fuel type ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 1317 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-283
Description And Operation
Engine Control Module (ECM) Description
RTW 66ESH001201
The engine control module (ECM) is designed to
withstand normal current draws associated with vehicle
operation. Avoid overloading any circuit. W hen testing
for opens and shorts, do not ground or apply voltage to
any of the ECM circuits unless instructed to do so. In
some cases, these circuits should only be tested using
a digital multi meter (DMM). The ECM should remain
connected to the ECM harness.
The ECM is located on the floor panel. The ECM mainl
y
controls the following.
• The fuel system control
• The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system
control
• The preheating (glow) system control
• The A/C compressor control
• On-board diagnostics for engine control
The ECM constantly observes the information from
various sensor s. The ECM controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM performs the
diagnostic function of the system. The ECM can
recognize operational problems, alert the driver through
the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), and store
diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). DTCs identify the
system faults to aid the technician in making repairs.
ECM Voltage Description
The ECM supplies a buffered voltage to various
switches and sensor s. The ECM can do this because
resistance in the ECM is so high in value that a test
lamp may not illuminate when connected to the circuit.
An ordinary shop voltmeter may not give an accurate
reading because the voltmeter input impedance is too
low. Use a 10-megaohm input impedance DMM, to
ensure accurate voltage readings. The input and/o
r
output devices in the ECM include analog-to-digital
converters, signal buffers, counters, and special drivers.
The ECM controls most components with electronic
switches which complete a ground circuit when turned
ON.
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum Equipment
Aftermarket or add-on electrical and vacuum equipment
is defined as any equipment which connects to the
vehicle's electrical or vacuum systems that is installed
on a vehicle after the vehicle leaves the factory. No
allowances have been made in the vehicle design fo
r
this type of equipment. No add-on vacuum equipment
should be added to this vehicle. Add-on electrical
equipment must only be connected to the vehicle's
electrical system at the battery power and ground. Add-
on electrical equipment, even when installed to these
guidelines, may still cause the powertrain system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such as
portable telephones and audios. Therefore, the first
step in diagnosing any powertrain fault is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. Afte
r
this is done, if the fault still exists, the fault may be
diagnosed in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the ECM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused b
y
electrostatic discharge. By comparison, as much as
4,000 volts may be needed for a person to feel even the
zap of a static discharge. There are several ways for a
person to become statically charged. The most
common methods of charging are by friction and
induction. •
An example of charging by friction is a person
sliding across a vehicle seat.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1318 of 6020
6E-284 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Important:
To prevent possible electrostatic discharge damage,
follow these guidelines: • Do not touch the ECM connector pins or soldered
components on the ECM circuit board.
• Do not open the replacement part package until
the part is ready to be installed.
• Before removing the part from the package,
ground the package to a known good ground on
the vehicle.
• If the part has been handled while sliding across
the seat, while sitting down from a standing
position, or while walking a distance, touch a
known good ground before installing the part.
• Charge by induction occurs when a person with
well insulated shoes stands near a highly charged
object and momentarily touches ground. Charges
of the same polarity are drained off leaving the
person highly charged with opposite polarity.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Operation
The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) is located in the
instrument panel cluster (IPC). The MIL will display the
following symbols when commanded ON:
RTW 76ESH004001
The MIL indicates that an emission or performance
related fault has occurred and vehicle service is
required. The following is a list of the modes o
f
operation for the MIL: • The MIL illuminates for approximately 2 seconds
when the ignition switch is turned ON, with the
engine OFF. This is a bulb test to ensure the MIL
is able to illuminate.
•
The MIL remains illuminated after the engine is
started if the ECM detects a fault. A DTC is stored
any time the ECM illuminates the MIL due to an
emission or performance related fault.
Engine Control Component Description
Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor & Idle
Switch
RTW 66ESH001301
The accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor is mounted
on the throttle assembly. The engine control module
(ECM) uses the APP sensor s to determine the amount
of acceleration or deceleration desired by the person
driving the vehicle via the fuel injection control.
