engine oil DATSUN PICK-UP 1977 Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1977, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: DATSUN PICK-UP 1977Pages: 537, PDF Size: 35.48 MB
Page 194 of 537
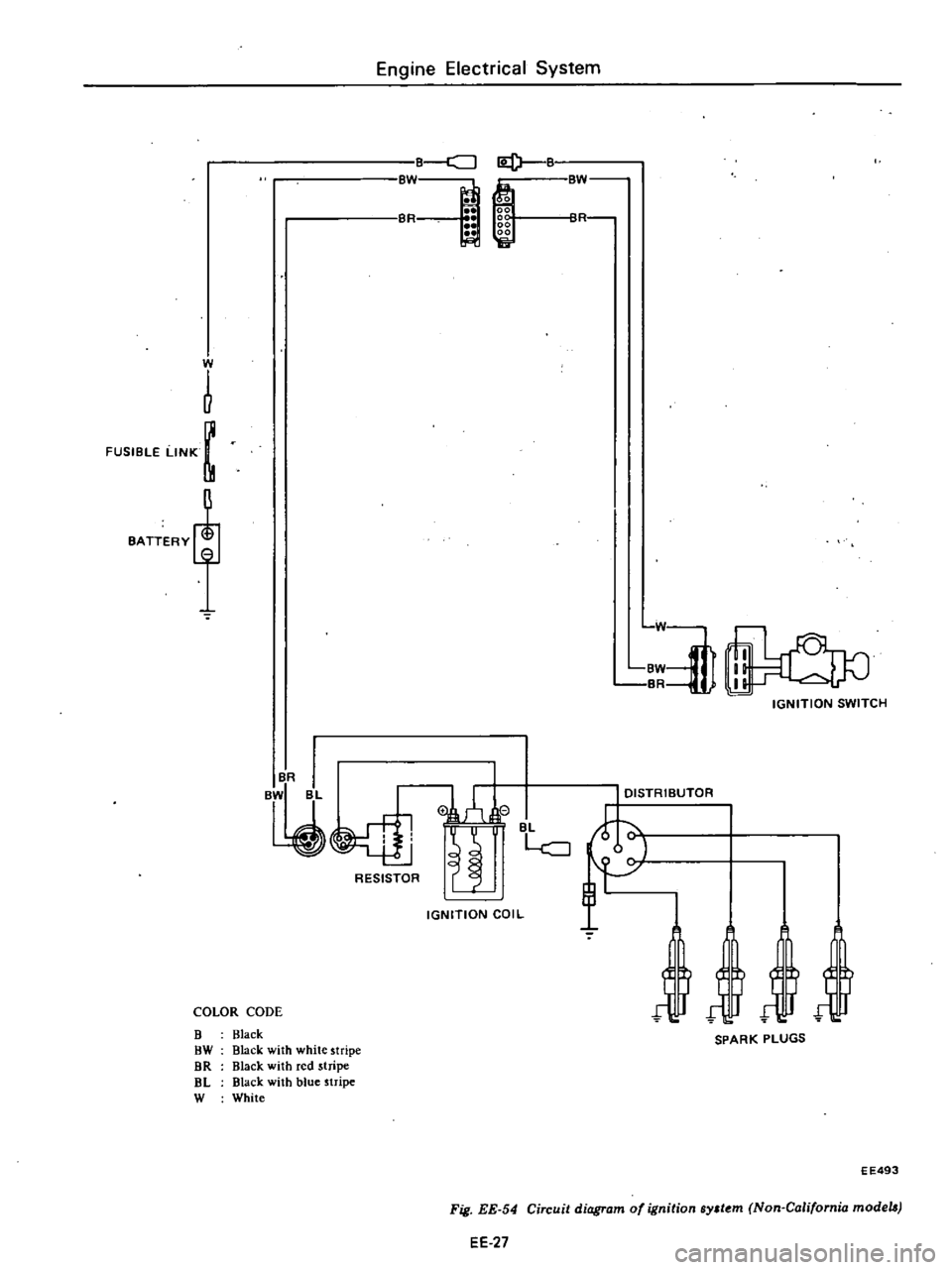
FUSIBLE
LtNK
m
Engine
Electrical
System
E
CJI2t
Bf
o
00
00
fOl
R
BL
I
ti
L
oj
L
C
J
RESISTOR
IGNITION
COIL
COLOR
CODE
B
Black
OW
Black
with
white
stripe
DR
Black
with
red
stripe
aL
Black
with
blue
stripe
W
White
W
R
Wj
BW
BR
IGNITION
SWtTCH
DISTRtBUTOR
jjj
SPARK
PLUGS
EE493
EE
27
Fig
EE
54
Circuit
diagram
of
ignition
ByJt
m
Non
California
models
Page 195 of 537
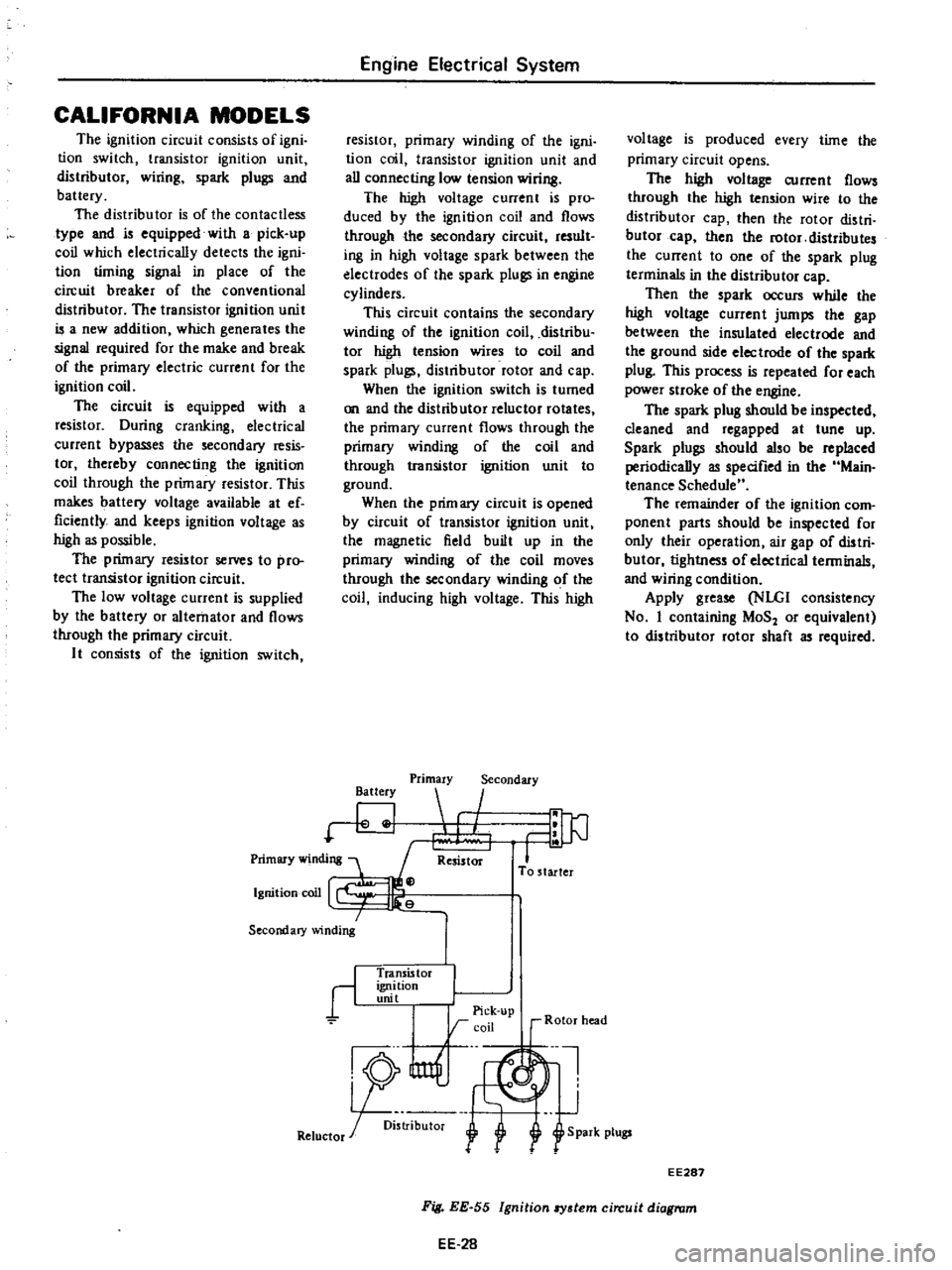
Primary
winding
1
Ignition
coo
I
Secondary
winding
CALIFORNIA
MODELS
The
ignition
circuit
consists
of
igni
tion
switch
transistor
ignition
unit
distributor
wiring
spark
plugs
and
battery
The
distributor
is
of
the
contactless
type
and
is
equipped
with
a
pick
up
coil
which
electrically
detects
the
igni
tion
timing
signal
in
place
of
the
circuit
breaker
of
the
conventional
distributor
The
transistor
ignition
unit
is
a
new
addition
which
generates
the
signal
required
for
the
make
and
break
of
the
primary
electric
current
for
the
ignition
coil
The
circuit
is
equipped
with
a
resistor
During
cranking
electrical
current
bypasses
the
secondary
resis
tor
thereby
connecting
the
ignition
coil
through
the
primary
resistor
This
makes
battery
voltage
available
at
ef
ficiently
and
keeps
ignition
voltage
as
high
as
possible
The
primary
resistor
selVeS
to
pro
tect
transistor
ignition
circuit
The
low
voltage
current
is
supplied
by
the
battery
or
alternator
and
flows
through
the
primary
circuit
It
consists
of
the
ignition
switch
Engine
Electrical
System
resistor
primary
winding
of
the
igni
tion
coil
transistor
ignition
unit
and
all
connecting
low
tension
wiring
The
high
voltage
current
is
pro
duced
by
the
ignition
coil
and
flows
through
the
secondary
circuit
result
ing
in
high
voltage
spark
between
the
electrodes
of
the
spark
plugs
in
engine
cylinders
This
circuit
contains
the
secondary
winding
of
the
ignition
coil
distribu
tor
high
tension
wires
to
coil
and
spark
plugs
distributor
rotor
and
cap
When
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
on
and
the
distributor
reluctor
rotates
the
primary
current
flows
through
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
and
through
transistor
ignition
unit
to
ground
When
the
prim
ary
circuit
is
opened
by
circuit
of
transistor
ignition
unit
the
magnetic
field
built
up
in
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
moves
through
the
secondary
winding
of
the
coil
inducing
high
voltage
