wheel CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 1903 of 2438

line. However, these could result in a rich or lean
condition causing an oxygen sensor fault to be stored in
the PCM. Secondary Ignition Circuit - The PCM cannot
detect an inoperative ignition coil, fouled or worn spark
plugs, ignition cross firing, or open spark plug cables. Engine Timing - The PCM cannot detect an incor-
rectly indexed timing chain, camshaft sprocket and
crankshaft sprocket. However, these could result in a
rich or lean condition causing an oxygen sensor fault to
be stored in the PCM. Cylinder Compression - The PCM cannot detect
uneven, low, or high engine cylinder compression. Exhaust System - The PCM cannot detect a
plugged, restricted or leaking exhaust system. Fuel Injector Malfunctions - The PCM cannot
determine if a fuel injector is clogged, the needle is
sticking or the wrong injector is installed. However,
these could result in a rich or lean condition causing an
oxygen sensor fault to be stored in the PCM. Excessive Oil Consumption - Although the PCM
monitors exhaust stream oxygen content when the
system is in closed loop, it cannot determine excessive
oil consumption. Throttle Body Air Flow - The PCM cannot detect a
clogged or restricted air cleaner inlet or filter element. Evaporative System - The PCM will not detect a
restricted, plugged or loaded evaporative purge canis-
ter. Vacuum Assist - Leaks or restrictions in the
vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control
system devices are not monitored by the PCM. How-
ever, these could result in a MAP sensor fault being
stored in the PCM. PCM System Ground - The PCM cannot determine
a poor system ground. However, a diagnostic trouble
code may be generated as a result of this condition. PCM Connector Engagement - The PCM cannot
determine spread or damaged connector pins. How-
ever, a diagnostic trouble code may be generated as a
result of this condition.
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The powertrain control module (PCM) compares in-
put signal voltages from each input device with estab-
lished high and low limits for the device. If the input
voltage is not within limits and other diagnostic
trouble code criteria are met, a diagnostic trouble code
will be stored in memory. Other diagnostic trouble code
criteria might include engine RPM limits or input
voltages from other sensors or switches that must be
present before a fault condition can be verified.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTION
A diagnostic trouble code indicates that the power-
train control module (PCM) has recognized an abnor- mal condition in the system. Diagnostic trouble codes
can be obtained from the malfunction indicator lamp
(Check Engine lamp on the instrument panel) or from
the DRBII scan tool. Diagnostic trouble codes indicate
the results of a failure but do not identify the failed
component directly.
SYSTEM TESTS
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR BLOCK
WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY TEST ON AN
OPERATING ENGINE.
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(1) Connect the DRBII scan tool to the data link
connector located in the engine compartment near the
driver side strut tower (Fig. 1). (2) Start the engine if possible, cycle the transaxle
selector and the A/Cswitch if applicable. Shut off the
engine. (3) Turn the ignition switch on, access Read Fault
Screen. Record all the fault messages shown on the
DRBII scan tool. Observe the malfunction indicator
lamp (check engine lamp on the instrument panel). The
lamp should light for 2 seconds then go out (bulb
check). Diagnostic trouble code erasure; access erase
diagnostic trouble code data
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs used by the powertrain control
module (PCM) have only two recognized states, HIGH
and LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize
the difference between a selected switch position ver-
sus an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective
switch. If the change is displayed, it can be assumed
that the entire switch circuit to the PCM is functional.
From the state display screen access either State
Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and access
the State Display screen. Then access Inputs and
Outputs. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Inputs and
Outputs screen. Park/Neutral Switch
Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
A/C Switch Sense
S/C Vent Solenoid
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 163
Page 1919 of 2438

STEERING
CONTENTS
page page
ACUSTAR STANDARD AND TILT STEERING COLUMN ............................ 28
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION SHIFTER/IGNITION INTERLOCK .......................... 36
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1 POWER STEERING GEAR
................ 25
POWER STEERING PUMPS ................ 1
SPECIFICATIONS AND TIGHTENING REFERENCE .......................... 42
GENERAL INFORMATION
Safety goggles should be worn at all times
when working on any steering gear or pump. Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the breakdown of these designations
is included in the Introduction Section at the front of
this service manual. The power steering system consists of these four
major components. Power Steering Pump, Power
Steering Gear, Pressure Hose, and Return Line.
