low oil pressure ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 846 of 6020

ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 41
Coolant Replenishment
Warning:
When the coolant is heated to a high temperature, be
sure not to loosen or remove the rediator cap.
Otherwise you might get scalded by hot vapor or
boiling water.
To open the radiator cap, put a piece of thick cloth on
the cap and loosen the cap slowly to reduce the
pressure when the coolant has become cooler.
1. Open rediator cap pour coolant up to filler neck
2. Pour coolant into reservoir tank up to "MAX" line
3. Tighten radiator cap and start the engine. After idling for 2 to 3 minutes, stop the engine and reopen radiator
cap. If the water level is lower, replenish.
4. After replenish the coolant tighten radiator cap, warm up the engine at about 2000 rpm. Set heater
adjustment to the highest temperature position, and let
the coolant circulate also into heater water system.
5. Check to see the thermometer, continuously idling 5 minutes and stop the engine.
6. W hen the engine has been cooled, check filler neck for water level and replenish if required. Should extreme
shortage of coolant is found, check the coolant system
and reservoir tank hose for leakage.
7. Pour coolant into the reservoir tank up to "MAX" line.
Coolant Capacity lit (US/UK gal)
4JA1 / TC 9.4 (2.5 / 2.1)
4JH1TC M/T: 10.1 (2.7 / 2.2)
A/T: 10.0 (2.6 / 2.2)
Engine Warm-Up
After completing the required maintenance procedures,
start the engine and allow it to idle until it is warm.
Check the following:
1. Engine idling speed.
2. Engine noise level.
3. Engine lubricating system and cooling system. Carefully check for oil and coolant leakage.
4. Clutch engagement.
5. Transmission operation.
6. Indicator warning light operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 931 of 6020
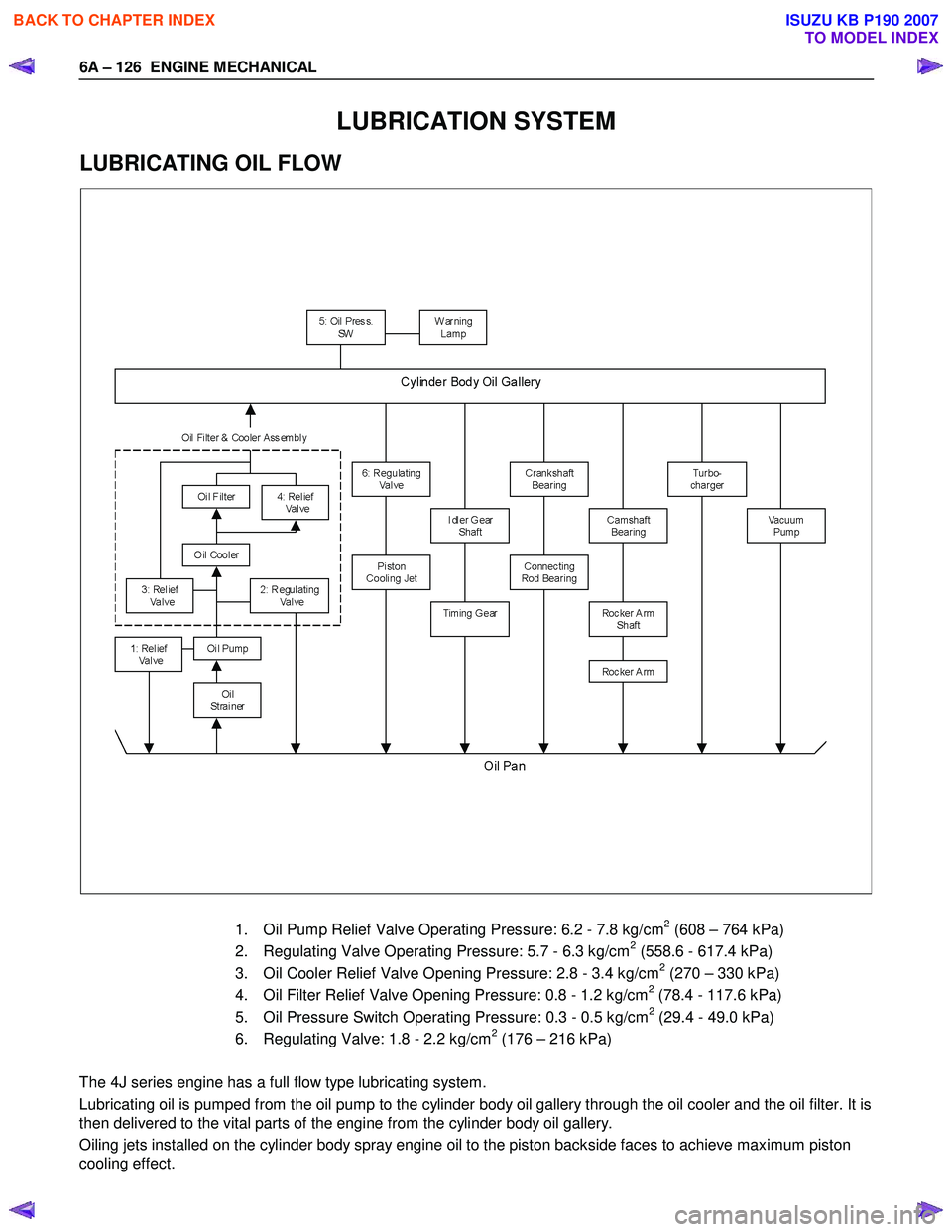
6A – 126 ENGINE MECHANICAL
LUBRICATION SYSTEM
LUBRICATING OIL FLOW
1. Oil Pump Relief Valve Operating Pressure: 6.2 - 7.8 kg/cm
2 (608 – 764 kPa)
2. Regulating Valve Operating Pressure: 5.7 - 6.3 kg/cm2 (558.6 - 617.4 kPa)
3. Oil Cooler Relief Valve Opening Pressure: 2.8 - 3.4 kg/cm2 (270 – 330 kPa)
4. Oil Filter Relief Valve Opening Pressure: 0.8 - 1.2 kg/cm2 (78.4 - 117.6 kPa)
5. Oil Pressure Switch Operating Pressure: 0.3 - 0.5 kg/cm2 (29.4 - 49.0 kPa)
6. Regulating Valve: 1.8 - 2.2 kg/cm2 (176 – 216 kPa)
The 4J series engine has a full flow type lubricating system.
Lubricating oil is pumped from the oil pump to the cylinder body oil gallery through the oil cooler and the oil filter. It is
then delivered to the vital parts of the engine from the cylinder body oil gallery.
Oiling jets installed on the cylinder body spray engine oil to the piston backside faces to achieve maximum piston
cooling effect.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 952 of 6020

6B – 8 ENGINE COOLING
Draining and Refilling Cooling System
Before draining the cooling system, inspect the system and
perform any necessary service to ensure that it is clean, does
not leak and is in proper working order. The engine coolant
(EC) level should be between the “MIN" and “MAX" lines o
f
reserve tank when the engine is cold. If low, check for leakage
and add EC up to the “MAX" line.
There should not be any excessive deposit of rust or scales
around the radiator cap or radiator filler hole, and the EC
should also be free from oil.
Replace the EC if excessively dirty.
P1010064
1. Completely drain the cooling system by opening the drain
plug at the bottom of the radiator.
2. Remove the radiator cap.
WARNING: To avoid the danger of being burned, do not
remove the cap while the engine and radiator are still hot.
Scalding fluid and steam can be blown out unde
r
pressure.
3. Disconnect all hoses from the EC reserve tank.
Scrub and clean the inside of the reserve tank with soap and water. Flush it well with clean water, then drain it.
Install the reserve tank and hoses.
4. Refill the cooling system with the EC using a solution that is at least 50 percent antifreeze.
Procedure for filling with coolant (in case of full change)
• Make sure that the engine is cool.
• Open radiator cap pour coolant up to filler neck.
• Pour coolant into reservoir tank up to “MAX" line.
• Tighten radiator cap and start the engine. After idling for 2
to 3 minutes, stop the engine and reopen radiator cap. If the
water level is lower, replenish.
