ESP JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 206 of 3039

Published: 12-May-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Parking Aid
Module (PAM)
Description and Operation
Parking Aid Control Module (PACM)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
warranty policy and procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation
of a new module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system)
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places and with a
current calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into account
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion
If diagnostic trouble codes are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent
concern may be the cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals
Where an 'on demand self-test' is referred to, this can be accessed via the 'diagnostic trouble code monitor' tab on the
manufacturers approved diagnostic system
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required
Physical damage to the sensor (impact damage or scratched sensor surface) must NOT be changed under warranty.
The table below lists all diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Parking Aid Control Module (PACM). For
additional diagnosis and testing information refer to the relevant diagnosis and testing section.
For additional information, refer to: Parking Aid (413-13 Parking Aid, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B1B36-01
Front Right Outer
Sensor - General
Electrical Failure
Wiring harness fault
Front right outer sensor
- Component internal
failure
Refer to electrical wiring diagrams and check the front
bumper harness for damage/corrosion. Check sensor
circuit for short circuit to ground, short circuit to
power, open circuit. Repair or replace any wiring
harness as required
Check the connector for integrity and damage, then
re-connect sensor to confirm connection
Using the manufacturers approved diagnostic system
clear the DTC and run the on demand self test
If the problem persists remove the suspect sensor
from the bumper. Inspect the sensor connector for
signs of water ingress/corrosion. Exchange the
suspect sensor with another sensor within the
bumper that is not reporting a fault. Clear the DTC
and run the on demand self test to confirm if the
fault code now appears for the new position of the
suspect sensor. Renew the faulty sensor www.JagDocs.com
Page 215 of 3039

Published: 18-Apr-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Pedestrian
Protection System Control Module (PPSCM)
Description and Operation
Pedestrian Protection System Control Module (PPSCM)
WARNING: TO AVOID ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY, THE BACKUP POWER SUPPLY MUST
BE DEPLETED BEFORE REPAIRING OR REPLACING ANY PEDESTRIAN PROTECTION SYSTEM COMPONENTS. TO DEPLETE THE
BACKUP POWER SUPPLY ENERGY, DISCONNECT THE BATTERY GROUND CABLE AND WAIT TWO MINUTES. FAILURE TO FOLLOW
THIS INSTRUCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
Warranty Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation
of a new module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required.
The table below lists all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Pedestrian Protection System Control
Module (PPSCM). For additional diagnosis and testing information, refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing section in the
workshop manual.
For additional information, refer to: Pedestrian Protection System (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B1001-11
Right Hood Deployment
Control - Circuit short to
ground
Right hood deployment
control circuit short circuit
to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the right hood deployment control circuit
for short circuit to ground. Install a new wiring
harness as necessary. If no wiring harness
fault exists, using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system, clear the DTCs and retest.
If the fault persists, install a new right hood
deployment control B1001-12
Right Hood Deployment
Control - Circuit short to
battery
Right hood deployment
control circuit short circuit
to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the right hood deployment control circuit
for short circuit to power. Install a new wiring
harness as necessary. If no wiring harness
fault exists, using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system, clear the DTCs and retest.
If the fault persists, install a new right hood
deployment control
Page 216 of 3039

Published: 17-Apr-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Rear
Differential Control Module (RDCM)
Description and Operation
Rear Differential Control Module (RDCM)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
warranty policy and procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation
of a new module/component
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system)
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places and with a
current calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into account
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals
If the rear differential control module, rear differential actuator or the rear differential are replaced, the on demand self
test (ODST) must be carried out to calibrate the components
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as needed
The table below lists all diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the rear differential control module, for
additional diagnosis and testing information refer to the relevant diagnosis and testing section.
For additional information, refer to: Rear Drive Axle and Differential (205-02 Rear Drive Axle/Differential, Diagnosis and
Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action P0562-00
System Voltage Low -
No sub type
information
Rear differential control
module voltage supply
below 9 volts
Check the battery charge condition, refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check the wiring to
the rear differential control module, repair as
necessary P0563-00
System Voltage High -
No sub type
information
System voltage high
(supply voltage supply
greater than 16 volts)
Check engine control module for stored DTCs,
suspect charging system fault. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check, power and
ground circuit for fault P0604-00
Internal Control Module
Random Access Memory
(RAM) Error - No sub
type information
Rear differential control
module internal error
Clear the DTC and retest. If the problem persists,
renew the control module. Refer to the warranty
policy and procedures manual, or determine if any
prior approval programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new module/component P0605-00
Internal Control Module
Read Only Memory
(ROM) Error - No sub
type information
Rear differential control
module internal error
Clear the DTC and retest. If the problem persists,
renew the control module. Refer to the warranty
policy and procedures manual, or determine if any www.JagDocs.com
Page 218 of 3039