Turning of the steering wheel is converted into lin-
ear travel through the meshing of the helical pinion teeth with the rack teeth. Power assist steering is
provided by an open center, rotary type control valve.
It is used to direct oil from the power steering pump
to either side of the integral steering rack piston. Road feel is controlled by the diameter of a torsion
bar which initially steers the vehicle. As steering ef-
fort increases as in a turn, the torsion bar twists,
causing relative rotary motion between the rotary
valve body and valve spool. This movement directs
oil behind the integral rack piston, which in turn,
builds up hydraulic pressure and assists in the turn-
ing effort.
POWER STEERING PUMPS
INDEX
page page
Checking Power Steering Fluid Level .......... 9
Flow Control Valve Fitting O-Ring Seal ........ 23
General Information ........................ 1
Power Steering Hoses ..................... 11
Power Steering Pressure Switch ............. 10
Power Steering Pump Fluid Reservoirs ........ 22 Power Steering Pump Pressure Test
........... 9
Power Steering Pump Pulley Service .......... 20
Power Steering Pump Removal .............. 12
Power Steering Pump Service ................ 2
Power Steering PumpÐInitial Operation ....... 24
Steering Components Service Diagnosis ........ 2
GENERAL INFORMATION
Hydraulic pressure for operation of the power
steering gear is provided by a belt driven power
steering pump. The power steering pump is a con-
stant flow rate and displacement, vane type pump.
Different styles of Saginaw power steering pumps are
used depending on the engine application of the ve-
hicle. On all four cylinder and 3.0-liter V-6 applications
the Saginaw Ham Can power steering pump is used
(Fig. 1). On the 3.3 & 3.8-liter V-6 and Turbo III applica-
tions, different versions of the Saginaw T/C style
power steering pump is used (Fig. 2). The 3.3 & 3.8 liter V-6 engine application uses the T/C style power
steering pump with a remote mounted reservoir for
the power steering fluid. On the Turbo III application
of the T/C style power steering pump, the power
steering fluid reservoir is integral to the power steer-
ing pump. On the integral reservoir type pump (Fig. 1) the
pump housing and internal components are combined
with the reservoir to form a one-piece mechanism. The Saginaw T/C style power steering pump (Fig.
2), consists of the power steering pump internal com-
ponents and pump housing. The Saginaw T/C style
power steering pump though has no internal reser-
voir for the power steering fluid. Depending on vehi-
Ä STEERING 19 - 1
Page 1927 of 2438

When steering conditions exceed maximum pres-
sure requirements, such as when the wheels are
turned against the stops. The pressure built up in
the steering gear exerts pressure on the spring end of
the flow control valve. The high pressure lifts the re-
lief valve ball from its seat and allows oil to flow
through a trigger orifice located in the outlet fitting.
This reduces pressure on the spring end of the flow
control valve which then opens and allows the oil to
return to the intake side of the pump. This action
limits maximum pressure output of the pump to a
safe level. Under normal power steering pump operating con-
ditions, pressure requirements of the pump are below
maximum, causing the pressure relief valve to re-
main closed.
CHECKING POWER STEERING FLUID LEVEL
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY FROM
MOVING PARTS. DO NOT USE AUTOMATIC TRANS-
MISSION FLUID IN THE POWER STEERING SYS-
TEM. DO NOT OVERFILL THE POWER STEERING
SYSTEM.
Wipe reservoir filler cap free of dirt, before check-
ing power steering fluid level. The dipstick should in- dicate FULL COLD when fluid is at normal ambient
temperature, approximately 21ÉC to 27ÉC (70ÉF to
80ÉF). In all pumps add fluid as necessary to obtain
proper level, using only MopartPower Steering
Fluid, or equivalent. DO NOT USE ANY TYPE
OF AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION FLUID.
POWER STEERING PUMP PRESSURE TEST
The following procedure can be used to test the op-
eration of the power steering system on the vehicle. (1) Check power steering pump drive belt tension
and adjust as necessary. (2) Disconnect power steering fluid pressure hose,
at steering gear or power steering pump. Use a con-
tainer for dripping fluid. (3) Connect Pressure Gauge, Special Tool C-3309-E
(Fig. 1) to both hoses using adapter fittings. Connect
spare pressure hose to gear or pump. (4) Completely open valve on Special Tool
C-3309-E (Fig. 1). (5) Start engine and let idle.
