engine TOYOTA RAV4 2006 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAV4, Model: TOYOTA RAV4 2006Pages: 2000, PDF Size: 45.84 MB
Page 716 of 2000
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNITEM–79
EM
(h) Check for smooth rotation.
(1) Turn the camshaft timing gear within its
movable range (21
) 2 or 3 times, but do not
turn it to the most retarded position. Make sure
that the gear turns smoothly.
NOTICE:
Do not use air pressure to perform the
smooth rotation check.
(i) Check the lock in the most retarded position.
(1) Confirm that the camshaft timing gear is locked
at the most retarded position.
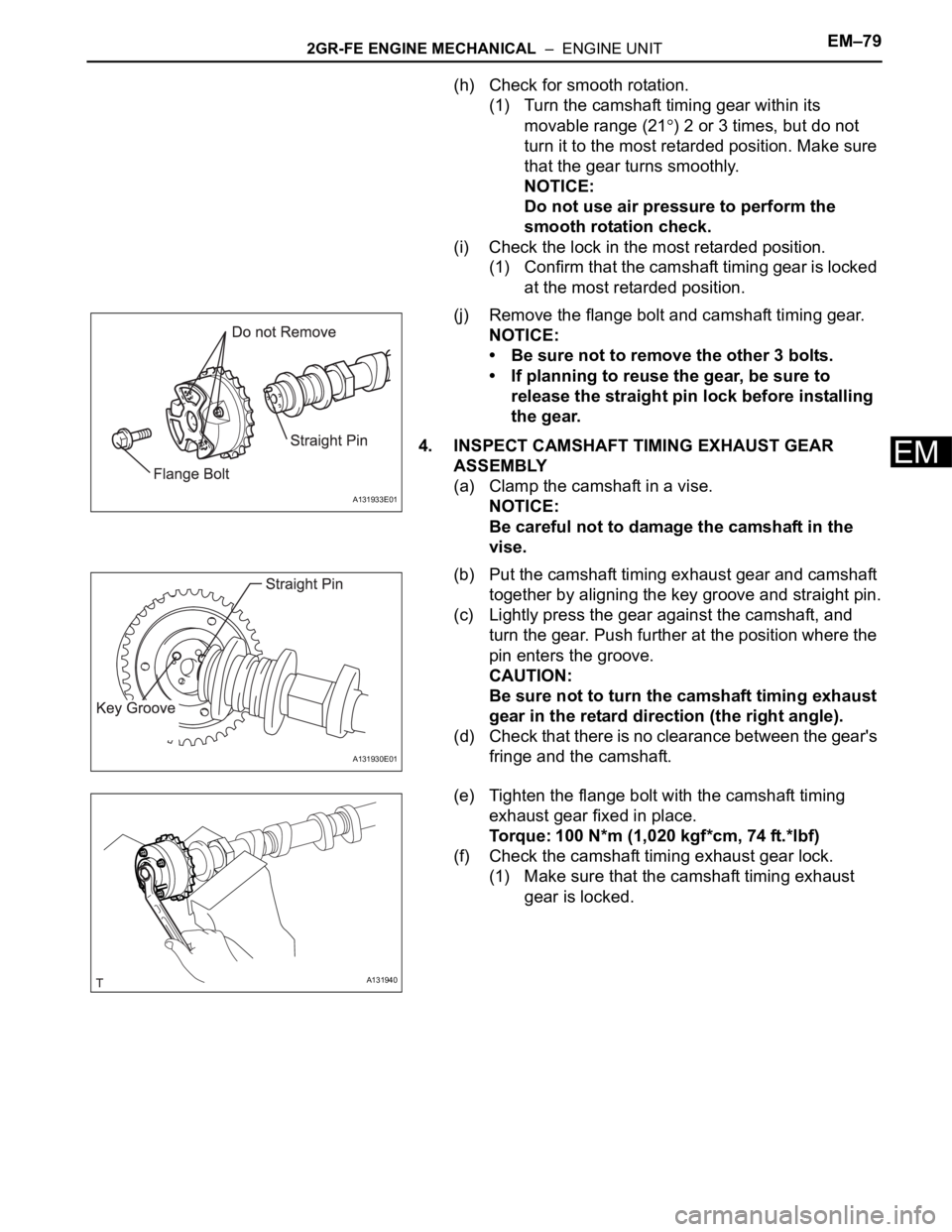
(j) Remove the flange bolt and camshaft timing gear.
NOTICE:
• Be sure not to remove the other 3 bolts.
• If planning to reuse the gear, be sure to
release the straight pin lock before installing
the gear.
4. INSPECT CAMSHAFT TIMING EXHAUST GEAR
ASSEMBLY
(a) Clamp the camshaft in a vise.
NOTICE:
Be careful not to damage the camshaft in the
vise.
(b) Put the camshaft timing exhaust gear and camshaft
together by aligning the key groove and straight pin.
(c) Lightly press the gear against the camshaft, and
turn the gear. Push further at the position where the
pin enters the groove.
CAUTION:
Be sure not to turn the camshaft timing exhaust
gear in the retard direction (the right angle).
(d) Check that there is no clearance between the gear's
fringe and the camshaft.
(e) Tighten the flange bolt with the camshaft timing
exhaust gear fixed in place.
Torque: 100 N*m (1,020 kgf*cm, 74 ft.*lbf)
(f) Check the camshaft timing exhaust gear lock.
(1) Make sure that the camshaft timing exhaust
gear is locked.