The idle switch is also mounted on the intake throttle
assembly. The idle switch is part of the APP senso
r
assembly. The idle switch is a normally closed type
switch. W hen the accelerator pedal is released, the idle
switch signal to the ECM is low voltage.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1322 of 6020
6E-288 Engine Control System (4JH1)
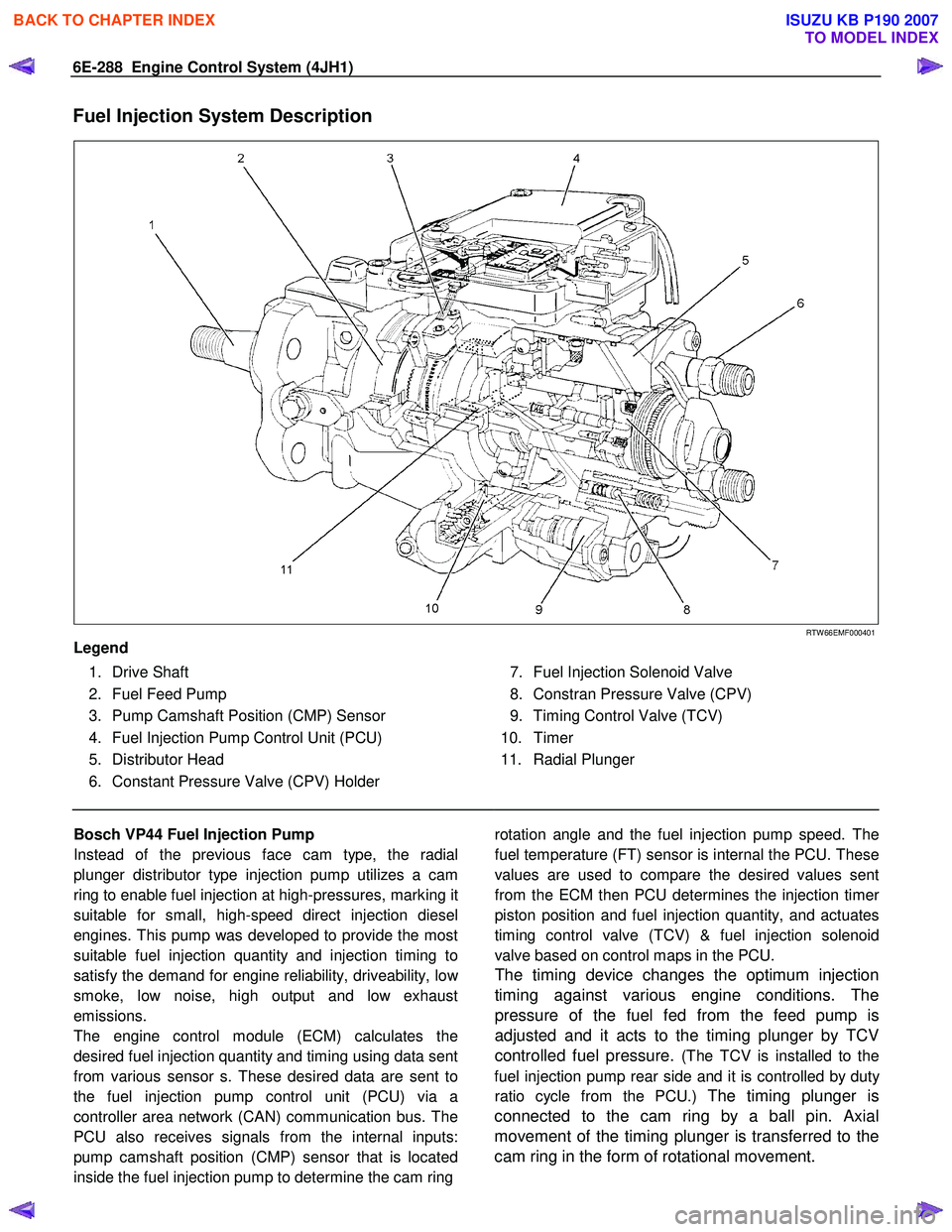
Fuel Injection System Description
RTW 66EMF000401
Legend
1. Drive Shaft
2. Fuel Feed Pump
3. Pump Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
4. Fuel Injection Pump Control Unit (PCU)
5. Distributor Head
6. Constant Pressure Valve (CPV) Holder
7. Fuel Injection Solenoid Valve
8. Constran Pressure Valve (CPV)
9. Timing Control Valve (TCV)
10. Timer
11. Radial Plunger
Bosch VP44 Fuel Injection Pump
Instead of the previous face cam type, the radial
plunger distributor type injection pump utilizes a cam
ring to enable fuel injection at high-pressures, marking it
suitable for small, high-speed direct injection diesel
engines. This pump was developed to provide the most
suitable fuel injection quantity and injection timing to
satisfy the demand for engine reliability, driveability, lo
w
smoke, low noise, high output and low exhaust
emissions.