This
high
Battery
Primary
Secondary
I
Resistor
To
starter
r
Transis
tor
ignition
unit
I
I
Pick
up
rcoil
r
Rotor
head
nl
J
R5
U1f
1
Retuctor
r
oi
l
f
S
park
plugs
voltage
is
produced
every
time
the
primary
circuit
opens
The
high
voltage
current
flows
through
the
high
tension
wire
to
the
distributor
cap
then
the
rotor
distri
butor
cap
then
the
rotor
distributes
the
current
to
one
of
the
spark
plug
terminals
in
the
distributor
cap
Then
the
spark
occurs
while
the
high
voltage
current
jumps
the
gap
between
the
insulated
electrode
and
the
ground
side
electrode
of
the
spark
plug
This
process
is
repeated
for
each
power
stroke
of
the
engine
The
spark
plug
should
be
inspected
cleaned
and
regapped
at
tune
up
Spark
plugs
should
also
be
replaced
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Main
tenance
Schedule
The
remainder
of
the
ignition
com
ponent
parts
should
be
inspected
for
only
their
operation
air
gap
of
distri
butor
tightness
of
electrical
terminals
and
wiring
condition
Apply
grease
NLGI
consistency
No
I
containing
MoS
or
equivalent
to
distributor
rotor
shaft
as
required
EE287
EE
28
Fig
EE
55
Ignition
8Y3tem
circuit
diagram
Page 196 of 537
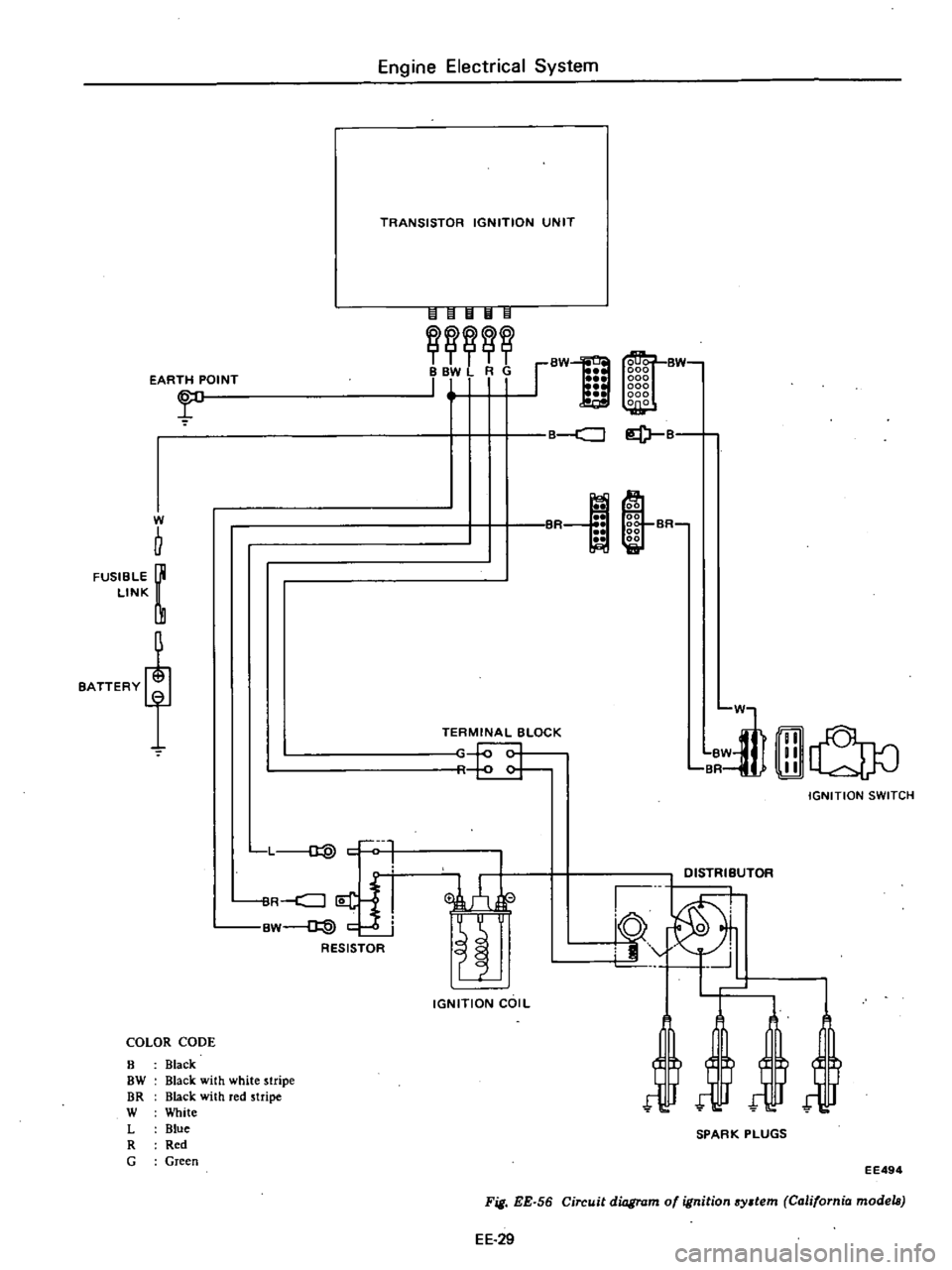
EARTH
POINT
r
W
b
FUSIBLE
LINK
BATTERY
L
d
l
ilR
j
i
BW
@
c
RESISTOR
COLOR
CODE
8
Black
OW
Black
with
white
stripe
DR
Black
with
red
stripe
W
White
L
Blue
R
Red
G
Green
Engine
Electrical
System
TRANSISTOR
IGNITION
UNIT
IHIIl
II
II
BW
BBV
RG
111
I
I
TERMINAL
BLOCK
r
c
IGNITION
COIL
BW
B
ml
BR
lliJ
LldJ0
IGNITION
SWITCH
EE
29
Fig
EE
56
Circuit
diagram
of
ignition
system
California
models
EE494
a
B
lof1
@
00
00
00
SR
00
00
Et
liiI
in
D1STRliUTOR
10
0
i9
J
SPARK
PLUGS
Page 198 of 537
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTMENT
CAP
AND
ROTOR
HEAD
Cap
and
rotor
head
should
be
in
spected
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Maintenance
Schedule
Remove
cap
and
clean
all
dust
and
carbon
deposits
from
cap
and
rotor
If
cap
is
cracked
or
is
leaking
replace
with
a
De
one
CONTACT
POINT
Contact
point
should
be
replaced
in
accordance
with
the
Maintenance
Schedule
Standard
point
gap
is
0
45
to
0
55
mm
O
OIS
to
0
022
in
In
case
size
is
off
the
standard
adjustment
is
made
by
loosening
point
screws
Gap
gauge
is
required
for
adjustment
When
point
surface
is
rough
take
off
any
irregularities
with
fine
sand
paper
of
No
500
or
600
or
with
oil
stone
When
wear
on
contact
points
is
noticeable
replace
points
together
with
contact
arm
To
replace
proceed
as
follows
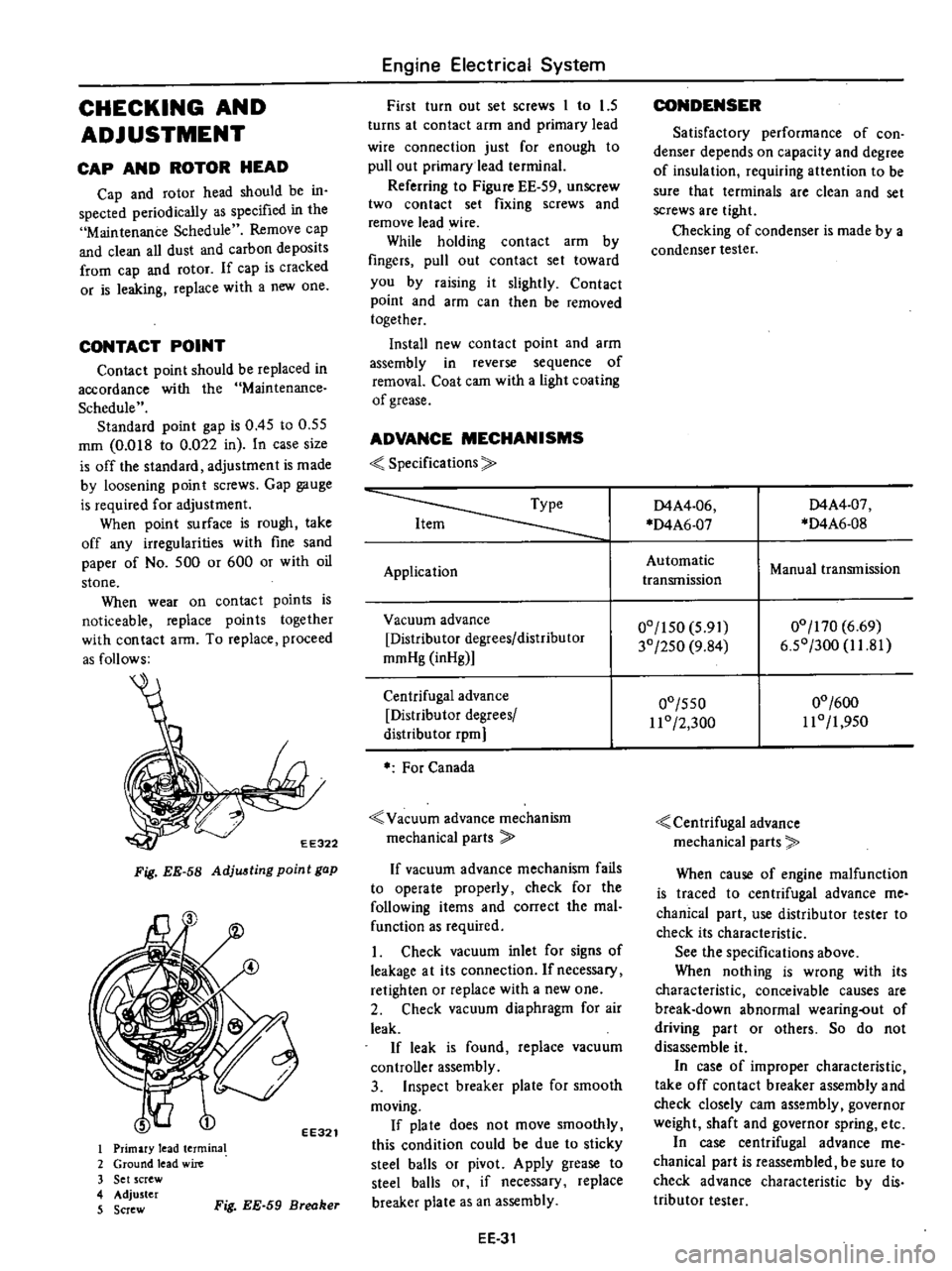
EE322
Fig
EE
58
Adju
ting
point
gap
EE321
I
Primary
lead
termina
2
Ground
lead
wire