Published: 12-May-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Rear
Junction Box (RJB)
Description and Operation
Rear Junction Box (RJB)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If a control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a new
module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required.
The table below lists all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Rear Junction Box (RJB). For additional
diagnosis and testing information, refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing section in the workshop manual.
For additional information, refer to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action P0460-11
Fuel Level Sensor A
Circuit - Circuit short to
ground
Fuel level sensor A
analogue input circuit -
short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
fuel level sensor A analogue input circuit for short to
ground P0460-15
Fuel Level Sensor A
Circuit - Circuit short to
battery or open
Fuel level sensor A
analogue input circuit -
short to power, open
circuit
Carry out any pinpoint test associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
fuel level sensor A analogue input circuit for short to
power, open circuit P0571-12
Brake Switch A Circuit -
Circuit short to battery
Footbrake switch digital
input signal circuits -
short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
footbrake switch digital input signal circuits for
short to power P1230-12
Fuel Pump Low Speed
Malfunction (VLCM) -
Circuit short to battery
High Side output not
driven - Diagnosis
feedback indicates
output is short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
fuel pump delivery module for short to power
Page 227 of 3039

Published: 18-Apr-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Remote
Keyless Entry Module (RFA)
Description and Operation
Remote Keyless Entry Module (RFA)
CAUTIONS:
Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not guarantee
confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle
When probing connectors to take measurements in the course of the pinpoint tests, use the adaptor kit, part number
3548-1358-00
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
warranty policy and procedures manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new module/component
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system)
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places and with a
current calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into account
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion
If diagnostic trouble codes are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent
concern may be the cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals
Where an 'on demand self-test' is referred to, this can be accessed via the 'diagnostic trouble code monitor' tab on the
manufacturers approved diagnostic system
The table below lists all diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the remote keyless entry module, for
additional diagnosis and testing information refer to the relevant diagnosis and testing section.
For additional information, refer to: Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) Module (419-10 Multifunction Electronic Modules, Diagnosis
and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B102B-00
Passive Key - No sub
type information
Response Error - general
failure
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system, clear all passive keys, re-learn all passive
keys B10C1-00
Left Front Unlock Pull
Switch - No sub type
information
No power supply to door
handle
Switch circuit open, or
short circuit to power
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the power supply to the door handle. Check
the switch circuit is not open circuit or short to
power. Repair wiring as required B10C1-24
Left Front Unlock Pull
Switch - Signal stuck
high
Signal stuck high - button
stuck in active position
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Check for stuck left front unlock switch.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
left front unlock switch circuit for short to ground
Page 231 of 3039

Published: 12-May-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Restraints
Control Module (RCM)
Description and Operation
Restraints Control Module (RCM)
WARNINGS:
TO AVOID ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY, THE BACKUP POWER SUPPLY MUST BE DEPLETED
BEFORE REPAIRING OR REPLACING ANY AIR BAG SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS) COMPONENTS. TO DEPLETE THE
BACKUP POWER SUPPLY ENERGY, DISCONNECT THE BATTERY GROUND CABLE AND WAIT ONE MINUTE. FAILURE TO FOLLOW
THIS INSTRUCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
Do not use a multimeter to probe the restraints control module. It is possible for the power from the meter battery to
trigger the activation of the airbags. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If a control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a new
module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required.
It is advisable not to use a cellular phone or to have a cellular phone in close proximity when working on the restraints
control module or associated systems.
Given the legal implications of a restraints system failure, harness repairs to air bag module circuits are not acceptable.
Where the text refers to "REPAIR the circuit", this will normally mean the replacement of a harness.
The table below lists all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Restraints Control Module (RCM). For
additional diagnosis and testing information, refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing section in the workshop manual.
For additional information, refer to: Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B0001-09
Driver Frontal Stage 1
Deployment Control -
Component failures
Driver front stage 1 air bag -
internal driver failure
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated
with this DTC using the manufacturer
approved diagnostic system www.JagDocs.com
Page 236 of 3039

