spark plugs CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 320 of 1938
SPECIFICATIONS
IGNITION COIL
SPARK PLUG
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION......................TORQUE
2.4L Target Magnet Screw.......3N´m(30in.lbs.)
2.4L Camshaft Position Sensoe Screw . .9 N´m (80 in.
lbs.)
Ignition Switch...............2N´m(17in.lbs.)
Spark Plugs.................28N´m(60in.lbs.)
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCEÐ2.4L
Coil ManufacturePrimary Resistance at 21ÉC-27ÉC
(70ÉF-80ÉF)Secondary Resistance at 21ÉC-
27ÉC (70ÉF-80ÉF)
Weastec (Steel Towers) 0.45 to 0.65 Ohms 7,000 to 15,800 Ohms
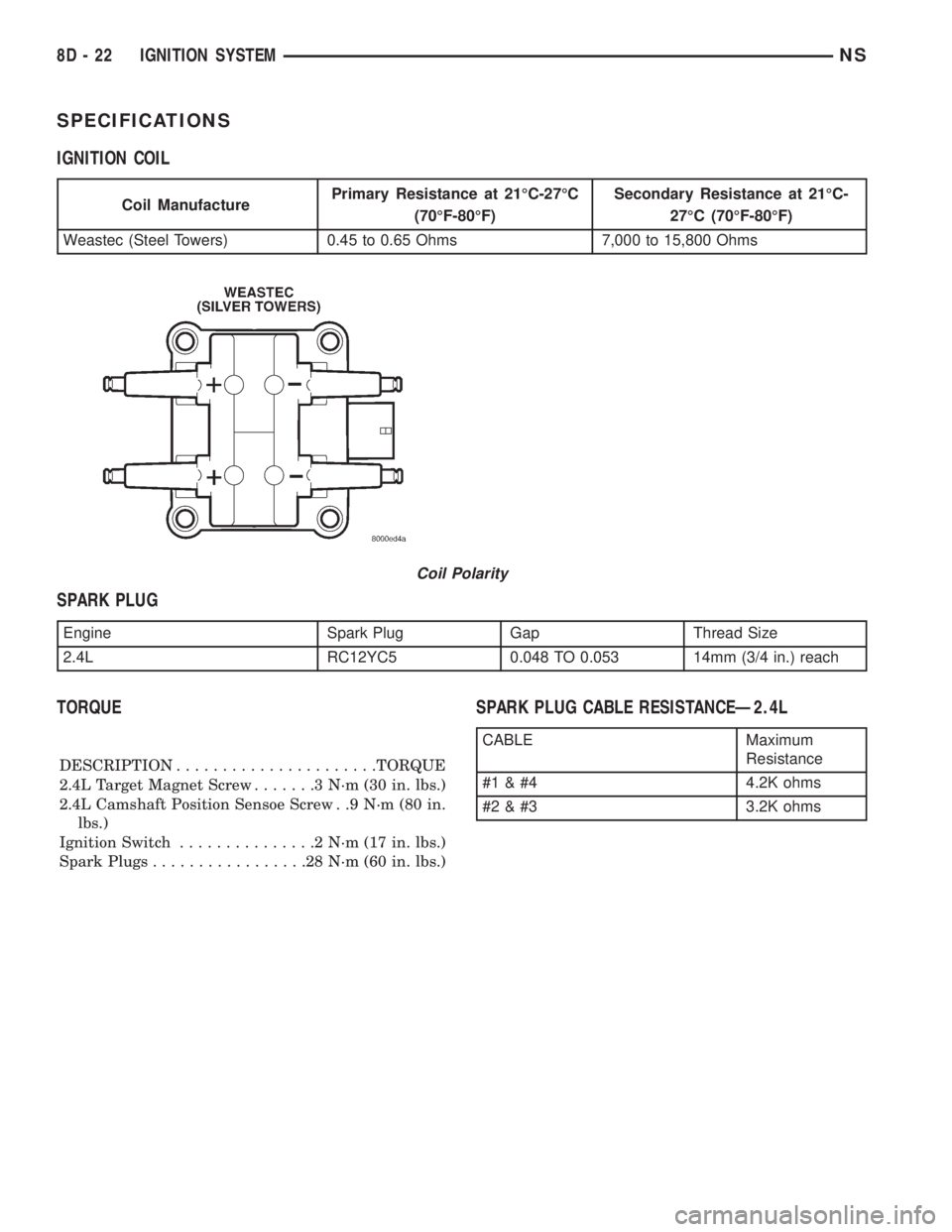
Coil Polarity
Engine Spark Plug Gap Thread Size
2.4L RC12YC5 0.048 TO 0.053 14mm (3/4 in.) reach
CABLE Maximum
Resistance
#1 & #4 4.2K ohms
#2 & #3 3.2K ohms
8D - 22 IGNITION SYSTEMNS
Page 322 of 1938

REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SPARK PLUG SERVICE
When replacing the spark plugs and spark plug
cables, route the cables correctly and secure them in
the appropriate retainers. Failure to route the cables
properly can cause the radio to reproduce ignition
noise, cross ignition of the spark plugs orshort cir-
cuit the cables to ground.
