low oil pressure ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 1372 of 6020
6A-12 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4JK1/4JJ1)
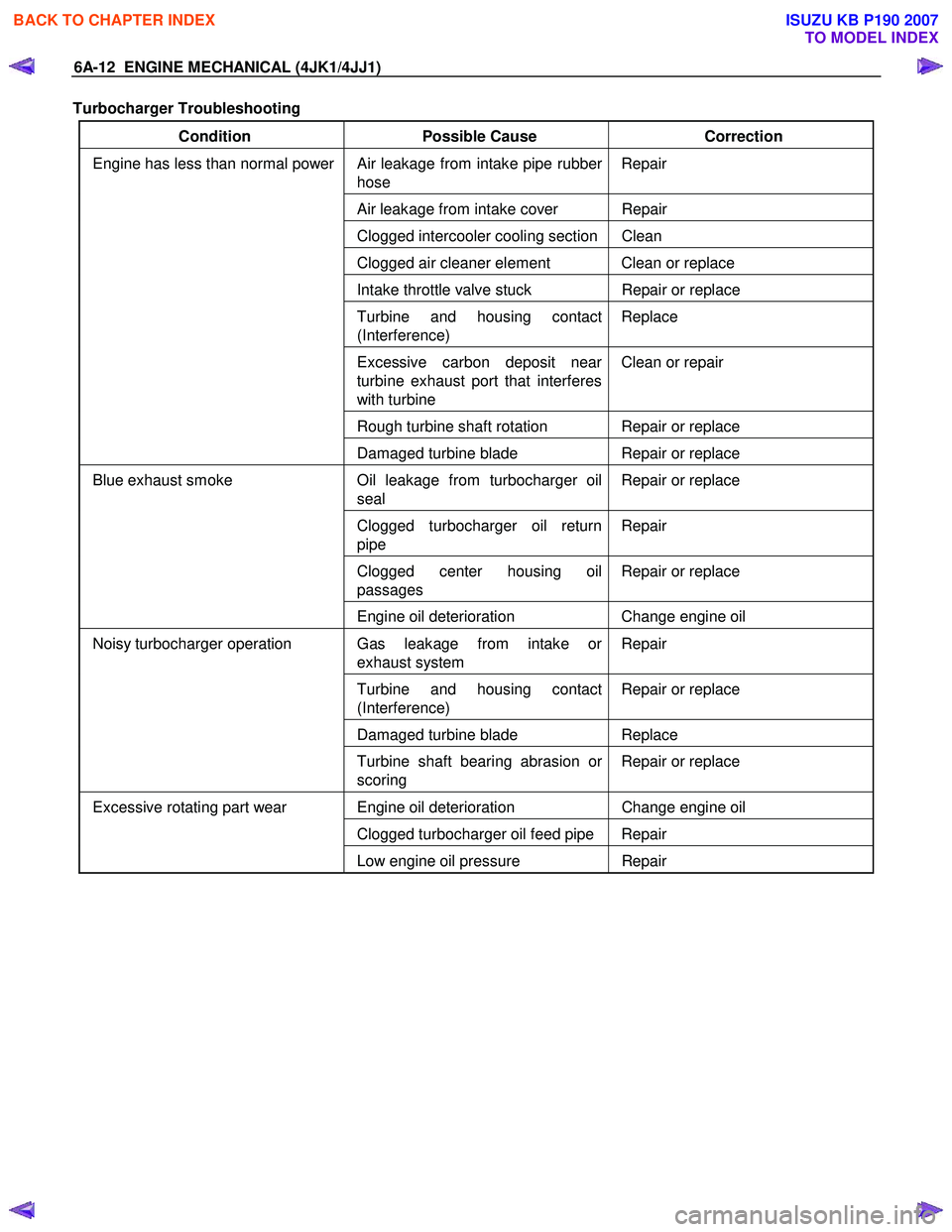
Turbocharger Troubleshooting
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Air leakage from intake pipe rubber
hose Repair
Air leakage from intake cover Repair
Clogged intercooler cooling section Clean
Clogged air cleaner element Clean or replace
Intake throttle valve stuck
Repair or replace
Turbine and housing contact
(Interference) Replace
Excessive carbon deposit near
turbine exhaust port that interferes
with turbine Clean or repair
Rough turbine shaft rotation Repair or replace
Engine has less than normal power
Damaged turbine blade Repair or replace
Oil leakage from turbocharger oil
seal Repair or replace
Clogged turbocharger oil return
pipe Repair
Clogged center housing oil
passages Repair or replace
Blue exhaust smoke
Engine oil deterioration Change engine oil
Gas leakage from intake or
exhaust system Repair
Turbine and housing contact
(Interference) Repair or replace
Damaged turbine blade
Replace
Noisy turbocharger operation
Turbine shaft bearing abrasion or
scoring Repair or replace
Engine oil deterioration
Change engine oil
Clogged turbocharger oil feed pipe Repair
Excessive rotating part wear
Low engine oil pressure Repair
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1373 of 6020

ENGINE MECHANICAL (4JK1/4JJ1) 6A-13
Main Data and specifications
Item Engine model 4JK1 Engine model 4JJ1
Type Diesel/4-cycle/water cooling-type in-line DOHC
Combustion chamber type Direct injection type
Cylinder liner type Liner less
Number of cylinders -cylinder
bore × strokes mm (in) 4-95.4 (3.76) × 87.4 (3.44) 4-95.4(3.76) × 104.9(4.13)
Displacement
