Compressor faulty Check compressor.
Air in A/C system Replace dryer, and perform evacuation
and charging.
Air leaking from cooling unit or air duct Repair as necessary.
Heater and ventilation system faulty Check air inlet box (cooling unit), heater
control assembly and heater unit referring
to Section 1A.
Blower fan motor faulty Check blower fan motor referring to Sec-
tion 1A.
Excessive compressor oil existing in A/
C systemPull out compressor oil in A/C system cir-
cuit, and check compressor.
Cool air won’t come
out only intermittentlyWiring connection faulty Repair as necessary.
Expansion valve faulty Check expansion valve.
Excessive moisture in A/C system Replace dryer, and perform evacuation
and charging.
Magnetic clutch faulty Check magnetic clutch.
Excessive charge of refrigerant Check charge of refrigerant.
Cool air comes out
only at high speedCondenser clogged Check condenser.
Insufficient charge of refrigerant Check charge of refrigerant.
Air in A/C system Replace dryer, and perform evacuation
and charging.
Compressor drive belt loosen or broken Adjust or replace drive belt.
Compressor faulty Check compressor.
Cool air won’t come
out only at high speedExcessive charge of refrigerant Check charge of refrigerant.
A/C evaporator frosted Check A/C evaporator and A/C evaporator
temperature sensor.
Insufficient velocity of
cooled airA/C evaporator clogged or frosted Check A/C evaporator and A/C evaporator
temperature sensor.
Air leaking from cooling unit or air duct Repair as necessary.
Blower fan motor faulty Check blower fan motor referring to Sec-
tion 1A.
Wiring or grounding faulty Repair as necessary. Condition Possible Cause Correction
Page 72 of 698
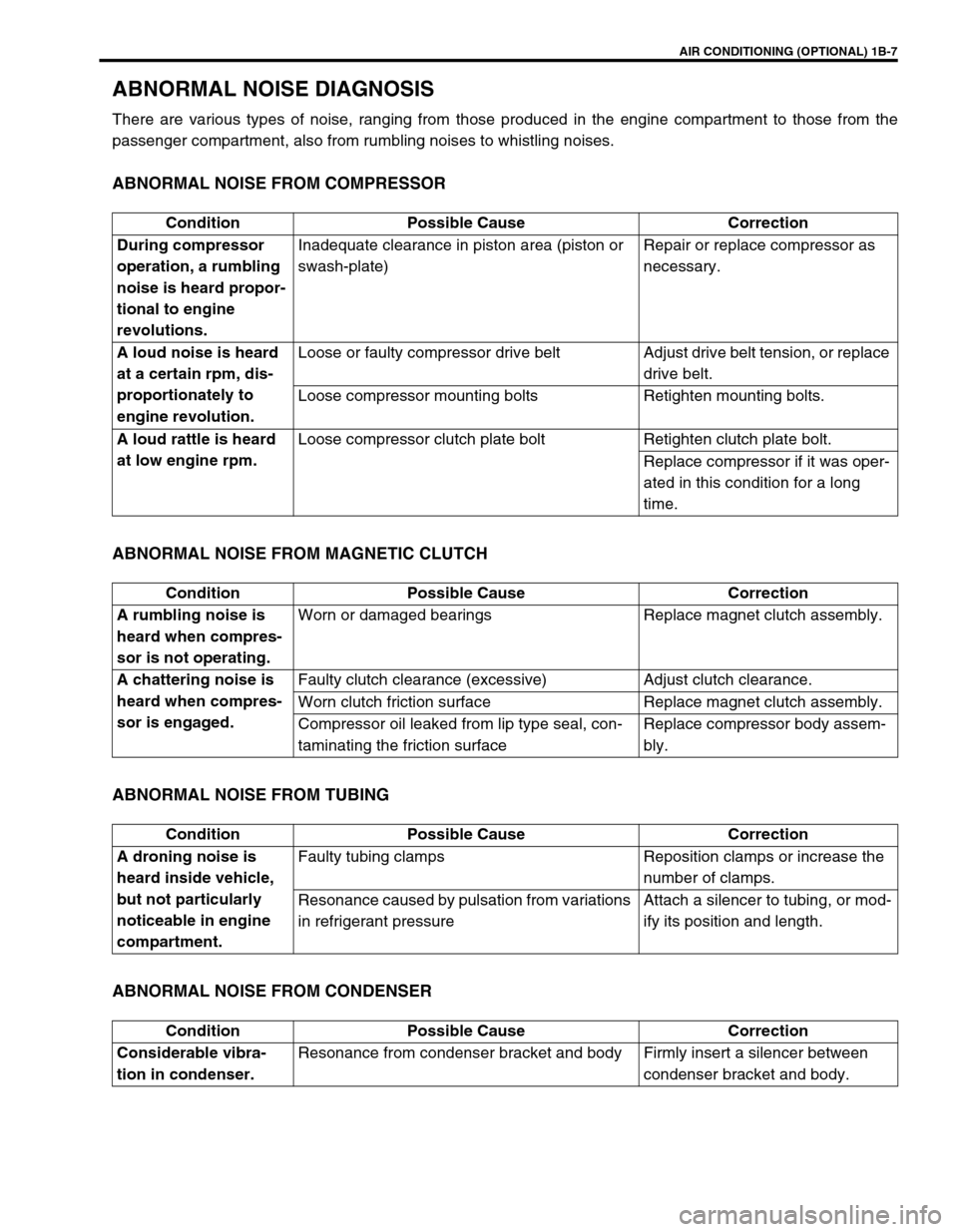
AIR CONDITIONING (OPTIONAL) 1B-7
ABNORMAL NOISE DIAGNOSIS
There are various types of noise, ranging from those produced in the engine compartment to those from the
passenger compartment, also from rumbling noises to whistling noises.
