oil TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 924 of 3000
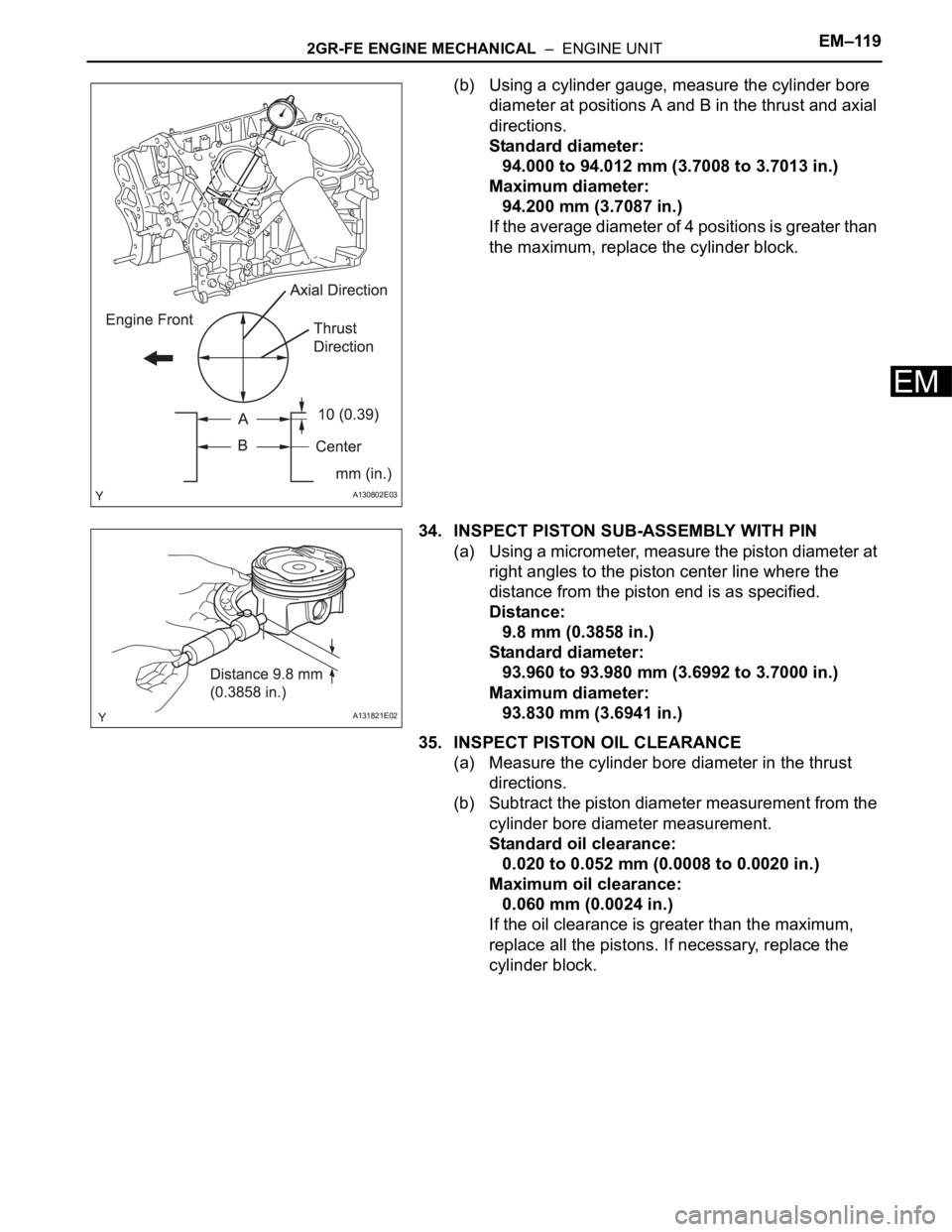
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNITEM–119
EM
(b) Using a cylinder gauge, measure the cylinder bore
diameter at positions A and B in the thrust and axial
directions.
Standard diameter:
94.000 to 94.012 mm (3.7008 to 3.7013 in.)
Maximum diameter:
94.200 mm (3.7087 in.)
If the average diameter of 4 positions is greater than
the maximum, replace the cylinder block.
34. INSPECT PISTON SUB-ASSEMBLY WITH PIN
(a) Using a micrometer, measure the piston diameter at
right angles to the piston center line where the
distance from the piston end is as specified.
Distance:
9.8 mm (0.3858 in.)
Standard diameter:
93.960 to 93.980 mm (3.6992 to 3.7000 in.)
Maximum diameter:
93.830 mm (3.6941 in.)
35. INSPECT PISTON OIL CLEARANCE
(a) Measure the cylinder bore diameter in the thrust
directions.
(b) Subtract the piston diameter measurement from the
cylinder bore diameter measurement.
Standard oil clearance:
0.020 to 0.052 mm (0.0008 to 0.0020 in.)
Maximum oil clearance:
0.060 mm (0.0024 in.)
If the oil clearance is greater than the maximum,
replace all the pistons. If necessary, replace the
cylinder block.
