PS control module SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.G Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2008, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2008 2.GPages: 1496, PDF Size: 34.44 MB
Page 642 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5-ii Table of Contents
DTC P1878: Torque Converter Clutch Shudder .......................................................... 5A-75
DTC P2762: Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Pressure Control Sole noid Control Circuit
Range /Performance ....................................... 5A-76
DTC P2763: Torque Converter Clutch Pressure Control Sole noid Control Circuit
High ................................................................. 5A-78
DTC P2764: Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Pressure Control Sole noid Control Circuit
Low ................................................................. 5A-80
Inspection of TCM and Its Circuits .................... 5A-82
TCM Power and Ground Circuit Check ............. 5A-86
Brake Interlock System Inspection .................... 5A-87
Repair Instructions ........... .................................5A-88
Learning Control Initializat ion ............................ 5A-88
A/T Fluid Level Check ....................................... 5A-89
A/T Fluid Change .............................................. 5A-90
Select Lever Components ... .............................. 5A-90
Select Lever Assembly Removal and Installation ....................................................... 5A-90
Select Lever Knob Installa tion........................... 5A-90
Select Lever Inspection .... ................................. 5A-91
“3” Position Switch Inspec tion ........................... 5A-91
Shift Lock Solenoid Inspec tion .......................... 5A-91
Shift Lock Solenoid Replacement ..................... 5A-91
Select Cable Components ................................ 5A-92
Select Cable Removal and Installation ............. 5A-92
Select Cable Adjustment ................................... 5A-93
Key Interlock Cable Removal and Installation... 5A-93
Transmission Range Sensor (Shift Switch) Inspection and Adjustment .............................. 5A-95
Output Shaft Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 5A-96
Output Shaft Speed Sensor Inspection ............. 5A-96
Input Shaft Speed Sensor Removal and Installation ....................................................... 5A-96
Input Shaft Speed Sensor Inspection................ 5A-97
Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Removal and Installation ................................. 5A-97
Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Inspection ........................................................ 5A-98
Solenoid Valves (Shift Solenoid Valves and Timing Solenoid Valve) Removal and
Installation ....................................................... 5A-98
Solenoid Valves (Shift Solenoid Valves, and Timing Solenoid Valve) Inspection .................. 5A-99
Pressure Control Soleno id Valves (Pressure
Control Solenoid and TCC Pressure Control
Solenoid) Removal and Inst allation .............. 5A-101
Pressure Control Solenoid Valve Inspection ... 5A-101
Transmission Control Module (TCM) Removal and Installation ............................... 5A-102
A/T Relay Inspection ....................................... 5A-103
Differential Side Oil Seal Replacement ........... 5A-103
A/T Fluid Cooler Hoses Replacement ............. 5A-104
Automatic Transaxle Unit Components........... 5A-105
Automatic Transaxle Unit Dismounting and Remounting ................................................... 5A-106
Automatic Transaxle Asse mbly Components . 5A-108 Automatic Transaxle Unit
Disassembly........... 5A-110
Oil Pump Assembly Components ................... 5A-121
Oil Pump Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly .................................................. 5A-122
Oil Pump Assembly Inspection ....................... 5A-122
Direct Clutch Assembly Components.............. 5A-124
Direct Clutch Assembly Preliminary Check ..... 5A-124
Direct Clutch Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly .................................................. 5A-125
Direct Clutch Assembly Inspection.................. 5A-127
Forward and Reverse Clutch Assembly Components .................................................. 5A-128
Forward and Reverse Clutch Assembly Preliminary Check ......................................... 5A-129
Forward and Reverse Clutch Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly ...................... 5A-129
Forward and Reverse Clutch Assembly Inspection ...................................................... 5A-133
2nd Brake Piston Assembly Components ....... 5A-134
2nd Brake Piston Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly .................................................. 5A-134
Transaxle Rear Cover (O/D and 2nd Coast Brake Piston) Assembly Components........... 5A-135
Transaxle Rear Cover (O/D and 2nd Coast Brake Piston) Assembly Disassembly and
Reassembly .................................................. 5A-136
Transaxle Rear Cover (O/D and 2nd Coast Brake Piston) Assembly Inspection............... 5A-137
Countershaft Assembly Co mponents.............. 5A-138
Countershaft Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly .................................................. 5A-138
Valve Body Assembly Components ................ 5A-139
Valve Body Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly .................................................. 5A-140
Differential Assembly Components ................. 5A-141
Differential Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly .................................................. 5A-142
Differential Assembly Inspection ..................... 5A-143
Torque Converter Housing Disassembly and Reassembly .................................................. 5A-144
Transaxle Case Disassembly and Reassembly .................................................. 5A-146
Automatic Transaxle Unit Inspection and Adjus
tment .................................................... 5A-147
Automatic Transaxle Unit Assembly ............... 5A-150
Specifications .................. .................................5A-167
Tightening Torque Specifications .................... 5A-167
Special Tools and Equipmen t .........................5A-168
Recommended Service Material ..................... 5A-168
Special Tool .................................................... 5A-168
Manual Transmission/Tr ansaxle ............ 5B-1
General Description .............................................5B-1
Manual Transaxle Construction and Servicing .... 5B-1
Diagnostic Information and Procedures ............5B-3 Manual Transaxle Symptom Diagnosis............... 5B-3
Repair Instructions ............ ..................................5B-3
Manual Transaxle Oil Change............................. 5B-3
Differential Side Oil Seal Replacement ............... 5B-4
Page 645 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-1
Transmission / Transaxle
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
Precautions
Precautions in Diagnosing TroubleS7RS0B5100001
• Do not disconnect couplers from TCM, battery cable from battery, TCM ground wire harness from engine or
main fuse before checking the diagnostic information
(DTC, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in TCM memory.
Such disconnection will clea r memorized information
in TCM memory.
• Diagnostic information stored in TCM memory can be cleared as well as checked by using SUZUKI scan
tool or generic scan tool. Before using scan tool, read
its Operator’s (Instruction) Manual carefully to have
good understanding as to what functions are available
and how to use it.
