oil pressure TOYOTA RAV4 2006 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAV4, Model: TOYOTA RAV4 2006Pages: 2000, PDF Size: 45.84 MB
Page 82 of 2000

ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
285EG24
Timing Chain Cover
Oil Pump
Housing
Oil Pump Rotors
(Cycloid Rotor)Crankshaft
To Cylinder
Block
From Oil
Filter
To
Oil FilterFrom
Oil Strainer
Oil passage in the oil pump
285EG25
Oil Jet Cross Section
Oil JetsCheck
Va l v eEngine Oil EG-86
2. Oil Pump
A compact cycloid rotor type oil pump directly driven by the crankshaft is used.
This oil pump has used an internal relief method which circulates relief oil to the suction passage in the
oil pump. This aims to minimize oil level change in the oil pan, reduce friction, and reduce air mixing rate
in the oil.
3. Oil Jet
Oil jets for cooling and lubricating the pistons have been provided in the cylinder block, in the center of
the right and left banks.
These oil jets contain a check valve to prevent oil from being fed when the oil pressure is low. This prevents
the overall oil pressure in the engine from dropping.
Page 102 of 2000
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
01MEG29Y
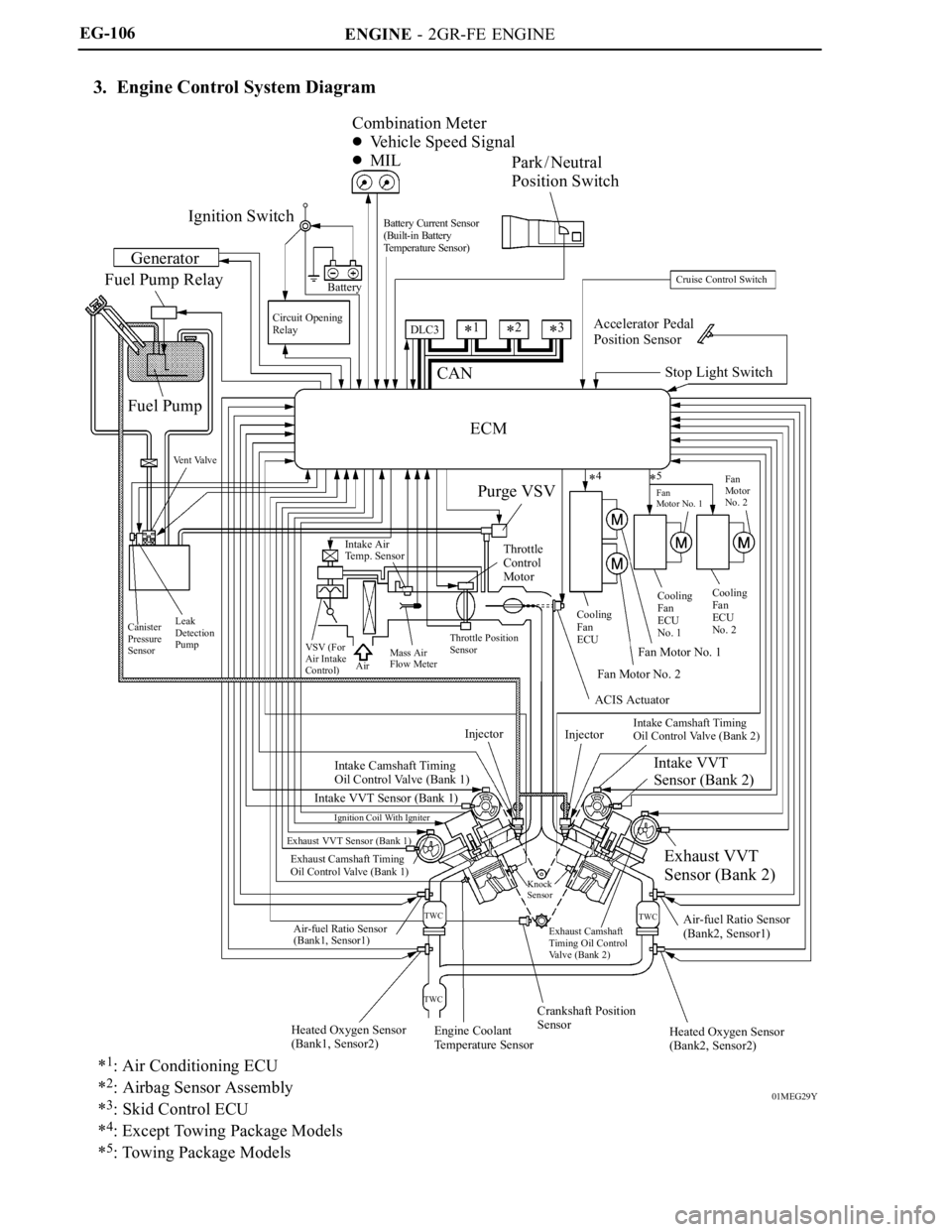
Ignition SwitchCombination Meter
Vehicle Speed Signal
MIL
Battery Current Sensor
(Built-in Battery
Temperature Sensor)
Park / Neutral
Position Switch
Battery
Generator
Fuel Pump Relay
Fuel Pump
Vent Valve
Circuit Opening
RelayDLC3*1*2*3
CAN
ECM
Cruise Control Switch
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Stop Light Switch
Canister
Pressure
SensorLeak
Detection
Pump
Intake Air
Temp. Sensor
VSV (For
Air Intake
Control)Mass Air
Flow Meter
AirThrottle Position
Sensor
Purge VSV
Throttle
Control
Motor
*4*5
Fan
Motor No. 1Fan
Motor
No. 2
Cooling
Fan
ECUCooling
Fan
ECU
No. 1Cooling
Fan
ECU
No. 2
Fan Motor No. 1
Fan Motor No. 2
ACIS Actuator
Intake Camshaft Timing
Oil Control Valve (Bank 2)Injector Injector
Intake Camshaft Timing
Oil Control Valve (Bank 1)
Intake VVT Sensor (Bank 1)
Ignition Coil With Igniter
Exhaust VVT Sensor (Bank 1)
Exhaust Camshaft Timing
Oil Control Valve (Bank 1)
Air-fuel Ratio Sensor
(Bank1, Sensor1)
TWC
Knock
Sensor
Intake VVT
Sensor (Bank 2)
Exhaust VVT
Sensor (Bank 2)
Air-fuel Ratio Sensor
(Bank2, Sensor1)Exhaust Camshaft
Timing Oil Control
Valve (Bank 2)
Crankshaft Position
Sensor
Engine Coolant
Temperature Sensor Heated Oxygen Sensor
(Bank1, Sensor2)Heated Oxygen Sensor
(Bank2, Sensor2)TWCTWC
EG-106
3. Engine Control System Diagram
*1: Air Conditioning ECU
*
2: Airbag Sensor Assembly
*
3: Skid Control ECU
*
4: Except Towing Package Models
*
5: Towing Package Models
Page 118 of 2000
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
271EG93
Timing RotorHousingLock PinSprocket
Intake Camshaft
Vane (Fixed on Intake Camshaft)
Oil Pressure
In Operation At a Stop
Lock Pin
281EG47
Housing
Advanced Angle Assist SpringVane (Fixed on Exhaust Camshaft)Lock PinExhaust Camshaft Sprocket EG-122
Construction
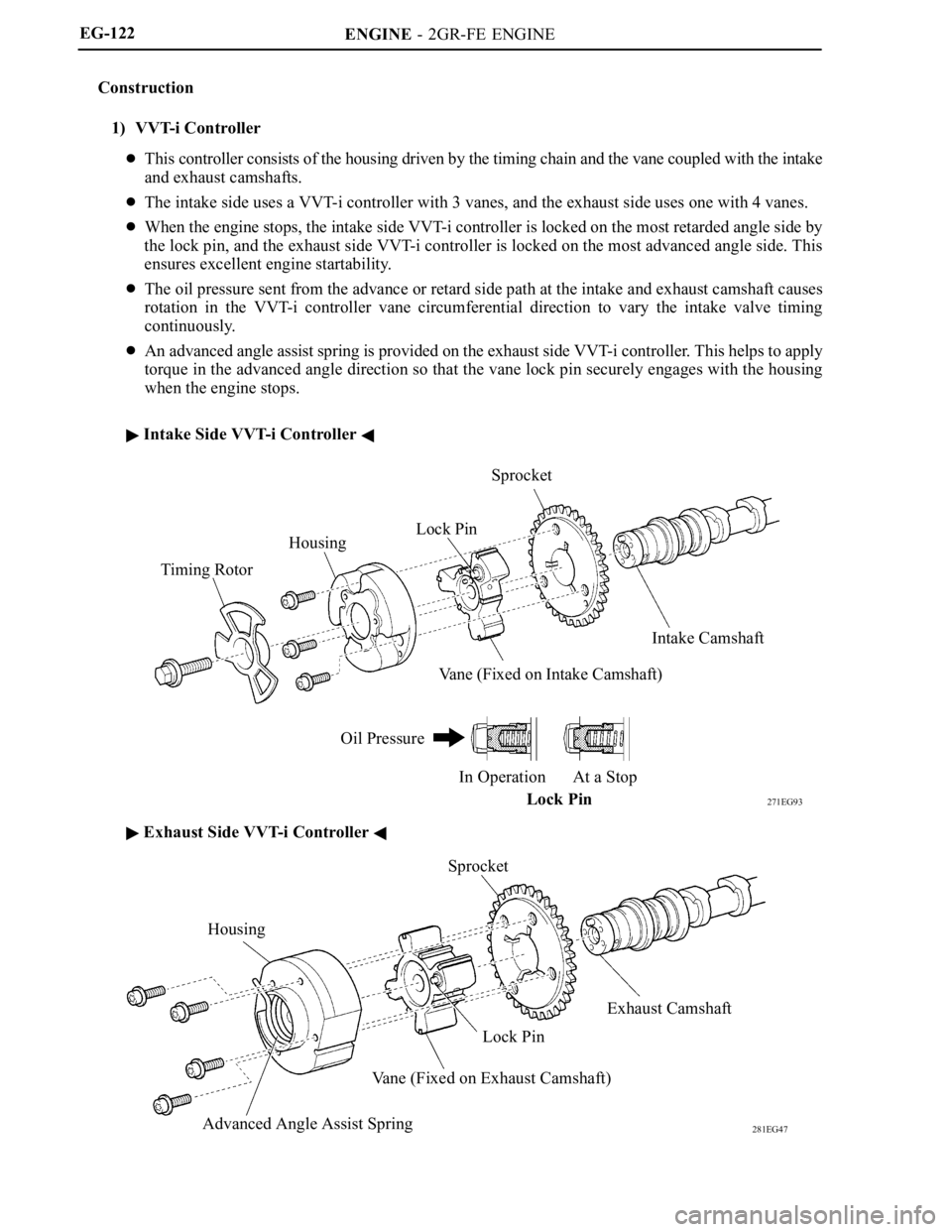
1) VVT-i Controller
This controller consists of the housing driven by the timing chain and the vane coupled with the intake
and exhaust camshafts.
The intake side uses a VVT-i controller with 3 vanes, and the exhaust side uses one with 4 vanes.
When the engine stops, the intake side VVT-i controller is locked on the most retarded angle side by
the lock pin, and the exhaust side VVT-i controller is locked on the most advanced angle side. This
ensures excellent engine startability.
The oil pressure sent from the advance or retard side path at the intake and exhaust camshaft causes
rotation in the VVT-i controller vane circumferential direction to vary the intake valve timing
continuously.
An advanced angle assist spring is provided on the exhaust side VVT-i controller. This helps to apply
torque in the advanced angle direction so that the vane lock pin securely engages with the housing
when the engine stops.
Intake Side VVT-i Controller
Exhaust Side VVT-i Controller
Page 119 of 2000
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
238EG62
To VVT-i Controller
(Advance Side) *To VVT-i Controller
(Retard Side) *
Sleeve
Spring
Drain
Oil PressureDrain
Spool ValveCoil
PlungerEG-123
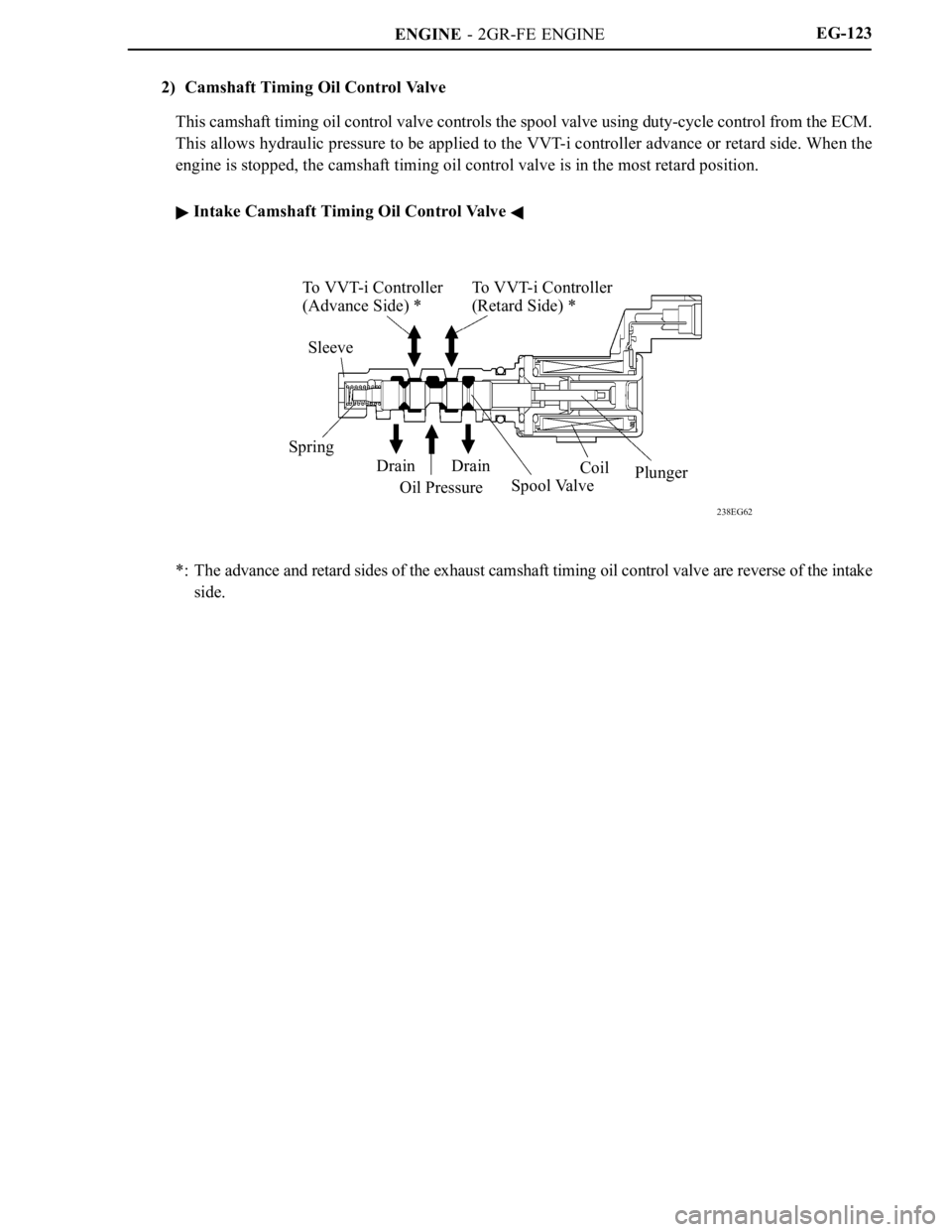
2) Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve
This camshaft timing oil control valve controls the spool valve using duty-cycle control from the ECM.
This allows hydraulic pressure to be applied to the VVT-i controller advance or retard side. When the
engine is stopped, the camshaft timing oil control valve is in the most retard position.
Intake Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve
*: The advance and retard sides of the exhaust camshaft timing oil control valve are reverse of the intake
side.
Page 120 of 2000
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
238EG63
Va n e
Rotational Direction
Oil Pressure
IN DrainECM
281EG48
Va n e
Rotational DirectionECM
Oil Pressure
IN Drain EG-124
Operation
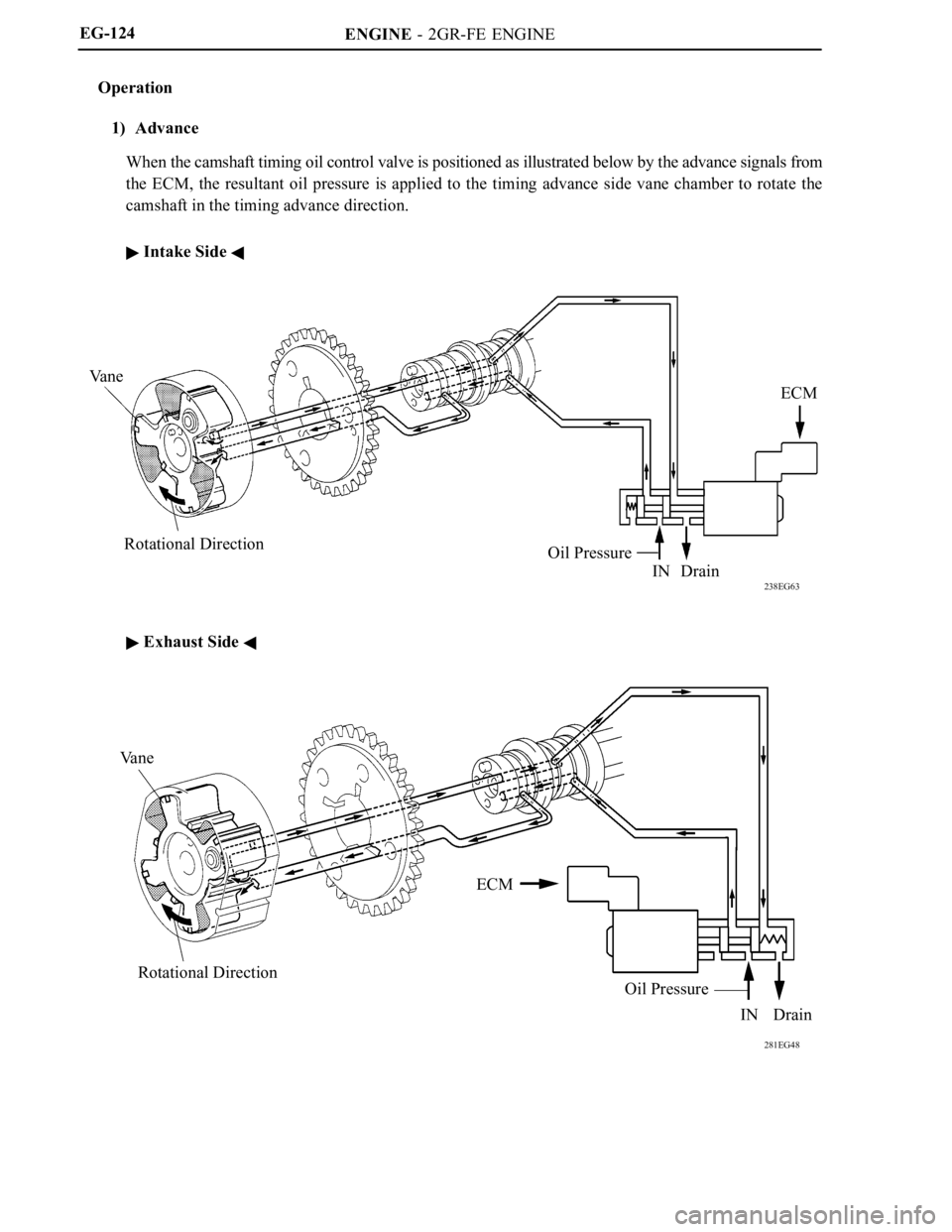
1) Advance
When the camshaft timing oil control valve is positioned as illustrated below by the advance signals from
the ECM, the resultant oil pressure is applied to the timing advance side vane chamber to rotate the
camshaft in the timing advance direction.
Intake Side
Exhaust Side
Page 121 of 2000
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
238EG64
Rotational Direction
Va n e
Drain INOil PressureECM
281EG49
Rotational Direction
Va n eECM
Drain INOil Pressure
EG-125
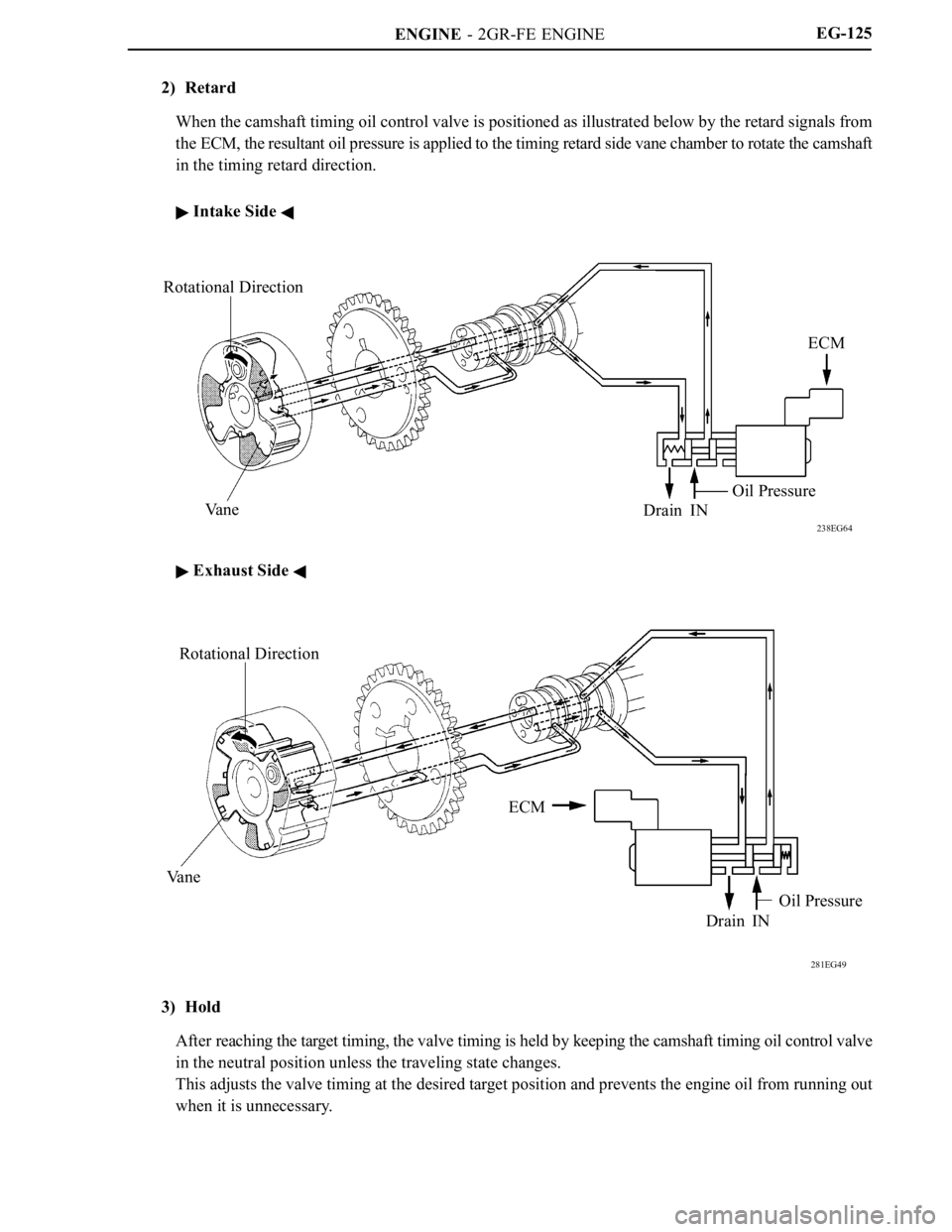
2) Retard
When the camshaft timing oil control valve is positioned as illustrated below by the retard signals from
the ECM, the resultant oil pressure is applied to the timing retard side vane chamber to rotate the camshaft
in the timing retard direction.
Intake Side
Exhaust Side
3) Hold
After reaching the target timing, the valve timing is held by keeping the camshaft timing oil control valve
in the neutral position unless the traveling state changes.
This adjusts the valve timing at the desired target position and prevents the engine oil from running out
when it is unnecessary.
Page 196 of 2000
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE ASSEMBLYEM–21
EM
REMOVAL
1. DISCHARGE REFRIGERANT FROM
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM (See page AC-172)
2. DISCHARGE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE (See page
FU-13)
3. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE BATTERY
TERMINAL
CAUTION:
Wait at least 90 seconds after disconnecting the
cable from the negative (-) battery terminal to
prevent airbag and seat belt pretensioner activation.
4. REMOVE NO. 1 ENGINE UNDER COVER
(a) Remove the 4 bolts, 12 clips and under cover.
5. REMOVE REAR ENGINE UNDER COVER RH
(a) Remove the 2 clips and under cover.
6. REMOVE REAR ENGINE UNDER COVER LH
(a) Remove the 2 clips and under cover.
7. REMOVE NO. 2 ENGINE UNDER COVER
(a) Remove the 2 clips and under cover.
8. REMOVE FRONT FLOOR COVER (See page FU-34)
9. DRAIN ENGINE COOLANT (See page CO-8)
10. DRAIN ENGINE OIL (See page LU-4)
11. DRAIN AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID
(a) 2WD:
Drain automatic transaxle fluid (see page AX-172).
(b) 4WD:
Drain automatic transaxle fluid (see page AX-173)
12. DRAIN TRANSFER OIL (for 4WD)
13. REMOVE HOOD SUB-ASSEMBLY (See page ED-4)
14. REMOVE V-BANK COVER SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Detach the 3 clips and remove the V-bank cover.
A137900
Page 205 of 2000
EM–302GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE ASSEMBLY
EM
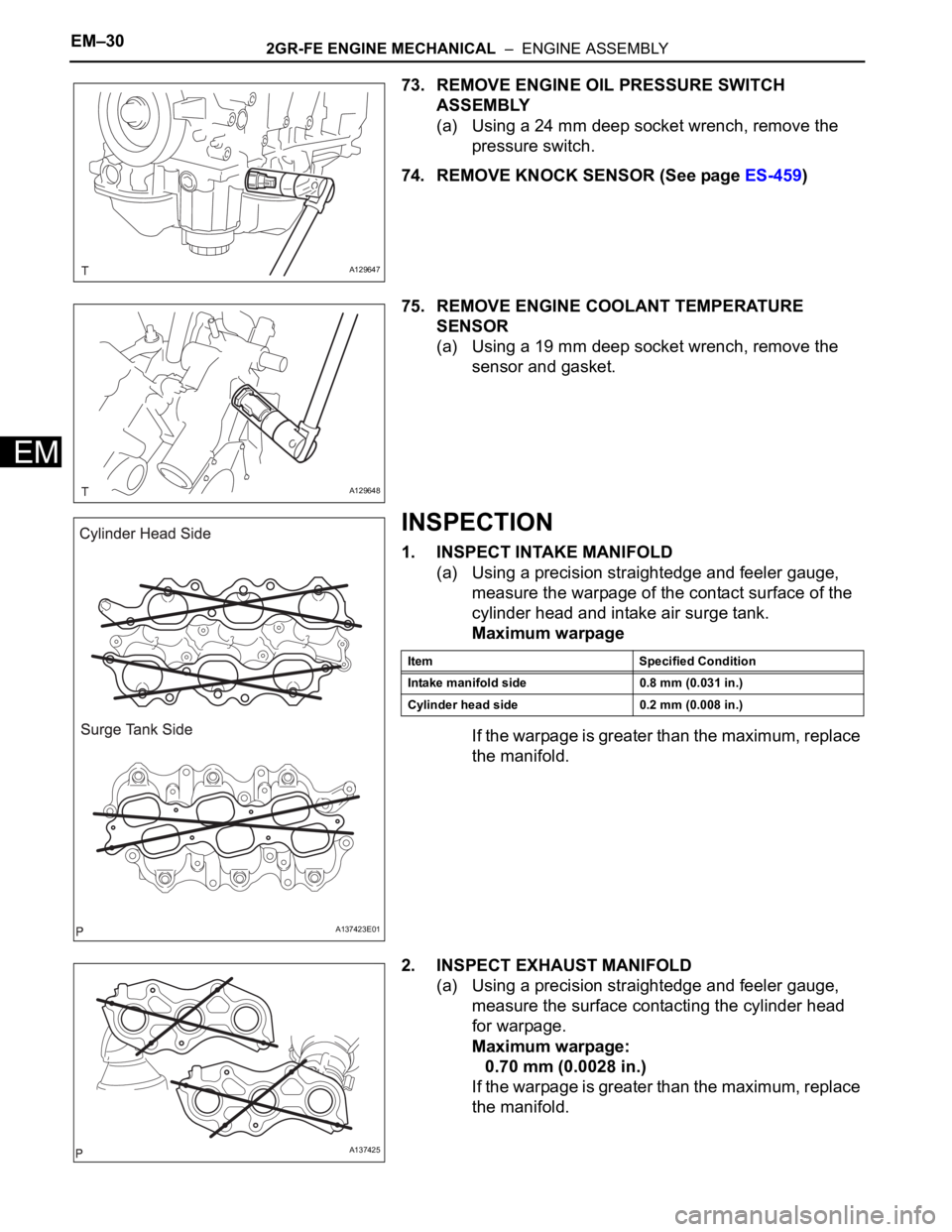
73. REMOVE ENGINE OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
ASSEMBLY
(a) Using a 24 mm deep socket wrench, remove the
pressure switch.
74. REMOVE KNOCK SENSOR (See page ES-459)
75. REMOVE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
(a) Using a 19 mm deep socket wrench, remove the
sensor and gasket.
INSPECTION
1. INSPECT INTAKE MANIFOLD
(a) Using a precision straightedge and feeler gauge,
measure the warpage of the contact surface of the
cylinder head and intake air surge tank.
Maximum warpage
If the warpage is greater than the maximum, replace
the manifold.
2. INSPECT EXHAUST MANIFOLD
(a) Using a precision straightedge and feeler gauge,
measure the surface contacting the cylinder head
for warpage.
Maximum warpage:
0.70 mm (0.0028 in.)
If the warpage is greater than the maximum, replace
the manifold.
A129647
A129648
A137423E01
Item Specified Condition
Intake manifold side 0.8 mm (0.031 in.)
Cylinder head side 0.2 mm (0.008 in.)
A137425
Page 227 of 2000
2AZ-FE EMISSION CONTROL – EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMEC–7
EC
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
1. CHECK FUEL CUT RPM
(a) Increase the engine speed to at least 3,500 rpm.
(b) Use a sound scope to check for injector operating
noise.
(c) Check that the operating sounds stop momentarily
and then resume when the throttle lever is released.
HINT:
Measure with the A/C OFF.
Fuel return rpm:
1,400 rpm
2. CHECK FOR LEAKS
(a) Visually check that the hoses, connections and
gaskets have no cracks, leaks or damage.
NOTICE:
• Detachment or other problems with the
engine oil dipstick, filler cap, PCV hose and
other components may cause the engine to
run improperly.
• Disconnection, looseness or cracks in the
parts of the air induction system between the
throttle body and cylinder head will allow air
suction and cause an engine failure or engine
malfunctions.
If the result is not as specified, replace parts as
necessary.
3. CHECK LINE AND CONNECTORS
(a) Visually check for loose connections, sharp bends
or damage.
4. CHECK FUEL TANK ASSEMBLY
(a) Visually check for deformation, cracks or fuel
leakage.
5. CHECK FUEL TANK AND VENT LINE
(a) Disconnect the vent line tube from the canister.
(b) Connect a pressure gauge to the vent line tube.
A124804E01
B011449E01
A127736E01
Page 247 of 2000
LU–122GR-FE LUBRICATION – OIL PUMP
LU
REMOVAL
1. DISCHARGE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE (See page
FU-9)
2. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE BATTERY
TERMINAL
CAUTION:
Wait at least 90 seconds after disconnecting the
cable from the negative (-) battery terminal to
prevent airbag and seat belt pretensioner activation.
3. REMOVE ENGINE ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the engine from the vehicle (see page EM-
21).
4. INSTALL ENGINE TO STAND
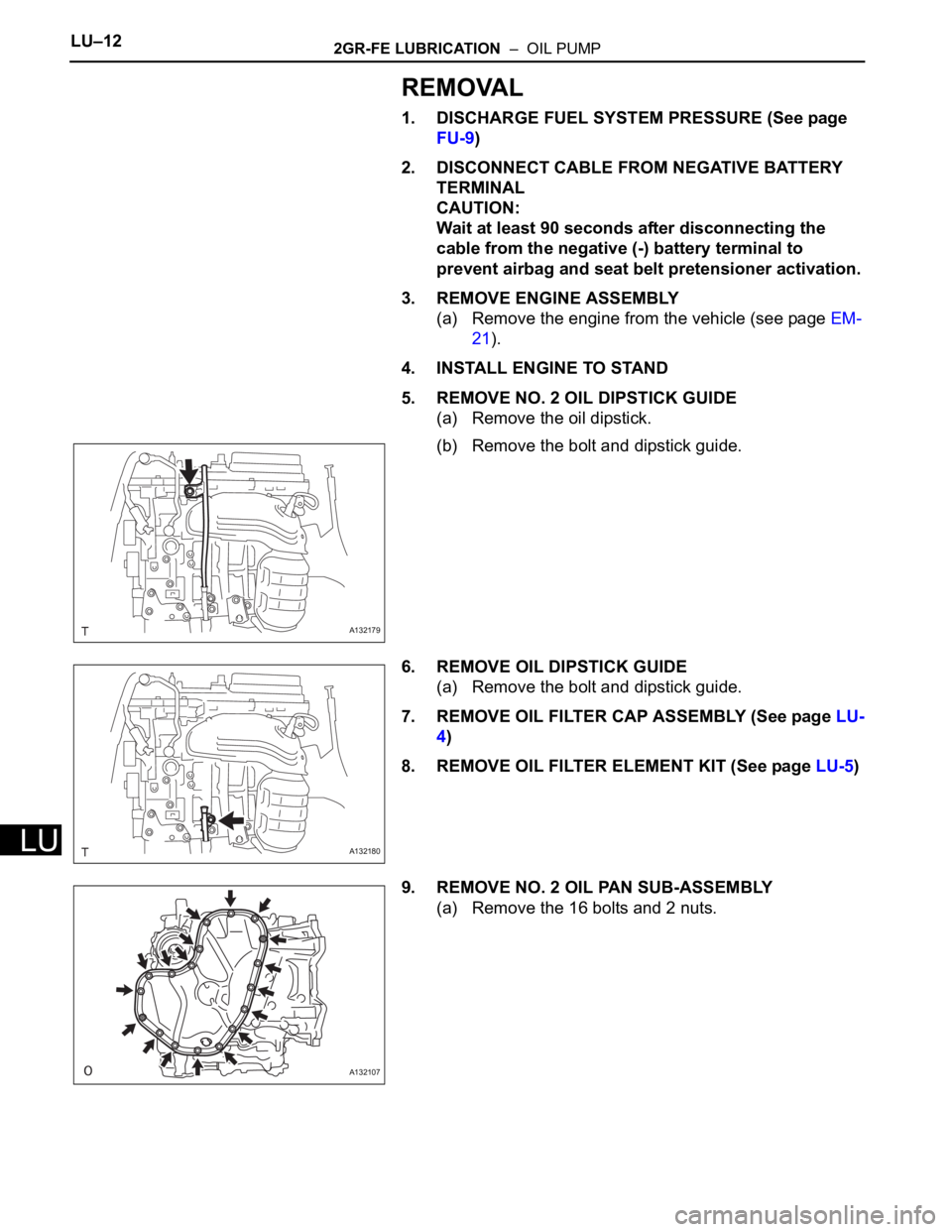
5. REMOVE NO. 2 OIL DIPSTICK GUIDE
(a) Remove the oil dipstick.
(b) Remove the bolt and dipstick guide.
6. REMOVE OIL DIPSTICK GUIDE
(a) Remove the bolt and dipstick guide.
7. REMOVE OIL FILTER CAP ASSEMBLY (See page LU-
4)
8. REMOVE OIL FILTER ELEMENT KIT (See page LU-5)
9. REMOVE NO. 2 OIL PAN SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the 16 bolts and 2 nuts.
A132179
A132180
A132107