cc (cu.in) 2499 (152) 2999 (183)
Compression ratio 18.3 17.5
Compression pressure MPa (psi)/rpm 3 (435)/200
Idling speed rpm 700 ± 25
Valve clearance Intake 0.15 (0.006) (cold)
mm (in) Exhaust 0.15 (0.006) (cold)
Ignition type Compressed ignition
Injection order 1 - 3 - 4 - 2
Lubricating system
Lubricating type Pressure delivery type
Oil pump type Gear type
Volume of lubricating oil L (qts) 8.0 (8.5)
Oil filter type Full flow filter (cartridge type)
Oil cooling type Built-in-type, water cooling
Cooling system
Cooling type W ater cooling type
Radiator type Corrugated fin (pressure type)
W ater pump type Centrifugal, belt drive type
Thermostat type W ax-type units
Thermostat valve-opening temperature °C ( °F) 85 (185)
Volume of coolant L (qts) M/T8.7 (9.2) A/T 8.6 (9.1) (incl. radiator)
Fuel system
Injection pump type Fuel supply pump fuel rail type
Fuel injector type Electronic control injector
6-hole
Fuel pump type Into the fuel tank type
Charging system
Generator type AC type
Power output V-A 12 - 90
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1500 of 6020
6A-140 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4JK1/4JJ1)
Lubrication System
Service Precautions
• During each disassembly, remove the old gasket
adhering to each part and mating part completel
y
using a scraper at the location, where the fluid
gasket is to be used, clean the traces of oil,
moisture, and dirt completely using waste cotton
and apply the specified new fluid gasket at each
location.
•
Avoid excessive or insufficient coating volume.
Note that seizure may occur in case of excessive
coating due to clogging of the oil gallery and oil jet,
and oil and water leakage may occur if the coating
is insufficient.
• Always, the start and end of the application should
be overlapped.
