torque DATSUN B110 1973 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 64 of 513

CHASSIS
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
General
specifications
Torque
converter
Type
Stall
torque
ratio
Transmission
Type
Control
elements
Gear
ratio
Selector
positions
Oil
pump
Type
Number
of
pump
Oil
Capacity
Hydraulic
control
system
Lubrication
system
Cooling
system
Multiple
disc
clutch
Band
brake
Multiple
disc
brake
One
way
clutch
1st
lnd
3rd
Reverse
P
Park
R
Reverse
N
Neutral
D
Drive
1
lnd
lock
I
Lock
up
AT
60
Symmetrical3
element
I
stage
l
phase
torque
converter
coupling
2
0
I
3
speed
forward
and
one
speed
reverse
with
planetary
gear
train
1
I
I
I
2
458
1
458
1
000
2
182
The
transmission
is
placed
in
neutral
The
output
shaft
is
fixed
The
engine
can
be
started
Backward
running
The
transmission
is
in
neutral
The
engine
can
be
started
Up
or
downshifts
automatically
to
and
from
1st
lnd
and
top
Fixed
at
2nd
Fixed
at
low
or
downshifts
from
2nd
Internally
intermeslting
involute
gear
pump
Automatic
transmission
fluid
Dexron
type
5
5
liters
57
8
U
S
qts
47
8
Imp
qts
Approximately
1
7
liters
27
8
U
S
qts
2
3
8
Imp
qts
in
torque
converter
Controlled
by
detecting
the
negative
pressure
of
intake
manifold
and
the
revolution
speed
of
output
shaft
Forced
lubrication
by
an
oil
pwnp
Air
cooled
Page 65 of 513

AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
Specifications
and
adjustment
Automatic
transmission
assembly
Model
code
number
Torque
converter
assembly
Stamped
mark
on
the
TIC
Front
clu
tch
Number
of
drive
plate
Number
of
driven
plates
Clearance
Thickness
of
retaining
plate
Rear
clutch
Number
of
drive
plates
Number
of
driven
plate
Clearance
Thickness
of
retaining
plate
Low
reverse
brake
Number
of
drive
plates
Number
of
driven
plates
Clearance
Thickness
of
retaining
plate
Brake
band
Piston
size
Big
dia
Small
dia
Control
valve
assembly
Stamped
mark
on
trainer
Governor
assembly
Stamped
mark
on
governor
body
mm
in
mm
in
mm
in
mm
in
mm
in
mm
in
mm
in
AT
61
x
0100
IO
C
3
3
1
6
to
1
8
0
0630
to
0
071
10
6
0
417
10
8
0
425
11
0
0
433
11
2
0
441
II
4
0
449
11
6
0
457
3
3
1
0
to
1
5
0
039
to
0
059
8
35
0
3287
3
3
0
80
to
1
05
0
0315
to
0
0413
15
8
0
622
16
0
0
630
16
2
0
638
16
4
0
646
16
6
0
654
16
8
0
661
64
2
520
44
I
732
E
35
Page 66 of 513

CHASSIS
Engine
idling
and
stall
revolution
Engine
with
emission
control
device
Idling
revolution
rpm
650
at
0
position
800
at
N
position
1
750
to
2
000
Stall
revolution
rpm
Tightening
torque
kg
m
ft
Ib
Test
plug
oil
pressure
inspection
hole
Support
actuator
parking
rod
inserting
position
to
rear
extension
Oil
charging
pipe
to
case
Dust
cover
to
converter
housing
Selector
range
lever
to
manual
shaft
Lower
shift
rod
lock
nut
6
5
t07
5
47
to
54
0
8
to
1
0
5
8
to
7
2
4
0
to
5
0
30
to
36
4
0
to
5
0
30
to
36
2
0
to
2
5
15
to
18
0
5
to
0
7
3
6
to
5
1
0
5
to
0
7
3
6toS
I
1
2
to
1
5
8
7
to
10
8
1
5
to
4
0
II
to
29
1
3
to
1
8
9
4
to
13
0
55
to
0
75
4
0
to
5
4
0
25
to
0
35
1
9
to
2
5
0
25
to
0
35
1
9
to
2
5
0
5
to
0
7
3
6
to
5
I
0
25
to
0
35
1
9
to
2
5
0
5
to
0
7
3
6
to
5
1
0
6
to
0
8
4
4
to
5
8
0
5
to
0
7
3
6
to
5
1
3
0
to
4
0
22
to
29
3
0
to
5
0
22
to
36
14
to
2
1
10
to
15
0
8
to
l
l
5
8
to
7
9
0
55
to
0
75
4
0
to
5
4
0
55
to
0
75
4
0
to
5
4
3
0
to
4
0
22
to
29
2
0
to
2
9
15
to
21
Drive
plate
to
crankshaft
Drive
plate
to
torque
converter
Converter
housing
to
engine
Transmission
case
to
converter
housing
Transmission
case
to
rear
extension
Oil
pan
to
transmission
case
Servo
piston
retainer
to
transmission
case
Piston
stem
when
adjuting
band
brake
Piston
stem
lock
nut
One
way
clutch
inner
race
to
transmission
case
Control
valve
body
to
transmission
case
Lower
valve
body
to
upper
valve
body
Side
plate
to
control
valve
body
Nut
for
control
valve
reamer
bolt
Oil
strainer
to
lower
valve
body
Governor
valve
body
to
oil
distributor
Oil
pump
housing
to
oil
pump
cover
Inhibitor
switch
to
transmh
sion
case
Manual
shaft
lock
nut
Oil
tube
to
transmission
case
Turn
back
two
turns
after
tightening
AT
62
Page 70 of 513
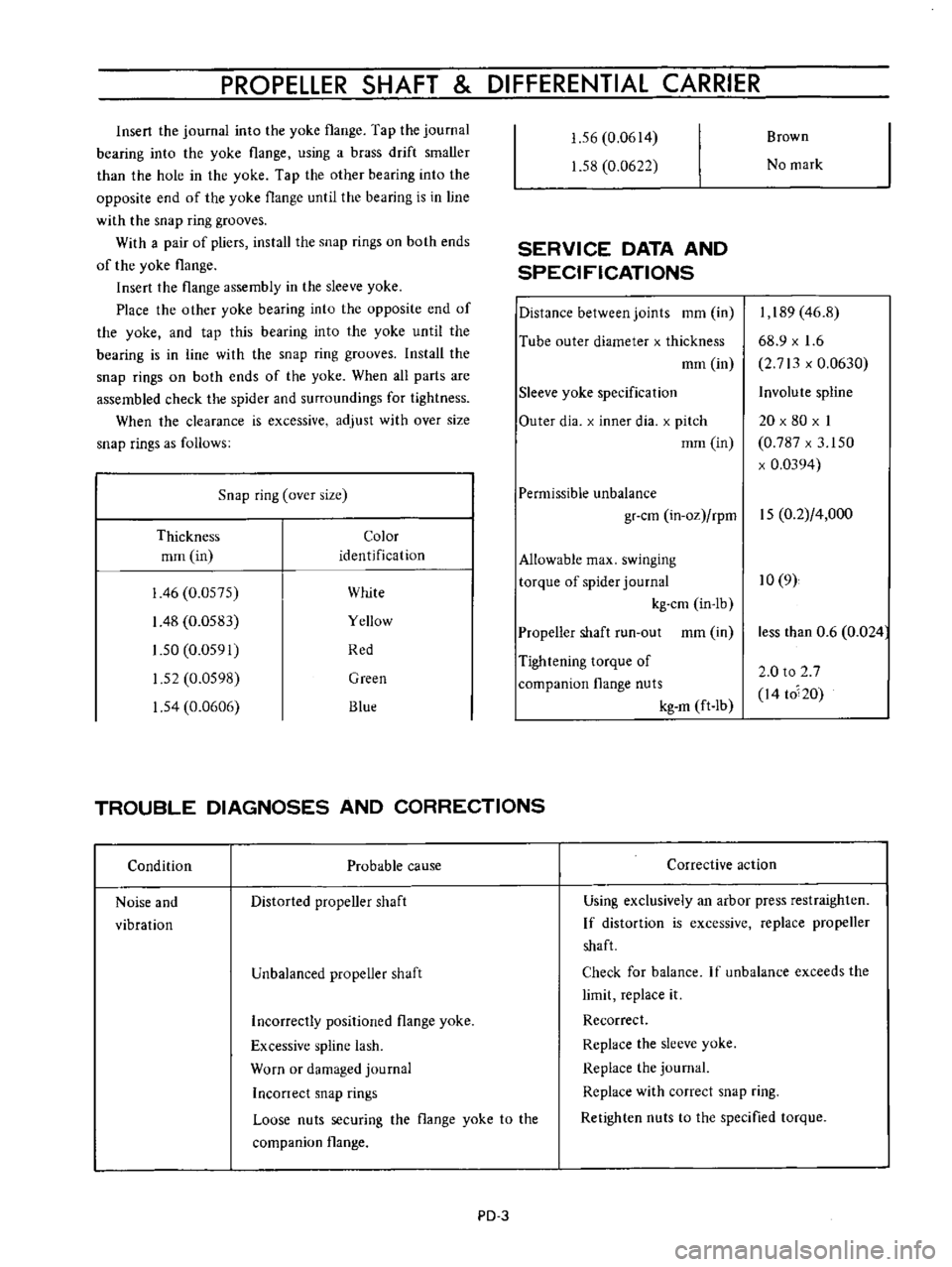
PROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
Insert
the
journal
into
the
yoke
flange
Tap
the
journal
bearing
into
the
yoke
flange
using
a
brass
drift
smaller
than
the
hole
in
the
yoke
Tap
the
other
bearing
into
the
opposite
end
of
the
yoke
flange
until
the
bearing
is
in
line
with
the
snap
ring
grooves
With
a
pair
of
pliers
install
the
snap
rings
on
both
ends
of
the
yoke
flange
Insert
the
flange
assembly
in
the
sleeve
yoke
Place
the
other
yoke
bearing
into
the
opposite
end
of
the
yoke
and
tap
this
bearing
into
the
yoke
until
the
bearing
is
in
line
with
the
snap
ring
grooves
Install
the
snap
rings
on
both
ends
of
the
yoke
When
all
parts
are
assembled
check
the
spider
and
surroundings
for
tightness
When
the
clearance
is
excessive
adjust
with
over
size
snap
rings
as
follows
Snap
ring
over
size
Thickness
Color
mrn
in
identification
I
46
0
0575
White
I
48
0
0583
Yellow
1
50
0
0591
Red
1
52
0
0598
Green
1
54
0
0606
Blue
1
56
0
0614
1
58
0
0622
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
Distance
between
joints
mm
in
Tube
outer
diameter
x
thickness
mm
in
Sleeve
yoke
specification
Outer
dia
x
inner
dia
x
pitch
mm
in
Brown
No
mark
I
189
46
8
68
9
x
1
6
2
713
x
0
0630
Involute
spline
20
x
80
x
I
0
787
x
3
150
x
0
0394
Permissible
unbalance
gr
cm
in
oz
rpm
15
0
2
4
000
Allowable
max
swinging
torque
of
spider
journal
10
9
kg
cm
in
lb
Propeller
shaft
run
out
mm
in
Tightening
torque
of
companion
flange
nuts
kg
m
ft
Ib
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Condition
Probable
cause
Noise
and
vibration
Distorted
propeller
shaft
Unbalanced
propeller
shaft
Corrective
action
less
than
0
6
0
024
2
0
to
2
7
I4
to
20
Using
exclusively
an
arbor
press
restraighten
If
distortion
is
excessive
replace
propeller
shaft
Check
for
balance
If
unbalance
exceeds
the
limit
replace
it
Recorrect
Replace
the
sleeve
yoke
Replace
the
journal
Replace
with
correct
snap
ring
Retighten
nuts
to
the
specified
torque
Incorrectly
positioned
flange
yoke
Excessive
spline
lash
Worn
or
damaged
journal
Inconect
snap
rings
Loose
nuts
securing
the
flange
yoke
to
the
companion
flange
PD
3
Page 71 of 513
CHASSIS
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
REMOVAL
DISASSEMBL
Y
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
ASSEMBLY
AND
ADJUSTMENT
Assembling
differential
gear
case
Setting
and
adjusting
drive
pinion
PD
4
PD
5
PD
5
PD
7
PD
8
PD
9
PD
10
Adjusting
drive
pinion
preload
Setting
and
adjusting
side
bearing
shims
INSTALLATION
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
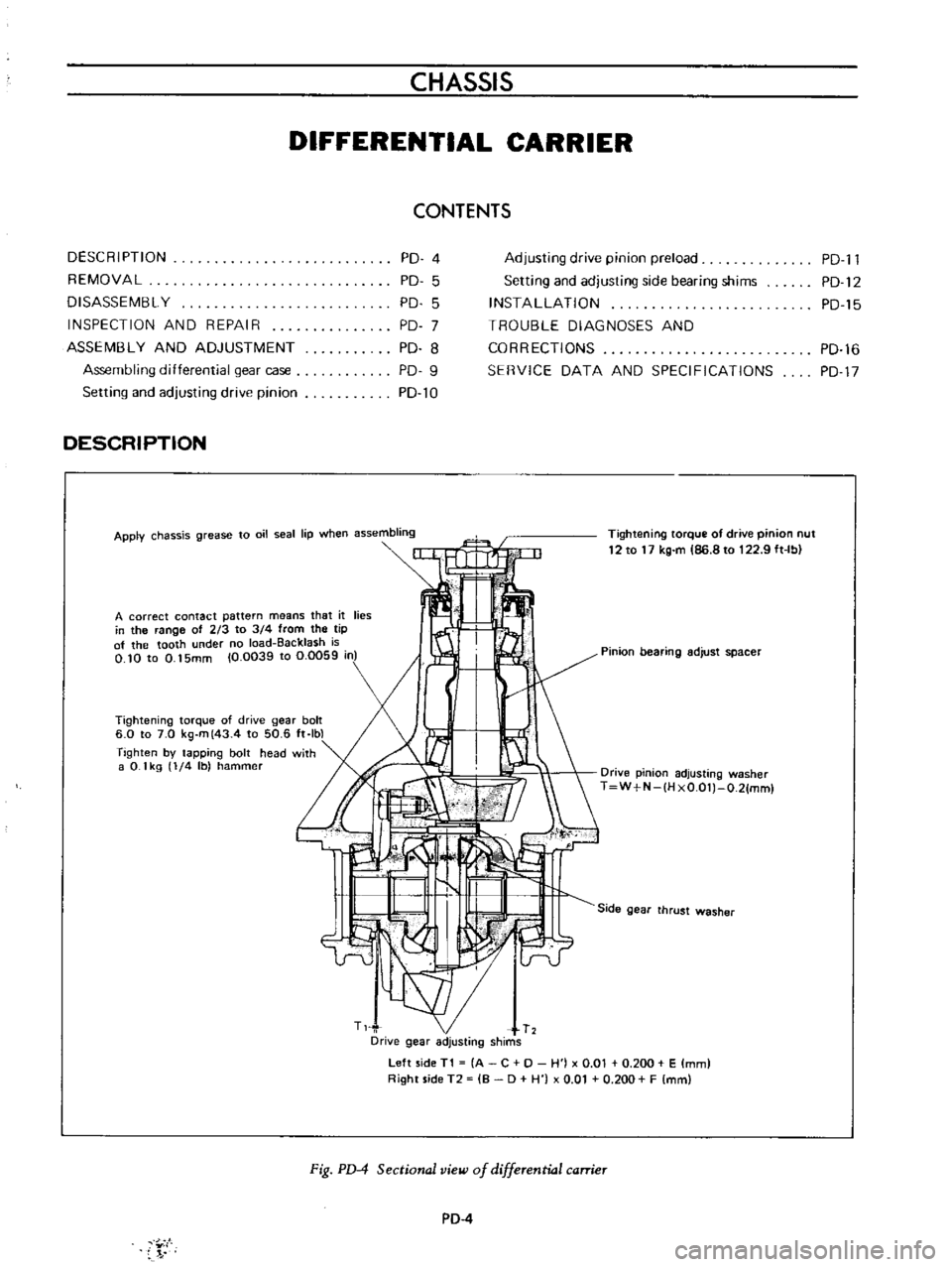
DESCRIPTION
Apply
chassis
grease
to
oil
seal
lip
when
assembling
Tightening
torque
of
drive
pinion
nut
12
to
17
kg
m
86
8
to
122
9
ft
Ib
A
correct
contact
pattern
means
that
it
lies
in
the
range
of
213
to
3
4
from
the
tip
of
the
tooth
under
no
load
Backlash
is
O
10
to
0
15mm
10
0039
to
0
0059
in
Pinion
bearing
adjust
spacer
Tightening
torque
of
drive
gear
bolt
6
0
to
7
0
kg
m
43
4
to
50
6
ft
Ibl
Tighten
by
tapping
bolt
head
with
a
0
1
kg
1
4
Ib
hammer
Drive
pinion
adjusting
washer
T
W
N
IH
xO
OlJ
O
21mml
Side
gear
thrust
washer
Left
side
T1
A
C
0
H
j
x
0
01
0
200
E
mm
Right
side
T2
B
0
H
0
01
0
200
F
mm
Fig
PD
4
Sectional
view
of
differential
carrier
PD
4
Y
I
PD
l1
PD
12
PD
15
PD
16
PD
17
Page 74 of 513
PROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
10
Measure
the
initial
turning
torque
drive
pinion
gear
by
using
Drive
Pinion
Preload
Gauge
Sn127S000
11
Remove
the
drive
pinion
nut
and
draw
out
the
companion
flange
assembly
Note
Use
the
Drive
Pinion
Flange
Wrench
to
hold
the
companion
flange
IST31540000
Fig
PD
12
Removing
drive
pinion
unit
12
Remove
the
drive
pinion
assembly
to
the
rearward
by
tapping
the
front
end
with
a
plastic
mallet
The
drive
pinion
can
be
taken
out
together
with
the
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
inner
race
of
rear
bearing
bearing
spacer
and
adjusting
washer
13
Remove
the
oil
seal
and
take
out
the
front
bearing
inner
race
Note
The
removed
oil
seal
should
not
be
reused
14
Draw
out
the
outer
races
of
both
front
and
rear
bearings
using
drift
15
Draw
out
drive
pinion
rear
bearing
inner
race
using
Drive
Pinion
Rear
Inner
Race
Replacer
ST30031000
ST30031
000
AI
n
Fig
PD
13
Removing
bearing
10
y@
@
0
0
0
00
eo
00
j
l
I
@
o
q@
@
t
I
7
c9
@
@@
@
l2
4
o
OO
r
j
T
I
i
cb
3
0
0
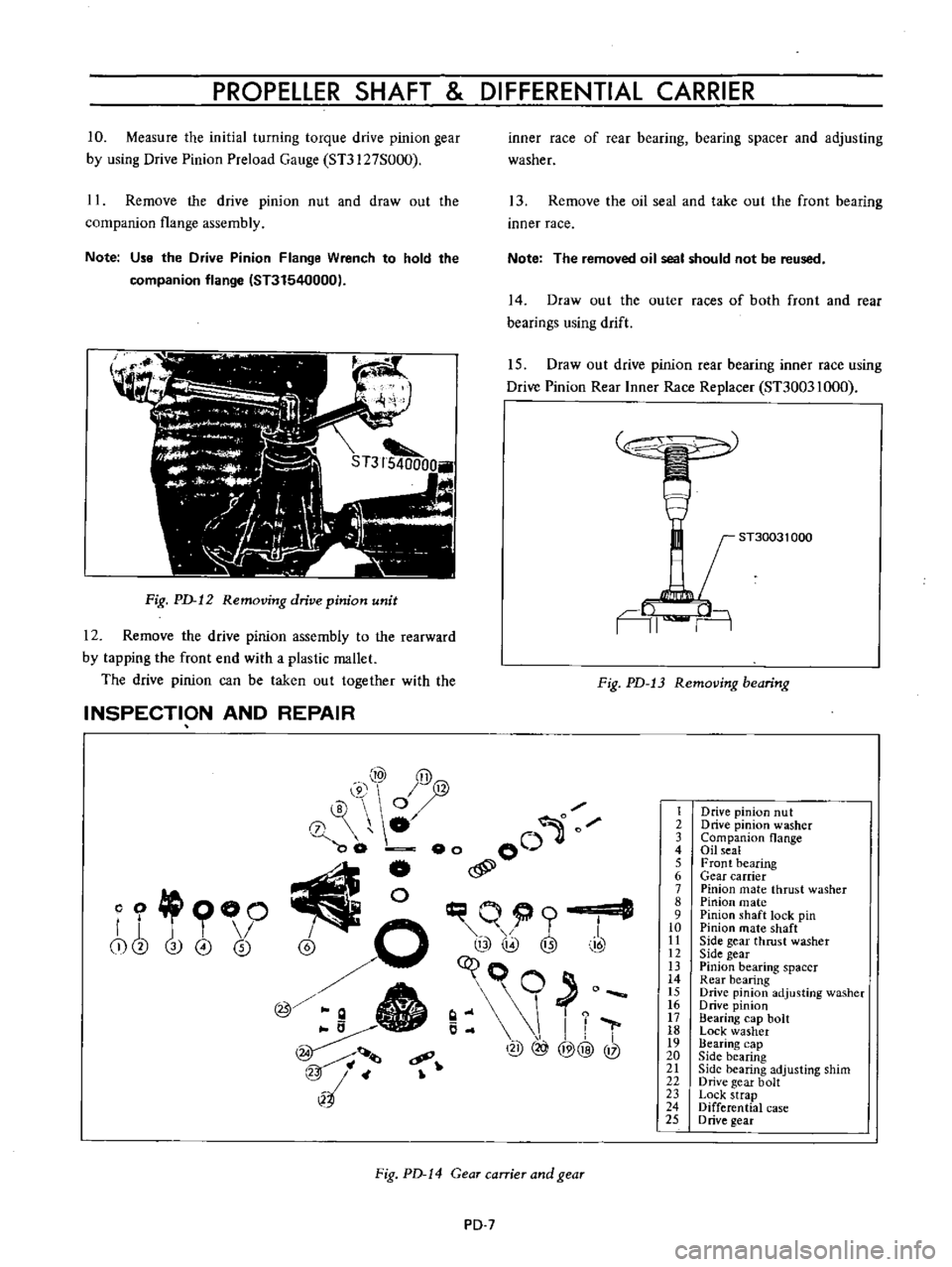
Fig
PD
14
Gear
carrier
and
gear
PD
7
1
2
3
4
S
6
7
8
9
10
II
12
IJ
14
IS
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
Drive
pinion
nut
Drive
pinion
washer
Companion
flange
Oil
seal
Front
bearing
Gear
carrier
Pinion
mate
thrust
washer
Pinion
mate
Pinion
shaft
lock
pin
Pinion
mate
shaft
Side
gear
thrust
washer
Side
gear
Pinion
bearing
spacer
Rear
bearing
Drive
pinion
adjusting
washer
o
rive
pinion
Bearing
cap
bolt
Lock
washer
Bearing
cap
Side
bearing
Side
bearing
adjusting
shim
Drive
gear
bolt
Lock
strap
Differential
case
D
rive
gear
Page 75 of 513
CHASSIS
Before
inspecting
various
parts
thoroughly
wash
them
so
that
damage
and
wear
can
be
easily
detected
Then
proceed
as
follows
Check
gear
teeth
for
scoring
cracking
and
chipping
and
make
sure
that
tooth
pattern
indicates
correct
meshing
depth
If
any
defect
is
evident
replace
parts
as
required
Note
Drive
pinion
and
drive
gear
are
supplied
for
replacement
as
a
set
therefore
should
either
part
be
damaged
replace
as
a
set
Check
the
pinion
gear
shaft
and
pinion
gear
mating
faces
for
scoring
and
signs
of
wear
and
replace
as
required
Follow
the
same
procedure
for
inner
faces
of
side
gear
and
their
seats
on
differential
case
3
Inspect
all
bearing
races
and
rollers
for
scoring
chipping
or
evidence
of
excessive
wear
They
should
be
in
tiptop
condition
not
worn
with
mirror
like
surfaces
Replace
if
there
is
a
doubt
on
their
efficiency
since
an
incorrect
bearing
operation
may
result
in
noisiness
and
gear
seizure
4
Inspect
thrust
washer
faces
Small
defects
can
be
corrected
with
emery
paper
In
ASSEMBLY
AND
AD
JUSTMENT
Tightening
torque
of
side
bearing
cap
bolts
5
to
6kg
m
36
2
to
43
4
ft
lb
co
g
E
E
on
N
case
the
clearance
between
the
side
gear
and
thrust
washer
exceeds
0
2
mm
0
0079
in
replace
the
thrust
washers
Three
kinds
of
thrust
washers
are
available
5
Measure
run
out
of
the
drive
gear
at
the
rear
side
using
a
dial
indicator
When
the
run
out
is
more
0
05
mm
0
0020
in
replace
the
drive
gear
and
pinion
gear
as
a
set
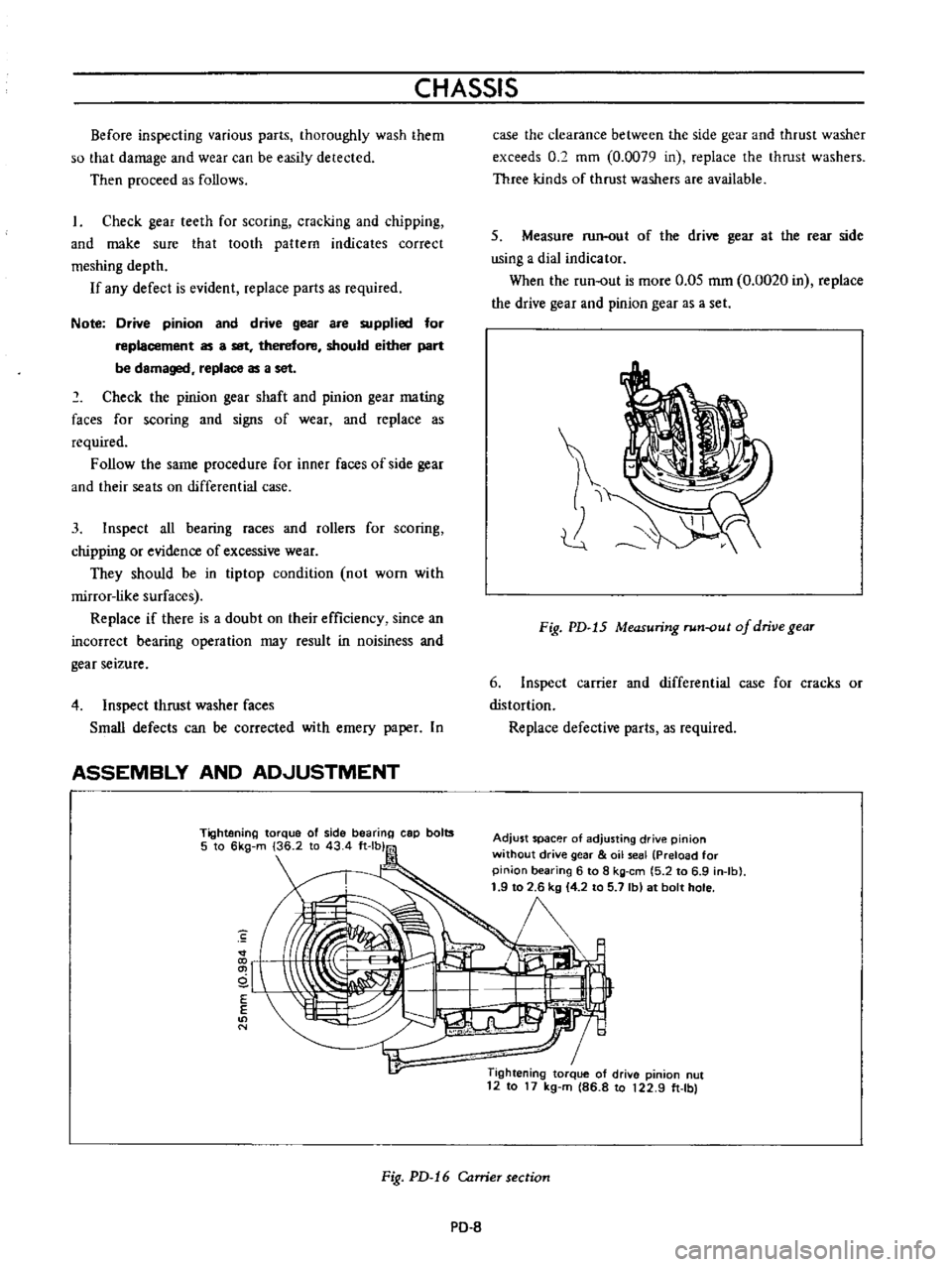
Fig
PD
15
Measuring
run
out
of
drive
gear
6
Inspect
carrier
and
differential
case
for
cracks
or
distortion
Replace
defective
parts
as
required
Adjust
spacer
of
adjusting
drive
pinion
without
drive
gear
oil
seal
Preload
for
pinion
bearing
6
to
8
kg
em
5
2
to
6
9
in
Ib
1
9
to
2
6
kg
4
2
to
5
7
Ib
at
bolt
hole
1
Tightening
torque
of
drive
pinion
nut
12
to
17
kg
m
86
8
to
122
9
ft
Ibl
Fig
PD
16
Carrier
section
PO
8
Page 76 of 513
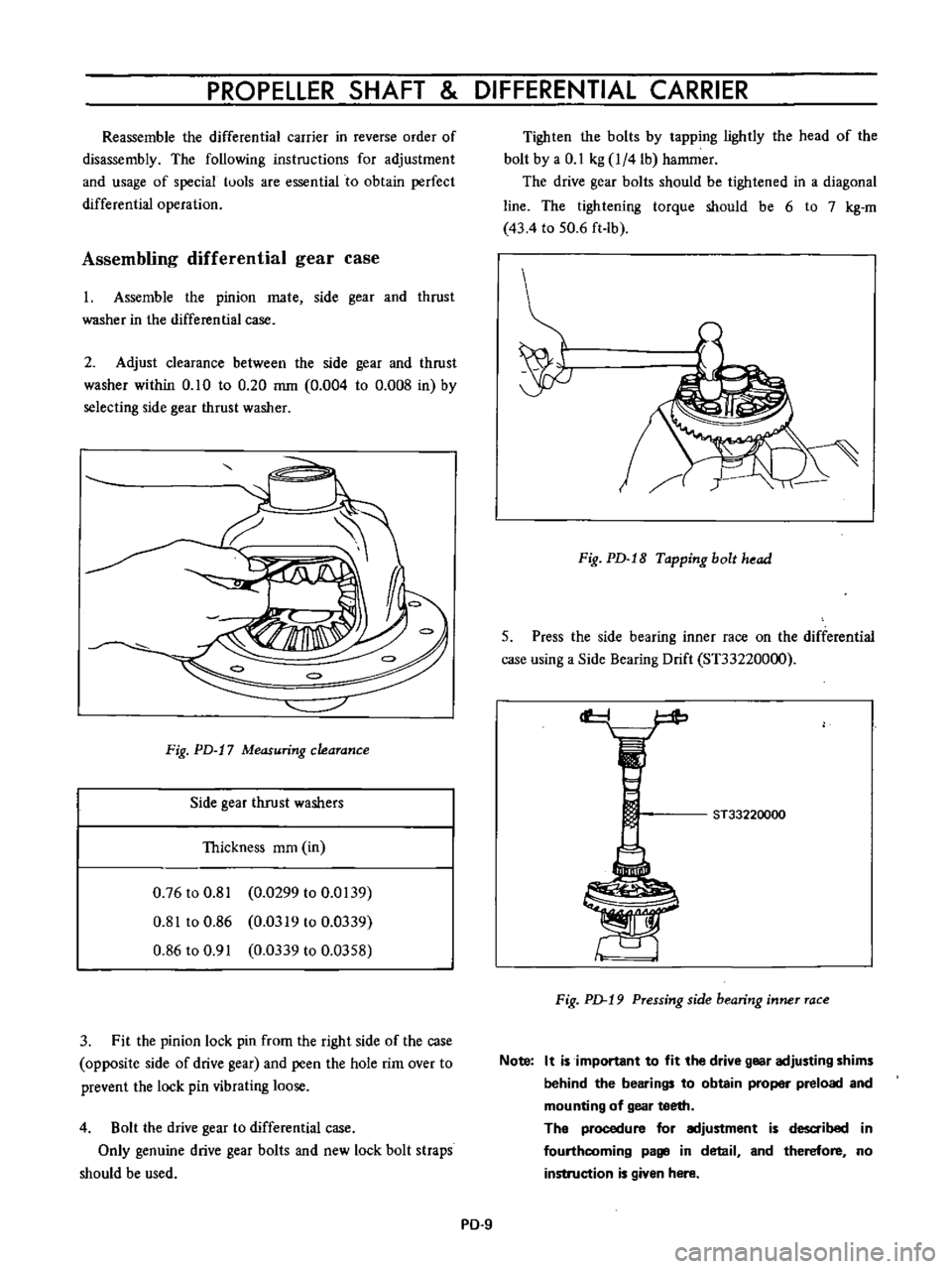
PROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
Reassemble
the
differential
carrier
in
reverse
order
of
disassembly
The
following
instructions
for
adjustment
and
usage
of
special
tuols
are
essential
to
obtain
perfect
differential
operation
Assembling
differential
gear
case
1
Assemble
the
pinion
mate
side
gear
and
thrust
washer
in
the
differential
case
2
Adjust
clearance
between
the
side
gear
and
thrust
washer
within
0
10
to
0
20
mm
0
004
to
0
008
in
by
selecting
side
gear
thrust
washer
Fig
PD
17
Measuring
clearance
Side
gear
thrust
washers
Thickness
mm
in
0
76
to
0
81
0
0299
to
0
0139
0
81
to
0
86
0
0319
to
0
0339
0
86
to
0
91
0
0339
to
0
0358
3
Fit
the
pinion
lock
pin
from
the
right
side
of
the
case
opposite
side
of
drive
gear
and
peen
the
hole
rim
over
to
prevent
the
lock
pin
vibrating
loose
4
Bolt
the
drive
gear
to
differential
case
Only
genuine
drive
gear
bolts
and
new
lock
bolt
straps
should
be
used
Tighten
the
bolts
by
tapping
lightly
the
head
of
the
bolt
by
a
0
1
kg
l
4lb
hammer
The
drive
gear
bolts
should
be
tightened
in
a
diagonal
line
The
tightening
torque
should
be
6
to
7
kg
m
43
4
to
50
6
ft
lb
Fig
PD
18
Tapping
bolt
head
5
Press
the
side
bearing
inner
race
on
the
differential
case
using
a
Side
Bearing
Drift
ST33220000
cf
ST33220000
F
ig
p
19
Pressing
side
bearing
inner
race
Note
It
is
important
to
fit
the
drive
gear
adjusting
shims
behind
the
bearings
to
obtain
proper
preload
and
mounting
of
gear
teeth
The
procedure
for
adjustment
is
d
ibed
in
fourthcoming
page
in
detail
and
therefore
no
instruction
is
given
here
PD
9
Page 78 of 513

PROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
6
Formula
to
calculate
thickness
of
drive
pinion
adjusting
shims
T
W
N
H
x
0
01
0
2
mm
Where
W
Thickness
of
shim
inserted
mm
T
Required
thickness
of
rear
bearing
ad
justing
shim
mm
N
Measured
clearance
between
Height
Gauge
and
Dummy
Shaft
face
mm
H
Figure
marked
on
the
drive
pinion
head
Example
W
2
92
mm
N
0
3
mm
H
1
T
2
92
0
3
1
x
0
01
0
2
3
03
mm
Use
a
3
04
mm
washer
7
Remove
the
Dummy
Shaft
from
the
gear
carrier
housing
8
Withdraw
the
pinion
rear
bearing
from
the
Dummy
Shaft
apply
a
shims
selected
based
on
the
above
formula
and
refit
the
pinion
rear
bearing
and
drive
pinion
together
using
Drive
Pinion
Bearing
Drift
STJ0600000
Note
Be
sure
to
face
inside
faced
surface
of
the
shimes
toward
back
of
the
pinion
gear
Drive
pinion
height
adjusting
shims
Thickness
mm
in
Thickness
mm
in
2
74
0
1079
2
77
0
i091
2
80
0
1102
2
83
0
1114
2
86
0
1126
2
89
0
1138
2
92
0
1150
2
95
0
1161
2
98
0
1173
3
01
0
1185
3
04
0
1197
3
07
0
1209
3
10
0
i
220
3
13
0
1232
3
16
0
1244
319
0
1256
3
22
0
1268
3
25
0
1280
PD
Adjusting
drive
pinion
preload
Adjust
the
preload
of
drive
pinion
with
collapsible
spacer
This
procedure
has
nothing
to
do
with
thickness
of
pinion
height
adjusting
washer
Note
Reuse
of
a
collapsible
spacer
must
not
be
allowed
After
adjusting
pinion
height
lubricate
front
bearing
with
gear
oil
and
place
it
in
carrier
2
Install
a
new
oil
seal
in
carrier
Lubricate
cavity
between
seal
lips
with
grease
when
installing
3
Place
a
new
collapsible
spacer
on
drive
pinion
and
lubricate
pinion
rear
bearing
with
gear
oil
4
Insert
companion
flange
into
oil
seal
and
hold
it
firmly
against
pinion
fron
bearing
cone
From
the
rear
of
the
carrier
insert
drive
pinion
into
companion
flange
5
Ascertain
that
threaded
portion
of
drive
pinion
a
new
pinion
nut
and
washer
are
free
from
oil
or
grease
6
Holding
companion
flange
with
Drive
Pinion
Flange
Wrench
ST31540000
tighten
nut
and
then
drive
pinion
is
pulled
into
front
bearing
cone
and
into
flange
As
drive
pinion
is
pulled
into
front
bearing
cone
drive
pinion
end
play
is
reduced
While
there
is
still
end
play
in
drive
pinion
companion
flange
and
cone
will
be
felt
to
bottom
This
indicates
that
bearing
cone
and
companion
flange
have
bottomed
on
collapsible
spacer
From
this
point
a
much
greater
torque
must
be
applied
to
turn
pinion
nut
since
spacer
must
be
collapsed
From
this
point
nut
should
also
be
tightened
very
slowly
and
drive
pinion
end
play
checked
often
so
that
pinion
bearing
preload
does
not
exceed
the
limits
When
the
drive
pinion
end
play
is
eliminated
the
specified
preload
is
being
approached
Replace
collapsible
spacer
if
this
specification
is
exceeded
Note
Do
not
decrease
preload
by
loosening
pinion
nut
This
will
remove
compression
between
pinion
front
and
rear
bearing
cones
and
collapsible
spacer
and
may
permit
front
bearing
cone
to
turn
on
drive
pinion
moreover
nut
becomes
loose
Page 79 of 513
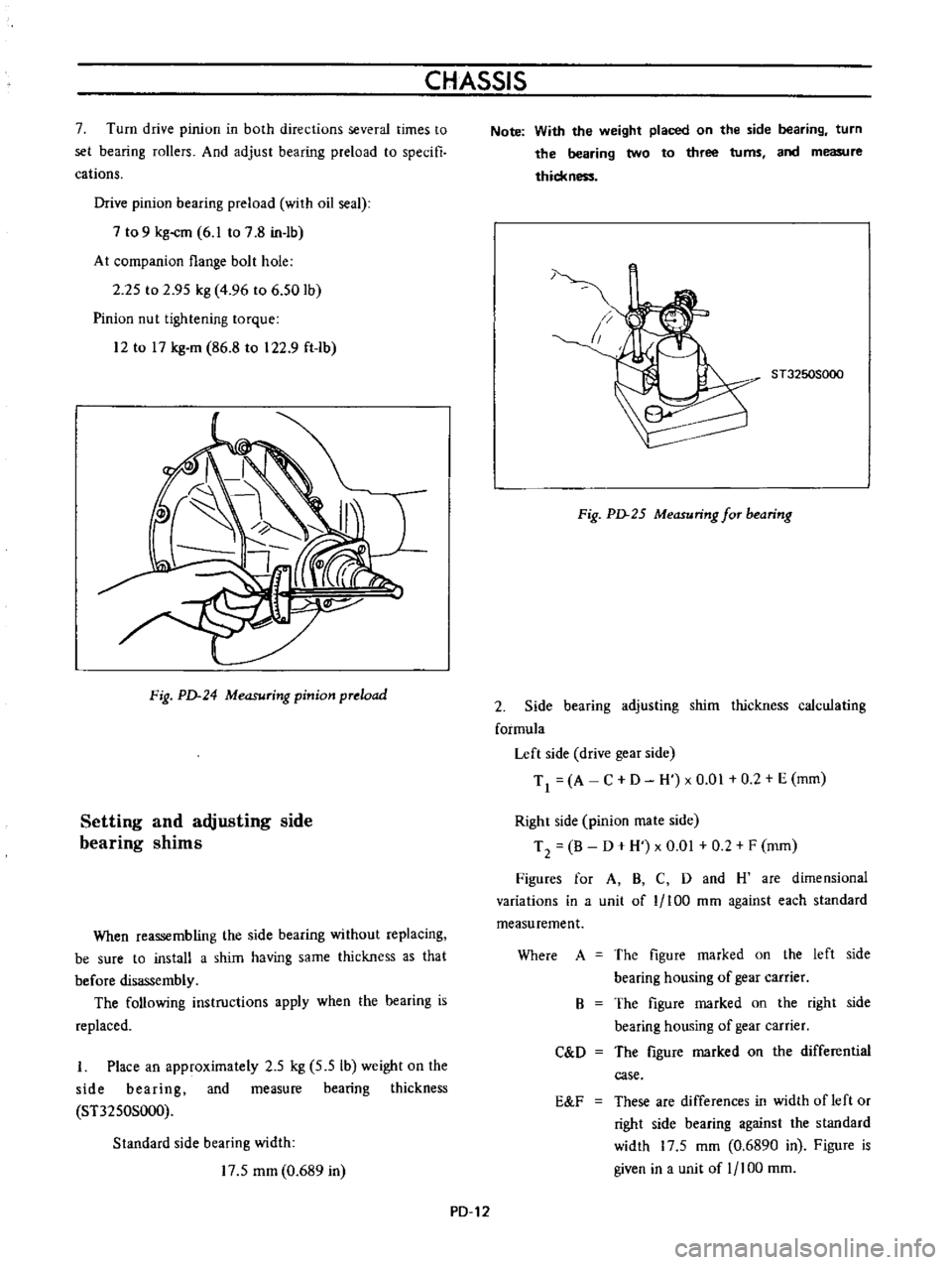
CHASSIS
7
Turn
drive
pinion
in
both
directions
several
times
to
set
bearing
rollers
And
adjust
bearing
preload
to
specifi
cations
Drive
pinion
bearing
preload
with
oil
seal
7
to
9
kg
cm
6
1
to
7
8
in
1b
At
companion
flange
bolt
hole
2
25
to
2
95
kg
4
96
to
6
50
1b
Pinion
nut
tightening
torque
12
to
17
kg
m
86
8
to
122
9
ft
1b
Fig
PD
24
Measuring
pinion
preload
Setting
and
adjusting
side
bearing
shims
When
reassembling
the
side
bearing
without
replacing
be
sure
to
install
a
shim
having
same
thickness
as
that
before
disassembly
The
following
instructions
apply
when
the
hearing
is
replaced
I
Place
an
approximately
2
5
kg
5
5
Ib
weight
on
the
side
bearing
and
measure
bearing
thickness
ST3250S000
Standard
side
bearing
width
17
5
mm
0
689
in
Note
With
the
weight
placed
on
the
side
bearing
turn
the
bearing
two
to
three
turns
and
measure
thickn
1
ST3250S000
Fig
PD
25
Measuring
for
bearing
2
Side
bearing
adjusting
shim
thickness
calculating
formula
Left
side
drive
gear
side
Tl
A
C
D
H
xO
01
0
2
E
mm
Right
side
pinion
mate
side
T
2
B
D
H
x
0
01
0
2
F
mm
Figures
for
A
B
C
D
and
H
are
dimensional
variations
in
a
unit
of
1
100
mm
against
each
standard
measurement
Where
A
The
figure
marked
on
the
left
side
bearing
housing
of
gear
carrier
The
figure
marked
on
the
right
side
bearing
housing
of
gear
carrier
The
figure
marked
on
the
differential
case
B
C
D
E
F
These
are
differences
in
width
of
left
or
right
side
bearing
against
the
standard
width
17
5
mm
0
6890
in
Figure
is
given
in
a
unit
of
1
100
mm
PD
12