display ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 5595 of 6020

Cruise Control – HFV6 Page 8C–17
Step Action Yes No
17
NOTE
This procedure is only required on vehicles fitted with
manual transmissions. If the vehicle is fitted with an
automatic transmission go to Step 26.
Test the clutch pedal switch, refer to
3.4 Clutch Pedal Switch.
Is the clutch pedal switch serviceable? Go to Step 28 Go to Step 21
18 Replace the faulty cruise control switch assembly with a serviceable
item. To replace the switch assembly, refer to 8 B Cruise Control
System. Go to Step 32 —
19 Replace the faulty stop lamp switch, refer to 3.3 Stop Lamp
Switch Assembly Go to Step 32 —
20 Replace the faulty stop lamp switch, refer to 3.3 Stop Lamp
Switch Assembly Go to Step 32 —
21
Replace the faulty clutch pedal switch, refer to
3.4 Clutch Pedal Switch Go to Step 32 —
22 1 Disconnect the PIM connector B – 97.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, back probe between the harness connector B – 97 pin 14 and a known ground.
3 W ith the aid of an assistant, monitor the voltage on the multimeter and press and release the cruise control switch ON–
OFF button.
• W ith the button in the rest position, the multimeter should
display 0 V.
• W ith the button pressed, the multimeter should display
battery voltage.
Does the multimeter display as described? Go to Step 30 Check for short to
ground or open circuit.
Repair as required
(refer to Note 1).
Go to Step 32
23 1 Disconnect the PIM connector B – 97.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, back probe between the harness connector B – 97 pin 16 and a known ground.
3 With the aid of an assistant, monitor the voltage on the multimeter and rotate and release the cruise control switch to
RES–ACC position.
• With the switch in the rest position, the multimeter should
display 0 V.
• With the switch rotated, the multimeter should display
battery voltage.
Does the multimeter display as described? Go to Step 30 Check for short to
ground or open
circuit on circuit.
Repair as required
(refer to Note 1).
Go to Step 32
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5596 of 6020
Cruise Control – HFV6 Page 8C–18
Step Action Yes No
24 1 Disconnect the PIM connector B – 97.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, back probe between the harness connector B – 97 pin 15 and a known ground.
3 With the aid of an assistant, monitor the voltage on the multimeter and press and release the cruise control switch to
SET–COAST button.
• With the switch in the rest position, the multimeter should
display 0 V.
• With the switch pressed, the multimeter should display
battery voltage.
Does the multimeter display as described? Go to Step 30 Check for short to
ground or open
circuit on circuit.
Repair as required (refer to Note 1).
Go to Step 32
25 1 Disconnect the PIM connector B – 97.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, back probe between the harness connector B – 97 pin 17 and a known ground.
3 W ith the aid of an assistant, monitor the voltage on the multimeter and rotate and release the cruise control switch to
CANCEL position.
• With the switch in the rest position, the multimeter should
display 0 V.
• W ith the switch rotated clockwise, the multimeter should
display battery voltage.
Does the multimeter display as described? Go to Step 30 Check for short to
ground or open
circuit on circuit.
Repair as required (refer to Note 1).
Go to Step 32
26 1 Disconnect the ECM connector C – 56.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, back probe between the harness connector C – 56 pin 10 and ground.
3 With the aid of an assistant, monitor the voltage on the multimeter and press and release the brake pedal.
• W ith the brake pedal in the rest position, the multimeter
should display 0 V
• W ith the brake pedal pressed, the multimeter should
display battery voltage
Does the multimeter display as described? Go to Step 30 Check for a blown
fuse C-18.
Check for short to
ground or open circuit
Repair as required (refer to Note 1).
Go to Step 32
27 1 Disconnect the ECM connector C – 56.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, back probe between the harness connector C – 56 pin 46 and ground.
3 With the aid of an assistant, monitor the voltage on the multimeter and press and release the brake pedal.
• W ith the brake pedal in the rest position, the multimeter
should display battery voltage
• W ith the brake pedal pressed, the multimeter should
display 0 V.
Does the multimeter display as described? Go to Step 28 Check for a blown
fuse C-10.
Check for short to ground or open
circuit
Repair as required (refer to Note 1).
Go to Step 32
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5597 of 6020

Cruise Control – HFV6 Page 8C–19
Step Action Yes No
28 1 Disconnect the ECM connector C – 56.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, back probe between the harness connector C – 56 pin 53 and ground.
3 W ith the aid of an assistant, monitor the voltage on the multimeter and press and release the clutch pedal.
• With the clutch pedal in the rest position, the multimeter
should display battery voltage
• W ith the clutch pedal pressed, the multimeter should
display 0 V
Does the multimeter display as described? Go to Step 31 Check for a blown
fuse C-4.
