sensor ISUZU KB P190 2007 Workshop Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 2007, Model line: KB P190, Model: ISUZU KB P190 2007Pages: 6020, PDF Size: 70.23 MB
Page 613 of 6020
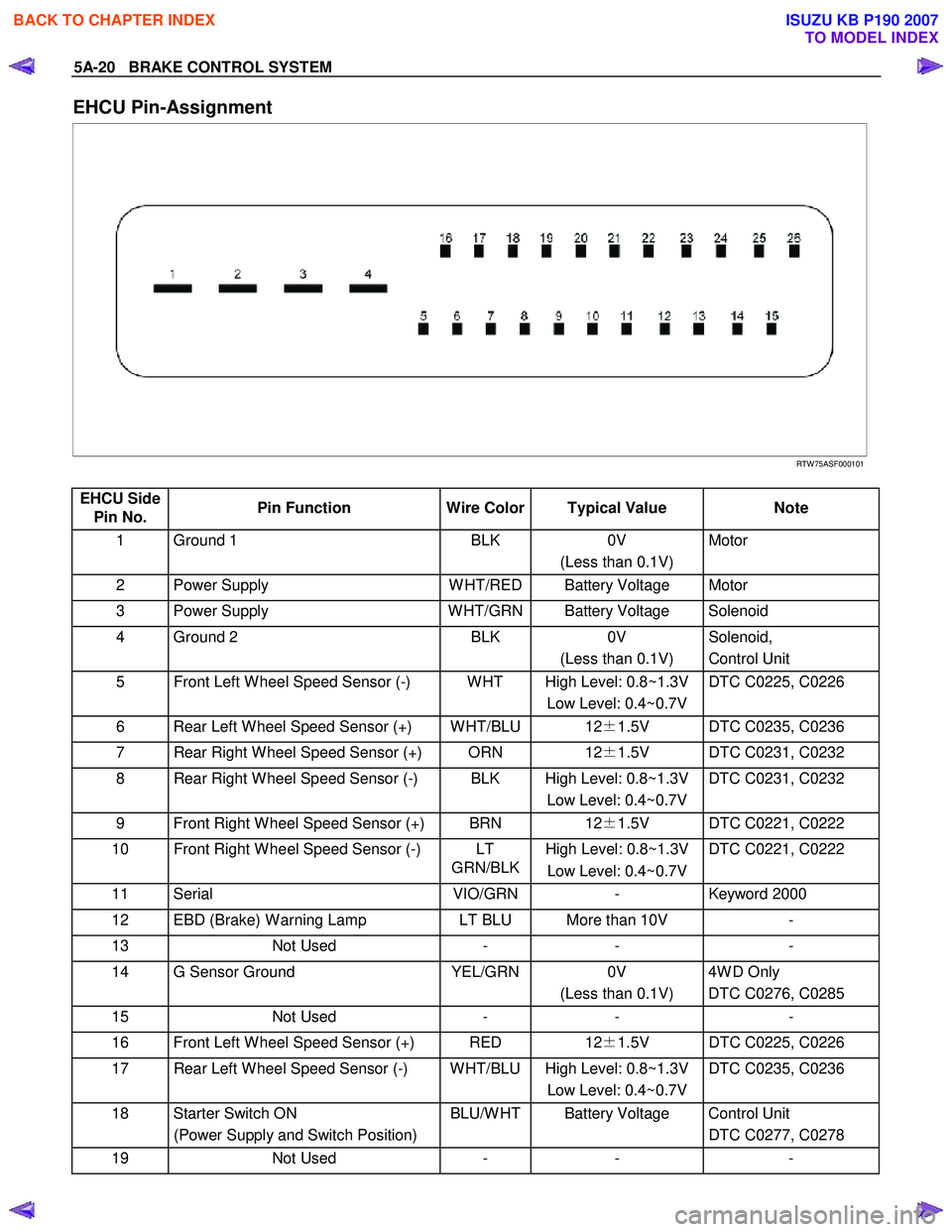
5A-20 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
EHCU Pin-Assignment
RTW 75ASF000101
EHCU Side Pin No. Pin Function
Wire Color Typical Value Note
1 Ground 1 BLK 0V
(Less than 0.1V) Motor
2 Power Supply
W HT/RED Battery Voltage Motor
3 Power Supply W HT/GRN Battery Voltage Solenoid
4 Ground 2 BLK 0V
(Less than 0.1V) Solenoid,
Control Unit
5 Front Left W heel Speed Sensor (-) W HT High Level: 0.8~1.3V Low Level: 0.4~0.7V DTC C0225, C0226
6 Rear Left W heel Speed Sensor (+) W HT/BLU 12
±1.5V DTC C0235, C0236
7 Rear Right W heel Speed Sensor (+) ORN 12±1.5V DTC C0231, C0232
8 Rear Right W heel Speed Sensor (-) BLK High Level: 0.8~1.3V
Low Level: 0.4~0.7V DTC C0231, C0232
9 Front Right W heel Speed Sensor (+) BRN
12±1.5V DTC C0221, C0222
10 Front Right W heel Speed Sensor (-) LT
GRN/BLKHigh Level: 0.8~1.3V
Low Level: 0.4~0.7V DTC C0221, C0222
11 Serial
VIO/GRN- Keyword 2000
12 EBD (Brake) W arning Lamp LT BLU More than 10V -
13 Not Used - - -
14 G Sensor Ground YEL/GRN0V
(Less than 0.1V) 4W D Only
DTC C0276, C0285
15 Not Used - - -
16 Front Left W heel Speed Sensor (+) RED 12±1.5V DTC C0225, C0226
17 Rear Left W heel Speed Sensor (-) W HT/BLU High Level: 0.8~1.3V
Low Level: 0.4~0.7V DTC C0235, C0236
18 Starter Switch ON
(Power Supply and Switch Position) BLU/W HT Battery Voltage Control Unit
DTC C0277, C0278
19 Not Used - - -
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 614 of 6020
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM 5A-21
