Control arm TOYOTA RAV4 2006 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAV4, Model: TOYOTA RAV4 2006Pages: 2000, PDF Size: 45.84 MB
Page 1944 of 2000

ES–562AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
HINT:
*: When cranking the engine, each cylinder measures the
engine rpm.
In this ACTIVE TEST, the fuel and ignition of all cylinders is
cut, and cranking occurs for approximately 10 seconds. Then,
each cylinder measures the engine rpm. If a cylinder's engine
rpm is higher than the others, that cylinder's compression
pressure is compared to the others, and whether or not the
compression pressure is low can be determined.
1. Warm up the engine.
2. Turn the ignition switch OFF.
3. Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
4. Turn the ignition switch ON and turn the intelligent tester
ON.
5. Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / ACTIVE TEST / COMPRESS
CHECK.
HINT:
If the results are not displayed normally, select the display
items from the DATA LIST before performing the ACTIVE
TEST. Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST / USER DATA / ENG
SPEED #1 and ENG SPEED #2, ENG SPEED #3, ENG
SPEED #4 (Press the YES button to change the ENG
SPEED #1 to #4 is YES) and then press the ENTER
button.
6. While the engine is not running, press the RIGHT or LEFT
button to change the COMPRESS CHECK to ON.
HINT:
After performing the above procedure, the ACTIVE TEST's
COMPRESS CHECK will start. Fuel injection for all
cylinders is prohibited, and the each cylinder's engine rpm
measurement will enter standby.
7. Fully open the throttle.
8. Crank the engine for about 10 seconds.
9. Monitor the engine speed (ENG SPEED #1 to #4)
displayed on the tester.
HINT:
At first, the tester's display will show each cylinder's
engine rpm measurement to be extremely high. After
approximately 10 seconds of engine cranking, each
cylinder's engine rpm measurement will change to the
actual engine rpm.
NOTICE:
• After the ACTIVE TEST's COMPRESS CHECK is
turned ON, it will automatically turn off after 255
seconds.
ALT VOLRequest output voltage of
generator regulator during forced
activationBetween 12.5 and 14.8 V Engine running
COMPRESS CHECKAll cylinder injector fuel cut and
ignition stopON/OFF * Intelligent Tester Displays Test Details Control Ranges Diagnostic Notes
A130534
A130535
Page 1959 of 2000
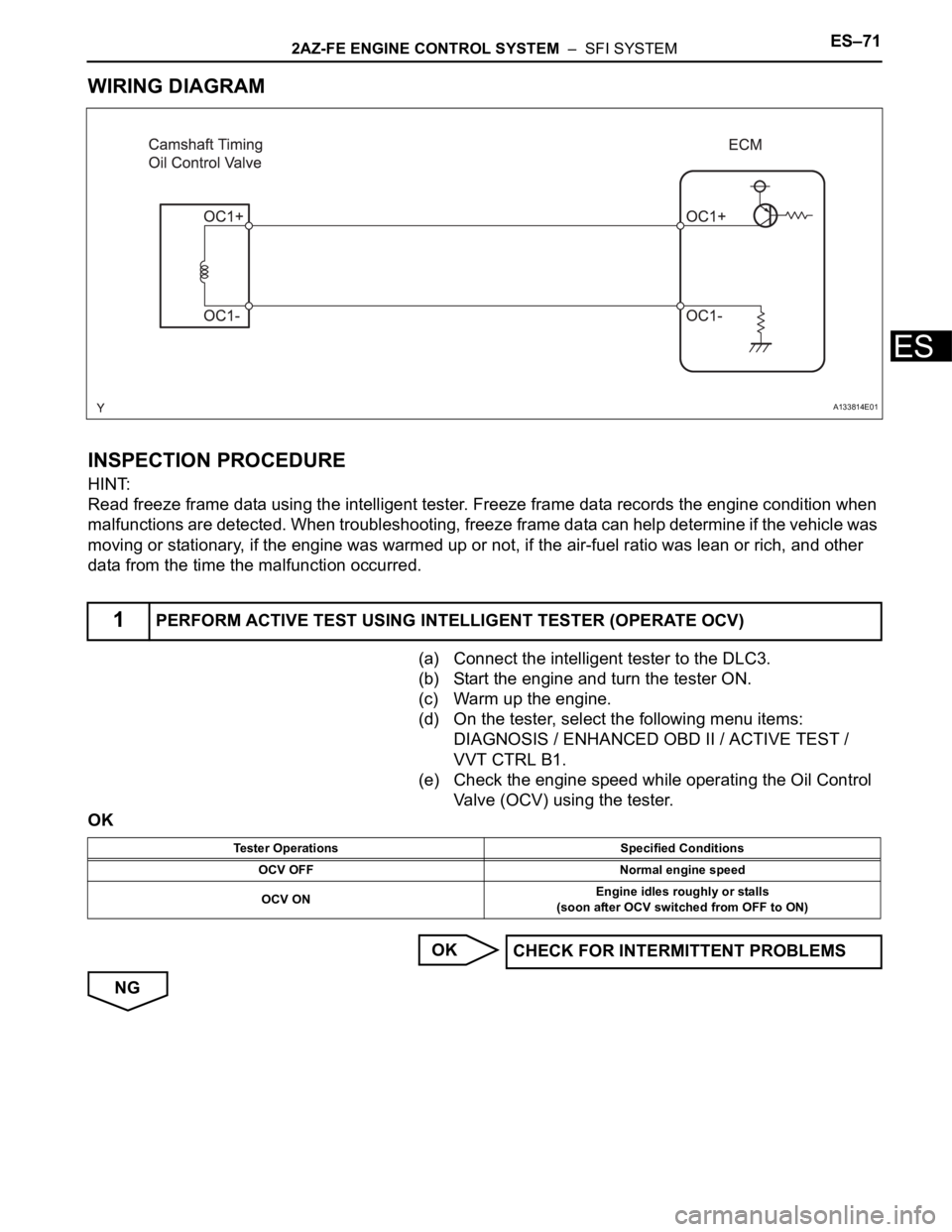
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–71
ES
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when
malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other
data from the time the malfunction occurred.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Start the engine and turn the tester ON.