ABNORMAL NOISE FROM COMPRESSOR
ABNORMAL NOISE FROM MAGNETIC CLUTCH
ABNORMAL NOISE FROM TUBING
ABNORMAL NOISE FROM CONDENSER
Condition Possible Cause Correction
During compressor
operation, a rumbling
noise is heard propor-
tional to engine
revolutions.Inadequate clearance in piston area (piston or
swash-plate)Repair or replace compressor as
necessary.
A loud noise is heard
at a certain rpm, dis-
proportionately to
engine revolution.Loose or faulty compressor drive belt Adjust drive belt tension, or replace
drive belt.
Loose compressor mounting bolts Retighten mounting bolts.
A loud rattle is heard
at low engine rpm.Loose compressor clutch plate bolt Retighten clutch plate bolt.
Replace compressor if it was oper-
ated in this condition for a long
time.
Condition Possible Cause Correction
A rumbling noise is
heard when compres-
sor is not operating.Worn or damaged bearings Replace magnet clutch assembly.
A chattering noise is
heard when compres-
sor is engaged.Faulty clutch clearance (excessive) Adjust clutch clearance.
Worn clutch friction surface Replace magnet clutch assembly.
Compressor oil leaked from lip type seal, con-
taminating the friction surfaceReplace compressor body assem-
bly.
Condition Possible Cause Correction
A droning noise is
heard inside vehicle,
but not particularly
noticeable in engine
compartment.Faulty tubing clamps Reposition clamps or increase the
number of clamps.
Resonance caused by pulsation from variations
in refrigerant pressureAttach a silencer to tubing, or mod-
ify its position and length.
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Considerable vibra-
tion in condenser.Resonance from condenser bracket and body Firmly insert a silencer between
condenser bracket and body.
Page 80 of 698

AIR CONDITIONING (OPTIONAL) 1B-15
COMPRESSOR DRIVE BELT
INSPECTION
Check compressor drive belt (6) for wear and cracks, and
replace as required.
Check compressor drive belt (6) tension by measuring how
much it deflects when pushed at intermediate point between
compressor pulley (1) and tension pulley (2) with about 100
N (10 kg) force after crankshaft pulley 1 rotating.
If belt tension is without specification, adjust belt tension
referring to below procedures.
Compressor drive belt tension
“a” : 3 – 5 mm (0.12 – 0.20 in.)
New compressor drive belt tension
“a” : 2 – 4 mm (0.08 – 0.16 in.)
ADJUSTMENT
1) Loosen tension pulley nut (3).
2) Adjust belt tension by tighten or loosen tension pulley adjust-
ing bolt (4).
3) Tighten tension pulley nut (3).
4) Turn the crank pulley (5) 1 revolution, then check belt ten-
sion.
REPLACEMENT
1) Loosen tension pulley nut (3).
2) Loosen belt tension by loosen tension pulley adjusting bolt
(4).
3) Remove compressor drive belt (6).
4) Install new compressor drive belt.
5) Adjust belt tension referring to above procedure.