It is indistinguishable wh ich module turns on MIL
because not only ECM but also TCM turns on MIL.
Therefore, check both ECM and TCM for DTC when
MIL lights on.
When checking TCM for DTC, keep in mind that DTC
is displayed on the scan tool as follows depending on
the scan tool used.
– SUZUKI scan tool displays DTC detected by TCM.
– Generic scan tool displays DTC detected by each of ECM and TCM simultaneously.
• Using SUZUKI scan tool the diagnostic information stored in TCM memory can be checked and cleared
as well. Before its use, be sure to read Operator’s
Manual supplied with it carefully to have good
understanding of its functions and usage.
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit Service in Section 00” befo re inspection and observe
what is written there.
• TCM replacement
– When substituting a known-good TCM, check that all relays and actuators have resistance of
specified value.
Neglecting this check may result in damage to good
TCM.
• Communication of ECUs , ECM, TCM, ABS control
module, keyless start control module and BCM is
established by CAN (Controller Area Network).
Therefore, handle CAN communication line with care
referring to “Precaution for CAN Communication
System in Section 00”.
Precautions for Disassembly and ReassemblyS7RS0B5100002
When repairing automatic transaxle, it is necessary to
conduct the on-vehicle test to investigate where the
cause of the trouble lies first.
Then whether overhaul should be done or not is
determined. If the transaxle is disassembled without
such preliminary procedure, not only the cause of the
trouble would be unknown, but also a secondary trouble
may occur and often time would be wasted.
As the automatic transaxle consists of high precision
component, the following cautions should be strictly
observed when handling its parts in disassembly and
reassembly.
• Disassembling valve body assembly is prohibited
essentially. However, a few parts can be
disassembled. When disassembling valve body
component parts, confirm whether their parts are
allowed to disassemble or not referring to “Valve Body
Assembly Disassembly and Reassembly”.
• When component part of forward clutch, direct clutch, 2nd brake and/or O/D and 2nd coast brake, namely
clutch disc, brake disc, retaining plate and/or
separator plate, have been replaced, all learned
contents, which have been stored in TCM memory by
executing learning control, should be initialized
referring to “Learning Control Initialization”.
• Make sure to wash dirt off from the transaxle so that no such dirt will enter the transaxle during
dismounting and remounting.
• Select a clean place free from dust and dirt for overhauling.
• Place a rubber mat on the work bench to protect parts from damage.
• Work gloves or shop cloth should not be used. (Use a nylon cloth or a paper towel.)
• When separating the case joint, do not pry with a screwdriver or such but tap with a plastic hammer
lightly.
• Make sure to wash dirt off from the transaxle so that no such dirt will enter the transaxle during
disassembly and reassembly.
• Wash the disassembled parts in ATF (Automatic Transaxle Fluid) or kerosene (using care not to allow
ATF or kerosene to get on your face, etc.) and confirm
that each fluid passage is not clogged by blowing air
into it. But use kerosene to wash the discs, resin
washers and rubber parts.
• Replace each gasket, oil seal and O-ring with a new one.
• Apply ATF to sliding or rotating parts before
reassembly.
Page 647 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-3
General Description
A/T DescriptionS7RS0B5101001
This automatic transaxle is electronic control full automatic transaxle with forward 4-speed and reverse 1-speed.
The torque converter is a 3-element, 1-step and 2-phase type and is equipped with an automatically controlled lock-up
mechanism.
The gear change device consists of a ravigneau type planet ary gear unit, 3 multiple disc type clutches, 3 multiple disc
type brakes and 2 one-way clutches.
The hydraulic pressure control device consists of a valve body assembly, pressure control solenoid valve (linear
solenoid), 2 shift solenoid va lves, TCC pressure control solenoid valve (lin ear solenoid) and a timing solenoid valve.
Optimum line pressure complying with engine torque is produced by the pressure control solenoid valve in
dependence upon control signal from transmission control module (TCM). This makes it possible to control the line
pressure with high accuracy in accordance with the engine power and running conditions to achieve smooth shifting
characteristics and high efficiency.
A clutch-to-clutch control system is prov ided for shifting between 3rd gear and 4th gear. This clutch-to-clutch control
system is made to function optimally , so that hydraulic pressure controls such as shown below are conducted.
• When upshifting from 3rd gear to 4th gear, to adjust the drain hydraulic pressure at releasing the forward clutch, a
timing solenoid valve is used to switch a hydraulic passage with an orifice to another during shifting.
• When downshifting from 4th gear to 3rd gear, to adjust the line pressure applied to the forward clutch at engaging the forward clutch, a timing solenoid valve is used to s witch a hydraulic passage with an orifice to another during
shifting.
• When upshifting from 3rd gear to 4th gear with engine throttle opened, to optimize the line pressure applied to the forward clutch at releasing the forward clutch, the learning control is processed to compensate the switching timing
of the timing solenoid at every shifting.
• When downshifting from 4th gear to 3rd gear with engine throttle opened, to optimize the line pressure applied to
the forward clutch at engaging the forw ard clutch, the learning control is processed to compensate the line pressure
at every shifting.
Employing the ravigneau type planetary gear unit and this clutch-to-clutch control system greatly simplifies the
construction to make possible a lightweight and compact transaxle.
A line pressure learning control is conducted to provide opti mum shifting time at every upshifting with engine throttle
opened. If long upshifting time is detected, the subsequent line pressure applied during upshifting is intensified. On the
contrary, if short upshifting time is detected, the subs equent line pressure applied during upshifting is weakened.
Slip controlled lock-up function
Even at a lower speed than when the TCC gets engaged completely, control over the TCC pressure control solenoid
works to cause the TCC to slip (be engaged slightly), ther eby improving the transmission efficiency. While such slip
control is being executed, the oil pressure applied to the TCC is controlled by the TCC pressure control solenoid so
that the difference between the engine speed and the input shaft speed becomes close to the specified value.
