clock DATSUN PICK-UP 1977 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1977, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: DATSUN PICK-UP 1977Pages: 537, PDF Size: 35.48 MB
Page 24 of 537

r
connected
hose
to
prevent
dust
from
entering
To
air
check
valve
Fig
ET
17
Disconnect
air
hose
from
ojr
check
valve
6
Race
engine
1
500
to
2
000
rpm
two
or
three
times
under
no
load
then
run
engine
for
one
minute
at
idling
speed
7
Adjust
throttle
adjusting
screw
until
engine
is
at
specified
speed
Engine
speed
Manual
transmission
750
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
D
position
650
rpm
8
Check
ignition
timing
If
neces
sary
adjust
it
to
specifications
This
operation
need
not
be
carried
out
at
1
600
Ian
1
000
miles
service
Ignition
timing
Manual
transmission
120
750
rpm
Non
California
100
750
rpm
California
Automatic
transmission
in
D
position
120
650
rpm
9
At
about
10
minutes
after
engine
is
run
at
idling
speed
adjust
idle
adjusting
screw
so
that
CO
percentage
is
at
specified
level
CO
percentage
Manual
transmission
2
t
I
at
750
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
D
position
2
t
I
at
650
rpm
10
Repeat
procedures
as
described
in
steps
6
7
and
9
above
so
that
CO
percentage
is
at
specified
level
Check
ing
idle
CO
in
step
9
can
be
carried
out
right
after
step
7
11
Race
engine
I
500
to
2
000
rpm
two
or
three
times
under
no
load
and
make
sure
that
specified
CO
per
centage
is
obtained
Engine
Tune
up
12
Connect
air
hose
to
air
check
valve
If
engine
speed
increases
readjust
it
to
the
specified
speed
with
throttle
adjusting
screw
CO
Idle
adjustment
without
CO
meter
If
CO
meter
is
not
available
the
following
procedures
may
be
used
I
Check
carburetor
pipes
for
proper
connection
2
Wann
up
engine
until
water
tern
perature
indicator
points
to
the
middle
of
gauge
The
procedure
to
warm
up
engine
is
not
specifically
recom
mended
Either
driving
vehicle
or
oper
ating
engine
at
no
load
will
be
good
3
Make
sure
that
water
temperature
indicator
points
to
the
middle
Further
keep
engine
running
at
about
2
000
rpm
for
about
5
minutes
without
applying
load
to
engine
in
order
to
stabilize
engine
condition
Engine
hood
should
be
open
4
Run
engine
for
about
10
minutes
at
idling
peed
During
this
10
minutes
proceed
as
described
in
steps
5
to
9
below
5
Remove
air
hose
between
3
way
connector
5
way
connector
for
Cali
fornia
modeis
and
air
check
valve
shown
in
Figure
ET
17
Plug
the
dis
connected
hose
to
prevent
dust
from
entering
6
Race
engine
1
500
to
2
000
rpm
two
or
three
times
under
no
load
then
run
engine
for
one
minute
at
idling
speed
7
Adjust
throttle
adjusting
screw
so
that
engine
speeds
are
as
indicated
below
Engine
speed
Manual
transmission
815
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
D
position
670
rpm
8
Check
ignition
timing
if
neces
sary
adjust
it
to
the
value
required
by
specifications
This
operation
need
not
be
carried
out
at
1
600
Ian
1
000
miles
service
9
At
about
10
minutes
after
engine
is
run
at
idling
speed
adjust
idle
adjusting
screw
until
maximum
rpm
is
obtained
ET
12
10
Repeat
procedures
as
described
in
steps
6
7
and
9
above
until
engine
speed
at
best
idle
mixture
is
815
rpm
for
manual
transmission
models
and
670
rpm
for
automatic
transmission
models
in
D
position
Adjustment
in
step
9
can
be
carried
out
right
after
step
7
II
Turn
the
idle
adjusting
screw
clockwise
until
engine
speed
drops
off
below
specified
rpm
Engine
speed
drops
off
Manual
transmission
60
to
70
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
D
position
15
to
