cooling ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 1752 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-135
DTC P0217 (Flash Code 542)
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is
installed to the thermostat housing. The ECT sensor is
a variable resistor and it measures the temperature of
the engine coolant. If the ECM detects an excessive
high coolant temperature, this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC • DTCs P0116, P0117 and P0118 are not set.
• The battery voltage is more than 9 volts.
• The ignition switch is ON.
• The engine is running.
Condition for Setting the DTC • The ECM detects that the engine coolant temperature is more than 110 °C (230 °F) for 5
seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets • The ECM will not illuminate the MIL or SVS lamp. Refer to DTC Type Definitions for Action Taken
When the DTC Sets - Type D. Condition for Clearing the DTC
• Refer to DTC Type Definitions for Condition for Clearing the DTC - Type D.
Diagnostic Aids • After starting the engine, the ECT should rise steadily to about 80 to 85 °C (176 to 185 °F) then
stabilize when the thermostat opens.
• Use the Temperature vs. Resistance table to test the ECT sensor at various temperature levels to
evaluate the possibility of a skewed sensor. A
skewed sensor could result in poor driveability
concerns.
• The Total Engine Coolant Overtemperature Events parameter on scan tool indicates number of
overheat events.
Notice: • This DTC is caused by an engine overheat condition (e.g. low engine coolant level). Since this
DTC does not illuminate any lamps, clear the DTC
and ensure there are no signs of engine damage.
Excessive engine overheat may damage internal
engine components.
Circuit/ System Testing DTC P0217
Step Action Value(s)Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check -
Engine Controls? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check -
Engine Controls
2 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with a scan tool.
Is DTC P0117 also set? —
Go to DTC P0117 Go to Step 3
3 1. Test the engine cooling system for the
following condition. Refer to diagnosis of the
engine cooling system section for testing.
• Engine coolant level
• Engine coolant leakage
• Cooling fan belt slippage
• Cooling fan clutch working
• Thermostat working
• Water pump working
• Radiator clogging
2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
4 Start the engine and wait until engine is fully warm
upped while observing the Coolant Temperature
parameter with a scan tool.
Does the scan tool indicate more than the specified
value? 11 0
°C (230 °F)
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1954 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-337
Fuel System ChecksInspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to Fuel System Check chart
and appropriate procedure in the Fuel System section.
• Air in the fuel system.
• Water contamination in the fuel.
• Fuel waxing or icing.
• Fuel filter indicator lamp is continuously or frequently turned ON with engine run.
• External fuel leaks or high engine oil level.
• In-tank fuel pump operation. Refer to In-tank Fuel Pump System Check in this section.
• Fuel leak off from the fuel pressure limiter valve and fuel injectors.
• Fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel supply pump for being crushed, kinked, tightness, cracks and plugged.
• A plugged fuel tank vent valve and hose.
• Inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition.
• Fuel supply pump operation.
Notice: The fuel supply pump must be timed to the engine and adjustment value must
be learned to the ECM.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Injector Force Drive with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• Perform the Swirl Control Solenoid Test with a scan tool. Inspect the diaphragm valve operation when it commanded ON/ OFF.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
• Turbocharger wastegate valve operation. Refer to wastegate valve inspection in the Engine Mechanical section. (Standard output)
• Turbocharger nozzle control actuator operation. Refer to Turbocharger Control System Check in this section. (High output)
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Poor cylinder compression.
• Improper valve gap.
• Broken or weak valve springs.
• Worn camshaft lobes.
Additional Checks • Inspect the EGR system operating correctly. Refer to EGR Control System Check in
this section.
• Observe the Park/ Neutral Switch parameter with a scan tool.
• Inspect for an engine overheat condition. Refer to Engine Cooling section.
• Inspect the A/C operation.
• Inspect the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. (A/T only).
Checks
Action
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1956 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-339
Fuel System ChecksInspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to Fuel System Check Chart
and appropriate procedure in the Fuel System section.
• Air in the fuel system.
• Water contamination in the fuel.
• Fuel waxing or icing.
• Fuel filter indicator lamp is continuously or frequently turned ON with engine run.
• External fuel leaks or high engine oil level.