EHCU Side
Pin No. Pin Function
Wire Color Typical Value Note
20 Stop Light Switch RED Open: 0V
Close: Battery Voltage Close Condition:
Step on the Brake
Pedal
21 G Sensor Signal YEL/BLK 2.0~3.0V
(MAX 4.0V, MIN 1.0V) 4W D Only
It checks in a flat place
(0G: 2.5V)
DTC C0276, C0285
22 ABS W arning Lamp YEL More than 10V -
23 Not Used - - -
24 Transfer (2-4W D Control Unit) GRY Pulse Signal
(High 4.5V, Low 1.5V) 4W D Only
DTC C0282
25 Serial ORN/W HT- Short to GND:
Flash out DTCs
26 Not Used - - -
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 615 of 6020

5A-22 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
System Components
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU), four W heel
Speed Sensors, two W arning Lamps, and G sensor.
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU)
The EHCU consists of ABS control circuits, fault
detector, and a fail-safe. It drives the EHCU according
to the signal from each sensor, cancelling ABS to return
to normal braking when a malfunction has occurred in
the ABS.
The EHCU has a self-diagnosing function which can
indicate faulty circuits during diagnosis.
The EHCU is mounted on the engine compartment rear
left side. It consists of a motor, solenoid valves and a
fail safe relay.
Solenoid Valves: Reduces or holds the caliper fluid
pressure for each front brake or both rear brakes
according to the signal sent from the EHCU.
Buffer chamber: Temporarily holds the brake fluid that
returns from the front and rear brake so that pressure of
front brake can be reduced smoothly.
Motor: Drives the pump according to the signal from
EHCU.
Fail safe Relay: W hen failure occurs in ABS.
The power supply to solenoid Valve is cut.
