coolant temperature SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.GPages: 698, PDF Size: 16.01 MB
Page 389 of 698
6-20 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
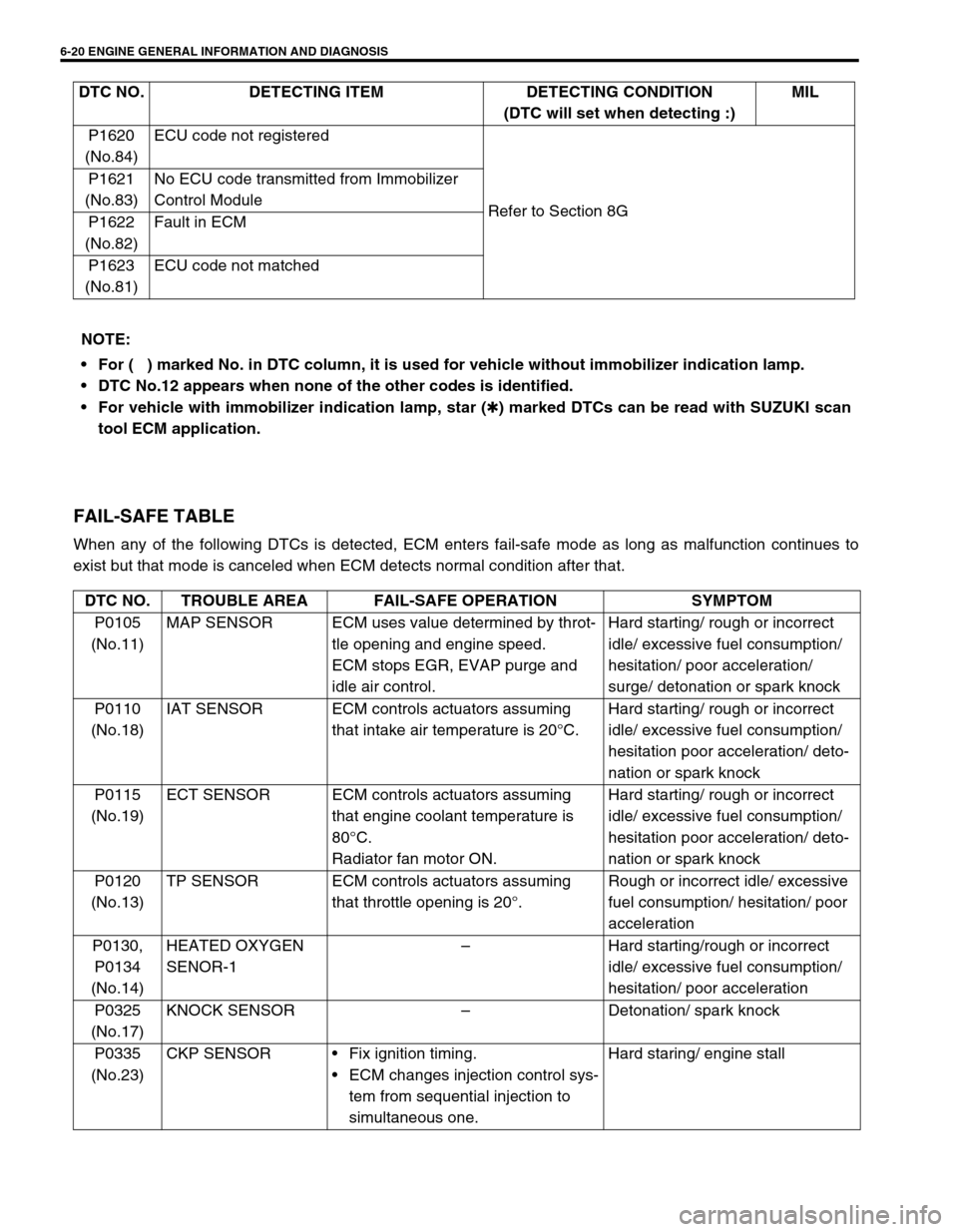
FAIL-SAFE TABLE
When any of the following DTCs is detected, ECM enters fail-safe mode as long as malfunction continues to
exist but that mode is canceled when ECM detects normal condition after that.P1620
(No.84)ECU code not registered
Refer to Section 8G P1621
(No.83)No ECU code transmitted from Immobilizer
Control Module
P1622
(No.82)Fault in ECM
P1623
(No.81)ECU code not matched DTC NO. DETECTING ITEM DETECTING CONDITION
(DTC will set when detecting :)MIL
NOTE:
For (
) marked No. in DTC column, it is used for vehicle without immobilizer indication lamp.
DTC No.12 appears when none of the other codes is identified.
For vehicle with immobilizer indication lamp, star (
✱) marked DTCs can be read with SUZUKI scan
tool ECM application.
DTC NO. TROUBLE AREA FAIL-SAFE OPERATION SYMPTOM
P0105
(No.11)MAP SENSOR ECM uses value determined by throt-
tle opening and engine speed.
ECM stops EGR, EVAP purge and
idle air control.Hard starting/ rough or incorrect
idle/ excessive fuel consumption/
hesitation/ poor acceleration/
surge/ detonation or spark knock
P0110
(No.18)IAT SENSOR ECM controls actuators assuming
that intake air temperature is 20°C.Hard starting/ rough or incorrect
idle/ excessive fuel consumption/
hesitation poor acceleration/ deto-
nation or spark knock
P0115
(No.19)ECT SENSOR ECM controls actuators assuming
that engine coolant temperature is
80°C.
