engine oil TOYOTA RAV4 2006 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAV4, Model: TOYOTA RAV4 2006Pages: 2000, PDF Size: 45.84 MB
Page 114 of 2000
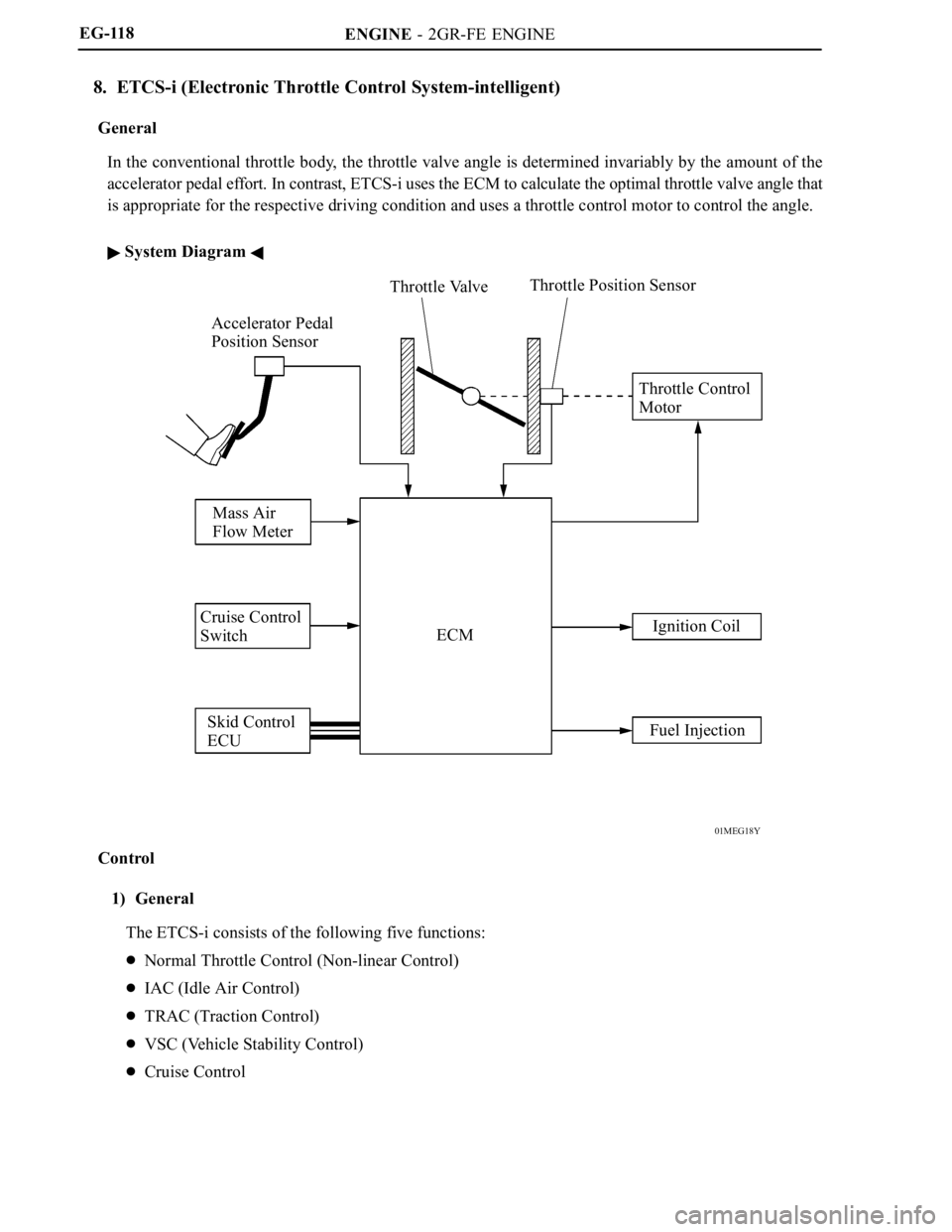
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
01MEG18Y
Accelerator Pedal
Position SensorThrottle ValveThrottle Position Sensor
Throttle Control
Motor
Mass Air
Flow Meter
Cruise Control
Switch
Skid Control
ECUECMIgnition Coil
Fuel Injection EG-118
8. ETCS-i (Electronic Throttle Control System-intelligent)
General
In the conventional throttle body, the throttle valve angle is determined invariably by the amount of the
accelerator pedal effort. In contrast, ETCS-i uses the ECM to calculate the optimal throttle valve angle that
is appropriate for the respective driving condition and uses a throttle control motor to control the angle.