A130802E03
A131821E02
Page 925 of 3000

EM–1202GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNIT
EM
36. INSPECT RING GROOVE CLEARANCE
(a) Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance
between a new piston ring and the wall of the ring
groove.
Ring groove clearance
If the clearance is not as specified, replace the
piston.
37. INSPECT PISTON RING END GAP
(a) Insert the piston ring into the cylinder bore.
(b) Using a piston, push the piston ring a little beyond
the bottom of the ring travel, 110 mm (4.33 in.) from
the top of the cylinder block.
(c) Using a feeler gauge, measure the end gap.
Standard end gap
Maximum end gap
If the end gap is greater than the maximum, replace
the piston ring. If the end gap is greater than the
maximum even with a new piston ring, rebore all the
6 cylinders or replace the cylinder block.
38. INSPECT PISTON PIN OIL CLEARANCE
(a) Using a caliper gauge, measure the inside diameter
of the piston pin hole.
Piston pin hole inside diameter
A131822
Item Clearance
No. 1 0.020 to 0.070 mm (0.0008 to 0.0028 in.)
No. 2 0.020 to 0.060 mm (0.0008 to 0.0024 in.)
Oil 0.070 to 0.150 mm (0.0028 to 0.0059 in.)
A106218E02
A109687
Item End Gap
No. 1 0.25 to 0.35 mm (0.0098 to 0.0138 in.)
No. 2 0.50 to 0.60 mm (0.0197 to 0.0236 in.)
Oil 0.10 to 0.40 mm (0.0039 to 0.0157 in.)
Item End Gap
No. 1 0.50 mm (0.0197 in.)
No. 2 0.85 mm (0.0335 in.)
Oil 0.60 mm (0.0236 in.)
A131823
Mark Diameter
A 22.001 to 22.004 mm (0.8662 to 0.8663 in.)
B 22.004 to 22.007 mm (0.8663 to 0.8664 in.)
C 22.007 to 22.010 mm (0.8664 to 0.8665 in.)
Page 926 of 3000
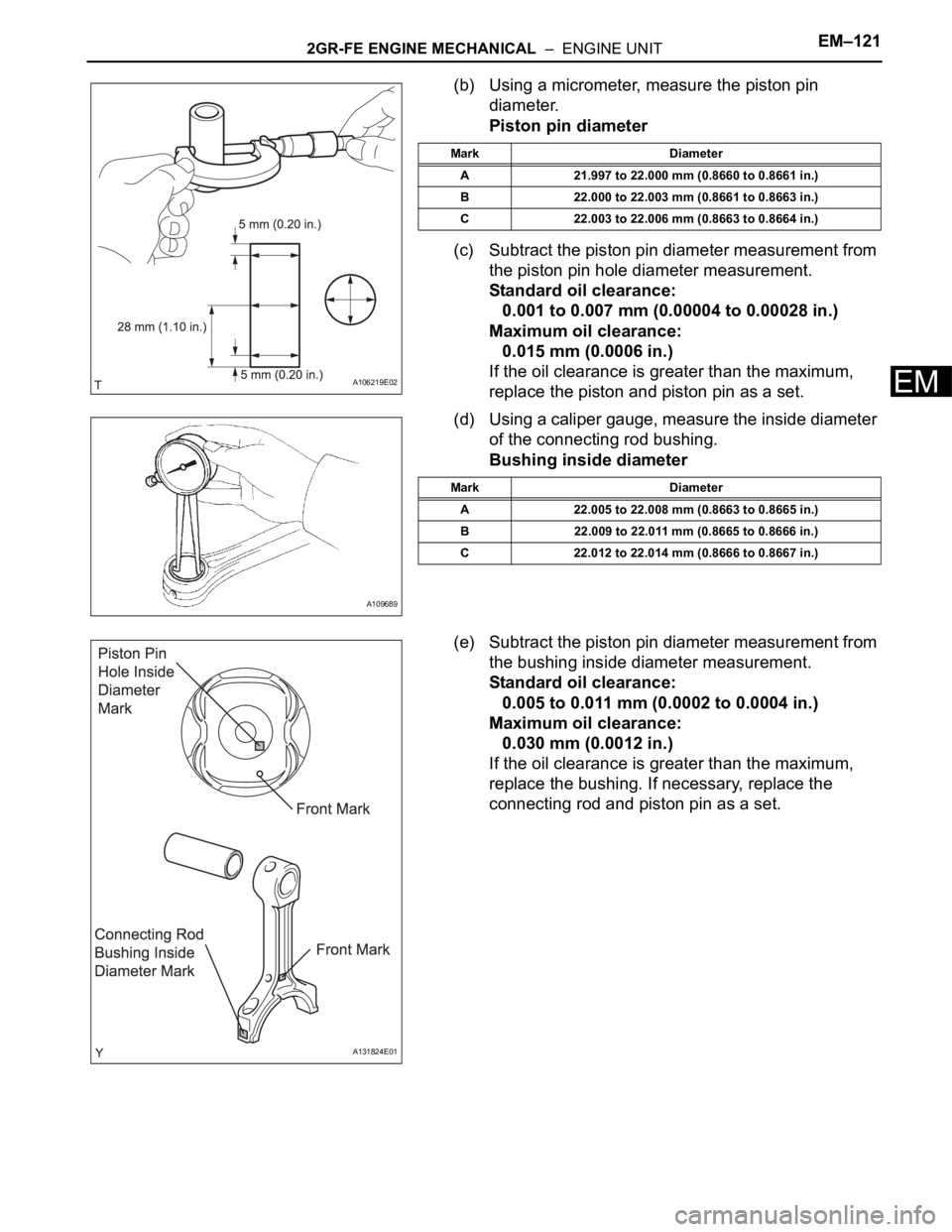
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNITEM–121
EM
(b) Using a micrometer, measure the piston pin
diameter.
Piston pin diameter
(c) Subtract the piston pin diameter measurement from
the piston pin hole diameter measurement.
Standard oil clearance:
0.001 to 0.007 mm (0.00004 to 0.00028 in.)
Maximum oil clearance:
0.015 mm (0.0006 in.)
If the oil clearance is greater than the maximum,
replace the piston and piston pin as a set.
(d) Using a caliper gauge, measure the inside diameter
of the connecting rod bushing.
Bushing inside diameter
(e) Subtract the piston pin diameter measurement from
the bushing inside diameter measurement.
Standard oil clearance:
0.005 to 0.011 mm (0.0002 to 0.0004 in.)
Maximum oil clearance:
0.030 mm (0.0012 in.)
If the oil clearance is greater than the maximum,
replace the bushing. If necessary, replace the
connecting rod and piston pin as a set.
A106219E02
Mark Diameter
A 21.997 to 22.000 mm (0.8660 to 0.8661 in.)
B 22.000 to 22.003 mm (0.8661 to 0.8663 in.)
C 22.003 to 22.006 mm (0.8663 to 0.8664 in.)
A109689
Mark Diameter
A 22.005 to 22.008 mm (0.8663 to 0.8665 in.)
B 22.009 to 22.011 mm (0.8665 to 0.8666 in.)
C 22.012 to 22.014 mm (0.8666 to 0.8667 in.)
A131824E01
Page 928 of 3000
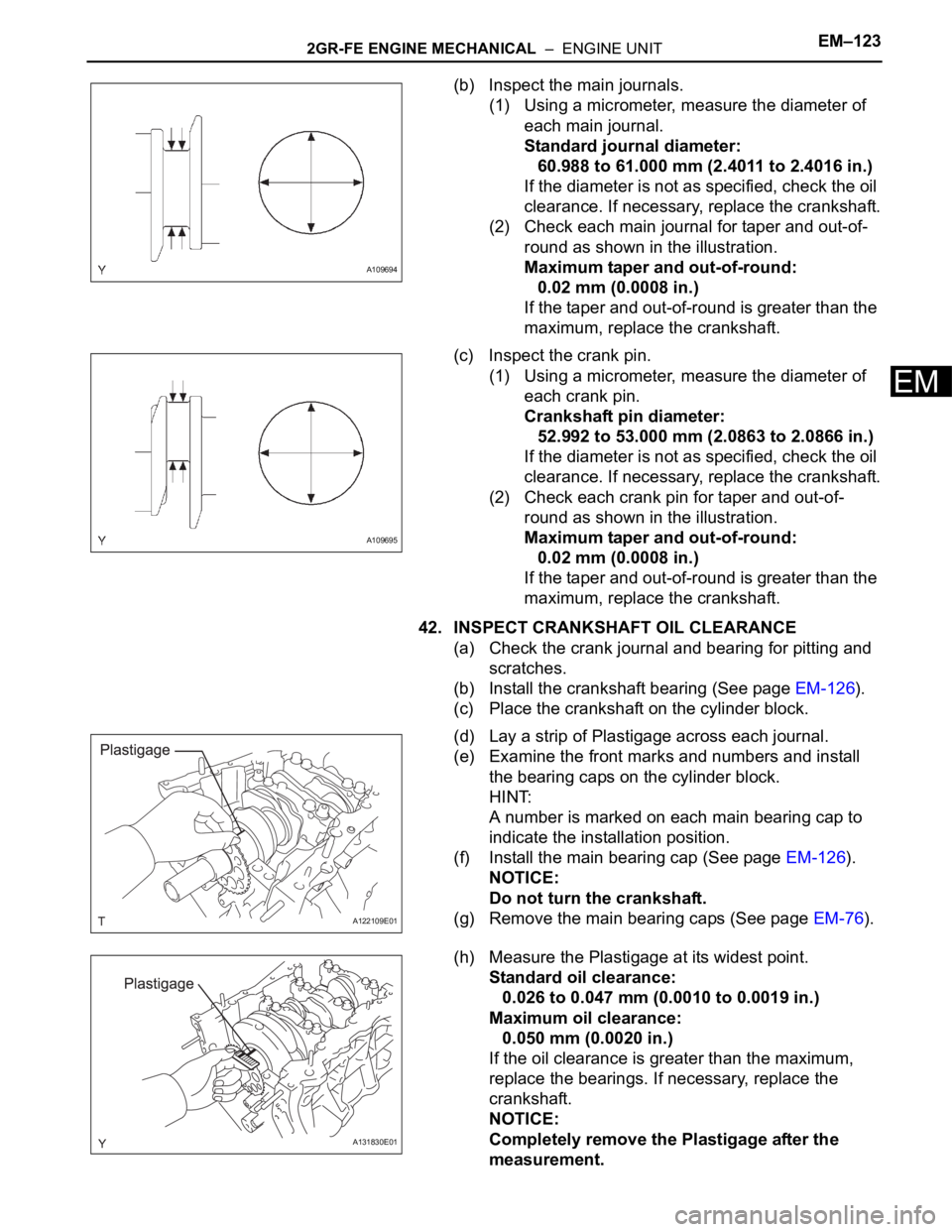
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNITEM–123
EM
(b) Inspect the main journals.
(1) Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of
each main journal.
Standard journal diameter:
60.988 to 61.000 mm (2.4011 to 2.4016 in.)
If the diameter is not as specified, check the oil
clearance. If necessary, replace the crankshaft.
(2) Check each main journal for taper and out-of-
round as shown in the illustration.
Maximum taper and out-of-round:
0.02 mm (0.0008 in.)
If the taper and out-of-round is greater than the
maximum, replace the crankshaft.
(c) Inspect the crank pin.
(1) Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of
each crank pin.
Crankshaft pin diameter:
52.992 to 53.000 mm (2.0863 to 2.0866 in.)
If the diameter is not as specified, check the oil
clearance. If necessary, replace the crankshaft.
(2) Check each crank pin for taper and out-of-
round as shown in the illustration.
Maximum taper and out-of-round:
0.02 mm (0.0008 in.)
If the taper and out-of-round is greater than the
maximum, replace the crankshaft.
42. INSPECT CRANKSHAFT OIL CLEARANCE
(a) Check the crank journal and bearing for pitting and
scratches.
(b) Install the crankshaft bearing (See page EM-126).
(c) Place the crankshaft on the cylinder block.
(d) Lay a strip of Plastigage across each journal.
(e) Examine the front marks and numbers and install
the bearing caps on the cylinder block.
HINT:
A number is marked on each main bearing cap to
indicate the installation position.
(f) Install the main bearing cap (See page EM-126).
NOTICE:
Do not turn the crankshaft.
(g) Remove the main bearing caps (See page EM-76).
(h) Measure the Plastigage at its widest point.
Standard oil clearance:
0.026 to 0.047 mm (0.0010 to 0.0019 in.)
Maximum oil clearance:
0.050 mm (0.0020 in.)
If the oil clearance is greater than the maximum,
replace the bearings. If necessary, replace the
crankshaft.
NOTICE:
Completely remove the Plastigage after the
measurement.
A109694
A109695
A122109E01
A131830E01
Page 931 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINEEM–1
EM
ENGINE
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
1. INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT
(a) Inspect the engine coolant (See page CO-1).
2. INSPECT ENGINE OIL
(a) Inspect the engine oil (See page LU-1).
3. INSPECT BATTERY
(a) Inspect the battery (See page CH-5).
4. INSPECT AIR CLEANER FILTER ELEMENT SUB-
ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the air cleaner filter element sub-assembly.
(b) Visually check that there is no dirt, blockage, and/or
damage to the air cleaner filter element.
HINT:
• If there is any dirt or a blockage in the air cleaner
filter element, clean it with compressed air.
• If any dirt or a blockage remains even after
cleaning the air cleaner filter element with
compressed air, replace it.
5. INSPECT SPARK PLUG
(a) Inspect the spark plugs (See page IG-5).
6. INSPECT VALVE LASH ADJUSTER NOISE
(a) Rev up the engine several times. Check that the
engine does not emit unusual noises.
If unusual noises occur, warm up the engine and
idle it for over 30 minutes. Then repeat this
procedure.
HINT:
If any defects or problems are found during the
inspection above, perform lash adjuster inspection
(See page EM-100).
7. INSPECT IGNITION TIMING
(a) Warm up the engine.
(b) When using the intelligent tester:
Check the ignition timing.
(1) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
(2) Enter DATA LIST mode with the intelligent
tester.
Ignition timing:
8 to 12
BTDC at idle
HINT:
Refer to the intelligent tester operator's manual
for help when selecting the DATA LIST.
C110200E02
Page 933 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINEEM–3
EM
• Switch off all accessories and air
conditioning before connecting the
intelligent tester.
HINT:
Refer to the intelligent tester operator's manual
for further details.
(c) When not using the intelligent tester:
Check the idle speed.
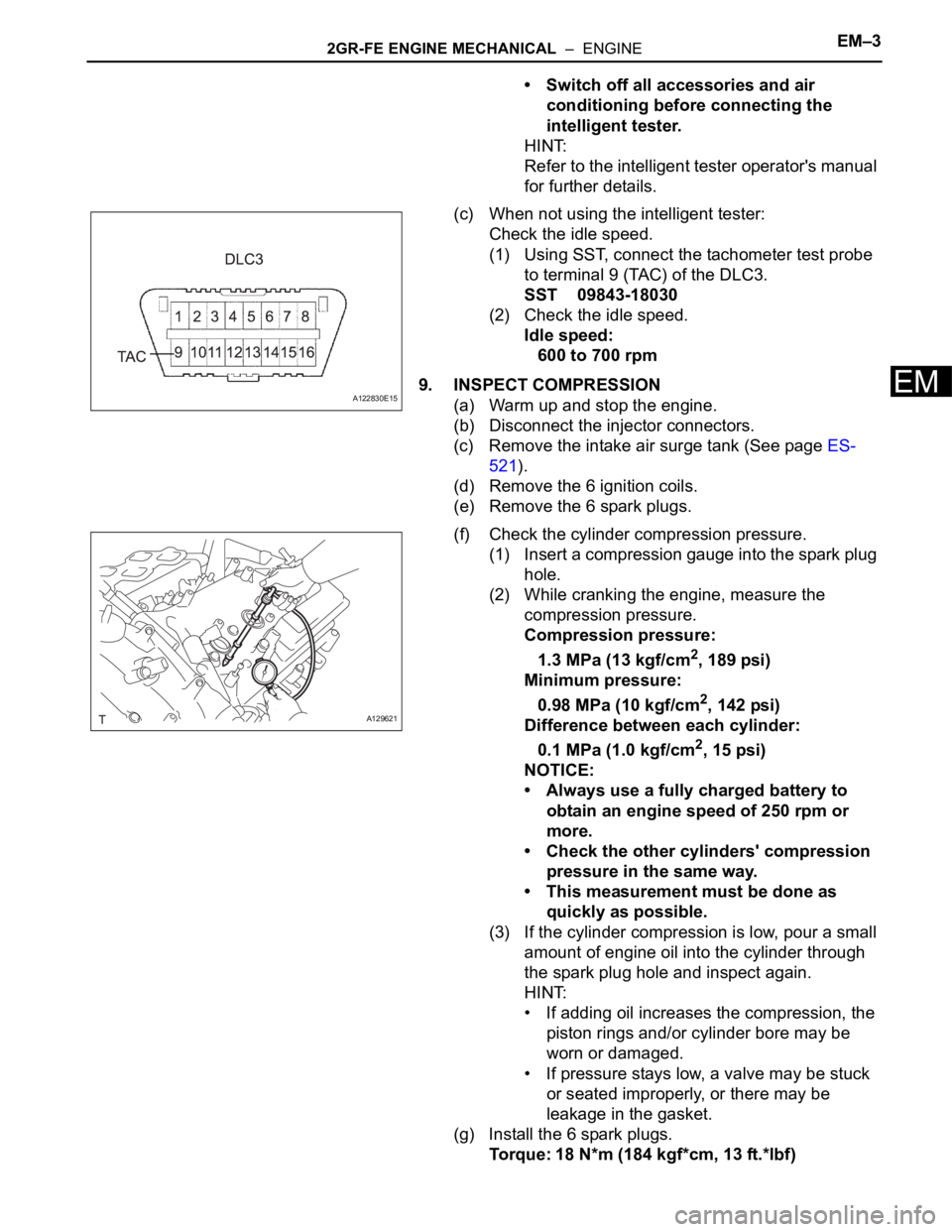
(1) Using SST, connect the tachometer test probe
to terminal 9 (TAC) of the DLC3.
SST 09843-18030
(2) Check the idle speed.
Idle speed:
600 to 700 rpm
9. INSPECT COMPRESSION
(a) Warm up and stop the engine.
(b) Disconnect the injector connectors.
(c) Remove the intake air surge tank (See page ES-
521).
(d) Remove the 6 ignition coils.
(e) Remove the 6 spark plugs.
(f) Check the cylinder compression pressure.
(1) Insert a compression gauge into the spark plug
hole.
(2) While cranking the engine, measure the
compression pressure.
Compression pressure:
1.3 MPa (13 kgf/cm
2, 189 psi)
Minimum pressure:
0.98 MPa (10 kgf/cm
2, 142 psi)
Difference between each cylinder:
0.1 MPa (1.0 kgf/cm
2, 15 psi)
NOTICE:
• Always use a fully charged battery to
obtain an engine speed of 250 rpm or
more.
• Check the other cylinders' compression
pressure in the same way.
• This measurement must be done as
quickly as possible.
(3) If the cylinder compression is low, pour a small
amount of engine oil into the cylinder through
the spark plug hole and inspect again.
HINT:
• If adding oil increases the compression, the
piston rings and/or cylinder bore may be
worn or damaged.
• If pressure stays low, a valve may be stuck
or seated improperly, or there may be
leakage in the gasket.
(g) Install the 6 spark plugs.
Torque: 18 N*m (184 kgf*cm, 13 ft.*lbf)
A122830E15
A129621
Page 934 of 3000

EM–42GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE
EM
(h) Install the 6 ignition coils.
Torque: 10 N*m (102 kgf*cm, 7 ft.*lbf)
(i) Install the intake air surge tank (See page ES-522).
10. INSPECT CO/HC
(a) Start the engine.
(b) Run the engine at 2500 rpm for approximately 180
seconds.
(c) Insert the CO/HC meter testing probe at least 40 cm
(1.3 ft.) into the tailpipe during idling.
(d) Check CO/HC concentration at idle and/or 2500
rpm.