3
Set
screw
4
Adjuster
5
Screw
Fig
EE
59
Breaker
Engine
Electrical
System
First
turn
out
set
screws
1
to
1
5
turns
at
contact
arm
and
primary
lead
wire
connection
just
for
enough
to
pull
out
primary
lead
terminal
Referring
to
Figure
EE
59
unSCrew
two
contact
set
fixing
screws
and
remove
lead
wire
While
holding
contact
arm
by
fingers
pull
out
contact
set
toward
you
by
raising
it
slightly
Contact
point
and
afm
can
then
be
removed
together
Install
new
contact
point
and
arm
assembly
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
Coat
cam
with
a
light
coating
of
grease
ADVANCE
MECHANISMS
Specifications
Application
Vacuum
advance
Distributor
degrees
distributor
mmHg
inHg
Centrifugal
advance
Distributor
degrees
distribu
tor
rpm
For
Canada
Vacuum
advance
mechanism
mechanical
parts
If
vacuum
advance
mechanism
fails
to
operate
properly
check
for
the
following
items
and
correct
the
mal
function
as
required
1
Check
vacuum
inlet
for
signs
of
leakage
at
its
connection
Ifnecessacy
retighten
or
replace
with
a
new
one
2
Check
vacuum
diaphragm
for
air
leak
If
leak
is
found
replace
vacuum
controller
assembly
3
Inspect
breaker
plate
for
smooth
moving
If
pia
te
does
not
move
smoothly
this
condition
could
be
due
to
sticky
steel
balls
or
pivot
Apply
grease
to
steel
balls
or
if
necessary
replace
breaker
plate
as
an
assembly
EE
31
CONDENSER
Satisfactory
performance
of
con
denser
depends
on
capacity
and
degree
of
insulation
requiring
attention
to
be
sure
that
terminals
are
clean
and
set
screws
are
tight
Checking
of
condenser
is
made
by
a
condenser
tester
D4A4
06
D4A6
07
D4A4
07
D4A6
0S
Automatic
transmission
Manual
transmission
00
150
5
91
30
250
9
S4
00
170
6
69
6
50
300
1I
S1
00
550
11
0
2
300
00
600
110
1
950
Centrifugal
advance
mechanical
parts
When
cause
of
engine
malfunction
is
traced
to
centrifugal
advance
me
chanical
part
use
distributor
tester
to
check
its
characteristic
See
the
specifications
above
When
nothing
is
wrong
with
its
characteristic
conceivable
causes
are
break
down
abnormal
wearing
out
of
driving
part
or
others
So
do
not
disassemble
it
In
case
of
improper
characteristic
take
off
contact
breaker
assembly
and
check
closely
cam
assembly
governor
weight
shaft
and
governor
spring
etc
In
case
centrifugal
advance
me
chanical
part
is
reassembled
be
sure
to
check
advance
characteristic
by
dis
tributor
tester
Page 200 of 537

Engine
Electrical
System
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
D4A4
06
D4A4
07
Type
D4A6
07
D4A6
08
Firing
order
1
3
4
2
13
4
2
Rotating
direction
Counterclockwise
Counterclockwise
Owen
angle
degree
490
to
550
490
to
550
Point
gap
mm
in
0