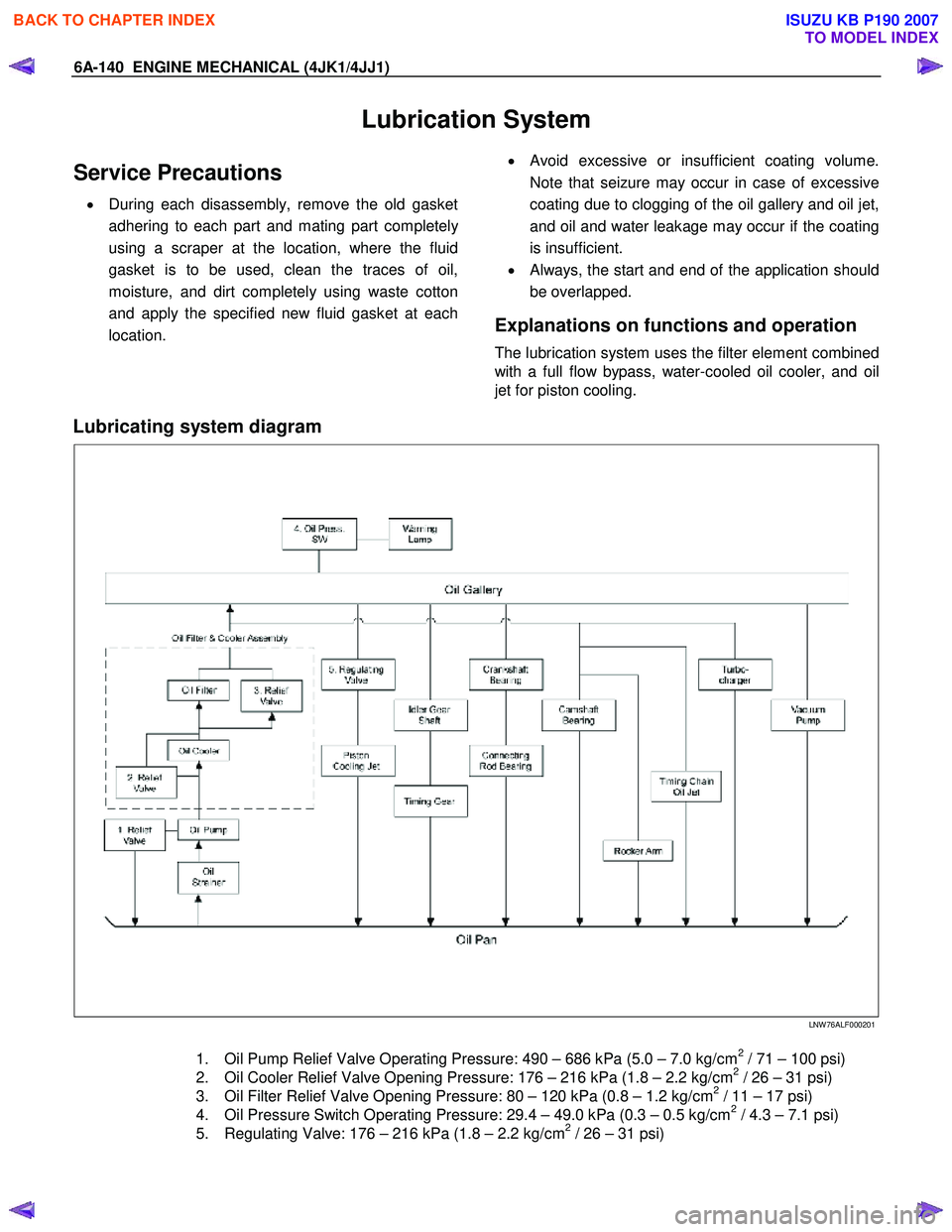
Explanations on functions and operation
The lubrication system uses the filter element combined
with a full flow bypass, water-cooled oil cooler, and oil
jet for piston cooling.
Lubricating system diagram
LNW 76ALF000201
1. Oil Pump Relief Valve Operating Pressure: 490 – 686 kPa (5.0 – 7.0 kg/cm2 / 71 – 100 psi)
2. Oil Cooler Relief Valve Opening Pressure: 176 – 216 kPa (1.8 – 2.2 kg/cm2 / 26 – 31 psi)
3. Oil Filter Relief Valve Opening Pressure: 80 – 120 kPa (0.8 – 1.2 kg/cm2 / 11 – 17 psi)
4. Oil Pressure Switch Operating Pressure: 29.4 – 49.0 kPa (0.3 – 0.5 kg/cm2 / 4.3 – 7.1 psi)
5. Regulating Valve: 176 – 216 kPa (1.8 – 2.2 kg/cm2 / 26 – 31 psi)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1501 of 6020

ENGINE MECHANICAL (4JK1/4JJ1) 6A-141
Functional Check
Oil pressure check
1. Check whether the engine oil is contaminated with
dirt, light oil, or water. If contaminated with dirt,
light oil, or water (after examining the cause and
taking the appropriate measures for light oil o
r
water contamination), replace the oil.
2. Check the engine oil level. The oil level should be between the two holes of the level gauge. If the oil
level is insufficient, replenish it.
3. Remove the oil pressure switch on the nipple.
4. Install the oil pressure gauge on the nipple.
RTW 56ASH015501
Legend
1. Oil Pressure Switch
5. W arm the engine.
6. Measure the oil pressure, to check whether it is more than 400 kPa (4 kg/cm
2 / 58 psi) at 3600
rpm.
7. Stop the engine.
8. Remove the oil pressure gauge.
9. Install the oil pressure switch.
10. Start the engine and check for oil leakage.
Engine oil
•
Ensure the car is on level ground. Before starting
the engine or when 30 minutes or more have
elapsed after stopping the engine, check the
engine oil volume using the level gauge. The
volume is appropriate if the engine oil is between
the upper and lower limits of the level gauge.
Replenish the engine oil, if level is below the lowe
r
limit. Also, check for contamination of the engine
oil.
RTW 56ASH015601
RTW 56ASH015701
Legend
1. Lower Limit
2. Upper Limit
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1530 of 6020

ENGINE COOLING (4JK1/4JJ1) 6B-7
Draining and Refilling Cooling System
Before draining the cooling system, inspect the system
and perform any necessary service to ensure that it is
clean, does not leak and is in proper working order.
The engine coolant (EC) level should be between the
“MIN" and “MAX" lines of the reserve tank when the
engine is cold. If low, check for leakage and add EC up
to the “MAX" line.
There should not be any excessive deposit of rust o
r
scales around the radiator cap or radiator filler hole, and
the EC should also be free from oil.
Replace the EC if excessively dirty.
1. Remove the radiator skid plate.
2. Completely drain the cooling system by opening the drain plug at the bottom of the radiator.
RTW 56BSH000301
3. Remove the radiator cap.
WARNING:
To avoid the danger of being burned, do not
remove the cap while the engine and radiator are
still hot. Scalding fluid and steam can be blown out
under pressure.
4. Disconnect all hoses from the EC reserve tank.
Scrub and clean the inside of the reserve tank with soap and water. Flush it well with clean water,
then drain it. Install the reserve tank and hoses.
5. Refill the cooling system with the EC using a
solution that is at least 50 percent antifreeze.
Procedure for filling with coolant (in case of full change).
• Make sure that the engine is cool.
• Open radiator cap and pour coolant up to fille
r
neck.
• Pour coolant into reservoir tank up to “MAX" line.
• Tighten radiator cap and start the engine. Afte
r
idling for 2 to 3 minutes, stop the engine and
reopen the radiator cap. If the water level is lower,
replenish.
WARNING:
When the coolant is heated to a high temperature,
be sure not to loosen or remove the radiator cap.
Otherwise you might get scalded by hot vapor o
r
boiling water. To open the radiator cap, put a piece
of thick cloth on the cap and loosen the cap slowly
to reduce the pressure when the coolant has
become cooler.
• After tightening the radiator cap, warm up the
engine at about 2000 rpm. Set heater adjustment
to the highest temperature position, and let the
coolant circulate also into heater water system.
• Check to see the thermostat has opened through
the needle position of the water thermometer,
conduct a 5–minute idling again and stop the
engine.
• W hen the engine has been cooled, check fille
r
neck for water level and replenish if required.