(c) Warm up the engine.
(d) On the tester, select the following menu items:
DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / ACTIVE TEST /
VVT CTRL B1.
(e) Check the engine speed while operating the Oil Control
Valve (OCV) using the tester.
OK
OK
NG
1PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (OPERATE OCV)
A133814E01
Tester Operations Specified Conditions
OCV OFF Normal engine speed
OCV ONEngine idles roughly or stalls
(soon after OCV switched from OFF to ON)
CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS
Page 1962 of 2000

ES–742AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM optimizes the intake valve timing using the VVT (Variable Valve Timing) system to control the
intake camshaft. The VVT system includes the ECM, the Oil Control Valve (OCV) and the VVT controller.
The ECM sends a target duty-cycle control signal to the OCV. This control signal regulates the oil
pressure supplied to the VVT controller. The VVT controller can advance or retard the intake camshaft.
If the difference between the target and actual intake valve timings is large, and changes in the actual
intake valve timing are small, the ECM interprets this as the VVT controller stuck malfunction and sets a
DTC.
Example:
A DTC is set when the following conditions 1, 2 and 3 are met:
1. The difference between the target and actual intake valve timing is more than 5
CA (Crankshaft
Angle) and the condition continues for more than 4.5 seconds.
2. It takes 5 seconds or more to change the valve timing by 5
CA.
3. After above conditions 1 and 2 are met, the OCV is forcibly activated 63 times or more.
DTC P0011 (Advanced Cam Timing) is subject to 1 trip detection logic.
DTC P0012 (Retarded Cam Timing) is subject to 2 trip detection logic.
These DTCs indicate that the VVT controller cannot operate properly due to OCV malfunctions or the
presence of foreign objects in the OCV.
The monitor will run if all of the following conditions are met:
– The engine is warm (the engine coolant temperature is 75
C [167F] or more).
– The vehicle has been driven at more than 64 km/h (40 mph) for 3 minutes.
– The engine has idled for 3 minutes.
MONITOR STRATEGY
DTC No. DTC Detection Conditions Trouble Areas
P0011Advanced camshaft timing:
With warm engine and engine speed of between 550 rpm and
4,000 rpm, all conditions (1), (2) and (3) met (1 trip detection
logic):
1. Difference between target and actual intake valve timings
more than 5
CA (Crankshaft Angle) for 4.5 seconds
2. Current intake valve timing fixed (timing changes less than
5
CA in 5 seconds)
3. Variations in VVT controller timing more than 19
CA of
maximum delayed timing (malfunction in advance timing)• Valve timing
•OCV
• OCV filter
• Camshaft timing gear assembly
•ECM
P0012Retarded camshaft timing:
With warm engine and engine speed of between 550 rpm and
4,000 rpm, all conditions (1), (2) and (3) met (2 trip detection
logic):
1. Difference between target and actual intake valve timings
more than 5
CA (Crankshaft Angle) for 4.5 seconds
2. Current intake valve timing fixed (timing changes less than
5
CA in 5 seconds)
3. Variations in VVT controller timing 19CA or less of
maximum delayed timing (malfunction in retarded timing)• Valve timing
•OCV
• OCV filter
• Camshaft timing gear assembly
•ECM
Related DTCsP0011: Advanced camshaft timing
P0012: Retarded camshaft timing
Required Sensors/Components (Main) VVT OCV and VVT Actuator
Required Sensors/Components (Related)Crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor and Engine
coolant temperature sensor
Frequency of Operation Once per driving cycle
Duration Within 10 seconds
MIL OperationAdvanced camshaft timing: Immediate
Retarded camshaft timing: 2 driving cycles
Sequence of Operation None
Page 1963 of 2000

2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–75
ES
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
Advanced camshaft timing:
Retard camshaft timing:
If the difference between the target and actual camshaft timings is greater than the specified value, the
ECM operates the VVT actuator.