45
to
0
55
0
45
to
0
55
0
018
to
0
022
0
018
to
0
022
Point
pressure
kg
lb
0
40
to
0
55
0
40
to
0
55
0
88
to
1
21
0
88
to
1
21
Condenser
capacity
JlF
0
20
to
0
24
0
20
to
0
24
Condenser
isolate
resistance
Mrl
5
5
Cap
isolate
resistance
Mrl
50
50
Rotor
head
isolate
resistance
Mrl
50
50
Cap
carbon
point
length
mm
in
10
0
39
10
0
39
For
Canada
DISTRIBUTOR
California
models
CONSTRUCTION
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTMENT
CAP
AND
ROTOR
HEAD
AIR
GAP
CONSTRUCTION
In
the
conventional
distributor
the
ignition
liming
is
detected
by
the
cam
and
breaker
arm
while
in
this
transis
tor
ignition
unit
it
is
detected
by
the
reluctor
on
the
shaft
and
the
pick
up
coil
provided
in
place
of
the
breaker
The
pick
up
coil
consists
of
a
magnet
coil
etc
The
amount
of
magnetic
flux
passing
through
the
pole
piece
in
the
coil
is
changed
at
the
moment
the
pole
CONTENTS
EE
33
EE
33
EE
33
EE
33
ADVANCE
MECHANISMS
DISASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLY
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
EE
33
EE
35
EE
35
EE
36
piece
faces
the
protrusion
of
the
re
luctor
and
then
the
electrical
signal
is
genera
ted
in
the
pick
up
coil
This
electric
signal
is
conducted
into
the
transistor
ignition
unit
which
in
turn
breaks
tI
e
primary
coil
current
running
through
the
ignition
coil
and
generates
high
voltage
in
the
secondary
winding
Also
this
transistor
ignition
EE
33
unit
utilizes
this
electric
signal
to
restore
the
primary
coil
to
the
original
state
after
cutting
off
the
primary
current
for
a
fIXed
time
The
centrifugal
and
vacuum
ad
vance
mechanisms
employ
the
con
ventional
mechanical
type
The
con
tactor
is
used
to
eliminate
vacuum
and
centrifugal
advance
hysteresis
I
Page 201 of 537

t3
l
l
J
@
r
9
V
fW
@
@
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTMENT
CAP
AND
ROTOR
HEAD
Cap
and
rotor
head
must
be
in
spected
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Maintenance
Schedule
Remove
cap
and
clean
all
dust
and
carbon
deposits
from
cap
and
rotor
from
time
to
time
If
cap
is
cracked
or
is
leaking
replace
with
a
new
one
AIR
GAP
Standard
air
gap
is
0
2
to
0
4
mm
0
008
to
0
016
in
If
the
gap
is
off
the
standard
adjustment
mould
be
made
by
loos
ening
pick
up
coil
screws
Gap
gauge
is
required
for
adjust
ment
Air
gaps
must
be
checked
from
time
to
time
Air
gap
0
2
to
0
4
mm
0
008
to
0
016
in
Engine
Electrical
System
tl
@
9
EE328
Fig
EE
67
Checking
oir
gap
To
remove
pick
up
cail
disconnect
distributor
harness
at
terminal
block
and
remove
screw
securing
pick
up
coil
ADVANCE
MECHANISMS
Specifications
Type
Item
Vacuum
advance
Distributor
degrees
Distributor