Also, during deceleration, the TCC is made to slip (be enga ged slightly) to raise the engine speed and enlarge the fuel
cut operation range so that better fuel consumption is achieved.
Due to this reason, it is absolutely necessary for the automati c transmission to use ATF suitable for slip control. Use of
any fluid other than the specified ATF may cause j uddering or some other faulty condition to occur.
Page 653 of 1496
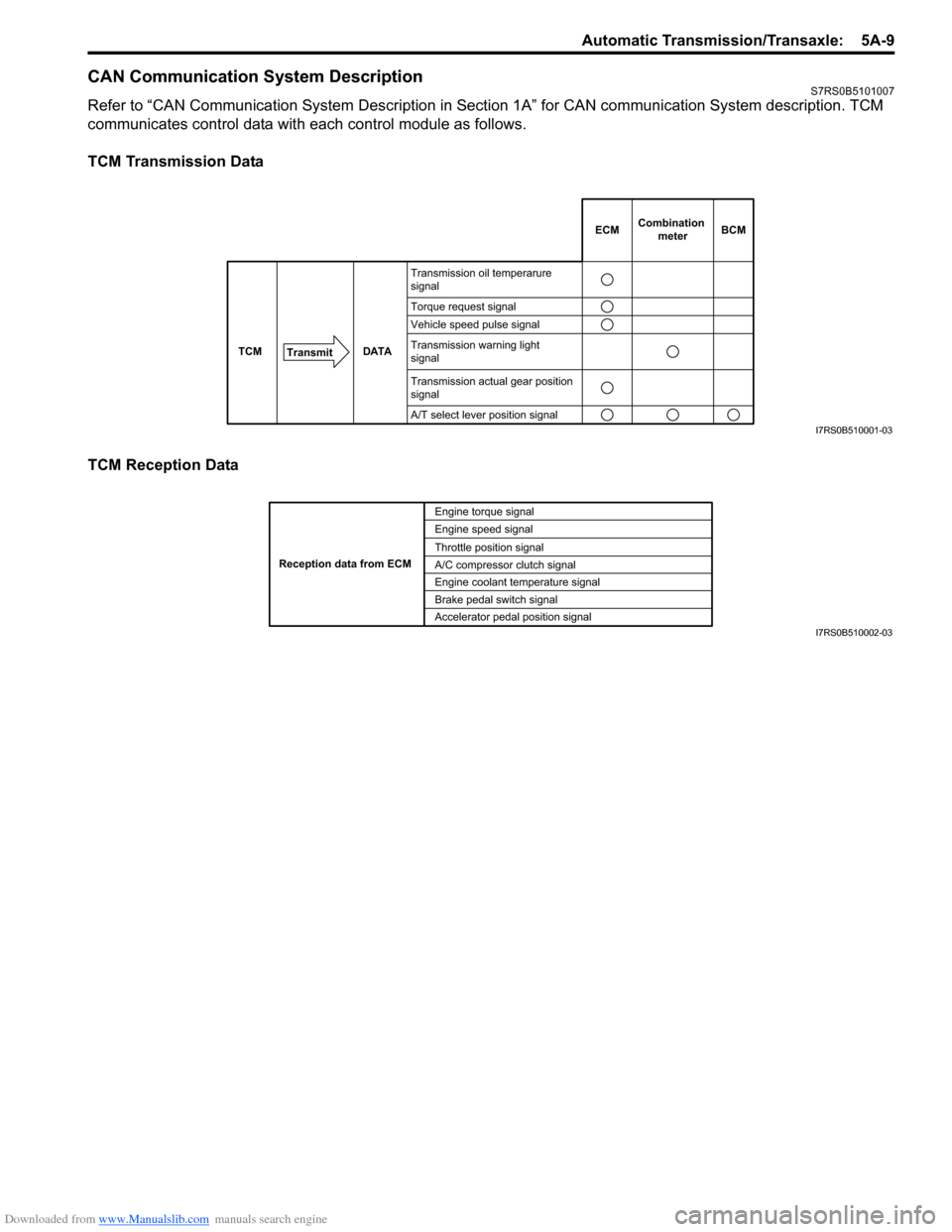
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-9
CAN Communication System DescriptionS7RS0B5101007
Refer to “CAN Communication System Description in Section 1A” for CAN communication System description. TCM
communicates control data with each control module as follows.
TCM Transmission Data
TCM Reception Data
DATA
TCM
Transmit
Transmission oil temperarure
signal
Torque request signal
Vehicle speed pulse signal
Transmission warning light
signal
Transmission actual gear position
signal
A/T select lever position signal
ECMCombination
meterBCM
I7RS0B510001-03
Engine torque signal
Engine speed signal
Throttle position signal
A/C compressor clutch signal
Engine coolant temperature signal
Brake pedal switch signal
Reception data from ECM
Accelerator pedal position signalI7RS0B510002-03
Page 654 of 1496
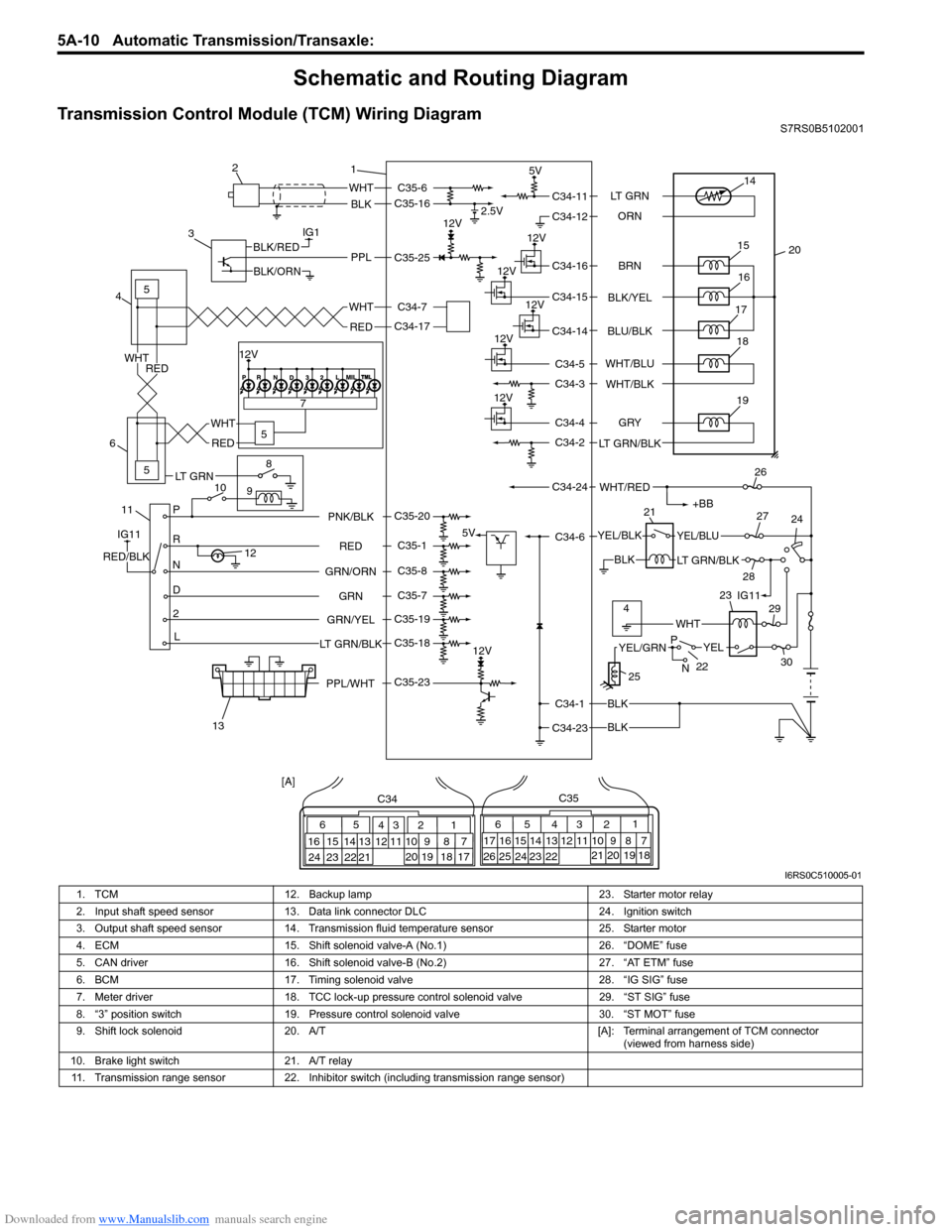
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-10 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
Schematic and Routing Diagram
Transmission Control Module (TCM) Wiring DiagramS7RS0B5102001
IG1
115
5
5
8
9
10 7
P
R
N
D
2
L
12
12V 2.5V
5V
12V
5V
12V
12V
12V
12V
WHT
BLK
BLK
BLK
BLK
PPLBLK/RED
BLK/ORN
IG11
RED/BLK
YEL/BLKYEL/BLU
LT GRN/BLK
+BB
WHT/RED
14
20
15
16
17
19
12V18
1
2
3
4
6
13 21
26
24
27
28 29
30
WHT
WHT
RED
RED
WHT
RED
65
16 15 14 13 12 11 43
24 23 2122 10 9 8 721
1920 18 17
C34
17 16
26 25
15 14
65 3
42
13 12
23 2224 11 10 9
21 20 19 87
18
1
C35
[A]
22
25
YELYEL/GRN
WHT
P
N
BRN
LT GRN
ORN
BLK/YEL
BLU/BLK
GRY
LT GRN/BLK WHT/BLU
WHT/BLK
C34-11
C34-12
C34-16
C34-15
C34-14
C34-4
C34-2
C34-1
C34-23 C34-6
C34-24 C34-5
C34-3
RED
GRN
GRN/ORN PNK/BLK
GRN/YEL
LT GRN/BLKC35-6
C35-16
C35-23 C35-25
C35-20
C35-1
C35-8
C35-7
C35-19
C35-18 C34-17 C34-7
4IG11
12V
23
PPL/WHT
LT GRN
I6RS0C510005-01
1. TCM 12. Backup lamp 23. Starter motor relay
2. Input shaft speed sensor 13. Data link connector DLC 24. Ignition switch
3. Output shaft speed sensor 14. Transmission fluid temperature sensor 25. Starter motor
4. ECM 15. Shift solenoid valve-A (No.1) 26. “DOME” fuse
5. CAN driver 16. Shift solenoid valve-B (No.2) 27. “AT ETM” fuse
6. BCM 17. Timing solenoid valve 28. “IG SIG” fuse
7. Meter driver 18. TCC lock-up pressure control solenoid valve 29. “ST SIG” fuse
8. “3” position switch 19. Pressure control solenoid valve 30. “ST MOT” fuse
9. Shift lock solenoid 20. A/T [A]: Terminal arrangement of TCM connector
(viewed from harness side)
10. Brake light switch 21. A/T relay
11. Transmission range sensor 22. Inhibitor switch (including transmission range sensor)
Page 663 of 1496
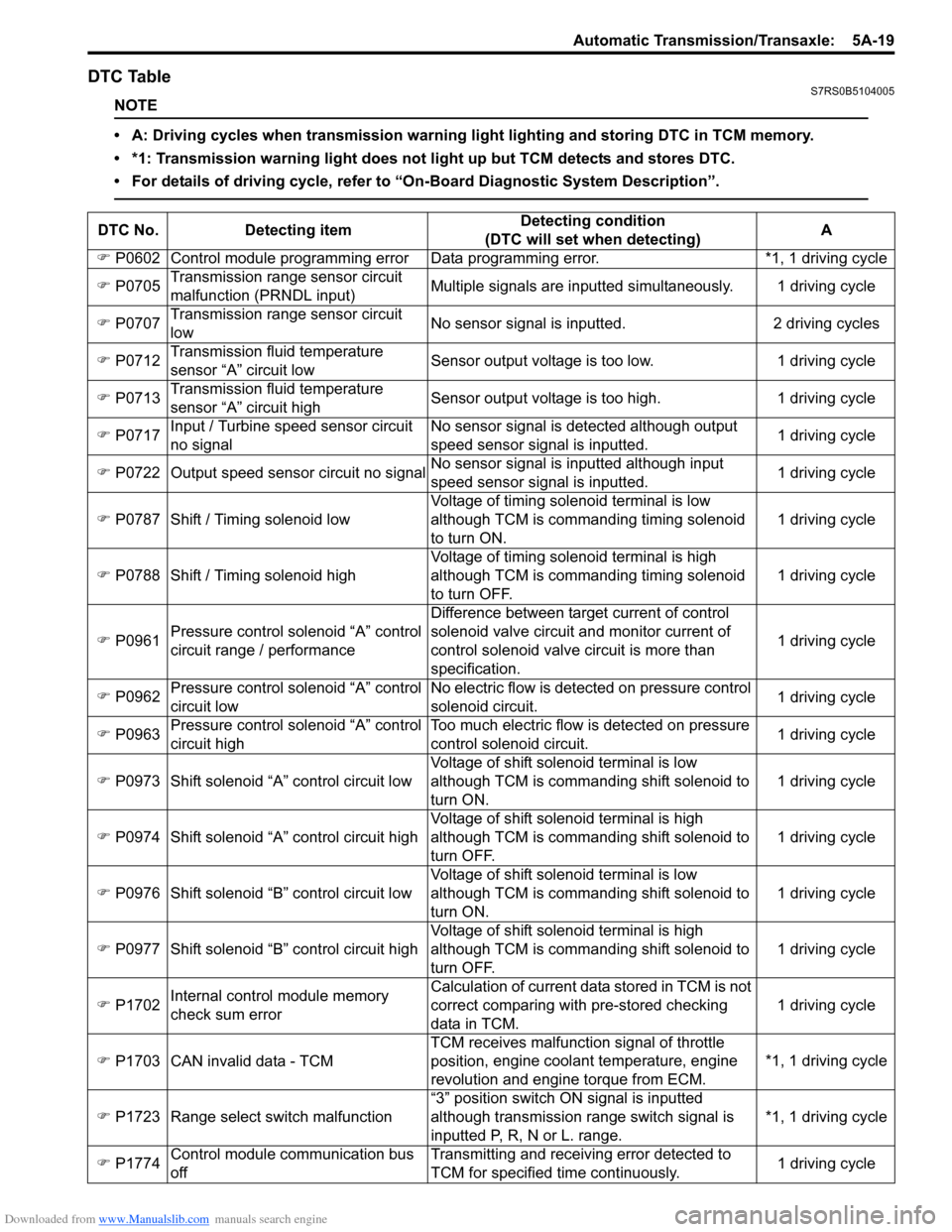
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-19
DTC TableS7RS0B5104005
NOTE
• A: Driving cycles when transmission warning light lighting and storing DTC in TCM memory.
• *1: Transmission warning light does not light up but TCM detects and stores DTC.