System Diagram
Control
1) General
The ETCS-i consists of the following five functions:
Normal Throttle Control (Non-linear Control)
IAC (Idle Air Control)
TRAC (Traction Control)
VSC (Vehicle Stability Control)
Cruise Control
Page 116 of 2000

ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
285EG57
Exhaust Camshaft Timing OCV* (Bank 1)
Intake Camshaft Timing OCV* (Bank 1)
Exhaust VVT Sensor (Bank 1)
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Intake Camshaft
Timing OCV* (Bank 2)
Exhaust VVT
Sensor (Bank 2)
Exhaust Camshaft
Timing OCV*
(Bank 2)
Intake VVT Sensor (Bank 2)
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Intake VVT Sensor (Bank 1)ECM
Mass Air Flow MeterThrottle Position Sensor
221EG16
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Mass Air Flow Meter
Throttle Position Sensor
Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor
Intake and Exhaust VVT Sensors
Vehicle Speed SignalECM
Ta r g e t Va l v e Ti m i n g
Feedback
Correction
Actual Valve Timing
Duty-cycle
Control
Camshaft Timing
Oil Control Valve
EG-120
9. Dual VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing-intelligent) System
General
The Dual VVT-i system is designed to control the intake and exhaust camshafts within a range of 40
and 35 respectively (of Crankshaft Angle) to provide valve timing that is optimally suited to the engine
condition. This improves torque in all the speed ranges as well as increasing fuel economy, and reducing
exhaust emissions.
*: Oil Control Valve
Using the engine speed signal, vehicle speed signal, and the signals from mass air flow meter, throttle
position sensor and engine coolant temperature sensor, the ECM calculates optimal valve timing for each