Published: 17-Apr-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Satellite
Digital Audio Radio System Module (SARM)
Description and Operation
Satellite Radio Module (SARM)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
warranty policy and procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation
of a new module/component
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system)
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places and with a
current calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into account
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion
If diagnostic trouble codes are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent
concern may be the cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals
Where an 'on demand self-test' is referred to, this can be accessed via the 'diagnostic trouble code monitor' tab on the
manufacturers approved diagnostic system
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as needed
The table below lists all diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that could be logged on the satellite radio module, for additional
diagnosis and testing information refer to the relevant diagnosis and testing section.
For additional information, refer to: Information and Entertainment System (415-00 Information and Entertainment System -
General Information, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B1A89-01
Satellite Antenna -
General electrical
failure
Wiring harness fault -
Coaxial cable between
satellite radio module and
the satellite antenna
Internal electronic failure
- Satellite digital audio
radio antenna
Internal electronic failure
- Satellite radio module
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
satellite digital audio radio antenna coaxial cable for
short circuit to ground, short circuit to power, open
circuit, high resistance. Repair wiring harness as
required, clear DTC and retest
If fault persists, check and install a new satellite digital
audio radio antenna
If fault persists, check and install a new satellite radio
module
Refer to the warranty policy and procedures manual, or
determine if any prior approval programme is in
operation, prior to the installation of a new
module/component B1A89-11
Satellite Antenna -
Circuit short to
ground
Satellite antenna circuit -
short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
satellite antenna circuit for short circuit to ground.
Repair wiring harness as required. Clear DTC and retest www.JagDocs.com
Page 238 of 3039

