Timing HONDA INTEGRA 1998 4.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1998, Model line: INTEGRA, Model: HONDA INTEGRA 1998 4.GPages: 1681, PDF Size: 54.22 MB
Page 173 of 1681
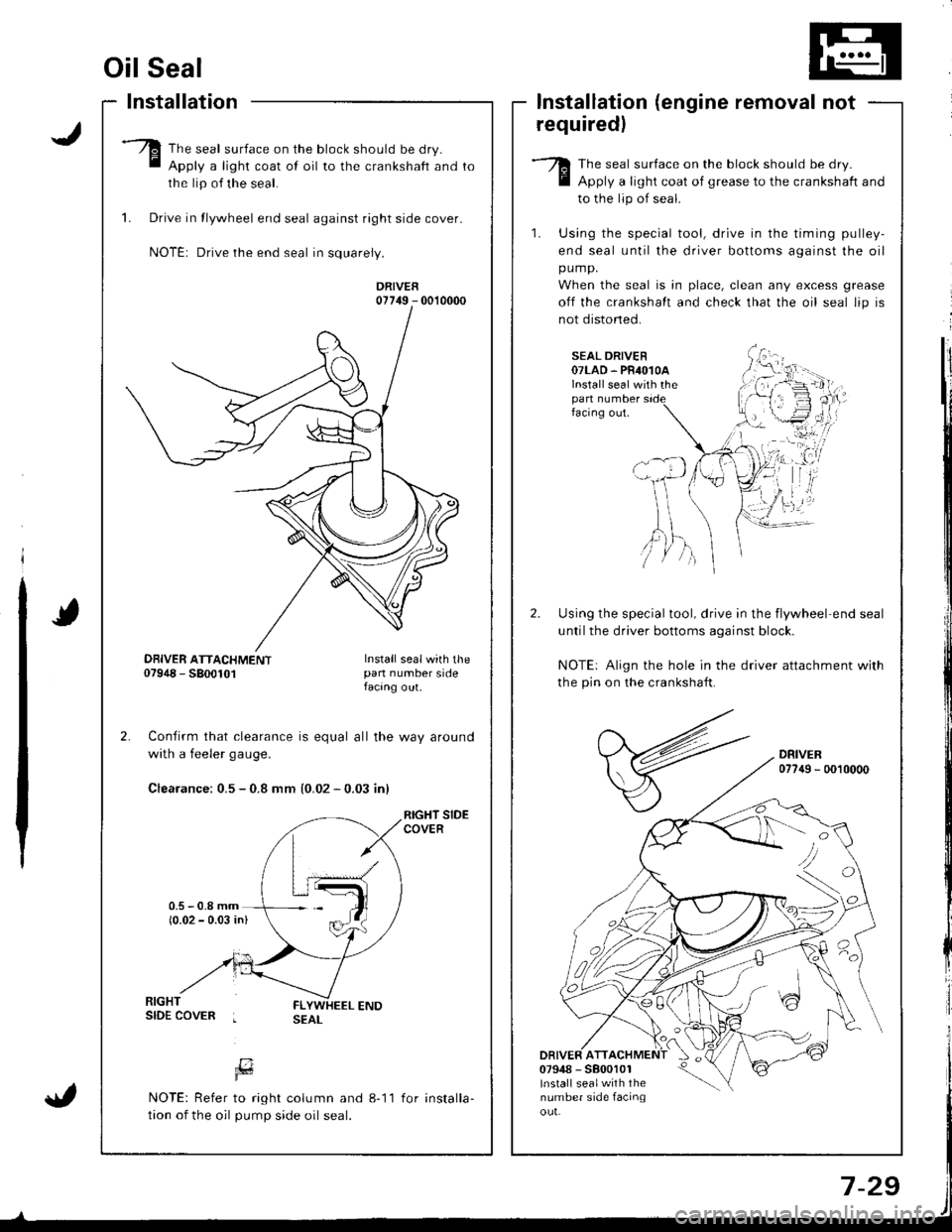
Oil Seal
Installation
The seal surface on the block should be dry.
Apply a light coat of oil to the crankshaft and
the lip of the seal.
1. Drive in tlywheel end seal against right side cover.
NOTE: Drive the end seal in squarely.
DRIVER07749 - 0010000
Confirm that clearance is equal all the way around
with a feeler gaug€.
Clearance: 0.5 - 0.8 mm {0.02 - 0.03 inl
RIGHT SIDECOVER
lnstallation (engine removal not
requiredl
The seal surface on the block should be dry.
Apply a light coat of grease to the crankshaft and
to the lip of seal.
1. Using the special tool, drive in the timing pulley-
end seal until the driver bottoms against the oil
pump.
When the seal is in place, clean any excess grease
off the crankshalt and check that the oil seal lip is
not distoned.
SEAL DRIVER07LAD. PR4O1OAlnstall seal with thepan numberfacing out.
Using the special tool, drive in the flywheel end seal
untilthe driver bottoms aqainst block.
NOTE: Align the hole in the driver attachment with
the pin on the crankshaft.
DRIVER077{9 - 0010000
DRIVER ATT07948 - 5800101lnstall sealwith thenumber side facinqou!.
'tvA,)/ )
DBIVER ATTACHMENT07948 - 5800101Install sealwith thepan number sidefacang out.
[7Fd
NOTE: Refer to right column and 8-11
tion of the oil pump side oil seal.