Check for short to ground or open circuit
Repair as required (refer to Note 2).
Go to Step 32
29 Check all associated circuits and connectors for the following:
• Loose or damaged connections
• Intermittent faults.
Refer to the Wiring Diagrams in this Section and repair as required.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 32 —
30 Replace the PIM, refer to 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module – V6.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 32 —
31 Replace the ECM module, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 32 —
32 Operate the system in order to verify the repair.
Did you correct the condition? System OK Go to Step 1
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5649 of 6020

9A-14 SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM
Component Description
SRS Control Unit
WARNING: DURING SERVICE PROCEDURES, BE
VERY CAREFUL WHEN HANDLING A SRS
CONTROL UNIT. NEVER STRIKE OR JAR THE SRS
CONTORL UNIT. NEVER POWER UP THE SRS
WHEN THE SRS CONTROL UNIT IS NOT RIGIDLY
ATTACHED TO THE VEHICLE. ALL SRS CONTROL
UNIT AND MOUNTING BRACKET FASTENERS
MUST BE CAREFULLY TORQUED AND THE
ARROW MUST BE POINTED TOWARD THE FRONT
OF THE VEHICLE TO ENSURE PROPER
OPERATION OF THE SRS. THE SRS CONTROL
UNIT COULD BE ACTIVATED WHEN POWERED
WHILE NOT RIGIDLY ATTACHED TO THE
VEHICLE WHICH COULD CAUSE DEPLOYMENT
AND RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
The SRS control unit is designed to perform the
following functions in the SRS:
1. Energy Reserve — The SRS control unit maintains 30–Volt Loop Reserve (30VLR) energy supply to
provide deployment energy when ignition voltage is
lost in a frontal crash.
2. Frontal Crash Detection — The SRS control unit monitors vehicle velocity changes to detect frontal
crashes which are severe enough to warrant
deployment.
3. Air Bag Deployment — W hen a frontal crash o
f
sufficient force is detected, the SRS control unit
will cause enough current to flow through the ai
r
bag assembly to deploy the air bag.
4. Malfunction Detection — The SRS control unit performs diagnostic monitoring of SRS electrical
components and sets a diagnostic trouble code
when a malfunction is detected.
5. Frontal Crash Recording — The SRS control unit records information regarding SRS status during
frontal crash.
6. Malfunction Diagnosis — The SRS control unit displays SRS diagnostic trouble codes and system
status information through the use of a scan tool.
7. Driver Notification — The SRS control unit warns the vehicle driver of SRS malfunctions b
y
controlling the “SRS” warning lamp.
The SRS control unit is connected to the SRS wiring
harness by a 52–pin connector. This harness
connector uses a shorting clip across certain terminals
in the contact area. This shorting clip connects the
“SRS” warning lamp to ground when the SRS control
unit harness connector is disconnected or CP
A
(Connector Position Assurance) is not inserted even i
f
completely connected. This will cause the “SRS”
warning lamp to come “ON” steady whenever the
ignition switch is at the ON or START positions with
the SRS control unit disconnected.
RTW 79ASH000401
Legend
(1) SRS Control Unit
(2) SRS Harness
“SRS” Warning Lamp
Ignition voltage is applied to the “SRS” warning lamp
when the ignition switch is at the ON or START
positions. The SRS control unit controls the lamp b
y
providing ground with a lamp driver. The “SRS”
warning lamp is used in the SRS to do the following:
1. Verify lamp and SRS control unit operation b
y
flashing SEVEN (7) times when the ignition switch
is first turned “ON”.
2. W arn the vehicle driver of SRS electrical system malfunctions which could potentially affect the
operation of the SRS. These malfunctions could
result in nondeployment in case of a frontal crash
or deployment for conditions less severe than
intended.
The “SRS “ warning lamp is the key to drive
r
notification of SRS malfunctions. For proper lamp
operation, refer to the “SRS Diagnostic System Check”
in this section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5686 of 6020

9A1-4 RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
Basic Knowledge Required
Before using this section of the Service Manual, some
basic knowledge is required. W ithout this knowledge,
you will have trouble using the diagnostic procedures in
this section. Use care to prevent any harm or unwanted
deployment. Read all cautions in the service manual
and on warning labels attached to SRS components.
Basic Electrical Circuits
You should understand the basic theory of electricity
including series and parallel circuits, and understand
the voltage drops across series resistors. You should
know the meaning of voltage (volts), current (amps),
and resistance (ohms). You should understand what
happens in a circuit with an open or a shorted wire. You
should be able to read and understand a wiring
diagram.