Never Wire Brush Spark Plugs.The spark plug
insulator tip is harder than the bristles of wire
brushes. Bristles of wire brushes can leave a conduc-
tive, metallic film on the insulator which could lead
to conductive deposits. Conductive deposits can cause
spark plug failure and engine misfire. Use a jewelers
file to remove deposits from the electrode gap or use
a spark plug cleaning machine to clean spark plugs.
REMOVAL
Always remove cables by grasping at the boot,
rotating the boot 1/2 turn, and pulling straight back
in a steady motion.
(1) Prior to removing the spark plug, spray com-
pressed air around the spark plug hole and the area
around the spark plug.
(2) Remove the spark plug using a quality socket
with a foam insert.
(3) Inspect the spark plug condition. Refer to
Spark Plug Condition in this section.
INSTALLATION
(1) To avoid cross threading, start the spark plug
into the cylinder head by hand.
(2) Tighten spark plugs to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Install spark plug cables over spark plugs. A
click will be heard and felt when the cable properly
attaches to the spark plug.
IGNITION COILÐ3.OL
The ignition coil is located at the back of the
intake manifold (Fig. 2).
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(2) Disconnect ignition cable from coil.
(3) Disconnect wiring harness connector from coil.
(4) Remove coil mounting screws.
INSTALLATION
(1) Loosely install ignition coil on intake manifold.
Tighten the intake manifold fastener to 13 N´m (115
in. lbs.) torque. Tighten ignition coil bracket fasten-
ers to 10 N´m (96 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect the wiring harness connector.
(3) Connect the coil to distributor ignition cable.
(4) Install the air cleaner assembly. Tighten the
air cleaner fasteners to 25 N´m (225 in. lbs.) torque.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSORÐ3.0L
REMOVAL
(1) Remove vacuum hose and mounting screws
from manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor (Fig.
3).
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
Remove sensor.
Fig. 1 Camshaft Position SensorÐ3.0L Engine
Fig. 2 Ignition CoilÐ3.0L Engine
8D - 24 IGNITION SYSTEMNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 325 of 1938
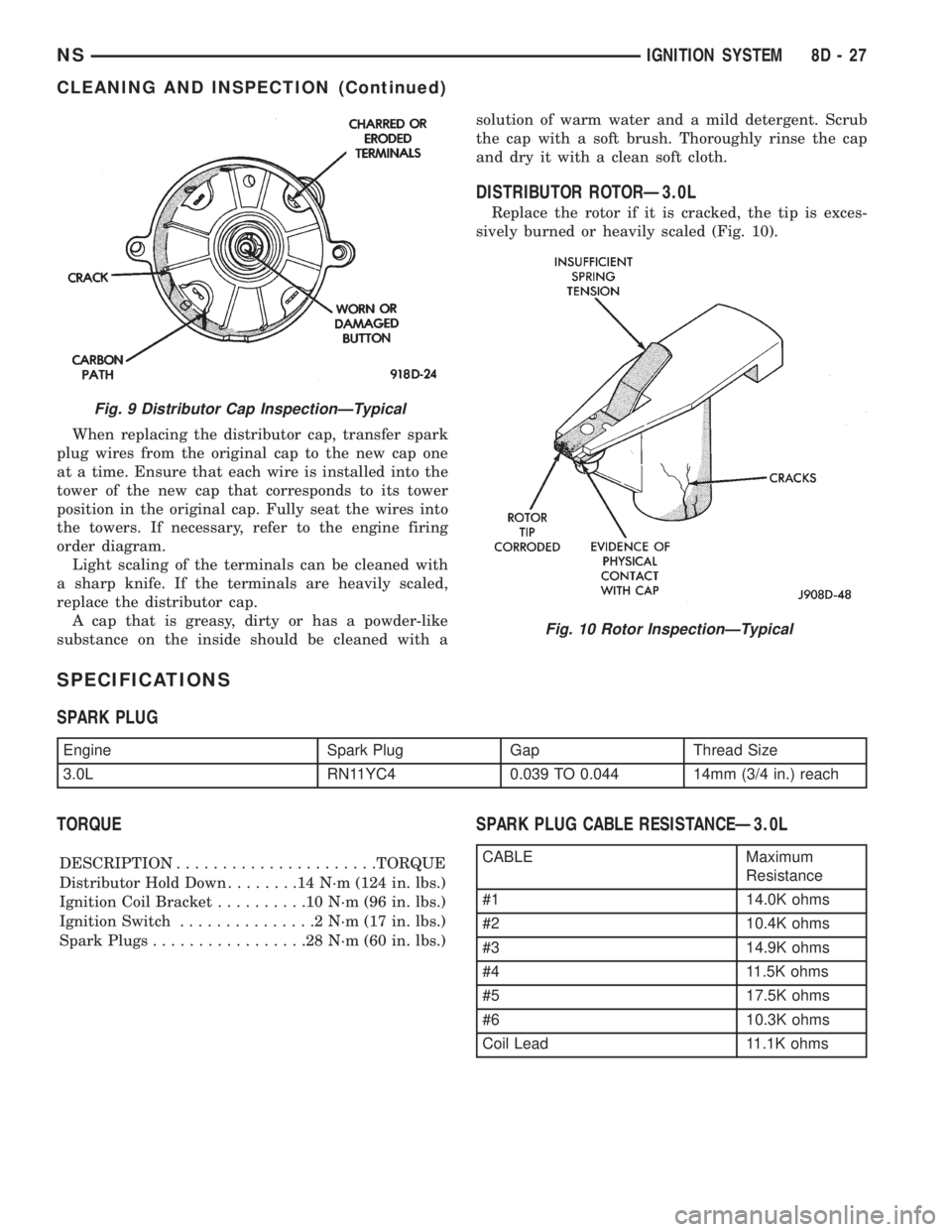
When replacing the distributor cap, transfer spark
plug wires from the original cap to the new cap one
at a time. Ensure that each wire is installed into the
tower of the new cap that corresponds to its tower
position in the original cap. Fully seat the wires into
the towers. If necessary, refer to the engine firing