WARNING: When the coolant is heated to a high
temperature, be sure not to loosen or remove the radiato
r
cap. Otherwise you might get scalded by not vapor or
boiling water. To open the radiator cap, put a piece of
thick cloth on the cap and loosen the cap slowly to reduce
the pressure when the coolant has become cooler.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1082 of 6020
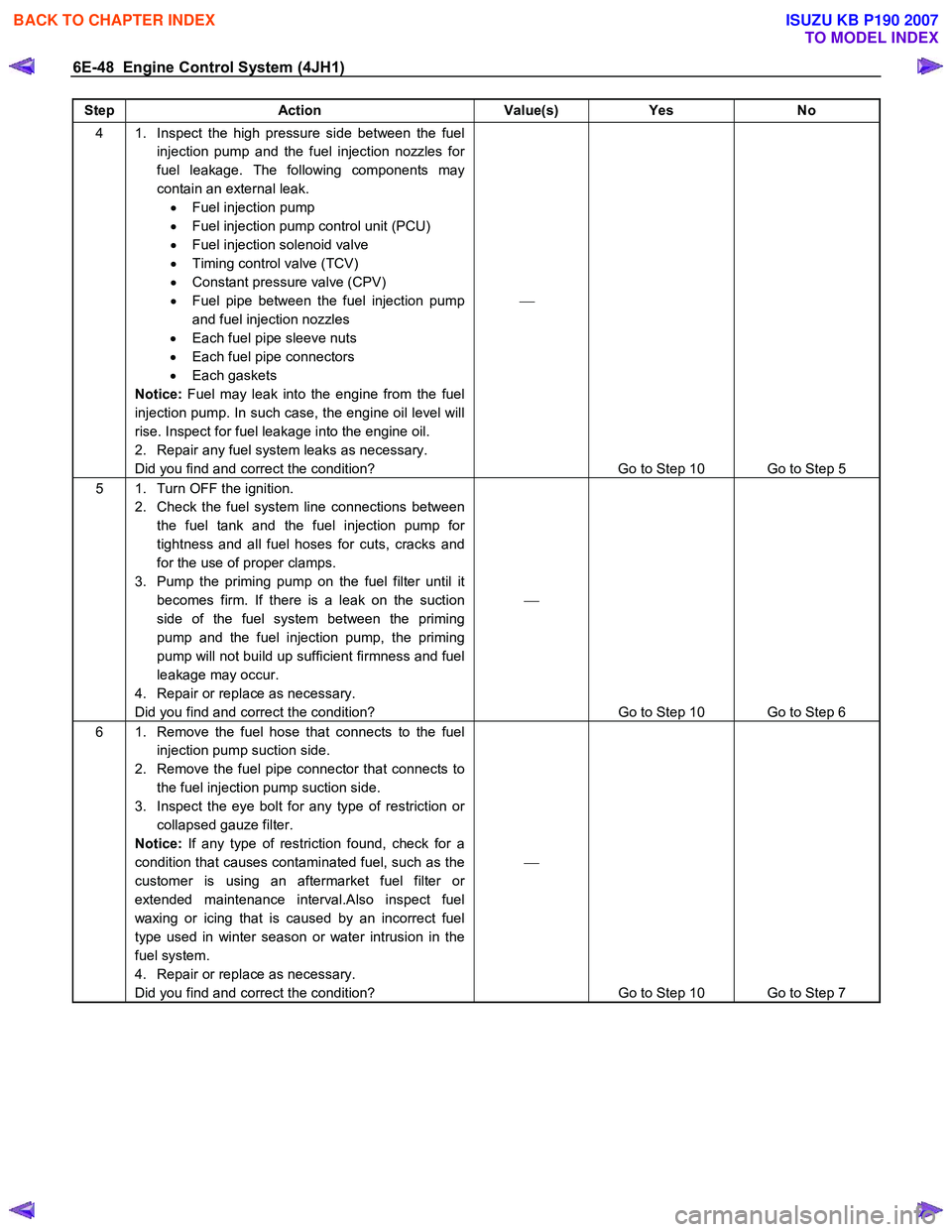
6E-48 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
4 1. Inspect the high pressure side between the fuel
injection pump and the fuel injection nozzles for
fuel leakage. The following components may
contain an external leak. • Fuel injection pump
• Fuel injection pump control unit (PCU)
• Fuel injection solenoid valve
• Timing control valve (TCV)
• Constant pressure valve (CPV)
• Fuel pipe between the fuel injection pump
and fuel injection nozzles
• Each fuel pipe sleeve nuts
• Each fuel pipe connectors
• Each gaskets
Notice: Fuel may leak into the engine from the fuel
injection pump. In such case, the engine oil level will
rise. Inspect for fuel leakage into the engine oil.
2. Repair any fuel system leaks as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 5
5 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Check the fuel system line connections between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for
tightness and all fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and
for the use of proper clamps.
3. Pump the priming pump on the fuel filter until it becomes firm. If there is a leak on the suction
side of the fuel system between the priming
pump and the fuel injection pump, the priming
pump will not build up sufficient firmness and fuel
leakage may occur.
4. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 6
6 1. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
2. Remove the fuel pipe connector that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
3. Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a
condition that causes contaminated fuel, such as the
customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or
extended maintenance interval.Also inspect fuel
waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel
type used in winter season or water intrusion in the
fuel system.
4. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1153 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-119
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
3 1. Inspect the following for possible causes of high
boost pressure. • W astegate valve for a stuck closed
condition. Refer to the Turbocharger in
Engine Mechanical section for diagnosis.
• Restricted intake or collapsed hose.
2. Repair the condition as necessary.
Did you find and correction the condition?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 4
4 1. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds. 2. Start the engine and warm up (allow engine coolant temperature to reach at least 60°C
[140°F]).
3. Perform the EGR Solenoid Valve test with the scan tool.
4. Command the EGR Solenoid Valve ON and OFF with the scan tool while observing the Mass Air
Flow (MAF) Sensor parameter.
Does the MAF Sensor parameter decrease by at
least 200 mg/strk within 2 seconds when the EGR
Solenoid Valve is commanded ON?
Go to Diagnostic Aids Go to Step 5
5 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Inspect for the following conditions: • An EGR valve control vacuum hose is
damaged or kinked.
• EGR solenoid valve vacuum hoses are
damaged or kinked.
• EGR solenoid valve ventilation is damaged.
• An EGR valve is stuck close.
• Restricted or collapsed EGR passage
between the exhaust manifold and EGR
valve.
• Oil in the air tubing causing an incorrect
MAF sensor signal. W hen there is
adhesion of oil, inside of the tubing,
intercooler and turbocharger needs to be
wipe off.
• Contaminated or skewed MAF sensor.
3. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 6
6 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the EGR valve control vacuum hose from the EGR valve.
3. Connect a hand-held vacuum pump (5-8840- 0279-0/J-23738-A) to the disconnected vacuum
hose.
4. Start the engine and let engine idle.
5. Perform the EGR Solenoid Valve test with the scan tool.
6. Command the EGR Solenoid Valve ON and OFF with the scan tool.
Does the hand-held vacuum pump indicate more
than 50 cmHg (20 inHg) when commanding the ON
and less than 10 cmHg (4 inHg) when commanding
OFF?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 10
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1181 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-147
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
4 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Inspect for the following conditions: • An EGR valve control vacuum hose is
damaged or kinked.
• EGR solenoid valve vacuum hoses are
damaged or kinked.
• EGR solenoid valve ventilation is damaged.
• An EGR valve is stuck open.
• Any type of restriction in the exhaust
system.
• Air leakage around the MAF sensor or
debris in the sensor housing.
• Air leaking around any of the air induction
tubing between the MAF sensor and intake
manifold.
• Turbine shaft binding causing lower
turbocharger shaft spinning speeds. Refer
to the Turbocharger in Engine Mechanical
section for diagnosis.
• Restricted air cleaner element, restricted or
collapsed air tubing between the air cleaner
and the turbocharger.
• Oil in the air tubing causing an incorrect
MAF sensor signal. W hen there is
adhesion of oil, inside of the tubing,
intercooler and turbocharger needs to be
wipe off.
• Contaminated, skewed or slow MAF
sensor.
3. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 5
5 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the EGR valve control vacuum hose from the EGR valve.
3. Connect a hand-held vacuum pump (5-8840- 0279-0/J-23738-A) to the disconnected vacuum
hose.
4. Start the engine and let engine idle.
5. Perform the EGR Solenoid Valve test with the scan tool.
6. Command the EGR Solenoid Valve ON and OFF with the scan tool.
Does the hand-held vacuum pump indicate more
than 50 cmHg (20 inHg) when commanding the ON
and less than 10 cmHg (4 inHg) when commanding
OFF?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 9
6 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the hand-held vacuum pump from the vacuum hose.
3. Connect the hand-held vacuum pump to the vacuum port of EGR valve.
4. Start the engine and let engine idle.
5. Apply vacuum pressure to the EGR valve while observing the MAF Sensor parameter.
Does the MAF Sensor parameter decrease by at
least 200 mg/strk when the vacuum pressure is
applied?
Go to Diagnostic Aids Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1187 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-153
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
4 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Inspect for the following conditions: • An EGR valve control vacuum hose is
damaged or kinked.
• EGR solenoid valve vacuum hoses are
damaged or kinked.
• EGR solenoid valve ventilation is damaged.
• An EGR valve is stuck close.
• Restricted or collapsed EGR passage
between the exhaust manifold and EGR
valve.
• A vacuum hose from the vacuum pump is
damaged or kinked.
• A vacuum pump is damaged.
• Oil in the air tubing causing an incorrect
MAF sensor signal. W hen there is
adhesion of oil, inside of the tubing,
intercooler and turbocharger needs to be
wipe off.
• Contaminated or skewed MAF sensor.
3. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 5
5 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the EGR valve control vacuum hose from the EGR valve.
3. Connect a hand-held vacuum pump (5-8840- 0279-0/J-23738-A) to the disconnected vacuum
hose.
4. Start the engine and let engine idle.
5. Perform the EGR Solenoid Valve test with the scan tool.
6. Command the EGR Solenoid Valve ON and OFF with the scan tool.
Does the hand-held vacuum pump indicate more
than 50 cmHg (20 inHg) when commanding the ON
and less than 10 cmHg (4 inHg) when commanding
OFF?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 9
6 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the hand-held vacuum pump from the vacuum hose.
3. Connect the hand-held vacuum pump to the vacuum port of EGR valve.
4. Start the engine and let engine idle.
5. Apply vacuum pressure to the EGR valve while observing the MAF Sensor parameter.
Does the MAF Sensor parameter decrease by at
least 200 mg/strk when the vacuum pressure is
applied?
Go to Diagnostic Aids Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1276 of 6020

6E-242 Engine Control System (4JH1)
DTC A/C Compressor System Check
Description
W hen air conditioning (A/C) and blower fan are
selected, and if the system has a sufficient refrigerant
charge. A 12-volt signal is supplied to the A/C request
input of the Engine Control Module (ECM). The A/C
request signal may be temporarily canceled during
system operation by the electronic thermostat in the
evaporator to prevent the evaporator icing. Also, it is
cancelled when the pressure switch detected abnormal
pressure in the line. W hen the A/C request signal is
received by the ECM, the ECM supplies a ground from
the A/C compressor relay if the engine operating
conditions are within acceptable ranges. W ith the A/C
compressor relay energized, voltage is supplied to the
compressor clutch coil. The ECM will enable the
compressor clutch to engage whenever A/C has been
selected with the engine running and enable conditions
are met.
Condition for Running the A/C Compressor:
• The engine is running.
• The A/C switch is ON.
• The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is less than
105 °C(221 °F).
A/C Compressor System Check
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or Engine Control Module (ECM)
Connector End Views
Chart 1 of 2
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check – Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
4. Monitor the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Information of the engine control system with the
scan tool and check whether following DTC(s) is
set: • P0115 (Symptom Code 1 & 2)
• P0645 (Symptom Code 4 & 8)
Are any of the above DTC(s) set?
Refer to Applicable DTC Go to Step 3
3 1. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
2. Turn ON the blower motor switch.
Does the blower motor turn ON and operate
correctly?
Go to Step 4 Refer to Applicable
Diagnostic Chart in Heating & Air Conditioning Section
4 1. Turn OFF the blower motor switch. 2. Keep the A/C switch OFF.
Does the A/C Request Signal parameter indicate
OFF?
Go to Step 5 Go to Chart 2 of 2
with heater Step 1 OR
Go to Chart 2 of 2
without heater Step 1
5 1. Start the engine and let the engine idle. 2. Keep the blower motor switch OFF.
3. Keep the A/C switch OFF.
Does the A/C compressor clutch keep OFF
(disengage)?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 11
6 1. Turn ON the blower motor switch. 2. Keep the A/C switch OFF.
Does the A/C compressor clutch keep OFF
(disengage)?
Go to Step 7 Go to Chart 2 of 2
with heater Step 7 OR
Go to Chart 2 of 2
without heater Step 4
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1293 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-259
Checks Action
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the scan tool
Data List in this section.
• Use the scan tool to compare the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) with the Intake
Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) on a cold engine condition. If the
difference among temperature reading is more than 5°C (9°F) on a cold engine,
check for high resistance on the low reference circuit and signal circuit or for a
skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT sensor may
indicate a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
FT sensor is internal to the PCU and it is part of the fuel injection pump assembly.
• Inspect the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is tight and the flywheel circumference
is not damaged.
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and
all fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a
slight vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if
these connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump
internal pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for
cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
c. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
d. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into
the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the
fuel line (as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a
clean stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-
23738-A with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not
cracked drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
• Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used
in winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
• Inspect the fuel injection nozzle(s) for proper splay condition or operating pressure.
Notice: Only first stage of operating pressure can be checked.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
• Inspect for a restriction in the catalytic converter or exhaust pipes.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1295 of 6020
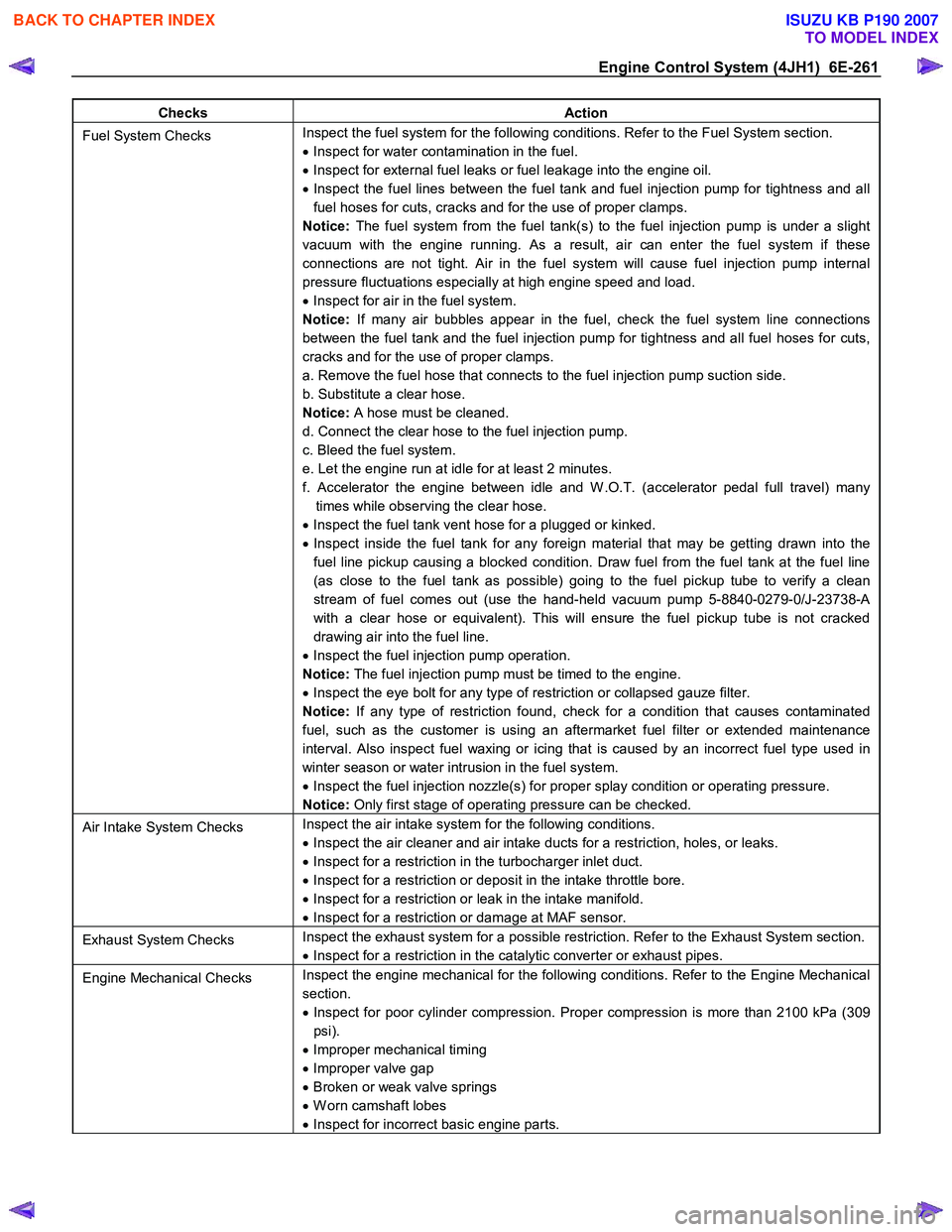
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-261
Checks Action
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and all
fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a slight
vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if these
connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump internal
pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for cuts,
cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
d. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
c. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into the
fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the fuel line
(as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a clean
stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-23738-A
with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not cracked
drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
• Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used in
winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
• Inspect the fuel injection nozzle(s) for proper splay condition or operating pressure.
Notice: Only first stage of operating pressure can be checked.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at MAF sensor.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System section.
• Inspect for a restriction in the catalytic converter or exhaust pipes.
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine Mechanical
section.
• Inspect for poor cylinder compression. Proper compression is more than 2100 kPa (309
psi).
• Improper mechanical timing
• Improper valve gap
• Broken or weak valve springs
• W orn camshaft lobes
• Inspect for incorrect basic engine parts.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007