torque DATSUN B110 1973 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 80 of 513
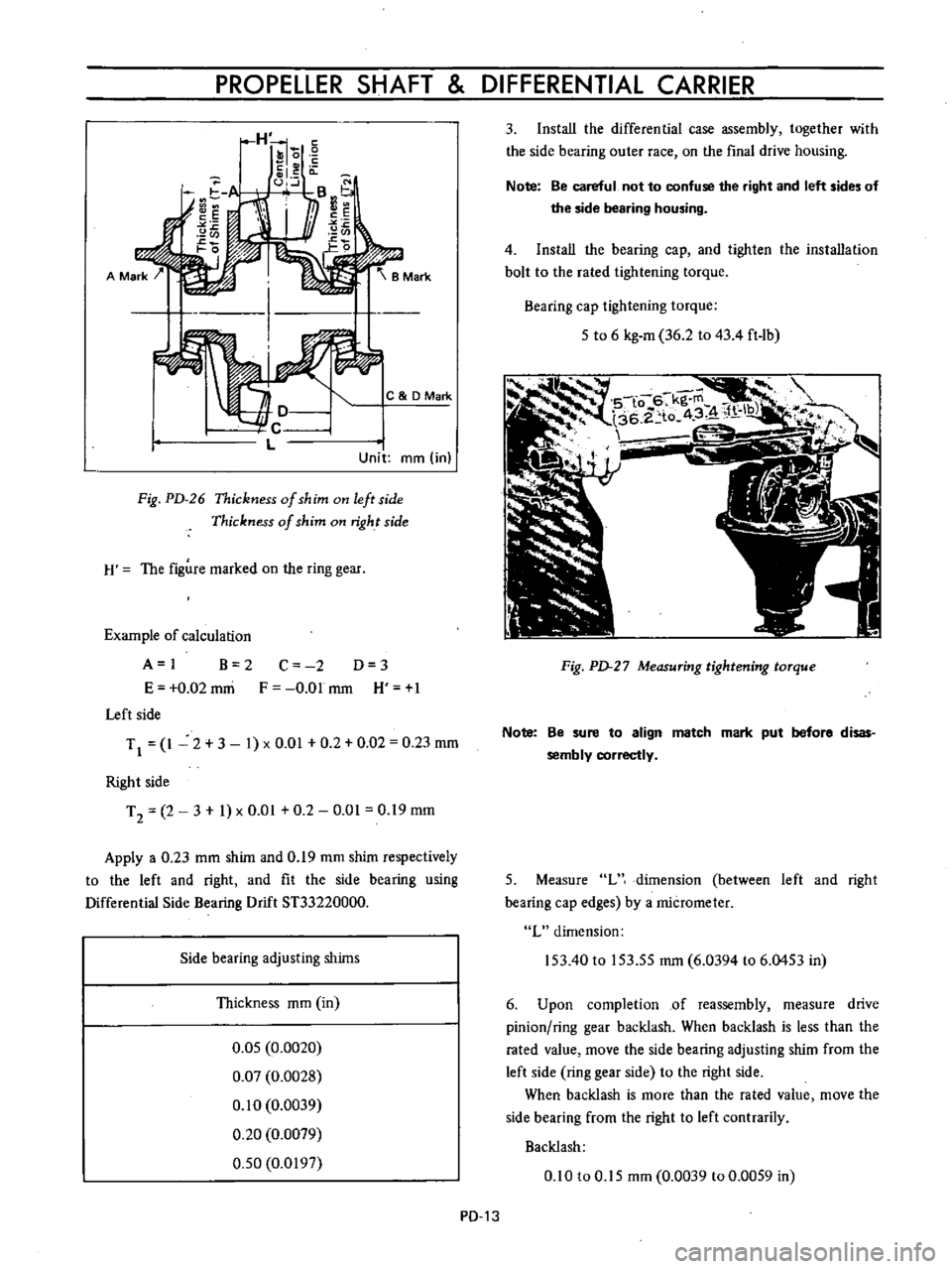
PROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
C
DMark
Unit
mm
in
Fig
PD
26
Thickness
of
shim
on
left
side
Thickness
of
shim
on
right
side
H
The
figure
marked
on
the
ring
gear
Example
of
calculation
A
I
B
2
E
0
02
mni
Left
side
C
2
D
3
F
O
Olmm
H
1
TJ
1
2
3
1
xO
01
0
2
0
02
0
23
mm
Right
side
T
2
2
3
1
x
0
01
0
2
0
01
0
19
mm
Apply
a
0
23
mm
shim
and
0
19
mm
shim
respectively
to
the
left
and
right
and
fit
the
side
bearing
using
Differential
Side
Bearing
Drift
ST33220000
Side
bearing
adjusting
shims
Thickness
mm
in
0
05
0
0020
0
07
0
0028
0
10
0
0039
0
20
0
0079
0
50
0
0197
PD
13
3
Install
the
differential
case
assembly
together
with
the
side
bearing
outer
race
on
the
final
drive
housing
Note
Be
careful
not
to
confuse
the
right
and
left
sides
of
the
side
bearing
housing
4
Install
the
bearing
cap
and
tighten
the
installation
bolt
to
the
rated
tightening
torque
Bearing
cap
tightening
torque
5
to
6
kg
m
36
2
to
43
4
ft
1b
Fig
PD
27
Measuring
tightening
torque
Note
Be
sure
to
align
match
mark
put
before
disas
sembly
correctly
5
Measure
L
dimension
between
left
and
right
bearing
cap
edges
by
a
micrometer
L
dimension
153
40
to
153
55
mm
6
0394
to
6
0453
in
6
Upon
completion
of
reassembly
measure
drive
pinion
ring
gear
backlash
When
backlash
is
less
than
the
rated
value
move
the
side
bearing
adjusting
shim
from
the
left
side
ring
gear
side
to
the
right
side
When
backlash
is
more
than
the
rated
value
move
the
side
bearing
from
the
right
to
left
contrarily
Backlash
0
10
to
0
15
mm
0
0039
to
0
0059
in
Page 81 of 513

CHASSIS
Fig
PD
28
Measuring
backlash
7
Existence
of
foreign
matter
between
the
drive
gear
and
differential
case
is
considered
when
backlash
fluctuates
considerably
Measure
drive
gear
back
deflection
8
Check
the
run
out
of
ring
gear
side
is
within
0
05
mm
0
0020
in
total
indicator
reading
ot
Fig
PD
29
Measuring
run
out
of
ring