Then, the ECM monitors the camshaft timing change for 5 seconds.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0010 (see page ES-64).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
NOTICE:
DTC P0011 or P0012 may be set when foreign objects in the engine oil are caught in some parts of
the system. The DTC will remain set even if the system returns to normal after a short time.
Foreign objects are filtered out by the oil filter.
HINT:
If DTC P0011 or P0012 is present, check the VVT (Variable Valve Timing) system.
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when
malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other
data from the time the malfunction occurred.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON and turn the tester ON.
(c) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
(d) Read DTCs.
Result
Monitor runs whenever following DTCs not presentP0100 - P0103 (MAF meter)
P0115 - P0118 (ECT sensor)
P0125 (Insufficient ECT for closed loop)
P0335 (CKP sensor)
P0340 (CMP sensor)
P0351 - P0354 (Igniter)
Battery voltage 11 V or more
Engine RPM 550 to 4,000 rpm
ECT 75
C (167F) to 100C (212F)
All of following conditions met -
Crank angle between reference position and actual intake camshaft
angle67
CA or more
Valve timing No change at advanced valve timing
All of following conditions met -
Crank angle between reference point and actual intake camshaft
angleLess than 67
CA
Valve timing No change at retarded valve timing
1CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0011 OR P0012)
Display (DTC Output) Proceed To
Page 1964 of 2000
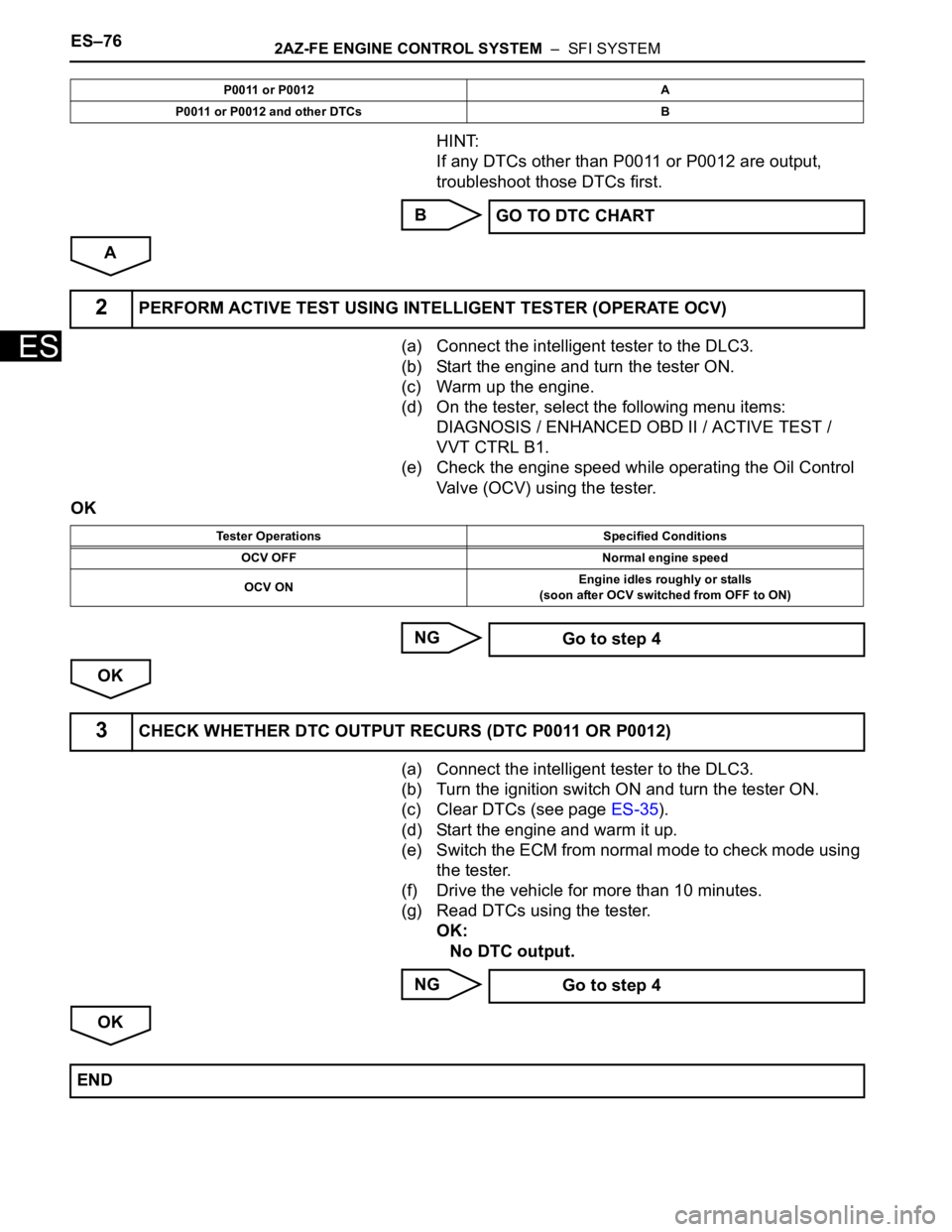
ES–762AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
HINT:
If any DTCs other than P0011 or P0012 are output,
troubleshoot those DTCs first.