for installa-
Page 184 of 1681
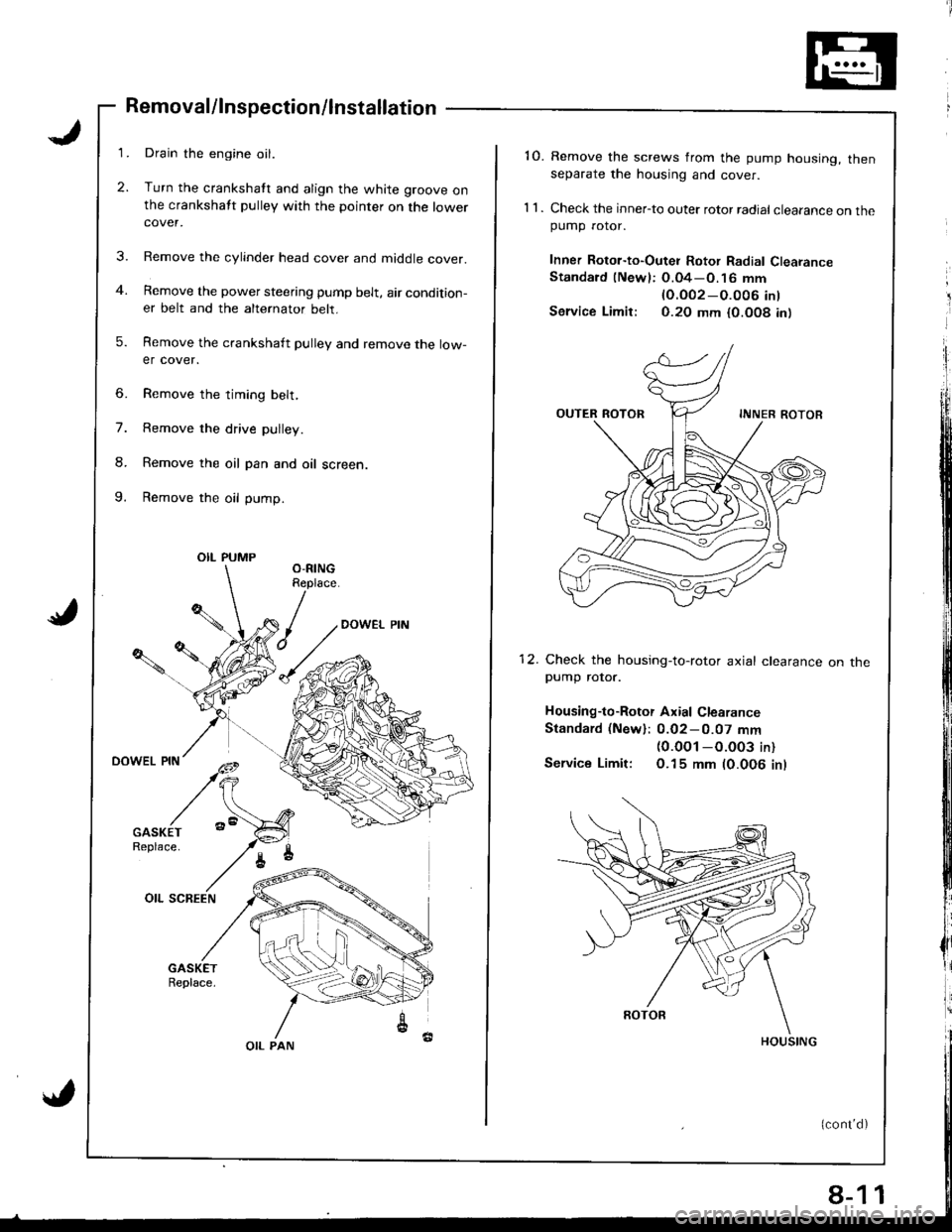
3.
Removal/lnspection/lnstallation
Drain the engine oil.
Turn the crankshatt and align the white groove onthe crankshatt pulley with the pointer on the lowercover.
Remove the cylinder head cover and middle cover.
Remove the power steering pump belt, air condition-er belt and the alternator belt.
Remove the crankshaft pulley and remove the low-er cover.
6. Remove the timing belt,
7. Remove the drive pulley.
8. Remove the oil pan and oil screen.
9. Remove the oil pump.
OIL PUMP
OIL PAN
8-1
'10. Remove the screws from the pump housing, thenseparate the housing and cover.
1 1 . Check the inner-to outer rotor radial clearance on thepumD rotor.
Inner Rotor-to-Outei Rotor Radial ClearanceStandard (Newl: O.04-O.16 mm
lO.OO2-O.O06 int
Service Limir: 0.20 mm {0.O08 in)
12. Check the housing-to-rotor axial clearancepump rotor.
Housing-to-Rotor Axial Clearance
Standard (New): 0.02-0.07 mm(0.0O1 -O.003 in)
Service Limit: O.15 mm (0.006 inl
on tne
1
Page 205 of 1681
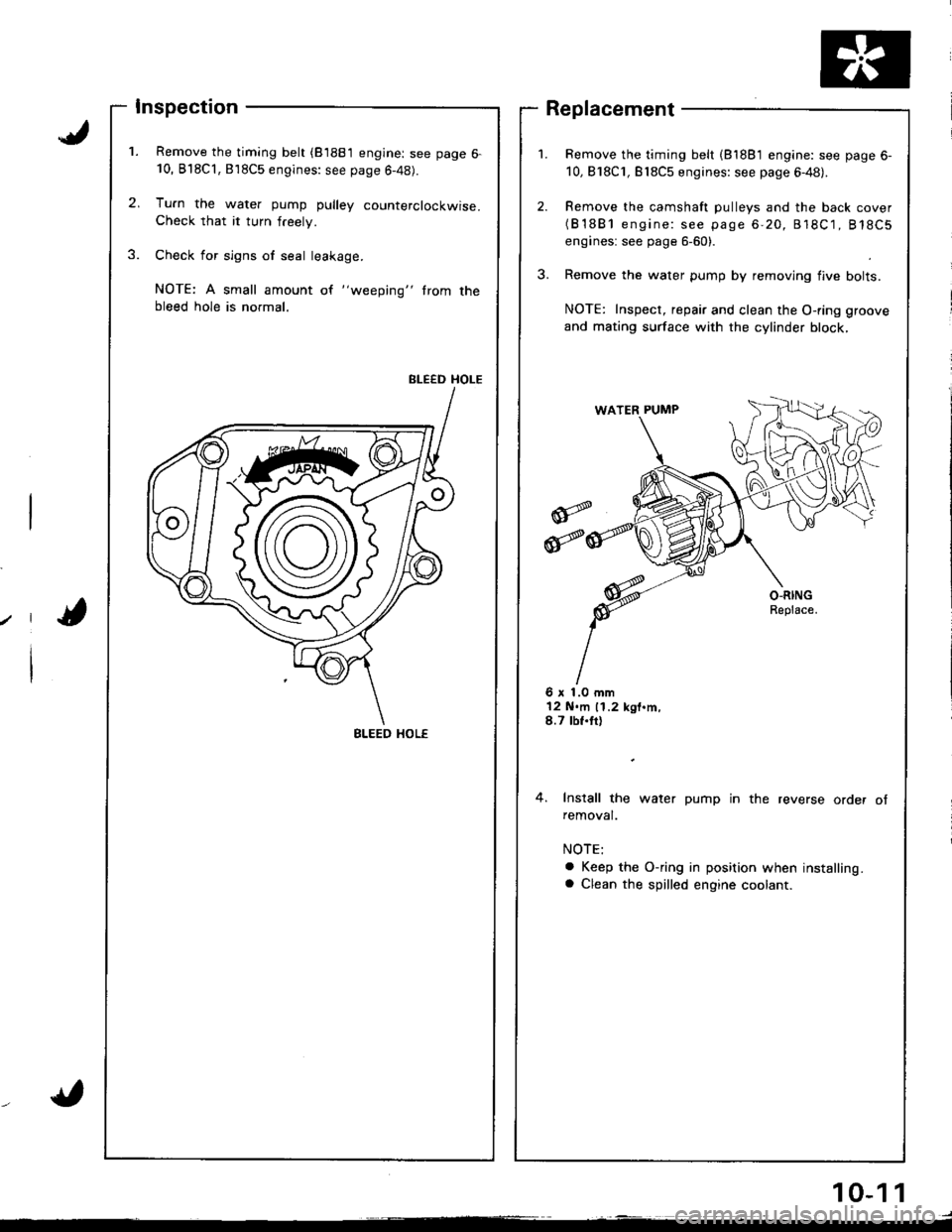
Inspection
Remove the timing belt (81881 engine: see page 6-10, B'l8Cl,818C5 engines: see page 6-48).
Tu.n the water pump pulley counterclockwise.Check that it turn freely.
Check for sign6 of seal leakage.
NOTE: A small amount of "weeping" trom thebleed hole is normal.
BLEED HOLE
Remove the timing belt (81881 engine: see page 6-
10,818C1, Bl8C5 engines: see page 6-48).
Remove the camshaft pulleys and the back cover(B'1881 engine: see page 6-20, 818C1, 818C5
engines: see page 6-60).
Remove the water pump by removing flve bolts.
NOTE: Inspect, repair and clean the O-ring groove
and mating surface with the cylinder block,
Replacement
6 x 1.0 mm12 N.m 11.2 kgt.m,8.7 tbf.tt)
4. Install the water pump in the reverse order ofremoval.
a Keep the O-ring in position when installing.a Clean the spilled engine coolant.
BLEED HOL€
10-1 1
Page 241 of 1681
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Procedures (cont'd)
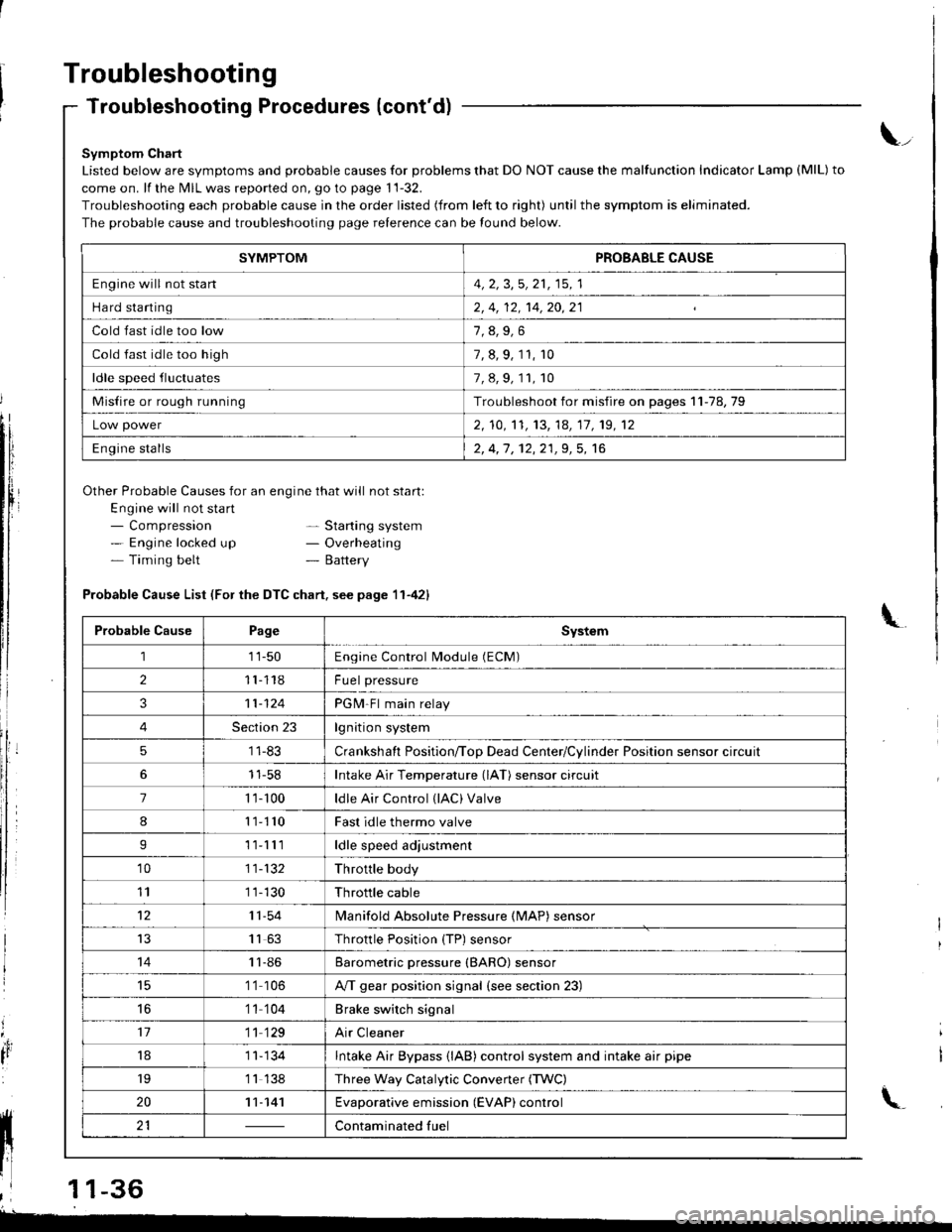
Symptom Chart
Listed below are symptoms and probable causes for problems that DO NOT cause the malfunction Indicator Lamp (MlL) to
come on. lf the MIL was reported on, go to page 11-32.
Troubleshooting each probable cause in the order listed (from left to right) until the symptom is eliminated.
The probable cause and troubleshooting page relerence can be found below.
