engine oil DATSUN PICK-UP 1977 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1977, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: DATSUN PICK-UP 1977Pages: 537, PDF Size: 35.48 MB
Page 238 of 537
REMOVAL
In
dismounting
transmission
from
the
vehicle
proceed
as
follows
I
Disconnect
battery
ground
cable
from
terminal
2
Place
transmission
control
lever
in
neutIal
position
3
Remove
E
ring
and
control
lever
pin
from
transmission
striking
rod
guide
and
remove
control
lever
See
Figure
MT
4
TM335
Fig
MT
4
Remouing
controllelJ
r
4
Jack
up
the
vehicle
and
support
its
weight
on
safety
stands
Use
a
hydraulic
hoist
or
open
pit
if
avail
able
Confirm
that
safety
is
insured
5
Disconnect
exhaust
front
tube
6
Disconnect
wires
from
reverse
lamp
switch
See
Figure
MT
5
7
Disconnect
speedometer
cable
from
rear
extension
housing
See
Figure
MT
5
8
Remove
clutch
operating
cylinder
from
transmission
case
See
Figure
MT5
O
m
J
@
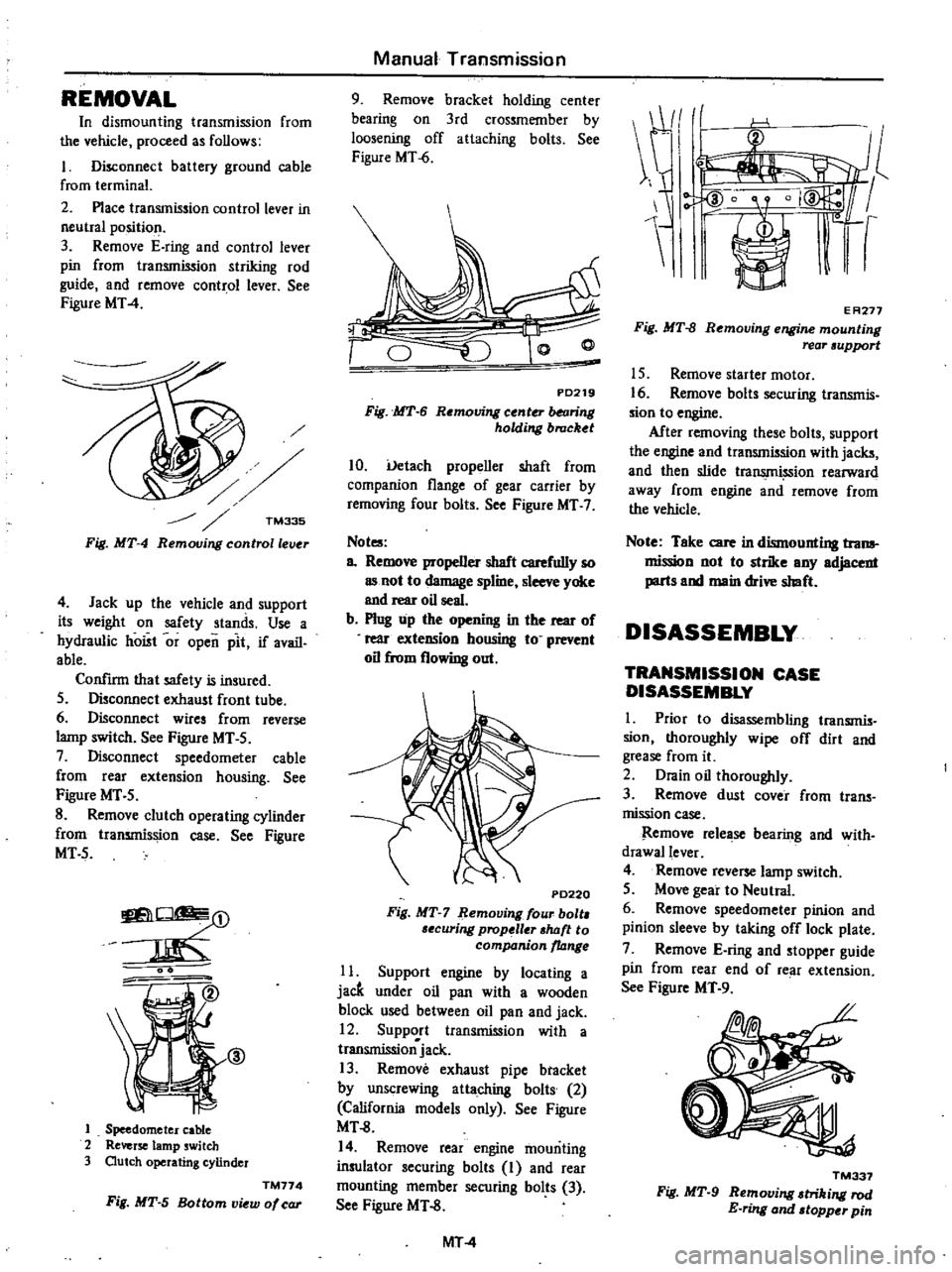
1
Speedometer
cable
2
Reverse
lamp
switch
3
Outch
operating
cylinder
TM774
Fig
MT
5
Bottom
view
of
car
Manual
Transmission
9
Remove
bracket
holding
center
bearing
on
3rd
crossmember
by
loosening
off
attaching
bolts
See
Figure
MT
6
PD219
Fig
MT
6
Removing
center
balring
holding
brucket
10
Uetach
propeller
shaft
from
companion
flange
of
gear
carrier
by
removing
four
bolts
See
Figure
MT
7
Not
a
Remove
propeller
shaft
carefully
so
as
not
to
damage
spline
sleeve
yoke
and
rear
oil
seal
b
Plug
up
the
opening
in
the
rear
of
rear
exteDSion
housing
to
prevent
oil
from
flowing
out
P0220
Fig
MT
7
Remouing
four
bolt
6ecuring
prop
ller
shtJft
to
companion
ltJnge
11
Support
engine
by
locating
a
jacft
under
oil
pan
with
a
wooden
block
used
between
oil
pan
and
jack
12
Support
transmission
with
a
transmissionjack
13
Remove
exhaust
pipe
btacket
by
unscrewing
attaching
bolts
2
California
models
only
See
Figure
MT
8
14
Remove
rear
engine
mounting
insulator
securing
bolts
I
and
rear
mounting
member
securing
bolts
3
See
Figure
MT
8
MT
4
E
A277
Fig
MT
8
Removing
engine
mounting
rear
support
15
Remove
starter
motor
16
Remove
bolt
securing
transmis
sion
to
engine
After
removing
these
bolts
support
the
engine
and
transmission
with
jacks
and
then
slide
tra
ion
rearward
away
from
engine
and
remove
from
the
vehicle
Note
Take
care
in
dismounting
trona
mission
not
to
strike
any
adjacent
parts
and
main
drive
shaft
DISASSEMBLY
TRANSMISSION
CASE
DISASSEMBLY
I
Prior
to
disassembling
transmis
sion
thoroughly
wipe
off
dirt
and
grease
from
it
2
Drain
oil
thoroughly
3
Remove
dust
cover
from
trans
mission
case
Remove
release
bearing
and
with
drawallever
4
Remove
reverse
lamp
switch
5
Move
gear
to
Neutral
6
Remove
speedometer
pinion
and
pinion
sleeve
by
taking
off
lock
plate
7
Remove
E
ring
and
stopper
guide
pin
from
rear
end
of
re
ll
extension
See
Figure
MT
9
TM337
Fig
MT
9
Removing
triking
rod
E
ring
and
topper
pin
Page 242 of 537
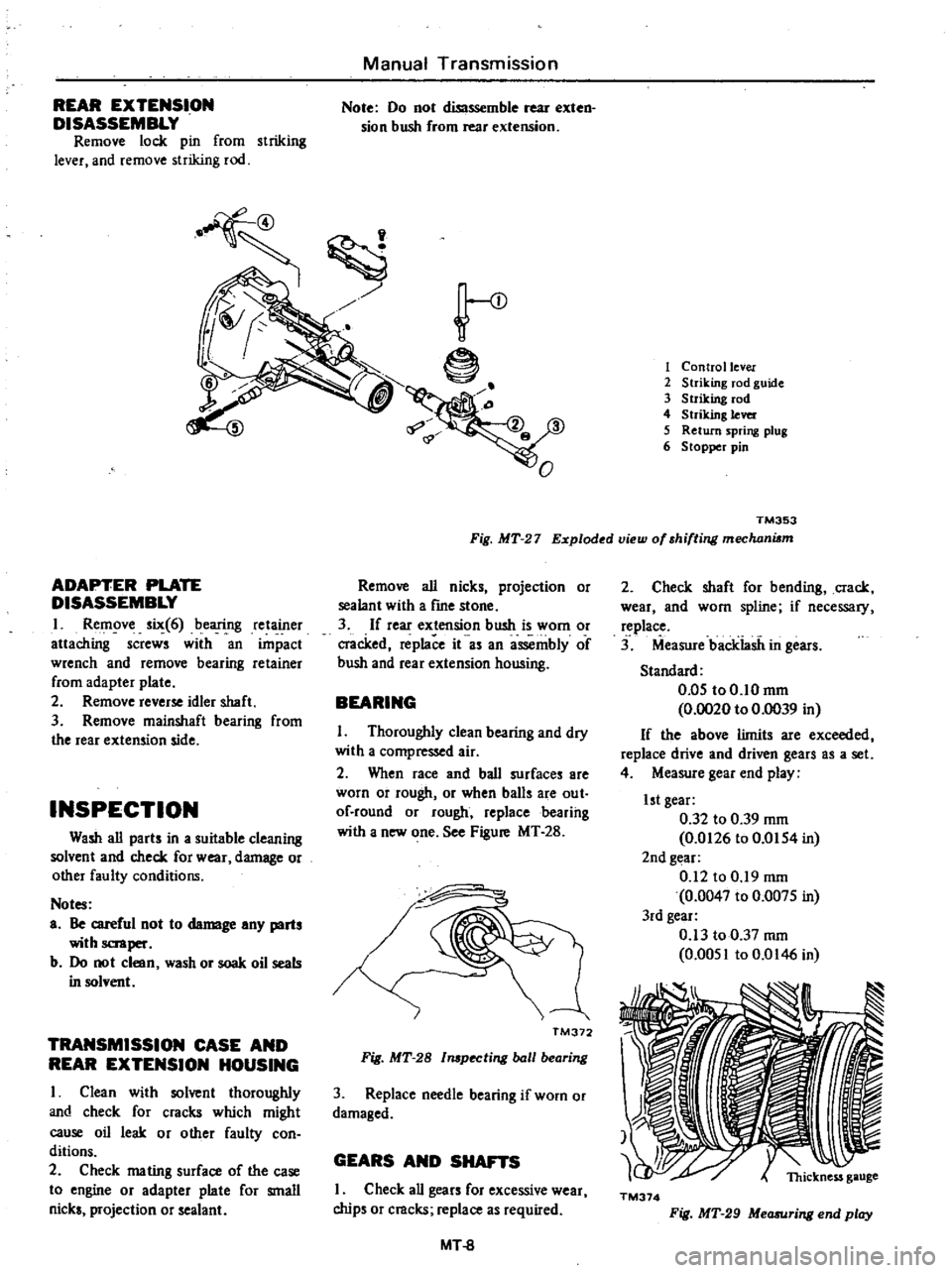
REAR
EXTENSION
DISASSEMBLY
Remove
lock
pin
from
striking
lever
and
remove
striking
rod
Manual
Transmission
Note
00
not
diSlssemble