B
A
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Start the engine and turn the tester ON.
(c) Warm up the engine.
(d) On the tester, select the following menu items:
DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / ACTIVE TEST /
VVT CTRL B1.
(e) Check the engine speed while operating the Oil Control
Valve (OCV) using the tester.
OK
NG
OK
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON and turn the tester ON.
(c) Clear DTCs (see page ES-35).
(d) Start the engine and warm it up.
(e) Switch the ECM from normal mode to check mode using
the tester.
(f) Drive the vehicle for more than 10 minutes.
(g) Read DTCs using the tester.
OK:
No DTC output.
NG
OK
P0011 or P0012 A
P0011 or P0012 and other DTCs B
GO TO DTC CHART
2PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (OPERATE OCV)
Tester Operations Specified Conditions
OCV OFF Normal engine speed
OCV ONEngine idles roughly or stalls
(soon after OCV switched from OFF to ON)
Go to step 4
3CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P0011 OR P0012)
Go to step 4
END
Page 1966 of 2000
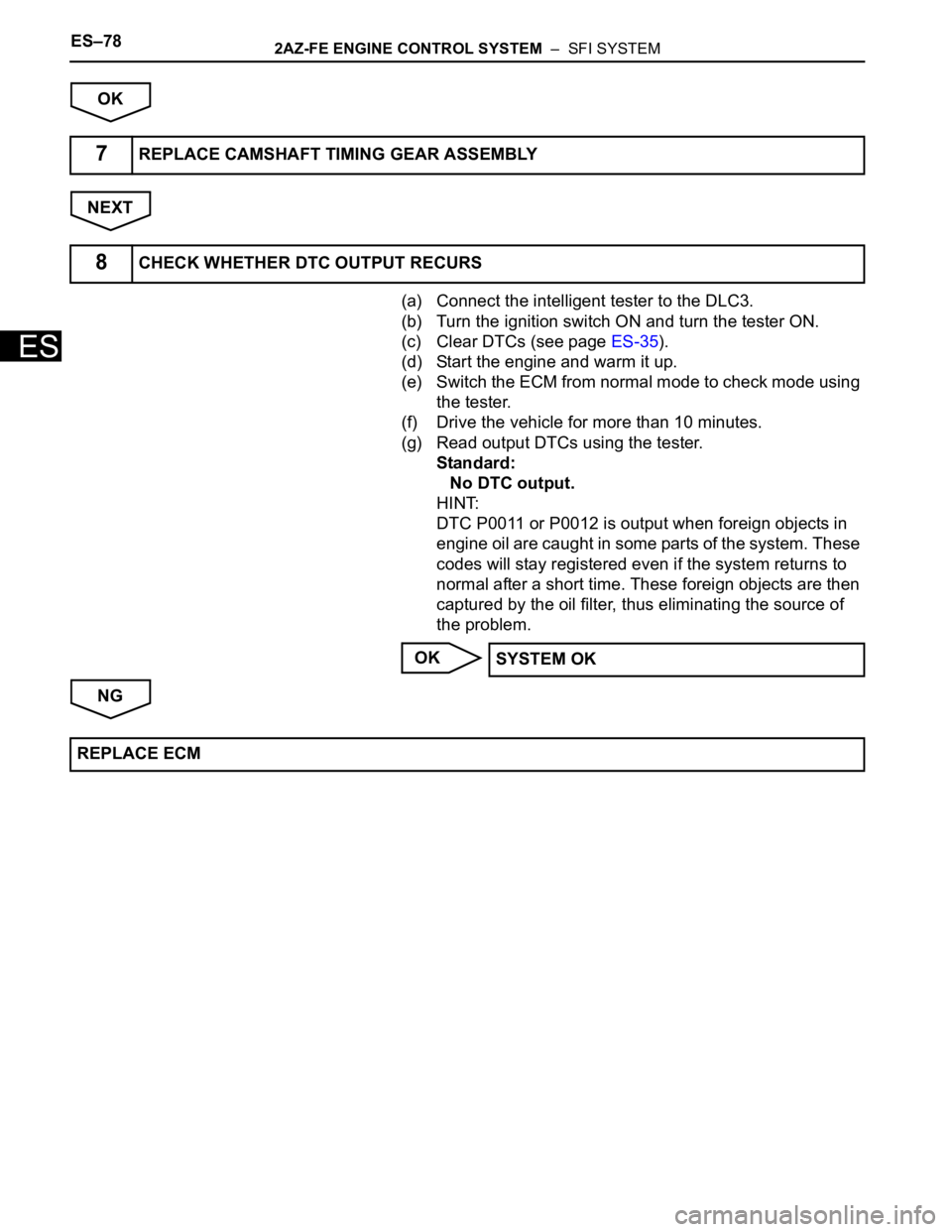
ES–782AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
OK
NEXT
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON and turn the tester ON.
(c) Clear DTCs (see page ES-35).
(d) Start the engine and warm it up.
(e) Switch the ECM from normal mode to check mode using
the tester.
(f) Drive the vehicle for more than 10 minutes.
(g) Read output DTCs using the tester.
Standard:
No DTC output.
HINT:
DTC P0011 or P0012 is output when foreign objects in
engine oil are caught in some parts of the system. These
codes will stay registered even if the system returns to
normal after a short time. These foreign objects are then
captured by the oil filter, thus eliminating the source of
the problem.
OK
NG
7REPLACE CAMSHAFT TIMING GEAR ASSEMBLY
8CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS
SYSTEM OK
REPLACE ECM
Page 1968 of 2000
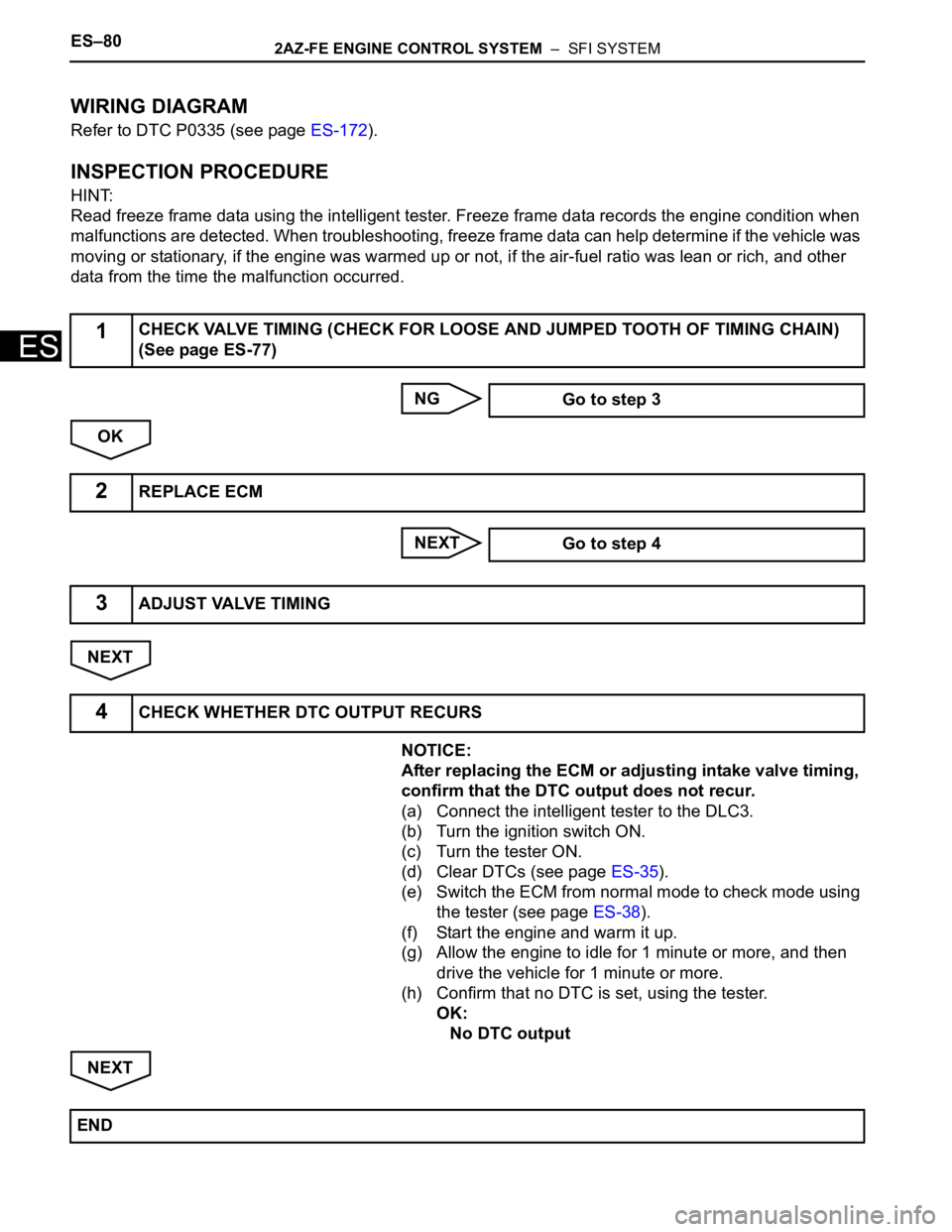
ES–802AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0335 (see page ES-172).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when
malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other
data from the time the malfunction occurred.
NG
OK
NEXT
NEXT
NOTICE:
After replacing the ECM or adjusting intake valve timing,
confirm that the DTC output does not recur.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON.
(c) Turn the tester ON.
(d) Clear DTCs (see page ES-35).
(e) Switch the ECM from normal mode to check mode using
the tester (see page ES-38).
(f) Start the engine and warm it up.
(g) Allow the engine to idle for 1 minute or more, and then
drive the vehicle for 1 minute or more.
(h) Confirm that no DTC is set, using the tester.
OK:
No DTC output
NEXT
1CHECK VALVE TIMING (CHECK FOR LOOSE AND JUMPED TOOTH OF TIMING CHAIN)
(See page ES-77)
Go to step 3
2REPLACE ECM
Go to step 4
3ADJUST VALVE TIMING
4CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS
END
Page 1971 of 2000
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–83
ES
COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P2195 (see page ES-296).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when
malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other
data from the time the malfunction occurred.
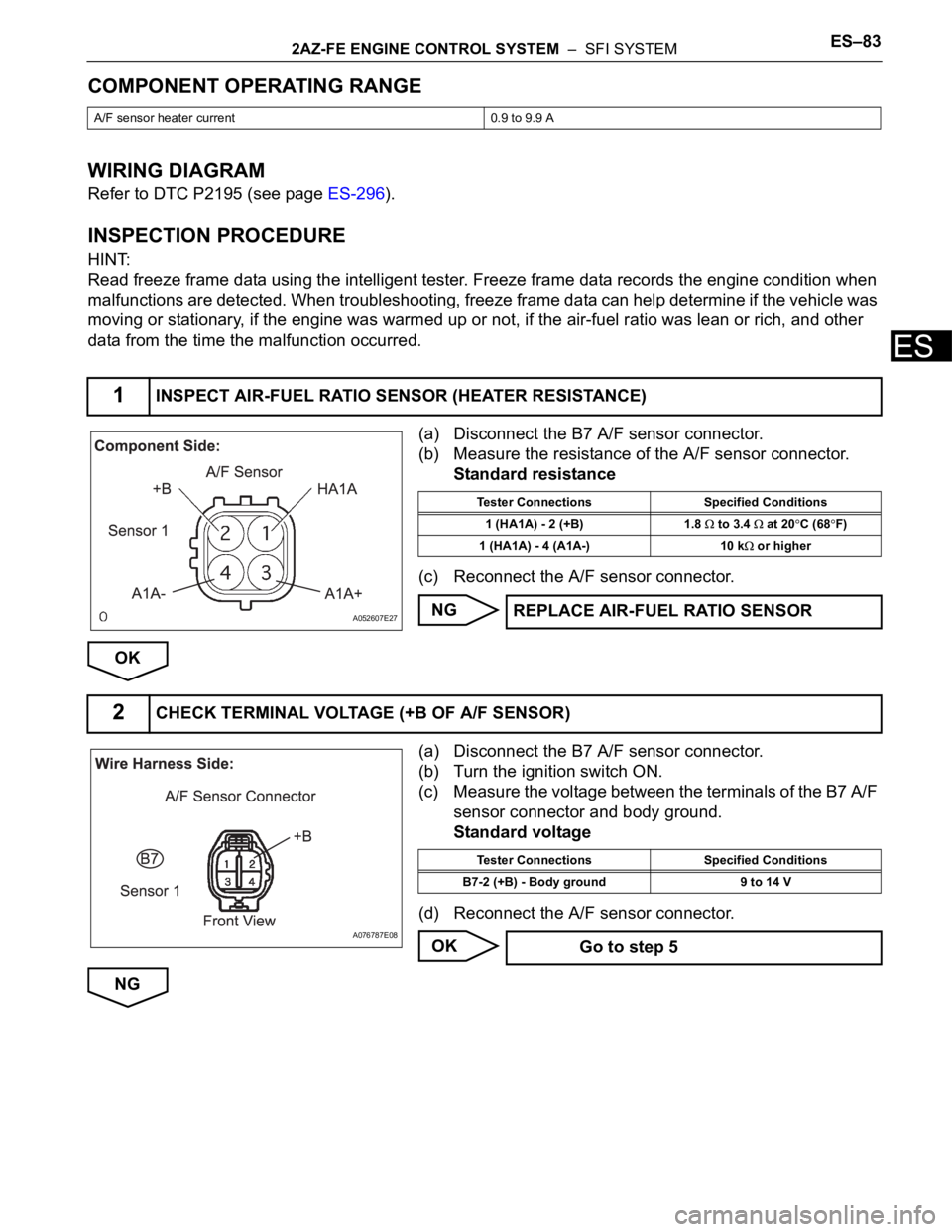
(a) Disconnect the B7 A/F sensor connector.
(b) Measure the resistance of the A/F sensor connector.
Standard resistance
(c) Reconnect the A/F sensor connector.
NG
OK
(a) Disconnect the B7 A/F sensor connector.
(b) Turn the ignition switch ON.
(c) Measure the voltage between the terminals of the B7 A/F
sensor connector and body ground.
Standard voltage
(d) Reconnect the A/F sensor connector.
OK
NG
A/F sensor heater current 0.9 to 9.9 A
1INSPECT AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR (HEATER RESISTANCE)
A052607E27
Tester Connections Specified Conditions
1 (HA1A) - 2 (+B) 1.8
to 3.4 at 20C (68F)
1 (HA1A) - 4 (A1A-) 10 k
or higher
REPLACE AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR
2CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (+B OF A/F SENSOR)
A076787E08
Tester Connections Specified Conditions
B7-2 (+B) - Body ground 9 to 14 V
Go to step 5
Page 1977 of 2000
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–89
ES
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
P0037:
P0038:
P0141 (Heater performance monitor check):
COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0136 (see page ES-136).
CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
These DTCs are detected when the engine idles for 110 seconds or more.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Sensor 2 refers to the sensor mounted behind the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) and located far
from the engine assembly.
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when
malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other
data from the time the malfunction occurred.
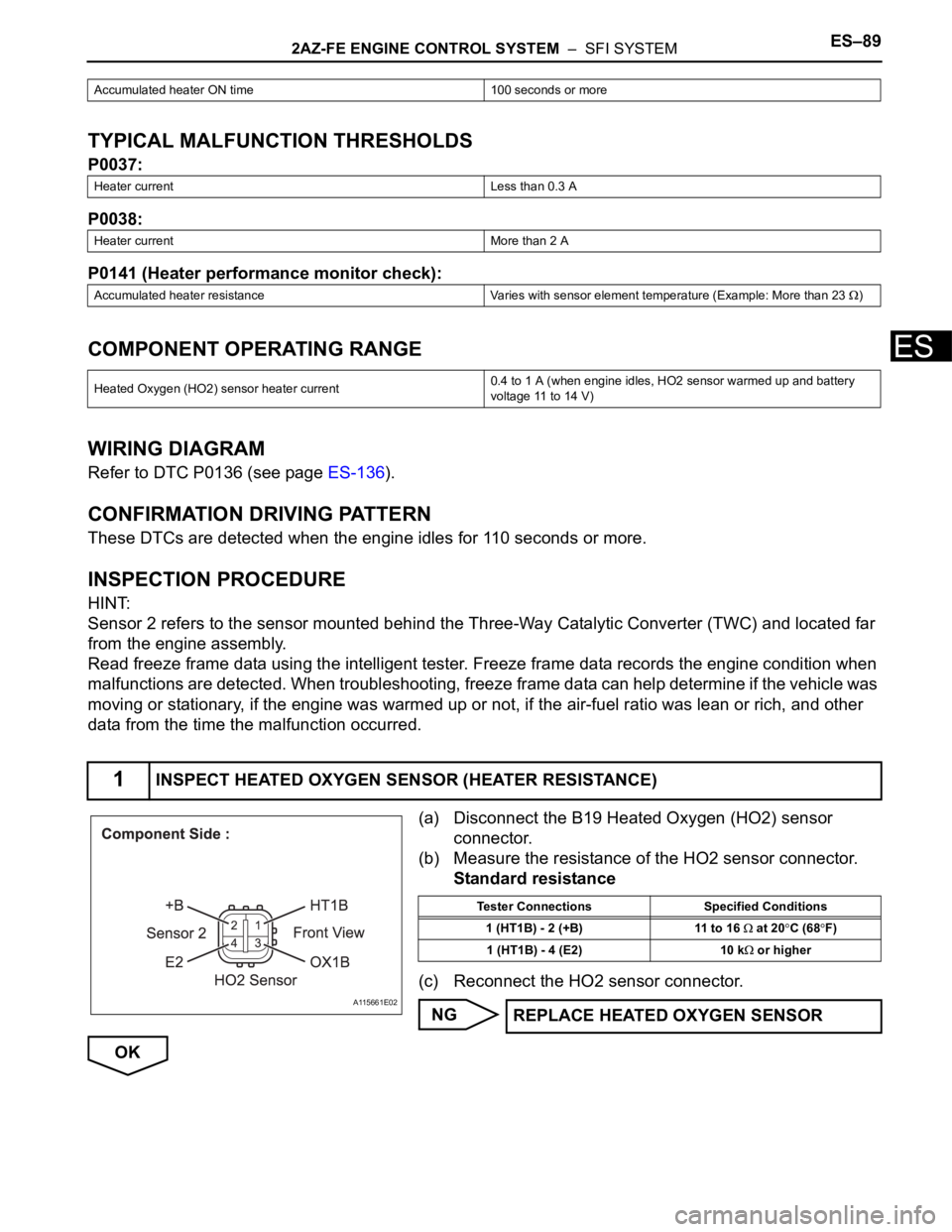
(a) Disconnect the B19 Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor
connector.
(b) Measure the resistance of the HO2 sensor connector.
Standard resistance
(c) Reconnect the HO2 sensor connector.