Other Probable Causes for an engine that will not start:
Engine will not sta rt- Compression- Engine locked up- Timing belt
\_
- Starting system- Overheating- Battery
'4,
It
Probable Cause List (For the DTC chart. see page 11-421
Probable CausePageSystem
111-50Engine Control Module (ECM)
211118Fuel pressure
311-124PGM-Fl main relay
4Section 23lgnition system
51 1-83Crankshaft Position/ToD Dead Center/Cylinder Position sensor circuit
11-58Intake Air Temperature (lAT) sensor circuit
71 '�t- 100ldle Air Control (lAC) Valve
811110Fast idle thermo valve
I11lllldle speed adjustment
'1011-132Throttle body
111 1-130Throttle cable
1211-54lvlanifold Absolute Pressure {MAP) sensor
IJ1163Throttle Position {TP) sensor
1411-86Barometric pressure (BARO) sensor
1 '1 106A/T gear position signal {see section 23)
16'1 1 104Brake switch signal
1711 129Air Cleaner
181 1- 134Intake Air Bypass {lAB} control system and intake air pipe
19'1 1 138Three Way Catalytic Convener (TWC)
2011-141Evaporative emission (EVAP) control
21Contaminated fuelll ll 21 | - | cont"-in"t"o tu"
11 l-
I
,l 11-36
-
SYMPTOMPROBABLE CAUSE
Engine will not stan4, 2, 3,5, 21, 15, 1
Hard starting2, 4, 12, 14,20,21
Cold fast idle too low
Cold fast idle too high7, 8, 9, 11, r0
ldle speed fluctuates7,8,9,11,10
Misfire or rough runningTroubleshoot for misfire on pages 11-78,79
Low power2, 10,'t1, 13, 14, 17, 19, 12
Engine stalls2, 4,1 , 12,21,9, 5, 16
Page 243 of 1681
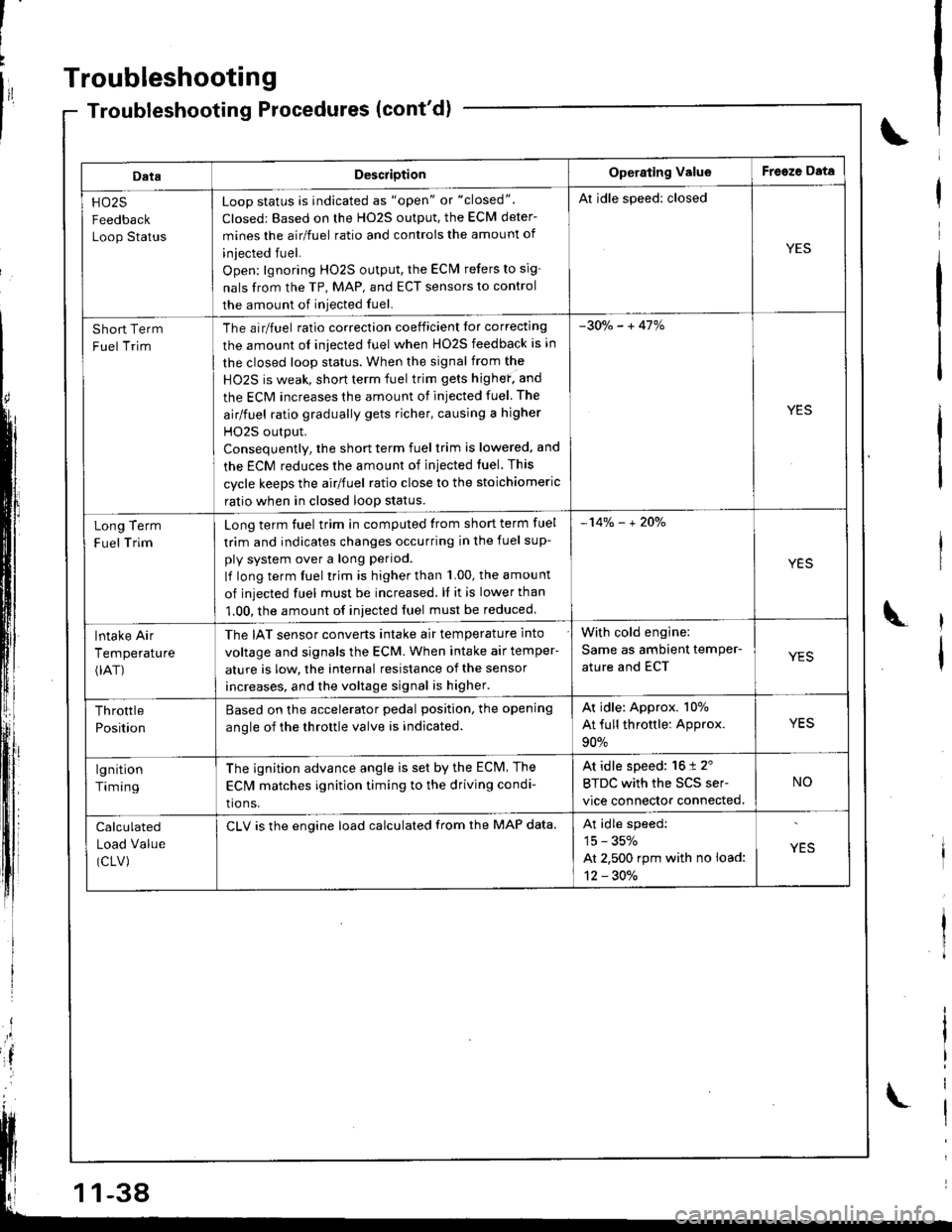
Troubleshooting
DataDescriotionOperating ValueFreeze Data
HO25
Feedback
Loop Status
Loop status is indicated as "open" or "closed".
Closed: Based on the H02S output, the ECM deter-
mines the airlfuel ratio and controis the amount of
iniected fuel.
Open: lgnoring HO2S output, the ECM refers to sig-
nals from the TP, MAP, and ECT sensors to control
the amount of iniected fuel.
Al idle speed: closed
YES
Short Term
Fuel Trim
The airlfuel ratio correclion coeificient lor correcting
the amount ol iniected fuel when HO2S feedback is in
the closed loop status. When the signal from the
HO2S is weak, short term fuel trim gets highef. and
the ECM increases the amount of injected fuel The
airlfuel ratio gradually gets richer, causing a higher
HO2S output.