mmHg
inHg
Centrifugal
advance
Distributor
degrees
Distributor
cpm
EE34
1
Cap
assembly
2
Rotor
head
a55embly
3
Roll
pin
4
ReJuctor
S
Pick
up
coil
6
Contactoi
7
Breaker
plate
assembly
8
Packing
9
Rotor
shaft
10
Governor
spring
11
Governor
weigh
t
12
Shaft
a
Jscmbly
13
Cap
setter
14
Vacuum
controller
15
Housing
16
Fixing
plate
17
O
ring
18
Collar
EE327
Fig
EE
66
Exploded
view
of
di3tributor
assembly
and
distributor
harness
to
their
positions
EE329
Fig
EE
68
Remouing
pick
up
coil
D4F4
04
D4F4
Q3
Manual
Automatic
00
150
5
91
30
250
9
84
00
550
110
2
300
00
600
110
1
950
Page 202 of 537

Vacuum
advance
mechanism
mechanical
parts
If
vacuum
advance
mechanism
fails
to
operate
properly
check
for
the
following
items
and
correct
the
prob
lem
as
required
1
Check
vacuum
inlet
for
signs
of
leakage
at
its
connection
If
necessary
retighten
or
replace
with
a
new
one
2
Check
vacuum
diaphragm
for
air
leak
If
leak
is
found
replace
vacuum
controller
assembly
3
Inspect
breaker
plate
for
smooth
moving
If
plate
does
not
move
smoothly
this
condition
could
be
due
to
sticky
steel
balls
or
pivot
Apply
grease
to
steel
balls
or
if
necessary
replace
distributor
assembly
Centrifugal
advance
mechanical
parts
When
cause
of
engine
malfunction
is
traced
to
centrifugal
advance
mecha
nical
parts
use
distributor
tester
to
check
its
characteristics
See
to
the
specifications
above
If
nothing
is
wrong
with
its
charac
teristics
conceivable
causes
are
faulty
or
abnormal
wear
of
driving
part
or
others
So
do
not
disassemble
it
In
the
event
of
improper
character
istics
check
closely
rotor
shaft
assem
bly
governor
weight
and
shaft
If
any
of
above
parts
are
malfunc
tioning
replace
distributor
assembly
DISASSEMBLY
To
disassemble
follow
the
pro
cedure
below
1
Take
off
cap
and
remove
rotor
head
2
Remove
two
screws
shown
in
Figure
EE
69
and
detach
vacuum
con
troller
Engine
Electrical
System
EE291
Fig
EE
69
Removing
vacuum
controller
3
Remove
pick
up
coil
assembly
4
Using
two
pry
bars
pry
reluctor
from
shaft
Be
careful
not
to
distort
or
damage
the
teeth
of
reluctor
Remove
roll
pin
S
Remove
breaker
plate
setscrews
and
remove
breaker
plate
assembly
E330
Fig
EE
70
Removing
breaker
plate
etscrews
6
Pull
roll
pin
out
and
remove
collar
7
Remove
rotor
shaft
and
drive
shaft
assembly
EE331
Fig
EE
71
Removing
rotor
shaft
and
drive
shaft
assembly
8
Mark
rotor
shaft
and
drive
shaft
Remove
packing
from
the
top
of
rotor
shaft
and
unscrew
rotor
shaft
setscrew
EE
35
EE075
Fig
EE
72
Removing
rotor
shaft
9
Mark
one
of
the
governor
springs
and
its
bracket
Also
mark
one
of
the
governor
weights
and
its
pivot
pins
10
Carefully
unhook
and
