Oil pump DODGE RAM 2003 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2003Pages: 2895, PDF Size: 83.15 MB
Page 2519 of 2895
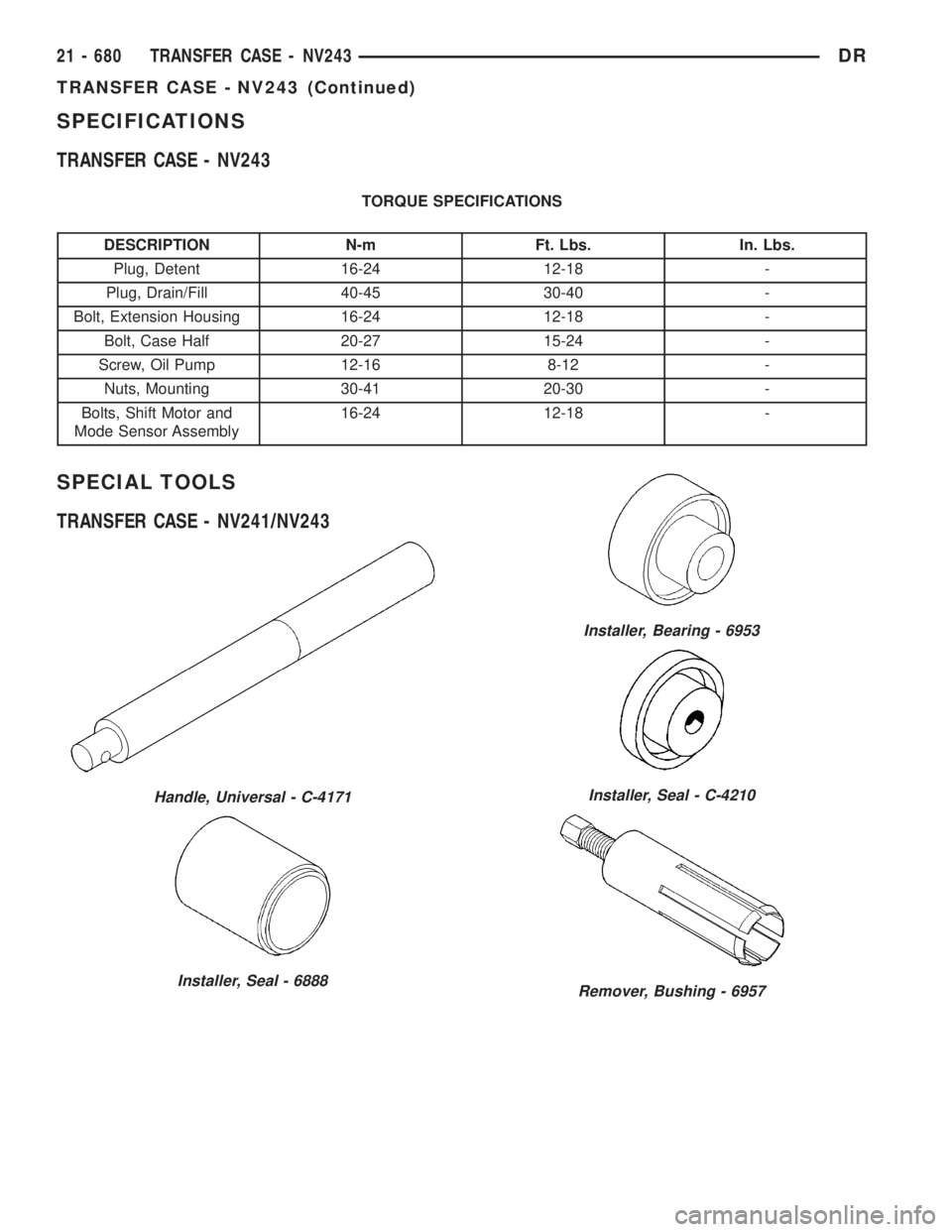
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV243
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Plug, Detent 16-24 12-18 -
Plug, Drain/Fill 40-45 30-40 -
Bolt, Extension Housing 16-24 12-18 -
Bolt, Case Half 20-27 15-24 -
Screw, Oil Pump 12-16 8-12 -
Nuts, Mounting 30-41 20-30 -
Bolts, Shift Motor and
Mode Sensor Assembly16-24 12-18 -
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV241/NV243
Handle, Universal - C-4171
Installer, Seal - 6888
Installer, Bearing - 6953
Installer, Seal - C-4210
Remover, Bushing - 6957
21 - 680 TRANSFER CASE - NV243DR
TRANSFER CASE - NV243 (Continued)
Page 2530 of 2895

(8) Remove rear extension housing (Fig. 6). Tap
extension once or twice with a plastic mallet to break
sealer bead and loosen it.
OIL PUMP AND REAR CASE
(1) Disengage the oil pump pick-up tube (Fig. 7)
from the oil pump.
NOTE: The oil pump pick-up tube seals to the oil
pump with an o-ring. Verify that the o-ring was
removed with the tube and is in good condition.
Replace the o-ring if necessary.
(2) Remove the oil pump (Fig. 8).(3) Remove rear case-to-front case bolts (Fig. 9).
Fig. 6 Remove Extension Housing
1 - REAR CASE HALF
2 - EXTENSION HOUSING
Fig. 7 Disengage The Oil Pick-up From Oil Pump
1 - OIL PUMP
2 - OIL PICK-UP TUBE
Fig. 8 Remove Oil Pump
1 - REAR CASE HALF
2 - REAR OUTPUT SHAFT
3 - OIL PUMP
Fig. 9 Remove Case Half Bolts
1 - FRONT CASE HALF
2 - REAR CASE HALF
3 - BOLTS
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 691
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2540 of 2895

be repaired with a thread chaser or tap if necessary.
Or the threads can be repaired with Helicoiltstain-
less steel inserts if required.
OIL PUMP/OIL PICKUP
Examine the oil pump pickup parts. Replace the
pump if any part appears to be worn or damaged. Do
not disassemble the pump as individual parts are not
available. The pump is only available as a complete
assembly. The pickup screen, hose, and tube are the
only serviceable parts and are available separately.
ASSEMBLY
BEARINGS AND SEALS
(1) Remove the input shaft bearing snap-ring from
the front case half with suitable snap-ring pliers.
(2) Remove the input shaft bearing from the front
case half with Installer 6953 and Handle C-4171
(Fig. 43).
(3) Install the input shaft bearing into the front
case half with Installer 8151 inverted on Handle
C-4171 (Fig. 44).
(4) Install the input shaft bearing snap-ring into
the front case half with suitable snap-ring pliers.
(5) Remove the front output shaft front bearing
snap-ring from the front case half.
(6) Using Installer 6953 and Handle C-4171 (Fig.
45), remove the front output shaft front bearing.
Fig. 45 Remove Front Output Shaft Front Bearing
1 - FRONT CASE HALF
2 - HANDLE C-4171
3 - INSTALLER 6953
Fig. 43 Remove Input Gear Bearing
1 - FRONT CASE HALF
2 - HANDLE C-4171
3 - INSTALLER 6953
Fig. 44 Install Input Gear Bearing
1 - FRONT CASE HALF
2 - HANDLE C-4171
3 - INSTALLER 8151 (INVERTED)
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 701
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2542 of 2895

chamfered at the top. Install the bearing so it is
flush with the lower edge of this chamfer (Fig. 50).
(13) Remove seal from oil pump with suitable pry
tool.
(14) Install new seal in oil pump with Installer
7888 (Fig. 51).
(15) Remove the rear output shaft bearing snap-
ring (Fig. 52) from the rear case half.
(16) Remove the rear output shaft bearing from
the rear case using Installer 7888 (Fig. 53).
Fig. 53 Remove Rear Output Shaft Bearing
1 - REAR CASE HALF
2 - INSTALLER 7888
Fig. 50 Output Shaft Rear Bearing Installation Depth
1 - BEARING (SEATED) AT LOWER EDGE OF CHAMFER
2 - CHAMFER
Fig. 51 Oil Pump Seal Installation
1 - HOUSING SEAL
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 7888
3 - OIL PUMP FEED HOUSING
Fig. 52 Remove Rear Output Bearing Outer
Snap-Ring
1 - REAR CASE HALF
2 - REAR OUTPUT SHAFT BEARING
3 - SNAP-RING
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 703
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2550 of 2895

(4) Install 4-5 rear case-to front case bolts (Fig. 81)
to hold rear case in position. Tighten bolts snug but
not to specified torque at this time.
CAUTION: Verify that shift rail, and case alignment
dowels are seated before installing any bolts. Case
could be cracked if shaft rail or dowels are mis-
aligned.
(5) Tighten bolts to 27-34 N´m (20-25 ft. lbs.),
(6) Install rear output bearing inner snap-ring
(Fig. 82) to output shaft.
OIL PUMP AND REAR EXTENSION
(1) Install the oil pump (Fig. 83) onto the output
shaft.
Fig. 83 Install Oil Pump
1 - REAR CASE HALF
2 - REAR OUTPUT SHAFT
3 - OIL PUMP
Fig. 81 Install Case Half Bolts
1 - FRONT CASE HALF
2 - REAR CASE HALF
3 - BOLTS
Fig. 82 Install Rear Bearing Inner Snap-Ring
1 - OUTPUT SHAFT
2 - REAR CASE HALF
3 - SNAP-RING
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 711
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2551 of 2895

(2) Engage the oil pump pick-up tube (Fig. 84) into
the oil pump. Verify that the pick-up tube o-ring is
on the tube and is correctly installed to the oil pump.
(3) Apply bead of MopartGasket Maker, or equiv-
alent, to mating surface of rear extension housing.
Keep sealer bead width to maximum of 3/16 inch. Do
not use excessive amount of sealer as excess could be
displaced into output bearing.
(4) Install extension housing (Fig. 85) onto the
rear case half.(5) Install rear extension bolts (Fig. 86). Tighten
the bolts to 27-34 N´m (20-25 ft.lbs.).
(6) Install the extension housing dust boot and
seal assembly with Installer 9037 and Handle C-4171
(Fig. 87).
Fig. 84 Engage The Oil Pick-up To Oil Pump
1 - OIL PUMP
2 - OIL PICK-UP TUBE
Fig. 85 Install Extension Housing
1 - REAR CASE HALF
2 - EXTENSION HOUSING
Fig. 86 Install Extension Housing Bolts
1 - EXTENSION HOUSING
2 - BOLTS
Fig. 87 Install Extension Housing Seal
1 - EXTENSION HOUSING
2 - HANDLE C-4171
3 - INSTALLER 9037
21 - 712 TRANSFER CASE - NV273DR
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2810 of 2895

erant system. Refer to the operating instructions sup-
plied by the equipment manufacturer for the proper
care and use of this equipment.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM EVACUATE
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
If the refrigerant system has been open to the
atmosphere, it must be evacuated before the system
can be charged. If moisture and air enters the system
and becomes mixed with the refrigerant, the com-
pressor head pressure will rise above acceptable
operating levels. This will reduce the performance of
the air conditioner and damage the compressor.
Evacuating the refrigerant system will remove the
air and boil the moisture out of the system at near
room temperature. To evacuate the refrigerant sys-
tem, use the following procedure:
(1) Connect a R-134a refrigerant recovery/recy-
cling/charging station that meets SAE Standard
J2210 and a manifold gauge set to the refrigerant
system of the vehicle.
(2) Recover the refrigerant(Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(3) Open the low and high side valves and start
the charging station vacuum pump. When the suc-
tion gauge reads 88 kPa (26 in. Hg.) vacuum or
greater, close all of the valves and turn off the vac-
uum pump.
(a) If the refrigerant system fails to reach the
specified vacuum, the system has a leak that must
be corrected. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/PLUMBING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAKS)
(b) If the refrigerant system maintains the spec-
ified vacuum for five minutes, restart the vacuum
pump, open the suction and discharge valves and
evacuate the system for an additional ten minutes.
(4) Close all of the valves, and turn off the charg-
ing station vacuum pump.
(5) The refrigerant system is now ready to be
charged with R-134a refrigerant. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM CHARGE
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
After the refrigerant system has been tested for
leaks and evacuated, a refrigerant charge can be
injected into the system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - SPECIFICA-
TIONS - CHARGE CAPACITY)
A R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging
station that meets SAE Standard J2210 must be
used to charge the refrigerant system with R-134a
refrigerant. Refer to the operating instructions sup-
plied by the equipment manufacturer for proper care
and use of this equipment.
The R-134a refrigerant charge capacity for this
vehicle is 0.7371 Kg (26 oz.).
NOTE: Always refer to the HVAC underhood sticker
for current refrigerant charge level and refrigerant
oil specifications.
SPECIFICATIONS - CHARGE CAPACITY
The R-134a refrigerant system charge capacity for
this vehicle is: 0.7371 Kg. (26 oz.).
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
The air conditioning system uses a Sanden SD-7
reciprocating swash plate-type compressor on all
models. This compressor has a fixed displacement of
165 cubic centimeter and has both the suction and
discharge ports located on the cylinder head. A label
identifying the use of R-134a refrigerant is located on
the compressor.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
A high pressure relief valve is located on the com-
pressor cylinder head, which is on the rear of the
compressor. This mechanical valve is designed to
vent refrigerant from the system to protect against
damage to the compressor and other system compo-
DRPLUMBING 24 - 35
PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 2811 of 2895

nents, caused by condenser air flow restriction or an
overcharge of refrigerant.
OPERATION
OPERATION
The compressor is driven by the engine through an
electric clutch, drive rotor and belt arrangement. The
compressor is lubricated by refrigerant oil that is cir-
culated throughout the refrigerant system with the
refrigerant.
The compressor draws in low-pressure refrigerant
vapor from the evaporator through its suction port. It
then compresses the refrigerant into a high-pressure,
high-temperature refrigerant vapor, which is then
pumped to the condenser through the compressor dis-
charge port.
The compressor cannot be repaired. If faulty or
damaged, the entire compressor assembly must be
replaced. The compressor clutch, pulley and clutch
coil are available for service.
OPERATION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
The high pressure relief valve vents the system
when a discharge pressure of 3445 to 4135 kPa (500
to 600 psi) or above is reached. The valve closes
when a minimum discharge pressure of 2756 kPa
(400 psi) is reached.
The high pressure relief valve vents only enough
refrigerant to reduce the system pressure, and then
re-seats itself. The majority of the refrigerant is con-
served in the system. If the valve vents refrigerant, it
does not mean that the valve is faulty.
The high pressure relief valve is a factory-cali-
brated unit. The valve cannot be adjusted or
repaired, and must not be removed or otherwise dis-
turbed. The valve is only serviced as a part of the
compressor assembly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COMPRESSOR
NOISE
When investigating an air conditioning related
noise, you must first know the conditions under
which the noise occurs. These conditions include:
weather, vehicle speed, transmission in gear or neu-
tral, engine speed, engine temperature, and any
other special conditions. Noises that develop during
air conditioning operation can often be misleading.
For example: What sounds like a failed front bearing
or connecting rod, may be caused by loose bolts, nuts,
mounting brackets, or a loose compressor clutch
assembly.
Drive belts are speed sensitive. At different engine
speeds and depending upon belt tension, belts can
develop noises that are mistaken for a compressornoise. Improper belt tension can cause a misleading
noise when the compressor clutch is engaged, which
may not occur when the compressor clutch is disen-
gaged. Check the serpentine drive belt condition and
tension as described in Cooling before beginning this
procedure.
(1) Select a quiet area for testing. Duplicate the
complaint conditions as much as possible. Switch the
compressor on and off several times to clearly iden-
tify the compressor noise. Listen to the compressor
while the clutch is engaged and disengaged. Probe
the compressor with an engine stethoscope or a long
screwdriver with the handle held to your ear to bet-
ter localize the source of the noise.
(2) Loosen all of the compressor mounting hard-
ware and retighten. Tighten the compressor clutch
mounting nut. Be certain that the clutch coil is
mounted securely to the compressor, and that the
clutch plate and rotor are properly aligned and have
the correct air gap. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH - INSTALLATION)
(3) To duplicate a high-ambient temperature condi-
tion (high head pressure), restrict the air flow
through the condenser. Install a manifold gauge set
to be certain that the discharge pressure does not
exceed 2760 kPa (400 psi).
(4) Check the refrigerant system plumbing for
incorrect routing, rubbing or interference, which can
cause unusual noises. Also check the refrigerant lines
for kinks or sharp bends that will restrict refrigerant
flow, which can cause noises. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAU-
TION)
(5) If the noise is from opening and closing of the
high pressure relief valve, evacuate and recharge the
refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIG-
ERANT SYSTEM CHARGE) If the high pressure
relief valve still does not seat properly, replace the
compressor.
(6) If the noise is from liquid slugging on the suc-
tion line. Check the refrigerant oil level and the
refrigerant system charge. (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIGER-
ANT OIL - STANDARD PROCEDURE) (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
SPECIFICATIONS - CHARGE CAPACITY) If either
is out of specification range reclaim, evacuate and
recharge the refrigerent system(Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIG-
ERANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE), (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/RE-
24 - 36 PLUMBINGDR
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2827 of 2895

air and boil the moisture out of the system at near
room temperature. To evacuate the refrigerant sys-
tem, use the following procedure:
(1) Connect a R-134a refrigerant recovery/recy-
cling/charging station that meets SAE Standard
J2210 and a manifold gauge set (if required) to the
refrigerant system of the vehicle and recover refrig-
erant.
(2) Open the low and high side valves and start
the charging station vacuum pump. When the suc-
tion gauge reads 88 kPa (26 in. Hg.) vacuum or
greater, close all of the valves and turn off the vac-
uum pump.
(a) If the refrigerant system fails to reach the
specified vacuum, the system has a leak that must
be corrected. See Refrigerant System Leaks in the
Diagnosis and Testing section of this group for the
procedures.
(b) If the refrigerant system maintains the spec-
ified vacuum for five minutes, restart the vacuum
pump, open the suction and discharge valves and
evacuate the system for an additional ten minutes.
(3) Close all of the valves, and turn off the charg-
ing station vacuum pump.
(4) The refrigerant system is now ready to be
charged with R-134a refrigerant(Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIG-
ERANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
STANDARD PROCEDURE- REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY
WARNING: (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) AND (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAU-
TION) BEFORE PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING
OPERATION.
A R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging
station that meets SAE Standard J2210 must be
used to recover the refrigerant from an R-134a refrig-
erant system. Refer to the operating instructions sup-
plied by the equipment manufacturer for the proper
care and use of this equipment.
STANDARD PROCEDURE- REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM CHARGE
WARNING: (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) AND (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAU-
TION) BEFORE PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING
OPERATION.
After the refrigerant system has been tested for
leaks and evacuated, a refrigerant charge can beinjected into the system. See Refrigerant Charge
Capacity in the Service Procedures section of this
group for the proper amount of the refrigerant
charge, this fill level can also be found on a label
attached under the hood of the vehicle..
A R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging
station that meets SAE Standard J2210 must be
used to charge the refrigerant system with R-134a
refrigerant. Refer to the operating instructions sup-
plied by the equipment manufacturer for the proper
care and use of this equipment.
The R-134a refrigerant system charge capacity for
this vehicle is:
²If equipped with a 3.7L or a 4.7L engine charge
to 0.6804 Kg. (24 oz.).
²If equipped with a 5.9L engine charge to 0.7371
Kg. ( 26 oz.).
REFRIGERANT LINE COUPLER
DESCRIPTION
Spring-lock type refrigerant line couplers are used
to connect many of the refrigerant lines and other
components to the refrigerant system. These couplers
require a special tool for disengaging the two coupler
halves.
OPERATION
The spring-lock coupler is held together by a garter
spring inside a circular cage on the male half of the
fitting (Fig. 16). When the two coupler halves are
connected, the flared end of the female fitting slips
behind the garter spring inside the cage on the male
fitting. The garter spring and cage prevent the flared
end of the female fitting from pulling out of the cage.
Three O-rings on the male half of the fitting are
used to seal the connection. These O-rings are com-
patible with R-134a refrigerant and must be replaced
with O-rings made of the same material.
Secondary clips are installed over the two con-
nected coupler halves at the factory for added blowoff
protection.
REMOVAL
WARNING: (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAU-
TION) BEFORE PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING
OPERATION.
(1) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
24 - 52 PLUMBINGDR
REFRIGERANT (Continued)
Page 2837 of 2895

²Upstream O2S VoltsÐ A live reading of the
Oxygen Sensor to indicate its performance. For
example, stuck lean, stuck rich, etc.
²SCW Time in Window (Similar Conditions
Window Time in Window)Ð A timer used by the
PCM that indicates that, after all Similar Conditions
have been met, if there has been enough good engine
running time in the SCW without failure detected.
This timer is used to increment a Good Trip.
²Fuel System Good Trip CounterÐATrip
Counter used to turn OFF the MIL for Fuel System
DTCs. To increment a Fuel System Good Trip, the
engine must be in the Similar Conditions Window,
Adaptive Memory Factor must be less than cali-
brated threshold and the Adaptive Memory Factor
must stay below that threshold for a calibrated
amount of time.
²Test Done This TripÐ Indicates that the
monitor has already been run and completed during
the current trip.
MISFIRE
²Same Misfire Warm-Up StateÐ Indicates if
the misfire occurred when the engine was warmed up
(above 160É F).
²In Similar Misfire WindowÐ An indicator
that 'Absolute MAP When Misfire Occurred' and
'RPM When Misfire Occurred' are all in the same
range when the failure occurred. Indicated by switch-
ing from 'NO' to 'YES'.
²Absolute MAP When Misfire OccurredÐ
The stored MAP reading at the time of failure.
Informs the user at what engine load the failure
occurred.
²Absolute MAPÐ A live reading of engine load
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²RPM When Misfire OccurredÐ The stored
RPM reading at the time of failure. Informs the user
at what engine RPM the failure occurred.
²Engine RPMÐ A live reading of engine RPM
to aid the user in accessing the Similar Conditions
Window.
²Adaptive Memory FactorÐ The PCM utilizes
both Short Term Compensation and Long Term Adap-
tive to calculate the Adaptive Memory Factor for
total fuel correction.
²200 Rev CounterÐ Counts 0±100 720 degree
cycles.
²SCW Cat 200 Rev CounterÐ Counts when in
similar conditions.
²SCW FTP 1000 Rev CounterÐ Counts 0±4
when in similar conditions.
²Misfire Good Trip CounterÐ Counts up to
three to turn OFF the MIL.
²Misfire DataÐ Data collected during test.²Test Done This TripÐ Indicates YES when the
test is done.
OPERATION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems and conditions that could have malfunctions
causing driveability problems. The PCM might not
store diagnostic trouble codes for these conditions.
However, problems with these systems may cause the
PCM to store diagnostic trouble codes for other sys-
tems or components.EXAMPLE:a fuel pressure
problem will not register a fault directly, but could
cause a rich/lean condition or misfire. This could
cause the PCM to store an oxygen sensor or misfire
diagnostic trouble code
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor or fuel system diag-
nostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system, although it may set a fuel
system fault.
FUEL INJECTOR MECHANICAL MALFUNCTIONS
The PCM cannot determine if a fuel injector is
clogged, the needle is sticking or if the wrong injector
is installed. However, these could result in a rich or
lean condition causing the PCM to store a diagnostic
trouble code for either misfire, an oxygen sensor, or
the fuel system.
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION
Although the PCM monitors engine exhaust oxygen
content when the system is in closed loop, it cannot
determine excessive oil consumption.
THROTTLE BODY AIR FLOW
The PCM cannot detect a clogged or restricted air
cleaner inlet or filter element.
25 - 8 EMISSIONS CONTROLDR
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)