Consequentlv, the short term fuel trim is lowered, and
the ECM reduces the amount of injected tuel. This
cycle keeps the airlfuel ratio close to the stoichiomeric
ratio when in closed loop status.
-30o/" - + 41%
YES
Term
Trim
Long
F uel
Long term fuel trim in computed trom short term fuel
trim and indicates changes occurring in the fuel sup-
ply system over a long period.
lf long term fuel trim is higher than 1.00, the amou nt
of injected fuel must be increased. ll it is lower than
1.00, the amount of iniected fuel must be reduced
-14% - + 2Oo/"
YES
lntake Air
Temperature(rAT)
The IAT sensor converts intake air temperature into
voltage and signals the ECM. When intake air temper-
ature is low, the internal resistance of the sensor
increases, and the voltage signal is higher.
With cold engine:
Same as ambient temPer-
ature and ECTYES
Throttle
Position
Based on the accelerator pedal position. the opening
anole of the throttle valve is indicated.
Ar idle: Approx. 107o
At full throttle: Approx.
90%
YES
lgnition
Timing
The ignition advance angle is set by the ECM. The
EClvl matches ignition timing to the driving condi-
tio ns.
At idle speed: 16 t 2'
BTDC with the SCS ser-
vice connector connected.
NO
Calculated
Load Value
(CLV)
CLV is the engine load calculated from the MAP data.At idle speedi
15 - 35%
At 2,500 rpm with no load:
12 - 30./.
YES
-38
Page 248 of 1681
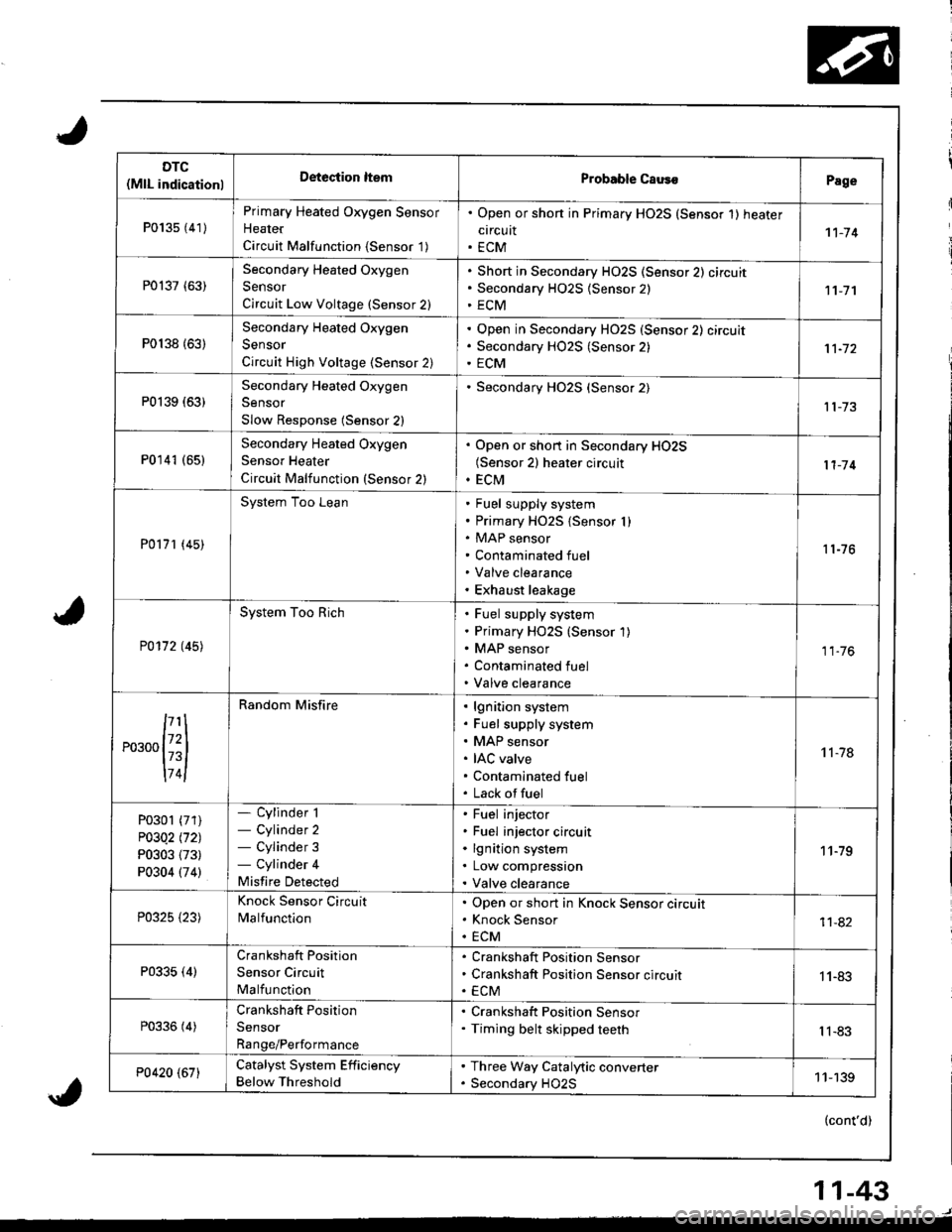
DTC(MlL indicationlDeteciion ltemProbable CausoPage
P013s {41)
Primary Heated Oxygen Sensor
Heater
Circuit Malfunction {Sensor '1)
. Open or shon in Primary HO2S (Sensor 1) heater
circuit. ECM1't-74
P0137 (63)Secondary Heated Oxygen
Sensor
Circuit Low Voltage (Sensor 2)
Short in Secondary HO2S (Sensor 2) circuit
Secondary H02S {Sensor 2)
ECM11-7'l
P0138 {63)
Secondary Heated Oxygen
Sensor
Circuit High Voltage (Sensor 2)
Open in Secondary HO2S (Sensor 2) circuit
Secondary HO2S (Sensor 2)
ECM
P0139 (63)Secondary Heated Oxygen
Sensor
Slow Response (Sensor 2)
Secondary HO2S (Sensor 2)
P0141 (651Secondary Heated Oxygen
Sensor Heater
Circuit Malfunction (Sensor 2)
. Open or short in Secondary HO2S(Sensor 2) heater circuit. ECM11-'14
P0171 (45)
System Too LeanFuel supply system
Primary HO2S {Sensor I )MAP sensor
Contaminated fuel
Valve clearance
Exhaust leakage
11-76
P0172 t45l
System Too RichFuel supply system
Primary HO2S (Sensor 1)
MAP sensor
Contaminated fuel
Valve clearance
11.76
,...,{iil
174l
Random Misfirelgnition system
Fuel supply system
MAP sensor
IAC valve
Contaminated fuel
Lack offuel
't 1-78
P0301 (71)
P03Q2 l'121
P0303 (73)
P0304 (74)
- Cylinder 1- Cylinder 2- Cylinder 3- Cylinder 4
Misfire Detected
Fuel injector
Fuel injector circuit
lgnition system
Low compression
Valve clearance
11-79
P0325 {23)
Knock Sensor Circuit
MalfunctionOpen or short in Knock Sensor circuit
Knock Sensor
ECM11-82
P0335 (4)Crankshaft Position
Sensor Circuit
Malfunction
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Crankshaft Position Sensor circuit
ECM1 1-83
P0336 (4)Crankshaft Position
Sensor
Range/Performance
. Crankshaft Position Sensor. Timing belt skipped teethIl-83
P0420 (67)Catalyst System Efficiency
Below Threshold
. Three Way Catalytic converter. Secondary HO2S11-139
(cont'd)
11-43
Page 253 of 1681

PGM-FI System
System Description
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)OUTPUTS
*1: USA*2: 818C1 engine*3: A,/T*4: 818C1, 818C5 engines
PGM-FI Sy3tem
The PGM-Fl system on this model is a sequential multiport fuel injection system.