25
rpm
12
Connect
air
hose
to
air
check
valve
If
engine
speed
increases
readjust
it
to
the
specified
speed
with
throttle
adjusting
screw
IDLE
LIMITER
CAP
Do
not
remove
this
idle
limiter
cap
unless
necessary
If
this
unit
is
removed
it
is
necessary
to
readjust
it
at
the
time
of
installation
To
adjust
proceed
as
follows
1
After
adjusting
throttle
or
idle
speed
adjusting
screws
check
to
be
Sure
that
the
amount
of
CO
con
tained
in
exhaust
gases
meets
the
established
standard
2
Install
idle
limiter
cap
in
position
making
sure
that
the
adjusting
screw
further
turn
1
8
rotation
in
the
CO
RICH
direction
Carburetor
stopper
3lSo
ldle
limiter
cap
T
ET031
Fig
ET
18
Setting
idle
limiter
cap
CHECKING
CARBURETOR
RETURN
SPRING
Check
throttle
return
spring
for
cracks
squarene
s
or
defonnation
if
necessary
replace
with
a
new
one
Page 26 of 537
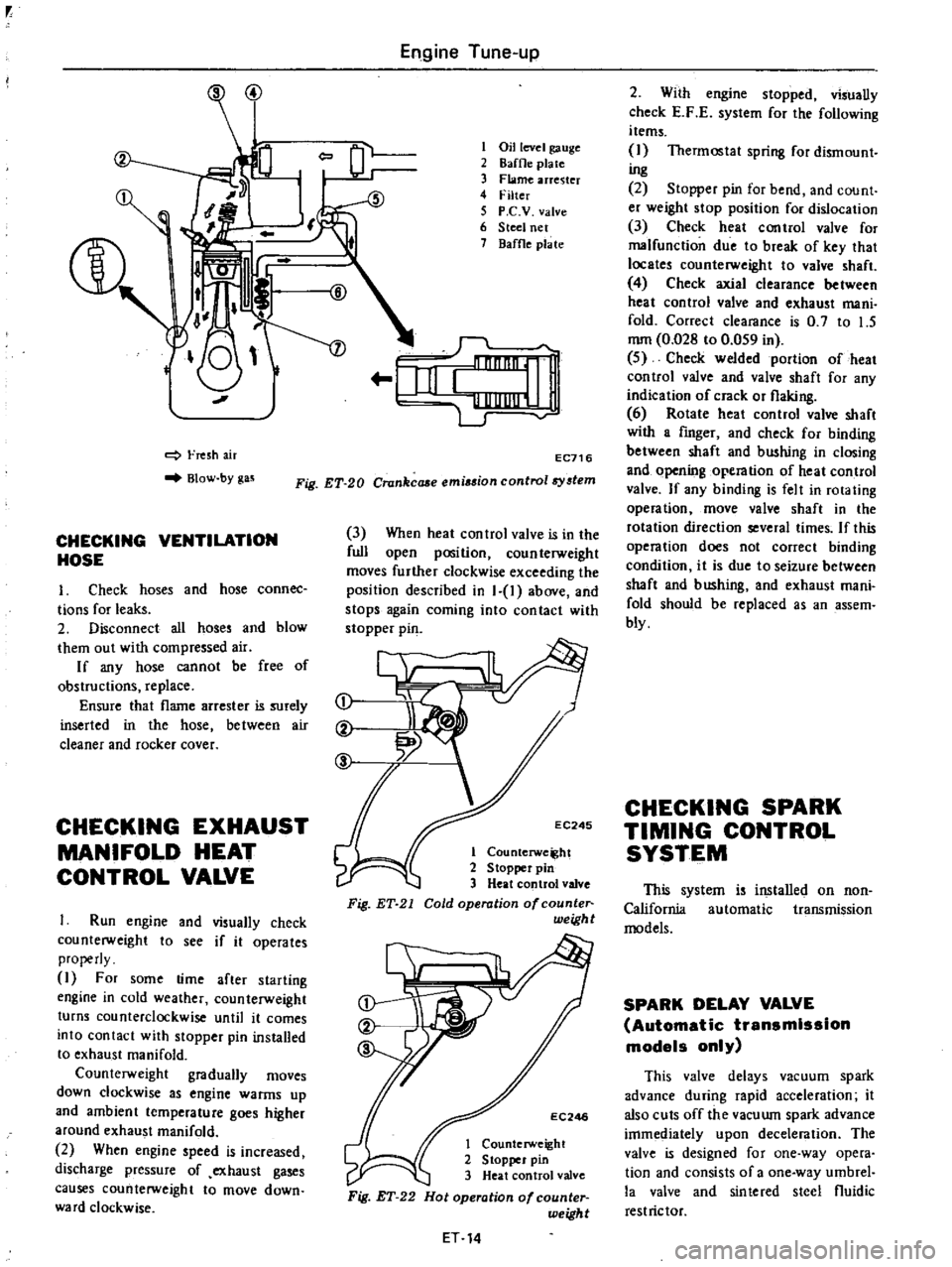
Fresh
air
Blow
by
gas
CHECKING
VENTILATION
HOSE
1
Check
hoses
and
hose
connec
tions
for
leaks
2
Disconnect
all
hoses
and
blow
them
out
with
compressed
air
If
any
hose
cannot
be
free
of
obstructions
replace
Ensure
that
flame
arrester
is
surely
inserted
in
the
hose
between
air
cleaner
and
rocker
cover
CHECKING
EXHAUST
MANIFOLD
HEAT
CONTROL
VALVE
Run
engine
and
visually
check
counterweight
to
see
if
it
operates
properly
I
For
some
time
after
starting
engine
in
cold
weather
counterweight
turns
counterclockwise
until
it
comes
into
contact
with
stopper
pin
installed
to
exhaust
manifold
Counterweight
gradually
moves
down
clockwise
as
engine
warms
up
and
ambient
temperature
goes
higher
around
exhaust
manifold
2
When
engine
speed
is
increased
discharge
pressure
of
exhaust
gases
causes
counterweight
to
move
down
ward
clockwise
Engine
Tune
up
CoOl
1
Oil
level
gauge
2
8affle
pia
te
3
Flame
arrester
4
Filter
5
P
C
V
valve
6
Steel
net
7
Baffle
plate
1fiI
o
EC716
Fig
ET
20
Crankcaae
emi
ion
control8
tem
3
When
heat
control
valve
is
in
the
full
open
position
counterweight
moves
further
clockwise
exceeding
the
position
described
in
1
1
above
and
stops
again
coming
into
contact
with
stopper
pin
ct
t
C
EC245
1
Counterwe
ht
2
Stopper
pin
3
Heat
control
valve
Fig
ET
21
Cold
operation
of
counte
weigh
t
EC246
1
Counterweight
2
Stopper
pin
3
Heat
control
valve
Fig
ET
22
Hot
operation
of
counter
weight
ET
14
2
With
engine
stopped
visually
check
E
F
E
system
for
the
following
items
I
Thermostat
spring
for
dismount
ing
2
Stopper
pin
for
bend
and
count
er
weight
stop
position
for
dislocation
3
Check
heat
control
valve
for
malfunction
due
to
break
of
key
that
locates
counterweight
to
valve
shaft
4
Check
axial
clearance
between
heat
control
valve
and
exhaust
mani
fold
Correct
clearance
is
0
7
to
1
5
mm
0
028
to
0
059
in
5
Check
welded
portion
of
heat
control
valve
and
valve
shaft
for
any
indication
of
crack
or
flaking
6
Rotate
heat
control
valve
shaft
with
a
fmger
and
check
for
binding
between
shaft
and
bushing
in
closing
and
opening
operation
of
heat
control
valve
If
any
binding
is
felt
in
rotating
operation
move
valve
shaft
in
the
rotation
direction
several
times
If
this
operation
does
not
correct
binding
condition
it
is
due
to
seizure
between
shaft
and
bushing
and
exhaust
mani
fold
should
be
replaced
as
an
assem
bly
CHECKING
SPARK
TIMING
CONTROL
SYSTEM
This
system
is
installed
on
non
California
automatic
transmission
models
SPARK
DELAY
VALVE
Automatic
transmission
models
only
This
valve
delays
vacuum
spark
advance
during
rapid
acceleration
it
also
cuts
off
the
vacuwn
spark
advance
imme
iately
upon
deceleration
The
valve
is
designed
for
one
way
opera
tion
and
consists
of
a
one
way
umbrel
la
valve
and
sintered
steel
fluidic
restrictor
Page 30 of 537

r
ADJUSTMENT
OF
SET
PRESSURE
OF
BOOST
CONTROLLED
DECELERATION
DEVICE
B
C
D
D
Generally
it
is
unnecessary
to
ad
just
the
B
C
D
D
however
if
it
should
become
necessary
to
adjust
it
the
procedure
is
as
follows
Prepare
the
foUowlnB
tools
I
Tachometer
to
measure
the
en
gine
speed
while
idling
and
a
screw
driver
2
A
vacuum
gauge
connecting
pipe
Note
A
qui
k
response
type
boost
gauge
such
as
Bourdon
s
type
is
recommended
a
mercury
type
manometer
should
not
be
used
To
properly
set
the
B
C
D
D
set
pressure
proceed
as
follows
I
Remove
the
harness
of
solenoid
valve
TO
D
D
solenrod
VT
FJ
1
B
C
D
D
solenni
valve
harness
J
ri
y
EF262
F
g
ET
32
Removing
harneS5
of
solenoid
valve
2
Connect
rubber
hose
between
vacuum
gauge
and
intake
manifold
as
shown
Fig
ET
33
Connecting
vacuum
gauge
3
Warm
up
the
engine
until
it
is
heated
to
operating
temperature
Then
adjust
the
engine
at
normal
Engine
Tune
up
idling
setting
Refer
to
the
item
Idling
Adjustment
in
page
ET
II
Idling
engine
speed
Manual
transmission
750
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
D
position
650
rpm
4
Run
the
engine
under
no
load
Increase
engine
speed
to
3
000
to
3
500
rpm
then
quickly
close
throttle
valve
5
At
the
time
the
manifold
vacuum
pressure
increases
abruptly
to
600
mmHg
23
62
inHg
or
above
and
then
gradually
decreases
to
the
level
set
at
idling
6
Check
that
the
B
C
D
D
set
pres
sure
is
within
the
specified
pressure
Specified
pressure
0
m
sea
level
and
760
mmHg
30
inHg
atmos
pheric
pressure
Manual
transmission
510
to
550
mmHg
20
1
to
21
7
inHg
Automatic
transmission
490
to
530
mmHg
19
3
to
20
9
inHg
Note
When
checking
the
set
pressure
of
B
C
D
D
find
the
specified
set
pressure
in
Figure
IT
36
from
the
atmospheric
pressure
and
altitutde
of
the
given
location
For
example
if
a
manual
transmis
sion
model
vehicle
is
located
at
an
altitude
of
1
000
m
3
280
ft
the
specified
set
preSsure
for
B
C
D
D
445
mmHg
17
5
inHg
7
If
it
is
higher
than
the
set
level
turn
the
adjusting
screw
counter
clockwise
or
nut
clockwise
until
correct
adjustment
is
made
Non
California
models
Adjusting
screw
type
California
models
Adjusting
nut
type
Note
When
adjusting
B
C
D
D
for
California
models
turn
adjusting
nut
in
or
out
with
lock
spring
in
place
Always
set
lock
spring
prop
erly
to
prevent
changes
in
set
pres
sure
ET
18
Non
california
models
1
Adjusting
screw
2
Cover
e
ET037
California
models
r
1
Adjusting
nut
2
Lock
spring
EC692
Fig
ET
34
Adjusting
Bet
pressure
8
Race
the
engine
and
check
for
adjustment
9
If
it
is
lower
than
the
set
level
turn
the
adjusting
screw
or
nut
until
correct
adjustment
is
made
10
Race
the
engine
and
check
for
adjustment
If
engine
speed
cannot
be
decreased
to
idling
when
checking
B
C
D
D
set
pressure
proceed
as
follows
When
the
engine
speed
does
not
fall
to
idling
speed
it
is
necessary
to
reduce
the
negative
idling
pressure
of
the
manifold
to
lower
than
the
set
pressure
of
the
B
C
D
D
The
engine
speed
will
not
drop
to
idling
speed
when
the
negative
idling
pressure
is
higher
than
the
set
pressure
of
the
B
C
D
D
In
this
case
the
engine
must
be
labored
by
I
road
test
or
2
chassis
dynamometer
or
3
by
raising
up
rear
suspension
member
on
a
stand
accel
erating
the
vehicle
to
64
to
80
krn
h
40
to
50
MPH
in
top
gear
manual
transmission
or
in
D
position
auto
matic
transmission
and
then
releasing
the
accelerator
pedal
and
letting
the
vehicle
decelerate
After
doing
this
check
whether
the
B
C
D
D
set
pres
sure
is
at
the
predetermined
value
or
not
Page 91 of 537

DESCRIPTION
COOLANT
LEVEL
DRAINING
AND
FLUSHING
THE
COOLING
SYSTEM
WATER
PUMP
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
AND
ADJUSTMENT
TORQUE
COUPLING
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
DESCRIPTION
The
cooling
system
is
of
the
con
ventional
pressure
type
A
centrifugal
pump
installed
on
the
timing
chain
cover
serves
to
circulate
the
coolant
The
pressure
type
radiator
filler
cap
installed
on
the
radiator
operates
the
cooling
system
at
higher
than
atmos
pheric
pressure
The
higher
pressure
raises
the
boiling
point
of
the
coolant
and
in
Cooling
System
COOLING
SYSTEM
CONTENTS
CO
2
CO
2
OISASSEMBL
Y
INSPECTION
TEM
COUPLlNG
INSPECTION
THERMOSTAT
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
RADIATOR
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
INSPECTION
CO
2
CO
2
CO
3
CO
3
CO
3
CO
3
CO
4
creases
the
cooling
efficiency
of
the
radiator
When
the
thermostat
is
closed
the
coolant
remains
in
the
cylinder
head
and
block
for
swift
warming
up
of
the
engine
After
it
reaches
normal
oper
ating
temperature
the
coolant
circu
lates
through
the
radiator
The
cooling
fan
drive
is
of
a
coupling
type
COOLANT
LEVEL
The
coolant
level
should
be
check
ed
and
maintained
at
SO
mm
1
97
in
below
the
upper
face
of
filler
neck
when
the
engine
is
cold
C0055
Fig
CO
I
Cooling
ry
lem
Caution
To
avoid
serious
personal
injury
never
remove
I3diator
cap
quickly
when
engine
is
hot
Sudden
release
of
cooling
system
pressure
is
very
dangerous
CO
2
CO
4
CO
4
CO
4
CO
5
CO
5
CO
5
CO
5
CO
5
CO
5
CO
6
If
it
is
necessary
to
remove
radiator
cap
wben
radiator
is
hot
turn
cap
slowly
counterclockwise
to
the
r
step
After
all
pressure
in
the
cool
ing
system
is
released
tom
cap
passing
the
stop
and
remove
it
DRAINING
AND
FLUSHING
THE
COOLING
SYSTEM
To
drain
the
cooling
system
re
move
radiator
cap
release
drain
cock
at
the
bottom
of
radiator
and
drain
plug
on
the
right
side
of
cylinder
block
If
the
heater
system
is
installed
set
heater
temperature
control
valve
to
open
position
After
the
coolant
is
drained
completely
close
drain
cock
and
plug
and
refill
the
system
with
clean
soft
water
WATER
PUMP
The
water
pump
cooling
fan
pulley
and
torque
coupling
are
a
unitized
construction
The
water
pump
is
of
a
centrifugal
type
which
is
mounted
on
the
engine
front
cover
Page 118 of 537
rpm
two
or
three
iimes
under
no
load
and
make
sure
that
specified
CO
per
centage
is
obtained
12
Connect
air
hose
to
air
check
valve
If
engine
speed
increases
readjust
it
to
the
specified
speed
with
throttle
adjustingsqew
CO
idle
edJustment
without
CO
meter
If
CO
meter
is
not
available
the
following
procedures
may
be
used
L
Check
carburetor
pipes
for
proper
connection
2
Warm
up
engine
until
water
tem
perature
indicator
points
to
the
middle
of
gauge
The
procedure
to
warm
up
engine
is
not
specifically
recom
mended
Either
driving
vehicle
or
oper
ating
engine
at
no
load
will
be
good
3
Make
sure
that
water
temperature
indicator
points
to
the
middle
Further
keep
engine
running
at
about
2
000
rpm
for
about
5
minutes
without
applying
load
to
engine
in
order
to
stabilize
engine
condition
Engine
hood
should
be
open
4
Run
engine
for
about
10
minutes
at
idling
speed
During
this
10
minutes
proceed
as
described
in
steps
5
to
9
below
5
Remove
air
hose
between
3
way
connector
5
way
connector
for
Cali
fornia
models
and
air
check
valve
shown
in
Figure
EF
35
Plug
the
dis
connected
hose
19
prevent
dust
from
entering
6
Race
engine
1
500
to
2
000
rpm
two
or
three
times
under
no
load
then
run
engine
for
one
minute
at
idling
speed
7
Adjust
throttle
adjusting
screw
so
that
engine
speeds
are
as
indicated
below
Engine
speed
Manual
transmission
815
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
D
position
670
rpm
8
Check
ignition
timing
if
neces
sary
adjust
it
to
the
value
required
by
specifications
This
operation
need
not
be
carried
out
at
1
600
km
1
000
miles
service
9
At
about
10
minutes
after
engine
Engine
Fuel
is
run
at
idling
speed
adjust
idle
adjusting
screw
until
maximum
rpm
is
obtained
10
Repeat
procedures
as
described
in
steps
6
7
and
9
above
until
engine
speed
at
best
idle
mixture
is
815
rpm
for
manual
transmission
models
and
670
rpm
for
automatic
transmission
models
in
D
position
Adjustment
in
step
9
can
be
carried
out
right
after
step
7
11
Turn
the
idle
adjusting
screw
clockwise
until
engine
speed
drops
off
below
specified
rpm
Engine
speed
drops
off
Manual
transmission
60
to
70
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
D
position
15
to
25
rpm
12
Connect
air
hose
to
air
check
valve
If
engine
speed
increases
readjust
it
to
the
specified
speed
with
throttle
adjusting
screw
Idle
limiter
cep
Do
not
remove
this
idle
limiter
cap
unless
necessary
If
this
unit
is
re
moved
it
must
be
readjusted
at
lime
of
installation
To
adjust
proceed
as
follows
I
After
adjusting
throttle
or
idle
speed
adjusting
screw
check
to
be
sure
that
the
amount
of
CO
contained
in
exhaust
gases
meets
the
established
standard
2
Install
idle
limiter
cap
in
position
making
sure
that
the
adjusting
screw
can
rotate
another
1
8
turn
in
the
CO
RICH
direction
Carbo
to
per
CO
rich
450
lIS
rotation
t
CO
lean
J
SQ
dl
lim
ET031
1
e
Iter
cap
Fig
EF
36
Setting
idle
limiter
cap
FUEL
LEVEL
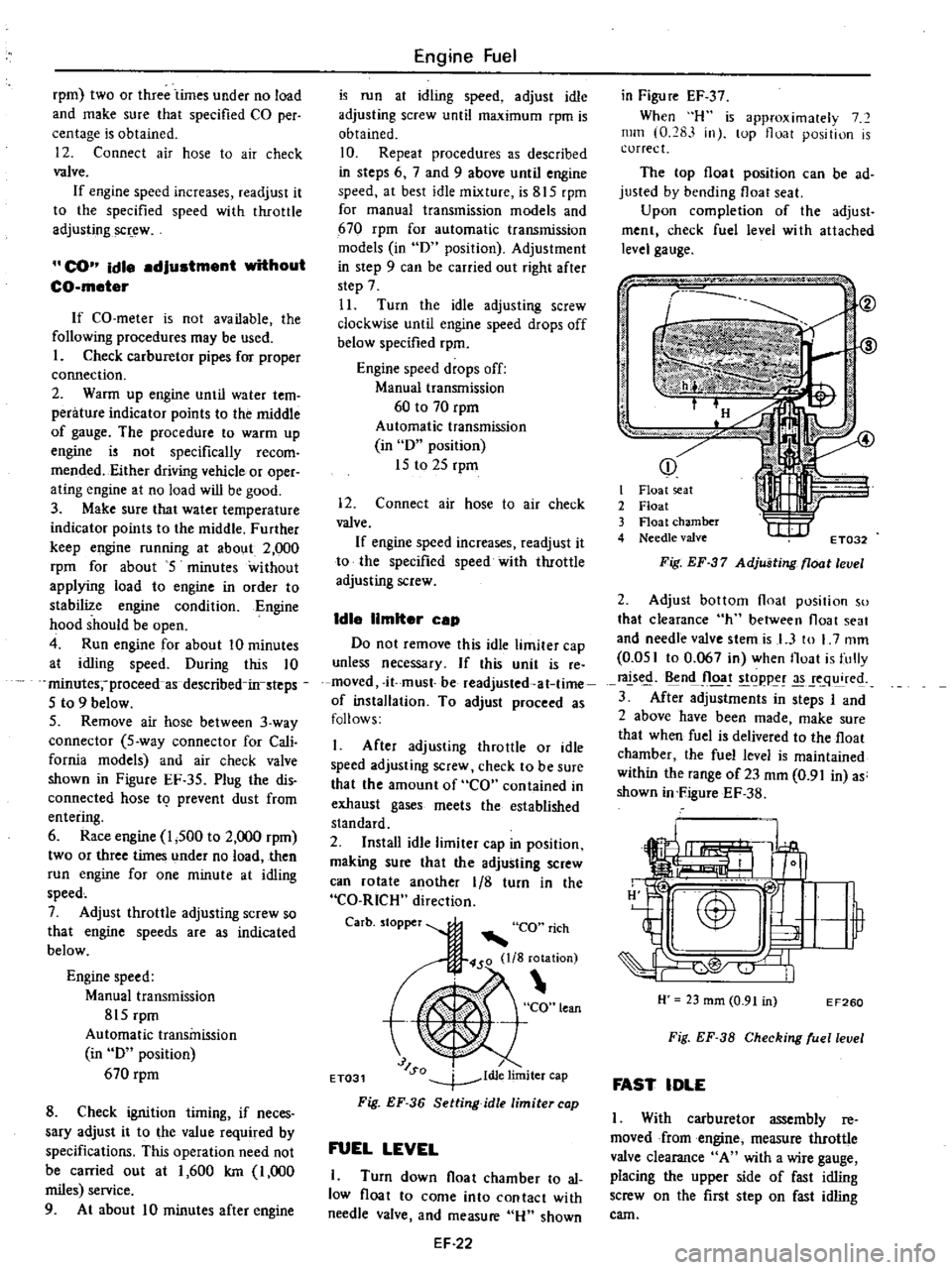
1
Turn
down
float
chamber
to
al
low
float
to
come
into
contact
with
needle
valve
and
measure
Hu
shown
EF
22
in
Figu
re
EF
37
When
H
is
approximalely
7
mill
0
283
in
lOp
float
position
is
correct
The
top
float
position
can
be
ad
justed
by
bending
float
seat
Upon
completion
of
the
adjust
ment
check
fuel
level
wi
th
attached
level
gauge
p
j
i
I
it
I
Float
seat
2
Float
3
Float
chamber
4
Needle
valve
t
I
IIf
ET032
Fig
EF
37
Adjusting
float
level
2
Adjust
bottom
float
position
so
that
clearance
h
between
float
seat
and
needle
valve
stemis
I
3
to
L
7
mm
0
051
to
0
067
in
when
Iloat
is
fully
rals
n
Jloa
t
goppe
q
re
3
After
adjustments
in
steps
I
and
2
above
have
been
made
make
sure
that
when
fuel
is
delivered
to
the
float
chamber
the
fuel
level
is
maintained
within
the
range
of23
mm
0
91
in
as
shown
in
FigureEF
38
H
23
mm
0
91
in
EF260
Fig
EF
38
Checking
ruellevel
FAST
IDLE
I
With
carburetor
assembly
reo
moved
from
engine
measure
throttle
valve
clearance
A
with
a
wire
gauge
placing
the
upper
side
of
fast
idling
screw
on
the
first
step
on
fast
idling
cam
Page 123 of 537
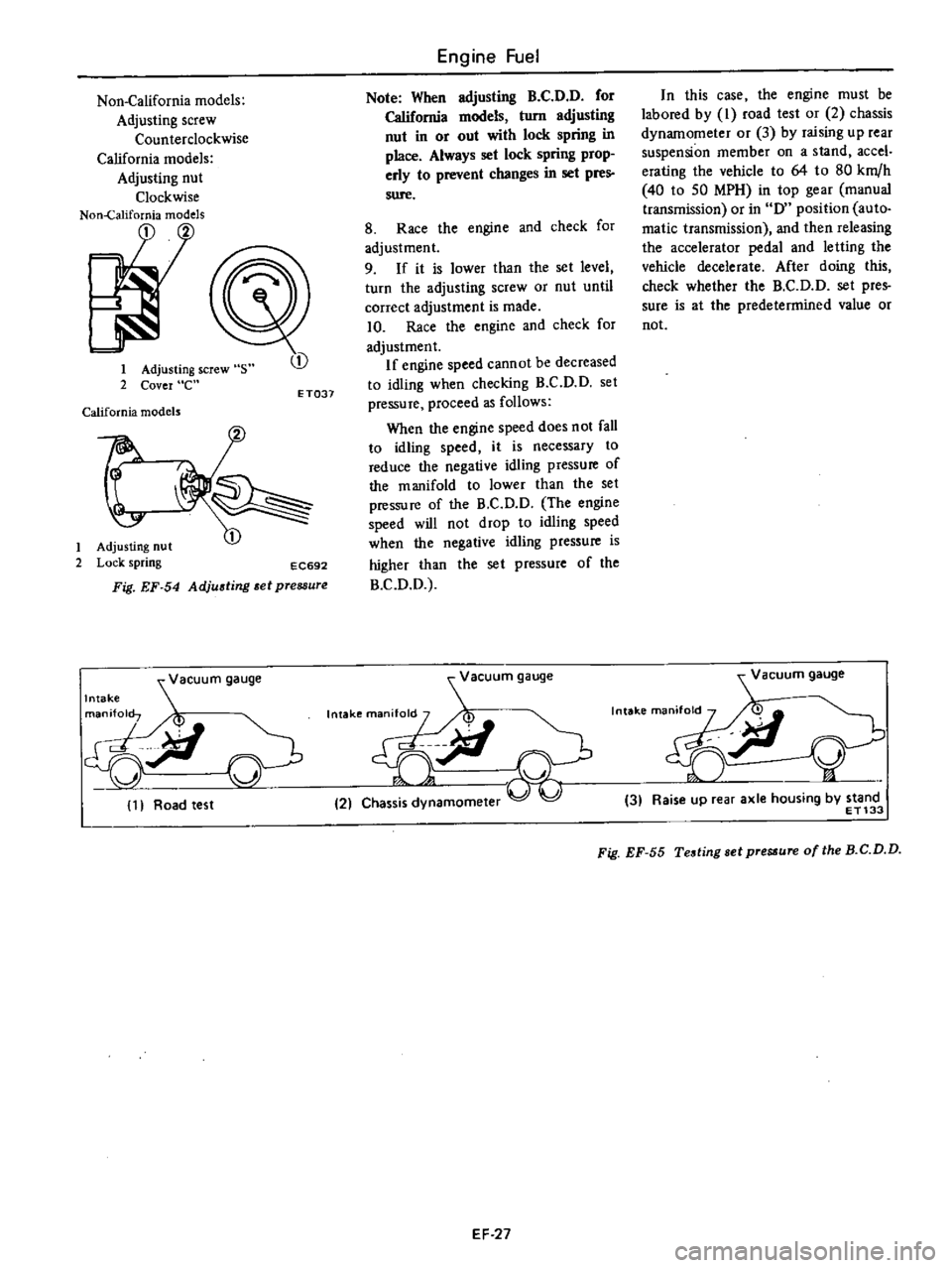
Non
California
models
Adjusting
screw
Counterclockwise
California
models
Adjusting
nut
Clockwise
Non
California
models
1
2
1
Adjusting
screw
s
2
Cover
e
California
models
t
1
Adjusting
nut
2
Lock
spring
EC692
Fig
EF
54
Adjusting
et
pressure
vacuum
gauge
Intake
gjl
11
Road
test
CD
ET037
Engine
Fuel
Note
When
adjusting
B
C
D
D
for
California
models
turn
adjusting
nut
in
or
out
with
lock
spring
in
place
Always
set
lock
spring
prop
erly
to
prevent
changes
in
set
pres
sure
8
Race
the
engine
and
check
for
adjustment
9
If
it
is
lower
than
the
set
level
turn
the
adjusting
screw
or
nut
until
correct
adjustment
is
made
10
Race
the
engine
and
check
for
adjustment
If
engine
speed
cannot
be
decreased
to
idling
when
checking
B
C
D
D
set
pressure
proceed
as
follows
When
the
engine
speed
does
not
fall
to
idling
speed
it
is
necessary
to
reduce
the
negative
idling
pressure
of
the
manifold
to
lower
than
the
set
pressure
of
the
B
C
D
O
The
engine
speed
will
not
drop
to
idling
speed
when
the
negative
idling
pressure
is
higher
Ihan
the
sel
pressure
of
the
B
C
O
O
acuum
gauge
Intakema
M
V
9iI
21
Chas
amomeler
In
this
case
the
engine
must
be
labored
by
I
road
test
or
2
chassis
dynamometer
or
3
by
raising
up
rear
suspension
member
on
a
stand
accel
erating
the
vehicle
to
64
to
80
km
h
40
10
50
MPH
in
top
gear
manual
transmission
or
in
0
position
auto
matic
transmission
and
then
releasing
the
accelerator
pedal
and
letting
the
vehicle
decelerate
After
doing
this
check
whether
the
B
C
O
D
set
pres
sure
is
at
the
predetermined
value
or
not
Vacuum
gauge
n
i
Y
3
Raise
up
rear
axle
housing
by
stand
ET133
Fig
EF
55
Testing
sel
pre
ure
of
the
B
C
D
D
EF
27
Page 139 of 537
Emission
Control
System
EARLY
FUEL
EVAPORATIVE
SYSTEM
E
F
E
DESCRIPTION
spring
and
counterweight
which
are
assembled
on
the
valve
shaft
projecting
to
the
rear
outside
of
the
exhaust
manifold
The
counterweight
is
se
cured
to
the
valve
shaft
with
key
bolt
and
snap
ring
EC
4
A
control
valve
welded
to
the
valve
shaft
is
wtalled
on
the
exhaust
manifold
through
bushing
This
con
trol
valve
is
called
Heat
control
valve
The
heat
control
valve
is
ac
luated
by
the
coil
spring
thermostat
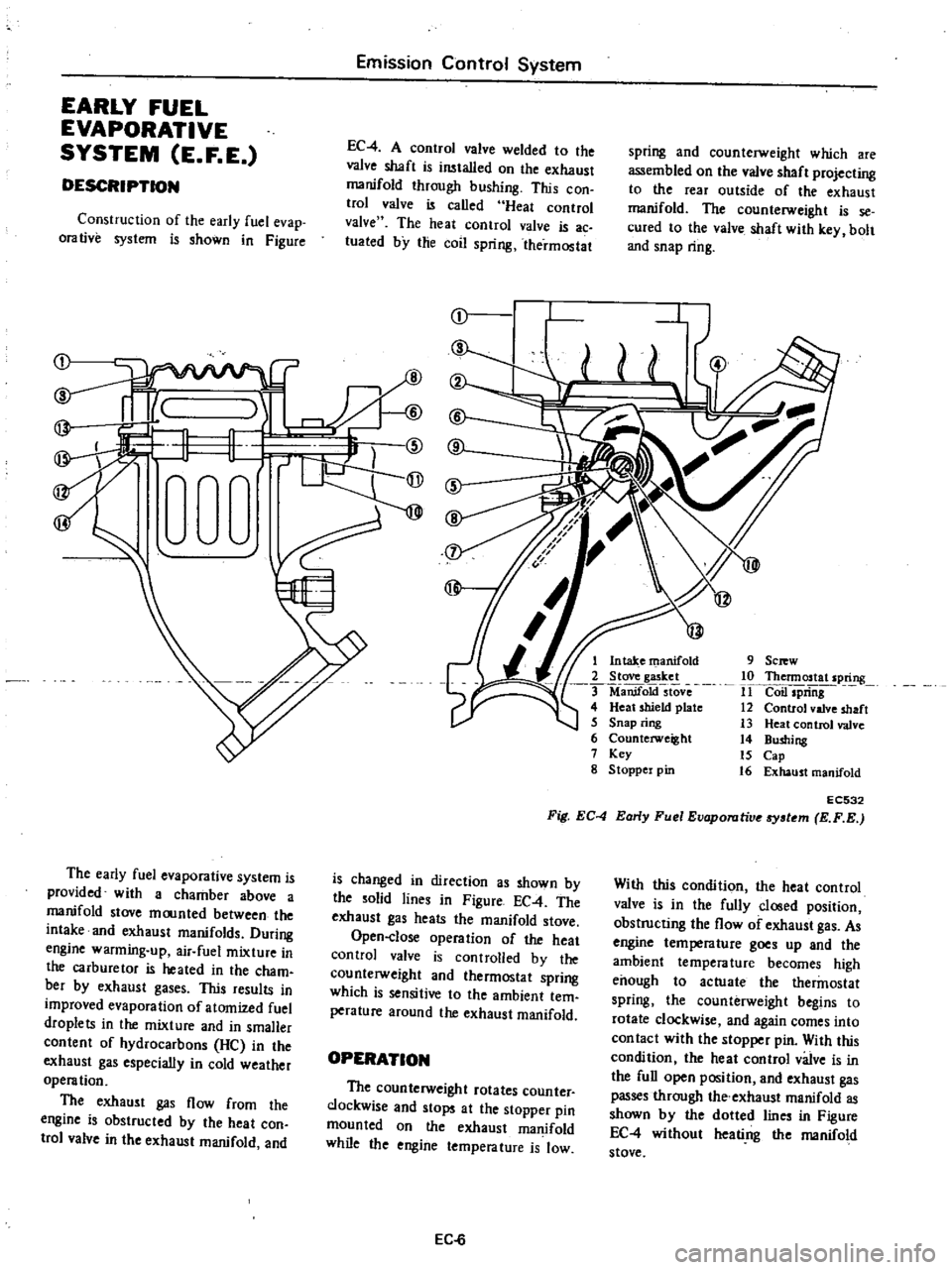
Construction
of
the
early
fuel
evap
orative
system
is
shown
in
Figure
r
I
1
@
rW
9
Sc
w
10
Thennostat
spring
11
Coil
spriiig
12
Control
valve
shaft
13
Heat
control
valve
14
Bushing
15
Cap
16
Exhaust
manifold
1
Intake
manifold
2
Stove
gasket
ManifoktstOve
4
Heat
shield
plate
5
Snap
ring
6
Counterweight
7
Key
g
Stoppel
pin
EC532
Fig
EC
4
Early
Fuel
Evaporutive
tem
E
F
E
The
early
fuel
evaporative
system
is
provided
with
a
chamber
above
a
manifold
stove
moonted
between
the
intake
and
exhaust
manifolds
During
engine
warming
up
air
fuel
mixture
in
the
carburetor
is
heated
in
the
cham
bet
by
exhaust
gases
This
results
in
improved
evaporation
of
atomized
fuel
droplets
in
the
mixture
and
in
smaller
content
of
hydrocarbons
He
in
the
exhaust
gas
especially
in
cold
weather
operation
The
exhaust
gas
flow
from
the
engine
is
obstructed
by
the
heat
con
trol
valve
in
the
exhaust
manifold
and
is
changed
in
direction
as
shown
by
the
solid
lines
in
Figure
EC
4
The
exhaust
gas
heats
the
manifold
stove
Open
close
operation
of
the
heat
control
valve
is
controlled
by
the
counterweight
and
thermostat
spring
which
is
sensitive
to
the
ambient
tem
perature
around
the
exhaust
manifold
With
this
condition
the
heat
control
valve
is
in
the
fully
closed
position
obstructing
the
flow
of
exhaust
gas
As
engine
tempera
lure
goes
up
and
the
ambient
temperature
becomes
high
enough
to
actuate
the
thermostat
spring
the
counterweight
begins
to
rotate
clockwise
and
again
comes
into
con
tact
with
the
stopper
pin
With
this
condition
the
heat
control
valve
is
in
the
full
open
position
and
exhaust
gas
passes
through
the
exhaust
manifold
as
shown
by
the
dotted
lines
in
Figure
EC
4
without
heati
ng
the
manifold
stove
OPERATION
The
counterweight
rotates
counter
clockwise
and
stops
at
the
stopper
pin
mounted
on
the
exhaust
manifold
while
the
engine
temperature
is
low
EC
6
Page 140 of 537
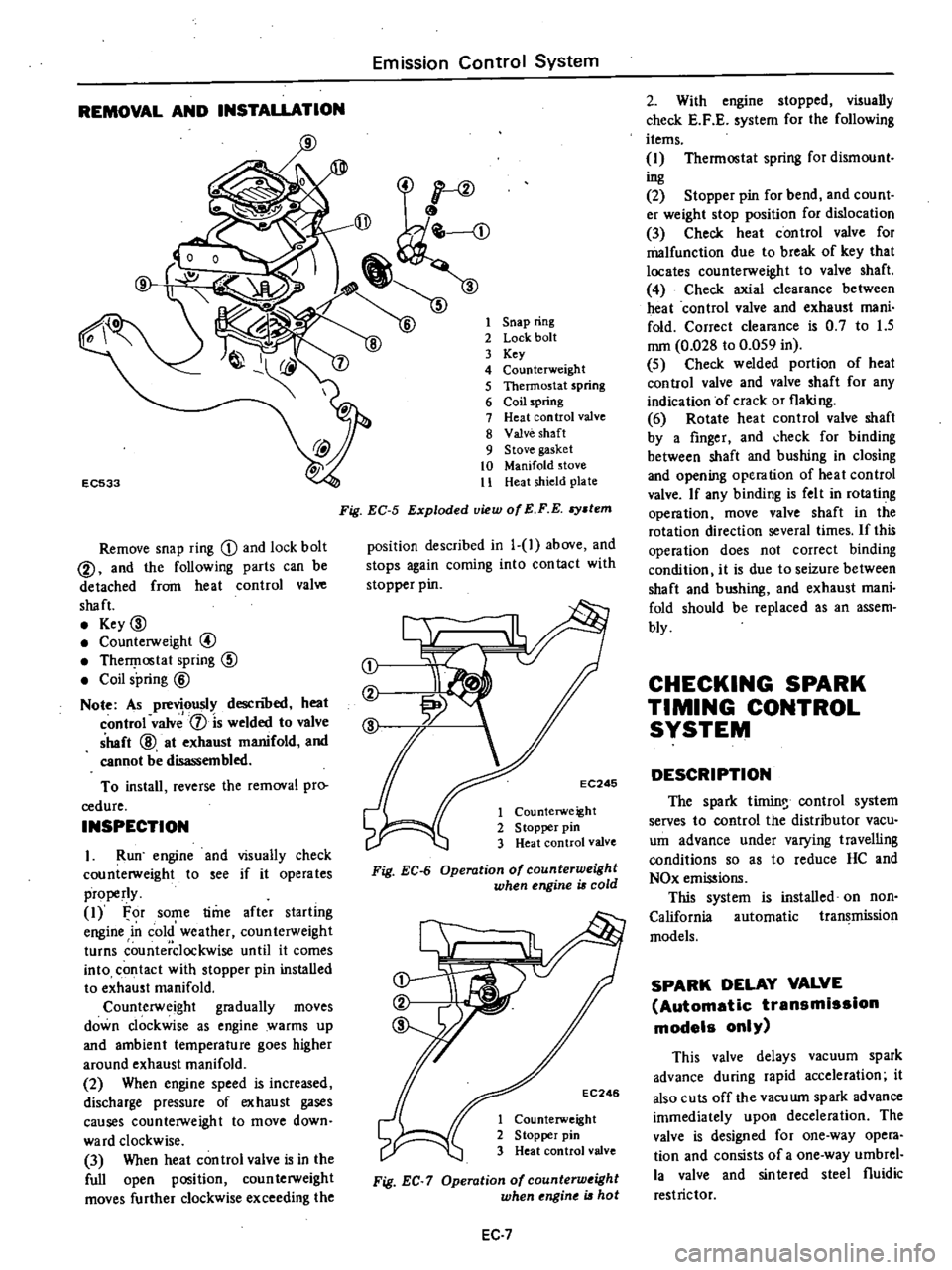
REMOVAL
AND
INSTAUATION
Emission
Control
System
EC533
Remove
snap
ring
D
and
lock
bolt
@
and
the
following
parts
can
be
detached
from
heat
control
valve
shaft
Key
00
Counterweight
@
TherI
lostat
spring
CID
Coil
spring
@
Note
As
previously
descnoed
heat
control
valv
1
is
welded
to
valve
shaft
@
at
exhaust
manifold
and
cannot
be
disassembled
To
install
reverse
the
removal
pro
cedure
INSPECTION
I
Run
engine
and
visually
check
counterweight
to
see
if
it
operates
properly
1
For
some
time
after
starling
engine
in
cold
weather
counterweight
turns
counterclockwise
until
it
comes
into
contact
with
stopper
pin
installed
to
exhaust
manifold
Counterweight
gradually
moves
down
clockwise
as
engine
warms
up
and
ambient
temperature
goes
higher
around
exhaust
manifold
2
When
engine
speed
is
increased
discharge
pressure
of
exhaust
gases
causes
counterweight
to
move
down
ward
clockwise
3
When
heat
con
trol
valve
is
in
the
full
open
position
coun
terweight
moves
further
clockwise
exceeding
the
1
Snap
ring
2
Lock
bolt
3
Key
4
Counterweight
5
Thermostat
spring
6
Coil
spring
7
Heat
control
valve
8
Valve
shaft
9
Stove
gasket
10
Manifold
stove
11
Heat
shield
plate
Fig
EC
5
Exploded
view
of
E
F
E
stem
position
described
in
1
1
above
and
stops
again
coming
into
con
tact
with
stopper
pin
j
EC246
1
Counterweight
2
S
topper
pin
3
Heat
control
valve
Fig
EC
6
Operation
of
counterweight
when
engine
is
cold
EC246
1
Counterweight
2
Stopper
pin
3
Heat
control
valve
Fig
EC
7
Operation
of
counterw
ight
when
ngine
is
hot
EC
7
2
With
engine
stopped
visually
check
E
F
E
system
for
the
following
items
1
Thermostat
spring
for
dismount
ing
2
Stopper
pin
for
bend
and
count
er
weight
stop
position
for
dislocation
3
Check
heat
control
valve
for
malfunction
due
to
break
of
key
that
locates
counterweight
to
valve
shaft
4
Check
axial
clearance
between
heat
control
valve
and
exhaust
mani
fold
Correct
clearance
is
0
7
to
1
5
mm
0
028
to
0
059
in
5
Check
welded
portion
of
heat
control
valve
and
valve
shaft
for
any
indication
of
crack
or
flaking
6
Rotate
heat
control
valve
shaft
by
a
finger
and
check
for
binding
between
shaft
and
bushing
in
closing
and
opening
operation
of
heat
control
valve
If
any
binding
is
felt
in
rotating
operation
move
valve
shaft
in
the
rotation
direction
several
times
If
this
operation
does
not
correct
binding
condition
it
is
due
to
seizure
between
shaft
and
bushing
and
exhaust
mani
fold
should
be
replaced
as
an
assem
bly
CHECKING
SPARK
TIMING
CONTROL
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The
spark
tirnin
control
system
serves
to
control
the
distributor
vacu
um
advance
under
varying
travelling
conditions
so
as
to
reduce
HC
and
NOx
emissions
This
system
is
installed
on
non
California
automatic
transmission
models
SPARK
DELAY
VALVE
Automatic
transmission
models
only
This
valve
delays
vacuum
spark
advance
during
rapid
acceleration
it
also
cuts
off
the
vacuwn
spark
advance
immediately
upon
deceleration
The
valve
is
designed
for
one
way
opera
tion
and
consists
of
a
one
way
umbrel
la
valve
and
sinlered
steel
fluidic
restrictor
Page 173 of 537
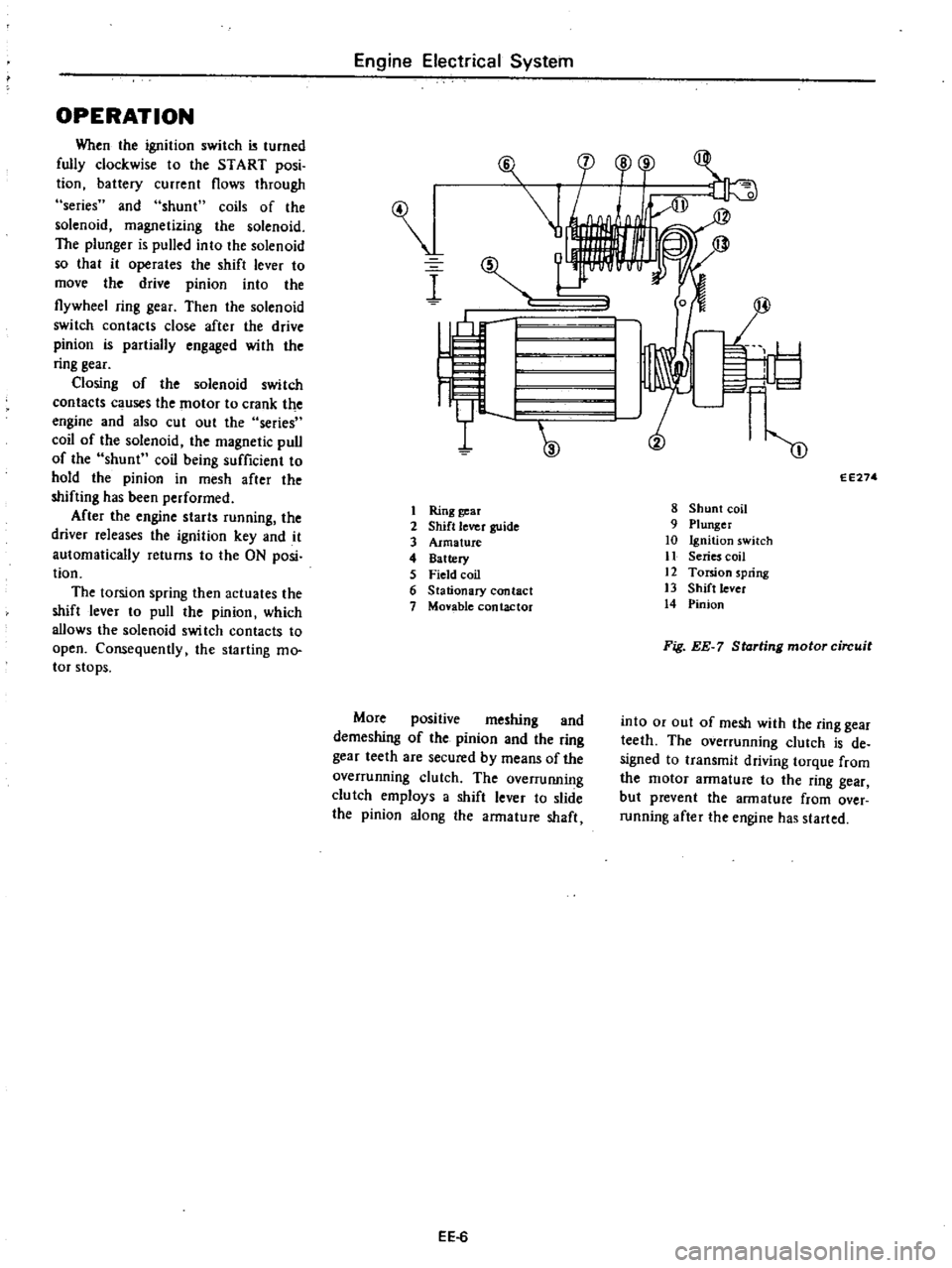
OPERATION
When
the
ignition
switch
turned
fully
clockwise
to
the
START
posi
tion
battery
current
flows
through
series
and
shunt
coils
of
the
solenoid
magnetizing
the
solenoid
The
plunger
is
pulled
into
the
solenoid
so
that
it
operates
the
shift
lever
to
move
the
drive
pinion
into
the
flywheel
ring
gear
Then
the
solenoid
switch
contacts
close
after
the
drive
pinion
is
partially
engaged
with
the
ring
gear
Closing
of
the
solenoid
switch
contacts
c
uses
the
motor
to
crank
the
engine
and
also
cut
out
the
series
coil
of
the
solenoid
the
magnetic
pull
of
the
shunt
coil
being
sufficient
to
hold
the
pinion
in
mesh
after
the
shifting
has
been
performed
After
the
engine
starts
running
the
driver
releases
the
ignition
key
and
it
automatically
returns
to
the
ON
posi
tion
The
torsion
spring
then
actuates
the
shift
lever
to
pull
the
pinion
which
allows
the
solenoid
swi
tch
contacts
to
open
Consequently
the
starting
mo
tor
stops
Engine
Electrical
System
I
I
Ring
gear
2
Shift
lever
guide
3
Armature
4
Battery
5
Field
coil
6
Stationary
contact
7
Monble
contactor
More
positive
meshing
and
demeshing
of
the
pinion
and
the
ring
gear
teeth
are
secured
by
means
of
the
overrunning
clutch
The
overruIUling
clutch
employs
a
shift
lever
to
slide
the
pinion
along
the
armature
shaft
EE
6
F
l
cp
o
r
1
I
I
W
m
EE274
8
Shunt
coil
9
Plunger
10
Ignition
switch
11
Series
coil
12
Torsion
spring
13
Shift
lever
14
Pinion
Fig
EE
7
Starting
motor
circuit
into
or
out
of
mesh
with
the
ring
gear
teeth
The
overrunning
clutch
is
de
signed
to
transmit
driving
torque
from
the
motor
armature
to
the
ring
gear
but
prevent
the
armature
from
over
running
after
the
engine
has
started
Page 190 of 537
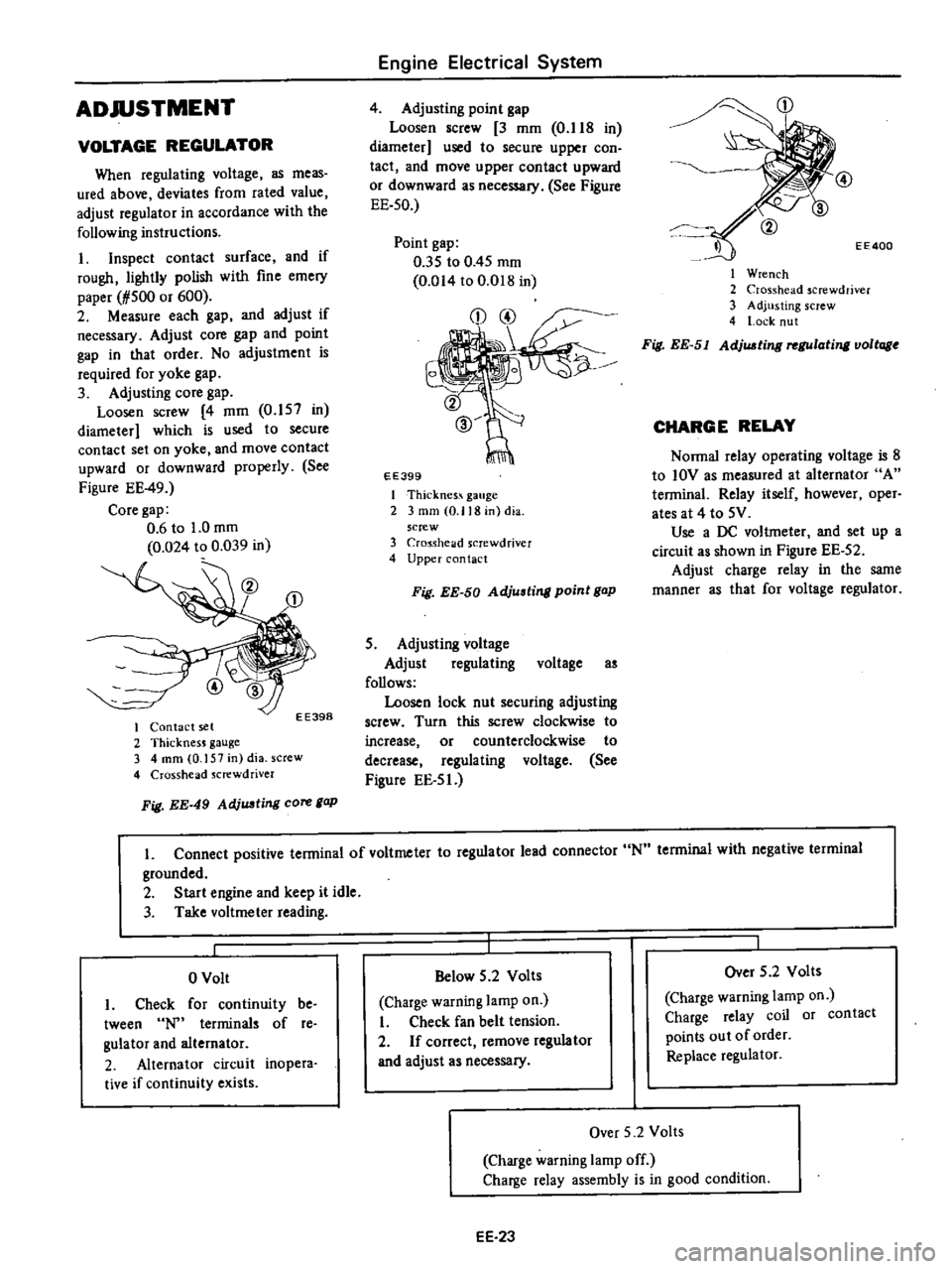
ADJUSTMENT
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
When
regulating
voltage
as
meas
ured
above
deviates
from
rated
value
adjust
regulator
in
accordance
with
the
following
instructions
I
Inspect
contact
surface
and
if
rough
lightly
polish
with
fine
emery
paper
1
500
or
600
2
Measure
each
gap
and
adjust
if
necessary
Adjust
core
gap
and
point
gap
in
that
order
No
adjustment
is
required
for
yoke
gap
3
Adjusting
core
gap
Loosen
screw
4
mm
0
157
in
diameter
which
is
used
to
secure
contact
set
on
yoke
and
move
contact
upward
or
downward
properly
See
Figure
EE
49
Core
gap
0
6
to
1
0
mm
0
024
to
0
039
in
EE398
I
Contact
set
2
ThicknesJ
gauge
3
4
mm
0
157
in
dia
screw
4
Crosshead
Jcrewdriver
Fig
EE
49
AdjUJJting
core
gap
Engine
Electrical
System
4
Adjusting
point
gap
Loosen
screw
3
mm
O
lIS
in
diameter
used
to
secure
upper
con
tact
and
move
upper
contact
upward
or
downward
as
necessary
See
Figure
EE
50
Point
gap
035
to
0
45
mm
0
014
to
O
D1S
in
EE399
I
Thicknes
gauge
2
3
mm
0
118
in
dia
screw
3
Cro
Sshelld
screwdriver
4
Upper
contact
Fig
EE
50
Adjusting
point
gap
5
Adjusting
voltage
Adjust
regulating
voltage
as
follows
Loosen
lock
nut
securing
adjusting
screw
Turn
this
screw
clockwise
to
increase
or
counterclockwise
to
decrease
regulating
voltage
See
Figure
EE
5
J
CD
EE400
I
Wrench
2
Crosshead
screwdriver
3
Adjusting
screw
4
l
ock
nut
Fig
EE
51
AdjUJJting
rel
Ulating
voltage
CHARGE
RELAY
Nonna
relay
operating
voltage
is
S
to
IOV
as
measured
at
alternator
A
tenninal
Relay
itself
however
oper
ates
at
4
to
5V
Use
a
DC
voltmeter
and
set
up
a
circuit
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
52
Adjust
charge
relay
in
the
same
manner
as
that
for
voltage
regulator
L
Connect
positive
tenninal
of
voltmeter
to
regulator
lead
connector
N
tenninal
with
negative
terminal
grounded
2
Start
engine
and
keep
it
idle
3
Take
voltmeter
reading
o
Volt
I
Check
for
continuity
be
tween
terminals
of
re
gulator
and
alternator
2
Alternator
circuit
inopera
tive
if
continuity
exists
Below
5
2
Volts
Charge
warning
lamp
on
I
Check
fan
belt
tension
2
If
correct
remove
regulator
and
adjust
as
necessary
Over
5
2
Volts
Charge
warning
lamp
on
Charge
relay
coil
or
contact
points
out
of
order
Replace
regulator
Over
5
2
Volts
Charge
warning
lamp
off
Charge
relay
assembly
is
in
good
condition
EE
23