Index FORD KUGA 2011 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2011, Model line: KUGA, Model: FORD KUGA 2011 1.GPages: 2057
Page 1783 of 2057
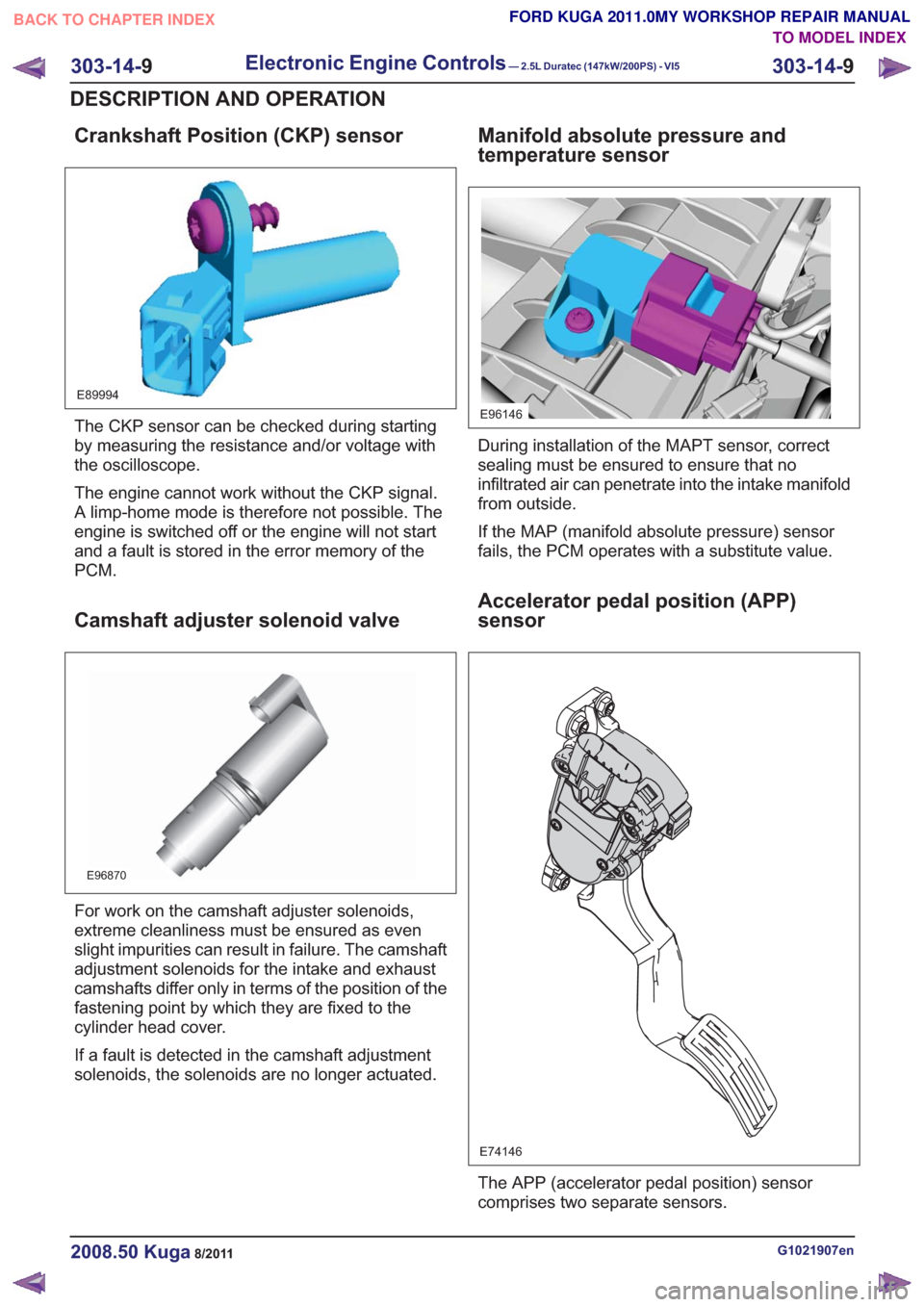
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
E89994
The CKP sensor can be checked during starting
by measuring the resistance and/or voltage with
the oscilloscope.