Fuel lniector Timing and Duration
The ECM contains memories for the basic discharge durations at various engine speeds and manifold pressures. The
basic discharge duration, after being read out from the memory. is further modified by signals sent from various sensors
to obtain the final discharge duration.
ldle Air Control
ldle Ai. Control Valve (lAC Valve)
When the engine is cold, the Ay'C compressor is on. the transmission is in gear (Ay'T only)the brake pedal is depressed, the
P/S load is high, or the alternator is charging, the ECM controls current to the IAC Valve to maintain correct idle speed.
lgnition Timing Control
. The ECM contains memories for basic ignition timing atvarious engine speeds and manifold pressures, lgnitiontiming
is also adjusted for engine coolant temperature.
. AKnockControl System isadoptedwhich sets the ideal ignition timing for the octane n um ber of gasoline used*r,
Other Control Functions
L Starting Control
When the engine is started, the ECM provides a rich mi{ure by increasing fuel injector duration.
2. Fuel PumD Control
. When the ignition switch is initially turned on, the ECM supplies ground to the PGM-FI main relay that supplies
current to the fuel pump for two seconds to pressurize the fuel system.
. When the engine is running, the ECM supplies ground to the PGM-FI main relay that supplies current to the fuel
DUmO.
. When the engine is not running and the ignition is on. the ECM cuts ground to the PGM-FI main relay which cuts
current to the fuel oumo.
INPUTS
TDc/CKP/CYP Sensor
CKF Sensor
MAP Sensor
ECT Sensor
IAT Sensor
TP Sensor
HO2S
VSS
BARO Sensor
ELD*1
Starter Signal
ALT FR Signal
Air Conditioning Signal
A,/T Gear Position Signal*3
Battery Voltage (lGN.1)
Brake Switch Signal
PSP Switch Signal*'�
Knock Sensor*1
VTEC Pressure Switch*4
Fuel Tank Prssure Sensor
Fuel InjectorTiming and Duration
Electronic ldle Control
Other Control Functions
lgnition Timing Control
ECM Back-uD Functions
Fuel-lnjectors
PGM-Fl Main Relay (Fuel Pump)
MIL
IAC Valve
A,/C Compressor Clutch Relay
Radiator Fan Belay*1
Condenser Fan Relay
ALT*1
rcM
EVAP Purge Control Solenoid
Valve
H02S Heater
VTEC Solenoid Valve*'
IAB Control Solenoid Valve*,
EVAP Bypass Solenoid Valve
EVAP Control Canister Vent
Shut Valve
11-48
Page 288 of 1681
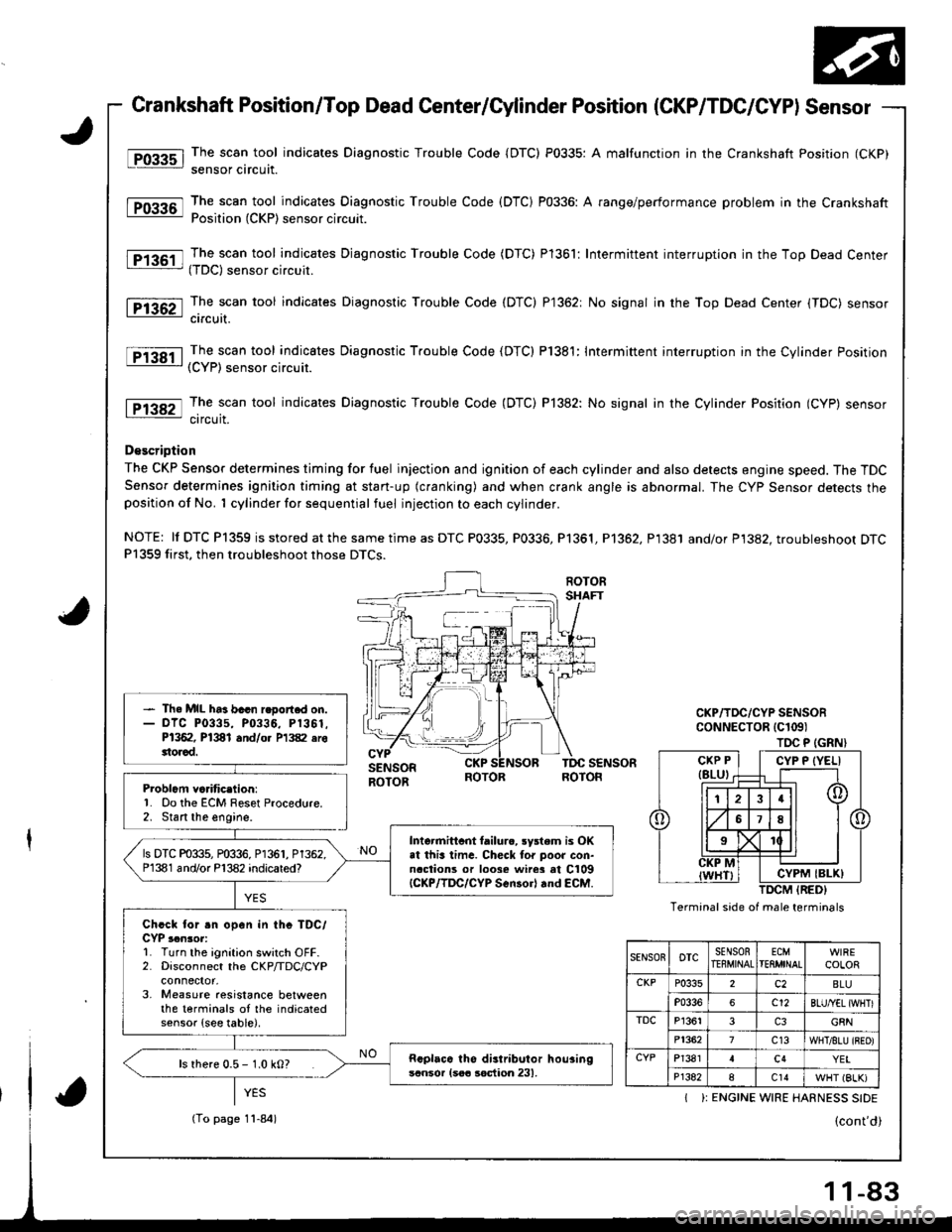
t@
tFffi6l
F136il
l-P1362l
Fi3BTl
tFE82-l
Crankshaft Position/Top Dead Center/Cylinder Position (CKP/TDC/CYPI Sensor
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code {DTC) P0335: A malfunction in the Crankshaft Position (CKP)
sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0336: A range/performance problem in the CrankshaftPosition (CKP) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Djagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Pl361: Intermittent interruption in the Top Dead Center(TDC) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1362: No signal in the Top Dead Center (TDC) sensorcircuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1381: Intermittent interruption in the Cylinder Position(CYP) sensor circuit.