order diagram.
Light scaling of the terminals can be cleaned with
a sharp knife. If the terminals are heavily scaled,
replace the distributor cap.
A cap that is greasy, dirty or has a powder-like
substance on the inside should be cleaned with asolution of warm water and a mild detergent. Scrub
the cap with a soft brush. Thoroughly rinse the cap
and dry it with a clean soft cloth.
DISTRIBUTOR ROTORÐ3.0L
Replace the rotor if it is cracked, the tip is exces-
sively burned or heavily scaled (Fig. 10).
SPECIFICATIONS
SPARK PLUG
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION......................TORQUE
Distributor Hold Down........14N´m(124 in. lbs.)
Ignition Coil Bracket..........10N´m(96in.lbs.)
Ignition Switch...............2N´m(17in.lbs.)
Spark Plugs.................28N´m(60in.lbs.)
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCEÐ3.0L
Fig. 9 Distributor Cap InspectionÐTypical
Fig. 10 Rotor InspectionÐTypical
Engine Spark Plug Gap Thread Size
3.0L RN11YC4 0.039 TO 0.044 14mm (3/4 in.) reach
CABLE Maximum
Resistance
#1 14.0K ohms
#2 10.4K ohms
#3 14.9K ohms
#4 11.5K ohms
#5 17.5K ohms
#6 10.3K ohms
Coil Lead 11.1K ohms
NSIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 27
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 326 of 1938
3.3/3.8L ENGINE
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FIRING ORDERÐ3.3/3.8L................. 28
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR............ 31
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR.......... 30
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR . . 32
IGNITION COIL......................... 30
KNOCK SENSORÐ3.3/3.8L................ 32
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSOR............................. 32SPARK PLUG CABLE SERVICEÐ3.3/3.8L
ENGINES............................ 28
SPARK PLUG SERVICEÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES . . . 29
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR............ 32
SPECIFICATIONS
IGNITION COIL......................... 33
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCEÐ3.3/3.8L . . 34
SPARK PLUG........................... 33
TORQUE.............................. 34
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FIRING ORDERÐ3.3/3.8L
The firing order for 3.3L and 3.8L engines is 1-2-3-
4-5-6.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SPARK PLUG CABLE SERVICEÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES
WARNING: The ignition cables should not be
removed while the engine is hot. This could cause
sever injury/burns and can cause damage to the
ignition cables.
The spark plug boot heat shield needs to be
installed correctly on the boot before being installed
on the engine (Fig. 1). If it is not installed correctly
engine misfire would occur.
Do not use pliers to pull the boot/heat shield
assembly from the spark plugs. This will damage the
shield assembly.
Spark plug boot heat shields must be replaced if
they are bent or damaged. It is extremely important
the shield is reinstalled correctly as shown. The bot-
tom of the spark plug heat shield must make contact
with the spark plug socket hex.
Firing OrderÐ3.3/3.8L
Fig. 1 Spark Plug Boot/Heat Shield Orientation
8D - 28 IGNITION SYSTEMNS
Page 327 of 1938

CAUTION: Never coat the inside of spark plug
boots with silicone grease. Some types of silicone
grease can damage the ignition cable conductor.
SPARK PLUG CABLES #3 AND #5
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the resonator.
(2) Grasp the spark plug boot/heat shield as close
as possible to the spark plug.Twist the boot
slightly to break its seal with the plug and pull
straight back. Do not use pliers, pull on the
ignition cable, or pull the spark plug boot at an
angle.This could damage the spark plug insulator,
terminal, or the cable insulation. Wipe spark plug
insulator clean with a dry cloth before installation.
(3) Remove the cable from the retaining bracket.
Make sure that they are also detached from the rear
retaining clip mounted on the rear of the intake
manifold.
INSTALLATION
(1) When installing the spark plug cables, make
sure the coil and spark plug insulator and terminals
are fully seated. Aclick sound should be heard or
terminal engagement is felt when the terminals
are properly attached.
(2) Install the cable into the retaining bracket.
Make sure that they are also attached to the rear
retaining clip mounted on the rear of the intake
manifold.
(3) Install the resonator.
SPARK PLUG CABLE #1
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the accessory drive belt, refer to Group
7, Cooling.
(2) Remove the four bolts from the upper half of
the generator bracket.
(3) Push the Generator rearward.
(4) Grasp the spark plug boot/shield assembly as
close as possible to the spark plug.Twist the boot
slightly to break its seal with the plug and pull
straight back. Do not use pliers, pull on the
ignition cable, or pull the spark plug boot at an
angle.This could damage the spark plug insulator,
terminal, or the cable insulation. Wipe spark plug
insulator clean with a dry cloth before installation.
(5) Remove the cable from the retaining bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) When installing the spark plug cables, make
sure the coil and spark plug insulator and terminals
are fully seated. Aclick sound should be heard orterminal engagement is felt when the terminals
are properly attached.
(2) Rotate Generator back into place.
(3) Install upper Generator bracket with the four
bolts.
(4) Install the accessory drive belt, refer to Group
7, Cooling.
SPARK PLUG SERVICEÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES
WARNING: The ignition cables should not be
removed while the engine is hot. This could cause
server injury/burns and can cause damage to the
ignition cables.
Use extreme care when removing and installing
the spark plug cables.
The spark plug boot heat shield needs to be
installed correctly on the boot before being installed
on the engine (Fig. 1). If it is not installed correctly
engine misfire would occur.
Do not use pliers to pull the boot/heat shield
assembly from the spark plugs. This will damage the
shield assembly.
SPARK PLUG #3 AND #5
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the resonator.
(2) Remove intake strut to cylinder head bolt at
cylinder head.
(3) Loosen bolt for intake strut at intake.
(4) Swing strut away.
(5) Grasp the spark plug boot/shield assembly as
close as possible to the spark plug.Twist the boot/
shield assembly slightly to break the seal with
the plug and pull straight out. Do not use pli-
ers, pull on the ignition cable, or pull the spark
plug boot at an angle.This could damage the
spark plug insulator, terminal, heat shield or the
insulation. Wipe spark plug insulator clean with a
dry cloth before installation.
(6) Remove spark plug
INSTALLATION
(1) Install spark plug and tighten to 28 N´m (20 ft.
lbs.).
(2) When installing the spark plug cables, make
sure spark plug insulator and terminals are fully
seated. Aclick sound should be heard or felt
when the terminals are properly attached.
(3) Install the cable into the retaining bracket.
Make sure that they are also attached to the rear
retaining clip mounted on the rear of the intake
manifold.
(4) Swing strut back into place.
NSIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 29
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 332 of 1938

SPARK PLUG
* New Spark Plug Gap
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION......................TORQUE
3.3L Camshaft Position
Sensor Screw.............12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
3.3L Engine Coolant Sensor......7N´m(60in.lbs.)
3.3L Crankshaft Position
Sensor Screw.............12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
3.3/3.8L Ignition Coil.........12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Ignition Switch...............2N´m(17in.lbs.)
Spark Plugs.................28N´m(20ft.lbs.)
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCEÐ3.3/3.8L
Engine Spark Plug Gap * Thread Size
3.3L RN14PMP5 0.048 TO 0.053 14mm (3/4 in.) reach
3.8L RN14PMP5 0.048 TO 0.053 14mm (3/4 in. ) reach
CABLE Maximum
Resistance
#1 18.5K ohms
#2 15.5K ohms
#3 20.4K ohms
#4 21.2K ohms
#5 27.7K ohms
#6 26.7K ohms
8D - 34 IGNITION SYSTEMNS
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 1052 of 1938

made to seal the area between the bedplate and cyl-
inder block without disturbing the bearing clearance
or alignment of these components.
GASKET DISASSEMBLY
Parts assembled with form-in-place gaskets may be
disassembled without unusual effort. In some
instances, it may be necessary to lightly tap the part
with a mallet or other suitable tool to break the seal
between the mating surfaces. A flat gasket scraper
may also be lightly tapped into the joint but care
must be taken not to damage the mating surfaces.
SURFACE PREPARATION
Scrape clean or wire brush all gasket surfaces to
remove all loose material. Inspect stamped parts to
ensure gasket rails are flat. Gasket surfaces must be
free of oil and dirt. Make sure old gasket material is
removed from blind attaching holes.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing the material off location.
TheMopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant
gasket material or equivalent should be applied in a
continuous bead approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in
diameter. All mounting holes must be circled. For
corner sealing, a 3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop
is placed in the center of the gasket contact area.
Uncured sealant may be removed with a shop towels.
Components should be torqued in place while the
sealant is still wet to the touch (within 10 minutes).
The usage of a locating dowel is recommended during
assembly to prevent smearing of material off loca-
tion.
CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET BOLT ACCESS PLUG
An Access plug is located in the right inner fender
shield. Remove the plug and insert the proper size
socket, extension and ratchet, when crankshaft rota-
tion is necessary.
ENGINE CORE PLUGS
REMOVAL
Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screwdriver
and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the cup
plug (Fig. 1). With the cup plug rotated, grasp firmlywith pliers or other suitable tool and remove plug
(Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting
as restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly remove all rust and clean inside of cup
plug hole in cylinder block or head. Be sure to
remove old sealer. Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole
with sealer. Make certain the new plug is cleaned of
all oil or grease. Using proper drive plug, drive plug
into hole so that the sharp edge of the plug is at
least 0.5 mm (0.020 inch.) inside the lead in chamfer
(Fig. 1).
It is in not necessary to wait for curing of the seal-
ant. The cooling system can be refilled and the vehi-
cle placed in service immediately.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
If a loss of performance is noticed, timing belt or
chain may have skipped one or two teeth. Camshaft
and crankshaft timing should be checked. Refer to
Group 9, Engine Timing belt or chain installation.
It is important that the vehicle is operating to its
optimum performance level to maintain fuel economy
and lowest vehicle emissions. If vehicle is not operat-
ing to these standards, refer to Engine Diagnosis out-
lined is this section. The following procedures can
assist in achieving the proper engine diagnosis.
(1) Test cranking amperage draw. Refer to Group
8B, Starting.
(2) Check intake manifold for vacuum leaks.
(3) Perform cylinder compression pressure test.
Refer to Engine Diagnosis, outlined in this section.
(4) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary and
adjust gap as specified in Group 8D, Ignition System.
Tighten to specifications.
Fig. 1 Core Hole Plug Removal
9 - 2 ENGINENS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1055 of 1938

CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original centerline.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
HYDROSTATIC LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, these
steps should be used.
CAUTION: Do Not Use Starter Motor To Rotate
Engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
any fluid that may possibly be in the cylinder under
pressure.
(4) With all spark plugs removed, rotate engine
crankshaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., cool-
ant, fuel, oil or other).
(6) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., Connecting
Rods, Pistons, Valves etc.)
(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
CAUTION: Squirt approximately 1 teaspoon of oil
into cylinders, rotate engine to lubricate the cylin-
der walls to prevent damage on restart.
(8) Install new spark plugs.
(9) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(10) Fill engine with specified amount of approved
oil and install new oil filter.
(11) Connect negative battery cable.
(12) Start engine and check for any leaks.
ENGINE OIL
Checking Oil Level
To assure proper engine lubrication, the engine oil
must be maintained at the correct level. Check the
oil level at regular intervals, such as every fuel stop.
The best time to check the oil level is about 5 min-
utes after a fully warmed-up engine is shut off, or
before starting the vehicle after it has sat overnight.
Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level
ground, will improve the accuracy of the oil level
readings. For 2.4L, 3.3L and 3.8L engines, maintain
the oil level between the MIN and MAX markings on
the dipstick. Adding one quart of oil when the read-ing is at the MIN mark will result in a MAX reading
on these engines. For the 3.0L engine, add one full
quart when the level on the dipstick is at or below
the ADD mark.
ENGINE OIL SERVICE
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-
MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase
lubricant. Engine failure can result.
NSENGINE 9 - 5
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1057 of 1938

ENGINE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CYLINDER COMBUSTION
PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST.............. 8
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST . . 7
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐMECHANICAL......... 12
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE...... 10GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 7
INSPECTION
(ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)......... 8
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS..... 7
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET)
NOISE DIAGNOSIS...................... 8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GENERAL INFORMATION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
Refer to the Service DiagnosisÐMechanical Chart
and the Service DiagnosisÐPerformance Chart, for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions. Refer
to Group 14, Fuel System, for the fuel system diag-
nosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If a change in RPM'S, the area of the suspected
leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.
(4) Disconnect coil wire from distributor and
secure to good ground to prevent a spark from start-
ing a fire (Conventional Ignition System). For Direct
Ignition System DIS disconnect the coil connector.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gage adaptor into the #1
spark plug hole in cylinder head. Crank engine until
maximum pressure is reached on gage. Record this
pressure as #1 cylinder pressure.
(7) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(8) Compression should not be less than (689kPa)
100 psi and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(9) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(10) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
NSENGINE 9 - 7
Page 1058 of 1938

cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
(11) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary
and adjust gap as specified in Group 8, Electrical.
Tighten to specifications.
(12) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System Secondary Cir-
cuit Inspection.
(13) Test coil output voltage, primary and second-
ary resistance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System.
(14) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and differ-
ent RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
Specifications.
(15) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance,.
(16) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out
lined in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. For
emission controls see Group 25, Emission Controls
for service procedures.
(17) Inspect and adjust accessory belt drives refer-
ring to Group 7, Cooling System, Accessory Drive
Belts for proper adjustments.
(18) Road test vehicle as a final test.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1 379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET) NOISE DIAGNOSIS
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) During this time, turn engine off and let set for
a few minutes before restarting. Repeat this several
times after engine has reached normal operating
temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor pressed into the vertical oil
passage to the cylinder head is plugged with debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head. Depress part of rocker
arm over adjuster. Normal adjusters should feel very
firm. Spongy adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and disassem-
bleDo not reuse retainer caps. Do not inter-
change parts and make sure that care and
cleanliness is exercised in the handling of parts.
c. Clean out dirt and varnish with solvent.
d. Reassemble with engine oil.
e. Check for sponginess.
f. If still spongy, replace with new adjuster.
INSPECTION (ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
9 - 8 ENGINENS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)