The engine cannot work without the CKP signal.
A limp-home mode is therefore not possible. The
engine is switched off or the engine will not start
and a fault is stored in the error memory of the
PCM.
Camshaft adjuster solenoid valve
E96870
For work on the camshaft adjuster solenoids,
extreme cleanliness must be ensured as even
slight impurities can result in failure. The camshaft
adjustment solenoids for the intake and exhaust
camshafts differ only in terms of the position of the
fastening point by which they are fixed to the
cylinder head cover.
If a fault is detected in the camshaft adjustment
solenoids, the solenoids are no longer actuated.
Manifold absolute pressure and
temperature sensor
E96146
During installation of the MAPT sensor, correct
sealing must be ensured to ensure that no
infiltrated air can penetrate into the intake manifold
from outside.
If the MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor
fails, the PCM operates with a substitute value.
Accelerator pedal position (APP)
sensor
E74146
The APP (accelerator pedal position) sensor
comprises two separate sensors.
G1021907en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-9
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1784 of 2057

If one of the two APP sensors fails, then only a
proportion of the engine's power will be available
when accelerating. Top speed can nevertheless
be achieved.
If both of the APP sensors fail, the engine is
regulated to a defined speed following a plausibility
check after the BPP (brake pedal position) switch
and brake light switch have been actuated once.
The vehicle can then only be accelerated to a
defined speed.
In either case, a fault is saved in the error memory
of the PCM.
Throttle control unit
E74167
1
2
Description
Item
TP (throttle position) sensor
1
Electric motor
2
CAUTION: The throttle control unit must
not be repaired or adjusted. The stop of
the throttle valve must on no account be
adjusted.
After disconnecting the battery or replacing the
throttle control unit or the PCM, initialization is
necessary. • engine off
• Accelerator pedal not pressed
• Battery voltage 11 ... 14 V
• Ignition key in ON position
• Wait approximately 30 seconds until initialization
is complete.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
sensor
E94804
The ECT (engine coolant temperature) sensor is
designed as an NTC (negative temperature
coefficient) resistor.
If the signal from the ECT sensor fails, the cooling
fan is on all the time and the A/C (air conditioning)
is turned off. When the ignition is switched on, the
value from the IAT (intake air temperature) sensor
is read. When the engine is running, the
temperature is calculated using a temperature map
stored in the PCM according to how long the
engine has been running. This substitute value is
then used as the basis for calculating the injected
fuel quantity and the ignition timing.
Ignition coil-on-plug
E73540
G1021907en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 10
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
10
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1785 of 2057

The resistance in the ignition coil primary circuit
cannot be checked using a multimeter because
the power output stage is integrated into the ignition
coil.