gear
9
When
run
out
of
ring
gear
is
normal
and
fluctuation
of
backlash
is
considerable
replace
the
gear
set
Before
replacing
the
gear
set
be
sure
to
measure
companion
flange
deflection
Fluctuation
of
backlash
may
be
con
siderable
due
to
deflection
of
pinion
bearing
Limit
of
deflection
A
portioo
B
portion
Less
than
0
05
mm
0
0020
in
Less
than
0
05
mm
0
0020
in
Ct
r
r
f
1
I
f
i
r
I
oj
j
12
r
Fig
PD
30
Measuring
place
10
At
the
same
time
check
bearing
preload
Bearing
preload
should
read
8
to
15
kg
cm
6
95
to
13
03
in
lb
of
rotating
torque
2
3
to
4
3
kg
5
1
to
9
5
1b
at
companion
flange
bolt
hole
If
preload
does
not
accord
with
this
specification
adjust
it
with
side
bearing
shims
II
Check
and
adjust
the
tooth
contact
pattern
of
ring
gear
and
drive
pinion
I
Thoroughly
clean
ring
and
drive
pinion
gear
teeth
2
Paint
ring
gear
teeth
lightly
and
evenly
with
a
mixture
of
powdered
red
lead
and
oil
of
a
suitable
consistency
to
produce
a
contact
pattern
3
Rorate
pinion
through
several
revolutions
in
the
forward
and
reverse
direction
until
a
definite
contact
pattern
is
developed
on
ring
gear
4
When
contact
pattern
is
incorrect
readjust
thickness
of
adjust
shim
Be
sure
to
wipe
out
red
lead
completely
upon
completion
of
adjustment
5
Incorrect
contact
pattern
of
teeth
can
be
adjusted
in
the
following
manner
a
Heel
contact
To
correct
increase
thickness
of
drive
pinion
adjusting
washer
in
order
to
bring
drive
pinion
close
to
ring
gear
PD
14
Page 83 of 513
CHASSIS
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
When
a
gear
carrier
is
suspected
of
being
noisy
it
is
advisable
to
make
a
thorough
test
to
determine
whether
the
noise
originates
in
the
tires
road
surface
exhaust
universal
joint
propeller
shaft
wheel
bearing
trans
Condition
Noise
on
drive
coast
and
float
Noise
on
turn
Knocking
sound
during
starting
or
gear
shifting
Seizure
or
breakage
mission
or
gear
carrier
Noise
which
originates
in
other
places
cannot
be
corrected
by
adjustment
or
replacement
of
parts
in
the
rear
axle