The engine control module (ECM) calculates the
desired fuel injection quantity and timing using data sent
from various sensor s. These desired data are sent to
the fuel injection pump control unit (PCU) via a
controller area network (CAN) communication bus. The
PCU also receives signals from the internal inputs:
pump camshaft position (CMP) sensor that is located
inside the fuel injection pump to determine the cam ring rotation angle and the fuel injection pump speed. The
fuel temperature (FT) sensor is internal the PCU. These
values are used to compare the desired values sent
from the ECM then PCU determines the injection time
r
piston position and fuel injection quantity, and actuates
timing control valve (TCV) & fuel injection solenoid
valve based on control maps in the PCU.
The timing device changes the optimum injection
timing against various engine conditions. The
pressure of the fuel fed from the feed pump is
adjusted and it acts to the timing plunger by TCV
controlled fuel pressure.
(The TCV is installed to the
fuel injection pump rear side and it is controlled by dut
y
ratio cycle from the PCU.) The timing plunger is
connected to the cam ring by a ball pin. Axial
movement of the timing plunger is transferred to the
cam ring in the form of rotational movement.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1364 of 6020
6A-4 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4JK1/4JJ1)
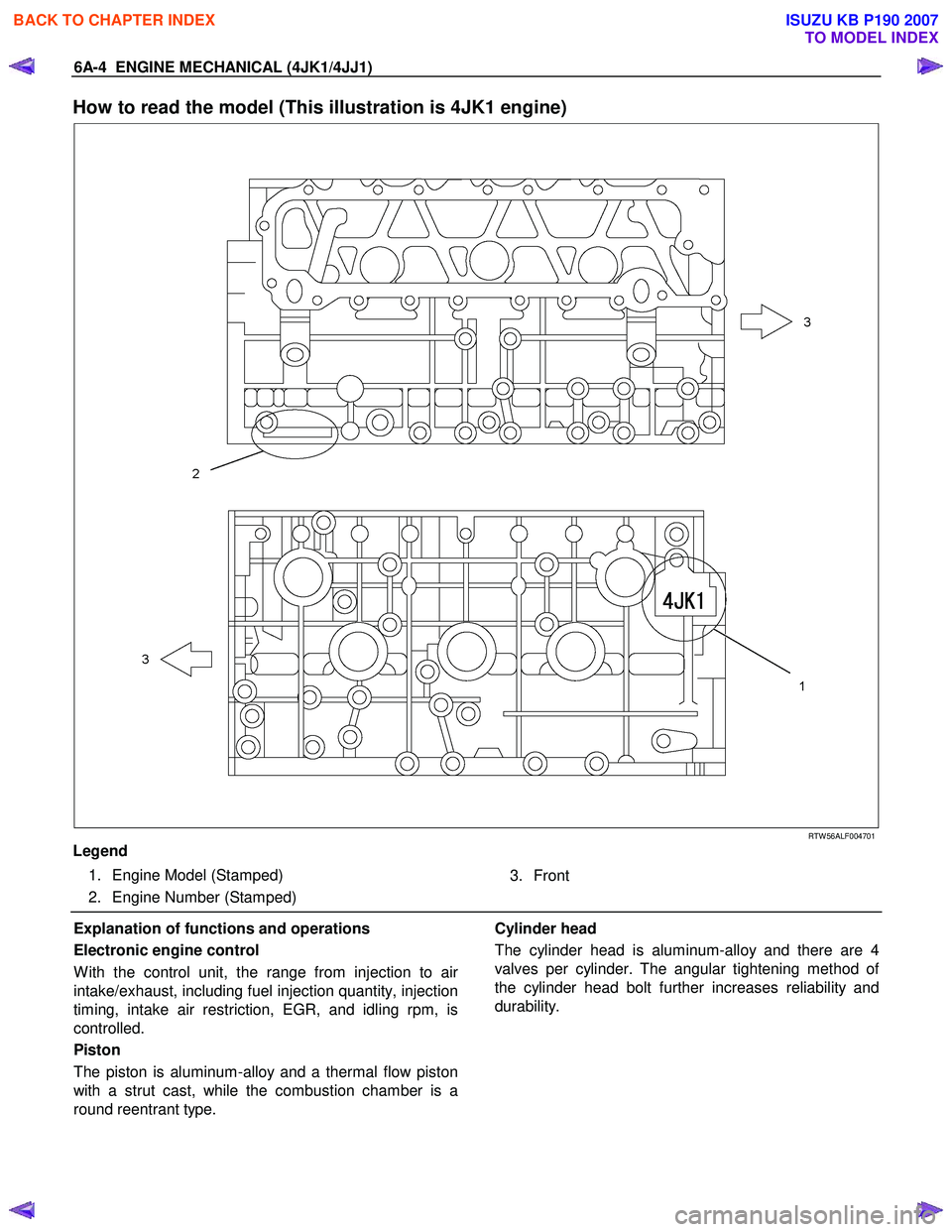
How to read the model (This illustration is 4JK1 engine)
RTW 56ALF004701
Legend
1. Engine Model (Stamped)
2. Engine Number (Stamped)
3. Front
Explanation of functions and operations
Electronic engine control
W ith the control unit, the range from injection to ai
r
intake/exhaust, including fuel injection quantity, injection
timing, intake air restriction, EGR, and idling rpm, is
controlled.
Piston
The piston is aluminum-alloy and a thermal flow piston
with a strut cast, while the combustion chamber is a
round reentrant type.
Cylinder head
The cylinder head is aluminum-alloy and there are 4
valves per cylinder. The angular tightening method o
f
the cylinder head bolt further increases reliability and
durability.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1365 of 6020

ENGINE MECHANICAL (4JK1/4JJ1) 6A-5
EGR system
Based upon data, including water temperature, engine
speeds or engine loads, it is controlled via Engine
Control Module (ECM) to purify exhaust by recycling
part of it.
Its main components include an EGR valve, an EGR
cooler and various sensors.
Connecting rod cap bolt
The angular tightening method of the connecting rod
cap bolt further increases reliability and durability.
Fuel rail-type electronic control injection system
The fuel rail-type electronic control injection system is
composed of a fuel supply pump that sets the target
pressure of high-pressure fuel and supply it, a fuel rail
that measures such high-pressure fuel and a fuel
injector that turns it into a fine spray and injects it. Each
is controlled via ECM based upon various signals, while
injection timing or fuel injection quantity is controlled
under every possible driving condition.
Fuel injector
The fuel injector is a 6-hole nozzle that adjusts fuel
injection quantity or injection timing by opening o
r
closing an electromagnetic valve on the head of the fuel
injector.
ECM corrects the dispersion of fuel injection quantit
y
between fuel injector according to ID code data in
memory. At the replacement of fuel injector, ID code
data should be stored in ECM.
Fuel filter with sedimenter
It is a fuel filter with sedimenter that gets rid of water by
making use of the difference in specific gravity between
light oil and water, which comes with an indicator that
notifies you that it is filled with water.
Preheating system
The preheating system consists of the ECM, the glow
relay, glow plugs and the glow indicator lamp. The
preheating system is operated when the engine coolant
temperature is low, and makes the engine easy to start.
Lubrication system
It is an oil filter with full-flow bypass, which uses a
water-cool oil cooler and oil jet to cool the piston.
Functional inspection
Inspection/adjustment of valve clearance 1. Inspection of valve clearance
• Remove the fuel injector harness assembly.
• Remove the leak off hose.
• Remove the cylinder head cover.
• Rotate the crankshaft to make the No.1
cylinder meet the compression top dead cente
r
(TDC).
RTW 76ASH001301
Legend
1. TDC
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1373 of 6020

ENGINE MECHANICAL (4JK1/4JJ1) 6A-13
Main Data and specifications
Item Engine model 4JK1 Engine model 4JJ1
Type Diesel/4-cycle/water cooling-type in-line DOHC
Combustion chamber type Direct injection type
Cylinder liner type Liner less
Number of cylinders -cylinder
bore × strokes mm (in) 4-95.4 (3.76) × 87.4 (3.44) 4-95.4(3.76) × 104.9(4.13)
Displacement
cc (cu.in) 2499 (152) 2999 (183)
Compression ratio 18.3 17.5
Compression pressure MPa (psi)/rpm 3 (435)/200
Idling speed rpm 700 ± 25
Valve clearance Intake 0.15 (0.006) (cold)
mm (in) Exhaust 0.15 (0.006) (cold)
Ignition type Compressed ignition
Injection order 1 - 3 - 4 - 2
Lubricating system
Lubricating type Pressure delivery type
Oil pump type Gear type
Volume of lubricating oil L (qts) 8.0 (8.5)
Oil filter type Full flow filter (cartridge type)
Oil cooling type Built-in-type, water cooling
Cooling system
Cooling type W ater cooling type
Radiator type Corrugated fin (pressure type)
W ater pump type Centrifugal, belt drive type
Thermostat type W ax-type units
Thermostat valve-opening temperature °C ( °F) 85 (185)
Volume of coolant L (qts) M/T8.7 (9.2) A/T 8.6 (9.1) (incl. radiator)
Fuel system
Injection pump type Fuel supply pump fuel rail type
Fuel injector type Electronic control injector
6-hole
Fuel pump type Into the fuel tank type
Charging system
Generator type AC type
Power output V-A 12 - 90
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1588 of 6020
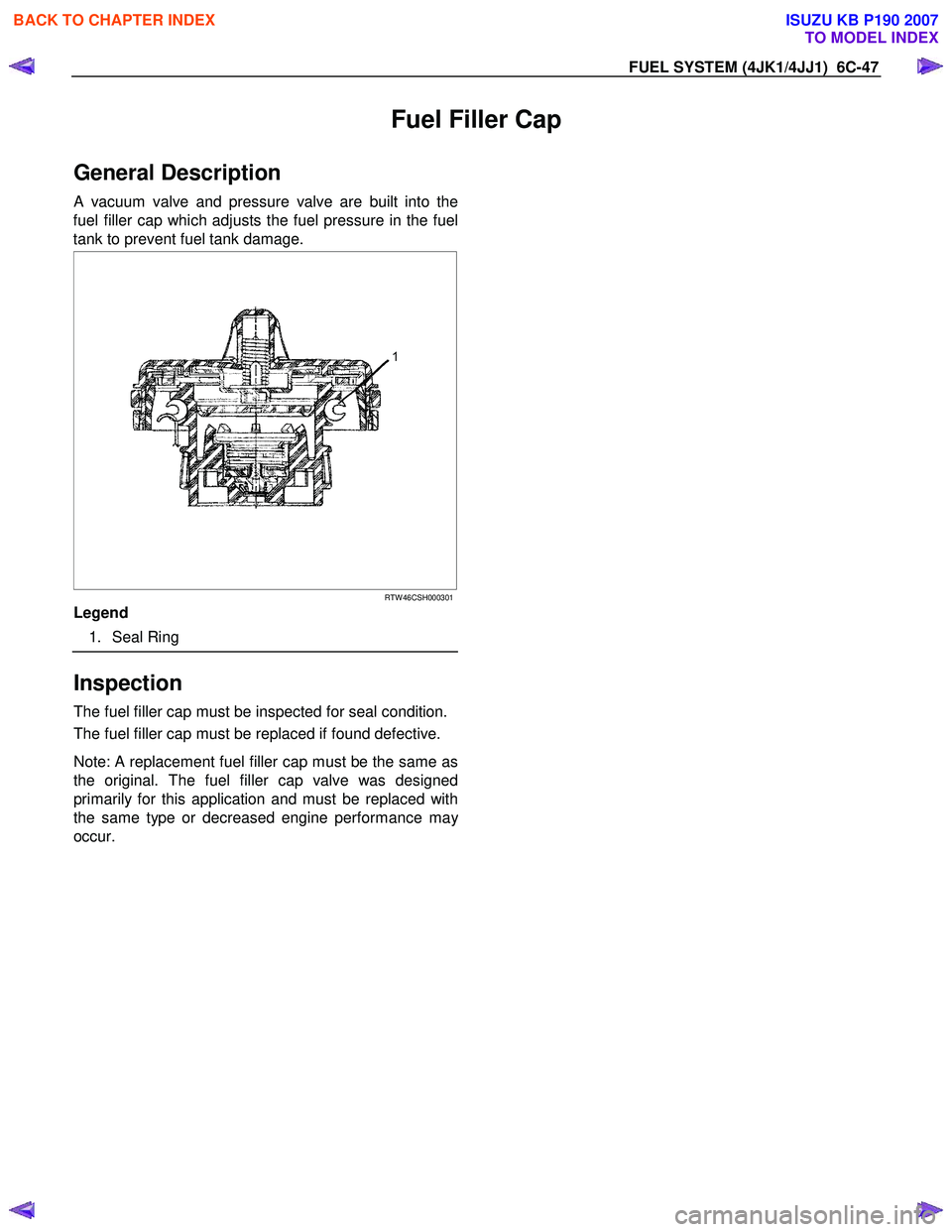
FUEL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6C-47
Fuel Filler Cap
General Description
A vacuum valve and pressure valve are built into the
fuel filler cap which adjusts the fuel pressure in the fuel
tank to prevent fuel tank damage.
RTW 46CSH000301
Legend
1. Seal Ring
Inspection
The fuel filler cap must be inspected for seal condition.
The fuel filler cap must be replaced if found defective.
Note: A replacement fuel filler cap must be the same as
the original. The fuel filler cap valve was designed
primarily for this application and must be replaced with
the same type or decreased engine performance ma
y
occur.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1618 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-1
SECTION 6E
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM(4JK1/4JJ1)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-3 Temperature vs Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-3
Altitude vs Barometric Pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-3
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Type Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-4
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List . . . . . . . . . 6E-4
Schematic and Rounting Diagrams. . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-9 Fuel System Routing Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-9
Vacuum Hose Routing Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-9
Engine Controls Schematics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-10
Component Locator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-27 Engine Controls Component Views . . . . . . . . . 6E-27
Engine Control Module (ECM) Connector End Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-30
Engine Control Connector End Views . . . . . . . 6E-33
Diagnostic Information and Procedures . . . . . . . 6E-42 Engine Control System Check Sheet . . . . . . . . 6E-42
Diagnostic Starting Point - Engine Controls . . . 6E-43
Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls . . 6E-44
Scan Tool Data List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-46
Scan Tool Data Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-49
Scan Tool Output Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-54
Scan Tool Does Not Power Up. . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-55
Scan Tool Does Not Communicate with CAN Device. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-56
Lost Communication with The Engine Control Module (ECM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-59
Engine Cranks but Does Not Run . . . . . . . . . . 6E-62
DTC P0016 (Flash Code 16) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-68
DTC P0045 (Flash Code 33) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-70
DTC P0087 (Flash Code 225) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-72
DTC P0088 (Flash Code 118) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-77
DTC P0089 (Flash Code 151) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-82
DTC P0091 or P0092 (Flash Code 247) . . . . . 6E-85
DTC P0093 (Flash Code 227) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-88
DTC P0101 (Flash Code 92) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-93
DTC P0102 or P0103 (Flash Code 91) . . . . . . 6E-96
DTC P0107 or P0108 (Flash Code 32) . . . . . 6E-100
DTC P0112 or P0113 (Flash Code 22) . . . . . 6E-104
DTC P0116 (Flash Code 23) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-108
DTC P0117 or P0118 (Flash Code 23) . . . . . 6E-110
DTC P0122 or P0123 (Flash Code 43) . . . . . 6E-114
DTC P0182 or P0183 (Flash Code 211) . . . . 6E-118
DTC P0192 or P0193 (Flash Code 245) . . . . 6E-122
DTC P0201, P0202, P0203 or P0204 (Flash Code 271, 272, 273 or 274) . . . . . . . . 6E-126
DTC P0217 (Flash Code 542) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-133
DTC P0219 (Flash Code 543) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-135
DTC P0231 or P0232 (Flash Code 69) . . . . . 6E-137
DTC P0234 (Flash Code 42) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-140 DTC P0299 (Flash Code 65) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-143
DTC P0335 (Flash Code 15) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-146
DTC P0336 (Flash Code 15) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-149
DTC P0340 (Flash Code 14) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-151
DTC P0341 (Flash Code 14) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-154
DTC P0380 (Flash Code 66) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-156
DTC P0401 (Flash Code 93) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-159
DTC P0403 (Flash Code 37) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-161
DTC P0404 (Flash Code 45) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-164
DTC P0405 or P0406 (Flash Code 44) . . . . . 6E-166
DTC P0500 (Flash Code 25) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-170
DTC P0501 (Flash Code 25) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-174
DTC P0512 (Flash Code 417) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-176
DTC P0562 or P0563 (Flash Code 35) . . . . . 6E-178
DTC P0565 (Flash Code 515) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-181
DTC P0566 (Flash Code 516) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-183
DTC P0567 (Flash Code 517) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-185
DTC P0568 (Flash Code 518) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-187
DTC P0571 (Flash Code 26) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-189
DTC P0601 (Flash Code 53) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-192
DTC P0602 (Flash Code 154) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-193
DTC P0604 or P0606 (Flash Code 153 or 51) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-195
DTC P0615 (Flash Code 19) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-196
DTC P0633 (Flash Code 176) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-198
DTC P0638 (Flash Code 61) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-199
DTC P0642 or P0643 (Flash Code 55) . . . . . 6E-201
DTC P0650 (Flash Code 77) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-204
DTC P0652 or P0653 (Flash Code 56) . . . . . 6E-207
DTC P0661 or P0662 (Flash Code 58) . . . . . 6E-211
DTC P0698 or P0699 (Flash Code 57) . . . . . 6E-215
DTC P0700 (Flash Code 185) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-219
DTC P1064 or P1065 (Flash Code 247) . . . . 6E-220
DTC P1093 (Flash Code 227) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-224
DTC P1094 (Flash Code 226) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-229
DTC P1196, P1197 or P1198 (Flash Code 461) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-235
DTC P124B (Flash Code 157) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-237
DTC P1261 (Flash Code 34) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-240
DTC P1262 (Flash Code 34) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-242
DTC P1404 (Flash Code 45) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-244
DTC P1411, P1412 or P1413 (Flash Code 445) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-246
DTC P156A or P156B (Flash Code 135) . . . . 6E-248
DTC P161B (Flash Code 179) . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-251
DTC P1621 (Flash Code 54, 254) . . . . . . . . . 6E-253
DTC P1664 (Flash Code 76) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-255
DTC P2100, P2101 or P2103 (Flash Code 446) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6E-258
DTC P2122 or P2123 (Flash Code 121) . . . . 6E-261
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1621 of 6020
6E-4 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Type
Definitions
Emission Related DTC
Action Taken When the DTC Sets - Type A • The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The ECM stores this
information in the Freeze Frame/ Failure Records.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets - Type B • The ECM illuminates the MIL on the second consecutive driving cycle when the diagnostic runs
and fails.
• The ECM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the
diagnostic fails, the ECM stores this information in
the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a
failure on the second consecutive driving cycle, the
ECM records the operating conditions at the time
of failure and stores this information in the Freeze
Frame and updates the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/ DTC - Type A or
Ty p e B
• The ECM turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive driving cycles when the diagnostic runs and does
not fail. (Euro 4 Specification)
• The ECM turns OFF the MIL after 1 driving cycle when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. (Except
Euro 4 Specification)
• A current DTC clears when the diagnostic runs and passes after 1 driving cycle.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported. • Use a scan tool to clear the MIL and the DTC.
Non-Emissions Related DTCs
Action Taken When the DTC Sets - Type C
• The ECM illuminates the Service Vehicle Soon (SVS) lamp when the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The ECM stores this
information in the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the SVS Lamp/ DTC - Type
C
• The ECM turns OFF the SVS lamp after 1 driving cycle when the diagnostic runs and does not fail.
• A current DTC clears when the diagnostic runs and passes after 1 driving cycle.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported.
• Use a scan tool to clear the SVS lamp and the DTC.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets - Type D • The ECM will not illuminate the MIL or SVS lamp.
• The ECM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The ECM stores this
information in the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC - Type D • A current DTC clears when the diagnostic runs and passes after 1 driving cycle.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported.
• Use a scan tool to clear the DTC.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List
DTC Flash
Code DTC Type
DTC Descriptor
Euro 4
Specification Except Euro 4
Specification
(High Output) Except Euro 4
Specification
(Standard Output)
P0016 16 C AA Crankshaft Position - Camshaft Position Correlation
P0045 33 A A- Turbocharger Boost Control Solenoid Circuit
P0087 225 A AA Fuel Rail/ System Pressure Too-Low
P0088 118 A AA Fuel Rail/ System Pressure Too-High (First Stage)
P0088 118 C AA Fuel Rail/ System Pressure Too-High (Second Stage)
P0089 151 A AA Fuel Pressure Regulator Performance
P0091 247 A AA Fuel Pressure Regulator Control Circuit Low
P0092 247 A AA Fuel Pressure Regulator Control Circuit High
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1622 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-5
P0093 227 AAA Fuel System Leak Detected
P0101 92 A -- Mass Air Flow Sensor Circuit Range/ Performance
P0102 91 A AA Mass Air Flow Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0103 91 A AA Mass Air Flow Sensor Circuit High Input
P0107 32 A A- Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0108 32 A A- Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Circuit High Input
P0112 22 A AA Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Low
P0113 22 A AA Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High
P0116 23 A --Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Range/
Performance
P0117 23 A AA Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Low
P0118 23 A AA Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit High
P0122 43 B AA Throttle Position Sensor Circuit Low
P0123 43 B AA Throttle Position Sensor Circuit High
P0182 211 A AA Fuel Temperature Sensor Circuit Low
P0183 211 A AA Fuel Temperature Sensor Circuit High
P0192 245 A AA Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit Low
P0193 245 A AA Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit High
P0201 271 A AA Injector Circuit Open - Cylinder 1
P0202 272 A AA Injector Circuit Open - Cylinder 2
P0203 273 A AA Injector Circuit Open - Cylinder 3
P0204 274 A AA Injector Circuit Open - Cylinder 4
P0217 542 D DD Engine Coolant Over Temperature Condition
P0219 543 C AA Engine Overspeed Condition
P0231 69 C AA Fuel Pump Secondary Circuit Low
P0232 69 C AA Fuel Pump Secondary Circuit High
P0234 42 A A- Turbocharger Overboost Condition
P0299 65 A A- Turbocharger Underboost
P0335 15 A AA Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0336 15 A AA Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Range/ Performance
P0340 14 C AA Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0341 14 C AA Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Range/ Performance
P0380 66 C AA Glow Plug Circuit
P0401 93 A -- EGR Flow Insufficient Detected
P0403 37 B AA EGR Control Circuit
P0404 45 A AA EGR Control Circuit Range/ Performance
P0405 44 B AA EGR Sensor Circuit Low
P0406 44 B AA EGR Sensor Circuit High
P0500 25 A AA Vehicle Speed Sensor
DTC
Flash
Code DTC Type
DTC Descriptor
Euro 4
Specification Except Euro 4
Specification
(High Output) Except Euro 4
Specification (Standard Output)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007