• In-tank fuel pump operation. Refer to In-tank Fuel Pump System Check in this section.
• Fuel leak off from the fuel pressure limiter valve and fuel injectors.
• Fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel supply pump for being crushed, kinked, tightness, cracks and plugged.
• A plugged fuel tank vent valve and hose.
• Inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition.
• Fuel supply pump operation.
Notice: The fuel supply pump must be timed to the engine and adjustment value must
be learned to the ECM.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Injector Force Drive with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• Perform the Swirl Control Solenoid Test with a scan tool. Inspect the diaphragm valve operation when it commanded ON/ OFF.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
• Turbocharger wastegate valve operation. Refer to wastegate valve inspection in the Engine Mechanical section. (Standard output)
• Turbocharger nozzle control actuator operation. Refer to Turbocharger Control System Check in this section. (High output)
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Poor cylinder compression.
• Improper valve gap.
• Broken or weak valve springs.
• Worn camshaft lobes.
Additional Checks • Inspect the EGR system operating correctly. Refer to EGR Control System Check in
this section.
• Inspect for an engine overheat condition. Refer to Engine Cooling section.
• Inspect the A/C operation.
• Inspect the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. (A/T only)
Checks
Action
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1958 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-341
Poor Fuel Economy
ChecksAction
Definition:
Fuel economy, as measured by actual road tests and several tanks of fuel, is noticeably lower than expected. Also, the
economy is noticeably lower than it was on this vehicle at one time, as previously shown by actual road tests.
Preliminary Checks • Remove the air cleaner and check for dirt, or for air ducts being plugged or
restricted. Replace as necessary.
• Inspect the driving habits of the owner.
• Is the A/C ON full time, defroster mode ON?
• Are the tires at the correct pressure?
• Are the tire sizes changed?
• Are excessively heavy loads being carried?
• Is the acceleration too much, too often?
• Inspect for clutch slip.
• Inspect brake drag.
• Inspect dive belt tension.
• Inspect for a proper transmission shift pattern and down shift operation.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the engine oil level and quality.
• Suggest to the owner to fill the fuel tank and recheck the fuel economy.
• Inspect the odometer is correctly operated.
• Inspect the Scan Tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletin.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the Scan Tool
Data List in this section.
• Compare the Coolant Temperature with the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) parameters on a cold engine condition. If the difference among
temperature reading is more than 5 °C (9 °F) on a cold engine, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT may indicate
a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Fuel type and quality.
• Check fuel leak.
Cooling System Checks Inspect the cooling system for the following conditions. Refer to the Cooling System
Section.
• Engine coolant level.
• Engine thermostat for always being open or for the wrong heat range.
• Engine cooling fan for always being ON.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1983 of 6020
6E-366 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
The EGR valve is mounted on the intake manifold. The
ECM controls the EGR valve opening based on the
engine running condition. The ECM controls the EGR
valve by controlling the solenoid. The solenoid is
controlled based on pulse width modulation (PWM)
signal sent from the ECM. A duty ratio change 0% to
appropriate percentage is EGR valve lift control. To
open the valve, duty ratio is increased. To close the
valve, duty ratio becomes small.
The EGR valve position is detected by the position
sensor, and relayed to the ECM. The position sensor
provides a signal to the ECM on the signal circuit,
which is relative to the position changes of the EGR
valve. The ECM should detect a low signal voltage at a
small lift amount or closed position. The ECM should
detect high signal voltage at a large lift amount.
Intake Throttle Valve
The intake throttle valve is located on the intake
manifold inlet. The ECM controls the intake throttle
valve opening based on the engine running condition.
The ECM controls the intake throttle valve by
controlling the solenoid. The solenoid is controlled
based on pulse width modulation (PWM) signal sent
from the ECM. A duty ratio change 0% to appropriate
percentage is intake throttle valve opening angle
control. To open the valve, duty ratio is increased. To
close the valve, duty ratio becomes small.