remove
governor
springs
11
Remove
governor
weights
Apply
grease
to
governor
weights
after
disassembling
ASSEMBLY
To
assem
ble
reverse
the
order
of
disassembly
Carefully
observe
the
fol
lowing
instructions
1
Align
match
marks
so
that
parts
are
assembled
to
their
original
posi
tions
2
If
for
any
reason
contactor
is
removed
from
breaker
plate
adjust
cam
to
contactor
clearance
to
0
3
mm
0
012
in
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
73
after
installation
T
EE298
Fig
EE
73
Cam
to
contactor
clearance
3
Ensure
that
reluctor
is
properly
orien
ted
when
installing
on
shaft
Always
drive
in
roll
pin
with
its
slit
toward
the
outer
end
of
shaft
See
Figure
EE
74
Be
sure
to
use
a
new
roll
pin
Page 203 of 537
EE299
Fig
EE
74
Driving
in
roll
pin
Engine
Electrical
System
4
Apply
grease
to
the
top
of
rotor
shaft
as
required
5
Check
the
operation
of
governor
before
installing
distributor
on
engine
6
Adjust
ignition
timing
after
distri
butor
is
installed
on
engine
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
Type
Firing
order
Rotating
direction
Duty
Air
gap
mm
in
MU
Cap
insulation
resistance
Rotor
head
insulation
resistance
MU
Cap
carbon
point
length
mm
in
D4F4
03
D4F4
04
1
3
4
2
Counterclockwise
70
20
to
40
at
idling
0
2
to
0
4
O
OOS
to
0
016
More
than
50
More
than
50
10
0
39
TRANSISTOR
IGNITION
UNIT
California
models
DESCRIPTION
TRANSISTOR
IGNITION
UNIT
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
1
POWER
SUPPLY
WI
RING
AND
BATTERY
CHECK
DESCRIPTION
TRANSISTOR
IGNITION
UNIT
The
transistor
ignition
unit
provides
the
following
functions
L
It
makes
and
breaks
the
electric
current
in
the
primacy
circuit
of
the
ignition
coil
2
CONTINUITY
CHECK
OF
PRIMARY
CIRCUIT
3
PICK
UP
COIL
CONTINUITY
CHECK
4
PICK
UP
COIL
POWER
SIGNAL
PULSE
CHECK
5
TRANSISTOR
IGNITION
UNIT
CHECK
CONTENTS
EE
36
EE
36
EE
37
EE
37
EE
37
2
The
duty
control
circuit
sets
the
rate
of
make
and
break
within
one
cycle
i
e
this
maintains
good
ignition
characteristics
of
engine
from
low
speed
to
high
speed
and
is
equal
to
the
dweU
angle
in
the
conventional
breaker
type
distributor
3
A
preventive
circuit
against
lock
EE
36
EE
36
EE
38
EE
38
EE
39
ing
is
provided
This
cuts
off
the
prilnaCY
electric
current
in
the
ignition
coil
when
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
on
with
the
engine
not
running
Each
component
part
of
this
unit
is
highly
reliable
however
should
any
part
be
found
faulty
the
entire
assem
bly
must
be
replaced
Page 204 of 537
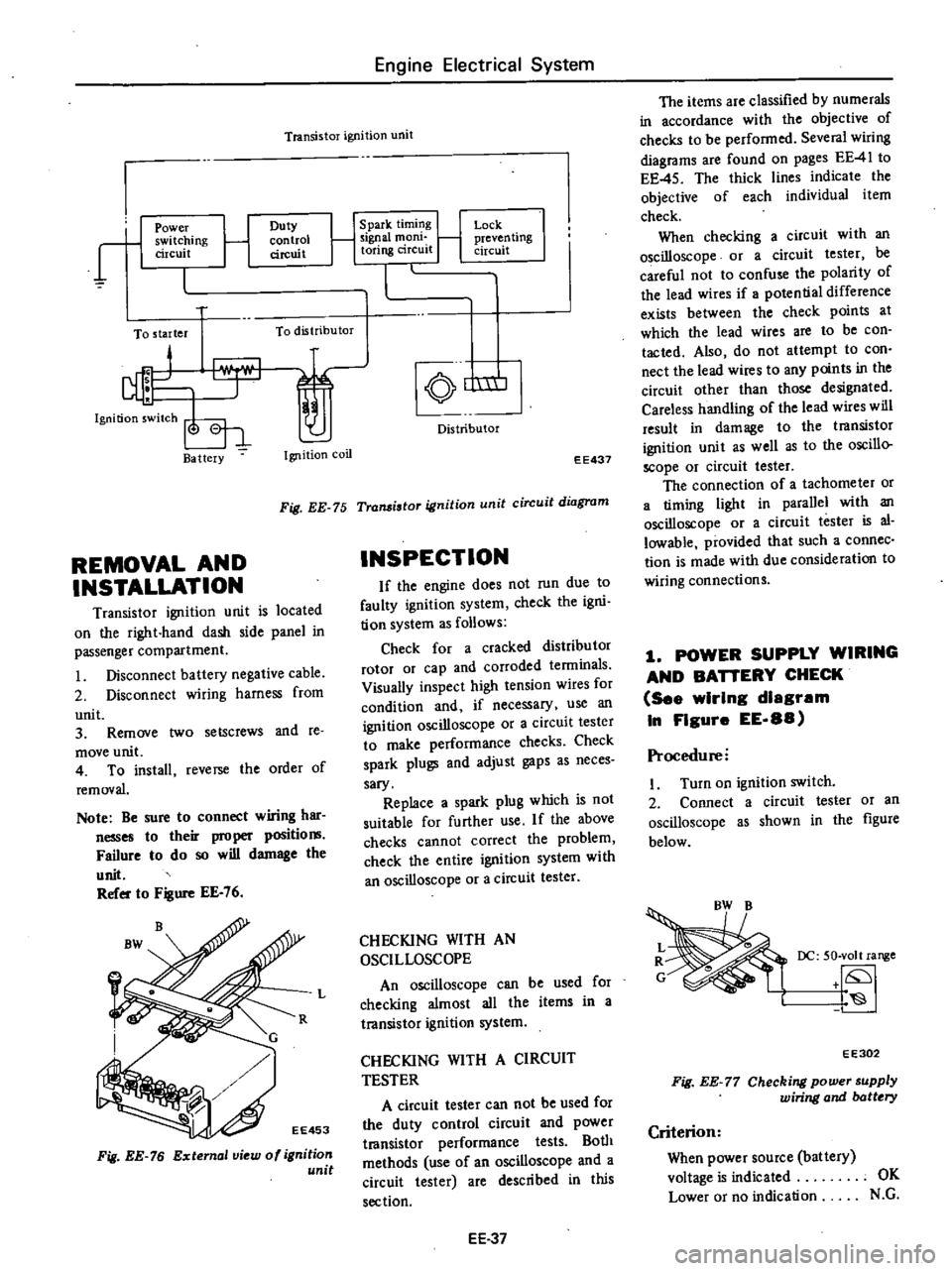
Engine
Electrical
System
Transistor
ignition
unit
r
1
Power
switching
circuit
Duty
control
circuit
To
starter
To