G1021907en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-11
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1786 of 2057

Electronic Engine Controls – System Operation and ComponentDescription
System Diagram
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 12
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
12
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
VIEW DIAGRAM ON THE NEXT PAGE
Page 1787 of 2057
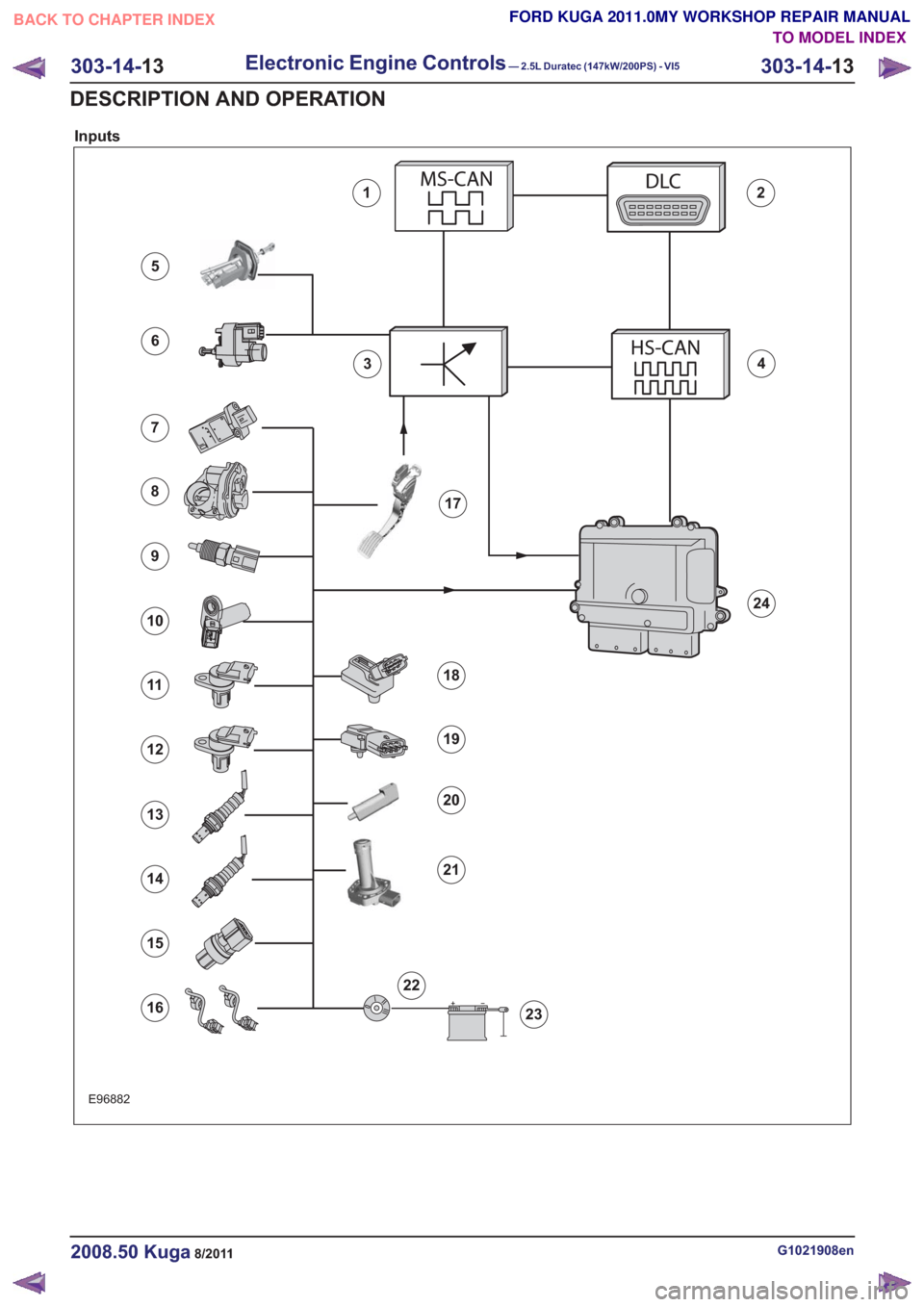
Inputs
E96882
12
34
6
5
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
22
17
21
19
20
24
18
23
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-13
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
13
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1788 of 2057
Description
Item
Medium speed CAN data bus (MS-CAN)
1
DLC (data link connector)
2
GEM (generic electronic module)
Comments:Serves as a gateway between the two
CAN databus systems.