The intake throttle valve position is detected by the
position sensor, and relayed to the ECM. The position
sensor provides a signal to the ECM on the signal
circuit, which is relative to the position changes of the
intake throttle valve. The ECM should detect a low
signal voltage at a small opening amount or closed
position. The ECM should detect high signal voltage at
a large opening amount.Turbocharger Description
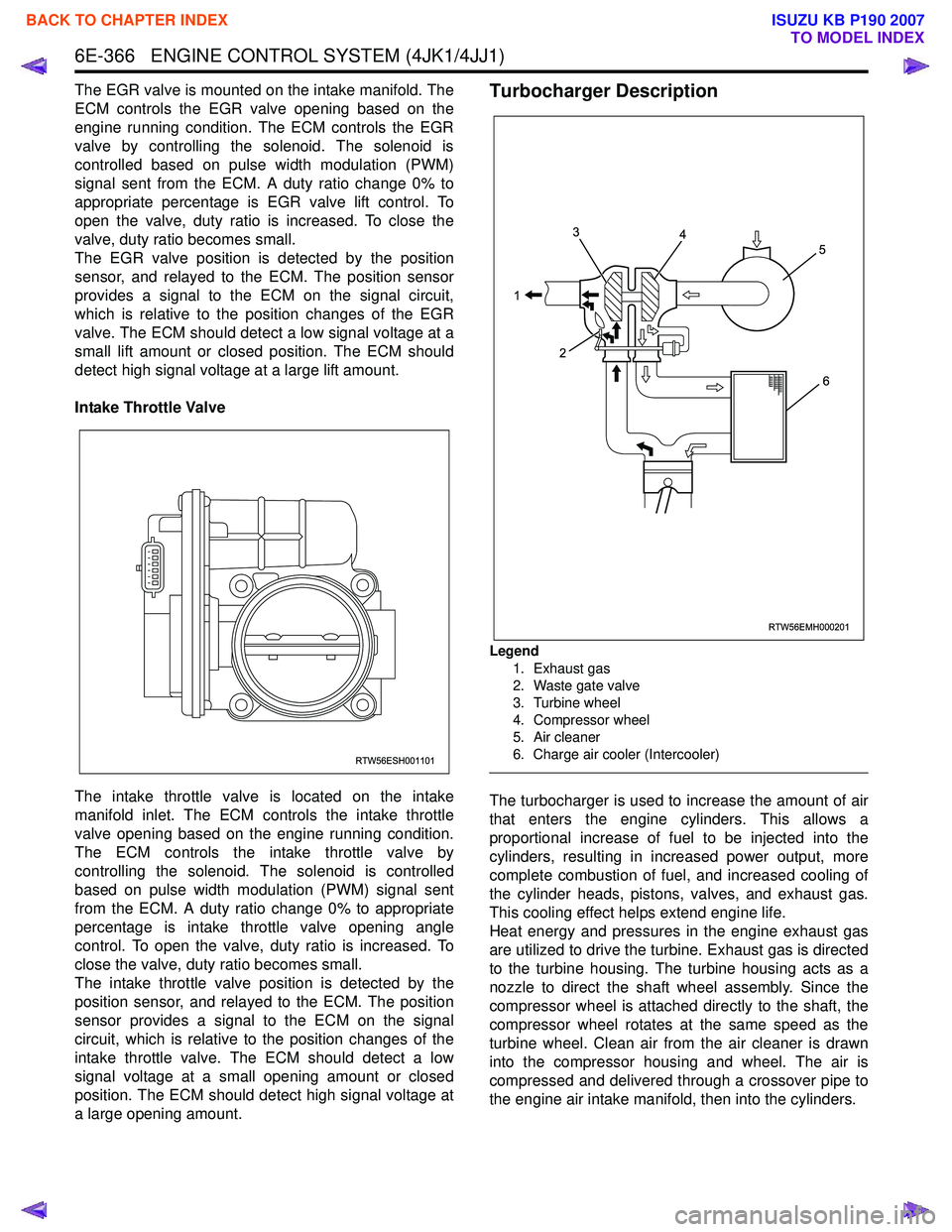
Legend
1. Exhaust gas
2. Waste gate valve
3. Turbine wheel
4. Compressor wheel
5. Air cleaner
6. Charge air cooler (Intercooler)
The turbocharger is used to increase the amount of air
that enters the engine cylinders. This allows a
proportional increase of fuel to be injected into the
cylinders, resulting in increased power output, more
complete combustion of fuel, and increased cooling of
the cylinder heads, pistons, valves, and exhaust gas.