A131933E01
A131930E01
A131940
Page 717 of 2000
EM–802GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNIT
EM
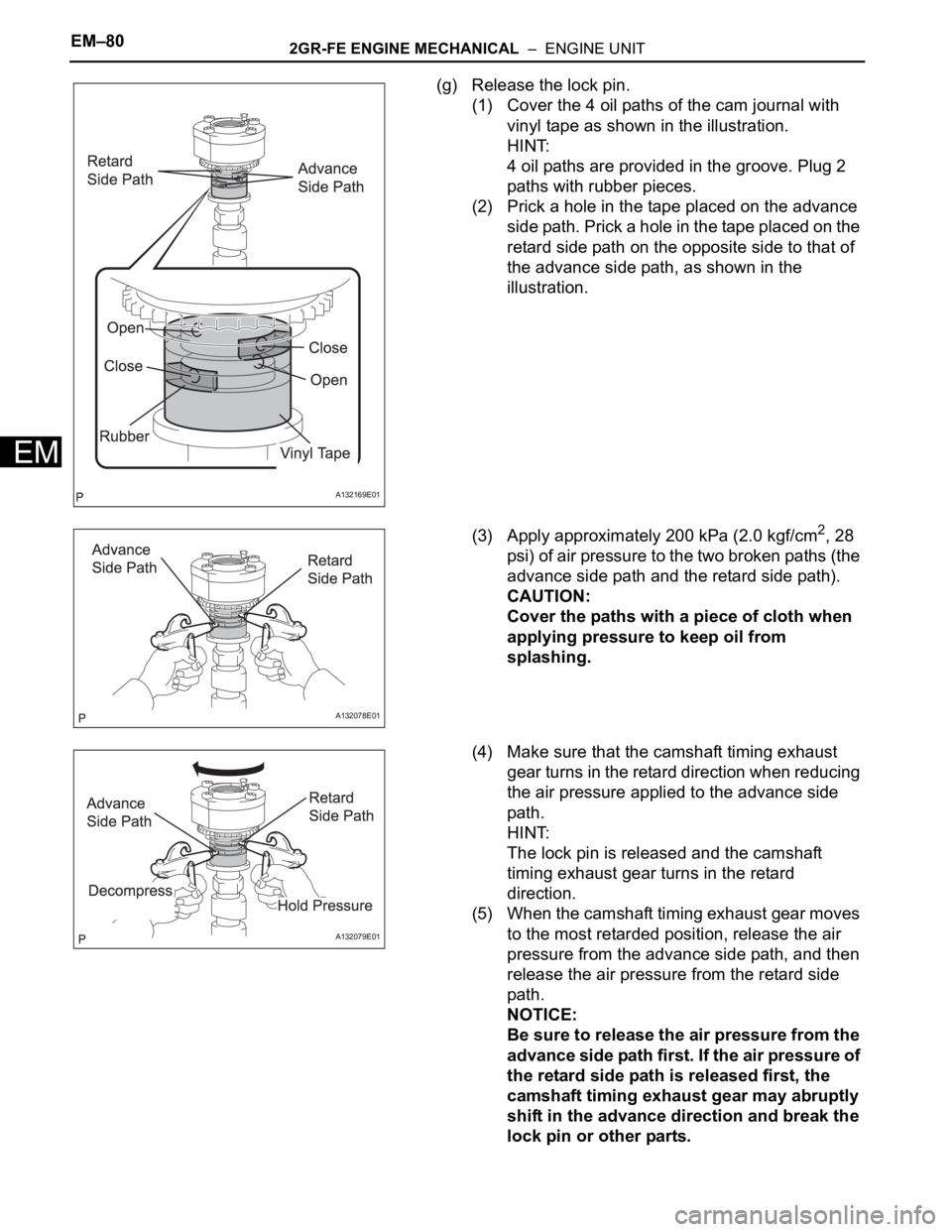
(g) Release the lock pin.
(1) Cover the 4 oil paths of the cam journal with
vinyl tape as shown in the illustration.
HINT:
4 oil paths are provided in the groove. Plug 2
paths with rubber pieces.
(2) Prick a hole in the tape placed on the advance
side path. Prick a hole in the tape placed on the
retard side path on the opposite side to that of
the advance side path, as shown in the
illustration.
(3) Apply approximately 200 kPa (2.0 kgf/cm
2, 28
psi) of air pressure to the two broken paths (the
advance side path and the retard side path).
CAUTION:
Cover the paths with a piece of cloth when
applying pressure to keep oil from
splashing.
(4) Make sure that the camshaft timing exhaust
gear turns in the retard direction when reducing
the air pressure applied to the advance side
path.
HINT:
The lock pin is released and the camshaft
timing exhaust gear turns in the retard
direction.
(5) When the camshaft timing exhaust gear moves
to the most retarded position, release the air
pressure from the advance side path, and then
release the air pressure from the retard side
path.
NOTICE:
Be sure to release the air pressure from the
advance side path first. If the air pressure of
the retard side path is released first, the
camshaft timing exhaust gear may abruptly
shift in the advance direction and break the
lock pin or other parts.
A132169E01
A132078E01
A132079E01
Page 718 of 2000
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNITEM–81
EM
(h) Check for smooth rotation.
(1) Turn the camshaft timing exhaust gear within
its movable range (18.5
) 2 or 3 times, but do
not turn it to the most advanced position. Make
sure that the gear turns smoothly.
NOTICE:
When the air pressure is released from the
advance side path and then from the retard
side path, the gear automatically returns to
the most advanced position due to the
advance assist spring operation and locks.
Gradually release the air pressure from the
retard side path before performing the
smooth rotation check.
(i) Check the lock at the most advanced position.
(1) Make sure that the camshaft timing exhaust
gear is locked at the most advanced position.