distributor
Ba
ttery
Ignition
coil
1
Spark
timing
1
Signal
mom
toring
circuit
Lock
j
preven
ling
circuit
nm
Distributor
EE437
Fig
EE
75
Transistor
ignition
unit
circuit
diagram
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Transistor
ignition
unit
is
located
on
the
right
hand
dash
side
panel
in
passenger
compartment
Disconnect
battery
negative
cable
2
Disconnect
wiring
harness
from
unit
3
Remove
two
setscrews
and
te
move
unit
4
To
install
reverse
the
order
of
removal
Note
Be
sure
to
connect
wiring
har
nesses
to
their
proper
positio
Failure
to
do
so
will
damage
the
unit
Refer
to
Figure
EE
76
Fig
EE
76
External
view
of
ignition
unit
INSPECTION
If
the
engine
does
not
run
due
to
faulty
ignition
system
check
the
igni
tion
system
as
follows
Check
for
a
cracked
distributor
rotor
or
cap
and
corroded
tenninals
Visually
inspect
high
tension
wires
for
condition
and
if
necessary
use
an
ignition
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
to
make
performance
checks
Check
spark
plugs
and
adjust
gaps
as
neces
sary
Replace
a
spark
plug
which
is
not
suitable
for
further
use
If
the
above
checks
cannot
correct
the
problem
check
the
entire
ignition
system
with
an
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
L
CHECKING
WITH
AN
OSCILLOSCOPE
An
oscilloscope
can
be
used
for
checking
almost
all
the
items
in
a
transistor
ignition
system
CHECKING
WITH
A
CIRCUIT
TESTER
A
circuit
tester
can
not
be
used
for
the
duty
control
circuit
and
power
t18nsistor
performance
tests
Both
methods
use
of
an
oscilloscope
and
a
circuit
tester
are
described
in
this
section
EE
37
The
items
are
classified
by
numerals
in
accordance
with
the
objective
of
checks
to
be
performed
Several
wiring
diagrams
are
found
on
pages
EE
41
to
EE
45
The
thick
lines
indicate
the
objective
of
each
individual
item
check
When
checking
a
circuit
with
an
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
be
careful
not
to
confuse
the
polarity
of
the
lead
wires
if
potential
difference
exists
between
the
check
points
at
which
the
lead
wires
are
to
be
con
tacted
Also
do
not
attempt
to
con
nect
the
lead
wires
to
any
points
in
the
circuit
other
than
those
designated
Careless
handling
of
the
lead
wires
will
result
in
damage
to
the
transistor
ignition
unit
as
well
as
to
the
oscillo
scope
or
circuit
tester
The
connection
of
a
tachometer
or
a
timing
light
in
parallel
with
an
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
is
al
lowable
provided
that
such
a
connec
tion
is
made
with
due
consideration
to
wiring
connections
1
POWER
SUPPLY
WIRING
AND
BAnERY
CHECK
See
wIrIng
diagram
In
FIgure
EE
88
Procedure
I
Turn
on