(6) Check power steering fluid level, and add fluid
as necessary. (7) Gauge should read below 862 kPa (125 psi), if
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure should be in the
range of 345-552 kPa (50-80 psi).
PUMP LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS
Ä STEERING 19 - 9
Page 1928 of 2438

CAUTION: The following test procedure involves test-
ing power steering pump maximum pressure output
and flow control valve operation. Do not leave valve
closed for more than 5 seconds as the pump could be
damaged.
(8) Close valve fully three times and record highest
pressure indicated each time. All three readings
must be above specifications and within 345 kPa
(50 psi) of each other. Power steering pump maximum relief pressure
is 8275 to 8975 kPa (1200 to 1300 psi.).
² Power steering pump pressures above specifications
but not within 345 kPa (50 psi) of each other, replace
pump.
² Pressures within 345 kPa (50 psi) of each other but
below specifications, replace pump.
CAUTION: Do not force the pump to operate against
the stops for more than 5 seconds at a time because,
pump damage will result.
(9) Open test valve. Turn steering wheel to the
extreme left and right positions until against the stops,
recording the highest indicated pressure at each posi-
tion. Compare pressure gauge readings to power steer-
ing pump specifications. If highest output pressures
are not the same against either stop, the steering gear
is leaking internally and must be replaced.
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH
New for 1993 M.Y., is the use of an idle quality power
steering pressure switch on some front wheel drive
passenger car applications. The purpose of this switch is to signal the power
train control module, that the power steering system is
putting additional load on the engine. This type of
condition exists when turning the front tires of the
vehicle, when the vehicle is stationary and the engine
is at idle speed. When this condition is sensed by the
power train control module, through a signal from the power steering pressure switch, engine idle
speed is increased. This increase in engine idle speed
compensates for the additional load, thus maintain-
ing the require engine idle speed and idle quality.
The power steering pressure switch is mounted to
the power steering pressure hose on the applications
that require its usage. Refer to (Fig. 1 and 2) below
for the pressure switch location on the different en-
gine applications.
REMOVE
(1) Locate power steering pressure switch on power
steering pressure hose. Refer to (Fig. 1 and 2) for the
engine application showing the location of the power
steering switch. (2) Remove vehicle wiring harness connector from
the power steering pressure switch. (3) Remove power steering pressure switch, from
power steering pressure hose.
Fig. 1 Power Steering Pressure Switch Location 3.0L
Fig. 2 Power Steering Pressure Switch Location 3.3 & 3.8L
Fig. 1 Pressure Test Gauge
19 - 10 STEERING Ä
Page 1929 of 2438

INSTALL
(1) Install power steering pressure switch into fit-
ting on power steering pressure hose by hand until
fully seated. Then torque power steering pressure
switch to 12 N Im (106 in. lbs.).
(2) Install vehicle wiring harness connector onto
power steering pressure switch. Be sure latch on wir-
ing harness connector is fully engaged with locking
tab on power steering pressure switch.
CAUTION: Do not use automatic transmission fluid
in power steering system. Only use Mopar T, Power
Steering Fluid, or equivalent.
(3) Fill power steering pump reservoir to correct
fluid level. (4) Connect negative cable back on negative post of
battery. (5) Start engine and turn steering wheel several
times from stop to stop to bleed air from fluid in sys-
tem. Stop engine, check fluid level, and inspect sys-
tem for leaks. See Checking Fluid Level.
POWER STEERING HOSES
Service all power steering hoses with the vehicle
raised on a hoist. Cap all open ends of hoses, power
steering pump fittings and steering gear ports to pre-
vent entry of foreign material into the components.
WARNING: POWER STEERING OIL, ENGINE PARTS
AND EXHAUST SYSTEM MAY BE EXTREMELY HOT
IF ENGINE HAS BEEN RUNNING. DO NOT START
ENGINE WITH ANY LOOSE OR DISCONNECTED
HOSES. DO NOT ALLOW HOSES TO TOUCH HOT
EXHAUST MANIFOLD OR CATALYST.
For part reference and part location on the vehicle
being serviced, refer to Figs. 3 to 6. These show the
hose bracket locations, hose routings and fitting loca-
tions by the engine application of the vehicle. Use
these figure numbers when referring to the removal
or installation procedures for the power steering
hoses listed below.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove vehicle's wiring harness connector (if
applicable to vehicle being serviced) from the power
steering pressure switch (Fig .1&2).