HINT:
Check regulations and restrictions in your area
when performing 2 mode CO/HC concentration
testing (engine check at both idle speed and at 2500
rpm).
If the CO/HC concentration does not comply with
regulations, perform troubleshooting in the order
given below.
(1) Check air fuel ratio sensor and heated oxygen
sensor operation.
(2) See the table below for possible causes, and
then inspect and repair.
CO HC Problems Causes
Normal High Rough idle1. Faulty ignitions:
– Incorrect timing
– Fouled, shorted or improperly gapped plugs
2. Incorrect valve clearance
3. Leaks in intake and exhaust valves
4. Leaks in cylinders
Low HighRough idle
(fluctuating HC reading)1. Vacuum leaks:
– PCV hoses
– Intake manifold
– Throttle body
– Brake booster line
2. Lean mixture causing misfire
High HighRough idle
(black smoke from exhaust)1. Restricted air filter
2. Plugged PCV valve
3. Faulty SFI system:
– Faulty fuel pressure regulator
– Defective ECT sensor
– Defective MAF meter
–Faulty ECM
– Faulty injectors
– Faulty throttle position sensor
Page 936 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNITEM–127
EM
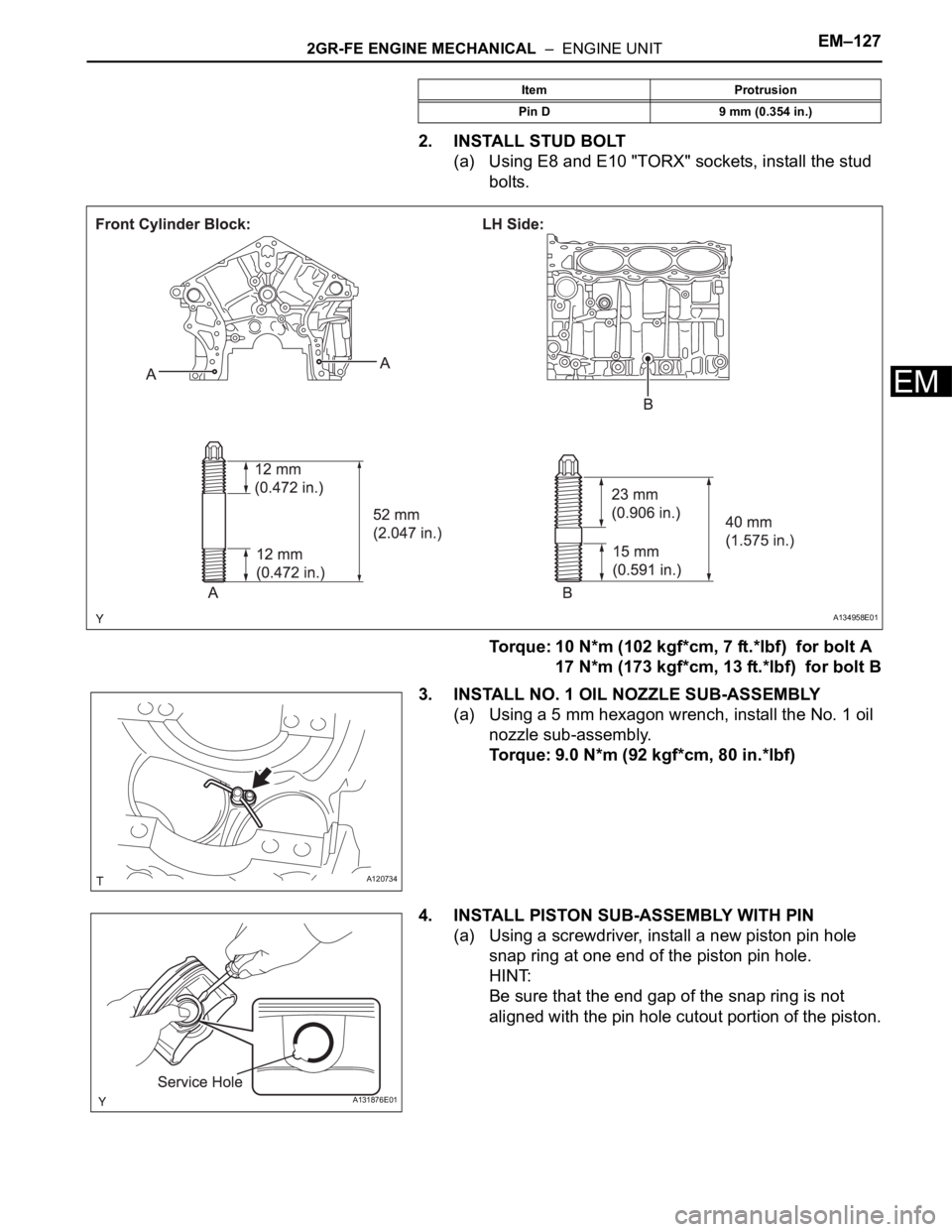
2. INSTALL STUD BOLT
(a) Using E8 and E10 "TORX" sockets, install the stud
bolts.