3
High speed CAN data bus (HS-CAN)
4
CPP (clutch pedal position) sensorRefertoComponentDescription:(page
29)
5
BPP switchesRefertoComponentDescription:(page
29)
6
MAF sensorRefertoComponentDescription:(page
27)
7
TP sensorRefer to Component Description: Throttle
controlunit(page33)
Comments: It is incorporated into the throttle control
unit
8
ECT sensorRefertoComponentDescription:(page
31)
9
CKP sensorRefertoComponentDescription:(page
24)
10
CMP sensor - intake camshaftRefertoComponentDescription:(page
8)
11
CMP sensor - exhaust camshaftRefertoComponentDescription:(page
8)
12Description
Item
Broadband HO2SRefertoComponentDescription:(page
25)
13
Catalyst monitor sensor
14
Air conditioning (A/C) pressure sensorRefertoComponentDescription:(page
30)
15
KSRefertoComponentDescription:(page
8)
16
APP sensorRefertoComponentDescription:(page
28)
17
MAPT sensorRefertoComponentDescription:(page
9)
18
Fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensorRefertoComponentDescription:(page
33)
19
Exterior aor temperature sensorRefertoComponentDescription:(page
34)
20
Engine oil level, temperature and quality
sensorRefertoComponentDescription:(page
34)
21
Ignition switch
22
Battery
23
PCMRefertoComponentDescription:(page
8)
24
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-
14
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
14
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1789 of 2057
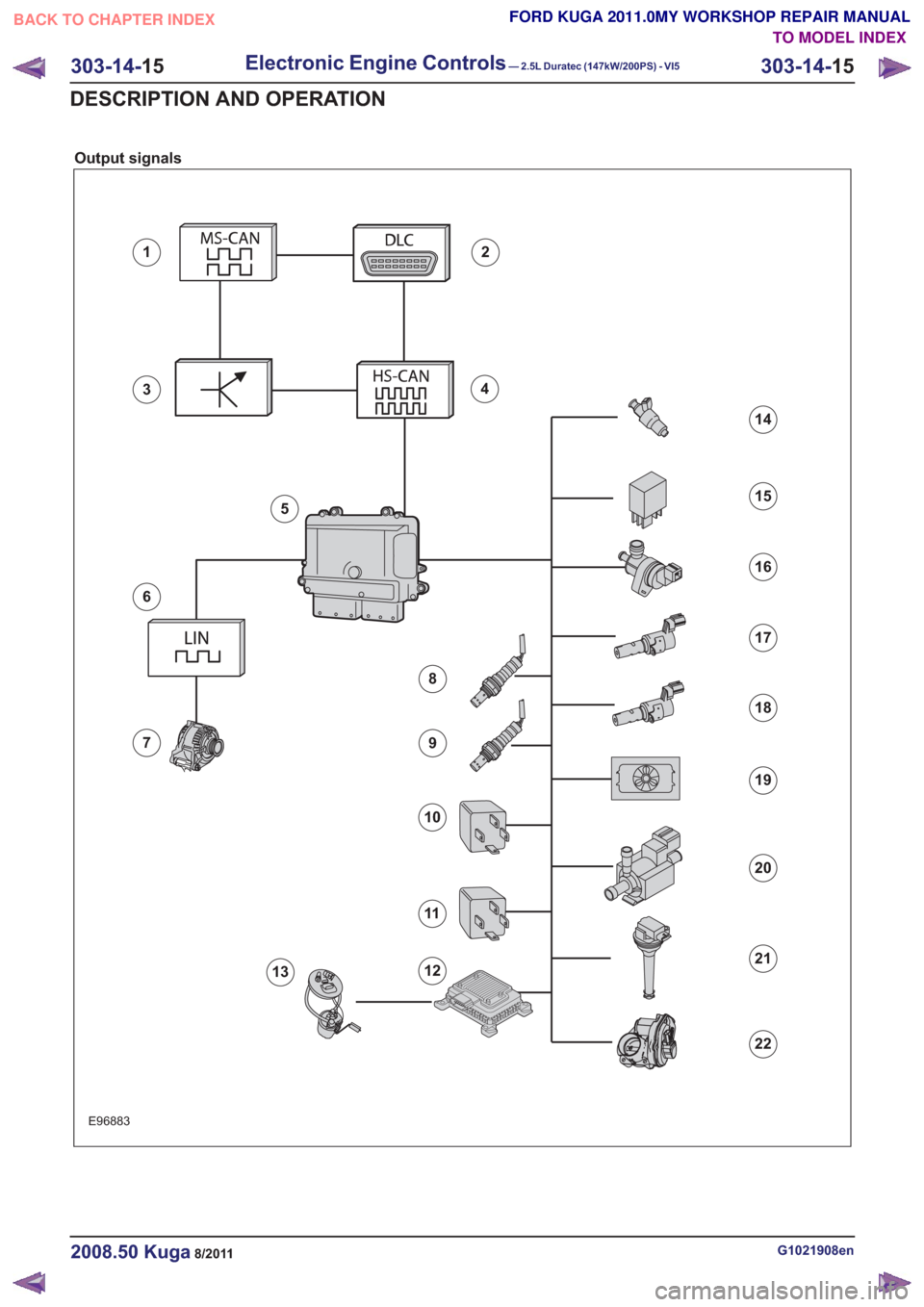
Output signals
E96883
8
1
3
7
6
5
13
2
4
9
10
11
12
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-15
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
15
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1790 of 2057

Description
Item
Medium speed CAN data bus (MS-CAN)
1
DLC
2
GEM
Comments:Serves as a gateway between the two
CAN databus systems.
3
High speed CAN data bus (HS-CAN)
4
PCMRefertoComponentDescription:(page
8)
5
LIN (local interconnect network) databus
6
Alternator
7
Heating element - broadband HO2S
8
Catalyst monitor sensor heating element
9
Powertrain Control Module relay
10
Starter Relay
11
FPDM
Comments:Refer to: Fuel Tank and Lines - 2.5L
Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5 (310-01
Fuel Tank and Lines, Description and
Operation).
12
Fuel pump
13
injectorsRefertoComponentDescription:(page
?)
Comments: 5x
14Description
Item
Air conditioning clutch relay
Comments:Refer to: Climate Control (412-01
Climate Control, Description and
Operation).
15
EVAP valve
Comments:
16
VCT oil control solenoid, exhaust camshaftRefer to Component Description:
solenoids(page26)
17
VCT oil control solenoid, intake camshaftRefer to Component Description:
solenoids(page26)
18
Cooling fan module
Comments:Refer to: Engine Cooling - 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5 (303-03 Engine
Cooling, Description and Operation).
19
Wastegate control valve
Comments:Refer to: Turbocharger (303-04 Fuel
Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
- 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5,
Description and Operation).
20
Ignition coil-on-plugRefertoComponentDescription:(page
10)
Comments: 5x
21
Throttle control unitRefertoComponentDescription:(page
30)
Comments: Actuator motor unit
22
System Operation
The engine is controlled by the PCM. For this
purpose, the PCM uses information from the
sensors, sender units and switches. In addition,
the PCM receives information from other control
modules via the CAN data bus. All the information
is processed in the PCM and is used to control or
regulate the different actuators.
These are:
• the throttle control unit,
• the fuel injectors, • the camshaft adjustment,
• the boost control solenoid valve
• and the ignition coils.
Some values are sent via the CAN databus to other
systems.
The following functions are regulated or controlled
by the PCM:
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-
16
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
16
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1791 of 2057

• Starting process
• Engine running– Fuel supply to the engine including lambdacontrol
– Ignition setting including knock control
– Idle speed control
– Boost pressure control
– Valve timing via the camshaft adjuster for the intake and exhaust camshafts (including
internal exhaust gas recirculation)
• Refrigerant compressor (activation, deactivation and delivery)
• EVAP purge valve
• Charging system
Fuel is supplied to the engine via a sequential
multi-point injection system. Ignition is performed
by a distributor-less ignition system with one
ignition coil unit for each cylinder.