Radiator fan motor ON.Hard starting/ rough or incorrect
idle/ excessive fuel consumption/
hesitation poor acceleration/ deto-
nation or spark knock
P0120
(No.13)TP SENSOR ECM controls actuators assuming
that throttle opening is 20°.Rough or incorrect idle/ excessive
fuel consumption/ hesitation/ poor
acceleration
P0130,
P0134
(No.14)HEATED OXYGEN
SENOR-1–Hard starting/rough or incorrect
idle/ excessive fuel consumption/
hesitation/ poor acceleration
P0325
(No.17)KNOCK SENSOR–Detonation/ spark knock
P0335
(No.23)CKP SENSORFix ignition timing.
ECM changes injection control sys-
tem from sequential injection to
simultaneous one.Hard staring/ engine stall
Page 402 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-33
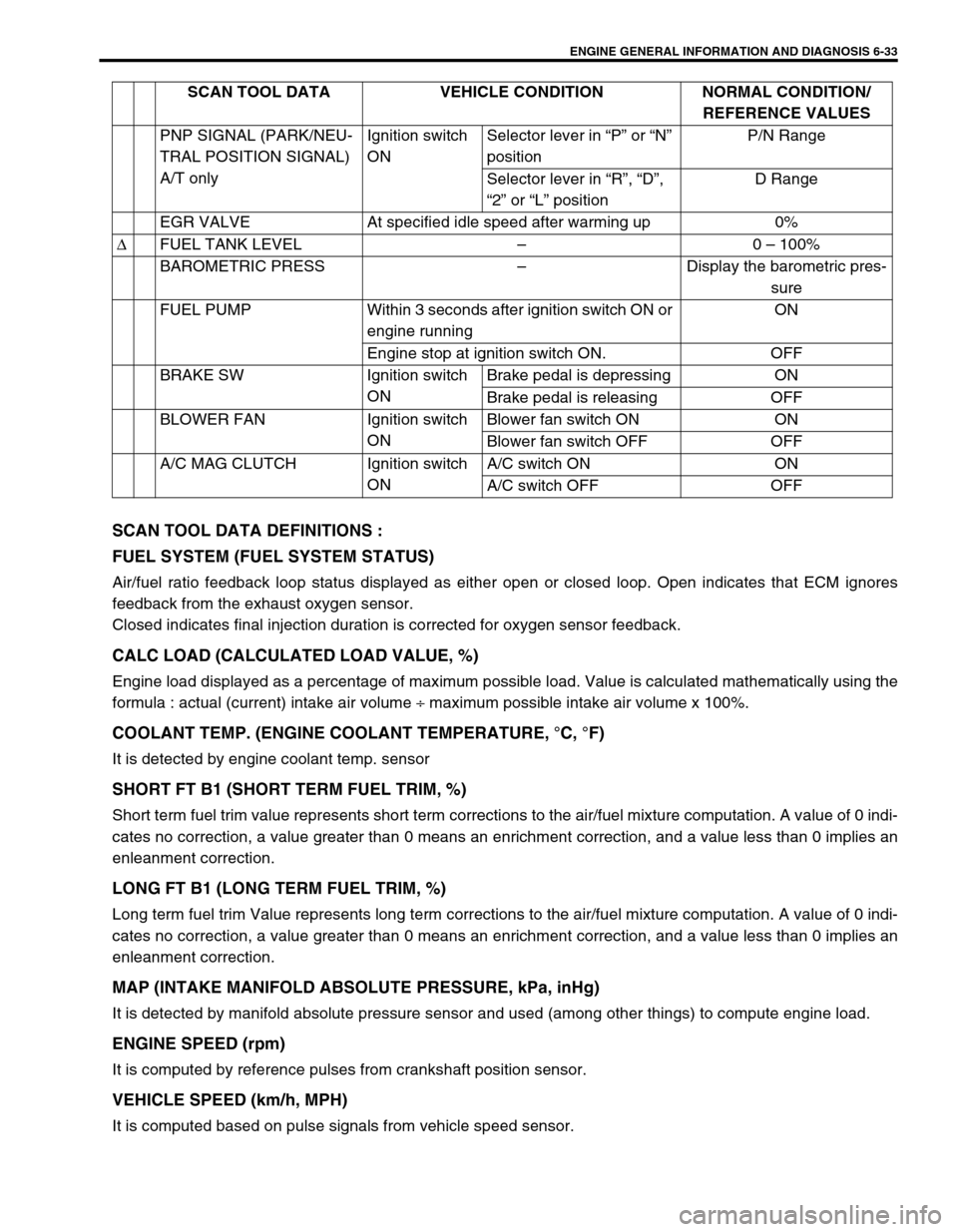
SCAN TOOL DATA DEFINITIONS :
FUEL SYSTEM (FUEL SYSTEM STATUS)
Air/fuel ratio feedback loop status displayed as either open or closed loop. Open indicates that ECM ignores
feedback from the exhaust oxygen sensor.
Closed indicates final injection duration is corrected for oxygen sensor feedback.
CALC LOAD (CALCULATED LOAD VALUE, %)
Engine load displayed as a percentage of maximum possible load. Value is calculated mathematically using the
formula : actual (current) intake air volume ÷ maximum possible intake air volume x 100%.