The scan tool indicates Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P]382: No signal in the Cylinder Position (CYP) sensorcircuit.
D€scription
The CKP Sensor determines timing for fuel injection and ignition of each cylinder and also detects engine speed. The TDCSensor determines ignition timing at stan-up (cranking) and when crank angle is abnormal. The Cyp Sensor detects theposition of No. 1 cylinder for sequential fuel injection to each cylinder.
NOTE: ll DTC P1359 is stored at the same time as DTC P0335, P0336, Pl361, P1362, P1381 and/or P1382. troubleshoot DTCP1359 first, then troubleshoot those DTCS.
Problcm va.itic.lion:'1. Do the ECM Reset Procedure.2. Stan the engine.
- Th. MIL ha3 bacn r.oort.d on.- olc P0335, P0336, P1361.P1362, P1381 and/o. P1382 erottorad.
Intormittcnt tailurc, rystem is OKat this lima. Checl tor poor con-naclions or loose wire3 at C109{CKP/lDC/CYP Scn30rl rnd €CM.
ls DTC P0335, P0336, P1361, P1362.P1381 and/or P'l382 indicared?
Chcck for .n open in thc TDC/CYP ,.n3or:L Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the CKP/TDC/CYP
3, Measure aesistance betweenthe terminals oI the indicatedsensor {see table).
Rcplaca tho distributor hou3ingscnsor {soa soction 231,ls rhere 0.5 - 1.0 kO?
TOC P (GRN}
Termanal side of male terminals
CYP P {YELI
CYPM IBLK)
SENSOnoTcSENSORTEEMINALECMTEflMINALCOLOR
CKPP0335c2BLU
P0336c12BLU/YEL {WHTI
TDCP13613G8N
P13627c13WHT/8LU {BEO)
CYPP13814c4YEI
P1382ac14WHT (BLK)
I ): ENGINE WIRE HARNESS SIDE
(To page 11-84)
-83
Page 316 of 1681
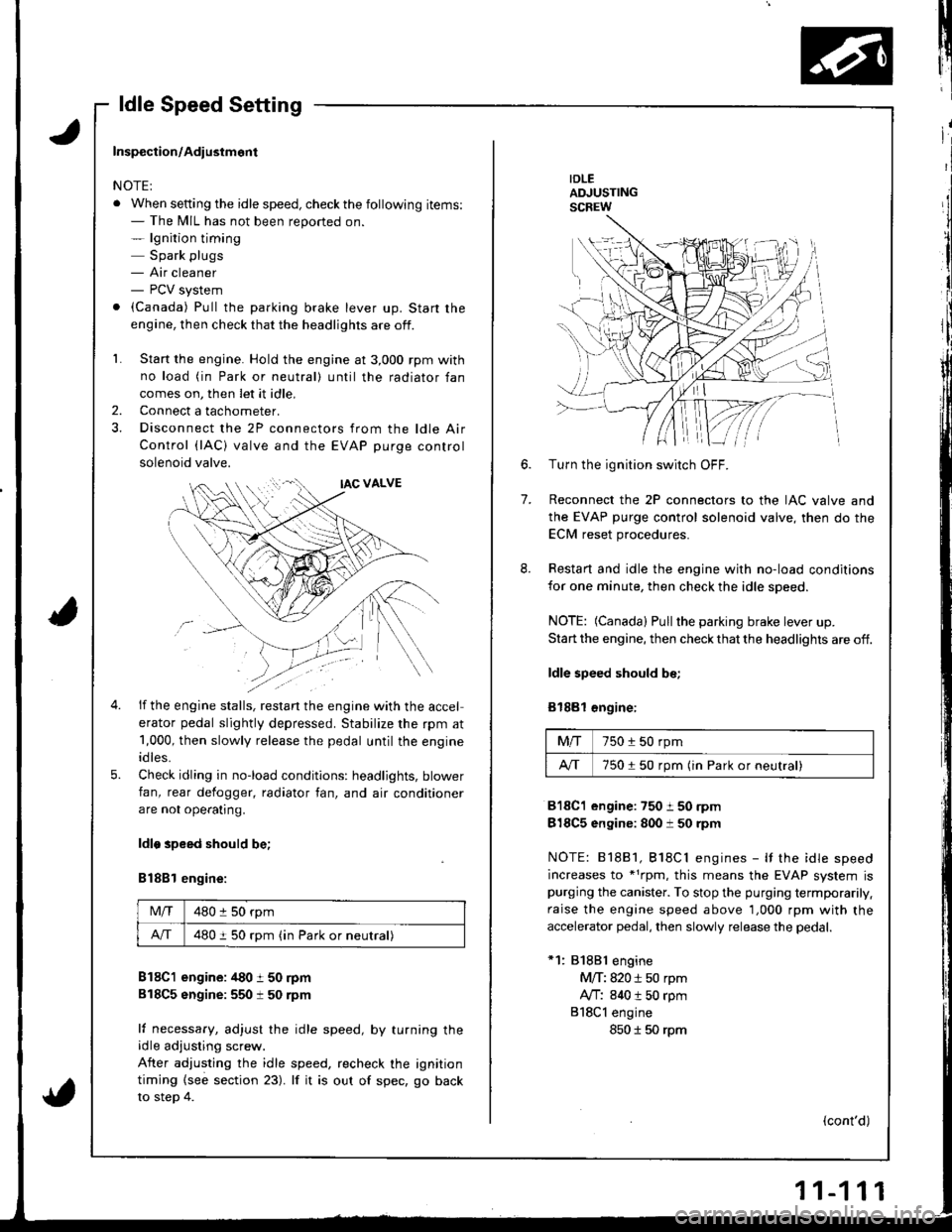
ldle Speed Setting
IDLEADJUSTINGSCREW
7.
6.Turn the ignition switch OFF.
Reconnect the 2P connectors to the IAC valve and
the EVAP purge control solenoid valve, then do the
ECM reset procedures.
Restart and idle the engine with no-load conditions
for one minute, then check the idle speed.
NOTE: (Canada) Pullthe parking brake lever up.
Start the engine, then check that the headlights are off.
ldle speed should be;
Bl88l €ngine:
Mfi750 i 50 rpm
A/T750150 rpm (in Park or neutral)
818C1 engine:750 i 50 rpm
818C5 engine: 800 i 50 rpm
NOTE: 81881, Bl8Cl engines - It the idle speed
increases to *1rpm, this means the EVAP system ispurging the canister. To stop the purging termporarily.
raise the engine speed above 1,000 rpm with the
accelerator pedal, then slowly release the pedal.
*1: 81881 engine
M/T: 820 i 50 rpm
Ay'T: 840 t 50 rpm
818Cl engine
850 I 50 rpm
(cont'd)
Inspection/Adiustmont
NOTE:
. When setting the idle speed, checkthe following items:- The MIL has not been reported on.- lgnition timing
Spark plugs- Air cleaner- PCV system
. (Canada) Pull the parking brake lever up. Start the
engine, then check that the headlights are off.
1. Start the engine. Hold the engine at 3,000 rpm with
no load (in Park or neutral) until the radiator fan
comes on, then let it idle,
Connect a tachometer.
Disconnect the 2P connectors from the ldle Air
Control (lAC) valve and the EVAP purge control
solenoid valve.
2.
5.
if the engine stalls, restan the engine with the accel
erator pedal slightly depressed. Stabilize the rpm at
1,000, then slowly release the pedal until the engine
idles.
Check idling in no-load conditions: headlights, blower
fan, rear defogger, radiator fan, and air conditioner
are not ope€tlng.
ldlo speed should be;
B188l engine:
Mlf480 :l 50 rpm
A/T480 i 50 rpm (in Park or neutral)
B18C1 engine: /t80 t 50 rpm
818C5 sngine:550 t 50 rpm
lf necessary, adjust the idle speed, by turning theidle adjusting screw.
After adjusting the idle speed, recheck the ignition
timing {see section 23). lf it is out of spec, go back
to steo 4.
Page 420 of 1681
Description
\J
t{
{
14-3
The automatic transmission is a combination of a 3-element torque converter and triple-shalt electronically controlled
automatic transmission which provides 4 speeds forward and 1 speed reverse. The entire unit is positioned in line with
the engrne.
Torque Converter, Gears, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine, and stator, assembled in sigle unit. The torque converter is connected to
the engine crankshaft so they turn torether as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque convener is a
ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started. The entire torque converter assembly
serves as a flywheel while transmitting power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has three parallel shafts; the mainshaft. the countershaft, and the sub shaft. The mainshaft is in-line with
the engine crankshaft.
The mainshaft includes the 1st, and 2ndl4th clutches,and gear for 3rd, 2nd, 4th, reverse, and 1st. (3rd gear is integral with
the mainshaft, while reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear.)
The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch and gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse, 1st, and parking. Reverse and 4th gears can
be loched to the countershaft at its center,providing 4th gear or reverse, depending on which way the selector is moved.
The sub-shaft includes the 1st-hold clutch and gears fo 1st and 4th.
The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the countersahft and sub-shaft.When certain combinations
of gears in the transmission are engaged by clutches. power in transmitted from the mainshaft to the countershaft via the
sub-shaft to orovude oil, lo'1. E, E. and E.
Electronic Control
The electronic control svstem consists of the Transmission Control Module (TCM), sensors, and four solenoid valves.
Shilting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions.
The TCM is located below the dashboard, behind the lelt side kick panel on the driver's side.
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main valve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the serbvo body, and
the lock-up valve body, through the respective separator plates, They are bolted to the torque converter housing,
The main valve body contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve, the 2-3 shitt valve, the Clutch Pressure Control
lCPC) valve, the 4th exhaust valve, the reliel valve, and the ATF pump gears.
The secondary valve body contains the 4-3 kick-down valve, the 3-2 kick-down valve, the 2-3 orifice control valve, the
3-4 shift valve, the orilice control valve, the modulator valve, and the servo control valve.
The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve, the lock-up control valve, the torque converter check
valve, and the cooler check valve.
The servo body contains the servo valve, which is integrated with shift fork shaft, the throttle valve B, and the accumula-
tors.
The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing B valve, and is bolted to the regulator valve
ooqy.
Fluid from the regulator passes through the manual valve to the various control valves.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input to the TCM from various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve should
be activated. Activating a shitt control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This
pressurizes a line to one ol the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear.
Lock-uD Mechanism
In @ position, in 2nd, 3rd and 4th, and @ position in 3rd, pressurized fluid can be drained lrom the back oI the tor-
que converter through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this
takes place, the mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the TCM
optimizes the timing of the lock-up mechanism.
The lock-up valves controlthe range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B, and throttle valve B.
When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, modulator pressure changes. Lock-up control solenoid valves
A and B are mounted on the torque converter housing, and are controlled by the TCM.
(cont'd)