Should extreme shortage of coolant be found,
check the cooling system and reservoir tank hose
for leakage.
• Pour coolant into the reservoir tank up to “MAX"
line.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1682 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-65
Circuit/ System Testing Engine Cranks but Does Not Run (2 of 2)
StepAction Value(s)Yes No
1 1. Remove the engine cover.
2. Perform the Injector Force Drive with a scan tool.
3. Command each injector ON and verify clicking noise (solenoid operating noise).
Is there an injector that does not create a clicking
noise (solenoid operating noise), contains an
interrupted noise or abnormal noise when
commanded ON? —
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 2
2 1. Inspect the high pressure side between the
fuel supply pump and the fuel injectors for fuel
leakage. The following components may
contain an external leak.
• Fuel supply pump
• Fuel rail
•Pressure limiter valve
• Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor
• Fuel pipe between the fuel supply pump and fuel rail
• Fuel pipe between the fuel rail and fuel injectors
• Each fuel pipe sleeve nuts
Notice: Fuel may leak under the cylinder head
cover from the inlet high pressure line. In such
case, the engine oil level will rise. Inspect for fuel
leakage into the engine oil.
2. Repair any fuel system leaks as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 3
3 1. Check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel supply
pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for cuts,
cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 4
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1708 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-91
21. Inspect the high pressure side between the
fuel supply pump and the fuel injectors for fuel
leakage. The following components may
contain an external leak.
• Fuel supply pump
• Fuel rail
•Pressure limiter valve
• Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor
• Fuel pipe between the fuel supply pump and fuel rail
• Fuel pipe between the fuel rail and fuel injectors
• Each fuel pipe sleeve nuts
Notice: Fuel may leak under the cylinder head
cover from the inlet high pressure line. In such
case, the engine oil level will rise. Inspect for fuel
leakage into the engine oil.
Notice: Remove and inspect the inlet high
pressure joint to the fuel injectors for fuel leaking
from the sleeve nut(s). Replace the fuel injector
and injection pipe when foreign material was in
contact.
2. Repair any fuel system leaks as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 16 Go to Step 3
3 1. Remove each glow plug from the cylinder
head.
2. Inspect for fuel leakage into the combustion chamber.
Is there a cylinder that fuel leakage into the
combustion chamber? —
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 4
4 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with a scan tool.
Is DTC P0087, P0091, P0092, P0192, P0193,
P0201 - P0204, P1064, P1065, P124B or P2146 -
P2151 set? —
Go to Applicable DTC Go to Step 5
5 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Wait 1 minute for the fuel pressure to bleed down from the fuel rail.
3. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF. DO NOT start the engine.
4. Observe the FRP Sensor parameter with the scan tool.
Does the scan tool indicate within the specified
value? 0.9 to 1.0 volt
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 11
Step
Action Value(s)Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1760 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-143
4Compare the BARO value to the range specified in
the altitude vs. barometric pressure table. Refer to
Altitude vs Barometric Pressure.
Is the BARO parameter within the range specified? —
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
5 1. Inspect the following for possible causes of
high boost pressure.
• Misrouted turbocharger nozzle control actuator vacuum hoses
• Turbocharger nozzle control actuator or solenoid valve for a stuck condition.
Refer to Turbocharger Control System
Check in this section.
• Intake throttle valve sticking. Perform the Intake Throttle Solenoid Control with a
scan tool
• Oil in the air induction tubing causing an incorrect boost pressure sensor signal.
When there is adhesion of oil inside of
the tubing, intercooler or turbocharger it
needs to be wiped off.
2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correction the condition? —
Go to Step 10 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
6 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the boost pressure sensor harness connector.
3. Inspect for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the harness connector of the
boost pressure sensor (pin 2 of E-107).
4. Disconnect the ECM harness connector.
5. Inspect for an intermittent, for a poor connection and corrosion at the harness
connector of the ECM (pin 23 of E-90).