Torque: 10 N*m (102 kgf*cm, 7 ft.*lbf) for bolt A
17 N*m (173 kgf*cm, 13 ft.*lbf) for bolt B
3. INSTALL NO. 1 OIL NOZZLE SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Using a 5 mm hexagon wrench, install the No. 1 oil
nozzle sub-assembly.
Torque: 9.0 N*m (92 kgf*cm, 80 in.*lbf)
4. INSTALL PISTON SUB-ASSEMBLY WITH PIN
(a) Using a screwdriver, install a new piston pin hole
snap ring at one end of the piston pin hole.
HINT:
Be sure that the end gap of the snap ring is not
aligned with the pin hole cutout portion of the piston.
Pin D 9 mm (0.354 in.)Item Protrusion
A134958E01
A120734
A131876E01
Page 937 of 3000
EM–1282GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNIT
EM
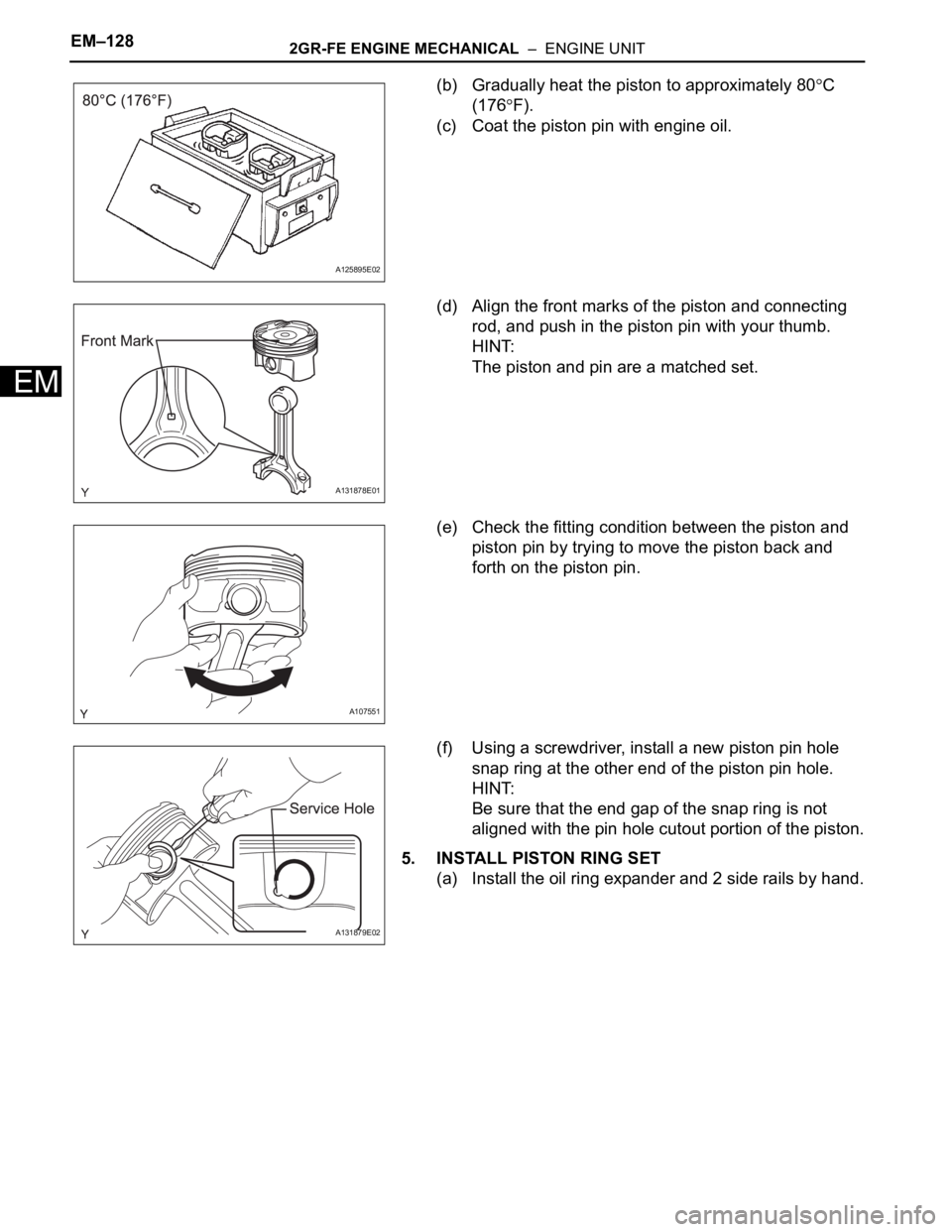
(b) Gradually heat the piston to approximately 80C
(176
F).
(c) Coat the piston pin with engine oil.
(d) Align the front marks of the piston and connecting
rod, and push in the piston pin with your thumb.
HINT:
The piston and pin are a matched set.
(e) Check the fitting condition between the piston and
piston pin by trying to move the piston back and
forth on the piston pin.
(f) Using a screwdriver, install a new piston pin hole
snap ring at the other end of the piston pin hole.
HINT:
Be sure that the end gap of the snap ring is not
aligned with the pin hole cutout portion of the piston.