Page 102 of 698
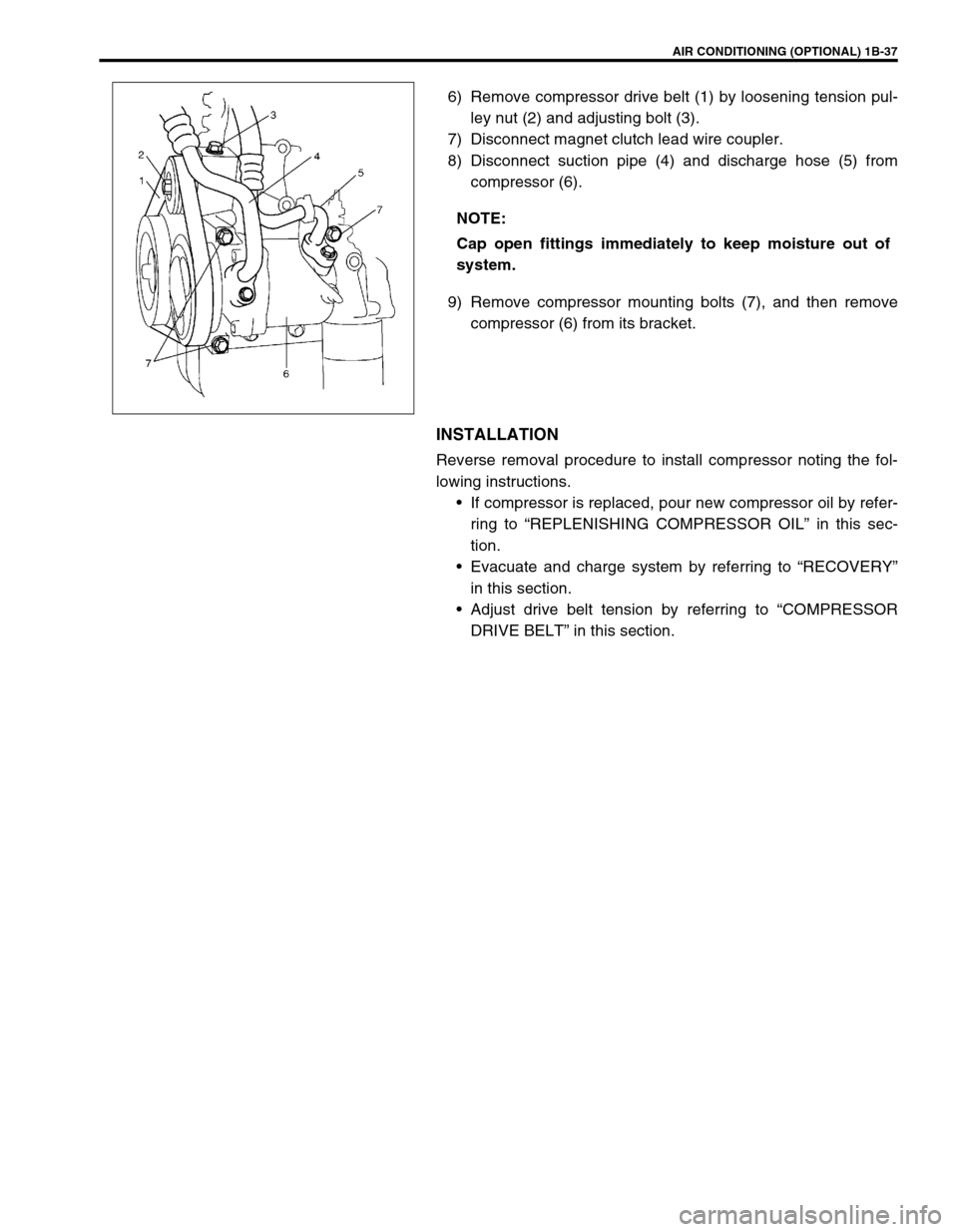
AIR CONDITIONING (OPTIONAL) 1B-37
6) Remove compressor drive belt (1) by loosening tension pul-
ley nut (2) and adjusting bolt (3).
7) Disconnect magnet clutch lead wire coupler.
8) Disconnect suction pipe (4) and discharge hose (5) from
compressor (6).
9) Remove compressor mounting bolts (7), and then remove
compressor (6) from its bracket.
INSTALLATION
Reverse removal procedure to install compressor noting the fol-
lowing instructions.
If compressor is replaced, pour new compressor oil by refer-
ring to “REPLENISHING COMPRESSOR OIL” in this sec-
tion.
Evacuate and charge system by referring to “RECOVERY”
in this section.