ignition
switch
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
or
an
oscilloscope
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
DC
50
volt
range
EE302
Fig
EE
77
Checking
power
supply
wiring
and
batt
ry
Criterion
When
power
source
battery
voltage
is
indicated
OK
Lower
or
no
indication
N
G
Page 205 of 537
If
the
result
is
N
C
Take
the
following
measures
I
Check
BW
and
B
color
wire
harness
respectively
for
proper
con
ductance
2
Check
battery
terminals
for
proper
connection
3
Check
charge
condition
of
bat
tery
if
an
excessively
low
voltage
is
indicated
2
CONTINUITY
CHECK
OF
PRIMARY
CIRCUIT
2
1
CheckIng
prImary
circuit
See
wiring
diagram
In
Fig
EE
89
Proced
ure
I
Disconnect
L
color
wire
from
ignition
unit
2
Turn
on
ignition
switch
3
C
ooneet
a
cireui
t
tester
or
an
oscilloscope
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
78
DC
50
volt
range
tf
S
EE303
Fig
EE
78
Checking
primary
circuit
Criterion
When
Donnal
power
Source
battery
voltage
is
indicated
OK
Lower
or
no
indication
N
G
If
the
result
is
N
C
Take
the
following
measures
1
Check
BW
and
L
color
wire
Engine
Electrical
System
harness
respectively
for
proper
con
ductance
2
Check
resistor
and
ignition
coil
terminals
for
loose
contact
3
Check
resistor
and
ignition
coil
for
discontinuity
4
Check
WB
color
wire
harness
of
ignition
coil
assembly
for
proper
continuity
2
2
Chacklng
IgnitIon
coil
auembly
See
wiring
diagram
In
Fig
EE
90
Procedure
I
Disconnect
ignition
coil
and
dis
tributor
harness
from
ignition
coil
external
resistor
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
Resistance
1
range
Q
o
fD
ro
EE336
Fig
EE
79
Checking
ignition
coil
assembly
Criterion
When
approximately
1
6
to
2
0
ohm
is
indicated
OK
More
than
2
0
ohm
N
C
If
the
result
is
N
C
Replace
ignition
coil
assembly
3
PICK
UP
COIL
CONTINUITY
CHECK
See
wirIng
dIagram
In
Figure
EE
91
Procedure
Disconnect
R
and
G
color
wires
from
ignition
unit
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
EE
3B
Resistance
10
range
fp
EE305
Fig
EE
BO
Checking
pick
up
coil
Criterion
When
approximately
720
ohm
is
indicated
OK
Far
less
than
or
more
than
720
ohm
N
C
If
the
result
is
N
C
Replace
pick
up
coil
assembly
4
PICK
UP
COIL
POWER
SIGNAL
PULSE
CHECK
Procedure
I
Disconnect
anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
connector
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
3
Rotate
starter
motor
4
Read
the
tester
indication
AC
2
S
volt
range
EE306
Fig
EE
81
Checking
pick
up
coil
power
aignal
pulse
Criterion
When
pointer
deflects
slightly
OK
When
pointer
does
not
deflect
at
all
N
C
If
the
result
is
N
C
Replace
pick
up
coil
assembly