rear
exten
sion
bush
from
rear
extension
ADAPTER
PLATE
DISASSEMBLY
I
Remove
six
6
bearing
retainer
attaching
screws
with
an
impact
wrench
and
remove
bearing
retainer
from
adapter
plate
2
Remove
reverse
idler
shaft
3
Remove
mainshaft
bearing
from
the
rear
extension
side
INSPECTION
Wash
all
parts
in
a
suitable
cleaning
solvent
and
check
for
wear
damage
or
other
faulty
conditions
Notes
a
Be
careful
not
to
damage
any
parts
with
scraper
b
00
not
clean
wash
or
soak
oil
seals
in
solvent
TRANSMISSION
CASE
AND
REAR
EXTENSION
HOUSING
I
Clean
with
solvent
thoroughly
and
check
for
cracks
which
might
cause
oil
leak
or
other
faulty
con
ditions
2
Check
mating
surface
of
the
case
to
engine
or
adapter
plate
for
small
nicks
projection
or
sealant
e
1
Control
lever
2
Striking
rod
guide
3
Striking
rod
4
Striking
lever
5
Return
spring
plug
6
Stopper
pin
TM353
Fig
MT
27
Exploded
view
of
shifting
mechani6m
Remove
all
nicks
projection
or
sealant
with
a
frne
stone
3
If
rear
extension
bush
is
worn
or
cracked
replace
it
as
an
assembly
of
bush
and
rear
extension
housing
BEARING
I
Thoroughly
clean
bearing
and
dry
with
a
compressed
air
2
When
race
and
ball
surfaces
are
worn
or
rough
or
when
balls
are
out
of
round
or
rough
replacebearihg
with
a
new
one
See
Figure
MT
28
I
TM372
Fig
MT
28
l
pecting
ball
bearing
3
Replace
needle
bearing
if
worn
or
damaged
GEARS
AND
SHAFTS
I
Check
all
gears
for
excessive
wear
chips
or
cracks
replace
as
required
MT
8
2
Check
shaft
for
bending
crack
wear
and
worn
spline
if
necessary
replace
3
Measure
backiasii
in
gears
Standard
0
05
to0
10mm
0
0020
to
0
0039
in
If
the
above
limits
are
exceeded
replace
drive
and
driven
gears
as
a
set
4
Measure
gear
end
play
1st
gear
0
32
to
0
39
mm
0
0126
to
0
0154
in
2nd
gear
0
12
to
0
19
mm
0
0047
to
0
0075
in
3rd
gear
0
13
to
0
37
mm
0
0051
to
0
0146
in
TM374
Fig
MT
29
Measuring
end
play
Page 248 of 537
5
Apply
a
light
coat
of
multi
purpose
grease
to
withdrawal
lever
release
bearing
and
bearing
sleeve
in
stall
them
on
clutch
housing
After
connecting
them
with
holder
spring
instaU
dust
cover
on
clutch
housing
6
Install
control
lever
temporarily
and
shift
control
lever
through
all
gears
to
make
sure
that
gears
opera
Ie
smoothly
Note
Install
drain
plug
and
filler
plug
ith
sealant
in
place
Manual
Transmission
INSTALLATION
Install
the
transmission
in
the
reo
verse
order
uf
removal
paying
atten
tion
to
the
following
points
1
Before
installing
dean
mating
surfaces
of
engine
rear
plate
and
trans
mission
case
2
Before
installing
lightly
apply
grease
to
spline
parts
of
clutch
disc
and
main
drive
gear
3
Tighten
bolts
securing
trans
mission
to
engine
to
specifications
See
Figure
MT
55
5
SPEED
TRANSMISSION
TYPE
DESCRIPTION
REMOVAL
DISASSEMBL
Y
TRANSMISSION
CASE
DISASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBL
Y
OF
GEAR
ASSEMBLY
REAR
EXTENSION
DISASSEMBLY
ADAPTER
PLATE
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
TRANSMISSION
CASE
AND
REAR
EXTENSION
HOUSING
DESCRIPTION
The
transmission
is
of
a
5
speed
forward
with
overdrive
4
OD
speed
fully
synchronized
constant
mesh
type
that
uses
helical
gears
The
5
speed
transmission
covered
in
this
section
is
similar
in
all
respects
to
the
4
speed
transmission
type
F4W71B
stated
previously
except
the
CONTENTS
MT14
MT17
MT17
MT17
MT17
MT18
MT19
MT19
4
4
to
5
9
kg
m
32
to
43
ft
Ib
1
0
9
to
1
2
kg
m
7
to
9
rt
lb
TM773
Fig
MT
55
Tightening
torque
4
Remove
filler
plug
and
fIll
trans
mission
with
recommended
gear
oil
to
the
level
of
the
plug
hole
Approxi
mately
I
7
liters
3
pt
3
pt
FS5W71B
BEARING
GEARS
AND
SHAFTS
BAULK
RING
OIL
SEAL
ASSEMBL
Y
FRONT
COVER
ASSEMBLY
REAR
EXTENSION
ASSEMBLY
GEAR
ASSEMBLY
TRANSMISSION
ASSEMBLY
INSTALLATION
MT19
overdrive
position
of
it
The
overdrive
gear
rides
on
the
mainshaft
freely
through
the
needle
roller
bearing
and
counter
overdrive
gear
is
fitted
to
the
countershaft
by
splines
The
overdrive
synchronizer
system
is
on
the
mainshaft
rear
side
MT14
MT19
MT19
MT19
MT19
MT19
MT19
MT19
MT19
MT
20
MT20
Placing
the
control
lever
in
over
drive
position
brings
the
reverse
OD
coupling
sleeve
reverse
gear
on
main
shaft
into
mesh
with
overdrive
clutch
gear
The
reverse
OD
synchronizer
hub
is
fItted
to
the
mainshaft
by
splines
so
the
overdrive
gear
on
main
shaft
turns
together
with
the
main
shaft
Page 256 of 537

Manual
iTransmission
TIGHTENING
TORQUE
Installa
tion
Engine
to
transmission
installation
bolt
Transmission
to
engine
rear
plate
bolt
Clutch
operating
cylinder
installation
bolt
Rear
mounting
insulator
to
transmission
installation
bolt
Crossmember
mounting
bolt
Propeller
shaft
to
diff
installation
bolt
Gear
assembly
Rear
extension
installation
bolt
Front
cover
installation
bolt
Bearing
retainer
to
adapter
plate
screw
Main
haft
nut
Check
ball
plug
Stri
lever
lock
pin
Reverse
select
return
plug
Speedometer
sleeve
locking
plate
nut
Reverse
lamp
switch
year
oil
Ier
pl
g
Ge
r
oil
drain
plug
Unit
kg
m
ft
lb
4
4
to
5
9
32
to
43
0
9
to
1
2
7
to
9
2
5
to
3
0
18
to
22
0
8
to
1
1
6
to
8
3
2
to
43
23
to
31
2
4
to
33
17
to
24
1
6
to
2
1
12
to
IS
1
6
to
2
1
12to
IS
1
9
to
2
S
14
to
18
14
0
to
17
0
101
to
123
1
9
to
2
S
14
to
18
0
9
to
1
2
7
to
9
0
9
1
2
7
to
9
0
4
to
O
S
3
to
4
2
0
to
3
0
14
to
22
2
S
to
3
5
18
t02S
2
S
toTS
l8
to
2S
or
SPECIFICATIONS
Gear
backlash
Maindrive
gear
to
counter
drive
gear
1st
gear
2nd
gear
3rd
gear
OD
gear
Gear
end
play
1st
gear
2nd
gear
3rd
gear
OD
gear
Counter
gear
Reverse
idler
gear
Clearance
between
baulk
ring
and
gear
All
gears
Counter
bearing
adjusting
shim
Unit
mm
in
0
05
to
0
10
0
0020
to
0
0039
0
05
to
0
20
0
0020
to
0
0079
O
OS
to
0
20
0
0020
to
0
0079
0
05
to
0
20
0
0020
to
0
0079
0
05
to
0
20
0
0020
to
0
0079
0
32
to
0
39
0
0126
to
0
0154
0
12
to
0
19
0
0047
to
0
0075
0
13
to
0
37
0
0051
to
0
0146
0
32
to
0
39
0
0126
to
0
0154
0
01
to
0
21
0
0004
to
0
0083
0
05
to
0
20
0
0020
to
0
0079
1
25
to
1
60
0
0492
to
0
0630
0
6
0
024
0
5
0
020
0
4
0
016
0
3
0
012
0
2
0
008
0
1
0
004
MT
22
Page 257 of 537
Manual
Transmission
I
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORREGTIONS
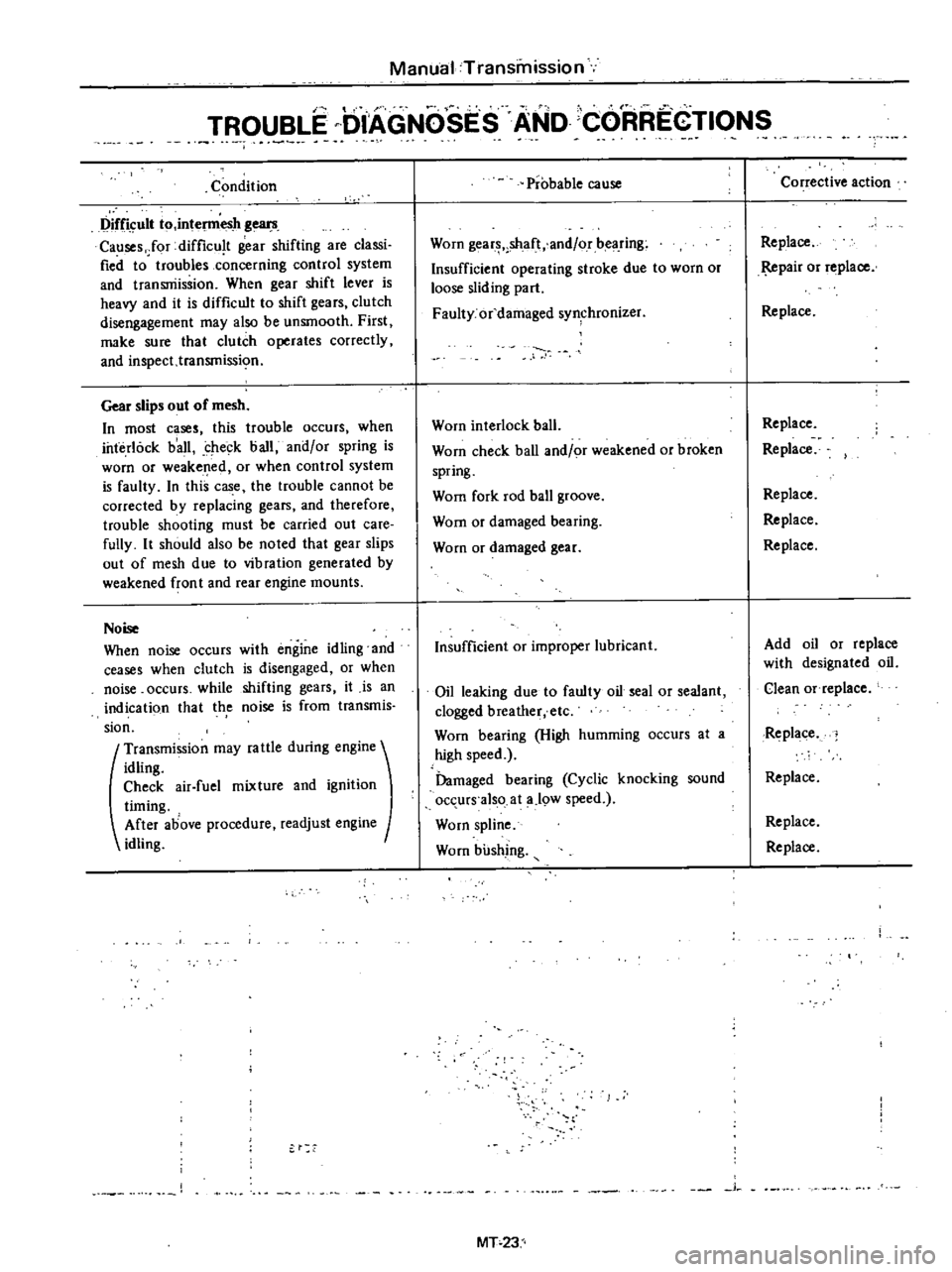
Condition
Difficult
to
intel11lesh
gears
Causes
Jor
difficu
t
gear
shifting
are
classi
fied
to
troubles
concerning
control
system
and
transniissioo
When
gear
shift
lever
is
heavy
and
it
is
difficult
to
shift
gears
clutch
disengagement
may
also
be
unsmooth
First
make
sure
that
clutch
operates
correctly
and
inspect
transmissi
o
Gear
slips
out
of
mesh
In
most
cases
this
trouble
occurs
when
interlock
b
all
check
ball
and
or
spring
is
worn
or
weakened
or
when
control
system
is
faulty
In
this
case
the
trouble
cannot
be
corrected
by
replacing
gears
and
therefore
trouble
shooting
must
be
carried
out
care
fully
It
should
also
be
noted
that
gear
slips
out
of
mesh
due
to
vibration
generated
by
weakened
fron
t
and
rear
engine
mounts
Noise
When
noise
occurs
with
engine
idling
and
ceases
when
clutch
is
disengaged
or
when
noise
occurs
while
shifting
gears
it
is
an
indicati90
that
th
e
noise
is
from
transmis
sion
t
Transmission
may
fa
ule
during
engine
idling
Check
air
fuel
mixture
and
ignition
timing
After
above
procedure
readjust
engine
idling
Probable
cause
Worn
gear
shaft
and
or
bearing
Insufficient
operating
stroke
due
to
worn
or
loose
sliding
part
Faulty
or
damaged
synchronizer
Worn
interlock
ball
Worn
check
ball
and
or
weakened
or
broken
spring
Wom
fork
rod
ball
groove
Wom
or
damaged
bearing
Worn
or
damaged
gear
Insufficient
or
improper
lubricant
Oil
leaking
due
to
faulty
oil
seal
or
sealant
clogged
breather
etc
Worn
bearing
High
humming
occurs
at
a
high
speed
Damaged
bearing
Cyclic
knocking
sound
occurs
also
at
a
19W
speed
Worn
spline
Worn
bushing
j
MT
23
Corrective
action
Replace
pair
or
replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Add
oil
or
replace
with
designated
oil
Clean
Of
replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Page 264 of 537

Automatic
Transmission
HYDRAULIC
CONTROL
SYSTEM
FUNCTIONS
OF
HYDRAULIC
CONTROL
UNIT
AND
VALVES
OIL
PUMP
MANUAL
LINKAGE
VACUUM
DIAPHRAGM
DOWNSHIFT
SOLENOID
GOVERNOR
VALVE
CONTROL
VALVE
ASSEMBLY
HYDRAULIC
SYSTEM
AND
MECHANICAL
OPERATION
FUNCTIONS
OF
HYDRAULIC
CONTROL
UNIT
AND
VALVES
The
hydraulic
control
system
con
CONTENTS
P
RANGE
PAR
K
R
RANGE
REVERSE
N
RANGE
NEUTRAL
D1
RANGE
LOW
GEAR
D2
RANGE
2ND
GEAR
D3
RANGE
TOP
GEAR
D
RANGE
KICK
DOWN
2
RANGE
2ND
GEAR
t
RANGE
LOW
GEAR
12
RANGE
2ND
GEAR
AT
4
AT
4
AT
4
AT
5
AT
5
AT
5
AT
6
AT13
tains
an
oil
pump
for
packing
p
oil
from
the
oil
pan
through
the
oil
strainer
A
shift
control
is
provided
by
two
centrifugally
operated
hydraulic
governors
on
the
output
shaft
vacuum
control
diaphragm
and
downshift
AT14
AT16
AT18
AT
20
AT
22
AT
24
AT
26
AT
28
AT
30
AT
32
solenoid
These
parts
work
in
conjunc
tion
with
valves
in
the
valve
body
assembly
located
in
the
base
of
the
transmission
The
valves
regulate
oil
pressure
and
direct
it
to
appropriate
transmission
components
Oil
pump
I
I
Control
valve
I
Torque
converter
1
I
I
I
Manual
linkage
Front
clutch
Vacuum
diaphragm
I
Rear
clutch
I
Low
and
reverse
brake
Downshift
solenoid
I
Band
brake
Governor
valve
r
I
Lubrication
OIL
PUMP
The
oil
pump
is
the
source
of
control
medium
i
e
oil
for
the
control
system
The
oil
pump
is
of
an
internal
involute
gear
type
The
drive
sleeve
is
a
part
of
the
torque
converter
pump
impeller
and
serves
to
drive
the
pump
inner
gear
with
the
drive
sleeve
direct
ly
coupled
with
the
engine
operation
The
oil
flows
through
the
following
route
Oil
pan
Oil
strainer
bottom
of
the
control
valve
Control
valve
lower
body
suction
port
Transmission
case
suction
port
Pump
housing
suction
port
Pump
gear
space
Pump
housing
delivery
port
Transmission
case
delivery
port
Lower
body
delivery
port
Control
valve
line
pressure
circuit
AT071
I
Housin
4
Inner
gear
2
Cover
5
Crescent
3
Ouler
gear
Fig
AT
3
Oil
pump
AT
4
MANUAL
LINKAGE
The
hand
lever
motion
the
hand
lever
is
localed
in
the
driver
s
compart
ment
mechanically
transmitted
from
lhe
remote
control
linkage
is
further
transmitted
to
the
inner
manual
lever
in
the
transmission
case
from
the
range
selector
lever
in
the
right
center
par
tion
of
the
transmission
case
through
the
manual
shaft
The
inner
manual
lever
is
thereby
turned
A
pin
installed
on
the
bottom
of
the
inner
manual
lever
slides
rhe
manu
al
valve
spool
of
the
conlrol
valve
thus
positioning
the
spool
opposite
rhe
appropriate
select
posilion
The
parking
rod
pin
is
held
in
rhe
groove
on
the
top
of
Ihe
inner
manual
Page 265 of 537
plate
The
parking
rod
pin
operates
the
rod
at
p
range
and
operates
the
mechanical
lock
system
The
above
described
manual
shaft
is
further
equipped
with
an
inhibitor
switch
A
rotor
inside
the
inhibitor
switch
rotates
in
response
to
each
range
When
tne
range
is
selected
at
p
or
N
the
rotor
closes
the
starter
magnet
circuit
so
that
the
engine
can
be
started
When
the
range
is
selected
at
R
the
rolor
closes
the
back
up
lamp
circuit
and
the
back
up
lamp
lights
CD
1
Manual
pia
te
2
Inhibitor
switch
ATOB7
Parking
rod
Manual
shaft
Fig
AT
4
Manual
linkage
VACUUM
DIAPHRAGM
The
vacuum
diaphragm
is
installed
on
the
left
center
portio
n
of
the
transmission
case
The
internal
con
struction
of
the
vacuum
diaphragm
is
as
follows
A
rubber
diaphragm
forms
a
parti
tion
in
the
center
The
engine
intake
manifold
negative
pressure
l
led
through
a
vacuum
tube
and
spring
force
is
applied
to
the
front
surfaceof
the
rubber
diaphragm
while
atmos
pheric
pressure
is
applied
to
the
back
surface
The
difference
between
pres
sure
applied
to
the
front
and
ba
K
I
surfaces
causes
a
vacuum
reactIOn
which
activates
the
throttle
valve
of
the
control
valve
inside
the
transrhis
sion
case
Wheri
accelerator
pedal
is
fully
de
pressed
and
the
buretor
is
fU
IIy
opened
but
th
engirie
sp
eed
is
not
suificientl
increased
the
manifold
negative
plre
sure
lowers
Le
tends
towards
atmospheric
pressure
and
the
Automatic
Transmission
vacuum
reaction
increases
since
the
flow
velocity
of
mixture
inside
the
intake
m
mifold
is
slow
Contrarily
when
the
engine
speed
increases
and
the
flow
velocity
of
the
mixture
in
creases
or
when
the
carburetor
is
closed
the
manifold
negative
pressure
increases
Le
tends
towards
vacuum
and
the
vacuum
reaction
is
reduced
Thus
a
signal
to
genera
Ie
hydraulic
pressure
P
rfe
tly
suited
to
the
engine
loading
at
trye
control
valve
is
trans
mitted
from
the
vacuum
diaphragm
and
the
most
suitable
timing
for
speed
change
and
lin
e
pressure
is
obtaine
so
that
the
most
proper
torque
capacity
is
obtained
against
the
transmitting
torque
To
inl
lkc
manifold
AT088
Fig
AT
5
Vacuum
diaphragm
DOWNSHIFT
SOLENOID
T
e
downshift
solenoid
is
of
a
magnetic
type
installed
on
the
left
re
r
portion
of
the
transmission
case
When
a
driver
requires
accelerating
power
and
dePresses
the
accelerator
pedal
down
to
the
stopper
a
kickdown
switch
19ca
ted
in
the
middle
of
the
accelerator
link
is
depressed
by
a
push
rod
he
kickdown
switch
doses
cur
rent
flows
to
the
solenoid
the
sole
noid
push
rod
is
depressed
the
down
shift
valve
of
the
control
valvc
insidc
the
transmi
ssion
case
is
depressed
nd
the
speed
is
changed
forcedly
fmm
3rd
to
2nd
within
a
cerlaill
vehi
cle
speed
limit
Note
Since
theki
kdown
switch
closes
when
the
accelerator
pedal
is
d
epr
ssed
from
7
i
t
I
S
I
6
of
tiie
whole
stroke
the
a
ccel
rator
ped
1
should
be
correctly
adjusted
so
as
arf
rd
a
omplete
stro
e
I
The
arrangement
of
the
swit
h
wries
ccording
m
eI
AT
S
c
C
r
11
I
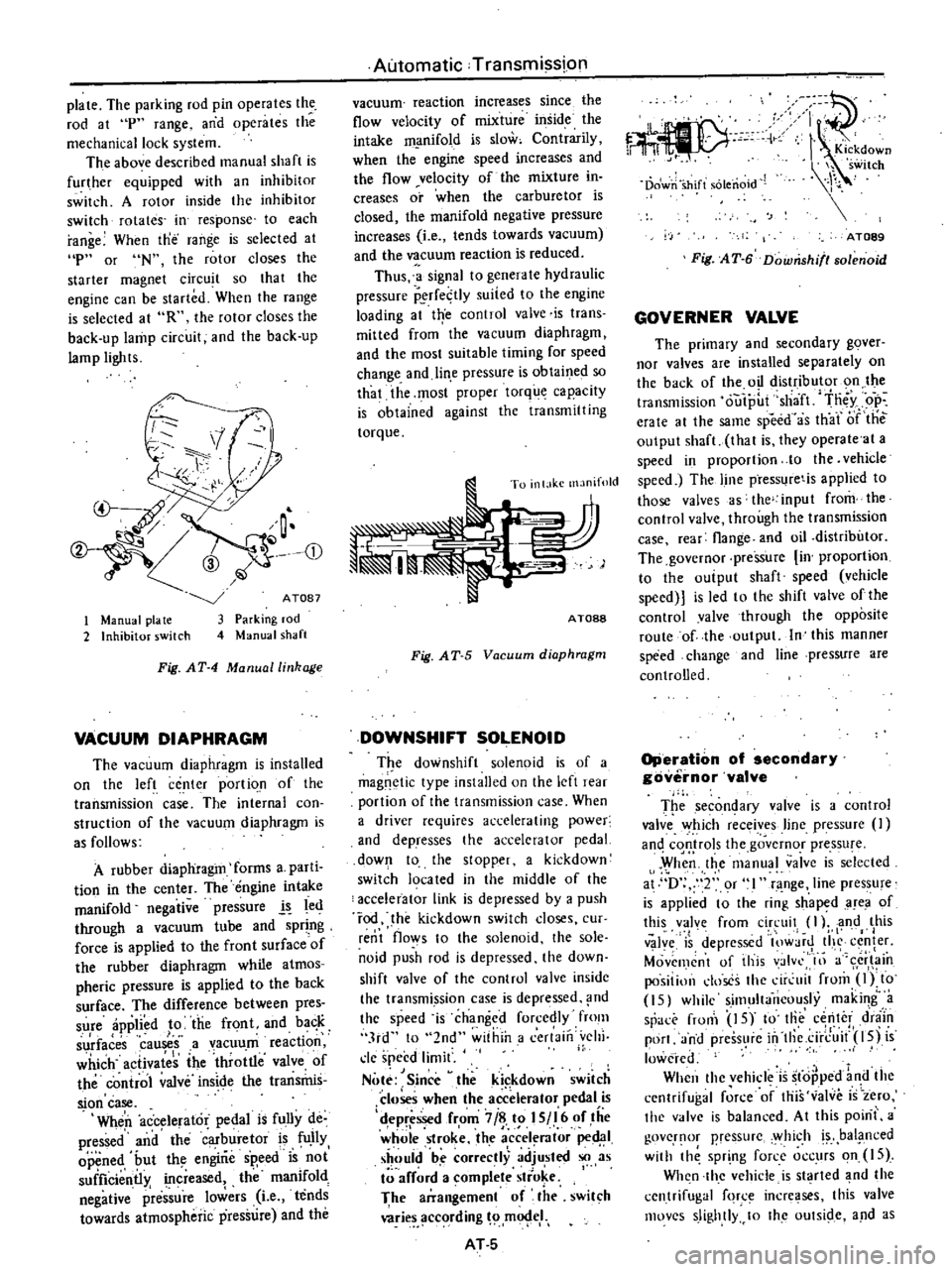
Kickdown
h
switch
Dowri
shift
solenoid
AT089
Fig
AT
6
Downshifl80lenoid
GOVERNER
VALVE
The
primary
and
secondary
gover
nor
valves
are
installed
separately
on
the
back
of
the
oil
distributor
on
the
transmission
outp
t
sha
ft
tn
y
op
erate
al
the
same
speed
as
th
ar
iJf
tile
output
shaft
thai
is
they
operate
at
a
speed
in
proportion
10
the
vehicle
speed
The
line
press
retis
applied
to
those
valves
s
the
input
from
the
control
valve
through
the
transmission
case
rear
flange
and
oil
distributor
The
governor
pressure
in
proportion
to
the
ouiput
shaft
speed
vehicle
speed
is
led
to
the
shift
valve
ofthe
control
valve
through
the
opposite
route
of
the
output
In
this
manner
speed
change
and
line
pressure
are
controlled
Operation
of
secondary
governor
valve
T
e
secon
ary
valve
is
a
contro
valve
Y
hich
receives
line
pressure
an
cqQ
rols
the
governor
pressu
e
When
the
manual
valve
is
selected
at
D
2
or
l
range
line
pressure
is
applied
t
the
ri
g
sh
aped
area
of
this
valve
from
circuit
I
l
and
this
I
v
Jy
is
depressed
lOW
jr
tI
c
fer
Movemcnt
of
this
valvl
III
a
cr
in
positillll
doses
the
dr
uit
from
Olto
15
while
simultaneously
making
a
sr
rronl
IS
to
Iii
center
d
niin
port
and
press
re
in
tllc
ci
rJ
it
l5j
is
lowered
When
thc
vehicle
is
stopped
1
d
the
cenlrifugal
force
of
this
valve
is
zero
the
v
lve
is
balanced
At
this
poini
a
govcr
lOr
pressurc
y
hich
bal
i1
nced
with
th
spr
ng
force
occurs
on
IS
Wh
n
thc
vehicle
is
st
rted
nd
the
centrifugal
fqr
incre
ses
this
valve
movcs
slightly
10
Ihc
oUlSide
and
as
Page 269 of 537

3
Jit
f
ng
valve
24
1
3
L
l
r
I
Js
I
i
ilr
t
pressure
6
when
shif
ing
from
3rd
to
2nd
at
D
range
Thus
the
throttle
of
line
pressure
6
reduces
the
shock
generated
fro
shifting
A
plug
in
the
SSV
left
end
readjust
the
throttle
piessu
e
I
6
which
varies
depending
on
the
engine
throttle
con
dition
to
a
throttle
pressure
19
suiled
to
the
sp
ed
change
control
Moreover
the
plug
is
a
valve
which
applies
line
P
esspre
13
in
lieu
of
the
throttle
pressure
to
the
SSV
and
the
FSV
when
kickdowri
is
performed
When
the
throttle
pressure
16
is
applied
to
the
left
side
of
this
plug
and
the
plug
is
epressed
toward
the
right
a
slight
space
is
formed
from
the
throttle
pressure
6
10
19
A
throt
tIepressu
19
w
1iFh
is
lower
by
the
pressure
loss
equivalent
to
this
space
is
rH
1
Pressure
Odifier
valve
PMV
I
Compared
to
the
operating
pressure
required
in
starting
th
vehicle
the
ppwer
trimsinitting
capacity
of
the
clutch
that
is
required
operating
pres
sure
may
be
lower
when
the
vehicle
is
once
started
When
the
line
pressure
is
retained
at
a
high
level
up
to
a
high
vehicle
speed
shock
gerieraled
from
the
shirring
increases
arid
the
oil
pump
loss
also
jncrdases
In
order
to
prevent
his
the
t
lrott
le
pressure
must
be
l
hanged
over
with
the
operation
of
the
governor
pressure
15
to
reduce
Ihe
line
pressure
The
PMV
is
used
for
this
purposc
Automatic
Transmission
generated
the
piessure
loss
is
adde
d
to
the
spring
force
and
the
plug
is
lhus
forced
back
from
the
right
to
the
left
When
this
pressure
19
increases
ex
cessively
the
plug
is
further
depressed
toward
the
left
space
from
the
lhrot
tle
pressure
19
to
the
drain
circuit
13
increases
and
the
throttle
press
ure
19
decreases
Thus
the
plug
is
balanced
imd
the
throttle
pressure
19
is
reduced
to
Ii
certain
value
against
the
throttle
pressure
6
Wheri
performing
kickdowri
the
SDV
moves
a
high
line
pressure
is
led
to
the
circuit
19
from
the
line
pressure
circuit
13
which
had
been
drained
the
plug
is
forced
toward
the
left
and
circuit
19
becomes
equal
to
the
line
pressure
13
I
W
15
I
A
TOgS
Fig
iT
13
2nd
3rd
shift
vallJe
I
When
the
governor
pressuie
IS
which
is
applied
to
the
right
side
of
the
PMV
is
low
the
valve
is
forced
toward
the
right
by
the
throttle
ines
sure
16
applied
to
the
area
differ
ence
of
the
value
and
the
spring
foice
and
t
he
circuit
from
circuit
16
to
circuit
18
is
closed
However
when
vehicle
speed
increases
andl
the
gaver
nor
pressure
15
exceeds
a
certain
level
the
governor
pressure
toward
the
left
which
is
applied
to
the
right
side
exceeds
the
spring
force
and
the
throt
tle
pressure
16
toward
thc
right
the
valve
is
depressed
loward
the
lefi
and
the
throttle
pressure
is
led
from
circuit
AT
9
16
to
circuit
18
This
throttle
pressure
18
is
applied
to
the
top
of
the
PRV
and
the
force
of
the
line
pressure
source
7
is
reduced
Contra
rily
when
the
vehicle
speed
decreases
arid
the
governor
ipressure
15
de
creases
the
force
toward
the
fight
exceeds
ithe
governor
pressure
the
valve
is
forced
back
toward
the
right
and
the
throttle
pressure
18
is
drained
to
the
spring
unit
This
valve
is
sWitched
when
the
throttle
pressure
and
the
governor
pressure
are
high
or
when
tIiey
are
both
Tow
i
i
I
11
18
16
n
r
I
I
15
AT099
Fig
AT
14
Pre
ure
modifier
valve
Vacuum
thro
le
valve
VTV
The
vacuum
t
rottle
valve
is
a
regula
tor
valve
whiCh
uses
the
line
pressure
7
for
the
pressure
source
and
regulates
the
throttle
pressure
16
I
which
is
proportioned
t
the
force
of
the
vacuum
diaphragm
The
vacuum
dia
phragm
yories
depending
on
the
engine
throt
le
condition
negative
pressure
in
the
inta
e
line
When
the
line
pressure
7
is
ap
plied
to
the
bottom
through
the
valve
hole
and
the
v
a
ve
is
forced
upward
space
from
the
line
pressure
7
to
the
throttle
pressure
16
is
dosed
and
the
space
from
the
Ihrottle
pressure
16
to
the
drain
circuit
17
is
about
to
open
In
this
operation
the
throttle
pressure
16
becomes
lower
than
the
linep
s
ureY
btthe
p
e
sur
9
iv
alenl
of
the
loss
of
space
and
Ihe
force
depressing
tlie
rod
if
the
vaeuum
diaphragm
is
balanced
wit
Ii
thethrot
tie
pressure
16
a
pplied
upward
tOlthe
bottom
When
the
erigine
torque
is
high
Ihe
negative
pressure
in
the
intake
iirie
rises
tending
ioward
atmospheric
pressure
and
the
force
of
the
rod
to
depress
the
valve
increases
As
a
result
the
valve
is
depressed
downward
the
Page 278 of 537

N
RANGE
NEUTRAL
In
N
range
none
of
the
clutches
and
band
are
applied
thus
no
power
is
transmitted
to
the
output
shaft
The
pressure
of
oil
discharged
from
the
oil
pump
is
regulated
by
the
pressure
regulator
valve
Dto
maintain
the
line
pressure
7
and
the
oil
is
led
to
the
manual
valve
@
vacuum
throt
tie
valve
@
and
solenoid
down
shift
valve
@
The
oil
is
further
introduced
into
the
torque
converter
at
its
op
erating
pressure
14
and
a
portion
of
this
oil
is
distributed
to
each
part
as
the
front
lubricant
The
oil
which
has
been
discharged
from
the
torque
con
verter
is
also
distributed
to
eacn
part
as
the
rear
lubricant
As
the
oil
pump
rotates
at
the
same
speed
as
the
engine
the
oil
pump
discharge
increases
with
engine
speed
But
the
surplus
oil
is
returned
to
the
oil
pan
by
the
pressure
regula
tor
valve
D
Automatic
Transmission
Geu
Clutch
Low
4
Band
crvo
One
Pultin
R
atio
WI
pawl
Front
Rear
brake
Operation
Release
clutch
Park
on
on
Reverse
2
182
on
on
on
Neutral
Dt
Low
2
458
on
on
Drive
D2
Second
1
458
on
on
m
Top
1
000
on
on
on
on
2
Second
1
458
on
on
12
Sec
ond
1
458
on
on
II
Low
2
458
on
on
AT
la
Page 282 of 537

N
RANGE
NEUTRAL
Automatic
Transmission
In
N
range
none
of
the
clutches
and
band
are
applied
thus
no
power
is
transmitted
to
the
output
shaft
The
pressure
of
oil
discharged
from
the
oil
pump
is
regulated
by
the
pressure
regulator
valve
CD
to
maintain
the
line
pressure
7
and
the
oil
is
led
to
the
manual
valve
V
vacuum
throt
tle
valve
@
and
solenoid
down
shift
valve
@
The
oil
is
further
introduced
into
the
torque
converter
at
its
op
erating
pressure
14
and
a
portion
of
this
oil
is
distributed
to
each
part
as
the
front
lubricant
The
oil
which
has
been
discharged
from
the
torque
con
verter
is
also
distributed
to
eacn
part
as
the
rear
lubricant
As
the
oil
pump
rotates
at
the
same
speed
as
the
engine
the
oil
pump
discharge
increases
with
engine
speed
But
the
surplus
oil
is
returned
to
the
oil
pan
by
the
pressure
regulator
valve
CD
G
Clutch
Low
Band
servo
One
Pukiq
R
w
pawl
ntlo
Front
Rur
br
ke
Optruion
Release
clutch
PIlIi
on
on
Reverse
2
182
on
on
on
Neut
1
01
Low
2
458
on
on
Drive
02
Second
t
458
on
on
03
Top
1
000
on
on
on
on
2
Setond
1
458
on
on
12
Second
1
4
58
on
on
1
II
Low
2
458
on
on
AT
18