(2) Remove bolts from power steering hose routing
brackets to crossmember attachment points. (3) Disconnect power steering hose at opening clos-
est to power steering gear assembly. Drain power
steering fluid from power steering pump and hose
through open end of hose. (4) Disconnect opposite end of hose and remove
power steering hose assembly from vehicle. (5) Discard O-ring or sealing washer located at end
of tube. (6) Remove power steering pressure switch, from
the removed power steering hose for installation into
the replacement power steering hose.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the removed power steering pressure
switch into replacement power steering pressure
hose. Torque power steering pressure switch to 12
N Im (106 in. lbs.).
Fig. 3 Power Steering Hose Routing 2.2 & 2.5L
Fig. 4 Power Steering Hose Routing 3.0L
Ä STEERING 19 - 11
Page 1932 of 2438

(10) Connect negative cable back on negative post
of battery. (11) Start engine and turn steering wheel several
times from stop to stop to bleed air from fluid in sys-
tem. Stop engine, check fluid level, and inspect sys-
tem for leaks. See Checking Fluid Level.
3.0 LITER
REMOVE
(1) REMOVE THE (-) NEGATIVE BATTERY CA-
BLE FROM THE BATTERY AND ISOLATE CA-
BLE. (2) Remove the serpentine accessory drive belt
from engine (Fig. 4). See Cooling, Group 7 for de-
tailed removal procedure.
(3) Remove the hose clamp and bolt mounting the
power steering pump filler tube and dipstick assem-
bly (Fig. 5) to power steering pump and generator
bracket. Remove filler tube and dipstick assembly
from power steering pump. (4) Raise vehicle See Hoisting, Group 0.
(5) Remove the 2 nut, bolt and spring assemblies
attaching the exhaust pipe to exhaust manifold. Re-
move exhaust pipe from exhaust manifold and move
to left side of vehicle. This is required for clear-
ance to remove power steering pump from vehi-
cle. (6) Remove vehicle's wiring harness connector (if
applicable to vehicle being serviced) from the power
steering pressure switch (Fig. 6). (7) Put oil drain pan under vehicle to catch power
steering fluid. Remove hose clamp and low pressure
fluid hose, from power steering gear fluid tube (Fig.
7). Allow excess power steering fluid to drain from
power steering pump and hose. (8) Loosen the high pressure power steering fluid
line fitting at the power steering pump (Fig. 7). Then
remove high pressure power steering fluid line from
power steering pump. (9) Remove nut holding the power steering pump
rear support bracket to pump (Fig. 8). Then remove
the 2 bolts (Fig. 7) mounting the power steering
pump support bracket to engine and remove bracket
from vehicle. (10) Remove the 2 bolts that mount the front of
the power steering pump to the mounting plate (Fig.
9). Access to the mounting bolts is through the holes
in power steering pump pulley using a deep well
socket. (11) Remove the power steering pump and pulley
assembly from vehicle. Remove pump assembly from
vehicle in area between floor pan and front suspen-
sion crossmember. Pump will fit through area of ex-
haust pipe tunnel in floor pan.