• For details of driving cycle, refer to “On-Board Diagnostic System Description”.
DTC No.Detecting item Detecting condition
(DTC will set when detecting) A
�) P0602 Control module programming error D ata programming error. *1, 1 driving cycle
�) P0705 Transmission range sensor circuit
malfunction (PRNDL input) Multiple signals are inputted
simultaneously. 1 driving cycle
�) P0707 Transmission range sensor circuit
low No sensor signal is inputted.
2 driving cycles
�) P0712 Transmission fluid temperature
sensor “A” circuit low Sensor output voltage is too low.
1 driving cycle
�) P0713 Transmission fluid temperature
sensor “A” circuit high Sensor output voltage is too high.
1 driving cycle
�) P0717 Input / Turbine speed sensor circuit
no signal No sensor signal is detected although output
speed sensor signal is inputted.
1 driving cycle
�) P0722 Output speed sensor circuit no signal No sensor signal is inputted although input
speed sensor signal is inputted. 1 driving cycle
�) P0787 Shift / Timing solenoid low Voltage of timing solenoid terminal is low
although TCM is commanding timing solenoid
to turn ON. 1 driving cycle
�) P0788 Shift / Timing solenoid high Voltage of timing solenoid terminal is high
although TCM is commanding timing solenoid
to turn OFF. 1 driving cycle
�) P0961 Pressure control solenoid “A” control
circuit range / performance Difference between target current of control
solenoid valve circuit and monitor current of
control solenoid valve circuit is more than
specification.
1 driving cycle
�) P0962 Pressure control solenoid “A” control
circuit low No electric flow is detected on pressure control
solenoid circuit.
1 driving cycle
�) P0963 Pressure control solenoid “A” control
circuit high Too much electric flow is detected on pressure
control solenoid circuit.
1 driving cycle
�) P0973 Shift solenoid “A” control circuit low Voltage of shift solenoid terminal is low
although TCM is commanding shift solenoid to
turn ON. 1 driving cycle
�) P0974 Shift solenoid “A” control circuit high Voltage of shift solenoid terminal is high
although TCM is commanding shift solenoid to
turn OFF. 1 driving cycle
�) P0976 Shift solenoid “B” control circuit low Voltage of shift solenoid terminal is low
although TCM is commanding shift solenoid to
turn ON. 1 driving cycle
�) P0977 Shift solenoid “B” control circuit high Voltage of shift solenoid terminal is high
although TCM is commanding shift solenoid to
turn OFF. 1 driving cycle
�) P1702 Internal control module memory
check sum error Calculation of current data stored in TCM is not
correct comparing with pre-stored checking
data in TCM.
1 driving cycle
�) P1703 CAN invalid data - TCM TCM receives malfunction signal of throttle
position
, engine coolan t temperature, engine
revolution and engine torque from ECM. *1, 1 driving cycle
�) P1723 Range select switch malfunction “3” position switch ON signal is inputted
although transmission range switch signal is
inputted P, R, N or L. range. *1, 1 driving cycle
�) P1774 Control module communication bus
off Transmitting and receiving error detected to
TCM for specified time continuously.
1 driving cycle
Page 666 of 1496
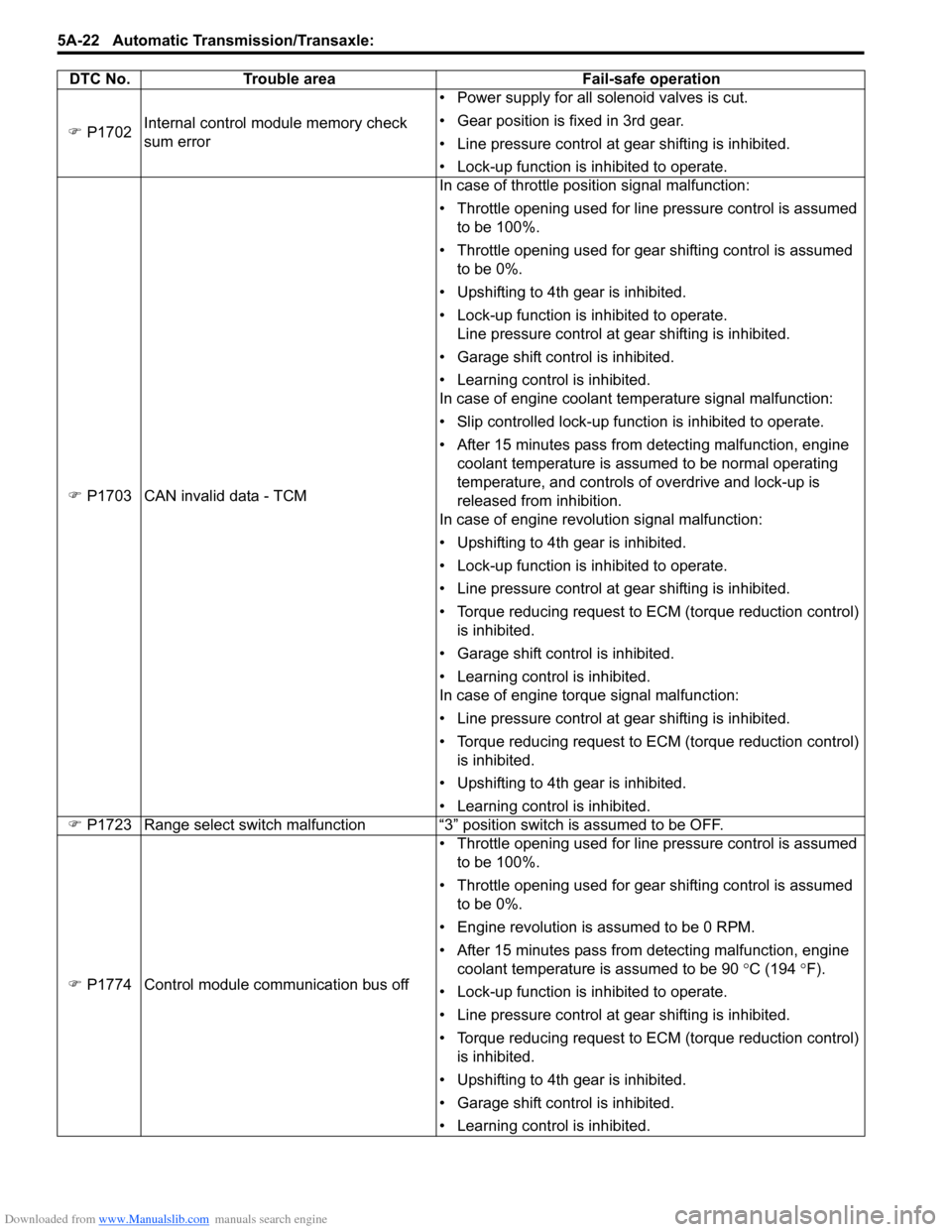
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-22 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
�) P1702 Internal control module memory check
sum error • Power supply for all solenoid valves is cut.
• Gear position is fixed in 3rd gear.
• Line pressure control at gear shifting is inhibited.
• Lock-up function is inhibited to operate.
�) P1703 CAN invalid data - TCM In case of throttle position signal malfunction:
• Throttle opening used for line pressure control is assumed
to be 100%.
• Throttle opening used for gear shifting control is assumed to be 0%.
• Upshifting to 4th gear is inhibited.
• Lock-up function is inhibited to operate. Line pressure control at gear shifting is inhibited.
• Garage shift control is inhibited.
• Learning control is inhibited.
In case of engine coolant temperature signal malfunction:
• Slip controlled lock-up function is inhibited to operate.
• After 15 minutes pass from detecting malfunction, engine coolant temperature is assumed to be normal operating
temperature, and controls of overdrive and lock-up is
released from inhibition.
In case of engine revolution signal malfunction:
• Upshifting to 4th gear is inhibited.
• Lock-up function is inhibited to operate.
• Line pressure control at gear shifting is inhibited.
• Torque reducing request to ECM (torque reduction control) is inhibited.
• Garage shift control is inhibited.
• Learning control is inhibited.
In case of engine torque signal malfunction:
• Line pressure control at gear shifting is inhibited.
• Torque reducing request to ECM (torque reduction control) is inhibited.
• Upshifting to 4th gear is inhibited.
• Learning control is inhibited.
�) P1723 Range select switch malfunction “3” position switch is assumed to be OFF.
�) P1774 Control module communication bus off • Throttle opening used for line pressure control is assumed
to be 100%.
• Throttle opening used for gear shifting control is assumed to be 0%.
• Engine revolution is assumed to be 0 RPM.
• After 15 minutes pass from detecting malfunction, engine coolant temperature is assumed to be 90 °C (194 °F).
• Lock-up function is inhibited to operate.