assembly
Probable
cause
Shortage
of
oil
Incorrect
tooth
contact
between
ring
gear
and
drive
pinion
Incorrect
backlash
between
ring
gear
and
drive
pinion
Seized
up
or
damaged
ring
gear
and
drive
pinion
Seized
up
damaged
or
broken
drive
pinion
bearing
Seized
up
damaged
or
broken
side
bearing
Loosen
clamp
bolts
or
nuts
holding
ring
gear
bearing
cap
etc
Seized
up
damaged
or
broken
side
and
pinion
gear
I
Seized
up
damaged
or
broken
side
gear
and
pinion
thrust
washer
Pinion
gears
too
tight
on
their
shaft
Excessive
backlash
Incorrect
backlash
between
ring
gear
and
drive
pinion
or
side
and
pinion
gear
Worn
gears
or
case
Worn
rear
axle
shaft
and
side
gear
spline
Pinion
bearing
under
preload
Loosened
drive
pinion
nut
Loosen
clamp
bolts
or
nuts
holding
ring
gear
bearing
cap
etc
Shortage
of
oil
or
use
of
unsuitable
oil
Excessively
small
backlash
PD
16
Corrective
action
Supply
gear
oil
Rebuild
gear
carrier
if
necessary
Adjust
tooth
contact
or
replace
the
hypoid
gear
set
Adjust
backlash
or
replace
the
hypoid
gear
set
if
necessary
Replace
the
hypoid
gear
set
Replace
the
pinion
bearing
and
defective
parts
Replace
the
side
bearing
and
defective
parts
Clamp
them
to
specified
torque
and
replace
defective
parts
Replace
defective
parts
Replace
defective
parts
Replace
defective
parts
Adjust
backlash
Replace
worn
parts
Replace
worn
parts
Adjust
preload
Repair
or
replace
Clamp
them
or
replace
if
necessary
Replace
defective
parts
Adjust
backlash
and
replace
as
required
Page 84 of 513
PROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
Incorrect
adjustment
of
bearings
or
gears
Severe
service
due
to
an
excessive
loading
improper
use
of
clutch
Loosened
bolts
and
nuts
such
as
ring
gear
clamp
bolts
Oil
leakage
Worn
out
damaged
or
improperly
driven
front
oil
seal
or
bruised
dented
or
abnormally
worn
slide
face
of
companion
flange
Loosened
bolts
holding
gear
carrier
Defective
gasket
Loosen
filler
or
drain
plug
Clogged
or
damaged
breather
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
Type
of
differential
gear
carrier
assembly
Final
gear
type
Final
gear
ratio
number
of
teeth
Sedan
Coupe
Van
Drive
pinion
Preload
with
oil
seal
Preload
without
oil
seal
Thickness
of
drive
pinion
adjusting
shims
kg
cm
in
lb
kg
cm
in
lb
mm
in
Pinion
bearing
adjusting
spacer
Ring
gear
Backlash
between
ring
gear
and
pinion
Run
out
of
rear
side
of
ring
gear
mm
in
mm
in
Side
gear
and
pinion
mate
Thickness
of
side
gear
thrust
washers
mm
in
PD
17
Replace
defective
parts
Replace
defective
parts
Replace
defective
parts
Replace
the
defective
oil
seal
Ammend
the
affected
flange
with
sand
paper
or
replace
if
necessary
Tighten
the
bolts
to
specified
torque
Replace
defective
parts
with
new
ones
Tighten
the
plug
Repair
or
replace
H145A
Hypoid
3
900
39
10
7
to
9
6
1
to
7
8
6
to
8
5
2
to
6
9
From
2
74
to
3
25
0
1079
to
0
1280
Spacing
0
Q3
0
0012
Non
adjustable
collapsible
spacer
0
10
to
0
15
0
0039
to
0
0059
Less
than
0
05
0
0020
0
76
to
0
91
0
0299
to
0
0358
Page 85 of 513
Clearance
between
side
gear
and
thrust
washer
CHASSIS
rrun
in
0
10
to
0
20
0
004
to
0
008
Side
bearing
Standard
width
rom
in
Thickness
of
side
bearing
adjusting
shims
rom
in
Tightening
torque
Drive
pinion
nut
Ring
gear
bolts
Side
bearing
cap
bolts
Differential
carrier
to
axle
housing
fIx
nuts
Companion
flange
to
propeller
shaft
fIx
nuts
Oil
filler
plug
17
5
0
689
0
05
0
07
0
10
0
20
0
50
0
0020
0
0028
0
0039
0
0078
0
0197
kg
m
ft
lb
kg
m
ft
lb
kg
m
ft
lb
12
to
17
86
8
to
123
6
to
7
43
4
to
50
6
5
to
6
36
2
to
43
4
kg
m
ft
1b
17
to
2
5
12
3
to
18
1
kg
m
ft
lb
kg
m
ft
lb
2
0
to
2
7
14
5
to
19
5
6
to
10
43
4
to
72
3
SERVICE
JOURNAL
OR
BULLETIN
REFERENCE
DATE
JOURNAL
or
BULLETIN
No
I
I
I
I
PAGE
No
SUBJECT
PO
1S
Page 91 of 513
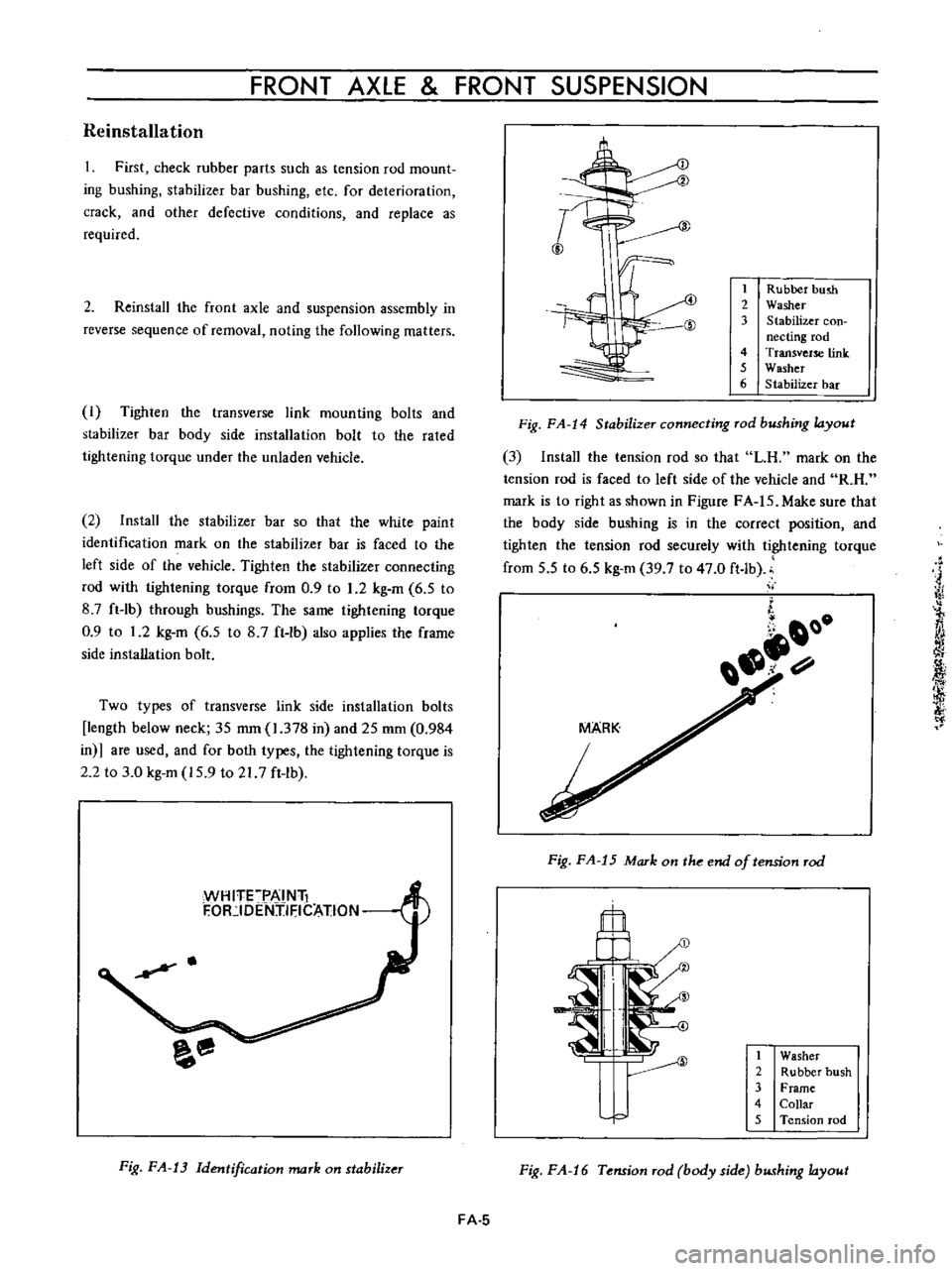
FRONT
AXLE
FRONT
SUSPENSION
Reinstalla
tion
First
check
rubber
parts
such
as
tension
rod
mount
ing
bushing
stabilizer
bar
bushing
etc
for
deterioration
crack
and
other
defective
conditions
and
replace
as
required
2
Reinstall
the
front
axle
and
suspension
assembly
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
noting
the
following
matters
1
Tighten
the
transverse
link
mounting
bolts
and
stabilizer
bar
body
side
installation
bolt
to
the
raled
tightening
torque
under
the
unladen
vehicle
2
Install
the
stabilizer
bar
so
that
the
white
paint
identification
mark
on
the
stabilizer
bar
is
faced
to
the
left
side
of
the
vehicle
Tighten
the
stabilizer
connecting
rod
with
tightening
torque
from
0
9
to
1
2
kg
m
6
5
to
8
7
ft
lb
through
bushings
The
same
tightening
torque
0
9
to
1
2
kg
m
6
5
to
8
7
ft
Ib
also
applies
the
frame
side
installation
bolt
Two
types
of
transverse
link
side
installation
bolts
length
below
neck
35
mm
1
378
in
and
25
mm
0
984
in
are
used
and
for
both
types
the
tightening
torque
is
2
2
to
3
0
kg
m
15
9
to
217
ft
lb
WH
ITFPAI
Nli
F
OR
IDENjIFICATION
H
Fig
FA
13
Identification
mark
on
stabilizer
I
J
1
Rubber
hush
2
Washer
3
Stabilizer
con
necting
rod
4
Transverse
link
5
Washer
6
Stabilizer
bar
Fig
FA
14
Stabilizer
connecting
rod
bushing
layout
3
Install
the
tension
rod
so
that
LH
mark
on
the
tension
rod
is
faced
to
left
side
of
the
vehicle
and
R
H
mark
is
to
right
as
shown
in
Figure
FA
IS
Make
sure
that
the
body
side
bushing
is
in
the
correct
position
and
tighten
the
tension
rod
securely
with
tightening
torque
from
5
5
to
6
5
kg
m
39
7
to
47
0
ft
lb
ii
j
iY
l
fj
i
f
i
Of
1
0
Fig
FA
15
Mark
on
the
end
of
tension
rod
il
1
Washer
2
Rubber
bush
3
Frame
4
Collar
5
Tension
rod
Fig
FA
16
Tension
rod
body
side
bushing
layout
FA
5
Page 92 of 513
CHASSIS
Tightening
torque
of
front
suspension
cross
member
and
body
is
3
2
to
4
0
kg
m
23
1
to
28
9
ft
Ib
5
Tightening
torque
of
bolt
used
to
secure
the
upper
portion
of
the
strut
assembly
on
the
body
is
1
6
to
2
1
kg
m
11
6
to
15
2ft
lb
FRONT
AXLE
Removal
I
Jack
up
the
vehicle
remove
the
wheel
and
discon
nect
the
brake
hose
at
the
strut
outer
casing
bracket
unit
For
details
see
Removal
of
front
axle
and
suspension
assembly
2
Remove
the
brake
caliper
installation
bolts
and
remove
the
caliper
assembly
Disc
type
brake
3
Remove
the
brake
druOL
Drum
type
brake
4
Remove
the
hub
cap
with
a
flal
headed
screwdriver
or
other
proper
tool
and
hammer
Be
sure
to
tap
lightly
5
Remove
cotter
pin
from
the
wheel
bearing
lock
nut
and
remove
the
lock
nut
6
With
the
wheel
bearing
washer
and
wheel
bearing
installed
on
the
wheel
hub
remove
the
wheel
hub
from
the
spindle
In
the
case
of
a
disc
type
brake
the
wheel
hub
may
be
removed
with
the
disc
rotor
installed
on
the
wheel
hub
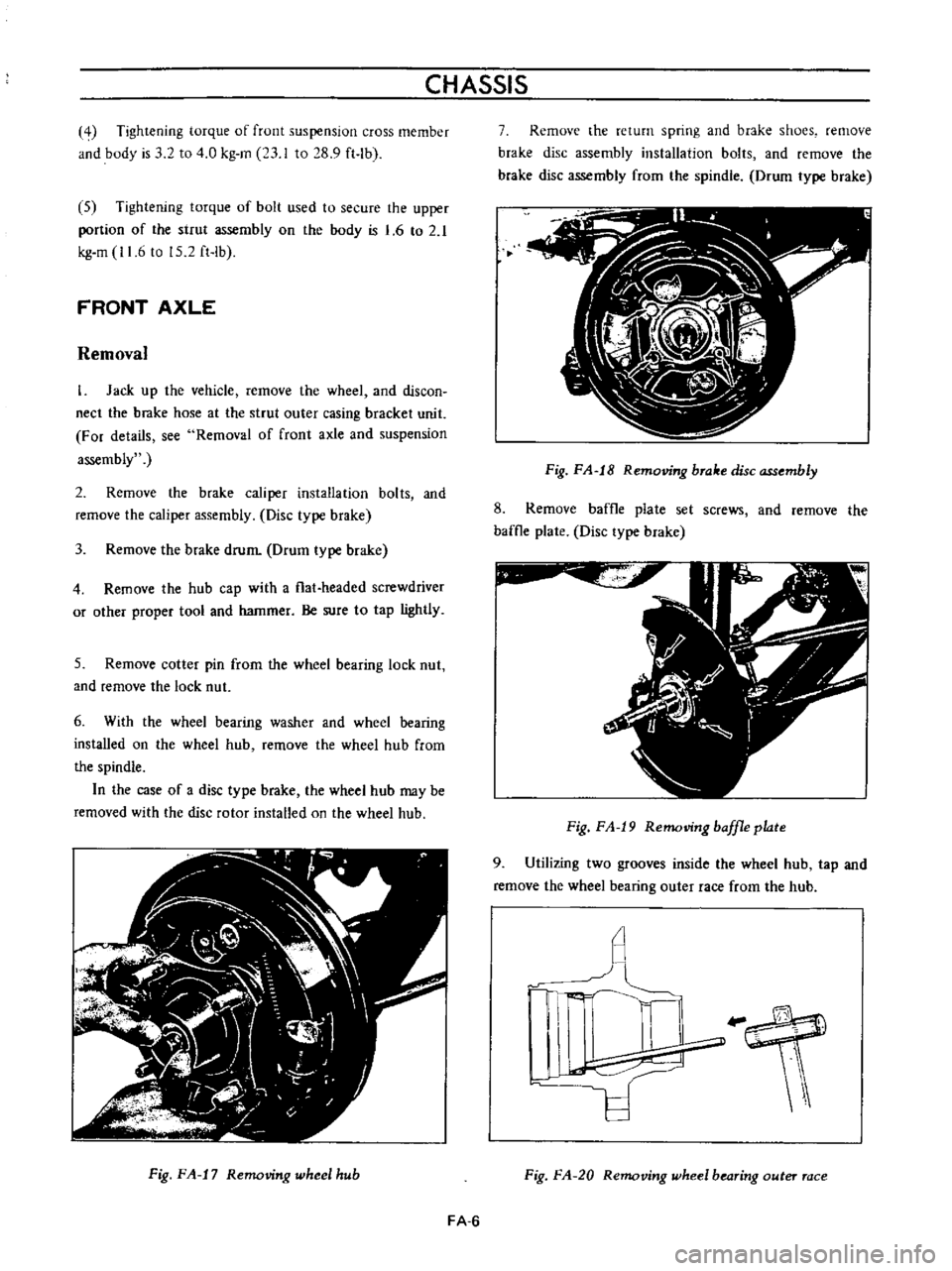
Fig
FA
17
Removing
wheel
hub
7
Remove
the
return
spring
and
brake
shoes
remove
brake
disc
assembly
installation
bolts
and
remove
the
brake
disc
assembly
from
the
spindle
Drum
type
brake
Fig
FA
IS
Removing
brake
disc
a
ssembly
8
Remove
baffle
plate
set
screws
and
remove
the
baffle
plate
Disc
type
brake
Fig
FA
19
Removingbaffleplate
9
Utilizing
two
grooves
inside
the
wheel
hub
tap
and
remove
the
wheel
bearing
outer
race
from
the
hub
Fig
FA
20
Removing
wheel
bearing
outer
race
FA
6
Page 96 of 513
CHASSIS
Reinstallation
Reinstall
the
wheel
bearing
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
2
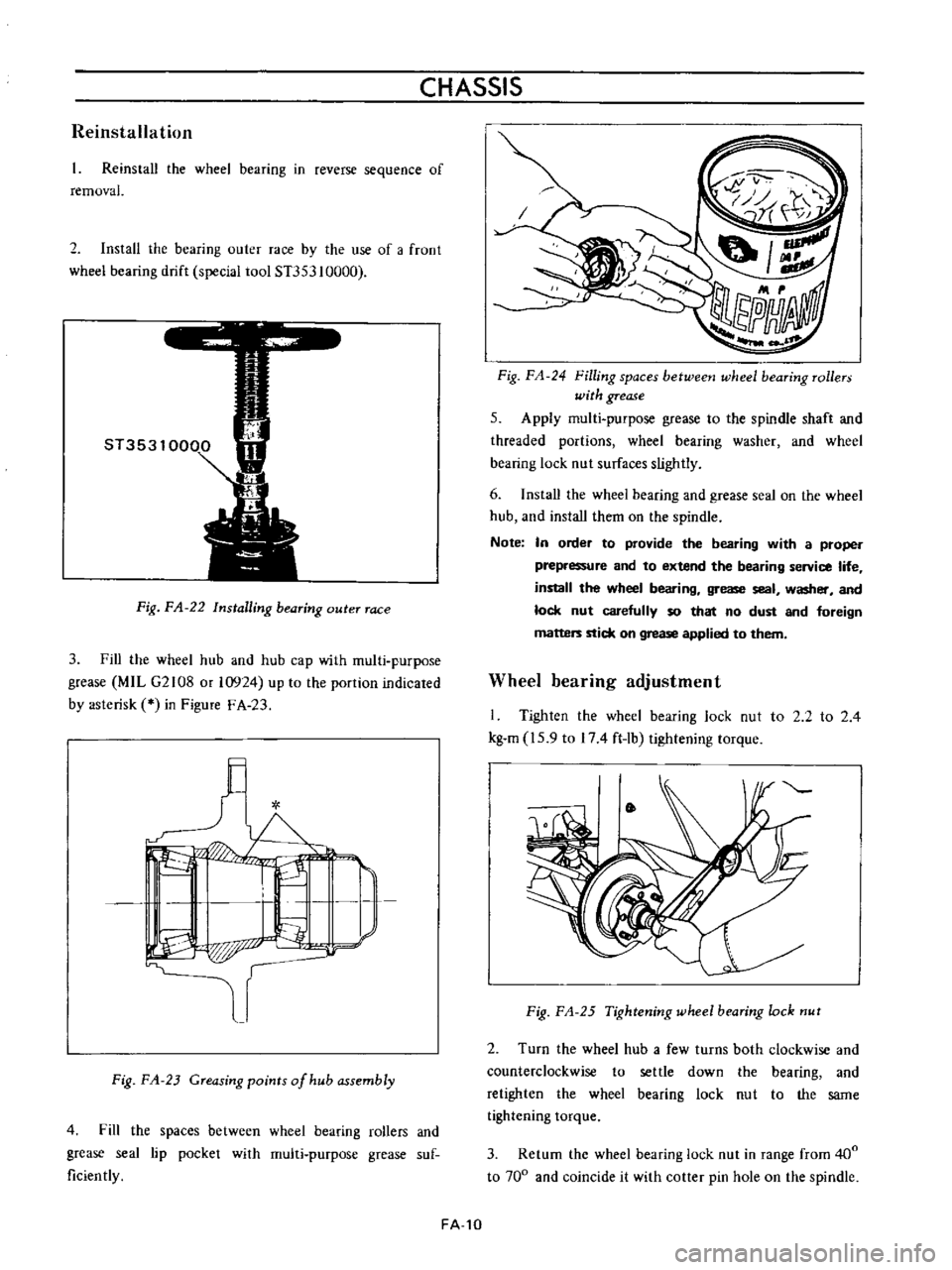
Install
the
bearing
outer
race
by
the
use
of
a
froot
wheel
bearing
drift
special
tool
ST353
10000
Fig
FA
22
Installing
bearing
outer
race
3
Fill
the
wheel
hub
and
hub
cap
with
multi
purpose
grease
MIL
G2108
or
10924
up
to
the
portion
indicated
by
asterisk
in
Figure
F
A
23
l
I
L
I
I
P
p
r
Fig
FA
23
Greasing
points
of
hub
assembly
4
Fill
the
spaces
between
wheel
bearing
rollers
and
grease
seal
lip
pocket
with
multi
purpose
grease
suf
ficiently
FA
10
Fig
FA
24
Filling
spaces
betweetJ
wheel
bearing
rollers
with
grease
5
Apply
multi
purpose
grease
to
the
spindle
shaft
and
threaded
portions
wheel
bearing
washer
and
wheel
bearing
lock
nut
surfaces
slightly
6
Install
the
wheei
bearing
and
grease
seal
on
the
wheel
hub
and
install
them
on
the
spindle
Note
In
order
to
provide
the
bearing
with
a
proper
prepressure
and
to
extend
the
bearing
service
life
install
the
wheel
bearing
grease
seal
washer
and
lock
nut
carefully
so
that
no
dust
and
foreign
matters
stick
on
grease
applied
to
them
Wheel
bearing
adjustment
I
Tighten
the
wheel
bearing
lock
nut
to
2
2
to
2
4
kg
m
15
9
to
174
ft
lb
tightening
torque
Fig
FA
25
Tightening
wheel
bearing
lock
nut
2
Turn
the
wheel
hub
a
few
turns
both
clockwise
and
counterclockwise
to
settle
down
the
bearing
and
retighten
the
wheel
bearing
lock
nut
to
the
same
tightening
torque
3
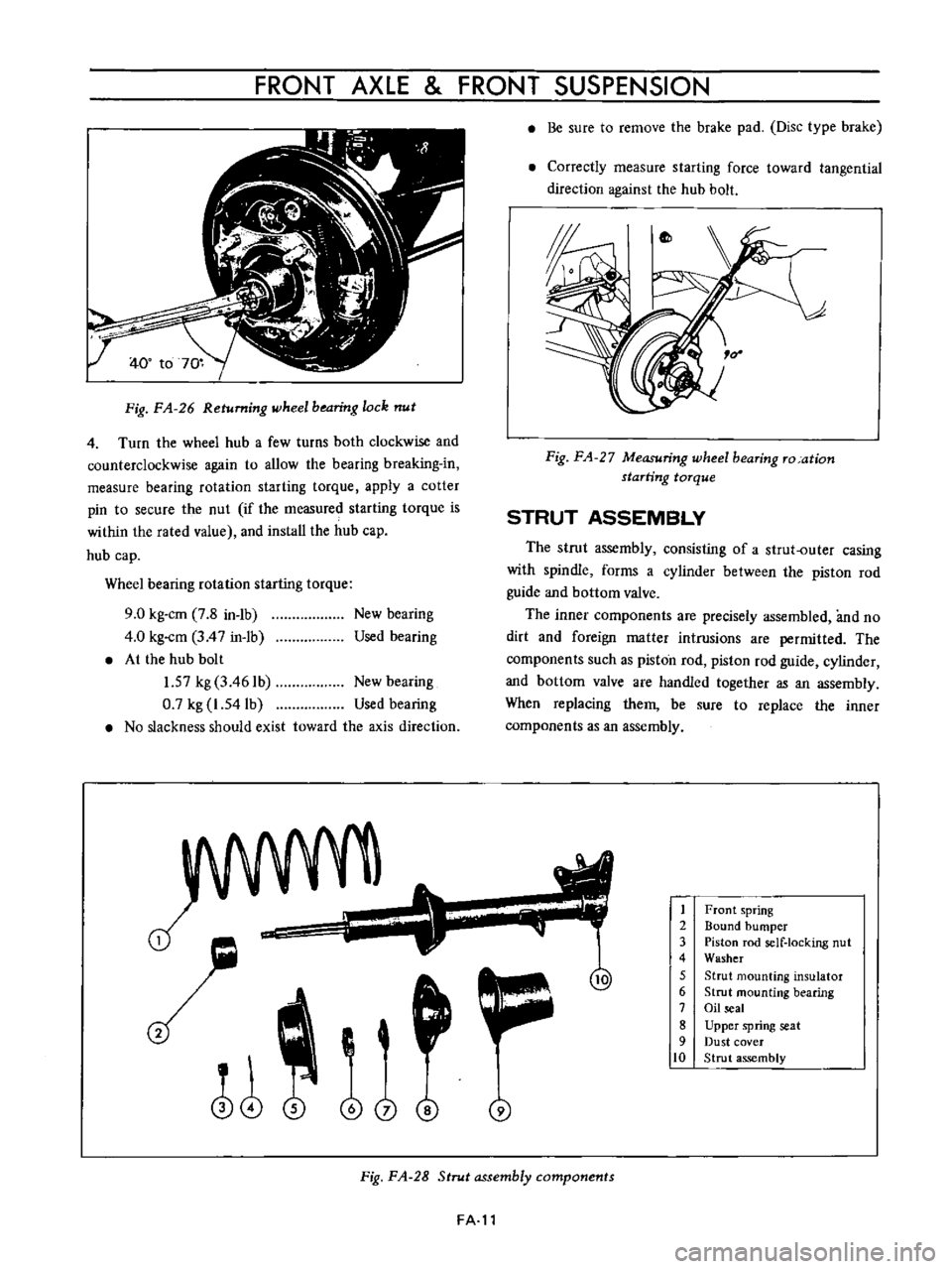
Return
the
wheel
bearing
lock
nut
in
range
from
400
to
700
and
coincide
it
with
cotter
pin
hole
on
the
spindle
Page 97 of 513
FRONT
AXLE
FRONT
SUSPENSION
t
t
Fig
FA
26
Returning
wheel
bearing
lock
nut
4
Turn
the
wheel
hub
a
few
turns
both
clockwise
and
counterclockwise
again
to
allow
the
bearing
breaking
in
measure
bearing
rotation
starting
torque
apply
a
cotter
pin
to
secure
the
nut
if
the
measured
starting
torque
is
within
the
rated
value
and
install
the
hub
cap
hub
cap
Wheel
bearing
rotation
starting
torque
9
0
kg
cm
7
8
in
1b
4
0
kg
cm
3
4
7
in
1b
At
the
hub
bolt
1
57
kg
3
461b
New
bearing
0
7
kg
1
54lb
Used
bearing
No
slackness
should
exist
toward
the
axis
direction
New
bearing
Used
bearing
J
o
i
@
j
Be
sure
to
remove
the
brake
pad
Disc
type
brake
Correctly
measure
starting
force
toward
tangential
direction
against
the
hub
bolt
Fig
FA
27
Measuring
wheel
bearing
ro
ation
starting
torque
STRUT
ASSEMBLY
The
strut
assembly
consisting
of
a
strut
outer
casing
with
spindle
forms
a
cylinder
between
the
piston
rod
guide
and
bottom
valve
The
inner
components
are
precisely
assembled
and
no
dirt
and
foreign
matter
intrusions
are
permitted
The
components
such
as
piston
rod
piston
rod
guide
cylinder
and
bottom
valve
are
handled
together
as
an
assembly
When
replacing
them
be
sure
to
replace
the
inner
components
as
an
assembly
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Front
spring
Bound
bumper
Piston
rod
self
locking
nut
Washer
Strut
mounting
insulator
Strut
mounting
bearing
Oil
seal
Upper
spring
seat
Dust
cover
Strut
assembly
Fig
FA
28
Strut
assembly
components
FA
l1
Page 102 of 513
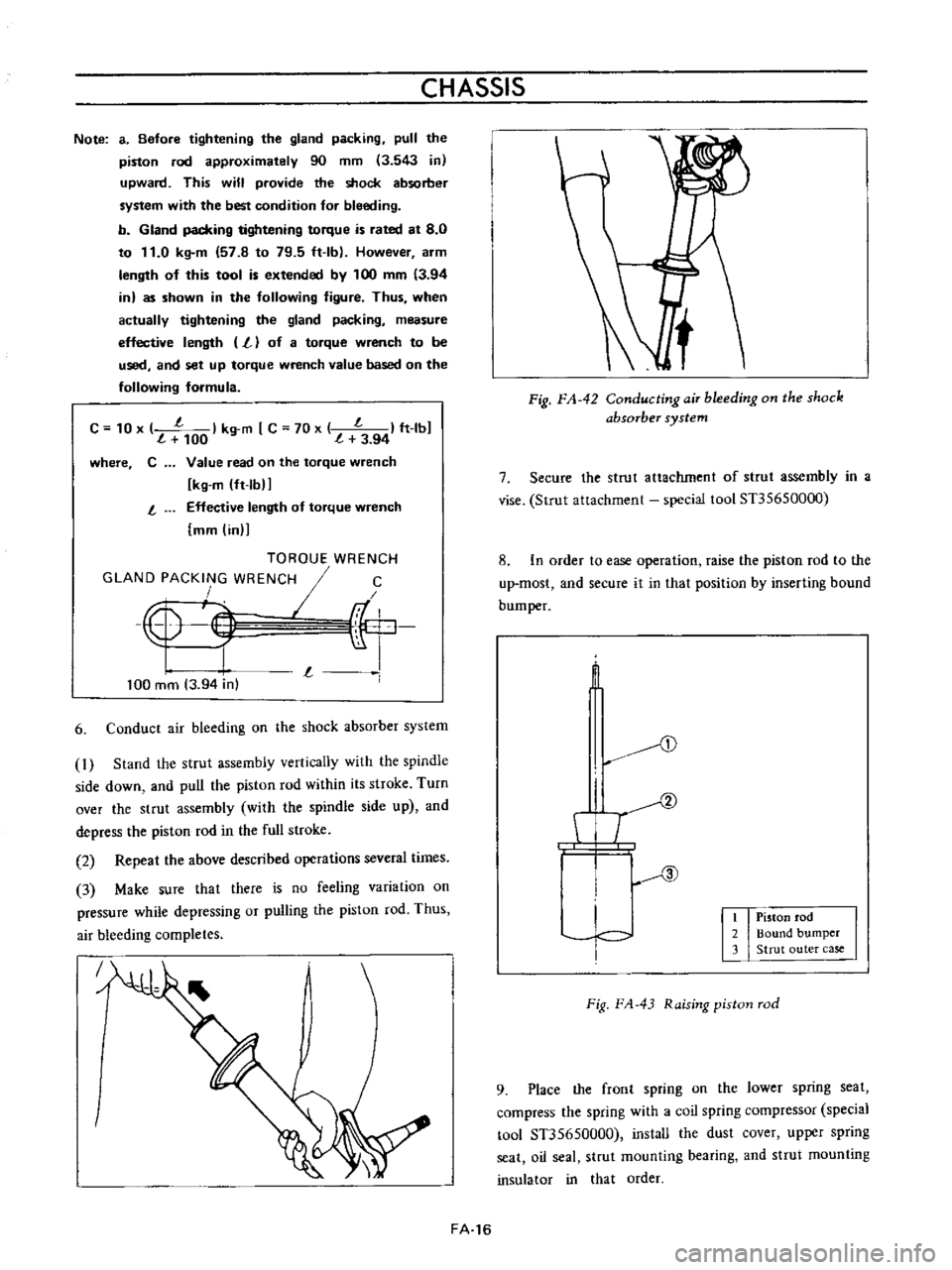
CHASSIS
Note
a
Before
tightening
the
gland
packing
pull
the
piston
rod
approximately
90
mm
3
543
in
upward
This
will
provide
the
shock
absorber
system
with
the
best
condition
for
bleeding
b
Gland
packing
tightening
torque
is
rated
at
8
0
to
11
0
kg
m
57
8
to
79
5
ft
Ib
However
arm
length
of
this
tool
is
extended
by
100
mm
3
94
in
as
shown
in
the
following
figure
Thus
when
actually
tightening
the
gland
packing
measure
effective
length
L
of
a
torque
wrench
to
be
used
and
set
up
torque
wrench
value
based
on
the
following
formula
C
10
x
l
I
kg
m
C
70
x
l
I
ft
lbJ
100
l
3
94
where
C
Value
read
on
the
torque
wrench
kg
m
ft
lbIJ
Effective
length
of
torque
wrench
mm
in
l
TOROUE
WRENCH
GLAND
PACKING
WRENCH
I
C
4
F
r
I
L
I
100
mm
3
94
in
6
Conduct
air
bleeding
on
the
shock
absorber
system
1
Stand
the
strut
assembly
vertically
with
the
spindle
side
down
and
pull
the
piston
rod
within
its
stroke
Turn
over
the
strut
assembly
with
the
spindle
side
up
and
depress
the
piston
rod
in
the
full
stroke
2
Repeat
the
above
described
operations
several
times
3
Make
sure
that
there
is
no
feeling
variation
on
pressure
while
depressing
or
pulling
the
piston
rod
Thus
air
bleeding
completes
J
FA
16
Fig
FA
42
ConductingaiT
bleeding
on
the
shock
absorber
system
7
Secure
the
strut
attachment
of
strut
assembly
in
a
vise
Strut
attachment
special
tool
Sn5650000
8
In
order
to
ease
operation
raise
the
piston
rod
to
the
up
most
and
secure
it
in
that
position
by
inserting
bound
bum
per
t
D
I
T
I
c
I
Piston
rod
2
Bound
bumper
3
Strut
outer
case
Fig
FA
43
Raising
piston
rod
9
Place
the
front
spring
on
the
lower
spring
seat
compress
the
spring
with
a
coil
spring
compressor
special
tool
Sn5650000
install
the
dust
cover
upper
spring
seat
oil
seal
strut
mounting
bearing
and
strut
mounting
insulator
in
that
order