FORD FIESTA 2007 Workshop Manual
Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2007, Model line: FIESTA, Model: FORD FIESTA 2007Pages: 1226, PDF Size: 61.26 MB
Page 931 of 1226
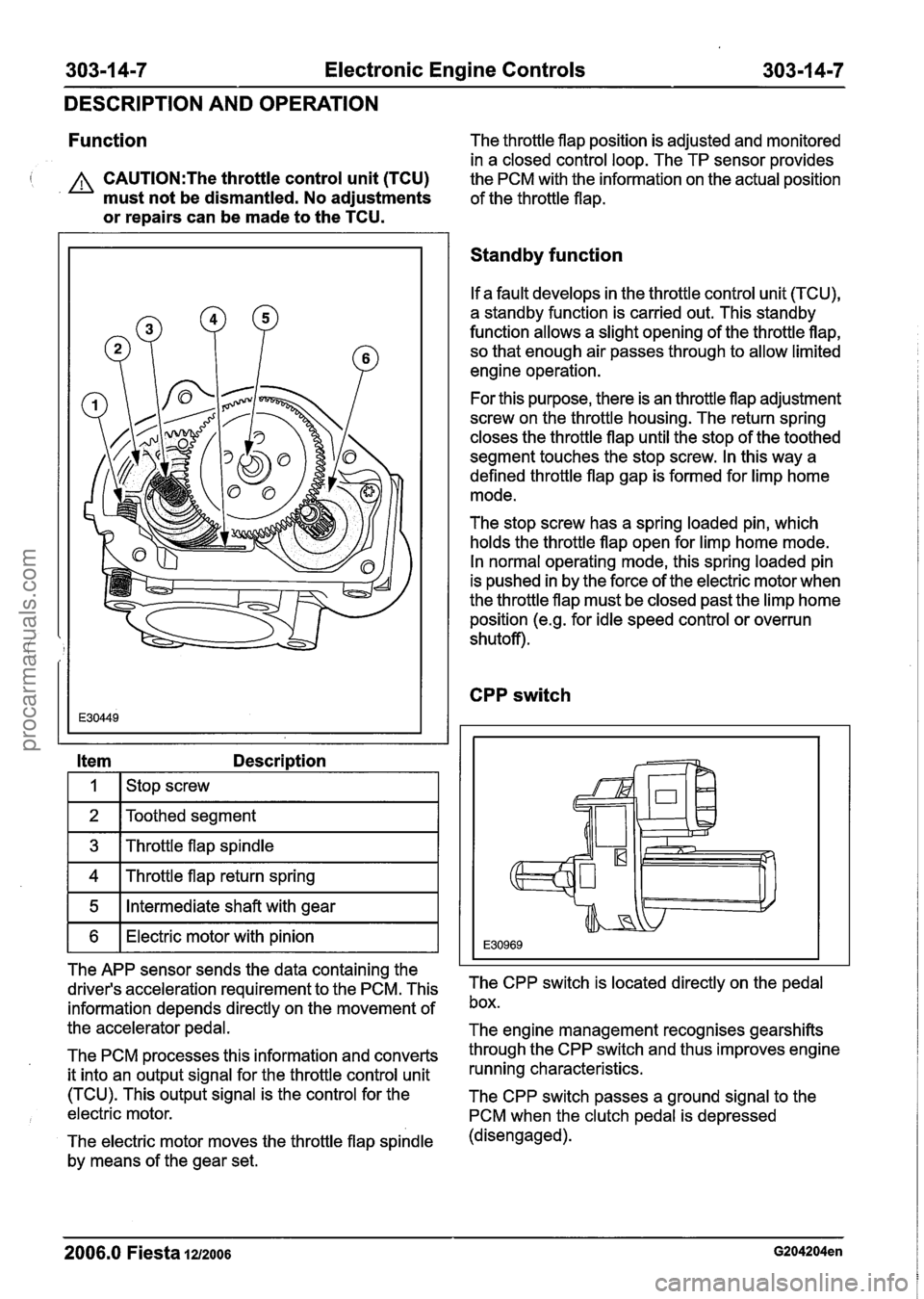
303-1 4-7 Electronic Engine Controls 303-1 4-7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Function The throttle flap position is adjusted and monitored
in a closed control loop. The TP sensor provides
I A CAUTI0N:The throttle control unit (TCU)
the PCM with the information on the actual position
must not be dismantled. No adjustments
of the throttle flap.
or repairs can be made to the TCU.
Item Description
I I I stop screw I
1 2 IToothed segment I
1 3 1 Throttle flap spindle I
1 4 1 Throttle flap return spring I
1 5 1 Intermediate shaft with gear I
1 6 1 Electric motor with pinion I
The APP sensor sends the data containing the
driver's acceleration requirement to the PCM. This
information depends directly on the movement of
the accelerator pedal.
The PCM processes this information and converts
it into an output signal for the throttle control unit
(TCU). This output signal is the control for the
electric motor.
The electric motor moves the throttle flap spindle
by means of the gear set.
Standby function
If a fault develops in the throttle control unit (TCU),
a standby function is carried out. This standby
function allows a slight opening of the throttle flap, so that enough air passes through to allow limited
engine operation.
For this purpose, there is an throttle flap adjustment
screw on the throttle housing. The return spring
closes the throttle flap until the stop of the toothed
segment touches the stop screw. In this way a
defined throttle flap gap is formed for limp home
mode.
The stop screw has a spring loaded pin, which
holds the throttle flap open for limp home mode.
In normal operating mode, this spring loaded pin
is pushed in by the force of the electric motor when
the throttle flap must be closed past the limp home
position
(e.g. for idle speed control or overrun
shutoff).
CPP switch
The CPP switch is located directly on the pedal
box.
The engine management recognises gearshifts
through the CPP switch and thus improves engine
running characteristics.
The CPP switch passes a ground signal to the
PCM when the clutch pedal is depressed
(disengaged).
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G204204en
procarmanuals.com
Page 932 of 1226
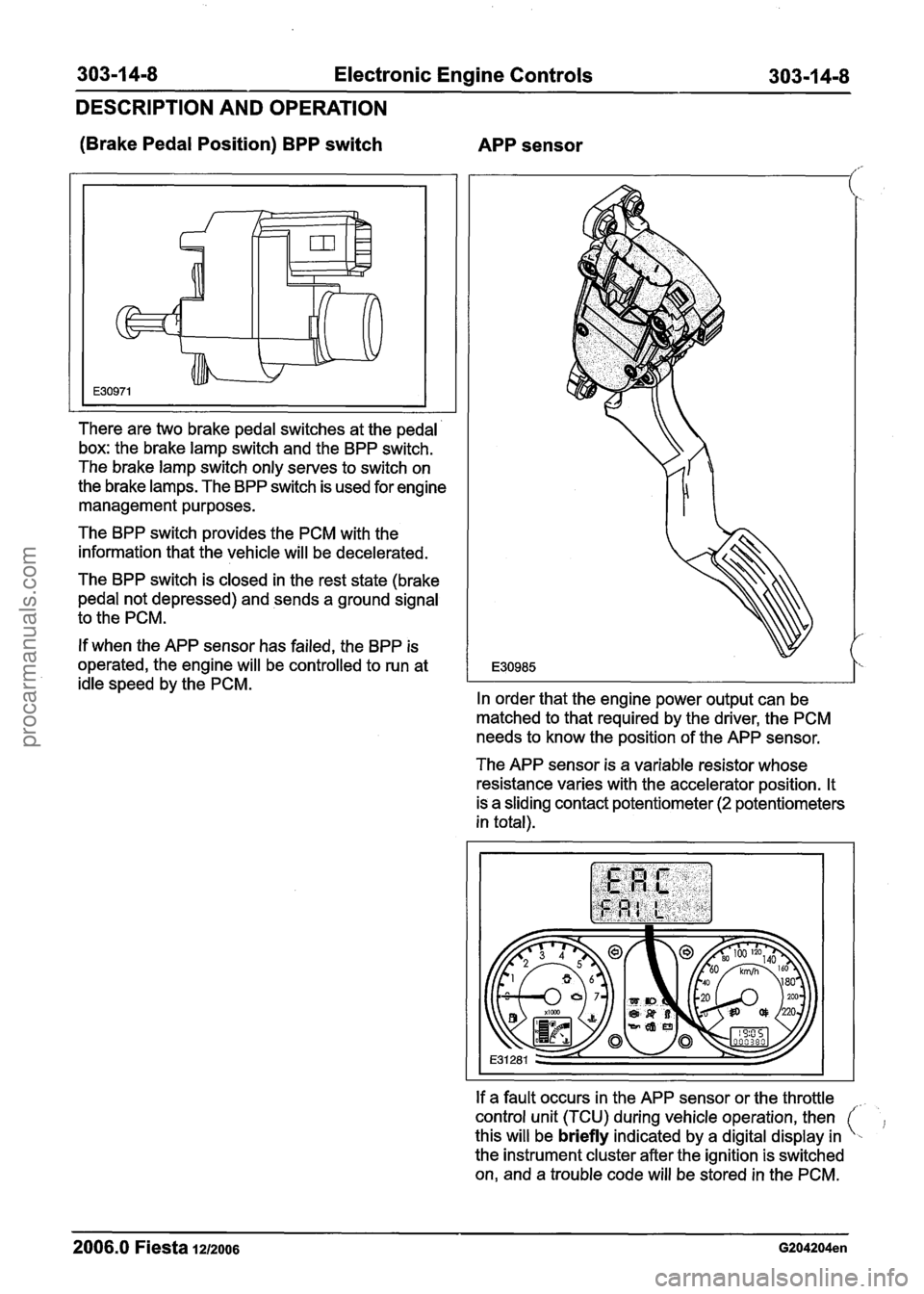
Electronic Engine Controls
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
(Brake Pedal Position) BPP switch
APP sensor
There are two brake pedal switches at the pedal
box: the brake lamp switch and the BPP switch.
The brake lamp switch only serves to switch on
the brake lamps. The BPP switch is used for engine
management purposes.
The BPP switch provides the PCM with the
information that the vehicle will be decelerated.
The BPP switch is closed in the rest state (brake
pedal not depressed) and sends a ground signal
to the PCM.
If when the APP sensor has failed, the BPP is
operated, the engine will be controlled to run at
idle speed by the PCM.
In order that the engine power output can be
matched to that required by the driver, the PCM
needs to know the position of the APP sensor.
The APP sensor is a variable resistor whose
resistance varies with the accelerator position. It
is a sliding contact potentiometer
(2 potentiometers
in total).
If a fault occurs in the APP sensor or the throttle
control unit (TCU) during vehicle operation, then
this will be
briefly indicated by a digital display in
the instrument cluster after the ignition is switched
on, and a trouble code will be stored in the PCM.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G204204en
procarmanuals.com
Page 933 of 1226

303-1 4-9 Electronic Engine Controls 303-1 4-9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
If one potentiometer fails, the engine will run with
reduced power (maximum torque
80 Nm), if both
potentiometers fail, the engine will run with reduced
power (maximum torque
55 Nm).
This warning may also be indicated if the engine
does not start. The cause may be a poor state of
charge of the battery.
The warning indication normally disappears once
the battery is re-charged.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G204204en
procarmanuals.com
Page 934 of 1226
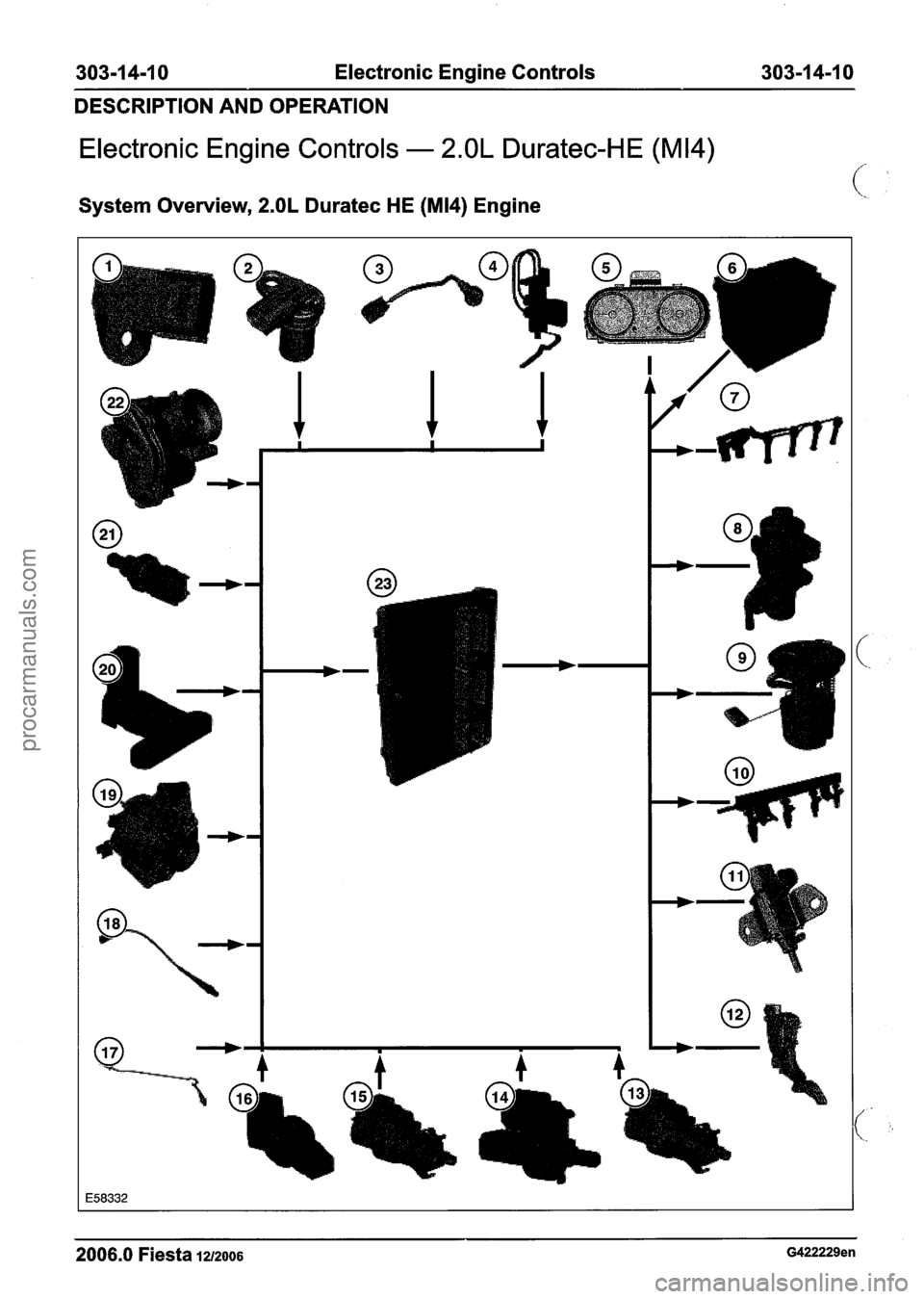
303-1 4-1 0 Electronic Engine Controls 303-1 4-1 0
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Electronic Engine Controls - 2.OL Duratec-HE (M14)
System Overview, 2.OL Duratec HE (M14) Engine
--
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G422229en
procarmanuals.com
Page 935 of 1226

303-1 4-1 1 Electronic Engine Controls 303-1 4-1 I
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Item Description Components
MAPT sensor
Manifold absolute pressure and
temperature (MAPT) sensor
1 2 1 Camshaft position (CMP) sensor I
1 3 1 Knock sensor (KS) I
vl~Ame%air temperature sensor I
1 5 1 Instrument cluster I
1 6 1 Battery I
1 7 1 Spark plug wires I
1 8 1 Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve I
1 9 1 Fuel pump module I
1 10 1 Fuel rail and fuel injectors I
I 11 I Intake manifold tuning valve solenoid The
MAPT sensor is attached to the housing of the
intake manifold valve behind the throttle body. The
signal from the MAPT sensor is used to modify the
ignition and fuel delivery.
1 12 1 Accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor
1 13 1 Clutch pedal position (CPP) switch
1 14 1 Brake pedal position (BPP) switch
CMP sensor 1 15 1 Stoplamp switch
1 16 1 Power steering pressure (PSP) switch I
1 17 1 Catalyst monitor sensor I
FIGted oxygen sensor (H02S) I
1 19 1 Generator (input signal) I
1 20 1 Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor I
1 21 1 Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor I
22 Throttle position
(TP) sensor (part of
I I throttle body)
1 23 1 Powertrain control module (PCM) I The CMP sensor is located on the right-hand side
of the valve cover above the intake camshaft. The
CMP sensors send signals to the PCM which are
then used by the PCM to calculate the position of
the camshaft.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G422229en
procarmanuals.com
Page 936 of 1226
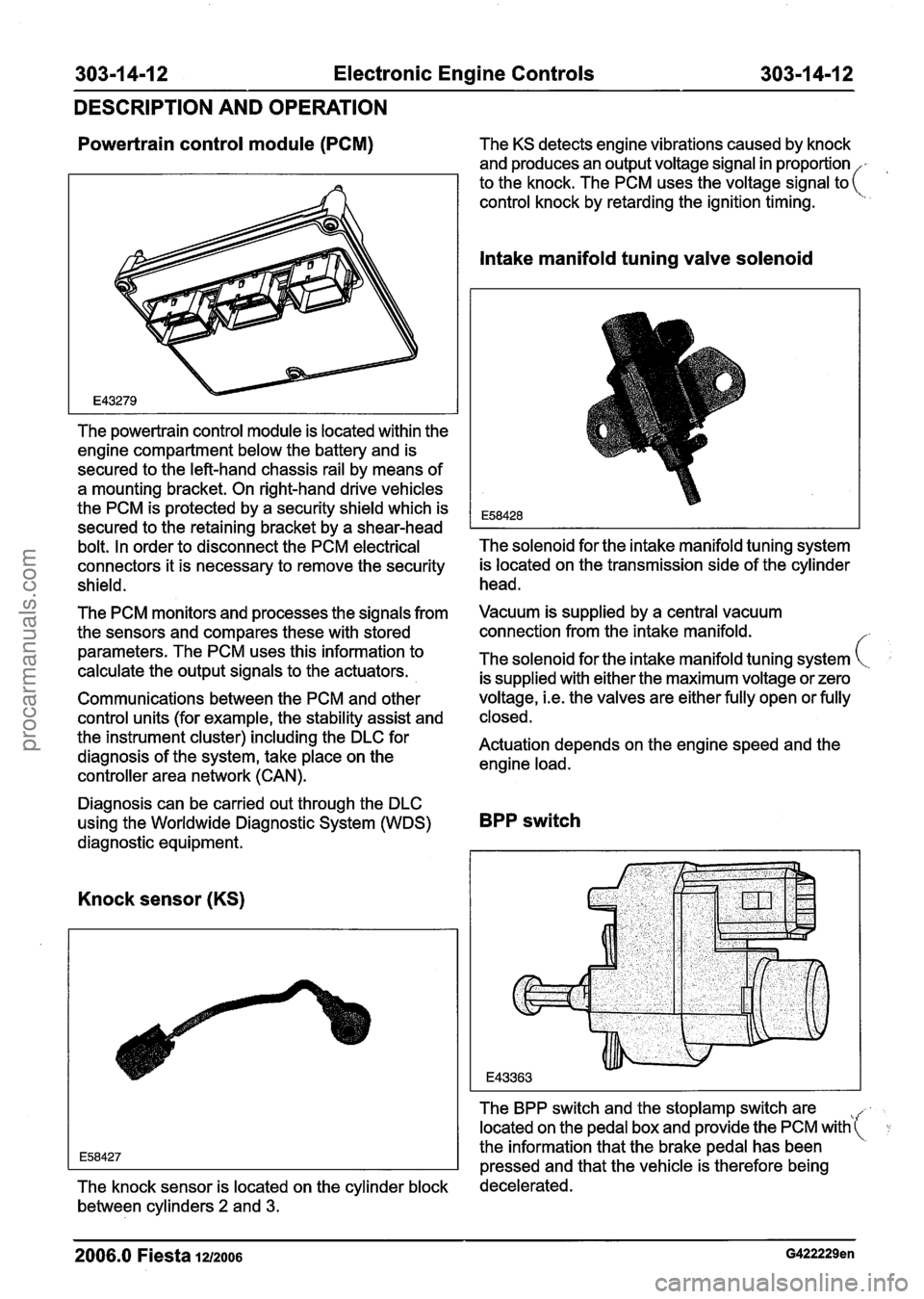
303-1 4-1 2 Electronic Engine Controls 303-1 4-1 2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Powertrain control module (PCM) The KS detects engine vibrations caused by knock
and produces an output voltage signal in proportion
, to the knock. The PCM uses the voltage signal to(
control knock by retarding the ignition timing.
The powertrain control module is located within the
engine compartment below the battery and is
secured to the left-hand chassis rail by means of
a mounting bracket. On right-hand drive vehicles
the PCM is protected by a security shield which is
secured to the retaining bracket by a shear-head
bolt. In order to disconnect the PCM electrical
connectors it is necessary to remove the security
shield.
The PCM monitors and processes the signals from
the sensors and compares these with stored
parameters. The PCM uses this information to
calculate the output signals to the actuators.
Communications between the PCM and other
control units (for example, the stability assist and
the instrument cluster) including the DLC for
diagnosis of the system, take place on the
controller area network (CAN).
Intake manifold tuning valve solenoid
The solenoid for the intake manifold tuning system
is located on the transmission side of the cylinder
head.
Vacuum is supplied by a central vacuum
connection from the intake manifold.
The solenoid for the intake manifold tuning system
is supplied with either the maximum voltage or zero
voltage,
i.e. the valves are either fully open or fully
closed.
Actuation depends on the engine speed and the
engine load.
Diagnosis can be carried out through the DLC
using the Worldwide Diagnostic System (WDS)
BPP switch
diagnostic equipment.
Knock sensor (KS)
The BPP switch and the stoplamp switch are tt(r located on the pedal box and provide the PCM with
the information that the brake pedal has been
pressed and that the vehicle is therefore being
The knock sensor is located on the cylinder block decelerated.
between cylinders
2 and 3.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G422229en
procarmanuals.com
Page 937 of 1226
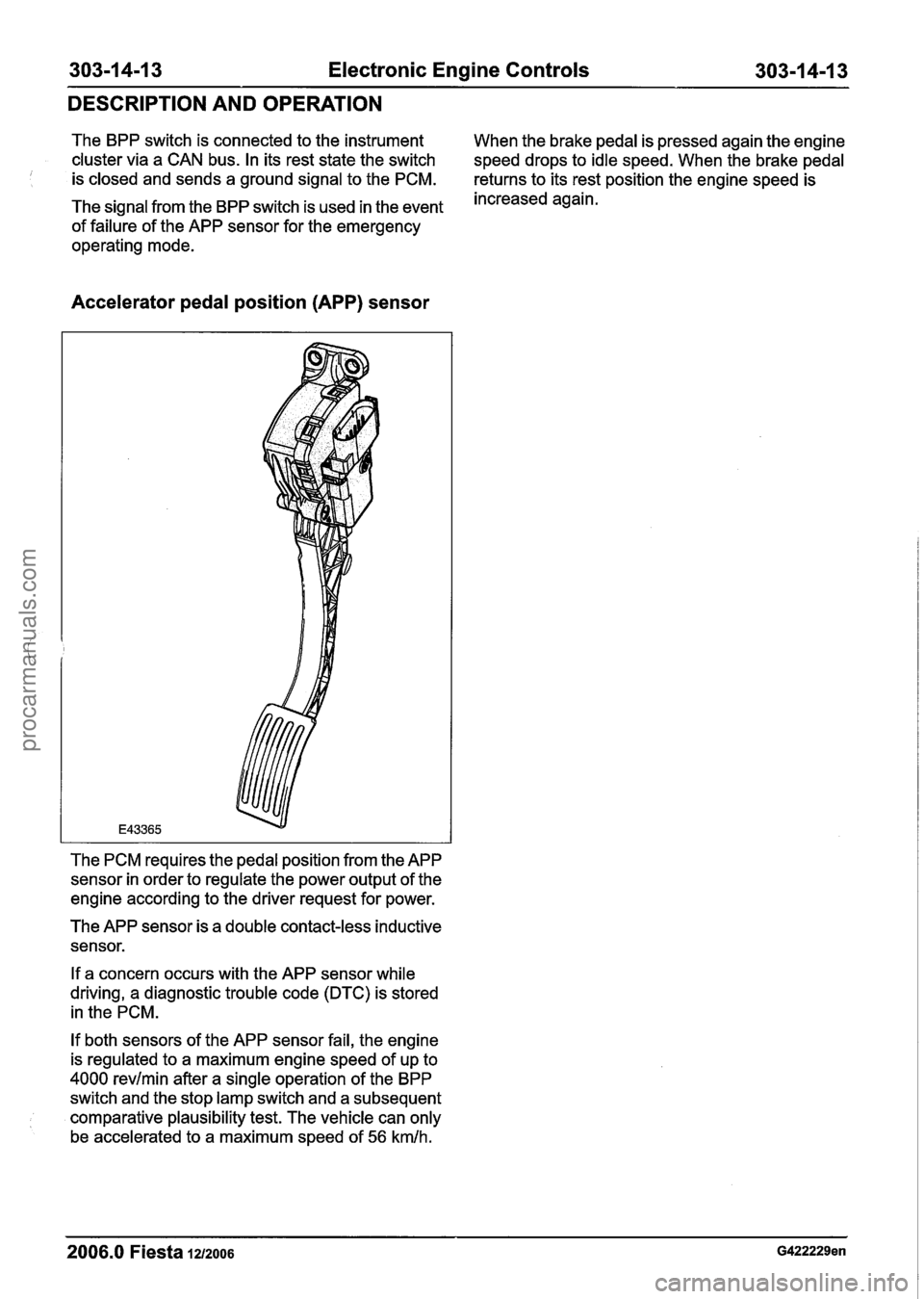
303-1 4-1 3 Electronic Engine Controls 303-1 4-1 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The BPP switch is connected to the instrument
When the brake pedal is pressed again the engine
cluster via a CAN bus. In its rest state the switch
speed drops to idle speed. When the brake pedal
is closed and sends a ground signal to the PCM.
returns to its rest position the engine speed is
The signal from the BPP switch is used in the event increased again.
of failure of the APP sensor for the emergency
operating mode.
Accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor
The PCM requires the pedal position from the APP
sensor in order to regulate the power output of the
engine according to the driver request for power.
The APP sensor is a double contact-less inductive
sensor.
If a concern occurs with the APP sensor while
driving, a diagnostic trouble code
(DTC) is stored
in the PCM.
If both sensors of the APP sensor fail, the engine
is regulated to a maximum engine speed of up to
4000 revlmin after a single operation of the BPP
switch and the stop lamp switch and a subsequent
comparative plausibility test. The vehicle can only
be accelerated to a maximum speed of
56 kmlh.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G422229en
procarmanuals.com
Page 938 of 1226

303-1 4-1 4 Electronic Engine Controls 303-1 4-1 4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Electronic Engine Controls
General Equipment
I Worldwide Diagnostic system (WDS)
Principles of Operation
For Principles of Operation on the electronic
accelerator control system
REFER to: Acceleration Control (31
0-02A,
Diagnosis and Testing).
European On-Board Diagnostics (EOBD)
EOBD is a diagnostic system integrated into the
powertrain control module (PCM). This system
continuously monitors vehicle emission
components. The system includes a malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) which indicates when there is
a concern that can affect emissions or the system
malfunctions. Data stored within the module DTC
memory can be accessed using a generic scan
tool or WDS.
EOBD is mandated within European Union
regulations from the year 2000 for passenger
vehicles with petrol engines and from 2003 onwards for passenger vehicles with diesel
engines.
EOBD Functions:
Establishes when and how emissions control
faults must be indicated.
Actuates emission control malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL) and fault memory.
Indicates operating conditions in which the
concern occurred (freeze frame data).
Standardized output of operating data such as
engine speed, engine coolant temperature etc.
Standardized names and abbreviations for
components and systems.
Standardized
DTCs for all manufacturers.
Standardized communication with the diagnostic
equipment.
Standardized 16-pin data link connector (DLC)
in area of the instrument panel.
Concern display must be possible using a
generic scan tool.
EOBD consists of the following elements:
Warm-up Cycle C'
The warm-up cycle is an operation that consists of
key on, engine start and a coolant temperature
increase of
22"C, exceeding 71 OC on completion.
Drive Cycle
A drive cycle commences when the engine is
started (cold or warm) and ends when the engine
is switched off.
Trip
A trip begins when the engine is started and is
complete when all the EOBD monitors have
completed a self-test. This may take place over a
number of drive cycles. On diesel variants, the
information gathered from one drive cycle is not
carried over to a subsequent cycle or cycles.
When a concern has been rectified, particularly
after electronic engine control components have
been changed, the DTC memory, which is part of
the EEPROM must be cleared of all trouble codes.
When the DTC memory has been cleared, the code
.
PI000 (known as the readiness code) is set in the
PCM memory, which indicates that since the
EEPROM has been cleared, not all of the
monitoring systems have completed their tests.
PI000 can only be cleared by carrying out a trip,
which includes driving the vehicle under variable
conditions of speed, load and time so that all of the
monitors are completed. As
PI000 will not
illuminate the MIL it is not necessary to carry out
the trip before returning the vehicle to the customer.
Freeze Frame Data
When a concern is detected, various data is stored
depending on application including:
Diagnostic trouble code.
Vehicle speed.
Engine coolant temperature.
Engine speed.
Engine load.
Mixture formation trim value (trim value for
engine wear) (All except vehicles with diesel
engine).
State of oxygen sensor control (open and closed
loop) (All except vehicles with diesel engine).
Distance covered since the concern was first
registered.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G384566en
procarmanuals.com
Page 939 of 1226

303-1 4-1 5 Electronic Engine Controls 303-1 4-1 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Monitors
The purpose of the monitors is to continuously
check the operation of the emission related sensors
and actuators. It then establishes if they are
operating within specified tolerances. All monitors
carry out their functions in such a way as to be
unnoticeable by the driver of the vehicle. Each one
is carried out under specific conditions of load,
speed and engine temperature. The Comprehensive Component Monitor, Combustion
Misfire Monitor and
AirIFuel Ratio Monitor operate
continuously. The remaining monitors are only
invoked under certain operating conditions. On
diesel variants, all of the monitors operate under
normal driving conditions: There are no monitors
which intervene and cause special operating
modes to enable the monitors to work. Some diesel
monitors are non-continuous. This means that in
a drive cycle, monitoring is done as and when
suitable driving conditions exist and potential faults
are accumulated and compared with acceptance
criteria. Examples of this type are the turbocharger
boost pressure and exhaust gas recirculation
(EGR) monitors on vehicles with common rail fuel
injection.
( Comprehensive Component Monitor (CCM)
When the CCM detects a component operating out
of tolerance, it sets a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC), which is stored in the EEPROM. If the same
concern is confirmed during the next trip the MIL
will be switched on. The CCM monitors many
components, sub-systems and signals. The
following is a list of those that can effect emissions
depending on application:
Electronic Ignition (El) System.
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor.
Ignition Coil.
Electronic Throttle Control Unit.
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor.
Air Conditioning
(AIC) Clutch.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve.
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor.
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor.
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor.
Cylinder Head Temperature (CHT) Sensor.
Heated Oxygen Sensor
(H02S).
Catalyst Monitor Sensor.
Charge Air Temperature Sensor.
Knock Sensor (KS).
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor.
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS).
Boost Pressure Sensor.
Cam-Crank Phasing Sensor.
EEPROM.
High Pressure Fuel Injection Pump.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve Monitor.
Fuel Injectors.
Turbocharger.
Combustion Noise Monitor.
Barometric Pressure (BARO) Sensor.
Combustion Misfire Monitor (All except vehicles
with diesel engine)
The combustion misfire monitor operates independently of the others, and can detect misfires
caused by the ignition system, fuel system or
mechanical engine components. As each cylinder
fires, a characteristic crankshaft acceleration is
produced. The monitor detects irregularities in the
acceleration pattern using the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor, thus detecting the misfire. It can
also detect which cylinder has misfired.
Combustion misfires can be categorized as follows:
Type
A: These can cause catalytic converter
damage due to excessive internal temperatures.
If a certain number of misfires occur over a
pre-determined number of engine revolutions, the
MIL will be switched on to alert the driver of the
concern.
Type B: These can lead to an increase in emissions
to a point above the EOBD threshold. If the misfire
is detected during a second trip, over a,
pre-determined number of engine revolutions, the
MIL will be switched on. If the misfire does not
occur over the next three trips, the MIL will be
extinguished
AirIFuel Ratio (AFR) Monitor (All except vehicles
with diesel engine)
The H02S fitted before the catalytic converter
(upstream) measures the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas and the variations in it. This then
enables the PCM to adjust the opening times of
the fuel injectors to maintain the correct AFR. This
is known as Short Term Fuel Trim (STFT). If the
same variation is registered a pre-determined
number of times, a permanent correction factor is
applied. This is known as Long Term Fuel Trim
(LTFT), which is stored in the EEPROM. When the
correction factors exceed pre-determined limits a
DTC will be set in the EEPROM. If a concern is
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G384566en
procarmanuals.com
Page 940 of 1226

Electronic Engine Controls
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
detected in either the STFT or LTFT, and it is still
present on a second trip, the MIL will be switched
on.
Heated Oxygen Sensor (H02S) Monitor (All except
vehicles with diesel engine)
This monitors the operation of the pre (upstream)
and post (downstream) catalytic converter
H02S
sensors. It will detect deviations in airlfuel ratios
(AFR) and sensor faults.
The
H02S will cause emission increase when its
response time increases too much. To diagnose
a sensor a period is measured and the number of
leanlrich transitions are counted. The sum of valid
periods is then calculated. To avoid
non-representative measurements, the period is
valid only if the
H02S has been below a low
threshold and above a high threshold between 2
consecutive leanlrich transitions.
A failure is
declared when the sum of the measured periods
exceeds the sum of the corresponding limit (held
within the PCM) and the MIL is illuminated.
Catalytic Converter Efficiency Monitor (All except
vehicles with diesel engine)
The efficiency of a catalytic converter is measured
by its ability to store and later release oxygen to
convert harmful gases. The efficiency is reduced
if the converter becomes contaminated as it ages,
and at high gas flow rates, because the exhaust
gas does not remain in the converter long enough
to complete the conversion process. switches
over or until the end of a delay. If this
delay expires or the sensor does not switch, the
sensor is treated as failed.
Combustion Noise Monitor (Vehicles with common
rail fuel injection)
In diesel variants, the Combustion Noise Monitor
is used to trim the fuel injection pulse lengths. Each
fuel injector has an associated set of correction
data that is determined during a production end of
line test. The Combustion Noise Monitor is used
to determine how the fuel injector characteristic
changes from this initial calibration over the life of
the fuel injector.
EGR Monitor (Vehicles with diesel engine)
The functionality of the EGR system is checked by
comparing either the MAP sensor output or EGR
valve lift potentiometer output (depending upon
application) with expected values.
Diagnostic Requirements
Vehicles equipped with EOBD, can be diagnosed
using the WDS. In order for the EOBD system to
be invoked, a number of criteria must be met. After
any repair, which could affect emissions, a trip must
be carried out on the vehicle, to make sure that
engine management system operates correctly.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The MIL is located in the instrument cluster and is
fitted to alert the driver to the fact that an abnormal
This monitor checks for the oxygen storage condition
has developed in the engine management
capacity (OSC) of the catalytic converter. During system,
that is having an adverse effect on
a controlled period, the catalyst monitor sensor emissions.
In cases of misfires which are likely to
signal is analyzed to evaluate the OSC of the cause
catalytic converter damage, it is switched
catalyst. It represents the quantity of oxygen that on immediately.
With all other faults it will illuminate
is really used for the oxidation-reduction reaction continuously
from the second trip after the condition
by the catalytic converter If a fault has occurred occurred.
Under normal operation it should
with the catalyst monitor sensor during the catalyst illuminate
at key-on and go out almost as soon as
diagnosis, a sensor diagnosis is carried out. During the
engine is started.
the controlled diagnosis phase, the catalyst monitor
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) sensor activity is measured and is compared to the
OSC of the catalyst. If this activity is high (low The
DTCs given
by the PCM are standardized,
0SC)theMILwillbeilluminated.Ifthroughoutthe whichmeansthatgenericscantoolscanread
controlled phase, repeated several times, the results from
all vehicles.
downstream sensor output has not moved, the
closed loop mode is delayed in order to test the
sensor. If the catalyst monitor sensor is set to rich,
the injection time is forced to lean and conversely
if the downstream sensor is set to lean, the
injection time is forced to rich until the sensor
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G384566en
procarmanuals.com