• Line pressure control at gear shifting is inhibited.
• Torque reducing request to ECM (torque reduction control) is inhibited.
• Upshifting to 4th gear is inhibited.
• Garage shift control is inhibited.
• Learning control is inhibited.
DTC No. Trouble area Fail-safe operation
Page 688 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-44 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
DTC P0602: Control Module Programming ErrorS7RS0B5104048
System Description
Internal control module is installed in ECM.
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure 1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Clear DTC, pending DTC and freeze frame data by using scan tool.
3) Start engine and run it at idle if possible.
4) Check DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting
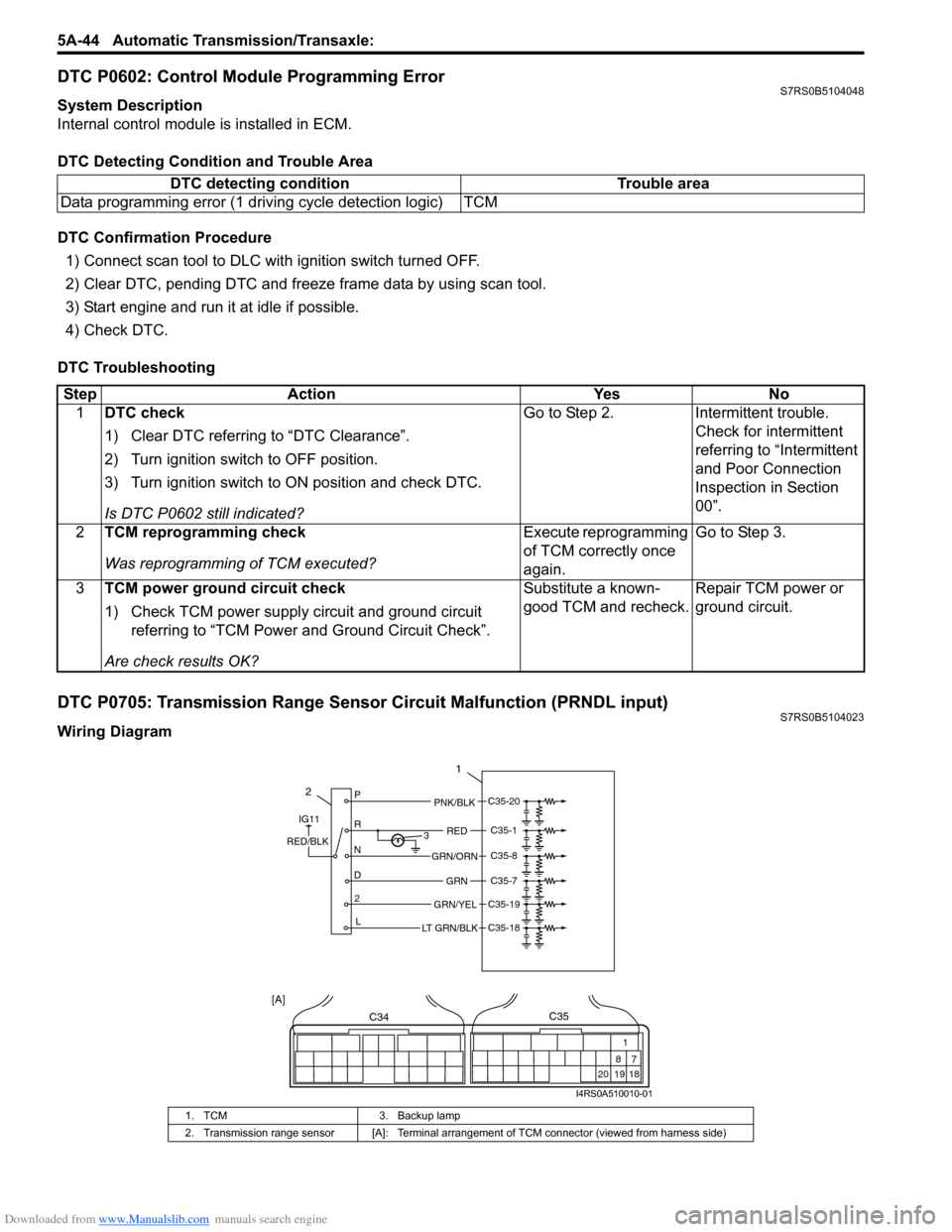
DTC P0705: Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Malfunction (PRNDL input)S7RS0B5104023
Wiring DiagramDTC detecting condition Trouble area
Data programming error (1 driving cycle detection logic) TCM
Step Action YesNo
1 DTC check
1) Clear DTC referring to “DTC Clearance”.
2) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
3) Turn ignition switch to ON position and check DTC.
Is DTC P0602 still indicated? Go to Step 2.
Intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection
Inspection in Section
00”.
2 TCM reprogramming check
Was reprogramming of TCM executed? Execute reprogramming
of TCM correctly once
again.Go to Step 3.
3 TCM power ground circuit check
1) Check TCM power supply circuit and ground circuit
referring to “TCM Power and Ground Circuit Check”.
Are check results OK? Substitute a known-
good TCM and recheck.
Repair TCM power or
ground circuit.
1. TCM
3. Backup lamp
2. Transmission range sensor [A]: Terminal arrangem ent of TCM connector (viewed from harness side)
2P
R
N
D 2 L 3
1
PNK/BLK
RED
GRN
GRN/ORN
GRN/YEL
IG11
RED/BLK
LT GRN/BLK
C35-20
C35-1
C35-8
C35-7
C35-19
C35-18
C34
20 19
87
18
1
C35
[A]
I4RS0A510010-01
Page 712 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5A-68 Automatic Transmission/Transaxle:
DTC P1702: Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum ErrorS7RS0B5104035
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
DTC Confirmation Procedure
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC in TCM memory.
3) After 10 seconds passed from turning ignition switch ON, check DTC.
DTC Troubleshooting
DTC P1703: Can Invalid Data - TCMS7RS0B5104036
DTC Detecting Condition and Trouble Area
When abnormality either on the gear shift control signal from ECM is detected by TCM, TCM sets DTC P1703.