Fig. 4 3.0L Serpentine Drive Belt Routing
Fig. 5 Power Steering Pump Filler Tube/Dipstick Assembly
Fig. 6 Power Steering Pressure Switch Location 3.0L
19 - 14 STEERING Ä
Page 1934 of 2438
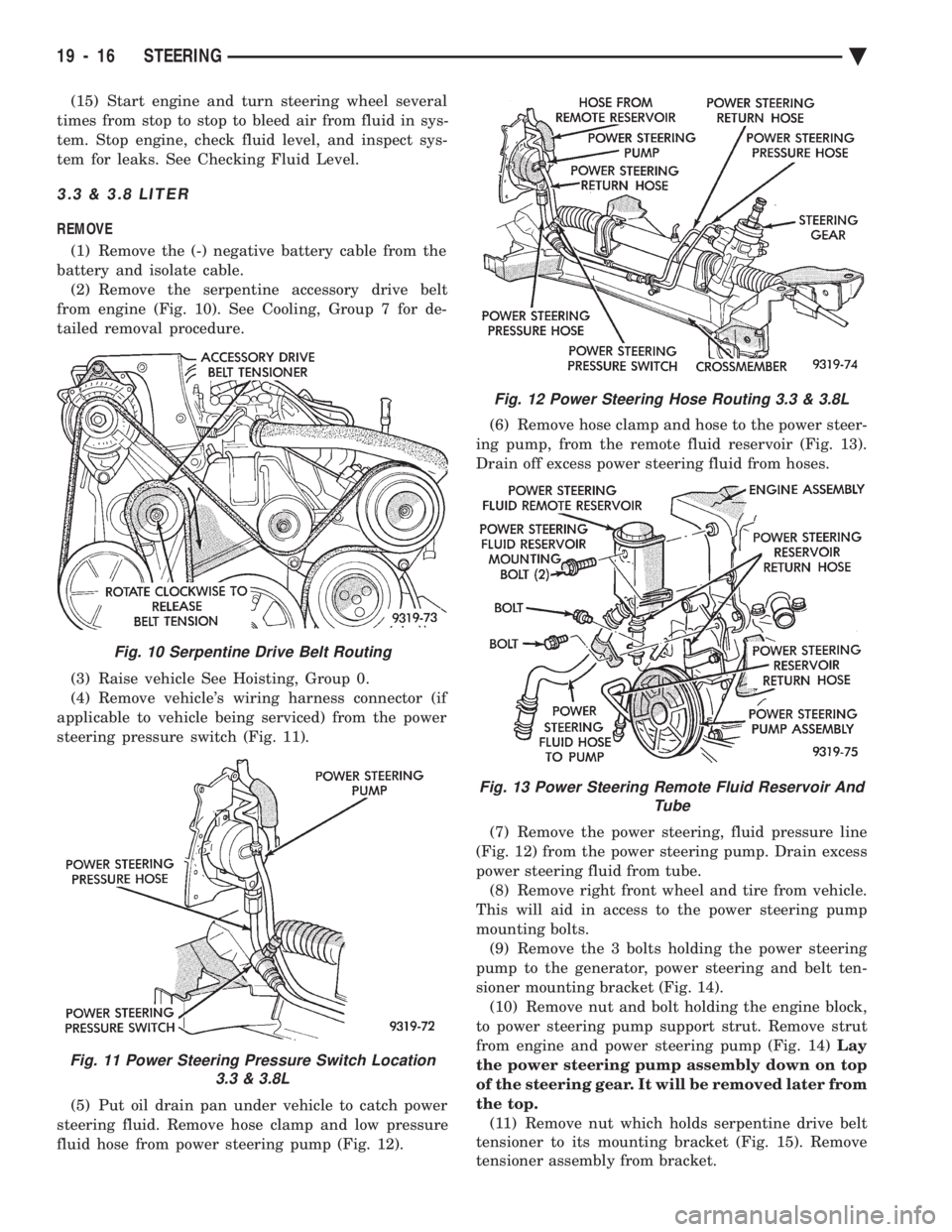
(15) Start engine and turn steering wheel several
times from stop to stop to bleed air from fluid in sys-
tem. Stop engine, check fluid level, and inspect sys-
tem for leaks. See Checking Fluid Level.
3.3 & 3.8 LITER
REMOVE
(1) Remove the (-) negative battery cable from the
battery and isolate cable. (2) Remove the serpentine accessory drive belt
from engine (Fig. 10). See Cooling, Group 7 for de-
tailed removal procedure.
(3) Raise vehicle See Hoisting, Group 0.
(4) Remove vehicle's wiring harness connector (if
applicable to vehicle being serviced) from the power
steering pressure switch (Fig. 11).
(5) Put oil drain pan under vehicle to catch power
steering fluid. Remove hose clamp and low pressure
fluid hose from power steering pump (Fig. 12). (6) Remove hose clamp and hose to the power steer-
ing pump, from the remote fluid reservoir (Fig. 13).
Drain off excess power steering fluid from hoses.
(7) Remove the power steering, fluid pressure line
(Fig. 12) from the power steering pump. Drain excess
power steering fluid from tube. (8) Remove right front wheel and tire from vehicle.
This will aid in access to the power steering pump
mounting bolts. (9) Remove the 3 bolts holding the power steering
pump to the generator, power steering and belt ten-
sioner mounting bracket (Fig. 14). (10) Remove nut and bolt holding the engine block,
to power steering pump support strut. Remove strut
from engine and power steering pump (Fig. 14) Lay
the power steering pump assembly down on top
of the steering gear. It will be removed later from
the top. (11) Remove nut which holds serpentine drive belt
tensioner to its mounting bracket (Fig. 15). Remove
tensioner assembly from bracket.