NG
OK
Accumulated heater ON time 100 seconds or more
Heater current Less than 0.3 A
Heater current More than 2 A
Accumulated heater resistance Varies with sensor element temperature (Example: More than 23
)
Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor heater current0.4 to 1 A (when engine idles, HO2 sensor warmed up and battery
voltage 11 to 14 V)
1INSPECT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HEATER RESISTANCE)
A115661E02
Tester Connections Specified Conditions
1 (HT1B) - 2 (+B) 11 to 16
at 20C (68F)
1 (HT1B) - 4 (E2) 10 k
or higher
REPLACE HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
Page 1983 of 2000
2AZ-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–95
ES
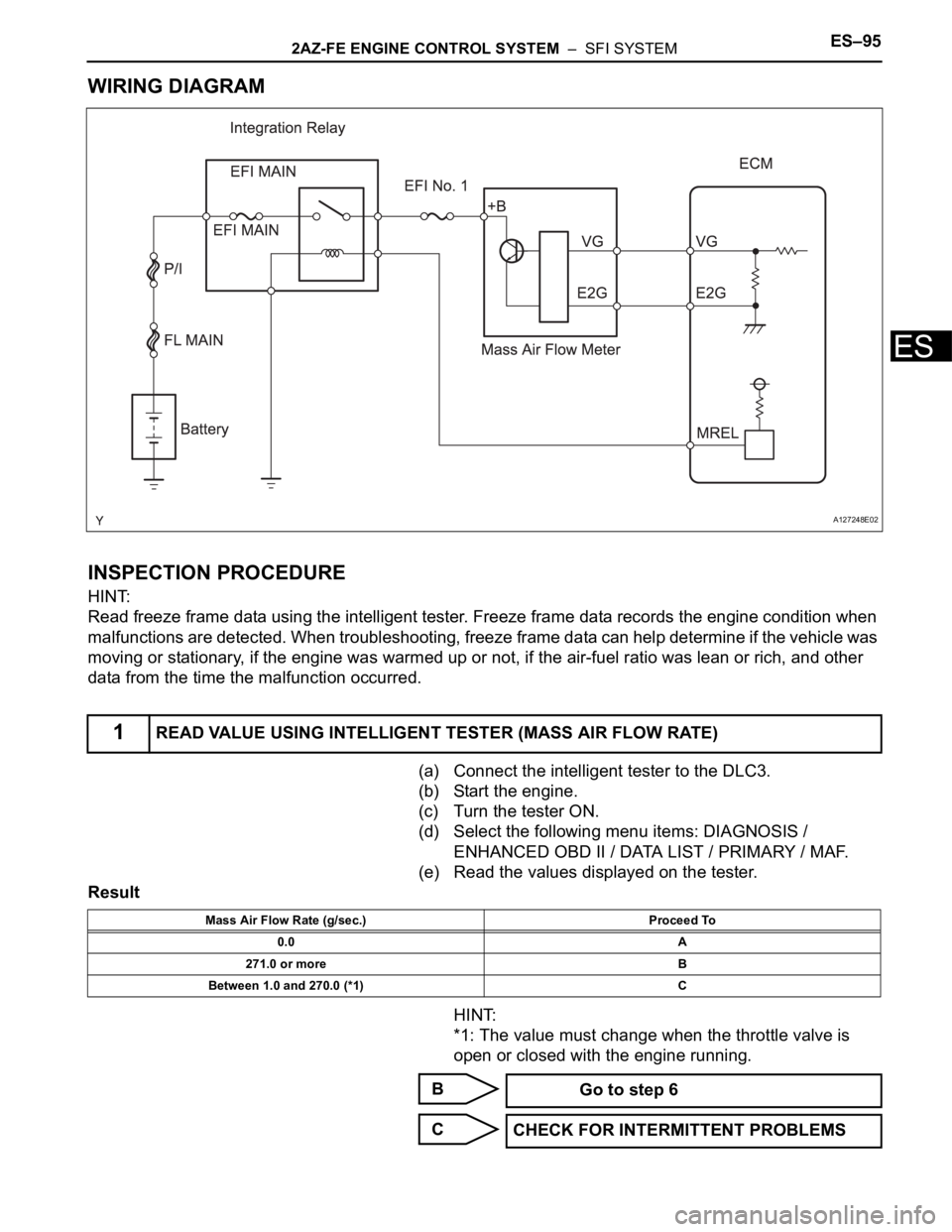
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when
malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other
data from the time the malfunction occurred.
(a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(b) Start the engine.
(c) Turn the tester ON.
(d) Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS /
ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST / PRIMARY / MAF.
(e) Read the values displayed on the tester.
Result
HINT:
*1: The value must change when the throttle valve is
open or closed with the engine running.
B
C
1READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (MASS AIR FLOW RATE)
A127248E02
Mass Air Flow Rate (g/sec.) Proceed To
0.0 A
271.0 or more B
Between 1.0 and 270.0 (*1) C
Go to step 6
CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS