lock DODGE NEON 1999 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 87 of 1200
portioning valve has a different part number. During
any service procedures identify valve assemblies by
supplier part number and or the color identification
band (Fig. 12).
CHASSIS TUBES AND HOSES
The purpose of the chassis brake tubes and flex
hoses is to transfer the pressurized brake fluid devel-
oped by the master cylinder to the wheel brakes of
the vehicle. The chassis tubes are steel with a corro-
sion resistant coating applied to the external surfaces
and the flex hoses are made of reinforced rubber. The
rubber flex hoses allow for the movement of the vehi-
cles suspension.
MASTER CYLINDER
This vehicle is available with three different mas-
ter cylinders. The vehicle uses screw-in proportioning
valves at the master cylinder or in-line proportioning
valves located in the rear chassis brake tubes instead
of a combination valve. With this new design, the
chassis brake tubes connect directly from the master
cylinder or HCU to the front and rear brake flex
hoses.
Vehicles not equipped with ABS use a standard
compensating port master cylinder, while vehicles
equipped with ABS use a center valve design mastercylinder. In addition, the non-ABS master cylinders
are a four outlet design with two screw-in proportion-
ing valves attached directly to the inboard side of the
master cylinder housing (Fig. 13). The ABS master
cylinder is a two outlet design (Fig. 14). The primary
and secondary outlet on the master cylinder are con-
nected directly to the hydraulic control portion of the
ICU (Fig. 14) Vehicles equipped with antilock brakes
use in-line proportioning valves mounted in the chas-
sis brake tubes going to the rear brakes. Vehicles
equipped with rear drum brakes use a master cylin-
der with a 21.0 mm bore diameter, while vehicles
equipped with rear disc brake use a 22.2 mm bore
master cylinder.
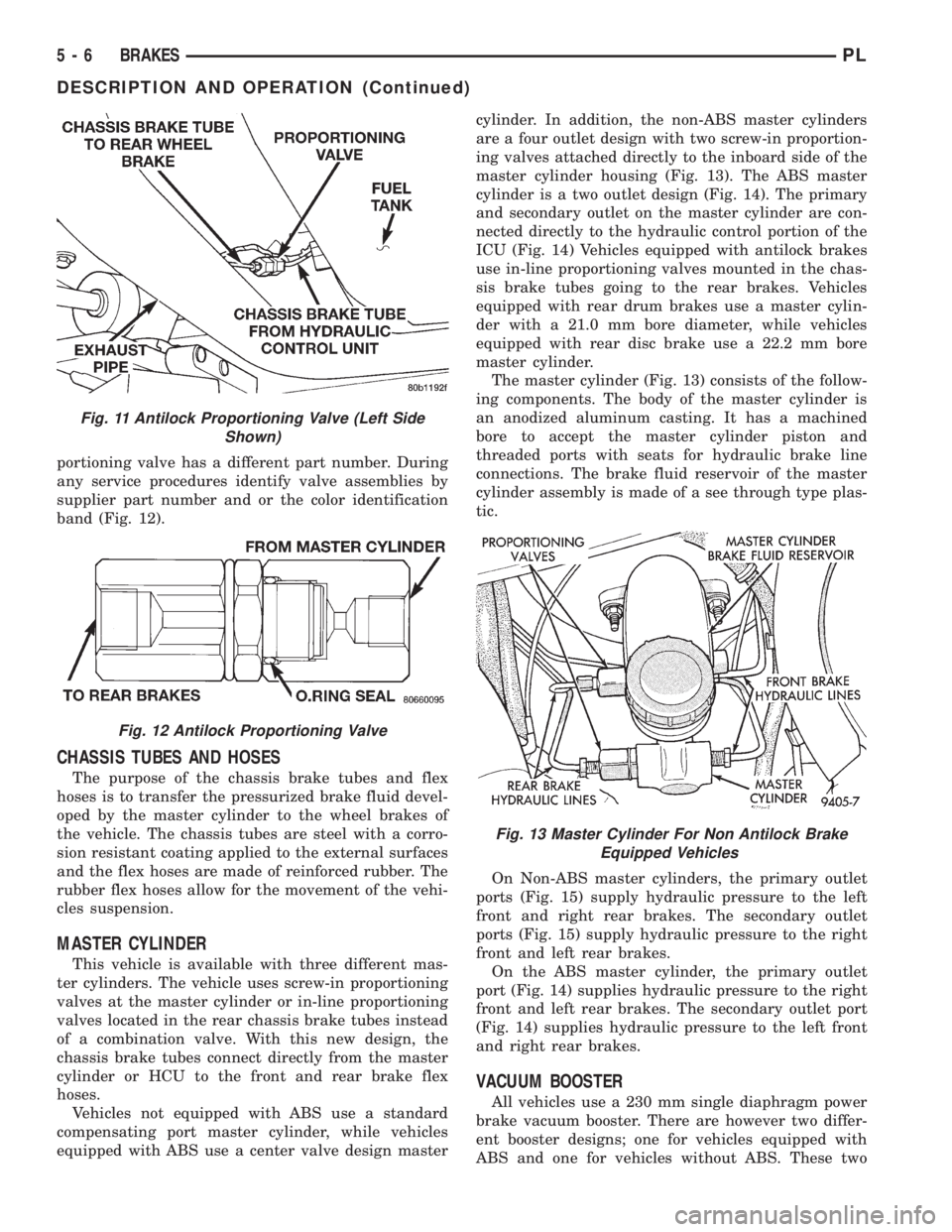
The master cylinder (Fig. 13) consists of the follow-
ing components. The body of the master cylinder is
an anodized aluminum casting. It has a machined
bore to accept the master cylinder piston and
threaded ports with seats for hydraulic brake line
connections. The brake fluid reservoir of the master
cylinder assembly is made of a see through type plas-
tic.
On Non-ABS master cylinders, the primary outlet
ports (Fig. 15) supply hydraulic pressure to the left
front and right rear brakes. The secondary outlet
ports (Fig. 15) supply hydraulic pressure to the right
front and left rear brakes.
On the ABS master cylinder, the primary outlet
port (Fig. 14) supplies hydraulic pressure to the right
front and left rear brakes. The secondary outlet port
(Fig. 14) supplies hydraulic pressure to the left front
and right rear brakes.
VACUUM BOOSTER
All vehicles use a 230 mm single diaphragm power
brake vacuum booster. There are however two differ-
ent booster designs; one for vehicles equipped with
ABS and one for vehicles without ABS. These two
Fig. 11 Antilock Proportioning Valve (Left Side
Shown)
Fig. 12 Antilock Proportioning Valve
Fig. 13 Master Cylinder For Non Antilock Brake
Equipped Vehicles
5 - 6 BRAKESPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 88 of 1200

boosters differ at the interface to the master cylinder.
If the power brake booster requires replacement be
sure it is replaced with the correct part.
The power brake booster can be identified by the
tag attached to the body of the booster assembly (Fig.
16). This tag contains the following information: The
production part number of the power booster assem-
bly, the date it was built, who manufactured it, and
brake sales code.
NOTE: The power brake booster assembly is not a
repairable part and must be replaced as a complete
unit if it is found to be faulty in any way. The power
booster vacuum check valve is not repairable but
can be replaced as an assembly.The power brake booster reduces the amount of
force required by the driver to obtain the necessary
hydraulic pressure to stop vehicle.
The power brake booster is vacuum operated. The
vacuum is supplied from the intake manifold on the
engine through the power brake booster check valve
(Fig. 16).
As the brake pedal is depressed, the power booster
input rod moves forward (Fig. 17). This opens and
closes valves in the power booster, allowing atmo-
spheric pressure to enter on one side of a diaphragm.
Engine vacuum is always present on the other side.
This difference in pressure forces the output rod of
the power booster (Fig. 17) out against the primary
piston of the master cylinder. As the pistons in the
master cylinder move forward this creates the
hydraulic pressure in the brake system.
Different engine options available for this vehicle
require that different vacuum hose routings be used.
The power brake vacuum booster assembly mounts
on the engine side of the dash panel. It is connected
to the brake pedal by the input push rod (Fig. 17). A
vacuum line connects the power booster to the intake
manifold. The master cylinder is bolted to the front
of the power brake vacuum booster assembly.
RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP
The red Brake warning lamp is located in the
instrument panel cluster and is used to indicate a
low brake fluid condition or that the parking brake is
applied. In addition, the brake warning lamp is
turned on as a bulb check by the ignition switch
when the ignition switch is placed in the crank posi-
tion. Problems with this system will generally be of
the type where the warning lamp fails to turn on
when it should, or remains on when it should not.
The warning lamp bulb is supplied a 12 volt igni-
tion feed anytime the ignition switch is on. The bulb
is then illuminated by completing the ground circuit
Fig. 14 Master Cylinder For Antilock Brake
Equipped Vehicles
Fig. 15 Non-ABS Master Cylinder Primary And
Secondary Ports
Fig. 16 Power Brake Booster Identification
PLBRAKES 5 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 89 of 1200

either through the park brake switch, the fluid level
sensor in the master cylinder reservoir, or the igni-
tion switch in the crank position.
The Brake Fluid Level sensor is located in the
brake fluid reservoir of the master cylinder assembly
(Fig. 18). The purpose of the sensor is to provide the
driver with an early warning that the brake fluid
level in the master cylinder reservoir has dropped to
below normal. This may indicate an abnormal loss of
brake fluid in the master cylinder fluid reservoir
resulting from a leak in the hydraulic system.
As the fluid drops below the minimum level, the
fluid level sensor closes the brake warning light cir-
cuit. This will turn on the red brake warning light.
At this time, master cylinder fluid reservoir shouldbe checked and filled to the full mark with DOT 3
brake fluid.If brake fluid level has dropped in
master cylinder fluid reservoir, the entire
brake hydraulic system should be checked for
evidence of a leak.
STOP LAMP SWITCH
The stop lamp switch controls operation of the
vehicles stop lamps. Also, if the vehicle is equipped
with speed control, the stop lamp switch will deacti-
vate speed control when the brake pedal is
depressed.
The stop lamp switch controls operation of the
right and left tail, stop and turn signal lamp and
CHMSL lamp, by supplying battery current to these
lamps.
The stop lamp switch controls the lamp operation
by opening and closing the electrical circuit to the
stop lamps.
REAR WHEEL HUB/BEARING
CAUTION: If a vehicle is equipped with antilock
brakes the tone wheels for the rear wheel speed
sensors are pressed onto the hub. The tone wheels
used on this vehicle equipped with the Teves Mark
20 Antilock Brake System are different then those
used on past models of this vehicle equipped with
antilock brakes. Reduced braking performance will
result if this part is used on earlier model vehicles
and an accident could result. Do not use on
pre-1998 model year vehicles.
All vehicles are equipped with permanently lubri-
cated and sealed for life rear wheel bearings. There
is no periodic lubrication or maintenance recom-
mended for these units. However, if servicing of a
rear wheel bearing is required, refer to procedures in
the diagnosis and testing section and the removal
and installation section in this group of the service
manual for the inspection and replacement of the
rear wheel bearing.Fig. 17 Power Brake Booster Assembly
Fig. 18 Master Cylinder Fluid Level Sensor
5 - 8 BRAKESPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 90 of 1200
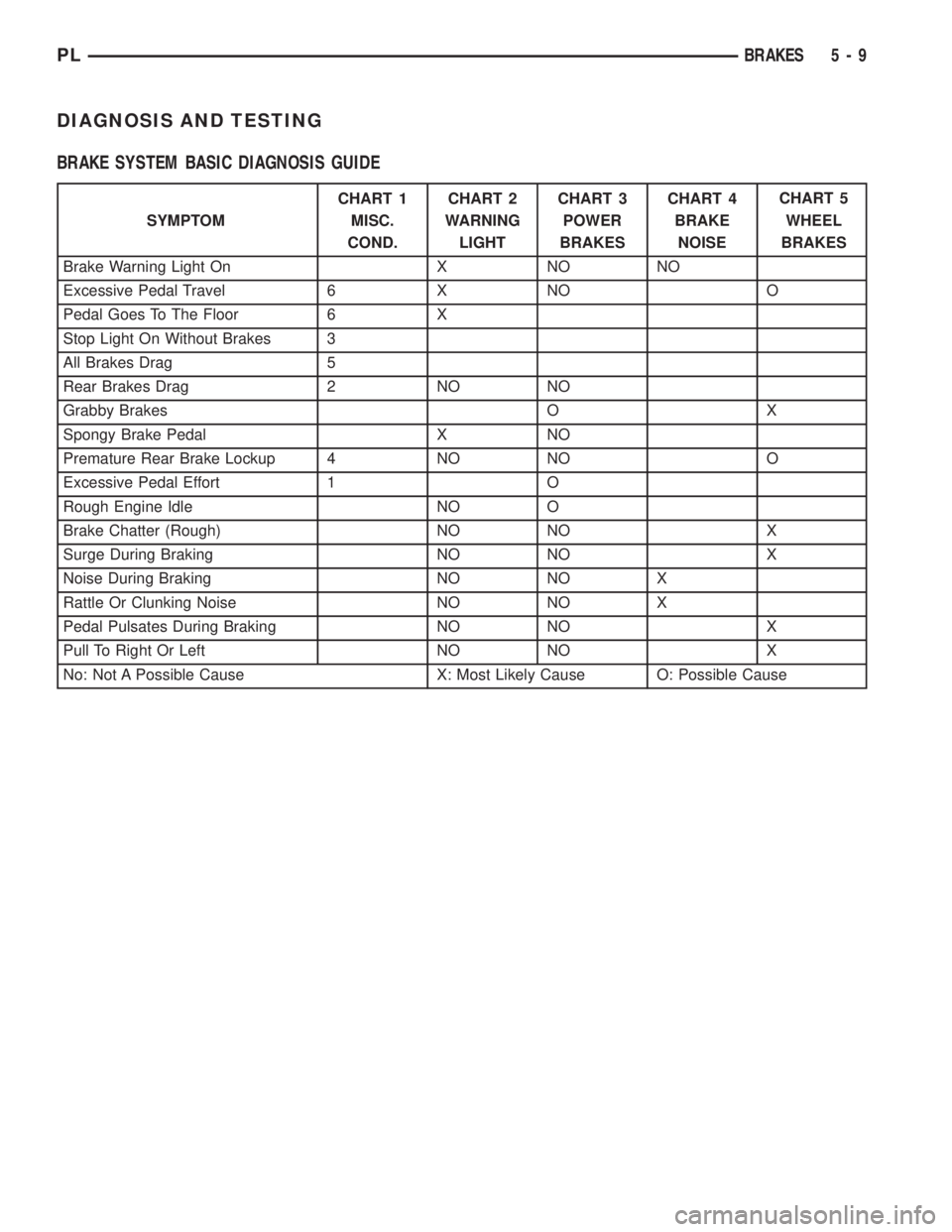
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BRAKE SYSTEM BASIC DIAGNOSIS GUIDE
SYMPTOMCHART 1
MISC.
COND.CHART 2
WARNING
LIGHTCHART 3
POWER
BRAKESCHART 4
BRAKE
NOISECHART 5
WHEEL
BRAKES
Brake Warning Light On X NO NO
Excessive Pedal Travel 6 X NO O
Pedal Goes To The Floor 6 X
Stop Light On Without Brakes 3
All Brakes Drag 5
Rear Brakes Drag 2 NO NO
Grabby Brakes O X
Spongy Brake Pedal X NO
Premature Rear Brake Lockup 4 NO NO O
Excessive Pedal Effort 1 O
Rough Engine Idle NO O
Brake Chatter (Rough) NO NO X
Surge During Braking NO NO X
Noise During Braking NO NO X
Rattle Or Clunking Noise NO NO X
Pedal Pulsates During Braking NO NO X
Pull To Right Or Left NO NO X
No: Not A Possible Cause X: Most Likely Cause O: Possible Cause
PLBRAKES 5 - 9
Page 100 of 1200

(7) With the aid of a helper, apply pressure to the
brake pedal until reading on proportioning valve
inlet gauge, is at the pressure shown on the following
chart. Then check the pressure reading on the pro-
portioning valve outlet gauge. If proportioning valve
outlet pressure does not agree with value shown on
the following chart, when inlet pressure shown on
chart is obtained, replace the proportioning valve. If
proportioning valve is within pressure specifications
do not replace proportioning valve.
(8) Check rear wheel brake shoe linings for con-
tamination or for replacement brake shoes not meet-
ing OEM brake lining material specifications. These
conditions can also be a possible cause for a prema-
ture rear wheel skid.
(9) Install proportioning valve in chassis brake
tube (Fig. 29). Tighten the proportioning valve to a
torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.).
(10) Bleed the affected brake line. See Bleeding
Brake System in the Service Adjustments section of
the manual for proper bleeding procedure.
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts.
Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of
petroleum in the brake fluid.
To test for contamination, put a small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil or other fluid
contamination of the brake fluid.
If brake fluid is contaminated, drain and thor-
oughly flush system. Replace master cylinder, propor-
tioning valve, caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals,
Antilock Brakes hydraulic unit and all hydraulic
fluid hoses.
RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP TEST
For diagnosis of specific problems with the red
brake warning lamp system, refer to Brake System
Diagnostics Chart 2, located in the Diagnosis And
Testing section in this group of the service manual.
STOP LAMP SWITCH TEST PROCEDURE
The required procedure for testing the stop lamp
switch is covered in Group 8H, Vehicle Speed Control
System in this service manual. The electrical circuit
tests for stop lamps is covered in Group 8W Rear
Lighting in this service manual.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL CHECK
Check master cylinder reservoir brake fluid level a
minimum of twice a year.
Master cylinder reservoirs are marked with the
wordsFULL AND MINindicating proper range of
the master cylinder fluid level (Fig. 34).
Fig. 33 Pressure Gauges Installed On Pressure Test
Fittings
BRAKE PROPORTIONING VALVE APPLICATIONS AND PRESSURE SPECIFICATIONS
Sales CodeBrake
System
TypeSplit
PointSlopeIdentifi-
cationInlet
PressureOutlet
Pressure
BRA 149
Disc/Drum400 psi 0.43 Black
Band1000 psi 600-700
psi
BRD 149
Disc/Disc300 psi 0.34 Bar Code
Band1000 psi 550-650
psi
BRF 149
Disc/Disc
W/ABS300 psi 0.34 Bar Code
Band1000 psi 550-650
psi
PLBRAKES 5 - 19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 104 of 1200

The use of a double straddle cutter (Fig. 41) that
machines both sides of the rotor at the same time is
highly recommended.
RESURFACNG BRAKE ROTOR
This operation can be used when rotor surface is
rusty, has lining deposits or excessive lateral runout
or thickness variation is evident.
A sanding rotor attachment will remove surface
contamination without removing much rotor mate-
rial.
It will generally follow variations in thickness that
are in the rotor.
BRAKE DRUM MACHINING
Measure drum runout and diameter. If not to spec-
ification, reface drum. (Runout should not exceed
0.1524 mm or 0.006 inch). The diameter variation
(oval shape) of the drum braking surface must not
exceed either 0.0635 mm (0.0025 inch) in 30É or
0.0889 mm (0.0035 inch) in 360É.All brake drums are marked with the maximum
allowable brake drum diameter (Fig. 44).
PARK BRAKE LEVER AUTO ADJUSTER
MECHANISM
WARNING: THE AUTO ADJUSTING FEATURE OF
THIS PARKING BRAKE LEVER CONTAINS A CLOCK
SPRING LOADED TO APPROXIMATELY 20 POUNDS.
DO NOT RELEASE THE AUTO ADJUSTER LOCK-
OUT DEVICE BEFORE INSTALLING CABLES INTO
THE EQUALIZER. KEEP HANDS OUT OF AUTO
ADJUSTER SECTOR AND PAWL AREA. FAILURE TO
OBSERVE CAUTION IN HANDLING THIS MECHA-
NISM COULD LEAD TO SERIOUS INJURY.
WARNING: WHEN REPAIRS TO THE PARK BRAKE
LEVER OR CABLES IS REQUIRED, THE AUTO
ADJUSTER MUST BE RELOADED AND LOCKED
OUT.
Fig. 43 Minimum Brake Rotor Thickness Markings
(Typical)
BRAKE ROTOR REFINISHING LIMITS
Braking RotorRotor
ThicknessMinimum
Rotor
ThicknessRotor
Thickness
VariationRotor Run
Out*Rotor Micro
Finish
All Front Disc Brakes 20.13-19.87
mm
.792 -.782
in.18.4 mm
.724 in.0.013 mm
0.0005 in.0.13 mm
0.005 in.15-80 RMS
All Rear Disc Brakes 9.25-8.75
mm.364
-.344 in.7.25 mm
.285 in.0.013 mm
0.0005 in.0.13 mm
0.005 in.15-80 RMS
*
TIR Total Indicator Reading (Measured On Vehicle)
Fig. 44 Brake Drum Maximum Diameter
Identification
PLBRAKES 5 - 23
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 105 of 1200

(1) Remove screws attaching rear of center console
assembly to console bracket (Fig. 45) or (Fig. 46).
(2) Remove the 2 screws located in cup holders
(Fig. 47), attaching front of center console assembly
to console bracket.
(3) Raise park brake hand lever assembly as high
as it will go for required clearance to remove center
console.
(4) Remove center console assembly from vehicle.
(5) Lower park brake lever handle.
(6) Grasp park brake lever output cable by hand
and pull upward (Fig. 48). Continue pulling on cable
until a 3/16 in. drill bit can be inserted into handle
and sector gear of park brake mechanism (Fig. 48).
This will lock the park brake mechanism and take
tension off park brake cables.
RELEASING PARK BRAKE AUTO ADJUSTER
NOTE: The park brake lever can be in any position
when releasing the auto adjuster. To ease installa-
tion of center console, it is advisable to pull park
brake lever handle all the way up before removing
lockout pin
(1) Be sure rear park brake cables are properly
installed in the equalizer (Fig. 49).
(2) Pull park brake lever handle all the way up.
(3) Firmly grasp park brake lever locking pin (Fig.
50), and quickly remove it from the park brake lever
mechanism. This will allow the park brake lever
mechanism to correctly adjust the park brake cables.
(4) Install center console.
(5) Install the 4 console assembly attaching screws
(Fig. 45) or (Fig. 46).
(6) Cycle park brake lever once to position park
brake cables. Then return the park brake lever its
Fig. 45 Attaching Screws At Rear Of Center Console
W/O Arm Rest
Fig. 46 Attaching Screws At Rear Of Center Console
With Arm Rest
Fig. 47 Attaching Screws At Front Of Center
Console
Fig. 48 Locking Pin Installed In Park Brake
Mechanism
5 - 24 BRAKESPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 106 of 1200

released position. Check the rear wheels of the vehi-
cle, they should rotate freely without dragging.
BRAKE TUBE REPAIR
Only double wall 4.75mm (3/16 in.) steel tubing
with Al-rich/ZN-AL alloy coating and the correct tube
nuts are to be used for replacement of a hydraulic
brake tube.
Care should be taken when repairing brake tubing,
to be sure the proper bending and flaring tools and
procedures are used, to avoid kinking. Do not route
the tubes against sharp edges, moving components or
into hot areas. All tubes should be properly attached
with recommended retaining clips.
Using Tubing Cutter, Special Tool C-3478-A or
equivalent, cut off damaged seat or tubing (Fig. 51).
Ream out any burrs or rough edges showing on
inside of tubing (Fig. 52). This will make the ends of
tubing square (Fig. 52) and ensure better seating offlared end tubing.PLACE TUBE NUT ON TUB-
ING BEFORE FLARING THE TUBING.
DOUBLE INVERTED TUBING FLARES
To make a double inverted tubing flare (Fig. 53)
and (Fig. 54). Open handles of Flaring Tool, Special
Tool C-4047 or equivalent. Then rotate jaws of tool
until the mating jaws of tubing size are centered
between vertical posts on tool. Slowly close handles
with tubing inserted in jaws but do not apply heavy
pressure to handle as this will lock tubing in place.
Fig. 49 Park Brake Cables Properly Installed In
Equalizer
Fig. 50 Removing Lockout Pin From Park Brake
Lever
Fig. 51 Cutting And Flaring Of Brake Fluid Tubing
Fig. 52 Brake Fluid Tube Preparation For Flaring
PLBRAKES 5 - 25
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 107 of 1200
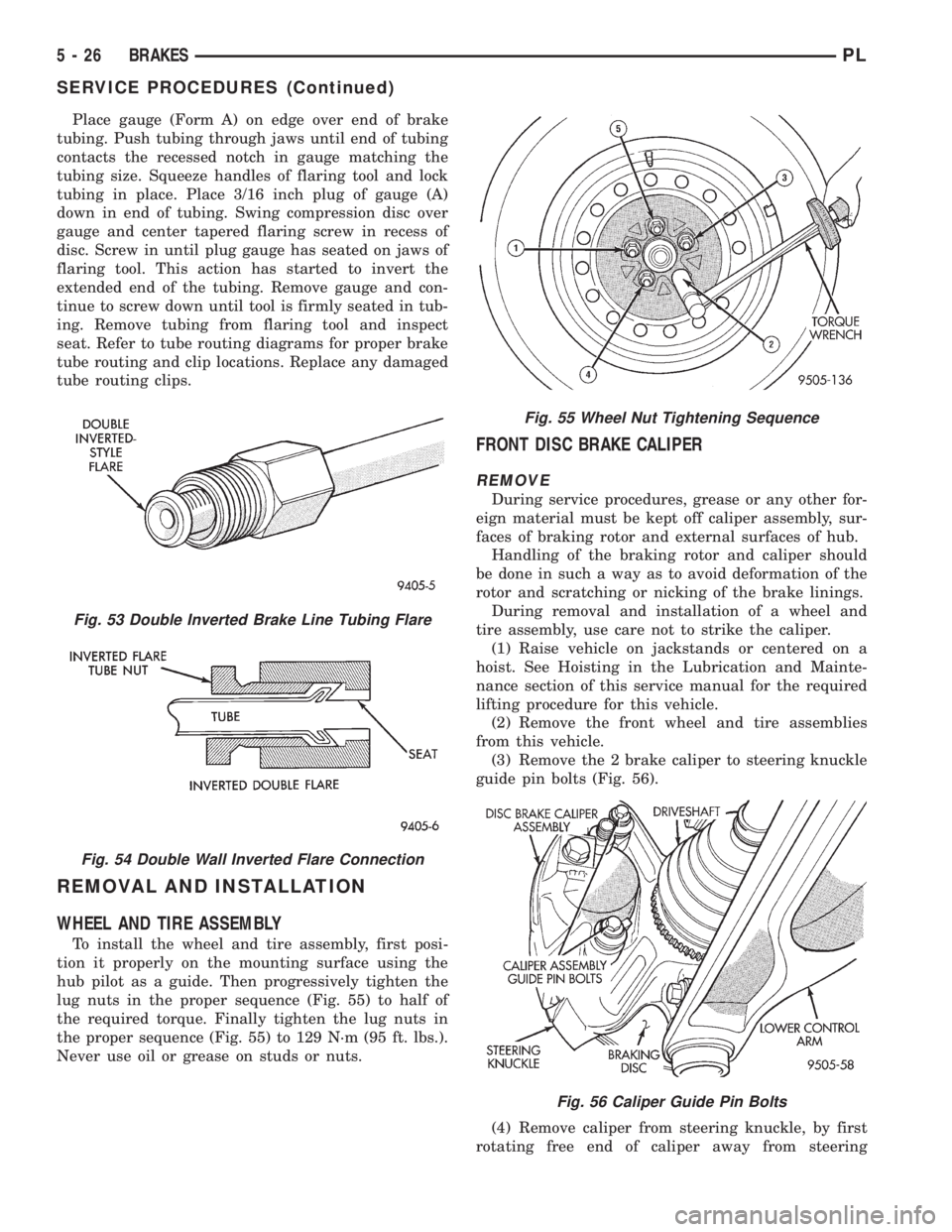
Place gauge (Form A) on edge over end of brake
tubing. Push tubing through jaws until end of tubing
contacts the recessed notch in gauge matching the
tubing size. Squeeze handles of flaring tool and lock
tubing in place. Place 3/16 inch plug of gauge (A)
down in end of tubing. Swing compression disc over
gauge and center tapered flaring screw in recess of
disc. Screw in until plug gauge has seated on jaws of
flaring tool. This action has started to invert the
extended end of the tubing. Remove gauge and con-
tinue to screw down until tool is firmly seated in tub-
ing. Remove tubing from flaring tool and inspect
seat. Refer to tube routing diagrams for proper brake
tube routing and clip locations. Replace any damaged
tube routing clips.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
WHEEL AND TIRE ASSEMBLY
To install the wheel and tire assembly, first posi-
tion it properly on the mounting surface using the
hub pilot as a guide. Then progressively tighten the
lug nuts in the proper sequence (Fig. 55) to half of
the required torque. Finally tighten the lug nuts in
the proper sequence (Fig. 55) to 129 N´m (95 ft. lbs.).
Never use oil or grease on studs or nuts.
FRONT DISC BRAKE CALIPER
REMOVE
During service procedures, grease or any other for-
eign material must be kept off caliper assembly, sur-
faces of braking rotor and external surfaces of hub.
Handling of the braking rotor and caliper should
be done in such a way as to avoid deformation of the
rotor and scratching or nicking of the brake linings.
During removal and installation of a wheel and
tire assembly, use care not to strike the caliper.
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
hoist. See Hoisting in the Lubrication and Mainte-
nance section of this service manual for the required
lifting procedure for this vehicle.
(2) Remove the front wheel and tire assemblies
from this vehicle.
(3) Remove the 2 brake caliper to steering knuckle
guide pin bolts (Fig. 56).
(4) Remove caliper from steering knuckle, by first
rotating free end of caliper away from steering
Fig. 53 Double Inverted Brake Line Tubing Flare
Fig. 54 Double Wall Inverted Flare Connection
Fig. 55 Wheel Nut Tightening Sequence
Fig. 56 Caliper Guide Pin Bolts
5 - 26 BRAKESPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 126 of 1200

brake vacuum booster. Vacuum seal is removed by
carefullyinserting a small screw driver between the
push rod of the power brake vacuum booster and vac-
uum seal (Fig. 118) and prying seal out of power
brake vacuum booster.Do not attempt to pry seal
out of master cylinder by inserting a tool
between seal and power brake vacuum booster.
(8) Disconnect vacuum hoses from check valve on
power brake vacuum booster (Fig. 119).Do not
remove check valve from power brake vacuum
booster.
NOTE: If vehicle is equipped with antilock brakes,
the hydraulic control unit (HCU) needs to be
removed from the vehicle to allow removal of the
power brake vacuum booster. Refer to Antilock
Brake System Hydraulic Control Unit in the
Removal And Installation Section of the Antilock
Brake System Section of this service manual for the
required procedure.(9) Locate the power brake vacuum booster input
rod to brake pedal attachment under instrument
panel. Position a small screwdriver (Fig. 120) under
the center tang of the retaining clip.
CAUTION: Discard retaining clip when removed, it
is not to be reused. Replace only with a new retain-
ing clip when assembled.
(10) Rotate screwdriver (Fig. 120) enough to allow
retaining clip tang to pass over the end of the brake
pedal pin.
(11) Remove the 4 nuts attaching the power brake
vacuum booster to the dash panel (Fig. 121). The
nuts are accessible from under the instrument panel
in the area of the steering column and brake pedal
bracket.
(12) Slide power brake vacuum booster forward
until mounting studs clear dash panel, then tilt the
booster up and to the center of the vehicle to remove.
Fig. 118 Vacuum Seal Removal From Power Brake
Booster
Fig. 119 Power Brake Vacuum Booster Check Valve
Fig. 120 Input Rod Retaining Pin
Fig. 121 Power Brake Booster Mounting
PLBRAKES 5 - 45
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)