Adjust drive belt tension by referring to “COMPRESSOR
DRIVE BELT” in this section. NOTE:
Cap open fittings immediately to keep moisture out of
system.
Page 115 of 698
3-6 STEERING, SUSPENSION, WHEELS AND TIRES
RADIAL TIRE WADDLE
Waddle is side to side movement at the front and/or rear of the
vehicle. It is caused by the steel belt not being straight within the
tire. It is most noticeable at a low speed, 8 to 48 kph (5 to 30
mph).
It is possible to locate the faulty tire by road testing the vehicle. If
it is on the rear, the rear end of the vehicle shakes from side to
side or “waddles”. To the driver in the seat, it feels as though
someone is pushing on the side of vehicle.
If the faulty tire is on the front, waddling is more visual. The front
sheet metal appears to be moving back and forth and the driver
feels as though he is at the pivot point in vehicle.
Waddle can be quickly diagnosed by using Tire Problem Detector
(TPD) and following the equipment manufacture’s recommenda-
tions.
If TPD is not available, an alternative method of substituting
known-good tire/wheel assemblies can be used as follows,
although it takes a longer time.
1) Ride vehicle to determine whether the front or rear waddles.
2) Install tires and wheels that are known to be good (on similar vehicle) in place of those on waddling end of
vehicle. If waddling end cannot be identified, substitute rear ones.
3) Road test again. If improvement is noted, reinstall originals one at a time till waddle causal tire is found. If no
improvement is noted, install known-good tires in place of all four. Then reinstall originals in the same man-
ner as above.
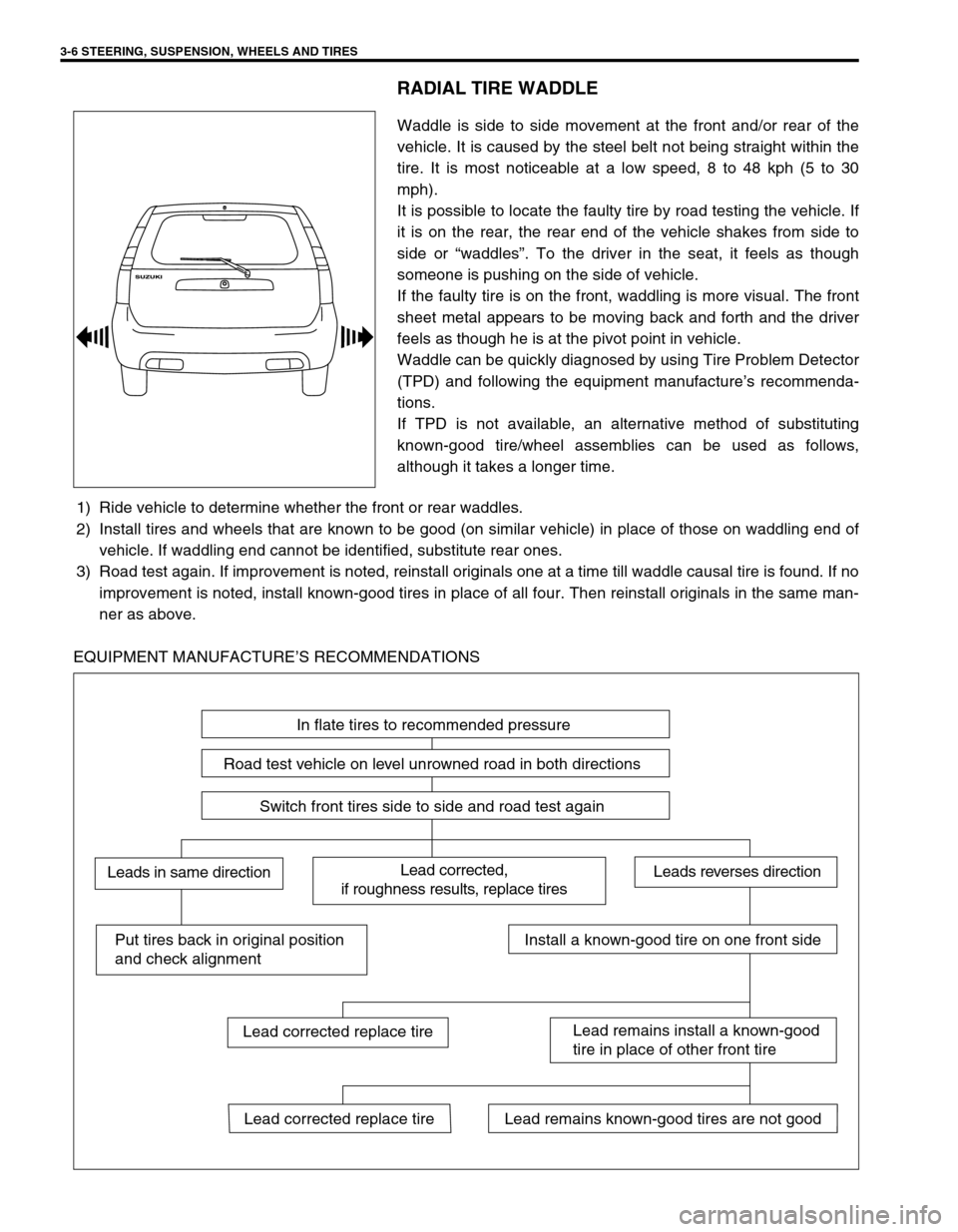
EQUIPMENT MANUFACTURE’S RECOMMENDATIONS
In flate tires to recommended pressure
Road test vehicle on level unrowned road in both directions
Switch front tires side to side and road test again
Lead corrected,
if roughness results, replace tiresLeads in same directionLeads reverses direction
Put tires back in original position
and check alignmentInstall a known-good tire on one front side
Lead remains install a known-good