The PCM optimizes engine power and emissions
at all times by processing the sensor signals and
information received via the CAN databus and
using these for open or closed loop control of the
different variables.
The PCM contains part of the PATS (passive
anti-theft system).
The PCM is supplied with battery voltage via a fuse
in the BJB (battery junction box). This power supply
is needed to ensure that saved data is not lost
when the engine is switched off.
For other power supply requirements, the PCM
switches on a relay in the BJB which is responsible
for supplying power to the PCM and to some
sensors and actuators. Each of these are protected
by fuses in the BJB.
To guarantee optimum engine running at all times,
the PCM has several adaptive (self-learning)
functions. These adapt the output signals to
changing circumstances, such as wear or system
faults.
In some cases a faulty signal is replaced with a
substitute value or limited. A substitute value can
be calculated from other signals or it can be
predefined by the PCM. The substitute value allows
the vehicle to keep on running without the emission
values changing unduly. Depending on the signal
failure, the PCM operates in emergency mode. In
this mode, the engine power and/or the engine
speed is reduced to prevent further damage.
Depending on the faulty signal, a fault code is
stored in the error memory of the PCM. These can be read out using IDS (Integrated Diagnostic
System) via the DLC.
The PCM processes and evaluates the signals
from the sensors. The following sensors send
signals to the PCM:
• CMP sensors
• CKP sensor
• MAF sensor
•KS
• ECT sensor
• TP sensor
• APP sensor
• Broadband HO2S
• Catalyst monitor sensor
• MAPT sensor
• Air conditioning (A/C) pressure sensor
• Alternator
• Fuel temperature and fuel pressure sensor
• Engine oil level, temperature and quality sensor
• Outside air temperature sensor
The following components receive signals from the
PCM:
• Powertrain Control Module relay
• A/C clutch relay
• injectors
• Direct ignition coils
• Cooling fan module
• Throttle control unit
• Camshaft adjuster solenoid valve
• Starter Relay
• EVAP purge valve
• Alternator
• Heating element - broadband HO2S
• Catalyst monitor sensor heating element
• FPDM
• Wastegate control valve
• Air conditioning compressor
The PCM receives the following signals via the
CAN databus:
• APP
•CPP
• BPP
• Vehicle speed.
• Refrigerant compressor request
• PAT S
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-
17
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
17
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1792 of 2057

• Torque reduction request (stability assistmodule)
• Cruise control request
The PCM sends the following signals via the CAN
databus:
• Fuel pump relay on/off
• Engine speed
• Warning lights on/off (MIL (malfunction indicator lamp), battery warning lamp)
• PAT S
•ECT
• Air conditioning pressure transducer
• Outside air temperature
With the aid of the input and output signals listed
above, the PCM controls / regulates engine
starting, fuel injection and fuel pressure, ignition,
boost pressure, camshaft adjustment, tank purging,
the radiator fan and the refrigerant compressor.
Speed and TDC recording
The CKP uses the PCM sensor to record engine
speed and detect 1st cylinder TDC (top dead
center). An additional sensor wheel for the CKP sensor is
located on the flywheel. This has 60-2 teeth. The
gaps between the teeth are required for detection
of TDC. The CKP sensor works according to the
induction principle and generates a sinusoidal
signal voltage whose level and frequency are
speed-dependent.
From the frequency of the signal the PCM
calculates the engine speed. Each time the engine
rotates, the double gap in the sensor wheel alters
the sinusoidal oscillation that is generated; this
helps the PCM to detect the TDC position of
cylinder 1.
The signal from the CKP sensor is used to
determine
• the crankshaft position,
• the engine speed,
• the ignition timing,
• the injection timing and
• the adjustment angle of the VVT units.
2
3
4
1
9
7
8
6
5
2
3
4
1
9
7
8
6
5
E96631
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-
18
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
18
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL