Timing DODGE NEON 1999 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 811 of 1200

TORQUE CHART 2.0L DOHC
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Camshaft Sensor Pick-Up
Bolts....................9.6 N´m (85 in. lbs.)
Camshaft Sprocket
Bolt.....................115N´m(85ft.lbs.)
Connecting Rod Cap
Bolts..........27N´m(20ft.lbs.) Plus 1/4 Turn
CollarÐOil Pan to Transaxle
Step 1: Collar to Oil Pan Bolts . .3 N´m (30 in. lbs.)
Step 2: Collar to Transaxle Bolts.108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.)
Step 3: Collar to Oil Pan Bolts .54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap/Bedplate
M8 Bedplate Bolts...........30N´m(22ft.lbs.)
M11 Main Cap Bolts.........81N´m(60ft.lbs.)
Crankshaft Damper
Bolt....................142 N´m (105 ft. lbs.)
Cylinder Head
Bolts........Refer To Cylinder Head Installation
Cylinder Head Cover
Bolts....................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Drive Plate to Crankshaft
Bolts.....................95N´m(70ft.lbs.)
Engine Mount Bracket
Bolts.....................41N´m(30ft.lbs.)
Exhaust Manifold to Cylinder Head
Bolts....................23N´m(200 in. lbs.)
Exhaust Manifold Heat Shield
Bolts....................15N´m(130 in. lbs.)
Intake Manifold
Bolts....................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Oil Filter Adapter
Fastener..................80N´m(60ft.lbs.)
Oil Filter..................20N´m(15ft.lbs.)
Oil Pan
Bolts....................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Drain Plug.................34N´m(25ft.lbs.)
Oil Pump Attaching
Bolts....................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Cover Fastener. . . .12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Pick-up Tube Bolt . .28 N´m (250 in. lbs.)
Oil Pump Relief Valve Cap. . . .55 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
Spark Plugs
Plug......................28N´m(20ft.lbs.)
Thermostat Housing
Bolts....................23N´m(200 in lbs.)
Timing Belt Tensioner AssemblyÐMechanical
Bolts....................28N´m(250 in. lbs.)
Timing Belt Tensioner AssemblyÐHydraulic
Bolts....................31N´m(275 in. lbs.)
Timing Belt TensionerÐHydraulic
Bolts....................31N´m(275 in. lbs.)DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Timing Belt Idler Pulley
Bolt........................61N´m(45ft.lbs.)
Timing Belt Cover
Bolts M6.................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
Water Pump Mounting
Bolts....................12N´m(105 in. lbs.)
SPECIAL TOOLS
2.0L DOHC
Puller 1026
Crankshaft Damper Removal Insert 6827-A
Camshaft Sprocket Remover/Installer C-4687
9 - 98 2.0L DOHC ENGINEPL
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 862 of 1200

GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
All engines used in this section have a sequential
Multi-Port Electronic Fuel Injection system. The MPI
system is computer regulated and provides precise
air/fuel ratios for all driving conditions. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) operates the fuel injec-
tion system.
The PCM regulates:
²Ignition timing
²Air/fuel ratio
²Emission control devices
²Cooling fan
²Charging system
²Idle speed
²Vehicle speed control
Various sensors provide the inputs necessary for
the PCM to correctly operate these systems. In addi-
tion to the sensors, various switches also provide
inputs to the PCM.
All inputs to the PCM are converted into signals.
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet chang-
ing operating conditions.
Fuel is injected into the intake port above the
intake valve in precise metered amounts through
electrically operated injectors. The PCM fires the
injectors in a specific sequence. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the PCM maintains an air fuel ratio
of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel by constantly adjust-
ing injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time the injector is open.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injector. Engine
RPM (speed) and manifold absolute pressure (air
density) are the primary inputs that determine injec-
tor pulse width.
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). There are several differ-
ent modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.
There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP.
During OPEN LOOP modes the PCM receives
input signals and responds according to preset PCM
programming. Inputs from the upstream and down-
stream heated oxygen sensors are not monitored dur-
ing OPEN LOOP modes, except for heated oxygen
sensor diagnostics (they are checked for shorted con-
ditions at all times).During CLOSED LOOP modes the PCM monitors
the inputs from the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The upstream heated oxygen
sensor input tells the PCM if the calculated injector
pulse width resulted in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7
to one. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content
through the upstream heated oxygen sensor, the
PCM can fine tune injector pulse width. Fine tuning
injector pulse width allows the PCM to achieve opti-
mum fuel economy combined with low emissions.
For the PCM to enter CLOSED LOOP operation,
the following must occur:
(1) Engine coolant temperature must be over 35ÉF.
²If the coolant is over 35É the PCM will wait 44
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 50ÉF the PCM will wait 38
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 167ÉF the PCM will wait
11 seconds.
(2) For other temperatures the PCM will interpo-
late the correct waiting time.
(3) O2 sensor must read either greater than .745
volts or less than .1 volt.
(4) The multi-port fuel injection systems has the
following modes of operation:
²Ignition switch ON (Zero RPM)
²Engine start-up
²Engine warm-up
²Cruise
²Idle
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide Open Throttle
²Ignition switch OFF
(5) The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up,
deceleration with fuel shutoff and wide open throttle
modes are OPEN LOOP modes. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the acceleration, deceleration (with
A/C on), idle and cruise modes,with the engine at
operating temperatureare CLOSED LOOP modes.
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injec-
tion system, the following actions occur:
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor and throttle position sensor input. The
PCM determines basic fuel injector pulse width from
this input.
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to modify injector pulse
width.
When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the Auto Shutdown (ASD)
and fuel pump relays de-energize after approximately
1 second. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injectors and heated
oxygen sensors.
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 21
Page 863 of 1200

ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. If the vehicle is in
park or neutral (automatic transaxles) or the clutch
pedal is depressed (manual transaxles) the ignition
switch energizes the starter relay. The following
actions occur when the starter motor is engaged.
²If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) and fuel pump relays. If
the PCM does not receive both signals within approx-
imately one second, it will not energize the ASD
relay and fuel pump relay. The ASD and fuel pump
relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump, fuel
injectors, ignition coil and heated oxygen sensors.
²The PCM energizes all four injectors (on the 69É
degree falling edge) for a calculated pulse width until
it determines crankshaft position from the camshaft
position sensor and crankshaft position sensor sig-
nals. The PCM determines crankshaft position within
1 engine revolution.
²After determining crankshaft position, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. It adjusts
injector pulse width and controls injector synchroni-
zation by turning the individual ground paths to the
injectors On and Off.
²When the engine idles within664 RPM of its
target RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor
value with the atmospheric pressure value received
during the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode. If
the PCM does not detect a minimum difference
between the two values, it sets a MAP diagnostic
trouble code into memory.
Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM determines injector pulse width
based on the following:
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine RPM
²Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Throttle position
²The number of engine revolutions since cranking
was initiated
During Start-up the PCM maintains ignition tim-
ing at 9É BTDC.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
²Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²A/C switch
²Battery voltage²Power steering pressure switch
²Vehicle speed
²Speed control
²Both O2 sensors
²All diagnostics
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing and engine idle
speed. Engine idle speed is adjusted through the idle
air control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising or idle
the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²Exhaust gas oxygen content
²A/C control positions
²Power steering pressure switch
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas (measured
by the upstream and downstream heated oxygen sen-
sor).
The PCM monitors for engine misfire. During
active misfire and depending on the severity, the
PCM either continuously illuminates or flashes the
malfunction indicator lamp (Check Engine light on
instrument panel). Also, the PCM stores an engine
misfire DTC in memory.
The PCM performs several diagnostic routines.
They include:
²Oxygen sensor monitor
²Downstream heated oxygen sensor diagnostics
during open loop operation (except for shorted)
²Fuel system monitor
²EGR monitor
²Purge system monitor
²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range.
²All monitored components (refer to Group 25 for
On-Board Diagnostics).
The PCM compares the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensor inputs to measure catalytic
convertor efficiency. If the catalyst efficiency drops
14 - 22 FUEL SYSTEMPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 865 of 1200

POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 2). The
PCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors that are referred to as PCM Inputs.
Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts various
engine and vehicle operations through devices that
are referred to as PCM Outputs.
PCM Inputs:
²Air Conditioning Controls
²Battery Voltage
²Battery Temperature Sensor
²Brake Switch
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Fuel Level Sensor
²Ignition Switch
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Knock Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Oxygen Sensors
²Power Steering Pressure Switch
²SCI Receive
²Speed Control Switches
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Transmission Park/Neutral Switch (automatic
transmission)
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
PCM Outputs:
²Air Conditioning WOT Relay
²Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay
²Charging Indicator Lamp
²Data Link Connector
²Duty Cycle EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid
²EGR Solenoid
²Fuel Injectors
²Fuel Pump Relay²Generator Field
²Idle Air Control Motor
²Ignition Coils
²Malfunction Indicator (Check Engine) Lamp
²Radiator Fan Relay
²Speed Control Solenoids
²Tachometer
²Torque Convertor Clutch Solenoid
Based on inputs it receives, the PCM adjusts fuel
injector pulse width, idle speed, ignition spark
advance, ignition coil dwell and EVAP canister purge
operation. The PCM regulates the cooling fan, air
conditioning and speed control systems. The PCM
changes generator charge rate by adjusting the gen-
erator field. The PCM also performs diagnostics.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel
ratio) based on the following inputs.
²Battery voltage
²Coolant temperature
²Intake air temperature
²Exhaust gas content (oxygen sensor)
²Engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
²Coolant temperature
²Intake air temperature
²Engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
²Transmission gear selection (park/neutral
switch)
The PCM also adjusts engine idle speed through
the idle air control motor based on the following
inputs.
²Air conditioning sense
²Battery voltage
²Battery temperature
²Brake switch
²Coolant temperature
²Engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Engine run time
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Power steering pressure switch
²Throttle position
²Transmission gear selection (park/neutral
switch)
²Vehicle distance (speed)
The Auto Shutdown (ASD) and fuel pump relays
are mounted externally, but turned on and off by the
PCM.
The crankshaft position sensor signal is sent to the
PCM. If the PCM does not receive the signal within
approximately one second of engine cranking, it deac-
Fig. 2 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
14 - 24 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 867 of 1200

CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The PCM determines what cylinder to fire from the
crankshaft position sensor input and the camshaft
position sensor input. The second crankshaft counter-
weight has two sets of four timing reference notches
including a 60 degree signature notch (Fig. 7). From
the crankshaft position sensor input the PCM deter-
mines engine speed and crankshaft angle (position).
The notches generate pulses from high to low in
the crankshaft position sensor output voltage. When
a metal portion of the counterweight aligns with the
crankshaft position sensor, the sensor output voltage
goes low (less than 0.5 volts). When a notch aligns
with the sensor, voltage goes high (5.0 volts). As a
group of notches pass under the sensor, the outputvoltage switches from low (metal) to high (notch)
then back to low.
If available, an oscilloscope can display the square
wave patterns of each voltage pulses. From the width
of the output voltage pulses, the PCM calculates
engine speed. The width of the pulses represent the
amount of time the output voltage stays high before
switching back to low. The period of time the sensor
output voltage stays high before switching back to
low is referred to as pulse width. The faster the
engine is operating, the smaller the pulse width on
the oscilloscope.
By counting the pulses and referencing the pulse
from the 60 degree signature notch, the PCM calcu-
lates crankshaft angle (position). In each group of
timing reference notches, the first notch represents
69 degrees before top dead center (BTDC). The sec-
ond notch represents 49 degrees BTDC. The third
notch represents 29 degrees. The last notch in each
set represents 9 degrees before top dead center
(TDC).
The timing reference notches are machined at 20É
increments. From the voltage pulse width the PCM
tells the difference between the timing reference
notches and the 60 degree signature notch. The 60
degree signature notch produces a longer pulse width
than the smaller timing reference notches. If the
camshaft position sensor input switches from high to
low when the 60 degree signature notch passes under
the crankshaft position sensor, the PCM knows cylin-
der number one is the next cylinder at TDC.
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the
engine block behind the alternator, just above the oil
filter (Fig. 8).
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
The combination coolant temperature sensor has
two elements. One element supplies coolant temper-
ature signal to the PCM. The other element supplies
coolant temperature signal to the instrument panel
gauge cluster. The PCM determines engine coolant
temperature from the coolant temperature sensor.
As coolant temperature varies the coolant temper-
ature sensors resistance changes resulting in a differ-
ent input voltage to the PCM and the instrument
panel gauge cluster.
When the engine is cold, the PCM will provide
slightly richer air- fuel mixtures and higher idle
speeds until normal operating temperatures are
reached.
SOHC
The coolant sensor threads into the rear of the cyl-
inder head, next to the camshaft position sensor (Fig.
9). New sensors have sealant applied to the threads.
Fig. 5 Target MagnetÐTypical
Fig. 6 Target Magnet Polarity
14 - 26 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 868 of 1200
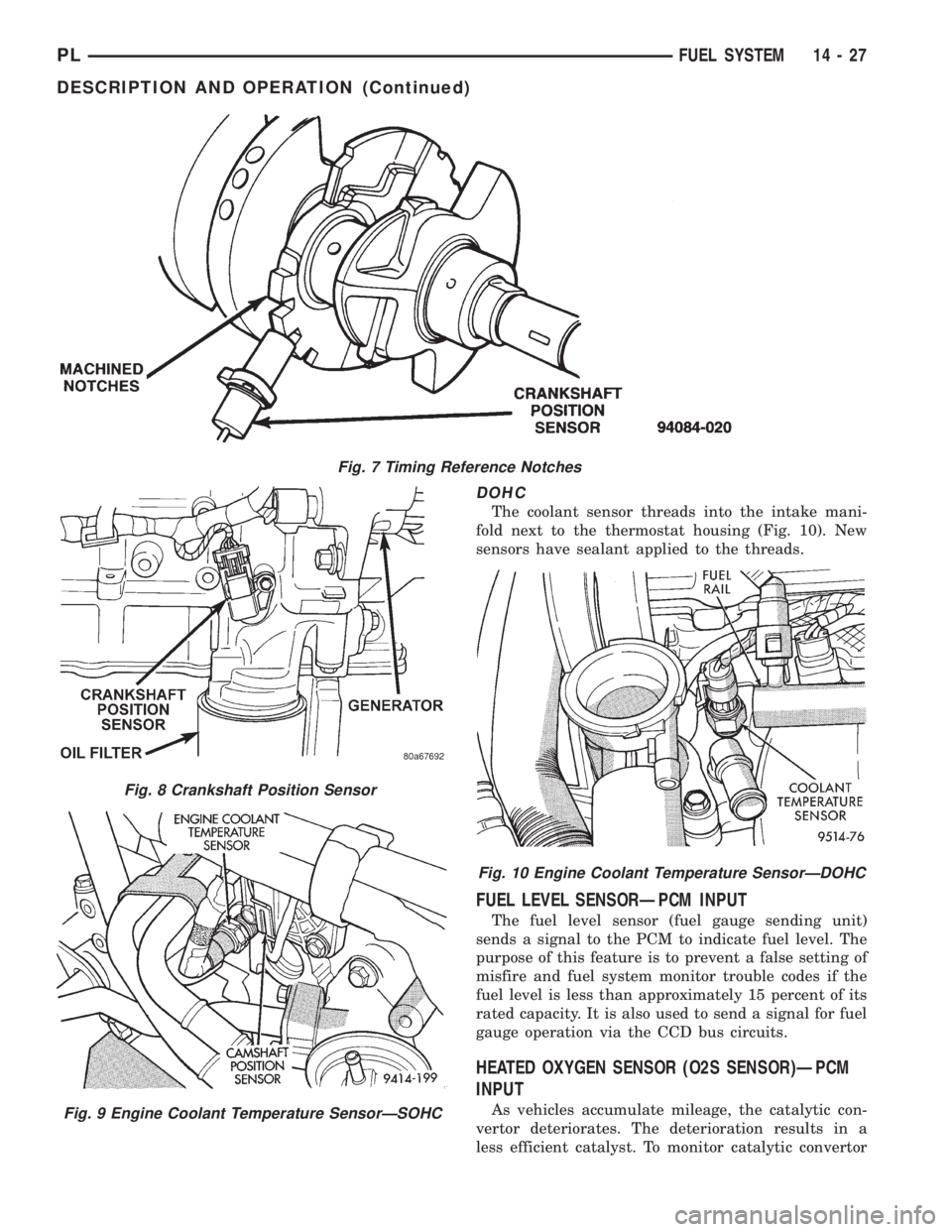
DOHC
The coolant sensor threads into the intake mani-
fold next to the thermostat housing (Fig. 10). New
sensors have sealant applied to the threads.
FUEL LEVEL SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The fuel level sensor (fuel gauge sending unit)
sends a signal to the PCM to indicate fuel level. The
purpose of this feature is to prevent a false setting of
misfire and fuel system monitor trouble codes if the
fuel level is less than approximately 15 percent of its
rated capacity. It is also used to send a signal for fuel
gauge operation via the CCD bus circuits.
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S SENSOR)ÐPCM
INPUT
As vehicles accumulate mileage, the catalytic con-
vertor deteriorates. The deterioration results in a
less efficient catalyst. To monitor catalytic convertor
Fig. 7 Timing Reference Notches
Fig. 8 Crankshaft Position Sensor
Fig. 9 Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐSOHC
Fig. 10 Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐDOHC
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 27
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 870 of 1200

As Intake Air temperature varies the Intake Air
Temperature sensors resistance changes resulting in
a different input voltage to the PCM.
The IAT sensor and Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) switch are a combined into a single sensor
that attachs to the intake manifold (Fig. 13) or (Fig.
14).
KNOCK SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in front of the starter (Fig. 15). When the
knock sensor detects a knock in one of the cylinders,
it sends an input signal to the PCM. In response, the
PCM retards ignition timing for all cylinders by a
scheduled amount.
Knock sensors contain a piezoelectric material
which sends an input voltage (signal) to the PCM. As
the intensity of the engine knock vibration increases,
the knock sensor output voltage also increases.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The PCM supplies 5 volts direct current to the
MAP sensor. The MAP sensor converts intake mani-
fold pressure into voltage. The PCM monitors the
MAP sensor output voltage. As vacuum increases,
MAP sensor voltage decreases proportionately. Also,
as vacuum decreases, MAP sensor voltage increases
proportionately.
At key on, before the engine is started, the PCM
determines atmospheric air pressure from the MAP
sensor voltage. While the engine operates, the PCM
determines intake manifold pressure from the MAP
sensor voltage. Based on MAP sensor voltage and
inputs from other sensors, the PCM adjusts spark
advance and the air/fuel mixture.
The MAP/Intake Air Temperature sensor mounts to
the intake manifold (Fig. 13) and (Fig. 14).
Fig. 12 Downstream Heated Oxygen Sensor
Fig. 13 / MAP/Intake Air Temperature SensorÐSOHC
Fig. 14 MAP/Intake Air Temperature SensorÐDOHC
Fig. 15 Knock Sensor
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 29
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 871 of 1200

POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCHÐPCM
INPUT
A pressure sensing switch is located on the power
steering gear. The switch (Fig. 16) provides an input
to the PCM during periods of high pump load and
low engine RPM; such as during parking maneuvers.
When power steering pump pressure exceeds 2758
kPa (400 psi), the switch is open. The PCM increases
idle air flow through the IAC motor to prevent
engine stalling. When pump pressure is low, the
switch is closed.
SENSOR RETURNÐPCM INPUT
The sensor return circuit provides a low electrical
noise ground reference for all of the systems sensors.
The sensor return circuit connects to internal ground
circuits within the powertrain control module.
SPEED CONTROL SERVOSÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM controls the speed control vacuum servo.
The PCM supplies power, through the brake switch,
to the servo. Based on the speed control switch
inputs to the PCM and the speed control strategy,
the PCM provides ground to the servo vacuum or
vent circuit as required. When the PCM supplies a
ground to the servo vacuum circuit, the speed control
system opens the throttle plate to obtain or maintain
the selected road speed. When the PCM supplies a
ground to the servo vent circuit, the speed control
system releases the throttle plate. Refer to Group 8H
for speed control information.
SCI RECEIVEÐPCM INPUT
SCI Receive is the serial data communication
receive circuit for the DRB scan tool. The Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) receives data from the DRB
through the SCI Receive circuit.
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
The park/neutral position switch is located on the
automatic transaxle housing (Fig. 17). Manual tran-
saxles do not use park/neutral switches. The switch
provides an input to the PCM to indicate whether
the automatic transaxle is in Park/Neutral, or a drive
gear selection. This input is used to determine idle
speed (varying with gear selection) and ignition tim-
ing advance. The park/neutral input is also used to
cancel vehicle speed control. The park/neutral switch
is sometimes referred to as the neutral safety switch.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The throttle position sensor mounts to the side of
the throttle body (Fig. 18) and (Fig. 19).
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) connects to the
throttle blade shaft. The TPS is a variable resistor
that provides the PCM with an input signal (voltage).
The signal represents throttle blade position. As the
position of the throttle blade changes, the resistance
of the TPS changes.
The PCM supplies approximately 5 volts DC to the
TPS. The TPS output voltage (input signal to the
powertrain control module) represents throttle blade
position. The TPS output voltage to the PCM varies
from approximately 0.35 to 1.03 volts at minimum
throttle opening (idle) to a maximum of 3.1 to 4.0
volts at wide open throttle.
Along with inputs from other sensors, the PCM
uses the TPS input to determine current engine oper-
ating conditions. The PCM also adjusts fuel injector
pulse width and ignition timing based on these
inputs.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The vehicle speed sensor is located in the transmis-
sion extension housing (Fig. 20) and (Fig. 21). The
sensor input is used by the PCM to determine vehicle
speed and distance traveled.
Fig. 16 Power Steering Pressure SwitchFig. 17 Park/Neutral Switch
14 - 30 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 873 of 1200

disables the A/C compressor clutch for several sec-
onds.
The air conditioning clutch relay is located in the
PDC. The inside top of the PDC cover has a label
showing relay and fuse location.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The automatic shutdown (ASD) relay supplies bat-
tery voltage to the fuel injectors, electronic ignition
coil and the heating elements in the oxygen sensors.
A buss bar in the power distribution center (PDC)
supplies voltage to the solenoid side and contact side
of the relay. The ASD relay power circuit contains a
20 amp fuse between the buss bar in the PDC and
the relay. The fuse also protects the power circuit for
the fuel pump relay and pump. The fuse is located in
the PDC. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams for
circuit information.
The PCM controls the relay by switching the
ground path for the solenoid side of the relay on and
off. The PCM turns the ground path off when the
ignition switch is in the Off position unless the 02
Heater Monitor test is being run. Refer to Group 25,
On-Board Diagnostics. When the ignition switch is in
the On or Crank position, the PCM monitors the
crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sen-
sor signals to determine engine speed and ignition
timing (coil dwell). If the PCM does not receive the
crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sen-
sor signals when the ignition switch is in the Run
position, it will de- energize the ASD relay.
The ASD relay is located in the PDC. The inside
top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay and
fuse location.
CHARGING SYSTEM INDICATOR LAMPÐPCM
OUTPUT
The PCM turns the instrument panel Charging
System Lamp on. Refer to Group 8C for charging sys-
tem information.
FUEL PUMP RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The fuel pump relay supplies battery voltage to the
fuel pump. A buss bar in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) supplies voltage to the solenoid side and
contact side of the relay. The fuel pump relay power
circuit contains a 20 amp fuse between the buss bar
in the PDC and the relay. The fuse also protects the
power circuit for the Automatic Shutdown (ASD)
relay. The fuse is located in the PDC. Refer to Group
8W, Wiring Diagrams for circuit information.
The PCM controls the fuel pump relay by switch-
ing the ground path for the solenoid side of the relay
on and off. The PCM turns the ground path off when
the ignition switch is in the Off position. When the
ignition switch is in the On position, the PCM ener-gizes the fuel pump. If the crankshaft position sensor
does not detect engine rotation, the PCM de-ener-
gizes the relay after approximately one second.
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
DUTY CYCLE EVAP PURGE SOLENOIDÐPCM
OUTPUT
The duty cycle EVAP purge solenoid regulates the
rate of vapor flow from the EVAP canister to the
throttle body. The powertrain control module oper-
ates the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the programmed
time delay ends. During closed loop operation, the
PCM energizes and de-energizes the solenoid 5 to 10
times per second, depending upon operating condi-
tions. The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by chang-
ing solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the amount
of time the solenoid is energized.
The solenoid attaches to a bracket near the front
engine mount (Fig. 22). To operate correctly, the sole-
noid must be installed with the electrical connector
on top.
ELECTRIC EGR TRANSDUCERÐPCM OUTPUT
The Electric EGR Transducer contains an electri-
cally operated solenoid and a back-pressure con-
trolled vacuum transducer (Fig. 23). The PCM
Fig. 22 Duty Cycle EVAP Purge Solenoid
14 - 32 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 888 of 1200

(7) Attach the other end of the jumper wire to
relay terminal 86. This activates the relay. The ohm-
meter should now show continuity between relay ter-
minals 87 and 30. The ohmmeter should not show
continuity between relay terminals 87A and 30.
(8) Disconnect jumper wires.
(9) Replace the relay if it did not pass the continu-
ity and resistance tests. If the relay passed the tests,
it operates properly. Check the remainder of the ASD
and fuel pump relay circuits. Refer to group 8W, Wir-
ing Diagrams.
CAMSHAFT AND CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Refer to Group 8D, Ignition for Diagnosis and Test-
ing of Camshaft and Crankshaft Sensors.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
(1) With the key off, disconnect wire harness con-
nector from coolant temperature sensor (Fig. 79) or
(Fig. 80).(2) Connect a high input impedance (digital) volt-
ohmmeter to terminals A and B (Fig. 81). The ohm-
meter should read as follows:
²Engine/Sensor at normal operating temperature
around 200ÉF should read approximately 700 to
1,000 ohms.
²Engine/Sensor at room temperature around 70ÉF
ohmmeter should read approximately 7,000 to 13,000
ohms.
(3) T
est the resistance of the wire harness between
the PCM 60-way connector terminal 28 and the sensor
harness connector. Also check for continuity between
PCM 60-way connector terminal 51 and the sensor har-
ness connector. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring diagrams for
circuit information. If the resistance is greater than 1
ohm, repair the wire harness as necessary.
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR
Use an ohmmeter to test the heating element of
the oxygen sensors. Disconnect the electrical connec-
tor from each oxygen sensor. The white wires in the
sensor connector are the power and ground circuits
for the heater. Connect the ohmmeter test leads to
terminals of the white wires in the heated oxygen
sensor connector. Replace the heated oxygen sensor if
the resistance is not between 4 and 7 ohms.
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) MOTOR TEST
To preform a complete test of IAC motor and its
circuitry, refer to DRB scan tool and the appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures manual.
KNOCK SENSOR
The engine knock sensor is affected by a number of
factors. A few of these are: ignition timing, cylinder
pressure, fuel octane, etc. The knock sensor generates
an AC voltage whose amplitude increases with the
increase of engine knock. The knock sensor can be
tested with a digital voltmeter. The RMS voltage starts
Fig. 79 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
LocationÐSOHC
Fig. 80 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
LocationÐDOHC
Fig. 81 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 47
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)