DTC Troubleshooting DTC detecting condition Trouble area
Calculation of current data stored in TCM is not correct comparing with
pre-stored checking data in TCM. TCM
Step
Action YesNo
1 Is DTC P1702 detected after performing “DTC Confirmation
Procedure”? Faulty TCM.
Replace TCM.Could be a temporary
malfunction of TCM.
Step
Action YesNo
1 Was “A/T System Check” performed? Go to Step 2.Go to “A/T System
Check”.
2 DTC check
1) Check DTC of ECM referring to “DTC Check in Section
1A”.
Is there any DTC(s)? Go to applicable DTC
diag. flow.
Substitute a known-
good TCM and recheck.
If OK, substitute a
known-good ECM and
recheck.
Page 713 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Automatic Transmission/Transaxle: 5A-69
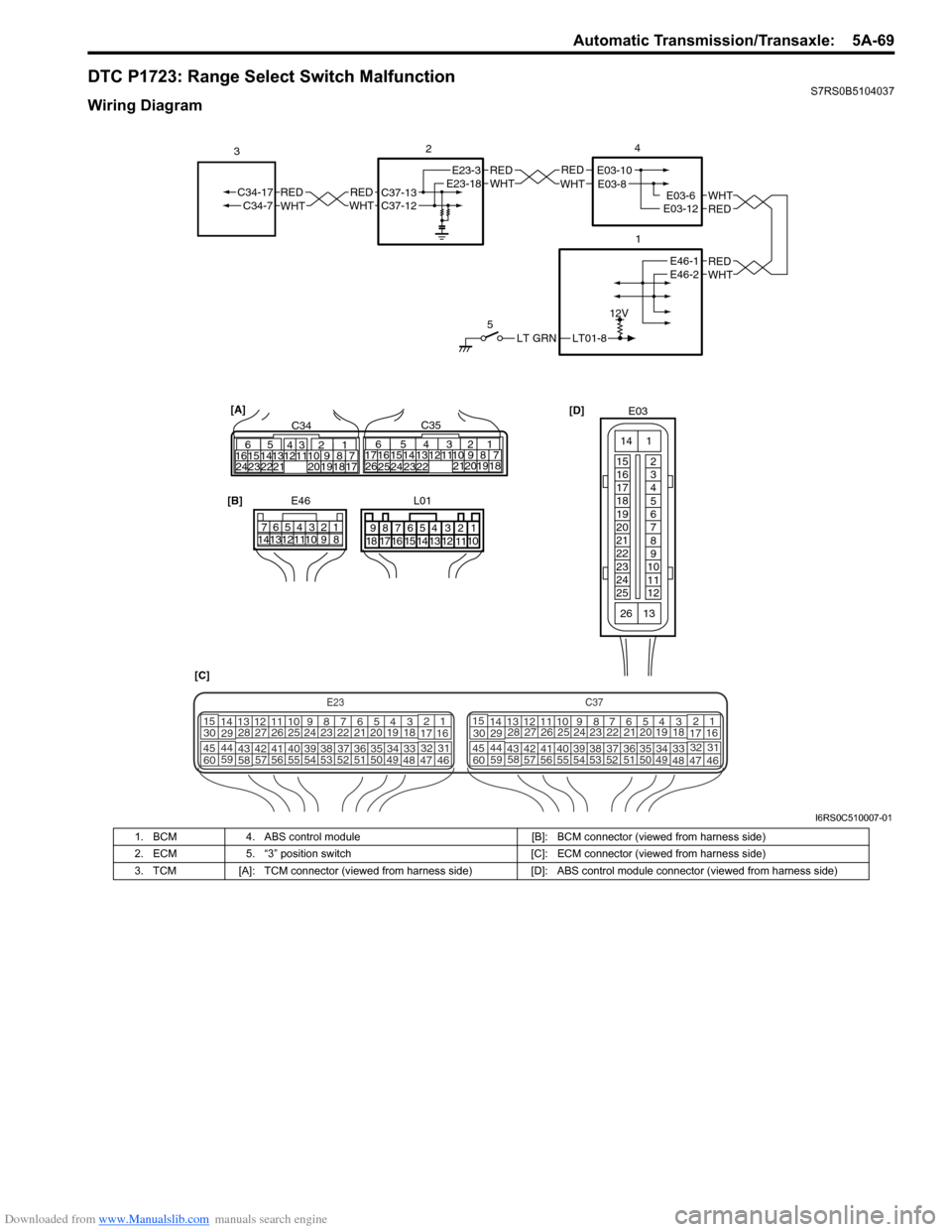
DTC P1723: Range Select Switch MalfunctionS7RS0B5104037
Wiring Diagram
LT01-8
12V
LT GRN
5
REDWHTE03-6E03-12
1
2
REDWHT
4
[D]
[C] [B]
E46
1234567
891011121314
REDWHTC37-13C37-12REDWHTC34-17C34-7
3
32
1110 9
212019 87
18
165
1615 14131211 43
2423 2122 10 9 8 7
21
1920 1817
C3417 16
26 2515 14
654
13 12
23 2224 C35
[A]
E23-3E23-18REDWHTE03-10E03-8
REDWHTE46-1E46-2
E03
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1
13
14
26
E23C37
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
5557 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
4042 39 38
44
45 43 41 33 1
1213
238
34
1819
567
1011
17
20
47 46
495051
2122
52 16
25 9
24
14
29
5557 54 53
59
60 58 2
262728
15
30
56 4832 31
34353637
4042 39 38
44
45 43 41 331
1213
238
L01
678
9 54321
15161718 14 13 12 1110
I6RS0C510007-01
1. BCM
4. ABS control module [B]: BCM connector (viewed from harness side)
2. ECM 5. “3” position switch [C]: ECM connector (viewed from harness side)
3. TCM [A]: TCM connector (viewed from harness side) [D]: ABS control module connector (viewed from harness side)