“Flash Code” Diagnostics
Flash code diagnostics can be used to read active
codes and to determine if history codes are present but
cannot be used to clear codes or read history codes.
Flash code diagnostics is enabled by grounding
terminal 4, shorting to terminal 13 of the DLC, with the
ignition switched “ON”. Grounding terminal 4 of the DLC
pulls the “Diagnostics Request” input (Terminal 1) of the
SRS control unit low and signals the SRS control unit to
enter the flash code diagnostic display mode.
060R300052
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5687 of 6020
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM 9A1-5
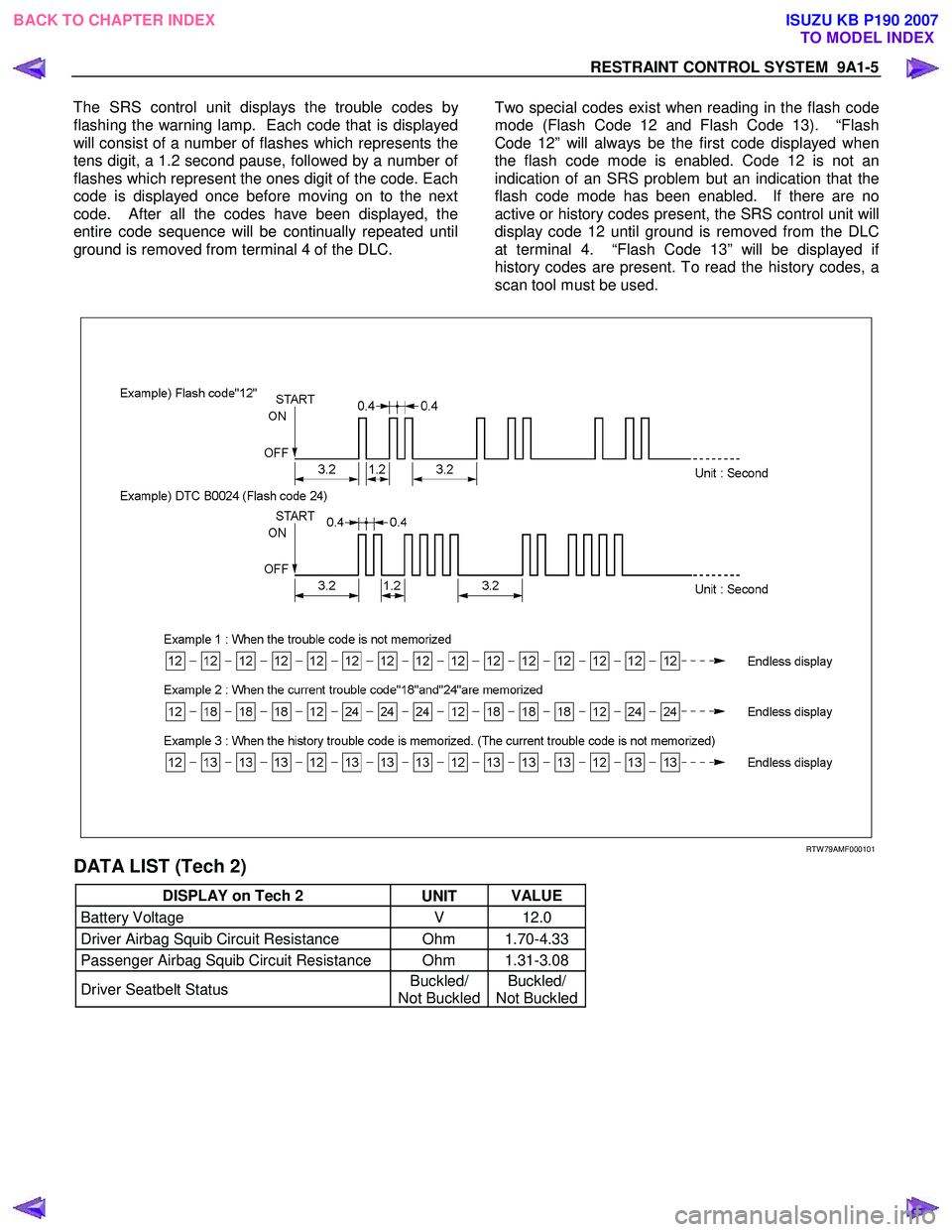
The SRS control unit displays the trouble codes b
y
flashing the warning lamp. Each code that is displayed
will consist of a number of flashes which represents the
tens digit, a 1.2 second pause, followed by a number o
f
flashes which represent the ones digit of the code. Each
code is displayed once before moving on to the next
code. After all the codes have been displayed, the
entire code sequence will be continually repeated until
ground is removed from terminal 4 of the DLC.
Two special codes exist when reading in the flash code
mode (Flash Code 12 and Flash Code 13). “Flash
Code 12” will always be the first code displayed when
the flash code mode is enabled. Code 12 is not an
indication of an SRS problem but an indication that the
flash code mode has been enabled. If there are no
active or history codes present, the SRS control unit will
display code 12 until ground is removed from the DLC
at terminal 4. “Flash Code 13” will be displayed i
f
history codes are present. To read the history codes, a
scan tool must be used.
RTW 79AMF000101
DATA LIST (Tech 2)
DISPLAY on Tech 2 UNIT VALUE
Battery Voltage
V 12.0
Driver Airbag Squib Circuit Resistance Ohm 1.70-4.33
Passenger Airbag Squib Circuit Resistance Ohm 1.31-3.08
Driver Seatbelt Status Buckled/
Not Buckled Buckled/
Not Buckled
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5688 of 6020

9A1-6 RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Choose and trace an appropriate flowchart by the numbers listed below to find fault and repair.
DTC Flash Code Description
– 12 Diagnostic Display Mode (Flash Code only)
– 13 Diagnostic Display Mode (Flash Code only)
B0015 15 Passenger Air Bag Squib Circuit High Resistance
B0016 16 Passenger Air Bag Squib Circuit Low Resistance
B0018 18 Passenger Air Bag Squib Circuit Short to GND
B0019 19 Passenger Air Bag Squib Circuit Short to Battery Voltage
B0021 21 Driver Air Bag Squib Circuit High Resistance
B0022 22 Driver Air Bag Squib Circuit Low Resistance
B0025 25 Driver Air Bag Squib Circuit Short to GND
B0026 26 Driver Air Bag Squib Circuit Short to Battery Voltage
B0029 29 Passenger Pretensioner Squib Circuit High Resistance
B0031 31 Passenger Pretensioner Squib Circuit Low Resistance
B0033 33 Passenger Pretensioner Squib Circuit Short to GND
B0034 34 Passenger Pretensioner Squib Circuit Short to Battery Voltage
B0041 41 Driver Pretensioner Squib Circuit High Resistance
B0042 42 Driver Pretensioner Squib Circuit Low Resistance
B0045 45 Driver Pretensioner Squib Circuit Short to GND
B0046 46 Driver Pretensioner Squib Circuit Short to Battery Voltage
B0051 51 Air Bag Squib Circuit Activated (Clash)
B0052 52 Pretensioner Squib Circuit Activated
B0055 55 Vehicle Variant Missing
B0061 61 Warning Lamp Circuit Failure
B0062 62 Battery Voltage Too High
B0063 63 Battery Voltage Too Low
B0071 71 SRS Control Unit Internal Fault
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5690 of 6020

9A1-8 RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
Circuit Description
W hen the ignition switch is first turned “ON”, “Ignition 1”
voltage is applied from the “SRS” fuse to the SRS
control unit at the “Ignition 1” input terminals “1”. The
SRS control unit responds by flashing the “SRS”
warning lamp seven times, while performing tests on
the SRS.
Notes On System Check Chart
1. The “SRS” warning lamp should flash seven times after the ignition is first turned “ON”.
2.
After the “SRS” warning lamp flashes seven times, it
should turn to “LOCK”
3. This test checks for the proper operation of the “Serial Data” line. This test will also determine
whether history diagnostic trouble codes are stored
and, if so, identify them.
4. Improper operation of the “SRS” warning lamp is indicated. This test differentiates between ‘a
warning lamp stays “ON” condition’ and ‘a warning
lamp does not come “ON” condition’.
5. This test checks for proper operation of the “Serial Data” line. This test will also identify the stored
diagnostic trouble codes and whether they are
current or history.
Diagnostic Aids
The order in which diagnostic trouble codes are
diagnosed is very important. Failure to diagnose the
diagnostic trouble codes in the order specified ma
y
result in extended diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis
and incorrect parts replacement.
SRS Diagnostic System Check
Step Action Yes No
1 Note the “SRS” warning lamp as the ignition switch is turned
“ON”.
Does the “SRS” warning lamp flash seven (7) times? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 3
2 Note the “SRS” warning lamp after it flashed 7 times.
Does the “SRS” warning lamp go “OFF”? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
3 Note the “SRS” warning lamp as the ignition switch is turned
“ON”.
Does the “SRS” warning lamp come “ON” steady? Go to Chart B. Go to Chart C.