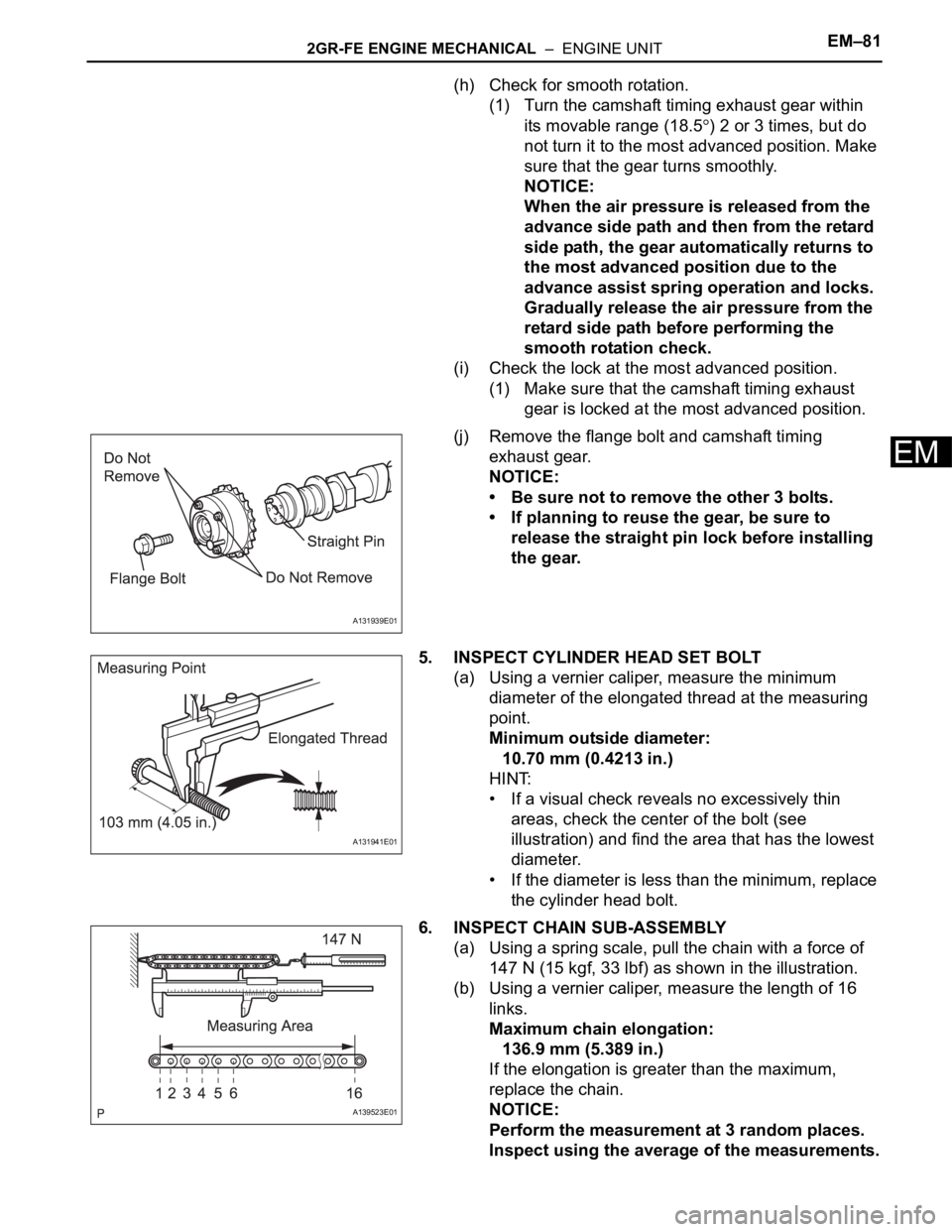
(j) Remove the flange bolt and camshaft timing
exhaust gear.
NOTICE:
• Be sure not to remove the other 3 bolts.
• If planning to reuse the gear, be sure to
release the straight pin lock before installing
the gear.
5. INSPECT CYLINDER HEAD SET BOLT
(a) Using a vernier caliper, measure the minimum
diameter of the elongated thread at the measuring
point.
Minimum outside diameter:
10.70 mm (0.4213 in.)
HINT:
• If a visual check reveals no excessively thin
areas, check the center of the bolt (see
illustration) and find the area that has the lowest
diameter.
• If the diameter is less than the minimum, replace
the cylinder head bolt.
6. INSPECT CHAIN SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Using a spring scale, pull the chain with a force of
147 N (15 kgf, 33 lbf) as shown in the illustration.
(b) Using a vernier caliper, measure the length of 16
links.
Maximum chain elongation:
136.9 mm (5.389 in.)
If the elongation is greater than the maximum,
replace the chain.
NOTICE:
Perform the measurement at 3 random places.
Inspect using the average of the measurements.
A131939E01
A131941E01
A139523E01
Page 719 of 2000
EM–822GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNIT
EM
7. INSPECT NO. 2 CHAIN SUB-ASSEMBLY
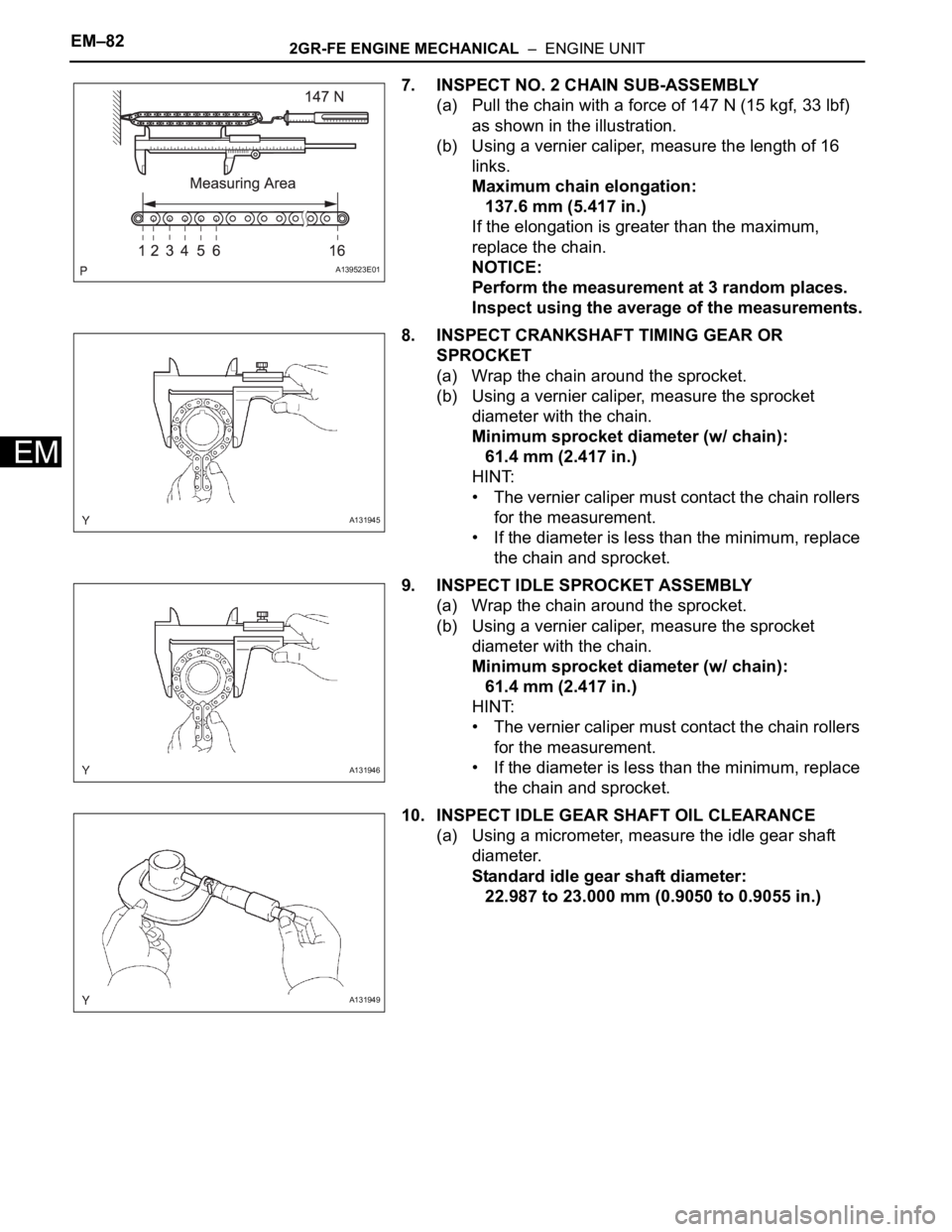
(a) Pull the chain with a force of 147 N (15 kgf, 33 lbf)
as shown in the illustration.
