check engine JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.G Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1997, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.GPages: 227, PDF Size: 7.2 MB
Page 117 of 227
42Also, check the reference voltage to the
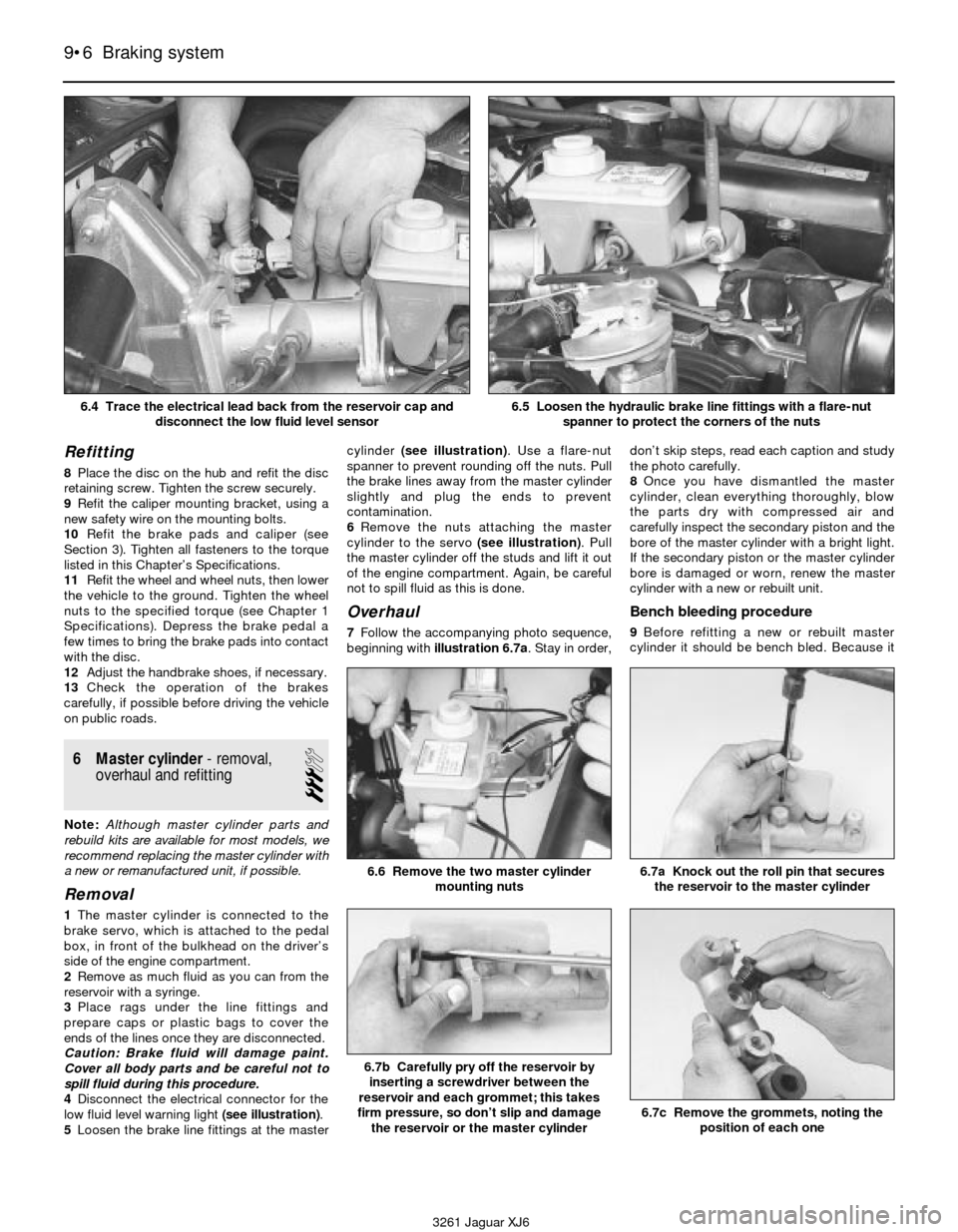
MAF sensor from the computer. Backprobe
terminal number 6 and make sure that
approximately 5 volts is present.
Renewal
43Disconnect the electrical connector from
the MAF sensor.
44Remove the air cleaner assembly (see
Chapter 4).
45Remove the four bolts and separate the
MAF sensor from the air intake duct.
46Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Intake air temperature
(IAT) sensor
General description
47The intake air temperature sensor is
located inside the air intake duct. This sensor
acts as a resistor which changes value
according to the temperature of the air entering
the engine. Low temperatures produce a high
resistance value (for example, at 68° F the
value is 2.0 to 2.6 k-ohms) while high
temperatures produce low resistance values (at
176° F the resistance is 260 to 330 ohms. The
ECU supplies around 5 volts (reference
voltage) to the air temperature sensor.
The voltage will change according to the
temperature of the incoming air. The voltage
will be high when the air temperature is cold
and low when the air temperature is warm. Any
problems with the air temperature sensor
will usually set a code 8 (1988 and 1989) or
code 16 (1990 to 1994).
Check
48To check the air temperature sensor,
disconnect the two prong electrical connector
and turn the ignition key ON but do not start
the engine.
49Measure the voltage (reference voltage),
which should be approximately 5 volts.
50If the voltage signal is not correct, havethe ECU diagnosed by a dealer service
department or other repair workshop.
51Measure the resistance across the air
temperature sensor terminals (see illustration).
The resistance should be HIGH when the air
temperature is LOW. Next, start the engine and
let it idle. Wait awhile and let the engine reach
operating temperature. Turn the ignition OFF,
disconnect the air temperature sensor and
measure the resistance across the terminals.
The resistance should be LOW when the air
temperature is HIGH. If the sensor does not
exhibit this change in resistance, renew it with a
new part.
EGR gas temperature sensor
(1991 to 1994 models)
General description
52The EGR gas temperature sensor is
mounted in the exhaust gas transfer pipe. This
sensor detects the temperature of the exhaust
moving through the EGR valve. The information
is sent to the ECU so the EGR on/off time is
regulated precisely and efficiently.
Check
53Disconnect the harness connector for the
EGR gas temperature sensor and measure
the resistance of the sensor at the various
temperatures. Refer to the Specifications
listed in this Chapter for a list of the
temperatures and the resistance values.
Removal and refitting
54Disconnect the harness connector for the
EGR gas temperature sensor and using an
open-end spanner, remove the sensor from
the EGR adapter under the intake manifold.
55Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Speed sensor
General description
56The speed sensor is mounted on thedifferential housing and monitors vehicle
speed by sensing the rotational speed of the
rear axle. A problem with this sensor or circuit
will set a code 68 and may also be the cause
of an inoperative speedometer. If the