ABS Warning Lamp
RTW 75ASH000101
Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System
have an amber “ABS” warning lamp on the instrument
panel. The “ABS” warning lamp will illuminate if a
malfunction in the Anti-lock Brake System is detected
by the Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU). In the
case of an electronic malfunction, the EHCU will turn
“ON” the “ABS” warning lamp and disable the anti-lock
braking function.
The “ABS” warning lamp will turn “ON” for
approximately three seconds after the ignition switch is
in the “ON” position.
If the “ABS” warning lamp stays “ON” after the ignition
switch is in the “ON” position, or comes “ON” and stays
“ON” while driving, the Anti-lock Brake System should
be inspected for a malfunction according to the
diagnostic procedure.
Wheel Speed Sensor (WSS)
It consists of a sensor and a rotor. The sensor is
attached to the knuckle on the front wheels and to the
rear wheels.
The rotor is press-fit in the axle shaft.
G Sensor
The G sensor detects the vehicle deceleration speed
and sends a signal to the EHCU. In 4W D operation, all
four wheels may be decelerated in almost the same
phase, since all wheels are connected mechanically.
This tendency is noticeable, particularly on roads with
low friction coefficient, and the ABS control is adversely
affected.
The G sensor judges whether the friction coefficient of
the road surface is low or high, and changes the
EHCU's operating system to ensure ABS and EBD
control.
Normal and Anti-lock Braking
Under normal driving conditions, the Anti-lock Brake
System functions the same as a standard power
assisted brake system. However, with the detection of
wheel lock-up, a slight bump or kick-back will be felt in
the brake pedal. This pedal “bump” will be followed by a
series of short pedal pulsations which occurs in rapid
succession. The brake pedal pulsation will continue
until there is no longer a need for the anti-lock function
or until the vehicle is stopped. A slight ticking or popping
noise may be heard during brake applications when the
anti-lock feature is being used.
W hen the anti-lock feature is being used, the brake
pedal may rise even as the brakes are being applied.
This is also normal. Maintaining a constant force on the
pedal will provide the shortest stopping distance.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 616 of 6020

BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM 5A-23
Electronic Brake-force Distribution (EBD) System
ABS has the EBD function. EBD is a function which
controls braking force distribution of a front wheel and a
rear wheel, and makes brake fluid pressure of a rear
wheel the optimal. If the rate of slip of a rear wheel
becomes greater compared to a front wheel, the brake
fluid pressure of a rear wheel will be controlled in order
to perform braking force distribution between the front
and rear wheels. EBD enables the braking power of a
rear wheel to always be utilized for the maximum
according to the load change concerning the back axis
according to the vehicle’s loading state (No luggage,
loading, etc.), deceleration, etc. Brake fluid pressure
control to a rear wheel is performed by the EBD function
which uses the ABS function without the mechanical
proportioning valve.
C05L300016
Brake Pedal Travel
Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System may
be stopped by applying normal force to the brake pedal.
Although there is no need to push the pedal beyond the
point where it stops or holds the vehicle, by applying
more force the pedal will continue to travel toward the
floor.
This extra brake pedal travel is normal.
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Several acronyms and abbreviations are commonly
used throughout this section:
ABS
Anti-lock Brake System
CKT
Circuit
DLC
Data Link Connector
EBD
Electronic Brake-force Distribution
EHCU
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit
FL
Front Left
FR
Front Right
GEN
Generator
H/U
Hydraulic Unit
MV
Millivolts
RR
Rear
RPS
Revolutions per Second
VDC
DC Volts
VAC
AC Volts
W/L
W arning Lamp
WSS
W heel Speed Sensor
General Diagnosis
General Information
ABS problems can be classified into two types, those
which can be detected by the ABS warning lamp and
those which can be detected as a vehicle abnormality
by the driver.
In either case, locate the fault in accordance with the
“BASIC DIAGNOSTIC FLOW CHART” and repair.
Please refer to Section 5C for the diagnosis of
mechanical troubles such as brake noise, brake judder
(brake pedal or vehicle vibration felt when braking),
uneven braking, and parking brake trouble.
ABS Service Precautions
Required Tools and Items:
• Box W rench
• Brake Fluid
• Special Tool
Some diagnosis procedures in this section require the
installation of a special tool.
5-8840-0366-0 High Impedance Multimeter
W hen circuit measurements are requested, use a circuit
tester with high impedance.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 617 of 6020

5A-24 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Computer System Service Precautions
The Anti-lock Brake System and Electronic Brake-force
Distribution interfaces directly with the Electronic
Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU) which is a control
computer that is similar in some regards to the Engine
Control Module. These modules are designed to
withstand normal current draws associated with vehicle
operation. However, care must be taken to avoid
overloading any of the EHCU circuits. In testing for
opens or shorts, do not ground or apply voltage to any
of the circuits unless instructed to do so by the
appropriate diagnostic procedure. These circuits should
only be tested with a high impedance multimeter
5-8840-0366-0 or special tools as described in this
section. Power should never be removed or applied to
any control module with the ignition in the “ON” position.
Before removing or connecting battery cables, fuses or
connectors, always turn the ignition switch to the “OFF”
position.
General Service Precautions
The following are general precautions which should be
observed when servicing and diagnosing the Anti-lock
Brake System and/or other vehicle systems. Failure to
observe these precautions may result in Anti-lock Brake
System and Electronic Brake-force Distribution
damage.
• If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle using an electric arc welder, the EHCU and valve
block connectors should be disconnected before the
welding operation begins.
• The EHCU and valve block connectors should never be connected or disconnected with the
ignition “ON”.
Note:
• If only rear wheels are rotated using jacks or drum tester, the system will diagnose a speed sensor
malfunction and the “ABS and Brake” warning lamp
will illuminate. But actually no trouble exists. W hen
the DTC is not detected and the ABS and BRAKE
warning lamp is on, “How to erase code” is
performed and an ABS and BRAKE warning lamp
are off.
If the battery has been discharged
The engine may stall if the battery has been completely
discharged and the engine is started via jumper cables.
This is because the Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) and
Electronic Brake-force Distribution (EBD) System
requires a large quantity of electricity. In this case, wait
until the battery is recharged, or set the ABS and EBD
to a non-operative state by removing the fuse for the
ABS. After the battery has been recharged, stop the
engine and install the ABS fuse. Start the engine again,
and confirm that the ABS warning Lamp does not light.
Note on Intermittents
As with virtually any electronic system, it is difficult to
identify an intermittent failure. In such a case duplicating
the system malfunction during a test drive or a good
description of vehicle behavior from the customer may
be helpful in locating a “most likely” failed component or
circuit. The symptom diagnosis chart may also be
useful in isolating the failure. Most intermittent
problems are caused by faulty electrical connections or
wiring. W hen an intermittent failure is encountered,
check suspect circuits for:
• Suspected harness damage.
• Poor mating of connector halves or terminals not fully seated in the connector body (backed out).
• Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Test Driving ABS Complaint Vehicles
If there has been an abnormality in the lighting pattern
of the “ABS” warning lamp, the fault can be located in
accordance with the “DIAGNOSIS BY “ABS” W ARNING
LAMP ILLUMINATION PATTERN”. Although such
problems can be detected by the driver as a vehicle
symptom, it is still necessary to perform a test drive
following the test procedure mentioned below, in order
to reproduce the symptom for problem diagnosis on a
symptom basis:
1. Start the engine and make sure that the “ABS” W /L
goes OFF. If the W /L remains ON, it means that
the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
Therefore, read the code and locate the fault.
Note: The DTC cannot be cleared if the vehicle speed
does not exceed about 10km/h (6mph) at DTC, even
though the repair operation is completed.
2. Start the vehicle and accelerate to about 30 km/h (19 mph) or more.
3. Slowly brake and stop the vehicle completely.
4. Then restart the vehicle and accelerate to about 40 km/h (25 mph) or more.
5. Brake at a time so as to actuate the ABS and stop the vehicle.
6. Be cautious of abnormality during the test. If the W /L is actuated while driving, read the DTC and
locate the fault.
7. If the abnormality is not reproduced by the test, make best efforts to reproduce the situation
reported by the customer.
8. If the abnormality has been detected, repair in accordance with the “SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS”.
Note:
• Be sure to perform a test drive on a wide, even road
with light traffic.
• If an abnormality is detected, be sure to suspend the test and start trouble diagnosis at once.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 625 of 6020
5A-32 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Data List (Tech 2)
The data displayed by DATA LIST are as follows:
Strings Units Description
FL W heel Speed (Front Left) Km/h (MPH)
FR W heel Speed (Front Right) Km/h (MPH)
RL W heel Speed (Rear Left) Km/h (MPH)
RR W heel Speed (Rear Right) Km/h (MPH) Start the vehicle and make sure of linear
change in each wheel speed.
Brake Switch On/Off Brake switch is “On” when brake pedal is stepped
on.
4 W heel Drive Status 2 W heel Drive/
4 W heel Drive
ABS W arning lamp
On/Off To be “Off” usually
EBD W arning Lamp On/Off To be “Off” usually
ABS State On/Off To be “Off” usually
Valve Relay Command Active/Inactive To be “Active” usually
Return Pump Relay Command Active/Inactive To be “Inactive” usually
EBD State
DTC Status No DTC/
DTCs Set To be “No DTC” usually
FL Release Solenoid Commanded
(Front Left) Active/Inactive
FL Hold Solenoid Commanded (Front
Left) Active/Inactive
FR Release Solenoid Commanded
(Front Right) Active/Inactive
FR Hold Solenoid Commanded (Front
Right) Active/Inactive
Rear Release Solenoid Valve
Commanded Active/Inactive
Rear Hold Solenoid Valve Commanded Active/Inactive
FL Release Solenoid Feedback (Front
Left) Active/Inactive
FL Hold Solenoid Feedback (Front Left) Active/Inactive
FR Release Solenoid Feedback (Front
Left) Active/Inactive
FR Hold Solenoid Feedback (Front Left) Active/Inactive
Rear Release Solenoid Feedback Active/Inactive
Rear Hold Solenoid Valve Feedback Active/Inactive Each valve is “Active” when each valve is operated.
Deceleration Sensor
V 2.0~3.0V when vehicle speed is 0km/h (flat place)
Battery Voltage V The voltage value currently supplied to EHCU
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 626 of 6020
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM 5A-33
Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Choose and trace an appropriate flowchart by the
numbers listed below to find the fault and repair.
Note:
A DTC cannot be erased when the DTC is present.
Warning Lamp System Control Main Items
DTC
(Flash Code) Description
ABS Brake
(EBD) ABS EBD
-
(12) Normal Condition
× × -
C0221
(21) Front Right W heel Speed Sensor
Short Circuit or Circuit Open ×*A × Sensor or W iring
C0222
(22) Front Right W heel Speed Sensor
Signal Malfunction *B ×*A × Sensor or install condition
C0225
(25) Front Left W heel Speed Sensor Short
Circuit or Circuit Open ×*A × Sensor or W iring
C0226
(26) Front Left W heel Speed Sensor Signal
Malfunction *B ×*A × Sensor or install condition
C0231
(31) Rear Right W heel Speed Sensor Short
Circuit or Circuit Open ×*A × Sensor or W iring
C0232
(32) Rear Right W heel Speed Sensor
Signal Malfunction *B ×*A × Sensor or install condition
C0235
(35) Rear Left W heel Speed Sensor Short
Circuit or Circuit Open ×*A × Sensor or W iring
C0236
(36) Rear Left W heel Speed Sensor Signal
Malfunction *B ×*A × Sensor or install condition
C0238
(38) Front Speed Sensor Correlation
× × Vehicle , Sensor or Tire
C0241
(41) Front Right Hold Solenoid Valve Circuit
× × Solenoid (EHCU)
C0242
(42) Front Right Release Solenoid Valve
Circuit × × Solenoid (EHCU)
C0245
(45) Front Left Hold Solenoid Valve Circuit
× × Solenoid (EHCU)
C0246
(46) Front Left Release Solenoid Valve
Circuit × × Solenoid (EHCU)
C0251
(51) Rear Hold Solenoid Valve Circuit
× × Solenoid (EHCU)
C0252
(52) Rear Release Solenoid Valve Circuit
× × Solenoid (EHCU)
×
C0265
(65) Valve Relay Circuit Malfunction
×
× Relay (EHCU)
C0267
(67) Return Pump Circuit Malfunction
× Motor (EHCU)
C0271
(71) ECU Malfunction
× × EHCU
C0276
(76) G Sensor Malfunction
× × Sensor or W iring
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 627 of 6020

5A-34 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Warning Lamp System Control Main Items DTC
(Flash Code) Description
ABS Brake
(EBD) ABS EBD
× × Battery, W iring or EHCU
(less than 8V) C0277 (77) System Voltage Low
× × Battery or W iring
(less than 10V)
C0278 (78) System Voltage High
× × Battery or W iring EHCU
C0282
(82) 4 W heel Drive State Input Signal
Failure × × W iring
C0285
(85) Control Module Vehicle Options
Incorrect × × Vehicle (Sensor or EHCU)
*A : W hen three or more failures are detected, the EBD warning lamp is "ON" and control is canceled.
*B : The ABS lamp is “OFF” when the ABS lamp is “ON” after a repair, until the vehicle’s speed becomes
more than 10km/h (6mph) in the following ignition
cycle and failure is not detected.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 634 of 6020

BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM 5A-41
Wheel Speed Sensor Inspection Procedure
Procedure
1.Ignition "OFF".
2.Disconnect each of the wheel speed sensors.
3.Connect the resistance (50 Ω~100 Ω) as follows.
4.Check the voltage at sensor harness connector.
Note: Voltage measurement is performed in the phase
where the wheel speed sensor is installed in vehicles.
RTW 75AMF000701
Connector Pin-outs
・Front W heel Speed Sensor
1 (+) (+12V)
2 (-) (signal)
・Rear W heel Speed Sensor
1 LH (+) (+12V)
2 LH (-) (signal)
3 RH (+)(+12V)
4 RH (-) (signal)
Output Value
High State 0.7~1.4V (±30%)
Low State 0.4~0.7V (±30%)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 635 of 6020
5A-42 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
Symptom Diagnosis
The symptoms that cannot be indicated by warning
lamp can be divided into the following six categories:
1. ABS works frequently but vehicle does not decelerate.
2. Uneven braking occurs while ABS works.
3. The wheels are locked.
4. Brake pedal feel is abnormal.
5. Braking sound (from EHCU) is heard while not braking.
6. No ABS warning lamp
These are all attributable to problems which cannot be
detected by EHCU self-diagnosis. Use the customer
complaint and a test to determine which symptom is
present.
ABS Works Frequently But Vehicle Does Not Decelerate
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Is braking force distribution normal between front and
rear of vehicle?
- Go to Step 2 Repair brake
parts.
Go to Step 7
2 Are axle parts installed normally?
- Go to Step 3 Repair axle
parts.
Go to Step 7
3 Is there play in each or any wheel speed sensor?
- Repair wheel
speed sensor.
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
4 Is there damage, or powered iron sticking to each or any wheel speed sensor/sensor rotor?
- Replace
wheel speed sensor or
sensor rotor.
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 Is the speed sensor of each wheel output normal?
- Go to Step 6 Replace
wheel speed sensor or repair
harness.
Go to Step 7
6 Is the 4W D control system function normal?
- 2-4W D Repair
or Go to Step 7 Repair or
replace 2-
4W D control System.
Go to Step 7
7 Reconnect all components, ensure all components are properly mounted.
Is this step finished? - Repeat the
“Basic
diagnostic
flow chart” Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007