6. Test for high resistance of the low reference circuit.
7. Repair the connection(s) or circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 8
7 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the BARO sensor harness connector.
3. Inspect for an intermittent and for poor connections at the harness connector of the
BARO sensor (pins 2 and 3 of E-40).
4. Disconnect the ECM harness connector.
5. Inspect for an intermittent, for poor connections and corrosion at the harness
connector of the ECM (pins 18 and 19 of E-
90).
6. Test for high resistance on each circuit.
7. Repair the connection(s) or circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
Step
Action Value(s)Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1763 of 6020

6E-146 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
31. Inspect the following for possible causes of
low boost pressure.
• Air leakage around the boost pressure sensor or objects that block the sensor
hole.
• Air leaking around any of the air induction tubing between the turbocharger and
intake manifold. Check for damaged
components and for loose clamps.
• Misrouted, disconnected or kinked turbocharger nozzle control actuator
vacuum hose.
• Turbine shaft binding causing lower turbocharger shaft spinning speeds.
Refer to the Turbocharger in Engine
Mechanical section for diagnosis.
• Turbocharger nozzle control actuator or solenoid valve for a stuck condition.
Refer to Turbocharger Control System
Check in this section.
• Intake throttle valve sticking. Perform the Intake Throttle Solenoid Control with a
scan tool.
• Restricted air cleaner element, restricted or collapsed air tubing between the air
cleaner and the boost pressure sensor.
• Oil in the air induction tubing causing an incorrect boost pressure sensor signal.
When there is adhesion of oil inside of
the tubing, intercooler or turbocharger it
needs to be wiped off.
2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 4
4 1. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
2. Observe the Boost Pressure and Barometric Pressure (BARO) with a scan tool.
Does the scan tool indicate that the difference
between the Boost Pressure and BARO is more
than the specified value? 10 kPa (1.5
psi)
Go to Step 5 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
5 Compare the BARO value to the range specified in
the altitude vs. barometric pressure table. Refer to
Altitude vs Barometric Pressure.
Is the BARO parameter within the range specified? —
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
Step
Action Value(s)Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1849 of 6020
6E-232 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Notice:• This DTC most likely indicates a loss of fuel pressure by a fuel leak from the high pressure
side. Inspect the high pressure side fuel leakage
between the fuel supply pump and fuel injector
first. • If the fuel tank is empty or near empty, air might be
allowed to go into the fuel system. With air in the
fuel system, smooth flow of fuel into the supply
pump is interrupted and this DTC may set. Perform
bleeding of fuel system after refilling.
Schematic Reference: Fuel System Routing Diagram
and Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or ECM Connector End Views
Circuit/ System Testing DTC P1094
Step Action Value(s)Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check -
Engine Controls? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check -
Engine Controls
2 1. Inspect the high pressure side between the
fuel supply pump and the fuel injectors for fuel
leakage. The following components may
contain an external leak.
• Fuel supply pump
• Fuel rail
• Pressure limiter valve
• Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor
• Fuel pipe between the fuel supply pump and fuel rail
• Fuel pipe between the fuel rail and fuel injectors
• Each fuel pipe sleeve nuts
Notice: Fuel may leak under the cylinder head
cover from the inlet high pressure line. In such
case, the engine oil level will rise. Inspect for fuel
leakage into the engine oil.
Notice: Remove and inspect the inlet high
pressure joint to the fuel injectors for fuel leaking
from the sleeve nut(s). Replace the fuel injector
and injection pipe when foreign material was in
contact.
2. Repair any fuel system leaks as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 19 Go to Step 3
3 1. Remove each glow plug from the cylinder
head.
2. Inspect for fuel leakage into the combustion chamber.
Is there a cylinder that fuel leakage into the
combustion chamber? —
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 4
4 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with a scan tool.
Is DTC P0087, P0091, P0092, P0192, P0193,
P0201 - P0204, P1064, P1065, P124B or P2146 -
P2151 set? —
Go to Applicable DTC Go to Step 5
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007