driving condition and controls the camshaft timing oil control valve. In addition, the ECM uses signals
from the camshaft position sensor and the crankshaft position sensor to detect the actual valve timing,
thus providing feedback control to achieve the target valve timing.
Page 118 of 2000
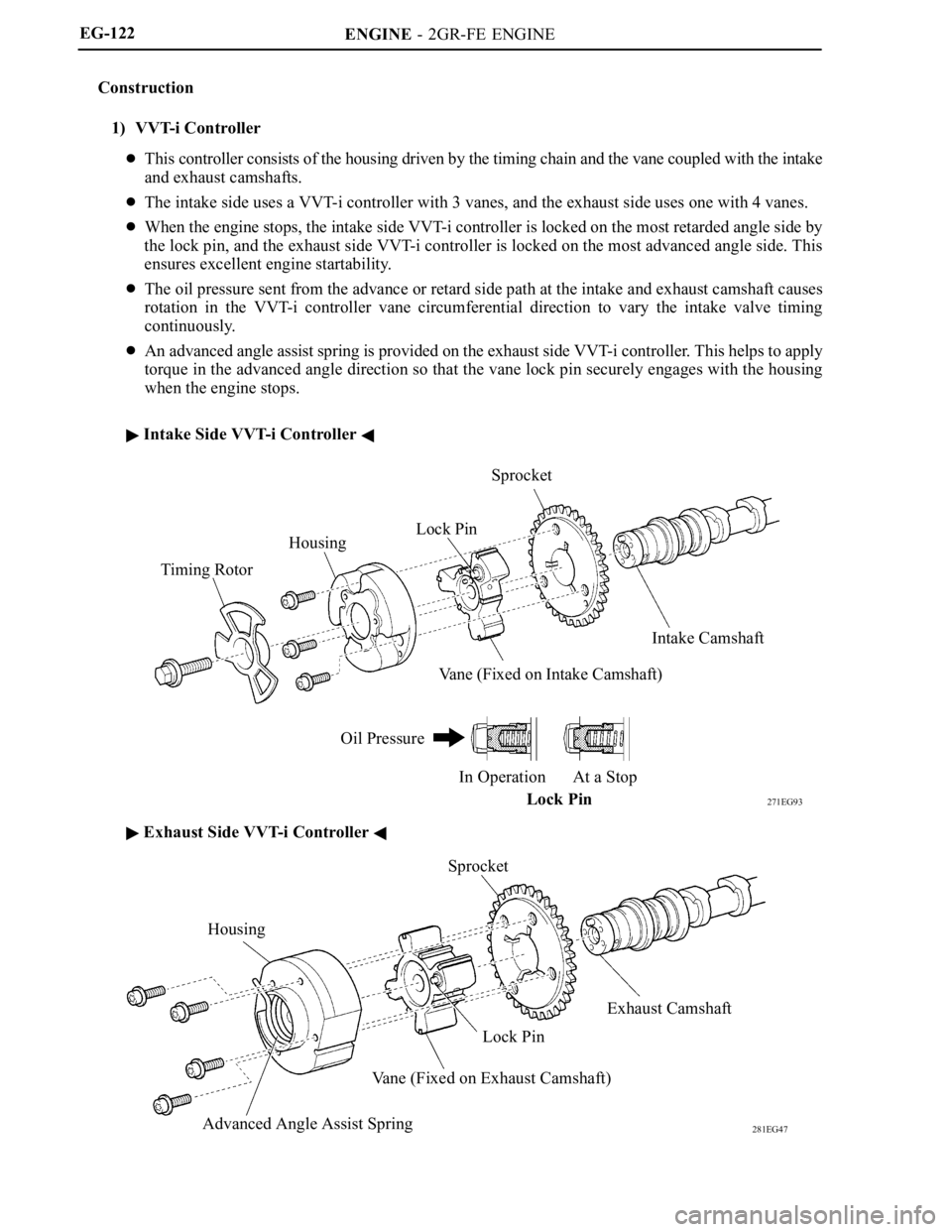
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
271EG93
Timing RotorHousingLock PinSprocket
Intake Camshaft
Vane (Fixed on Intake Camshaft)
Oil Pressure
In Operation At a Stop
Lock Pin
281EG47
Housing
Advanced Angle Assist SpringVane (Fixed on Exhaust Camshaft)Lock PinExhaust Camshaft Sprocket EG-122
Construction
1) VVT-i Controller
This controller consists of the housing driven by the timing chain and the vane coupled with the intake
and exhaust camshafts.
The intake side uses a VVT-i controller with 3 vanes, and the exhaust side uses one with 4 vanes.
When the engine stops, the intake side VVT-i controller is locked on the most retarded angle side by
the lock pin, and the exhaust side VVT-i controller is locked on the most advanced angle side. This
ensures excellent engine startability.
The oil pressure sent from the advance or retard side path at the intake and exhaust camshaft causes
rotation in the VVT-i controller vane circumferential direction to vary the intake valve timing
continuously.
An advanced angle assist spring is provided on the exhaust side VVT-i controller. This helps to apply
torque in the advanced angle direction so that the vane lock pin securely engages with the housing
when the engine stops.
Intake Side VVT-i Controller
Exhaust Side VVT-i Controller
Page 119 of 2000
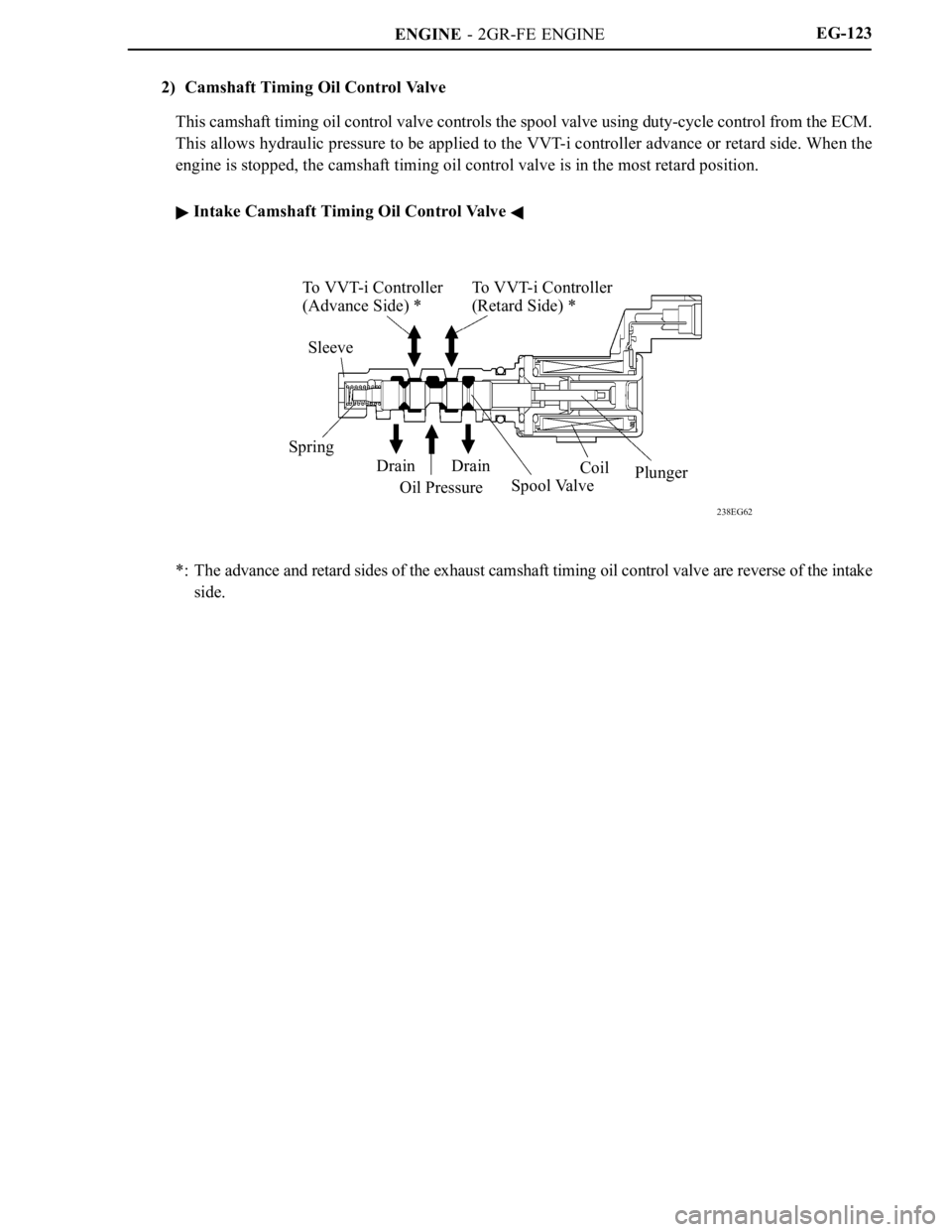
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
238EG62
To VVT-i Controller
(Advance Side) *To VVT-i Controller
(Retard Side) *
Sleeve
Spring
Drain
Oil PressureDrain
Spool ValveCoil
PlungerEG-123
2) Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve
This camshaft timing oil control valve controls the spool valve using duty-cycle control from the ECM.
This allows hydraulic pressure to be applied to the VVT-i controller advance or retard side. When the
engine is stopped, the camshaft timing oil control valve is in the most retard position.
Intake Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve
*: The advance and retard sides of the exhaust camshaft timing oil control valve are reverse of the intake
side.
Page 120 of 2000
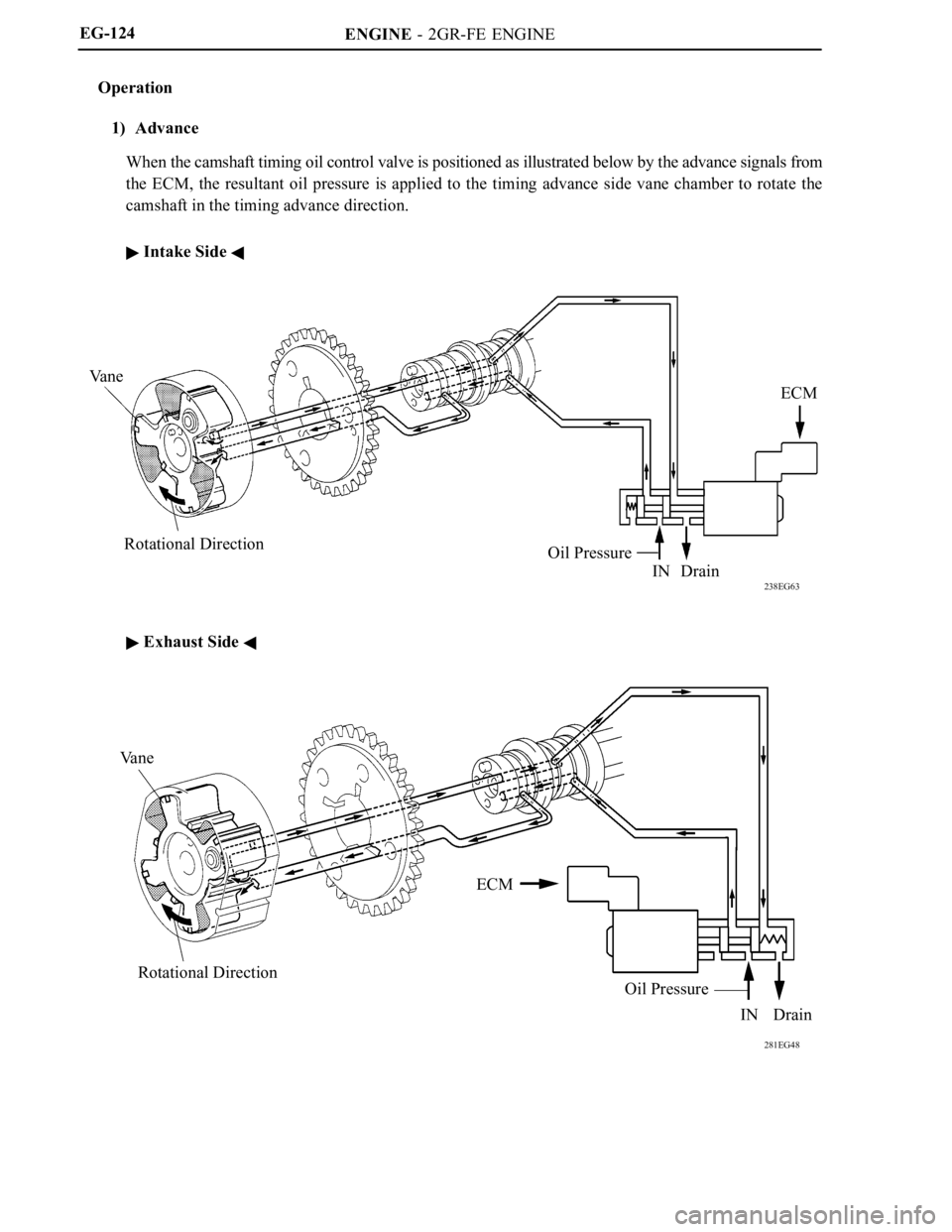
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
238EG63
Va n e
Rotational Direction
Oil Pressure
IN DrainECM
281EG48
Va n e
Rotational DirectionECM
Oil Pressure
IN Drain EG-124
Operation
1) Advance
When the camshaft timing oil control valve is positioned as illustrated below by the advance signals from
the ECM, the resultant oil pressure is applied to the timing advance side vane chamber to rotate the
camshaft in the timing advance direction.
Intake Side
Exhaust Side
Page 121 of 2000
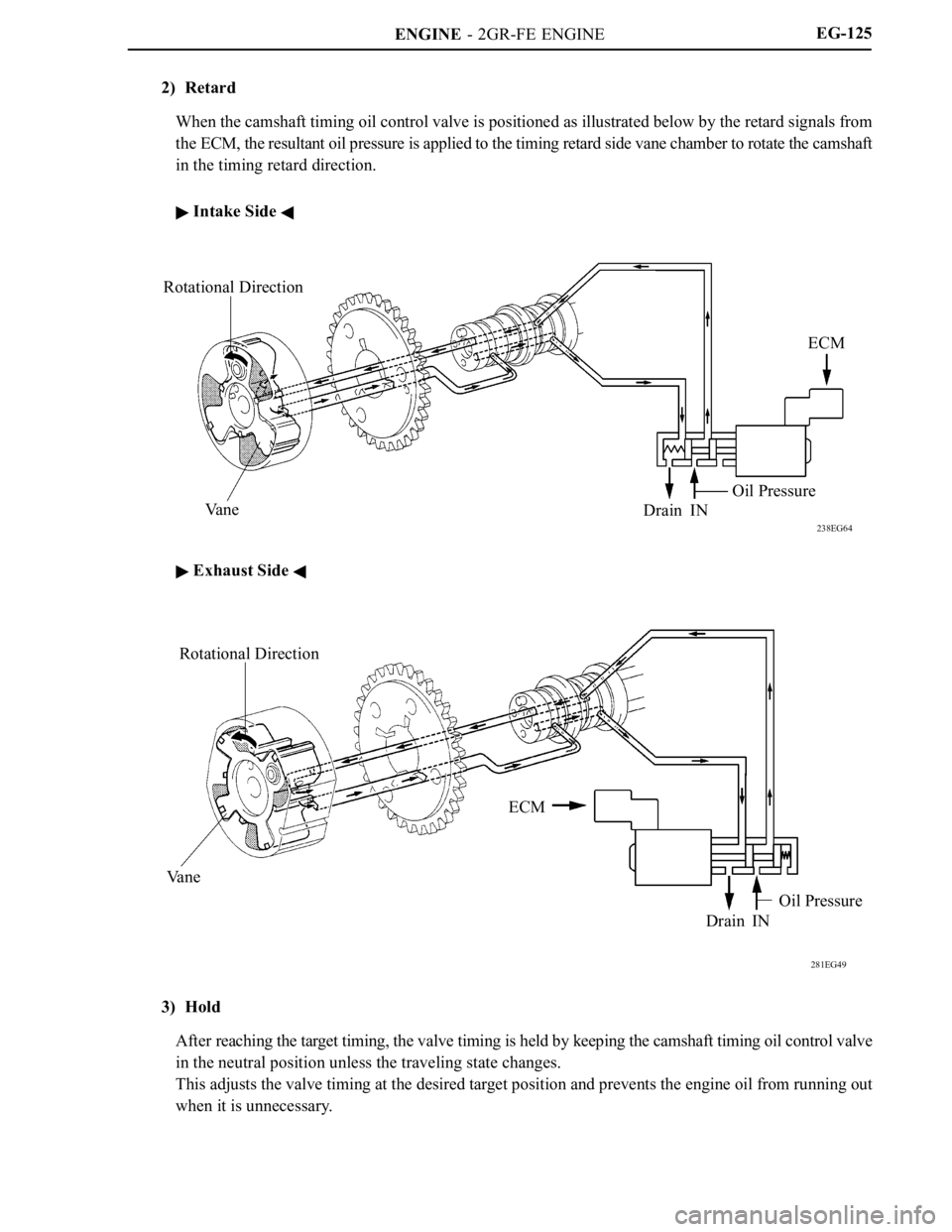
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
238EG64
Rotational Direction
Va n e
Drain INOil PressureECM
281EG49
Rotational Direction
Va n eECM
Drain INOil Pressure
EG-125
2) Retard
When the camshaft timing oil control valve is positioned as illustrated below by the retard signals from
the ECM, the resultant oil pressure is applied to the timing retard side vane chamber to rotate the camshaft
in the timing retard direction.
Intake Side
Exhaust Side
3) Hold
After reaching the target timing, the valve timing is held by keeping the camshaft timing oil control valve
in the neutral position unless the traveling state changes.
This adjusts the valve timing at the desired target position and prevents the engine oil from running out
when it is unnecessary.
Page 131 of 2000
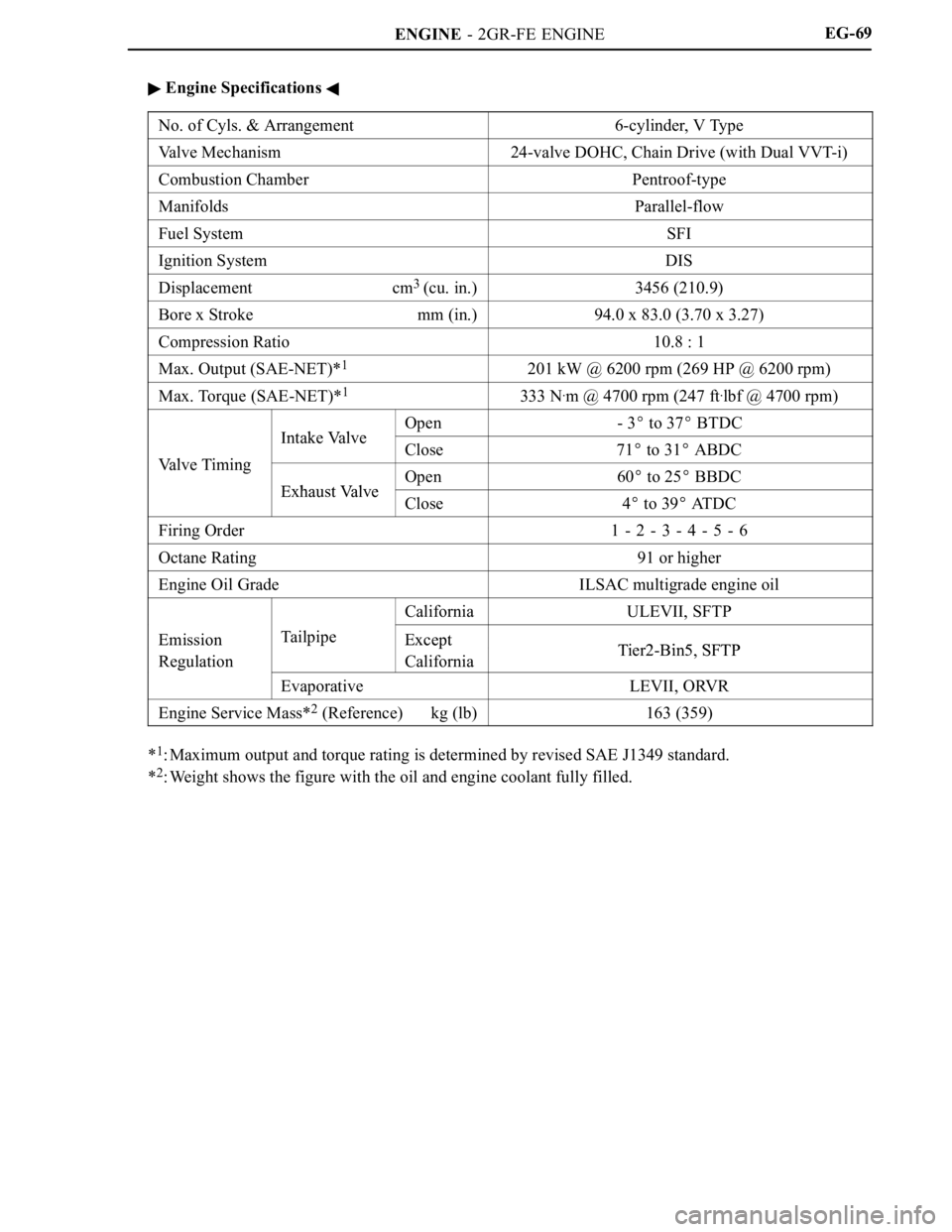
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINEEG-69
Engine Specifications
No. of Cyls. & Arrangement6-cylinder, V Type
Valve Mechanism24-valve DOHC, Chain Drive (with Dual VVT-i)
Combustion ChamberPentroof-type
ManifoldsParallel-flow
Fuel SystemSFI
Ignition SystemDIS
Displacement cm3
(cu. in.)3456 (210.9)
Bore x Stroke mm (in.)94.0 x 83.0 (3.70 x 3.27)
Compression Ratio10.8 : 1
Max. Output (SAE-NET)*1201 kW @ 6200 rpm (269 HP @ 6200 rpm)
Max. Torque (SAE-NET)*1333 N.m @ 4700 rpm (247 ft.lbf @ 4700 rpm)
Intake ValveOpen-3 to 37 BTDC
Valve Timing
Intake ValveClose71 to 31 ABDCVa l v e T i m i n g
Exhaust ValveOpen60 to 25 BBDCExhaust ValveClose4 to 39 ATDC
Firing Order1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6
Octane Rating91 or higher
Engine Oil GradeILSAC multigrade engine oil
CaliforniaULEVII, SFTP
EmissionTailpipeExceptTier2 Bin5 SFTPEmission
Regulation
ppExcept
CaliforniaTier2-Bin5, SFTPg
EvaporativeLEVII, ORVR
Engine Service Mass*2 (Reference) kg (lb)163 (359)
*1: Maximum output and torque rating is determined by revised SAE J1349 standard.
*
2: Weight shows the figure with the oil and engine coolant fully filled.
Page 179 of 2000

SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS – U151E AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONSS–47
SS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
Automatic Transaxle Assembly
Part Tightened N*m kgf*cm ft*lbf
Park/neutral position switch Nut 6.9 70 61 in.*lbf
Bolt 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
Control shaft lever x Control shaft 13 133 10
Shift control cable x Control shaft lever 15 153 11
Transaxle housing x Engine block Upper side bolt 64 653 47
Lower side bolt
A37 377 27
Lower side bolt
B46 470 34
Torque converter clutch x Drive plate 41 418 30
Flywheel housing under cover x Automatic transaxle 7.8 80 69 in.*lbf
Front engine mounting bracket x Transaxle 64 653 47
Rear engine mounting bracket x Transaxle 45 459 33
Engine mounting bracket LH x Transaxle 64 653 47
Oil filler tube x Transaxle
Oil filler tube x Front engine mounting bracket5.5 56 49 in.*lbf
Control cable bracket No. 1 x Transaxle 12 122 9
Control cable bracket No. 2 x Transaxle 12 122 9
Oil cooler inlet elbow x Transaxle 27 276 20
Oil cooler outlet elbow x Transaxle 27 276 20
Starter x Transaxle37 377 27
Starter wire x Starter9.8 100 88 in.*lbf
Speed sensor (NC) x Transaxle 11 112 8
Speed sensor (NT) x Transaxle 11 112 8
Drain plug x Oil pan47 479 35
Transmission wire x Transaxle 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
ATF temperature sensor x Valve body 6.6 67 58 in.*lbf
Oil pan x Transaxle7.8 80 69 in.*lbf
Solenoid valve x Valve body SL2, DSL, S4 11 110 8
SL1, SL3 6.6 67 58 in.*lbf
Valve body x Transaxle11 11 2 8
Oil strainer x Valve body11 11 2 8
Floor shift assembly x Body12 122 9
Control cable clamp x Engine mounting insulator 12 122 9
Differential gear lube apply tube x Transaxle housing 9.8 100 87 in.*lbf
Front planetary gear lock nut 280 3,355 207
Brake apply tube clamp x Transaxle case 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
Transaxle case No. 1 plug x Transaxle rear cover 7.4 75 65 in.*lbf
Transaxle rear cover x Transaxle case Bolt A 19 194 14
Other bolt 25 255 18
Parking lock pawl shaft x Transaxle case 9.8 100 87 in.*lbf
Oil pump assembly x Transaxle case 22 226 16
Transaxle housing x Transaxle case Bolt A 22 254 16
Bolt B 29 295 21
Bolt C 29 295 21
Bolt D 22 254 16
Automatic transmission case plug x Transaxle housing 7.4 75 65 in.*lbf
Automatic transmission case plug x Transaxle case 7.4 75 65 in.*lbf
Page 182 of 2000

MAINTENANCE – UNDER HOODMA–7
MA
GENERAL MAINTENANCE
(2006/01- )
1. GENERAL NOTES
• Maintenance requirements vary depending on the
country.
• Check the maintenance schedule in the owner's
manual supplement.
• Following the maintenance schedule is mandatory.
• Determine the appropriate time to service the vehicle
using either miles driven or time elapsed, whichever
reaches the specification first.
• Maintain similar intervals between periodic
maintenance, unless otherwise noted.
• Failing to check each vehicle part could lead to poor
engine performance and increase exhaust emissions.
2. WINDSHIELD WASHER FLUID
(a) Check that there is sufficient fluid in the tank.
3. ENGINE COOLANT LEVEL
(a) Check that the coolant level is between the "FULL"
and "LOW" lines on the see-through reservoir.
4. RADIATOR AND HOSES
(a) Check that the front of the radiator is clean and not
blocked by leaves, dirt or bugs.
(b) Check the hoses for cracks, kinks, rot or loose
connections.
5. BATTERY ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
(a) Check that the electrolyte level of all the battery
cells is between the upper and lower level lines on
the case.
HINT:
If the electrolyte level is difficult to see, lightly shake
the vehicle.
6. BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
(a) Check that the brake fluid levels are near the upper
level lines on the see-through reservoirs.