COOLANT TEMP. (ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE, °C, °F)
It is detected by engine coolant temp. sensor
SHORT FT B1 (SHORT TERM FUEL TRIM, %)
Short term fuel trim value represents short term corrections to the air/fuel mixture computation. A value of 0 indi-
cates no correction, a value greater than 0 means an enrichment correction, and a value less than 0 implies an
enleanment correction.
LONG FT B1 (LONG TERM FUEL TRIM, %)
Long term fuel trim Value represents long term corrections to the air/fuel mixture computation. A value of 0 indi-
cates no correction, a value greater than 0 means an enrichment correction, and a value less than 0 implies an
enleanment correction.
MAP (INTAKE MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE, kPa, inHg)
It is detected by manifold absolute pressure sensor and used (among other things) to compute engine load.
ENGINE SPEED (rpm)
It is computed by reference pulses from crankshaft position sensor.
VEHICLE SPEED (km/h, MPH)
It is computed based on pulse signals from vehicle speed sensor.PNP SIGNAL (PARK/NEU-
TRAL POSITION SIGNAL)
A/T onlyIgnition switch
ONSelector lever in “P” or “N”
positionP/N Range
Selector lever in “R”, “D”,
“2” or “L” positionD Range
EGR VALVE At specified idle speed after warming up 0%
∆FUEL TANK LEVEL–0 – 100%
BAROMETRIC PRESS–Display the barometric pres-
sure
FUEL PUMP Within 3 seconds after ignition switch ON or
engine runningON
Engine stop at ignition switch ON. OFF
BRAKE SW Ignition switch
ONBrake pedal is depressing ON
Brake pedal is releasing OFF
BLOWER FAN Ignition switch
ONBlower fan switch ON ON
Blower fan switch OFF OFF
A/C MAG CLUTCH Ignition switch
ONA/C switch ON ON
A/C switch OFF OFF SCAN TOOL DATA VEHICLE CONDITION NORMAL CONDITION/
REFERENCE VALUES
Page 426 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-57
Fig. 3 for Step 4
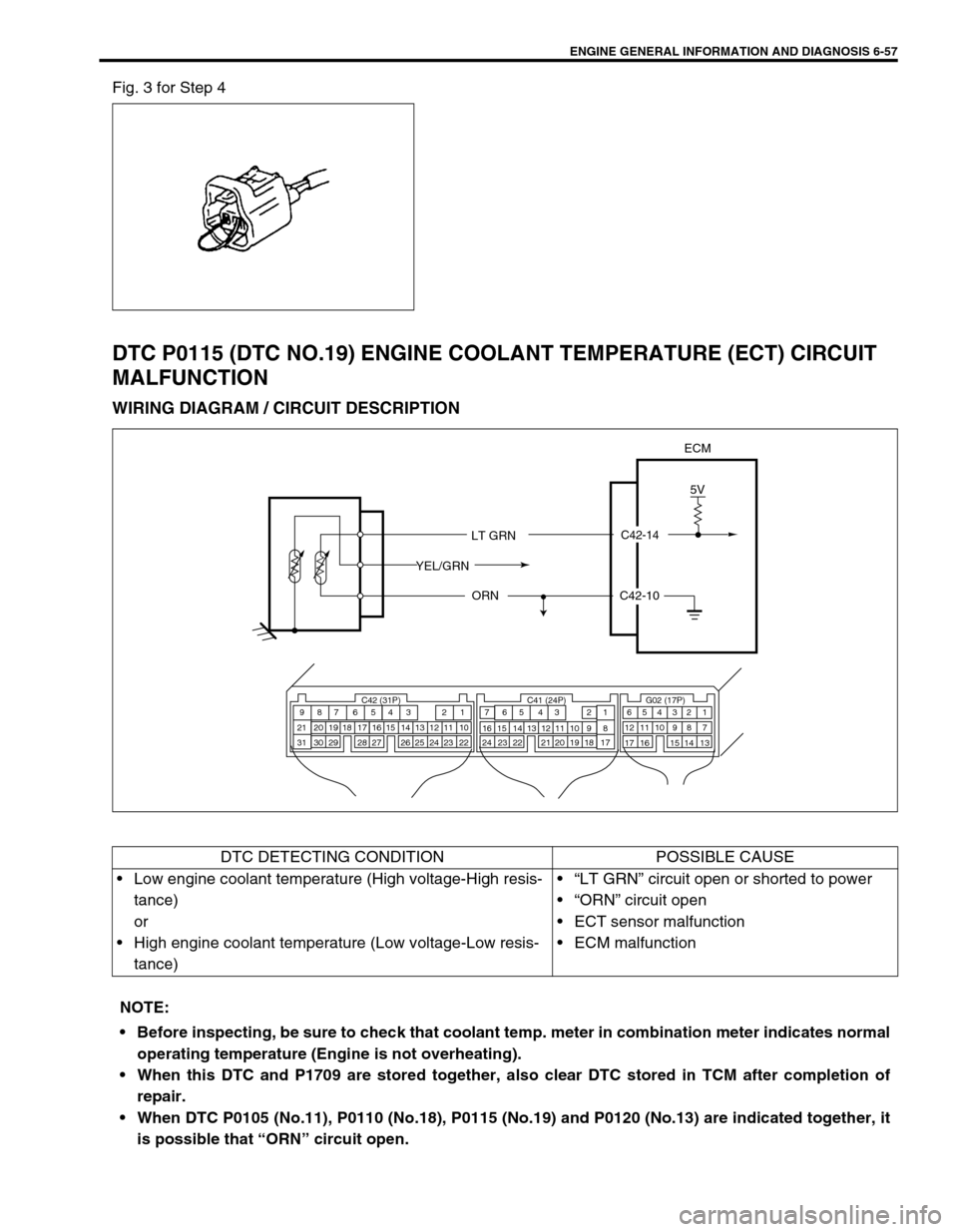
DTC P0115 (DTC NO.19) ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
C42-14
5V
ECM
LT GRN
ORN
YEL/GRN
C42-10
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
Low engine coolant temperature (High voltage-High resis-
tance)
or
High engine coolant temperature (Low voltage-Low resis-
tance)“LT GRN” circuit open or shorted to power
“ORN” circuit open
ECT sensor malfunction
ECM malfunction
NOTE:
Before inspecting, be sure to check that coolant temp. meter in combination meter indicates normal
operating temperature (Engine is not overheating).