This cooling effect helps extend engine life.
Heat energy and pressures in the engine exhaust gas
are utilized to drive the turbine. Exhaust gas is directed
to the turbine housing. The turbine housing acts as a
nozzle to direct the shaft wheel assembly. Since the
compressor wheel is attached directly to the shaft, the
compressor wheel rotates at the same speed as the
turbine wheel. Clean air from the air cleaner is drawn
into the compressor housing and wheel. The air is
compressed and delivered through a crossover pipe to
the engine air intake manifold, then into the cylinders.
RTW56ESH001101
RTW56EMH000201
1 3
2 4
5
6
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2000 of 6020
Section 6 Engine Diagnosis .......................................................................................... 2001 PAGE
Section 6A Engine Mechanical .................................................................................... 2015
Section 6B Engine Cooling .......................................................................................... 2105
Section 6C Fuel System .......................................................................... ..................... 2119
Section 6D Engine Electrical ....................................................................................... 2137
Section 6E Engine Driveability and Emissions .......................................................... 2171
Section 6F Exhaust System ........................................................................................ 2450
SECTION 6
ENGINE
TA BLE OF CONTENTS
C24SE MODEL
EN G IN E (C 24SE) 6
Section 6 G En gine L ubri ca tio n.................................................................................... 24 65
Section 6H Engine Speed Control System ................................................................ 2472
Section 6J Induction ................................................................................................... 2476
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2008 of 6020
6-8 ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE)
Condition Possible cause Correction
Engine overheating Level of Engine Coolant too low Replenish
Thermo switch or fan motor
defective Replace
Thermostat
defective Replace
Engine Coolant pump defective Correct or replace
Radiator clogged Clean or replace
Radiator filter cap defective Replace
Level of oil in engine crankcase
too low or wrong oil in engine Change or replenish
Resistance in exhaust system
increased Clean exhaust system or replace
defective parts
Throttle Position Sensor
adjustment incorrect Adjust Wide Open Throttle switch
setting
Throttle Position Sensor circuit
open or shorted Correct or replace
Cylinder head gasket damaged Replace
Cooling Fan clutch defective Replace
Fan belt slipping Adjust tension of V-belt or replace
V-belt
Engine overcooling Thermostat defective Replace (Use a thermostat set to
open at 92 °C (197.6 °F))
Engine lacks compression - Refer to Hard Start
Others Tire inflation pressure abnormal Adjust to recommend pressures
Brake drag Adjust
Clutch slipping Adjust or replace
Level of oil in engine crankcase
too high Correct level of engine oil
Engine Noisy
Abnormal engine noise often consists of various
noises originating in rotating parts, sliding parts and
other moving parts of the engine. It is, therefore,
advisable to locate the source of noise systematically.