7. ENGINE DRIVE BELT
(a) Check the drive belt for fraying, cracks, wear or
oiliness.
8. ENGINE OIL LEVEL
(a) Check the level on the dipstick with the engine
stopped.
9. AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID LEVEL
10. EXHAUST SYSTEM
(a) Check for unusual exhaust sounds or abnormal
exhaust fumes. Inspect the cause and repair it.
Type See procedures
U151E See page AX-126
U151F See page AX-126
Page 196 of 2000
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE ASSEMBLYEM–21
EM
REMOVAL
1. DISCHARGE REFRIGERANT FROM
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM (See page AC-172)
2. DISCHARGE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE (See page
FU-13)
3. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE BATTERY
TERMINAL
CAUTION:
Wait at least 90 seconds after disconnecting the
cable from the negative (-) battery terminal to
prevent airbag and seat belt pretensioner activation.
4. REMOVE NO. 1 ENGINE UNDER COVER
(a) Remove the 4 bolts, 12 clips and under cover.
5. REMOVE REAR ENGINE UNDER COVER RH
(a) Remove the 2 clips and under cover.
6. REMOVE REAR ENGINE UNDER COVER LH
(a) Remove the 2 clips and under cover.
7. REMOVE NO. 2 ENGINE UNDER COVER
(a) Remove the 2 clips and under cover.
8. REMOVE FRONT FLOOR COVER (See page FU-34)
9. DRAIN ENGINE COOLANT (See page CO-8)
10. DRAIN ENGINE OIL (See page LU-4)
11. DRAIN AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID
(a) 2WD:
Drain automatic transaxle fluid (see page AX-172).
(b) 4WD:
Drain automatic transaxle fluid (see page AX-173)
12. DRAIN TRANSFER OIL (for 4WD)
13. REMOVE HOOD SUB-ASSEMBLY (See page ED-4)
14. REMOVE V-BANK COVER SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Detach the 3 clips and remove the V-bank cover.
A137900