When this DTC and P1709 are stored together, also clear DTC stored in TCM after completion of
repair.
When DTC P0105 (No.11), P0110 (No.18), P0115 (No.19) and P0120 (No.13) are indicated together, it
is possible that “ORN” circuit open.
Page 432 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-63
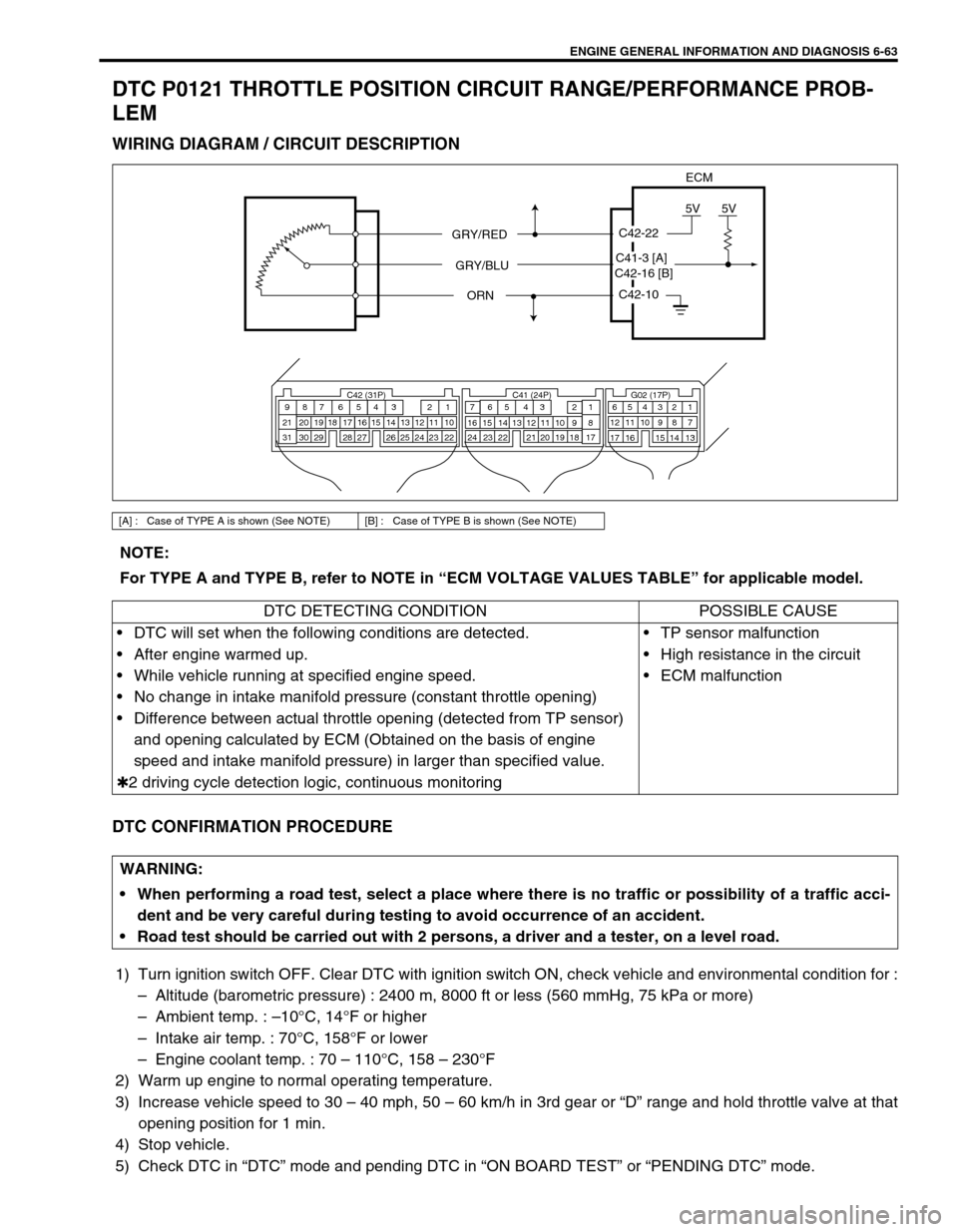
DTC P0121 THROTTLE POSITION CIRCUIT RANGE/PERFORMANCE PROB-
LEM
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF. Clear DTC with ignition switch ON, check vehicle and environmental condition for :
–Altitude (barometric pressure) : 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
–Ambient temp. : –10°C, 14°F or higher
–Intake air temp. : 70°C, 158°F or lower
–Engine coolant temp. : 70 – 110°C, 158 – 230°F
2) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
3) Increase vehicle speed to 30 – 40 mph, 50 – 60 km/h in 3rd gear or “D” range and hold throttle valve at that
opening position for 1 min.
4) Stop vehicle.
5) Check DTC in “DTC” mode and pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode.
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
C42-10
C42-22
5V5V
ECM
GRY/RED
GRY/BLU
ORN
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
C42-16 [B]C41-3 [A]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
DTC will set when the following conditions are detected.
After engine warmed up.
While vehicle running at specified engine speed.
No change in intake manifold pressure (constant throttle opening)
Difference between actual throttle opening (detected from TP sensor)
and opening calculated by ECM (Obtained on the basis of engine
speed and intake manifold pressure) in larger than specified value.
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitoringTP sensor malfunction
High resistance in the circuit
ECM malfunction
WARNING:
When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic acci-
dent and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
Page 510 of 698
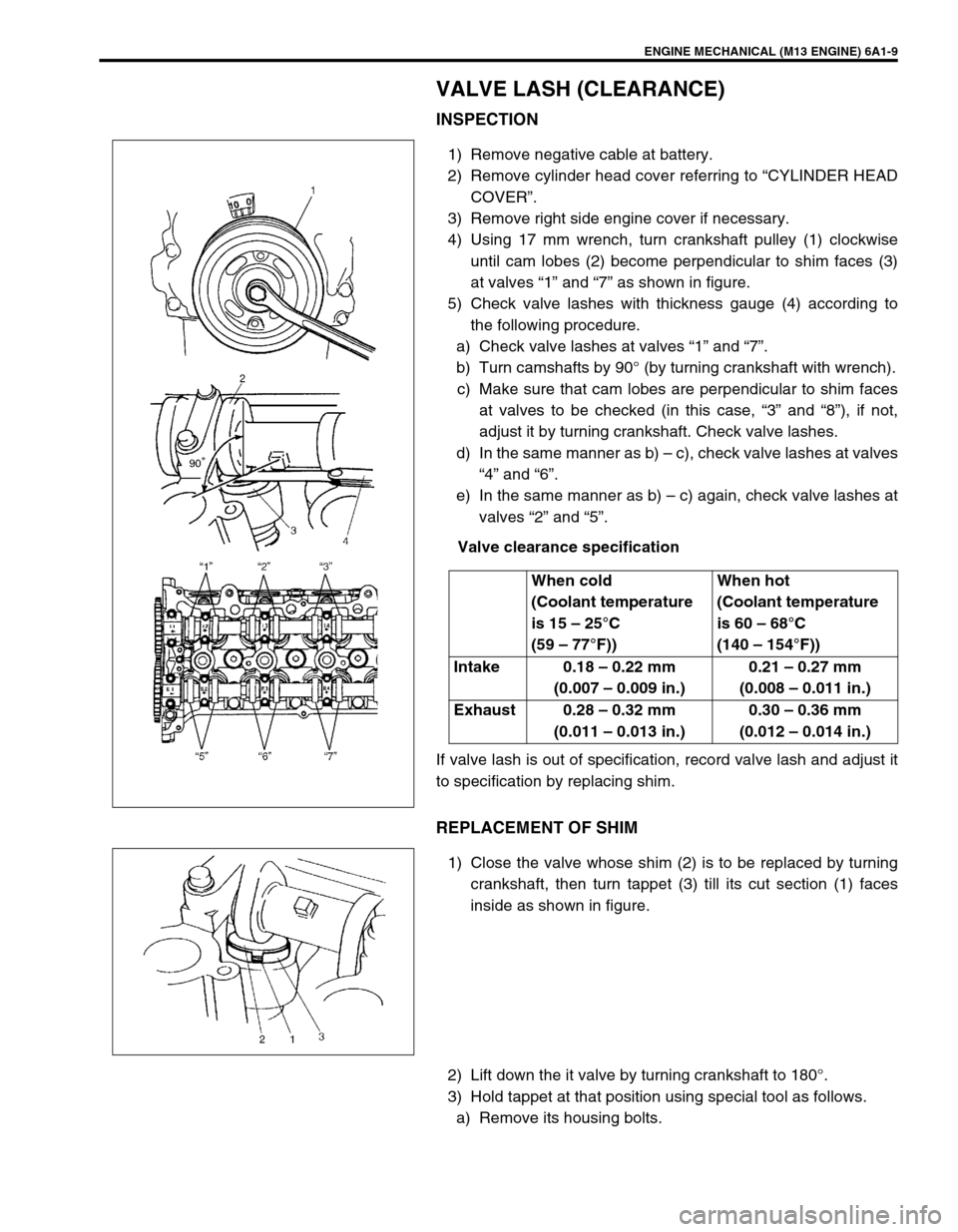
ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE) 6A1-9
VALVE LASH (CLEARANCE)
INSPECTION
1) Remove negative cable at battery.
2) Remove cylinder head cover referring to “CYLINDER HEAD
COVER”.
3) Remove right side engine cover if necessary.
4) Using 17 mm wrench, turn crankshaft pulley (1) clockwise
until cam lobes (2) become perpendicular to shim faces (3)
at valves “1” and “7” as shown in figure.
5) Check valve lashes with thickness gauge (4) according to
the following procedure.
a) Check valve lashes at valves “1” and “7”.
b) Turn camshafts by 90° (by turning crankshaft with wrench).
c) Make sure that cam lobes are perpendicular to shim faces
at valves to be checked (in this case, “3” and “8”), if not,
adjust it by turning crankshaft. Check valve lashes.
d) In the same manner as b) – c), check valve lashes at valves
“4” and “6”.
e) In the same manner as b) – c) again, check valve lashes at
valves “2” and “5”.
Valve clearance specification
If valve lash is out of specification, record valve lash and adjust it
to specification by replacing shim.
REPLACEMENT OF SHIM
1) Close the valve whose shim (2) is to be replaced by turning
crankshaft, then turn tappet (3) till its cut section (1) faces
inside as shown in figure.
2) Lift down the it valve by turning crankshaft to 180°.
3) Hold tappet at that position using special tool as follows.
a) Remove its housing bolts.When cold
(Coolant temperature
is 15 – 25°C
(59 – 77°F))When hot
(Coolant temperature
is 60 – 68°C
(140 – 154°F))
Intake 0.18 – 0.22 mm
(0.007 – 0.009 in.)0.21 – 0.27 mm
(0.008 – 0.011 in.)
Exhaust 0.28 – 0.32 mm
(0.011 – 0.013 in.)0.30 – 0.36 mm
(0.012 – 0.014 in.)
Page 591 of 698
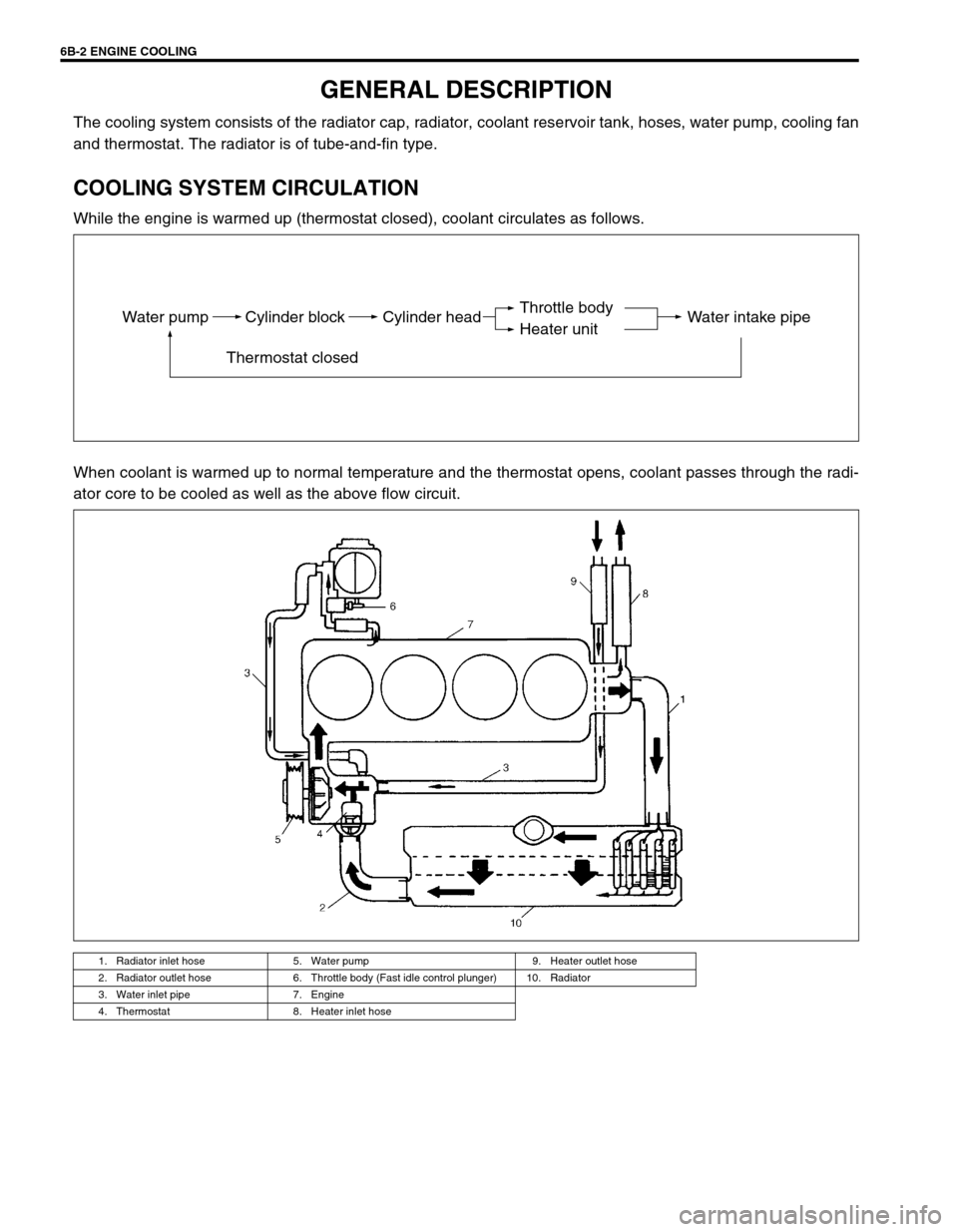
6B-2 ENGINE COOLING
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The cooling system consists of the radiator cap, radiator, coolant reservoir tank, hoses, water pump, cooling fan
and thermostat. The radiator is of tube-and-fin type.
COOLING SYSTEM CIRCULATION
While the engine is warmed up (thermostat closed), coolant circulates as follows.
When coolant is warmed up to normal temperature and the thermostat opens, coolant passes through the radi-
ator core to be cooled as well as the above flow circuit.
1. Radiator inlet hose 5. Water pump 9. Heater outlet hose
2. Radiator outlet hose 6. Throttle body (Fast idle control plunger) 10. Radiator
3. Water inlet pipe 7. Engine
4. Thermostat 8. Heater inlet hose
Water pump Cylinder block
Thermostat closedCylinder head Water intake pipeThrottle body
Heater unit
Page 592 of 698
ENGINE COOLING 6B-3
COOLANT
The coolant recovery system is standard. The coolant in the radiator expands with heat, and the overflow is col-
lected in the reservoir.
When the system cools down, the coolant is drawn back into the radiator.
The cooling system has been filled at the factory with a quality coolant that is a 50/50 mixture of water and eth-
ylene glycol antifreeze (70/30; in a market where no freezing temperature is anticipated).
This 50/50 mixture coolant solution provides freezing protection to –36°C (–33°F).
Maintain cooling system freeze protection at –36°C (–33°F) to ensure protection against corrosion and loss
of coolant from boiling. This should be done even if freezing temperatures are not expected.
Add ethylene glycol base coolant when coolant has to be added because of coolant loss or to provide added
protection against freezing at temperature lower than –36°C (–33°F).
Anti-freeze proportioning table
Coolant capacity NOTE:
Alcohol or methanol base coolant or plain water alone should not be used in cooling system at any
time as damage to cooling system could occur.
Even in a market where no freezing temperature is anticipated, mixture of 70% water and 30% ethyl-
ene glycol antifreeze (Antifreeze/Anticorrosion coolant) should be used for the purpose of corro-
sion protection and lubrication.
Freezing temperature°C–16–36
°F3–33
Anti-freeze/Anti-corrosion
coolant concentration%30 50
Ratio of compound
to cooling waterItr. 1.38/3.22 2.30/2.30
US pt. 2.92/6.80 4.86/4.86
Imp pt. 2.43/5.67 4.05/4.05
Engine radiator and heater 4.20 liters (8.87/7.39 US/lmp. pt.)
Reservoir tank 0.40 liters (0.85/0.70 US/lmp. pt.)
Total 4.60 liters (9.72/8.10 US/lmp. pt.)
Page 595 of 698

6B-6 ENGINE COOLING
MAINTENANCE
COOLANT LEVEL CHECK
To check level, lift hood and look at “see-through” coolant reser-
voir tank.
It is not necessary to remove radiator cap to check coolant level.
When engine is cool, check coolant level in reservoir tank (1).
A normal coolant level should be between FULL mark (2) and
LOW mark (3) on reservoir tank (1).
If coolant level is below LOW mark (3), remove reservoir tank cap
(4) and add proper coolant to tank to bring coolant level up to
FULL mark (2). Then, reinstall cap (4) and align match marks (5)
on tank and cap (4). WARNING:
Do not remove radiator cap to check engine coolant level; check coolant visually at the see-through
coolant reservoir.
Coolant should be added only to reservoir as necessary.
As long as there is pressure in the cooling system, the temperature can be considerably higher
than the boiling temperature of the solution in the radiator without causing the solution to boil.
Removal of the radiator cap while engine is hot and pressure is high will cause the solution to boil
instantaneously and possibly with explosive force, spewing the solution over engine, fenders and
person removing cap. If the solution contains flammable anti-freeze such as alcohol (not recom-
mended for use at any time), there is also the possibility of causing a serious fire.
WARNING:
To help avoid danger of being burned :
do not remove reservoir tank cap while coolant is boil-
ing, and
do not remove radiator cap while engine and radiator
are still hot.
Scalding fluid and steam can be blown out under pres-
sure if either cap is taken off too soon.
NOTE:
If proper quality antifreeze is used, there is no need to
add extra inhibitors or additives that claim to improve
system.
They may be harmful to proper operation of system,
and are unnecessary expense.
When installing reservoir cap, align arrow marks on
reservoir and cap.
LOW FULL
5 41
1 32 1
Page 599 of 698
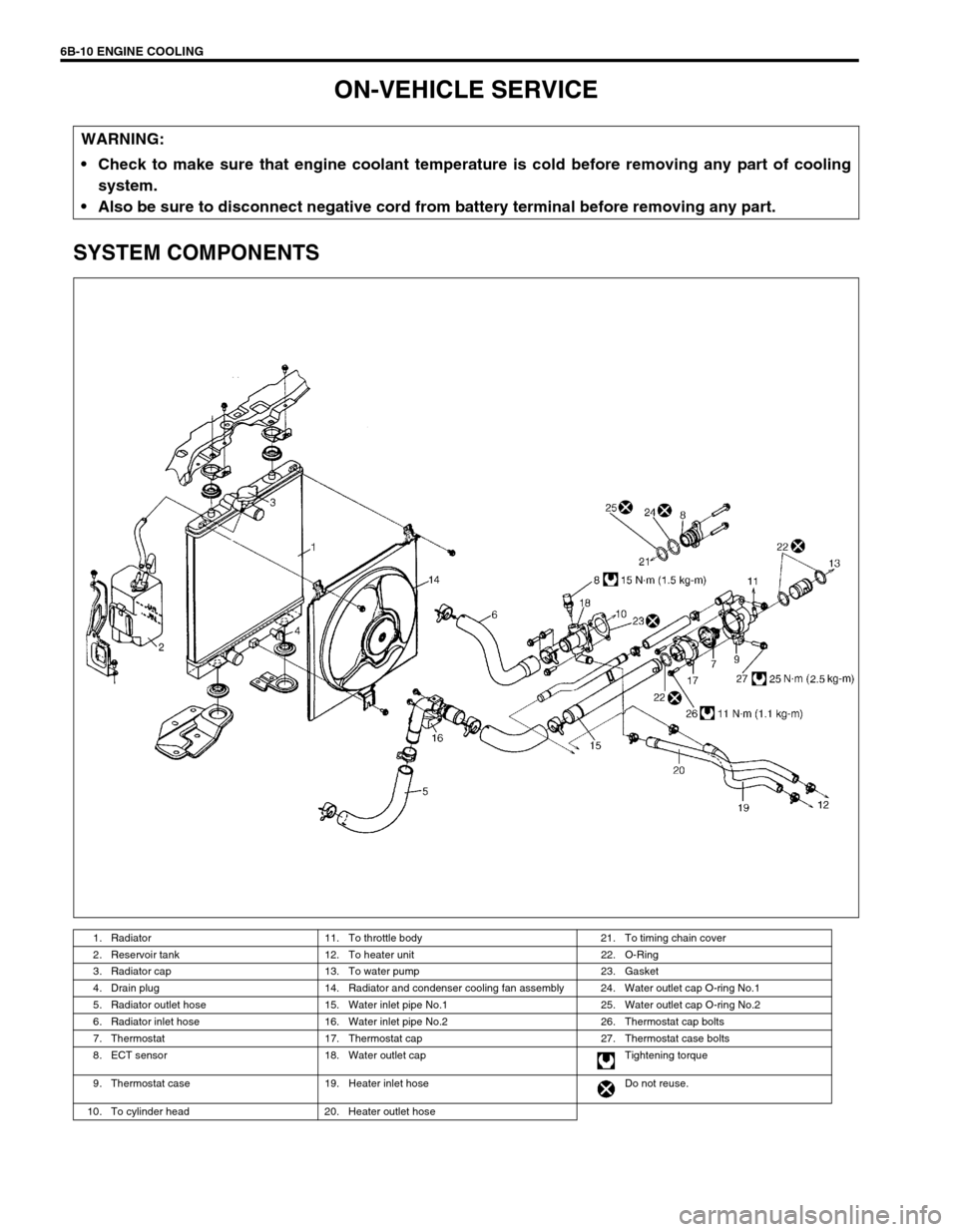
6B-10 ENGINE COOLING
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
WARNING:
Check to make sure that engine coolant temperature is cold before removing any part of cooling
system.
Also be sure to disconnect negative cord from battery terminal before removing any part.
1. Radiator 11. To throttle body 21. To timing chain cover
2. Reservoir tank 12. To heater unit 22. O-Ring
3. Radiator cap 13. To water pump 23. Gasket
4. Drain plug 14. Radiator and condenser cooling fan assembly 24. Water outlet cap O-ring No.1
5. Radiator outlet hose 15. Water inlet pipe No.1 25. Water outlet cap O-ring No.2
6. Radiator inlet hose 16. Water inlet pipe No.2 26. Thermostat cap bolts
7. Thermostat 17. Thermostat cap 27. Thermostat case bolts
8. ECT sensor 18. Water outlet cap Tightening torque
9. Thermostat case 19. Heater inlet hose Do not reuse.
10. To cylinder head 20. Heater outlet hose
Page 602 of 698

ENGINE COOLING 6B-13
Check thermostatic movement of wax pellet as follows :
a) Immerse thermostat (1) in water, and heat water gradually.
b) Check that valve starts to open at specific temperature.
Temperature at which valve begins to open
: 80 – 84°C (176 – 183°F)
Temperature at which valve become fully open
: 95 – 97°C (203°F)
Valve lift
: More than 8 mm at 95°C (203°F)
If valve starts to open at a temperature substantially below or
above specific temperature, thermostat unit should be replaced
with a new one. Such a unit, if reused, will bring about overcool-
ing or overheating tendency.
INSTALLATION
Reverse removal procedure for installation noting the following
points.
When positioning thermostat (1) on thermostat case (2), be
sure to position it so that air bleed valve (3) comes at posi-
tion as shown in figure.
Use new O-rings when installing.
Adjust water pump belt tension referring to WATER PUMP/
GENERATOR DRIVE BELT TENSION INSPECTION AND
ADJUSTMENT in this section.
Adjust A/C compressor belt tension (if equipped) referring to
Section 1B.
Refill cooling system with proper coolant referring to “COOL-
ING SYSTEM REFILL”.
Verify that there is no coolant leakage at each connection.
2. Thermometer
3. Heater