Fig. 10 Serpentine Drive Belt Routing
Fig. 11 Power Steering Pressure Switch Location 3.3 & 3.8L
Fig. 12 Power Steering Hose Routing 3.3 & 3.8L
Fig. 13 Power Steering Remote Fluid Reservoir And Tube
19 - 16 STEERING Ä
Page 1936 of 2438

INSTALL (1) Install power steering pump back in vehicle,
laying it on the steering gear. Do not mount it to the
power steering pump bracket. (2) Install generator back on the lower generator
bracket and install bolt and nut (Fig. 19). Do not
tighten bolt at this time. (3) Install the generator bracket back on engine and
intake manifold. Loosely install the 4 generator
bracket to engine attaching bolts (Fig. 19). Be sure
the SPACER (Fig. 18) is installed between the
engine mounting strut and the generator
bracket. (4) Temporarily install the serpentine belt tensioner
bolt through both generator brackets. This will align
all generator bracket mounting holes (Fig. 15). Then
torque the 4 generator bracket to engine and intake manifold mounting bolts to 54 N
Im (40 ft.
lbs.). Then remove the serpentine belt tensioner from
bracket. It will be installed on the bracket in a
later step. (5) Tighten the bolt holding the engine bracket as-
sembly to the engine support assembly (Fig. 18) to 150
N Im (110 ft. lbs.).
(6) Attach the engine wiring harness routing clip to
the generator bracket. (7) Install the generator to generator bracket attach-
ing bolt (Fig. 19). Torque bolt to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.).
Tighten the lower generator pivot bolt to 54 N Im (40 ft.
lbs.). (8) Install the power steering pump fluid reservoir
and tube/hose assembly onto the power steering pump
bracket and generator bracket (Fig. 17). Torque the 2
bolts holding the reservoir to the generator bracket to
5N Im (45 in. lbs.). Torque the 1 bolt holding the
tube/hose assembly to the power steering pump
bracket to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.).
(9) Raise vehicle See Hoisting, Group 0.
(10) Install the strut assembly power
steering/generator bracket to engine (Fig. 16). Torque
the nut and bolt holding the strut assembly to bracket
and the exhaust manifold stud to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs).
(11) Install the serpentine drive belt tensioner onto
the power steering/generator bracket (Fig. 15). Install
the tensioner to bracket retaining nut and torque to 54
N Im (40 ft. lbs.).
(12) Install the power steering pump on bracket, by
aligning the 3 mounting holes in pump with mounting
holes in bracket (Fig. 14). Install the 3 power steering
pump to bracket mounting bolts. Torque power steer-
ing pump mounting bolts to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the support strut, engine block to power
steering pump on pump stud (Fig. 14). Install the nut
and bolt holding the strut to the power steering pump
and engine block and torque to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.).
(14) Install the power steering fluid pressure line
onto the output fitting of the power steering pump (Fig.
12). Torque the pressure line pump fitting nut to 31
N Im (275 in. lbs.). Before connecting the pressure
line to power steering pump inspect the O-ring
on the pressure line for damage. (15) Install vehicle's wiring harness connector (if
applicable to vehicle being serviced) onto the power
steering pressure switch (Fig. 11). (16) Install the power steering fluid, low pressure
return hose on the power steering pump low pressure
fitting (Fig. 12). Then install the hose from the remote
reservoir onto the power steering pump (Fig. 13). Be
sure all hose clamps are properly reinstalled. (17) Install right front tire and wheel on vehicle.
Install the wheel stud nuts and torque to 129 N Im (95
ft. lbs.).
Fig. 18 Engine Bracket Support Assembly
Fig. 19 Generator Mounting
19 - 18 STEERING Ä
Page 1937 of 2438

(18) Lower vehicle.
(19) Install the serpentine drive belt. Refer to (Fig.
10) for correct serpentine belt routing. See Cooling,
Group 7 for detailed installation procedure.
CAUTION: Do not use automatic transmission fluid
in power steering system. Only use Mopar T, Power
Steering Fluid, or equivalent.
(20) Fill power steering pump reservoir to correct
fluid level. (21) Connect the negative battery cable on the
negative battery post. (22) Start engine and turn steering wheel several
times from stop to stop to bleed air from fluid in sys-
tem. Stop engine, check fluid level, and inspect sys-
tem for leaks. See Checking Fluid Level.
TURBO III
REMOVE
(1) Disconnect the battery (-) negative cable from
the battery and isolate cable. (2) Raise vehicle See Hoisting, Group 0. Put oil
drain pan under vehicle to catch power steering
fluid. (3) Remove the right front underhood splash shield
for access to the serpentine belt tensioner. (4) Release the tension on the serpentine drive belt
tensioner and remove drive belt from power steering
pump pulley (Fig. 20). Drive belt does not have to be
fully removed from engine.
(5) Remove the power steering fluid return hose at
the steering gear metal tube. Let power steering
fluid drain from the hose and power steering pump
into drain pan. (6) Remove the high pressure fluid line banjo bolt
fitting from the power steering pump. Remove high
pressure power steering fluid line from the power
steering pump. (7) Remove the lower power steering pump to
bracket mounting nut and fluid hose routing clip. Re-
move the 2 bolts and the stud attaching the power
steering pump to its mounting bracket (Fig. 21).
(8) Lower vehicle.
(9) Remove the wiring harness electrical connector
from the H-valve on the air conditioning fluid lines. (10) Remove the power steering pump from the ve-
hicle out through the area between the cylinder head
and the dash panel (Fig. 22).
(11) Transfer the required components from the
failed power steering pump to the replacement power
steering pump. See the appropriate area of this ser-
vice manual section for the component replacement
procedures.
Fig. 20 Turbo III Accessory Drive Belt Routing
Fig. 21 Power Steering Pump Mounting
Fig. 22 Power Steering Pump Removal From Vehicle
Ä STEERING 19 - 19
Page 1938 of 2438

INSTALL (1) Install the power steering pump back into the
vehicle in the reverse order of removal, between cyl-
inder head and dash panel (Fig. 20). (2) Install the wiring harness connector back on
the H-valve located on the air conditioning fluid
lines (Fig. 20). (3) Raise vehicle See Hoisting, Group 0.
(4) Install the power steering pump on its mount-
ing bracket, and the hose locator bracket. Install the
bolt/stud and 2 bolts attaching the power steering
pump to its mounting bracket, and the bolts attach-
ing the hose locator bracket (Fig. 19). Torque all fas-
teners to 31 N Im (280 in. lbs.).
(5) Install the power steering fluid pressure hose,
banjo bolt and seal washer onto power steering pump
(Fig. 4). Pressure hose is to be installed so it is
routed to the left of the hose locator bracket (Fig.
19). Torque the banjo bolt to 31 N Im (275 in. lbs.).
Inspect the O-rings on the banjo bolt to ensure
they are not damaged and located correctly. (6) Install the low pressure fluid return hose from
the power steering pump back on the steel tube on
the steering gear (Fig. 4). Install hose clamp, be sure
the hose clamp is installed past the retaining bead
the steel tube. Install the hose routing clip on the
power steering pump bolt/stud, install clip retaining
nut and tighten. (7) Install the serpentine accessory drive belt (Fig.
18). Be sure the belt is correctly installed and
aligned on all pulleys before starting engine. (8) Install the right front underhood splash shield.
CAUTION: Do not use automatic transmission fluid
in power steering system. Only use Mopar T, Power
Steering Fluid, or equivalent.
(9) Fill power steering pump reservoir to correct
fluid level. (10) Connect the negative battery cable on the
negative battery post. (11) Start engine and turn steering wheel several
times from stop to stop to bleed air from fluid in sys-
tem. Stop engine, check fluid level, and inspect sys-
tem for leaks. See Checking Fluid Level.
POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY SERVICE
SAGINAW VANE SUBMERGED PUMP
REMOVE
(1) Remove the pulley with Puller C-4333 (C-4068)
(Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Do not hammer on power steering pump
pulley. This will damage the pulley and the power
steering pump. (2) Replace pulley if bent, cracked, or loose.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the pulley with Installer C-4063 (Fig.2).
Do not use the tool adapters.
(2) Ensure that the tool and the pulley remain
aligned with the pump shaft. Prevent the pulley from
being cocked on the shaft. (3) Force pulley flush with the end of the shaft.
Fig. 1 Pulley Removal (Typical)
Fig. 2 Pulley Installation (Typical)
19 - 20 STEERING Ä