Condition Possible cause Correction
Noise from crank journals or from
crank bearings
(Faulty crank journals and crank
bearings usually make dull noise
that becomes more evident when
accelerating) Oil clearance increased due to
worn crank journals or crank
bearings Replace crank bearings and
crankshaft or regrind crankshaft
and install the over size bearing
Crankshaft out of round Replace crank bearings and
crankshaft or regrind crankshaft
and install the over size bearing
Crank bearing seized Replace crank bearings and
crankshaft or regrind crankshaft
and install the over size bearing
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2016 of 6020

6A-2 ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE)
PAGE
Camshaft Housing, Check for Plance Surface ......................................................... 6A-39
Cylinder Head, Removal and Installation.................................................................. 6A-39
Cylinder Head, Disassemble and Assemble............................................................. 6A-42
Valve, Grind ................................................................................................................. 6 A-44
Valve Guide, Ream .................................................................................................... 6A-44
Valve Seating, Mill ...................................................................................................... 6A-45
Cylinder Head, Overhaul ............................................................................................ 6A-45
Flywheel....................................................................................................................... 6A-46
Starter Ring Gear(Manual Transmission) ................................................................. 6A-47
Seal Ring, Crankshaft................................................................................................. 6A-48
Seal Ring, Crankshaft Rear ........................................................................................ 6A-48
Oil Pan and Bearing Bridge ....................................................................................... 6A-49
OPERATIONS ON CRANK DRIVE ................................................................................... 6A-51 Con-Rod Bearing ........................................................................................................ 6A-51
Piston with Con-Rod................................................................................................... 6A-51
Con-Rod....................................................................................................................... 6A-52
Pistion Rings ............................................................................................................... 6A -53
OPERATIONS ON REMOVED ENGINE........................................................................... 6A-55 Crankshaft ................................................................................................................... 6 A-55
Bearing Free Play Measurement ............................................................................... 6A-57
Plastigage Method ...................................................................................................... 6A-57
Micrometer and gauge method.................................................................................. 6A-58
Bypass Valve ............................................................................................................... 6A- 59
Oil Filter ..................................................................................................................... .. 6A-59
Oil Pump ...................................................................................................................... 6A-59
Oil Pump Safety Valve ................................................................................................ 6A-60
Oil Pump(Overhaul) .................................................................................................... 6A-60
OPERATIONS ON OIL CIRCULATION ............................................................................ 6A-61 Cylinder Head Safety Valve ........................................................................................ 6A-61
OPERATIONS ON COOLING SYSYTEM ......................................................................... 6A-63 Cooling System, Check for Leakes ........................................................................... 6A-63
Cooling System, Fill Up and Bleed ............................................................................ 6A-63
Refill Coolant............................................................................................................... 6 A-64
Ignition Timing, Check ............................................................................................... 6A-64
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2025 of 6020
ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE) 6A-11
Main Data and Specifications
Engine - General C24SE
Engine type Four-cycle, water cooled cross-flow with single over head
camshaft
Micro-computer control, fuel injection
Combustion chamber type (Volume) Hemispherical (43.3cm3)
Timing train system Belt drive
No. of cylinders-bore × stroke mm (in) 4-87.5 ×100.0 (3.44 ×3.93)
Bore Spacing(C/L to C/L) 93.0 mm (3.66 in)
Firing Order 1-3-4-2
Bore×Stroke mm (in) 87.5 ×100.0 (3.44 ×3.93)
Total piston displacement cm3 (in3) 2,405(146.80)
Combustion Chamber Volume 43.3cm3
No. of piston ring Compression ring: 2, Oil ring: 1
Compression pressure kg/cm2 (psi/pa) 12.2-16.3 (174-232/1200-1600)
Ignition timing (BTDC) No adjustment
Idling speed: rpm(W O/AC,W /AC) A/C off 825
Valve clearances (At cold)
Intake mm (in) 0 (0) (Hydraulic valve lash adjustment)
Exhaust mm (in) 0 (0) ( " )
Open at (BTDC) deg 17°30’
Close at (ABDC) deg 76°30’
Exhaust valves
Open at (BBDC) deg 58°30’
Close at (ATDC) deg 35°30’
Ignition system Fully transistorized battery ignition
Distributor type Not applicable, Electronic Spark Timing control
Distributor advance type Not applicable, Electronic Spark Timing control
Spark plug type RN9YC4
Spark plug gap mm (in) 1.0--1.1 (0.039--0.043)
Lubrication system
Lubricating method Fully flow pressure circulation
Special engine oil (API grade) SE, SF, SG or SH grade
Oil pressure kg/cm2 (psi/Pa) rpm 4-4.6 (56.9-65.4/400-450)
Oil pump type Gear
Oil filter type Cartridge full flow
Oil capacity lit. (US/UK gal.) 4.25
Cooling system
Radiator type Corrugated fin with reserve tank
Coolant capacity lit.
(US/UK gal.) 2.3 (0.66/0.55)
W ater pump type
Centrifugal
Thermostat W ax pellet with jiggle hole
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2031 of 6020
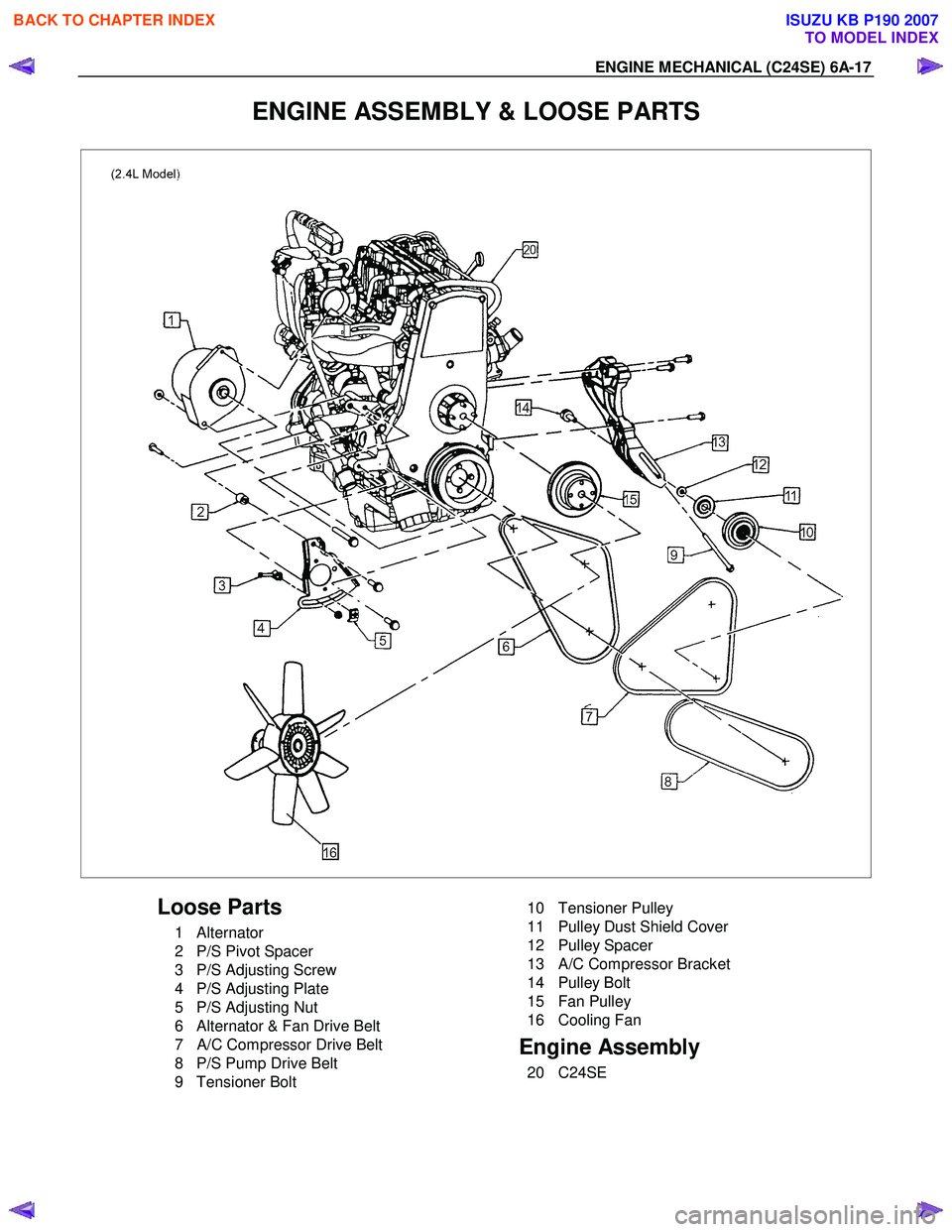
ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE) 6A-17
ENGINE ASSEMBLY & LOOSE PARTS
Loose Parts
1 Alternator
2 P/S Pivot Spacer
3 P/S Adjusting Screw
4 P/S Adjusting Plate
5 P/S Adjusting Nut
6 Alternator & Fan Drive Belt
7 A/C Compressor Drive Belt
8 P/S Pump Drive Belt
9 Tensioner Bolt
10 Tensioner Pulley
11 Pulley Dust Shield Cover
12 Pulley Spacer
13 A/C Compressor Bracket
14 Pulley Bolt
15 Fan Pulley
16 Cooling Fan
Engine Assembly
20 C24SE
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007