(b) Using a vernier caliper, measure the length of 16
links.
Maximum chain elongation:
137.6 mm (5.417 in.)
If the elongation is greater than the maximum,
replace the chain.
NOTICE:
Perform the measurement at 3 random places.
Inspect using the average of the measurements.
8. INSPECT CRANKSHAFT TIMING GEAR OR
SPROCKET
(a) Wrap the chain around the sprocket.
(b) Using a vernier caliper, measure the sprocket
diameter with the chain.
Minimum sprocket diameter (w/ chain):
61.4 mm (2.417 in.)
HINT:
• The vernier caliper must contact the chain rollers
for the measurement.
• If the diameter is less than the minimum, replace
the chain and sprocket.
9. INSPECT IDLE SPROCKET ASSEMBLY
(a) Wrap the chain around the sprocket.
(b) Using a vernier caliper, measure the sprocket
diameter with the chain.
Minimum sprocket diameter (w/ chain):
61.4 mm (2.417 in.)
HINT:
• The vernier caliper must contact the chain rollers
for the measurement.
• If the diameter is less than the minimum, replace
the chain and sprocket.
10. INSPECT IDLE GEAR SHAFT OIL CLEARANCE
(a) Using a micrometer, measure the idle gear shaft
diameter.
Standard idle gear shaft diameter:
22.987 to 23.000 mm (0.9050 to 0.9055 in.)
A139523E01
A131945
A131946
A131949
Page 720 of 2000
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNITEM–83
EM
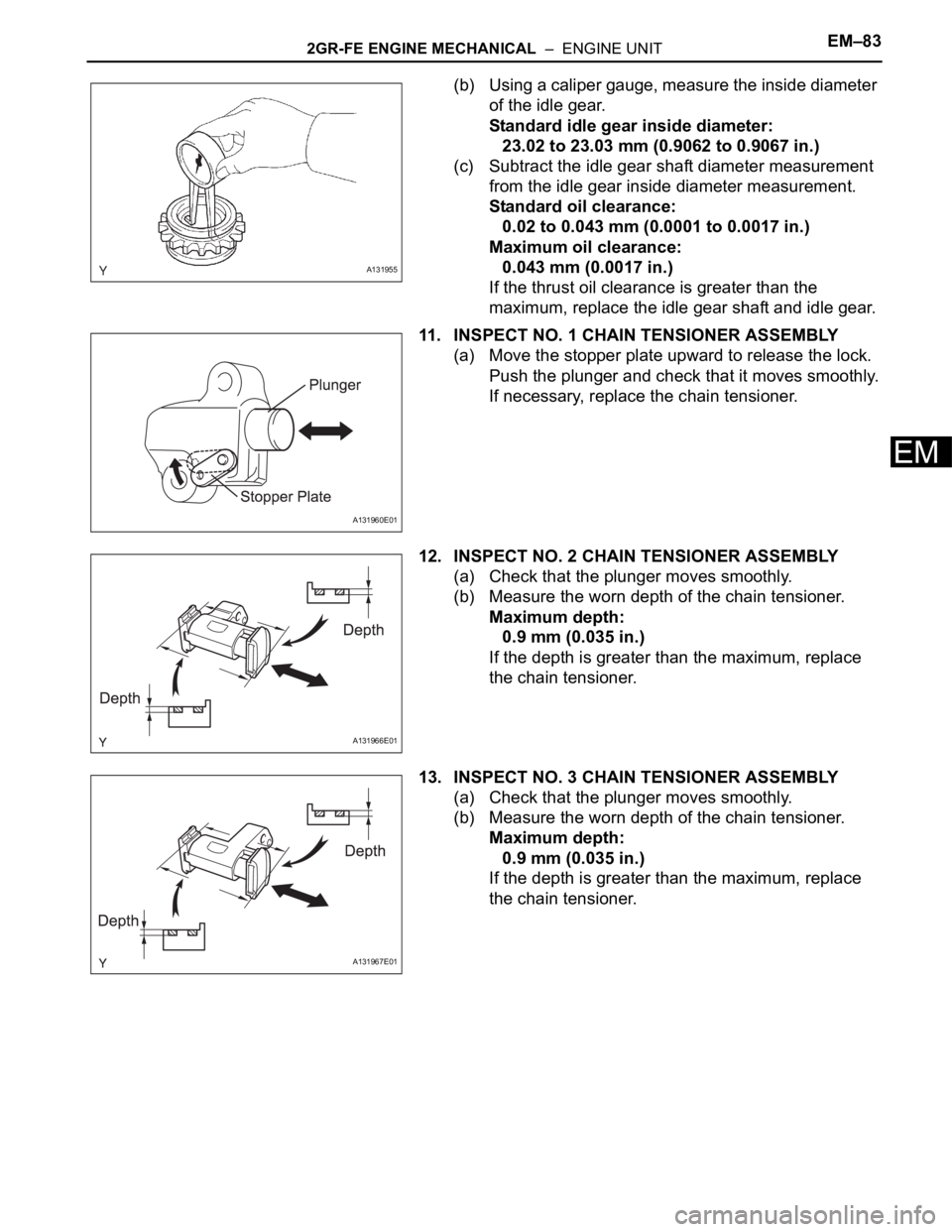
(b) Using a caliper gauge, measure the inside diameter
of the idle gear.
Standard idle gear inside diameter:
23.02 to 23.03 mm (0.9062 to 0.9067 in.)
(c) Subtract the idle gear shaft diameter measurement
from the idle gear inside diameter measurement.
Standard oil clearance:
0.02 to 0.043 mm (0.0001 to 0.0017 in.)
Maximum oil clearance:
0.043 mm (0.0017 in.)
If the thrust oil clearance is greater than the
maximum, replace the idle gear shaft and idle gear.
11. INSPECT NO. 1 CHAIN TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
(a) Move the stopper plate upward to release the lock.
Push the plunger and check that it moves smoothly.
If necessary, replace the chain tensioner.
12. INSPECT NO. 2 CHAIN TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
(a) Check that the plunger moves smoothly.
(b) Measure the worn depth of the chain tensioner.
Maximum depth:
0.9 mm (0.035 in.)
If the depth is greater than the maximum, replace
the chain tensioner.
13. INSPECT NO. 3 CHAIN TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
(a) Check that the plunger moves smoothly.
(b) Measure the worn depth of the chain tensioner.
Maximum depth:
0.9 mm (0.035 in.)
If the depth is greater than the maximum, replace
the chain tensioner.
A131955
A131960E01
A131966E01
A131967E01
Page 721 of 2000
EM–842GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNIT
EM
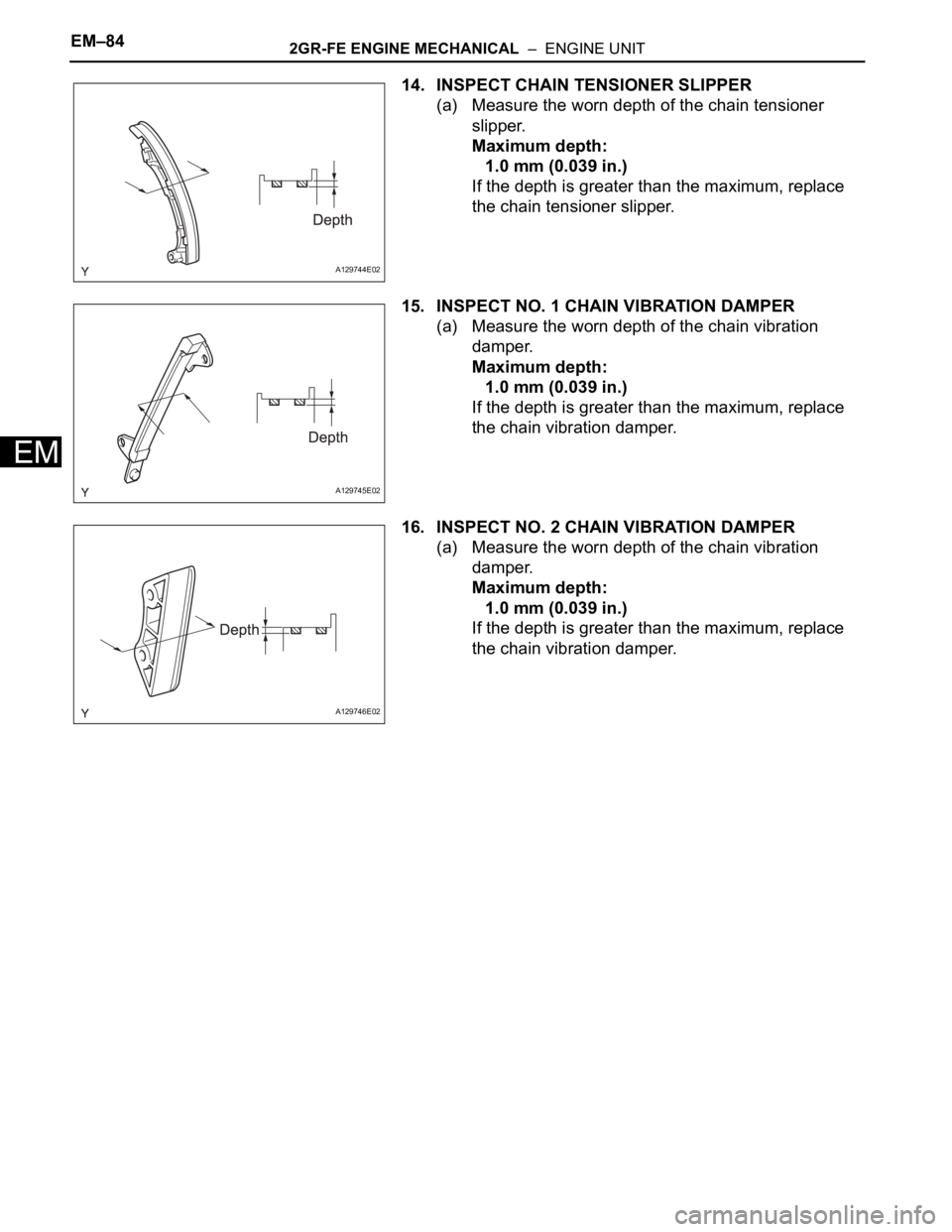
14. INSPECT CHAIN TENSIONER SLIPPER
(a) Measure the worn depth of the chain tensioner
slipper.
Maximum depth:
1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
If the depth is greater than the maximum, replace
the chain tensioner slipper.
15. INSPECT NO. 1 CHAIN VIBRATION DAMPER
(a) Measure the worn depth of the chain vibration
damper.
Maximum depth:
1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
If the depth is greater than the maximum, replace
the chain vibration damper.
16. INSPECT NO. 2 CHAIN VIBRATION DAMPER
(a) Measure the worn depth of the chain vibration
damper.
Maximum depth:
1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
If the depth is greater than the maximum, replace
the chain vibration damper.
A129744E02
A129745E02
A129746E02
Page 722 of 2000
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNITEM–85
EM
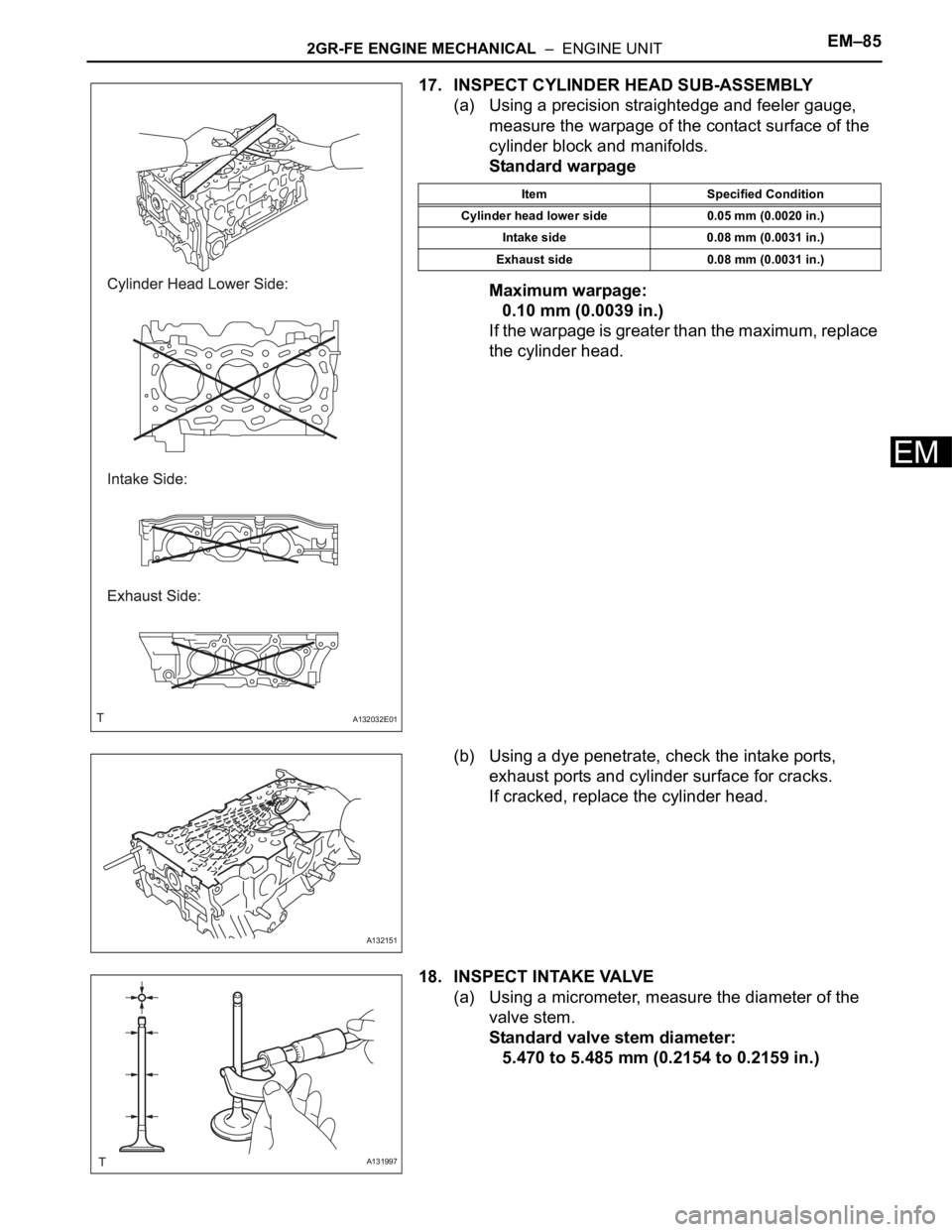
17. INSPECT CYLINDER HEAD SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Using a precision straightedge and feeler gauge,
measure the warpage of the contact surface of the
cylinder block and manifolds.
Standard warpage
Maximum warpage:
0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
If the warpage is greater than the maximum, replace
the cylinder head.
(b) Using a dye penetrate, check the intake ports,
exhaust ports and cylinder surface for cracks.
If cracked, replace the cylinder head.
18. INSPECT INTAKE VALVE
(a) Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of the
valve stem.
Standard valve stem diameter:
5.470 to 5.485 mm (0.2154 to 0.2159 in.)
A132032E01
Item Specified Condition
Cylinder head lower side 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.)
Intake side 0.08 mm (0.0031 in.)
Exhaust side 0.08 mm (0.0031 in.)
A132151
A131997
Page 723 of 2000
EM–862GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNIT
EM
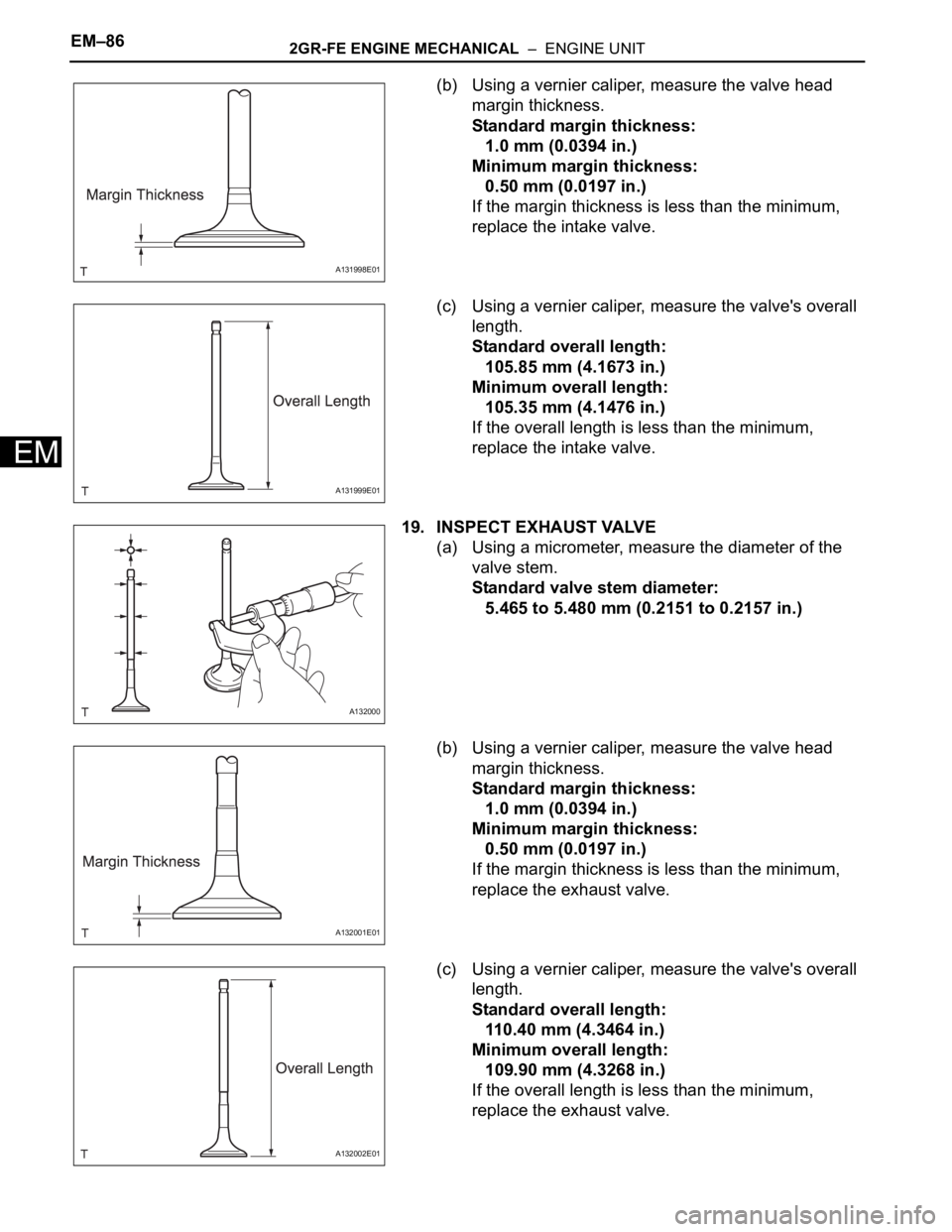
(b) Using a vernier caliper, measure the valve head
margin thickness.
Standard margin thickness:
1.0 mm (0.0394 in.)
Minimum margin thickness:
0.50 mm (0.0197 in.)
If the margin thickness is less than the minimum,
replace the intake valve.
(c) Using a vernier caliper, measure the valve's overall
length.
Standard overall length:
105.85 mm (4.1673 in.)
Minimum overall length:
105.35 mm (4.1476 in.)
If the overall length is less than the minimum,
replace the intake valve.
19. INSPECT EXHAUST VALVE
(a) Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of the
valve stem.
Standard valve stem diameter:
5.465 to 5.480 mm (0.2151 to 0.2157 in.)
(b) Using a vernier caliper, measure the valve head
margin thickness.
Standard margin thickness:
1.0 mm (0.0394 in.)
Minimum margin thickness:
0.50 mm (0.0197 in.)
If the margin thickness is less than the minimum,
replace the exhaust valve.
(c) Using a vernier caliper, measure the valve's overall
length.
Standard overall length:
110.40 mm (4.3464 in.)
Minimum overall length:
109.90 mm (4.3268 in.)
If the overall length is less than the minimum,
replace the exhaust valve.
A131998E01
A131999E01
A132000
A132001E01
A132002E01
Page 724 of 2000

2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNITEM–87
EM
20. INSPECT INTAKE VALVE SEAT
(a) Apply a light coat of Prussian blue to the valve face.
(b) Lightly press the valve face against the valve seat.
(c) Check the valve face and valve seat by using the
following procedure.
(1) If Prussian blue appears around the entire
valve face, the valve face is concentric. If not,
replace the valve.
(2) If Prussian blue appears around the entire
valve seat, the guide and valve face are
concentric. If not, resurface the valve seat.
(3) Check that the valve seat contacts in the
middle of the valve face with the width between
1.1 and 1.5 mm (0.043 and 0.059 in.).
21. INSPECT EXHAUST VALVE SEAT
(a) Apply a light coat of Prussian blue to the valve face.
(b) Lightly press the valve face against the valve seat.
(c) Check the valve face and valve seat by using the
following procedure.
(1) If Prussian blue appears around the entire
valve face, the valve face is concentric. If not,
replace the valve.
(2) If Prussian blue appears around the entire
valve seat, the guide and valve face are
concentric. If not, resurface the valve seat.
(3) Check that the valve seat contacts in the
middle of the valve face with the width between
1.2 and 1.6 mm (0.047 and 0.063 in.).
22. INSPECT INNER COMPRESSION SPRING
(a) Using a vernier caliper, measure the free length of
the inner compression spring.
Standard free length:
45.46 mm (1.7898 in.)
If the free length is not as specified, replace the
spring.
(b) Using a steel square, measure the deviation of the
inner compression spring.
Maximum deviation:
1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
Maximum angle (reference):
2
If the deviation is greater than the maximum,
replace the spring.
A132152E01
A132152E01
A101392
A101393E02
Page 725 of 2000
EM–882GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNIT
EM
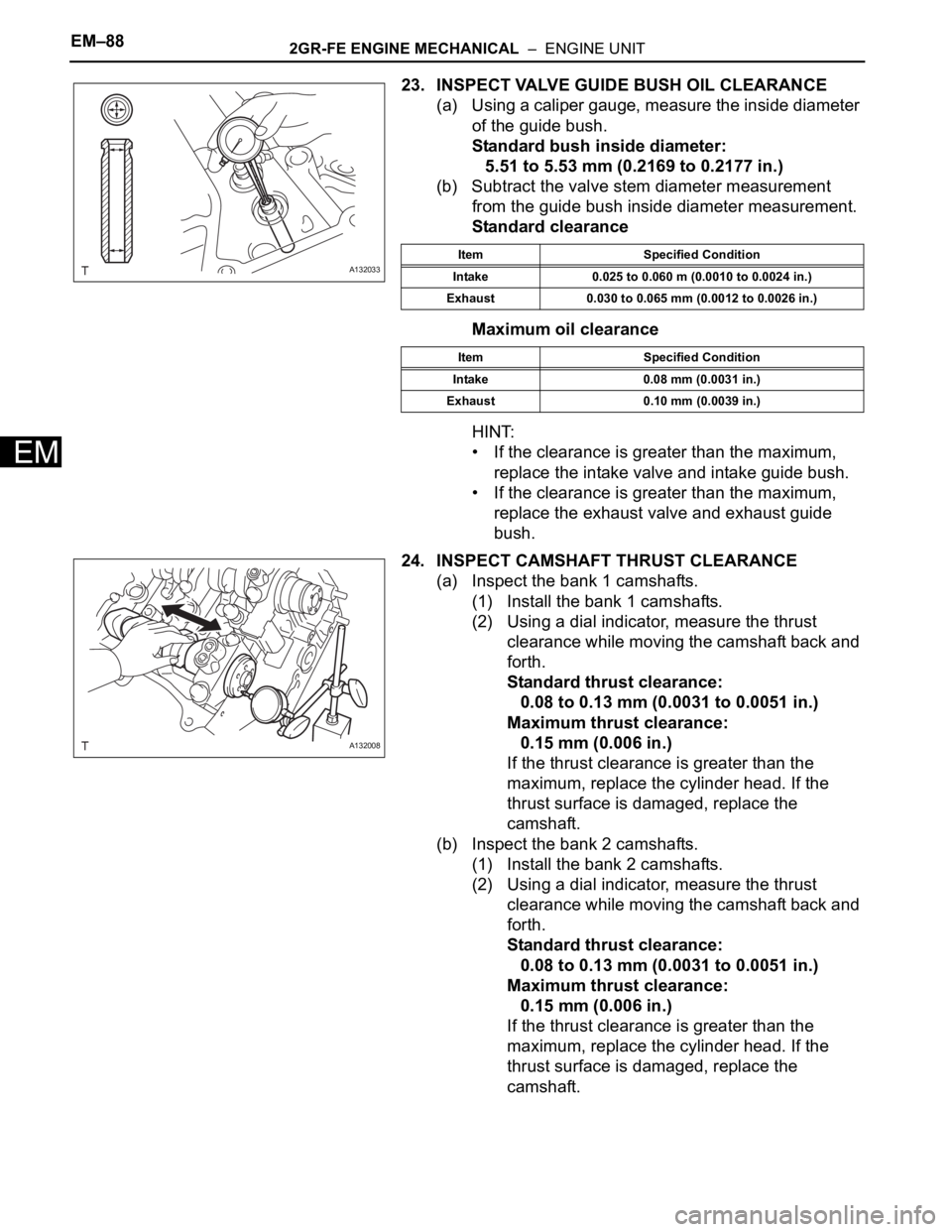
23. INSPECT VALVE GUIDE BUSH OIL CLEARANCE
(a) Using a caliper gauge, measure the inside diameter
of the guide bush.
Standard bush inside diameter:
5.51 to 5.53 mm (0.2169 to 0.2177 in.)
(b) Subtract the valve stem diameter measurement
from the guide bush inside diameter measurement.
Standard clearance
Maximum oil clearance
HINT:
• If the clearance is greater than the maximum,
replace the intake valve and intake guide bush.
• If the clearance is greater than the maximum,
replace the exhaust valve and exhaust guide
bush.
24. INSPECT CAMSHAFT THRUST CLEARANCE
(a) Inspect the bank 1 camshafts.
(1) Install the bank 1 camshafts.
(2) Using a dial indicator, measure the thrust
clearance while moving the camshaft back and
forth.
Standard thrust clearance:
0.08 to 0.13 mm (0.0031 to 0.0051 in.)
Maximum thrust clearance:
0.15 mm (0.006 in.)
If the thrust clearance is greater than the
maximum, replace the cylinder head. If the
thrust surface is damaged, replace the
camshaft.
(b) Inspect the bank 2 camshafts.
(1) Install the bank 2 camshafts.
(2) Using a dial indicator, measure the thrust
clearance while moving the camshaft back and
forth.
Standard thrust clearance:
0.08 to 0.13 mm (0.0031 to 0.0051 in.)
Maximum thrust clearance:
0.15 mm (0.006 in.)
If the thrust clearance is greater than the
maximum, replace the cylinder head. If the
thrust surface is damaged, replace the
camshaft.
A132033Item Specified Condition
Intake 0.025 to 0.060 m (0.0010 to 0.0024 in.)
Exhaust 0.030 to 0.065 mm (0.0012 to 0.0026 in.)
Item Specified Condition
Intake 0.08 mm (0.0031 in.)
Exhaust 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
A132008