4
1. Note the “SRS” warning lamp as the ignition switch is turned
“ON”.
Ignition switch is at “LOCK”.
2. Connect a scan tool to data link connector.
3. Follow direction given in the scan tool instruction manual.
Ignition switch is “ON”.
4. Request the SRS diagnostic trouble code display, recode all
history diagnostic trouble code(s), specifying as current or
history in repair order.
Is (are) diagnostic trouble code(s) displayed?
Ignition switch
“LOCK”.
W hen DTC B0071 is set, go to DTC B0071 Chart.
For all other history codes refer to
“Diagnostic Aids” For that specific DTC.
A history DTC indicates the
malfunction has
been repaired or is intermittent. SRS is functional
and free of
malfunctions, no
further diagnosis is required.
If scan tool
indicated “NO DATA
RECEIVED,” refer to chassis
electrical section 8.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5691 of 6020

RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM 9A1-9
Step Action Yes No
5 1. Ignition switch is at “LOCK”.
2. Connect a scan tool to data link connector.
3. Follow directions as given in the scan tool instruction manual.
4. Ignition switch is “ON”.
5. Request the SRS diagnostic trouble code display, Recode all diagnostic trouble code(s), specifying as current or history in
repair order.
Is (are) diagnostic trouble code (s) displayed? Ignition switch
“LOCK”.
W hen the current DTC is set, go to applicable DTC chart.
And then if DTC B0019, B0025,
B0051, B0055 or
B0071 is set, go to these DTC chart first.
W hen only history
DTCs exist, refer to “Diagnostics Aids” for that specific DTC.
A history DTC indicates the
malfunction has
been repaired or is intermittent. If scan tool indicates
“No Data Received,” refer to chassis
electrical section 8.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5693 of 6020

RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM 9A1-11
3. W hen all circuitry outside the SRS control unit has been found to operate properly, as indicated by the
appropriate diagnostic chart, then and only then
should the SRS control unit be replaced.
Chart A SRS control unit Integrity Check
WARNING: DURING SERVICE PROCEDURES. BE VERY CAREFUL WHEN HANDLING A SRS CONTROL UNIT.
NEVER STRIKE OR JAR THE SRS CONTROL UNIT. NEVER POWER UP THE SRS WHEN THE SRS CONTROL
UNIT IS NOT RIGIDLY ATTACHED TO THE VEHICLE. ALL SRS CONTROL UNIT AND MOUNTING BRACKET
FASTENERS MUST BE CAREFULLY TORQUED AND THE ARROW MUST BE POINTING TOWARD THE FRONT
OF THE VEHICLE TO ENSURE PROPER OPERATION OF THE SRS. THE SRS CONTROL UNIT COULD BE
ACTIVATED WHEN POWERED WHILE NOT RIGIDLY ATTACHED TO THE VEHICLE WHICH COULD CAUSE
DEPLOYMENT AND RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
Step Action Yes No
1 1. This chart assumes that the “SRS Diagnostic System Check”
and either a symptom chart or a diagnostic trouble code chart
diagnosis has been performed. W hen all circuitry outside the
SRS control unit has been found to operate properly, as
indicated by the appropriate diagnostic chart, and the
symptom or DTC remains current, check the following.
2. Diagnostic procedures must be performed to verify the need
for SRS control unit replacement.
3. Ignition switch is at “LOCK”.
4. Reconnect all SRS components and ensure all components are properly mounted.
5. Ensure the ignition switch has been in the “LOCK” position for
at least 15 seconds.
6. Note the “SRS” warning lamp as the ignition switch is turned
“ON”.
Does the warning lamp flash 7 times then go “OFF”? The symptom or
DTC is no longer occurring.
Clear SRS
diagnostic trouble codes.
Repeat “SRS
Diagnostic System Check” Go to Step 2
2 Using a scan tool, request the diagnostic trouble code display.
Is the same symptom or DTC occurring that was occurring when
the “SRS Diagnostic System Check” was first performed? Go to Step 3 Ignition switch
“LOCK”.
Go to the
appropriate chart for the indicated malfunction.
3 1. Clear the “SRS Diagnostic Trouble Codes”.
2. Ignition switch is in the “LOCK” position for at least two
minutes.
3. Note the “SRS” warning lamp as the ignition switch is turned
“ON”.
Does warning lamp flash 7 times then go “OFF”? SRS is functional
and free of
malfunctions.
No further
diagnosis is required.
Go to Step 4 Ignition switch
“LOCK”.
Replace SRS control unit.
Go to Step 4
4 Reconnect all SRS components, ensure all components are properly mounted.
Is this step finished? Repeat the “SRS
Diagnostic System Check” —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007