tire in place of other front tire
Lead remains known-good tires are not goodLead corrected replace tire
Lead corrected replace tire
Page 116 of 698
STEERING, SUSPENSION, WHEELS AND TIRES 3-7
RADIAL TIRE LEAD
“Lead” is the deviation of the vehicle from a straight path on a level rod even with no pressure on the steering
wheel.
Lead is usually caused by:
Incorrect alignment.
Uneven brake adjustment.
Tire construction.
The way in which a tire is built can produce lead in a vehicle. An example of this is placement of the belt. Off
center belts on radial tires can cause the tire to develop a side force while rolling straight down the road. If one
side of the tire has a little larger diameter than the other, the tire will tend to roll to one side. This will develop a
side force which can produce vehicle lead.
The procedure in above figure (Lead Diagnosis) should be used to make sure that front alignment is not mis-
taken for tire lead.
Part of the lead diagnosis procedure is different from the proper tire rotation pattern currently in the owner
and service manuals. If a medium to high mileage tire is moved to the other side of the vehicle, be sure to
check that ride roughness has not developed
Rear tires will not cause lead.
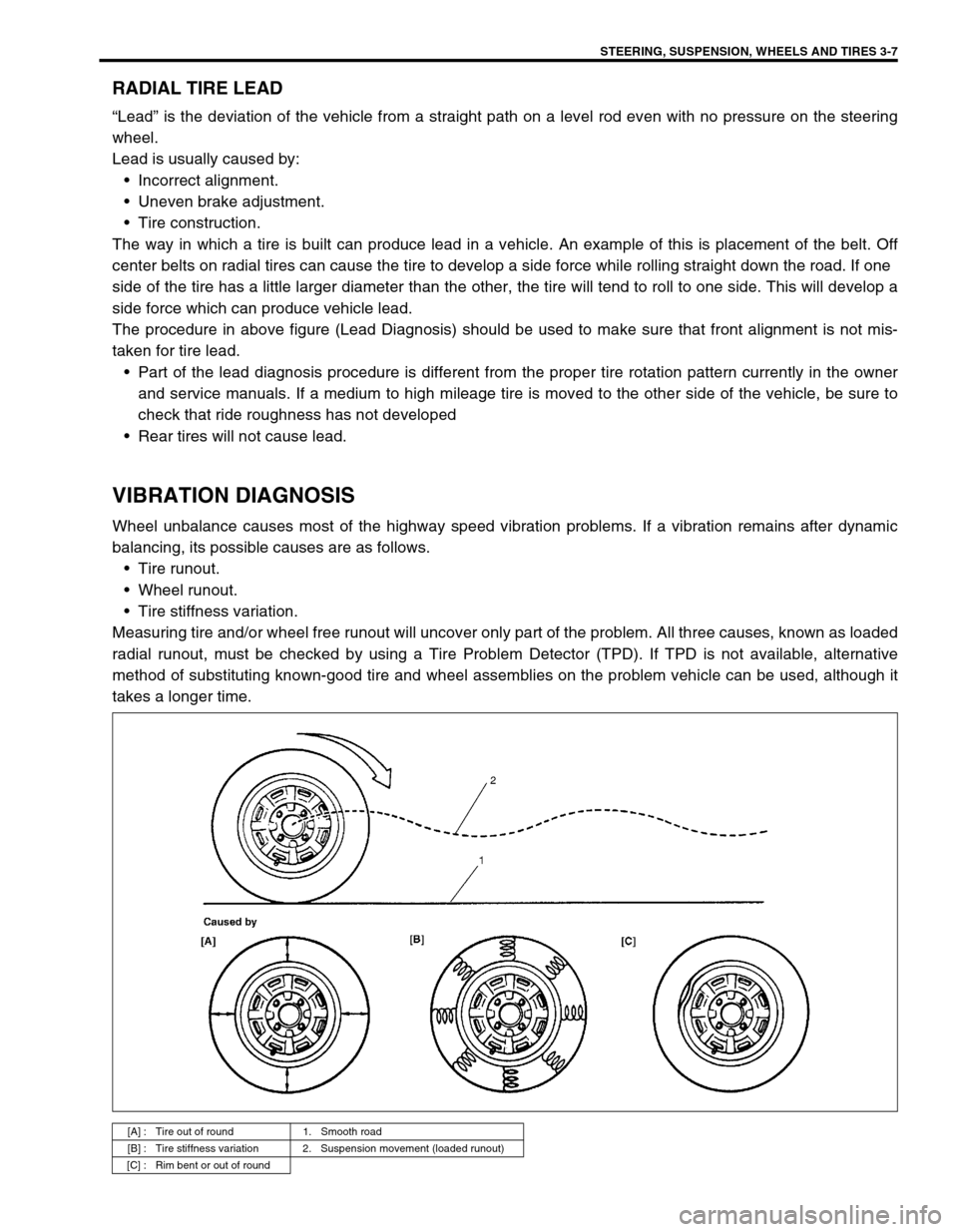
VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS
Wheel unbalance causes most of the highway speed vibration problems. If a vibration remains after dynamic
balancing, its possible causes are as follows.
Tire runout.
Wheel runout.
Tire stiffness variation.
Measuring tire and/or wheel free runout will uncover only part of the problem. All three causes, known as loaded
radial runout, must be checked by using a Tire Problem Detector (TPD). If TPD is not available, alternative
method of substituting known-good tire and wheel assemblies on the problem vehicle can be used, although it
takes a longer time.
[A] : Tire out of round 1. Smooth road
[B] : Tire stiffness variation 2. Suspension movement (loaded runout)
[C] : Rim bent or out of round
Page 175 of 698

3C-2 STEERING WHEEL AND COLUMN
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
STEERING COLUMN
This double tube type steering column has following three important features in addition to the steering function
:
The column is energy absorbing, designed to compress in a front-end collision.
The ignition switch and lock are mounted conveniently on this column.
With the column mounted lock, the ignition and steering operations can be locked to inhibit theft of the vehi-
cle.
To insure the energy absorbing action, it is important that only the specified screws, bolts, and nuts be used as
designated and that they are tightened to the specified torque.
When the column assembly is removed from the vehicle, special care must be taken in handling it. Use of a
steering wheel puller other than the one recommended in this manual or a sharp blow on the end of the steering
shaft, leaning on the assembly, or dropping the assembly could shear the plastic shear pins which maintain col-
umn length and position.
STEERING WHEEL AND DRIVER AIR BAG (INFLATOR) MODULE
The driver air bag (inflator) module is one of the supplemental restraint (air bag) system components and is
mounted to the center of the steering wheel. During certain frontal crashes, the air bag system supplements the
restraint of the driver’s and passenger’s seat belts by deploying the air bags.
The air bag (inflator) module should be handled with care to prevent accidental deployment. When servicing, be
sure to observe all WARNINGS and CAUTIONS and “SERVICE PRECAUTIONS” under “ON-VEHICLE SER-
VICE” in Section 10B.
DIAGNOSIS
For maintenance service of the steering wheel and column, refer to Section 0B.
For diagnosis of the steering wheel and column, refer to Section 3.
For diagnosis of the air bag system, refer to Section 10B.
INSPECTION AND REPAIR REQUIRED AFTER ACCIDENT
After an accident, whether the air bag has been deployed or not, be sure to perform checks, inspections and
repairs described under “CHECKING STEERING COLUMN ASSEMBLY AND LOWER SHAFT FOR ACCI-
DENT DAMAGE” as well as “REPAIRS AND INSPECTIONS REQUIRED AFTER ACCIDENT” under “DIAGNO-
SIS” in Section 10B.