Published: 12-May-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Speed
Control Module (CCM)
Description and Operation
Adaptive Speed Control Module (ASCM)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If a control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a new
module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required.
The table below lists all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Adaptive Speed Control Module (ASCM).
For additional diagnosis and testing information, refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing section in the workshop manual.
For additional information, refer to: Speed Control (310-03C Speed Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B1A84-81 Car Configuration Data
- Invalid serial data
received
RJB reporting invalid
data
Re-configure the RJB using manufacturer approved
diagnostic system C1A67-54 Forward Looking Sensor
- Missing calibration
Speed control sensor out
of alignment
Check speed control sensor for correct vertical
alignment, and carry out speed control sensor
alignment procedure using manufacturer approved
diagnostic system C1A67-81 Forward Looking Sensor
- Invalid serial data
received
Yaw voltage
unreasonable for 0.5
seconds or unchanged
for 1.2 seconds. Note:
Yaw sensor internal to
speed control sensor
Clear DTC and re-test, if DTC remains suspect speed
control sensor. Check and install a new sensor as
required, refer to the new module/component
installation note at the top of the DTC Index C1A67-87 Forward Looking Sensor
- Missing Message
Incorrect or missing data
from speed control
sensor
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check power and ground supplies for short, open
circuit. Check private CAN network between speed
control sensor and speed control module for failure,
clear DTC and re-test. If DTC remains suspect the
Page 240 of 3039
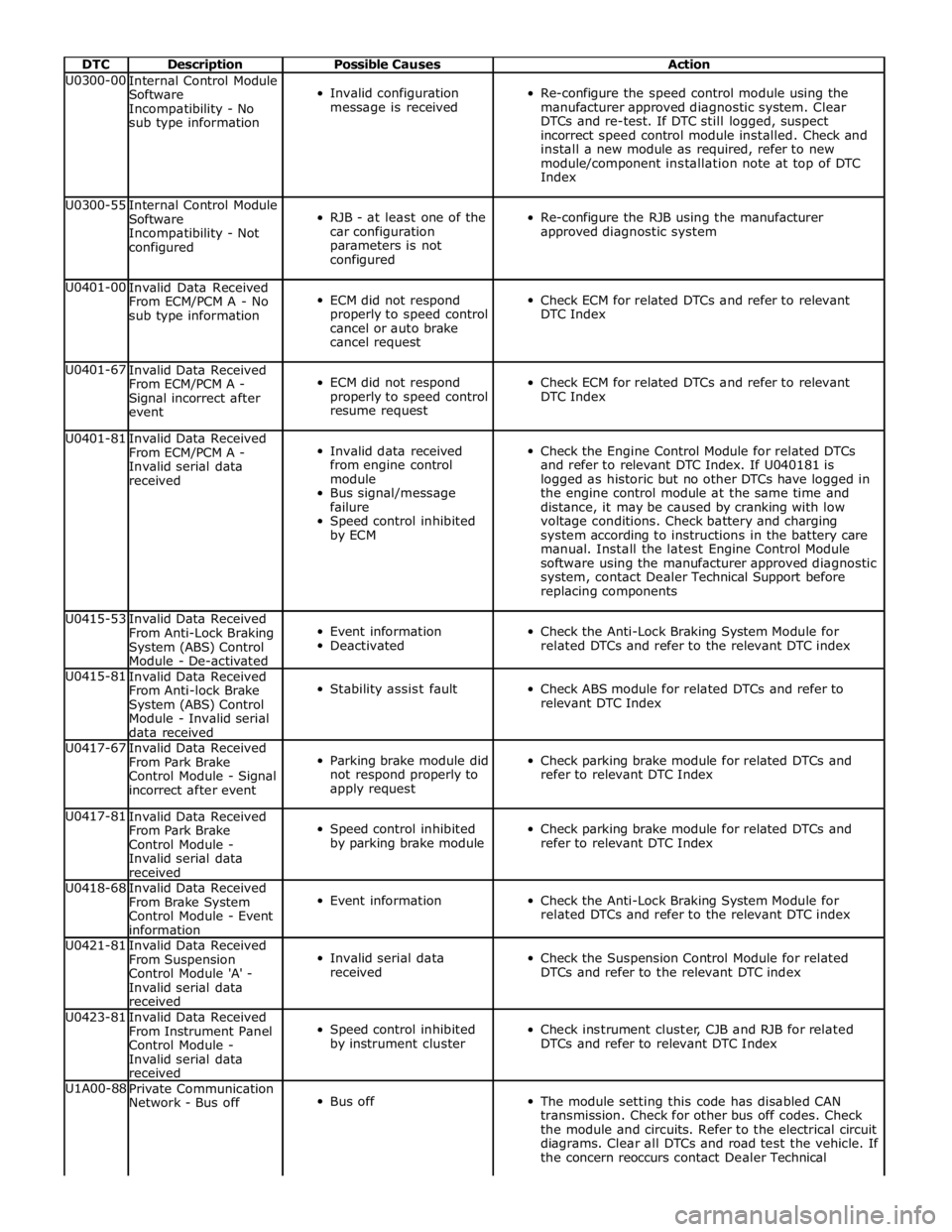
DTC Description Possible Causes Action U0300-00
Internal Control Module
Software
Incompatibility - No
sub type information
Invalid configuration
message is received
Re-configure the speed control module using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Clear
DTCs and re-test. If DTC still logged, suspect
incorrect speed control module installed. Check and
install a new module as required, refer to new
module/component installation note at top of DTC
Index U0300-55
Internal Control Module
Software
Incompatibility - Not
configured
RJB - at least one of the
car configuration
parameters is not
configured
Re-configure the RJB using the manufacturer
approved diagnostic system U0401-00
Invalid Data Received
From ECM/PCM A - No
sub type information
ECM did not respond
properly to speed control
cancel or auto brake
cancel request
Check ECM for related DTCs and refer to relevant
DTC Index U0401-67
Invalid Data Received
From ECM/PCM A -
Signal incorrect after
event
ECM did not respond
properly to speed control
resume request
Check ECM for related DTCs and refer to relevant
DTC Index U0401-81
Invalid Data Received
From ECM/PCM A -
Invalid serial data
received
Invalid data received
from engine control
module
Bus signal/message
failure
Speed control inhibited
by ECM
Check the Engine Control Module for related DTCs
and refer to relevant DTC Index. If U040181 is
logged as historic but no other DTCs have logged in
the engine control module at the same time and
distance, it may be caused by cranking with low
voltage conditions. Check battery and charging
system according to instructions in the battery care
manual. Install the latest Engine Control Module
software using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system, contact Dealer Technical Support before
replacing components U0415-53
Invalid Data Received
From Anti-Lock Braking
System (ABS) Control
Module - De-activated
Event information
Deactivated
Check the Anti-Lock Braking System Module for
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index U0415-81
Invalid Data Received
From Anti-lock Brake
System (ABS) Control
Module - Invalid serial
data received
Stability assist fault
Check ABS module for related DTCs and refer to
relevant DTC Index U0417-67
Invalid Data Received
From Park Brake
Control Module - Signal
incorrect after event
Parking brake module did
not respond properly to
apply request
Check parking brake module for related DTCs and
refer to relevant DTC Index U0417-81
Invalid Data Received
From Park Brake
Control Module -
Invalid serial data
received
Speed control inhibited
by parking brake module
Check parking brake module for related DTCs and
refer to relevant DTC Index U0418-68
Invalid Data Received
From Brake System
Control Module - Event
information
Event information
Check the Anti-Lock Braking System Module for
related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index U0421-81
Invalid Data Received
From Suspension
Control Module 'A' -
Invalid serial data
received
Invalid serial data
received
Check the Suspension Control Module for related
DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index U0423-81
Invalid Data Received
From Instrument Panel
Control Module -
Invalid serial data
received
Speed control inhibited
by instrument cluster
Check instrument cluster, CJB and RJB for related
DTCs and refer to relevant DTC Index U1A00-88
Private Communication
Network - Bus off
Bus off
The module setting this code has disabled CAN
transmission. Check for other bus off codes. Check
the module and circuits. Refer to the electrical circuit
diagrams. Clear all DTCs and road test the vehicle. If
the concern reoccurs contact Dealer Technical
Page 242 of 3039

Published: 17-Apr-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Steering
Column Lock Module (VIM)
Description and Operation
Steering Column Lock Module (VIM)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being checked and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
Warranty Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation
of a new module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to three decimal places,
and with an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the DMM leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Where an 'on demand self-test' is referred to, this can be accessed via the 'DTC Monitor' tab on the manufacturers
approved diagnostic system.
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required.
The table below lists all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Steering Column Lock Module, for
additional Diagnosis and Testing information refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing Section.
For additional information, refer to: Steering Column Switches (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B100D-51
Column Lock
Authorisation - Not
programmed
Module not programmed
Configure the Steering Column Lock Module using the
manufacturers approved diagnostic system B100D-62
Column Lock
Authorisation -
Signal compare
failure
Signal compare failure
- This DTC will be
logged if the
encrypted data
exchange does
not match
between Steering
Column Lock and
the Central
Junction Box
Configure the modules using the manufacturers approved
diagnostic system. If the problem persists, complete a
CAN network integrity test using the manufacturers
approved diagnostic system. Perform an on demand
self-test and retest B100D-64
Column Lock
Authorisation -
Signal plausibility
failure
Signal plausibility failure
Steering Column Lock
unable to perform lock
action
CAN Network fault
Anti-lock Braking
System, Engine Control
Module, Central Junction
Box fault
NOTE: Prior to clearing this DTC, carry out the Vehicle
Functional Reset application using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system
Check the serviceability of the steering column and lock.
Clear the DTC and retest. If the problem persists, carry
out CAN Network Integrity Test and Module Self Test
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Alternatively, refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and