5. INSTALL PISTON RING SET
(a) Install the oil ring expander and 2 side rails by hand.
A125895E02
A131878E01
A107551
A131879E02
Page 939 of 3000
EM–1302GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE UNIT
EM
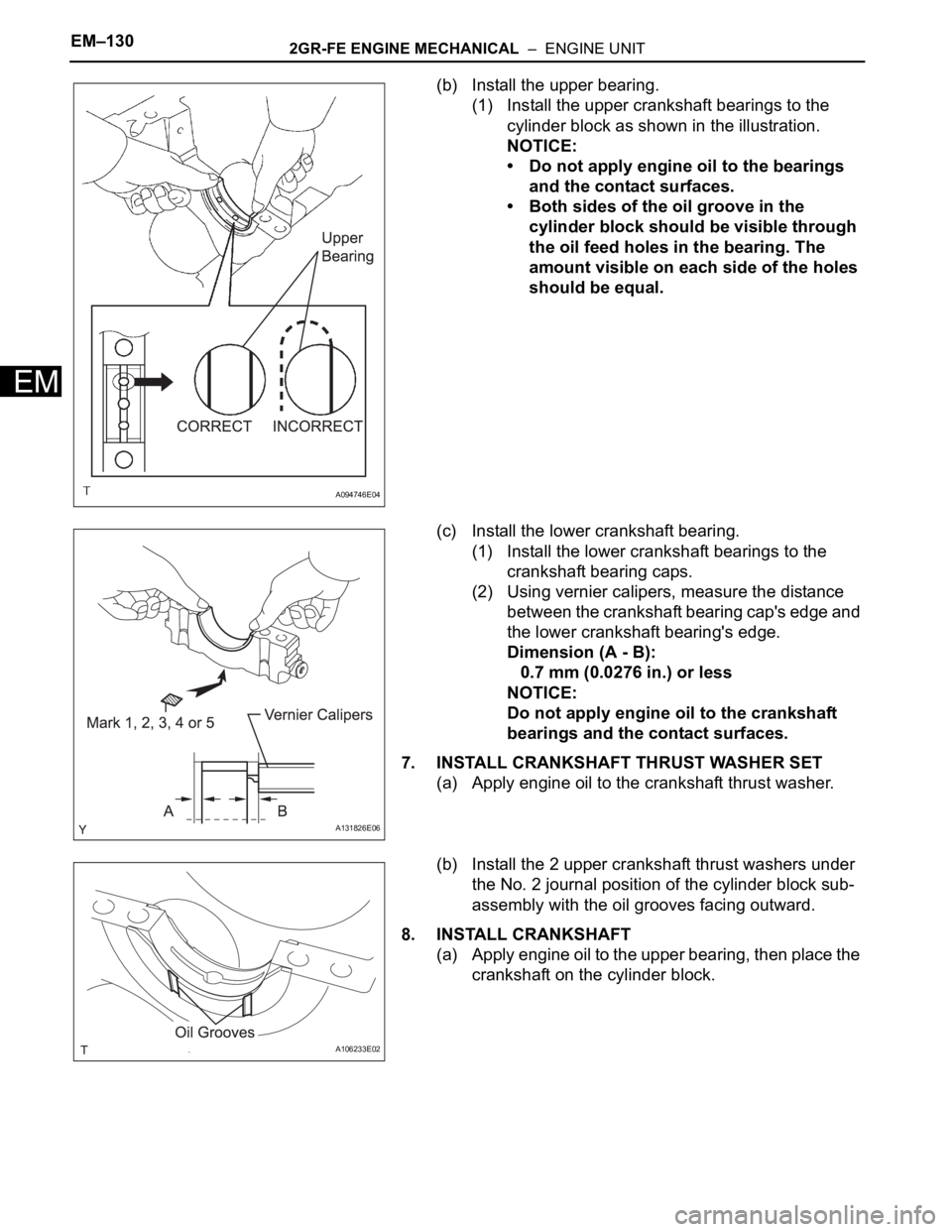
(b) Install the upper bearing.
(1) Install the upper crankshaft bearings to the
cylinder block as shown in the illustration.
NOTICE:
• Do not apply engine oil to the bearings
and the contact surfaces.
• Both sides of the oil groove in the
cylinder block should be visible through
the oil feed holes in the bearing. The
amount visible on each side of the holes
should be equal.
(c) Install the lower crankshaft bearing.
(1) Install the lower crankshaft bearings to the
crankshaft bearing caps.
(2) Using vernier calipers, measure the distance
between the crankshaft bearing cap's edge and
the lower crankshaft bearing's edge.
Dimension (A - B):
0.7 mm (0.0276 in.) or less
NOTICE:
Do not apply engine oil to the crankshaft
bearings and the contact surfaces.
7. INSTALL CRANKSHAFT THRUST WASHER SET
(a) Apply engine oil to the crankshaft thrust washer.
(b) Install the 2 upper crankshaft thrust washers under
the No. 2 journal position of the cylinder block sub-
assembly with the oil grooves facing outward.
8. INSTALL CRANKSHAFT
(a) Apply engine oil to the upper bearing, then place the
crankshaft on the cylinder block.
A094746E04
A131826E06
A106233E02