speedometer doesn’t work, the problem lies
in the speed sensor, the instrument cluster,
the ECU or the wiring in between. For further
diagnosis, take the vehicle to a dealer service
department or other suitably-equipped and
qualified repair workshop.
Crankshaft position sensor
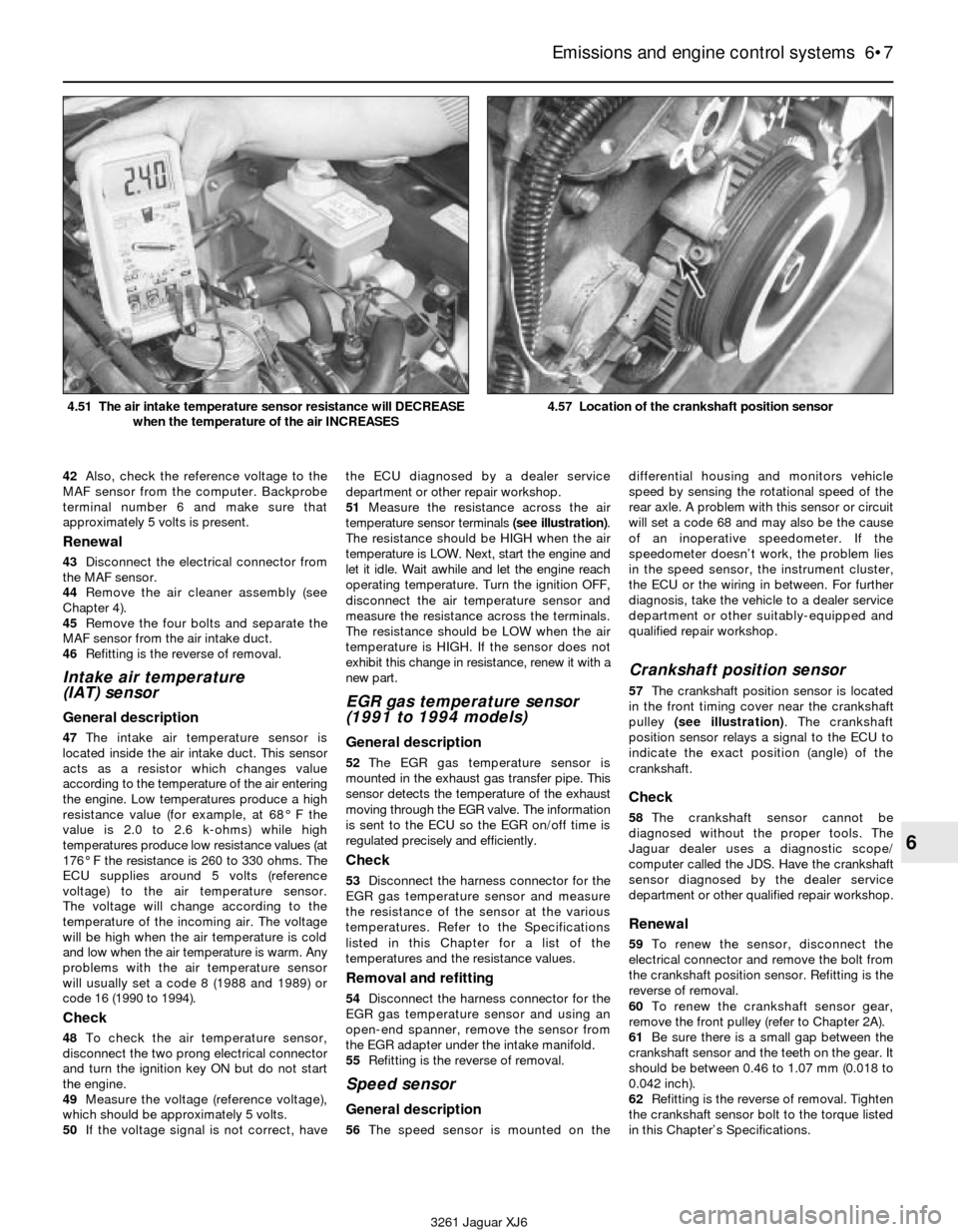
57The crankshaft position sensor is located
in the front timing cover near the crankshaft
pulley (see illustration). The crankshaft
position sensor relays a signal to the ECU to
indicate the exact position (angle) of the
crankshaft.
Check
58The crankshaft sensor cannot be
diagnosed without the proper tools. The
Jaguar dealer uses a diagnostic scope/
computer called the JDS. Have the crankshaft
sensor diagnosed by the dealer service
department or other qualified repair workshop.
Renewal
59To renew the sensor, disconnect the
electrical connector and remove the bolt from
the crankshaft position sensor. Refitting is the
reverse of removal.
60To renew the crankshaft sensor gear,
remove the front pulley (refer to Chapter 2A).
61Be sure there is a small gap between the
crankshaft sensor and the teeth on the gear. It
should be between 0.46 to 1.07 mm (0.018 to
0.042 inch).
62Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the crankshaft sensor bolt to the torque listed
in this Chapter’s Specifications.
Emissions and engine control systems 6•7
6
3261 Jaguar XJ6 4.51 The air intake temperature sensor resistance will DECREASE
when the temperature of the air INCREASES
4.57 Location of the crankshaft position sensor
Page 118 of 227

5 Air Injector Reactor
(AIR) system
General information
1The air injection reactor system reduces
carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon content
in the exhaust gases by injecting fresh air into
the hot exhaust gases leaving the exhaust
ports. When fresh air is mixed with hot
exhaust gases, oxidation is increased,
reducing the concentration of hydrocarbons
and carbon monoxide and converting them
into harmless carbon dioxide and water.
2The air injection system is composed of an
air pump, diverter valve (bypass), check valve,
air injection manifold, vacuum delay valve,
vacuum control solenoid, air pump magnetic
clutch, air pump clutch relay and hoses (see
illustration). The air pump is driven by a belt
from the crankshaft and supplies compressed
air to the exhaust manifold(s). The check valve
prevents the reverse flow of exhaust gases into
the system. The vacuum-operated (early
models) or electrically-operated (later models)air cut-off valve prevents air from being drawn
into the exhaust when the air pump is switched
off. System vacuum to the air cut-off valve is
controlled by the solenoid vacuum valve in
parallel circuit with the air pump. A delay valve
prevents vacuum loss to the solenoid valve
during wide open throttle operation.
3Injected air is controlled by the computer,
the air pump clutch and the air pump clutch
relay. The AIR system is used during warm-up
(58 to 83° F) to control emissions while the
engine is running rich. The oxygen sensor
feedback system cannot function while the AIR
system is operating. The computer controls
both systems during warm-up and operating
temperatures. If problems occur with the
AIR system relay or circuit, the on-board
diagnosis system will set a code 66.
Check
4Check the condition of the air pump
drivebelt, the injection hoses and the injection
manifold. Make sure that all components are
intact and there are no leaks.
5Check the operation of the air pump clutch
relay (see illustration)and the air pump
clutch. First remove the relay and check forbattery voltage to the relay. Also, check the
relay itself. Refer to the relay checking
procedure in Chapter 12. Extract codes from
the self-diagnosis system (see Section 3) and
check for a code 66, AIR relay malfunction.
6Make sure the electrical connector is
securely fastened to the diverter valve (see
illustration). If everything appears OK but a
fault code still sets, have the system
diagnosed by a dealer service department or
other qualified repair workshop.
Air pump renewal
7Disconnect the cable from the negative
terminal of the battery.
Caution: If the stereo in your vehicle is
equipped with an anti-theft system, make
sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
8Disconnect the electrical connector from
the air pump clutch.
9Loosen the clips from the air inlet and outlet
hose and separate them from the air injection
pump.
10Loosen the adjuster and pivot bolts (see
illustration)and nuts but do not remove them
from the air injection pump brackets.
6•8 Emissions and engine control systems
3261 Jaguar XJ6 5.2 Schematic of the Air Injection Reactor (AIR) system
5.6 Location of the AIR diverter valve on a 1992 model - check the
hoses for cracking and the electrical connector for security5.10 Loosen the pivot bolt and then the adjustment nut to remove
the drivebelt from the air pump. The adjustment nut has a lock bolt
that must be loosened before the pump will move down the adjuster
5.5 Location of the AIR pump relay on a 1992 model
Page 119 of 227

11Swing the pump toward the engine and
remove the drivebelt from the pump.
12Remove the link arm through-bolt.
13Remove the pivot bolt and front spacer,
rear cone and air injection pump from the
engine compartment.
14Remove the nut securing the front pulley
on the air injection pump.
15Remove the clutch snap-ring and the
clutch.
16Refitting is the reverse of removal.
6 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) system
Note 1: Some 1990 models have the EGR
vacuum hose routed incorrectly through the
bulkhead securing straps, thereby restricting
the vacuum signal to the EGR valve. Remove
the EGR vacuum hose from the bulkhead
harness and refit a new hose. Secure it to the
engine compartment using tie-wraps and do
not allow any restrictions in the hose.Note 2: Some models have copper sealing
washers that soften and leak around the EGR
valve causing engine performance and
starting problems. Refit steel washers and
pipe adapters into the EGR system. Contact a
Jaguar dealer for the VIN numbers and years
of the models that are affected by this defect.
1To reduce oxides of nitrogen emissions,
some of the exhaust gases are recirculated
through the EGR valve to the intake manifold
to lower combustion temperatures.
2The EGR system consists of the EGR valve,
an EGR solenoid, an EGR gas temperature
sensor and the transfer pipe (see illustration).
Check
EGR valve
3Start the engine and allow it to idle.
4Detach the vacuum hose from the EGR
valve and attach a hand vacuum pump in its
place (see illustration).
5Apply vacuum to the EGR valve. Vacuum
should remain steady and the engine should
run poorly. Note:This action will raise the
pintle and allow exhaust gases to recirculateinto the intake system and cause rough
running condition at idle.Double-check the
movement of the pintle by checking the
diaphragm using the tip of your finger (see
illustration). If the EGR diaphragm moves
smoothly and holds steady when vacuum is
applied, the EGR valve is working properly.
Warning: Don’t burn yourself. If
the EGR valve is hot, wear a
glove or wait until it cools.
a) If the vacuum doesn’t remain steady and
the engine doesn’t run poorly, renew the
EGR valve and recheck it.
b) If the vacuum remains steady but the
engine doesn’t run poorly, remove the
EGR valve and check the valve and the
intake manifold for blockage. Clean or
renew parts as necessary and recheck.EGR system
6Disconnect the hose from the EGR valve,
refit a vacuum gauge and check for vacuum
to the EGR valve. There should be vacuum
present with the engine warmed to operating
temperature (above 140° F) and between
1000 and 4000 rpm (see illustration).
Emissions and engine control systems 6•9
6
3261 Jaguar XJ6 6.2 Schematic of the EGR system
6.4 Apply vacuum to the EGR valve and confirm that the valve
opens and allows exhaust gases to circulate. Once it is activated,
the EGR valve should hold steady (no loss in vacuum)
6.5 Use a fingertip to move the diaphragm inside the EGR valve6.6 Check for vacuum to the EGR valve from the throttle body
Page 120 of 227
7Start the engine and observe the vacuum
gauge. At idle, there should be no vacuum
present. Raise the engine rpm and observe
the vacuum increase. This is a ported vacuum
source and therefore it should only register
vacuum when throttled.
8Check the operation of the EGR control
solenoid. Check for battery voltage to the EGR
control solenoid harness (see illustration). If
battery voltage is not available, check the
harness. Refer to the wiring diagrams at the
end of Chapter 12.
9If battery voltage is available to the EGR
control solenoid, have the EGR system
diagnosed by a dealer service department or
other qualified repair workshop.
EGR valve renewal
10Detach the vacuum hose, disconnect the
fitting that attaches the EGR pipe to the EGR
valve and remove the EGR valve from the
exhaust manifold and check it for sticking and
heavy carbon deposits. If the valve is sticking
or clogged with deposits, clean or renew it.
11Refitting is the reverse of removal.
7 Evaporative Emission
Control (EVAP) system
Note: Some models may have charcoal
canister vent plugs installed in the canister
from the factory. These blanking plugs must
be removed to allow proper pressure and
release within the EVAP system. Check the
charcoal canister for these additional plugs
and remove them. With the blanking plugs
installed, the fuel tank will collapse causing
rough running and hesitation and loss of
power under load.
General description
1This system is designed to trap and store
fuel that evaporates from the fuel tank, throttle
body and intake manifold that would normally
enter the atmosphere in the form of
hydrocarbon (HC) emissions.
2The Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP)
system consists of a charcoal-filled canister,
the lines connecting the canister to the fuel
tank, tank pressure control valve, purgecontrol valve and thermal vacuum valve (TVV)
(see illustration). Note: 1993 and 1994
models have a purge control solenoid that is
controlled by the ECU. This solenoid switches
vacuum to the purge control valve.
3Fuel vapours are transferred from the fuel
tank and throttle body to a canister where
they’re stored when the engine isn’t running.
When the engine is running, the fuel vapours
are purged from the canister by intake airflow
and consumed in the normal combustion
process.Note: The ECU will set a code 89 if
the purge control valve is defective or the
circuit has shorted.
4The fuel tank is equipped with a pressure
control valve. This valve opens and closes
according to the pressure increase and
decrease in the fuel tank.
Check
5Poor idle, stalling and poor driveability can
all be caused by an inoperative pressure relief
valve, split or cracked hoses or hoses
connected to the wrong fittings. Check the
fuel tank filler cap for a damaged or deformed
gasket.
6Evidence of fuel loss or fuel odour can be
caused by liquid fuel leaking from fuel lines, a
cracked or damaged canister, an inoperative
fuel tank control valve, disconnected,
misrouted, kinked, deteriorated or damaged
vapour or control hoses.
7Inspect each hose attached to the canister
for kinks, leaks and cracks along its entire
length. Repair or renew as necessary.
8Look for fuel leaking from the bottom of the
6•10 Emissions and engine control systems
6.8 Check for battery voltage to the EGR
control solenoid
3261 Jaguar XJ6
7.2 Schematic of the
EVAP system
Page 121 of 227
canister. If fuel is leaking, renew the canister
and check the hoses and hose routing.
9Inspect the canister. If it’s cracked or
damaged, renew it.
10Check for a clogged filter or a damaged
pressure relief valve. Using low pressure
compressed air (such as from a tyre pump),
blow into the canister tank pipe. Air should
flow freely from the other pipes. If a problem is
found, renew the canister.
11Check the operation of the thermal
vacuum valve (TVV). With the engine cold and
idling, check for ported vacuum to the
temperature vacuum switch. Vacuum should
be present (see illustration). Now warm the
engine to operating temperature (above
115°F/43°C) and confirm that ported vacuum
passes through the TVV (see illustration).
Renew the valve if the test results are
incorrect.
12Check the operation of the purge control
valve. Apply vacuum to the purge control valve
using a hand-held vacuum pump and observe
that the valve holds vacuum steadily (see
illustration). If the valve holds vacuum and the
valve is opening, it is working properly.
Charcoal canister renewal
13Clearly label, then detach the vacuum
hoses from the canister.
14Remove the mounting clamp bolts (see
illustration), lower the canister with thebracket, disconnect the hoses from the check
valve and remove it from the vehicle.
15Refitting is the reverse of removal.
8 Crankcase ventilation
system
General information
1The crankcase ventilation system reduces
hydrocarbon emissions by scavenging
crankcase vapours. It does this by circulating
fresh air from the air cleaner through the
crankcase, where it mixes with blow-by gases
and is then re-routed through a heating
element to the intake manifold(see
illustration).
2The main components of the crankcase
ventilation system are the control orifice, a
heating element and the vacuum hoses
connecting these components with the engine.
3Piston blow-by gasses are collected from
the crankcase and the camshaft housing
via the oil filler tube. These gasses are fed into
the intake manifold at part throttle through the
part throttle orifice and when the engine is at
full throttle, the gasses are fed through the air
intake elbow.
4To prevent possible icing-up during cold
weather operation, the control orifice and the
hose to the intake system is electronically
heated. The heater element is energised by a
relay signal from the windscreen washer jet
temperature sensor.
Check
5Remove the tubes and elbows that connect
the crankcase ventilation system and inspect
them for obstructions, oil deposits or clogging.
Make sure the ventilation system is free of all
Emissions and engine control systems 6•11
6
7.11a Check for vacuum to the thermal
vacuum valve (TVV)7.11b Check for vacuum from the TVV
before and after the engine has reached
normal operating temperature
7.12 Remove the front spoiler to gain
access to the purge control valve (see
Chapter 11). Apply vacuum to the valve and
make sure the valve holds vacuum7.14 Remove the bolts (arrowed) and lower
the charcoal canister from the wing
8.1 Schematic of the crankcase ventilation system
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 122 of 227

obstructions to ensure complete recirculation
of gasses from the crankcase back into the
intake manifold. In the event of clogging, the
pressure will increase causing blow-by and oil
leaks through seals and gaskets.
6Check the operation of the heating element.
Check for battery voltage to the element while
the engine is cold. If no voltage is available
to the heating element, check the circuit from
the windscreen washer jet temperature
sensor.
Renewal
7Disconnect the electrical connector from
the heating element (see illustration).
8Remove the clamps from the hoses and
separate the heating element from the engine.
9Remove the hoses from the intake
manifold. These crankcase ventilation hoses
are specially formed and must be replaced
with special factory parts from Jaguar.
10Refitting is the reverse of removal.
9 Catalytic converter
General description
1To reduce hydrocarbon, carbon monoxide
and oxides of nitrogen emissions, all vehicles
are equipped with a three-way catalyst
system which oxidises and reduces these
chemicals, converting them into harmless
nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water.
2The catalytic converter fits into the exhaust
system much like a silencer. Note:The
exhaust system configuration changes withlater model updates. Older models (1988 and
1989) are equipped with a pre-catalytic
converter near the exhaust manifold
incorporating a single exhaust pipe to the
silencer. Later models are equipped with dual
exhaust pipes, dual catalytic converters and
dual silencers.
Check
3Periodically inspect the catalytic converter-
to-exhaust pipe mating flanges and bolts.
Make sure that there are no loose bolts and
no leaks between the flanges.
4Look for dents in or damage to the catalytic
converter protector. If any part of the
protector is damaged or dented enough to
touch the converter, repair or renew it.
5Inspect the heat insulator for damage.
Make sure there is enough clearance between
the heat insulator and the catalytic converter.
Renewal
6To renew the catalytic converter, refer to
Chapter 4. It is recommended that catalytic
converters be renewed at a qualified silencer
workshop because of the numerous tack
welds on the exhaust pipes.
6•12 Emissions and engine control systems
3261 Jaguar XJ6
8.7 Disconnect the electrical connector
from the electronic heating element
Page 123 of 227

3261 Jaguar XJ6
9
Chapter 9
Braking system
General
Brake fluid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Minimum brake pad thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake disc minimum permissible thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cast into disc
Parallelism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.013 mm (0.0005 inch) maximum
Runout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.102 mm (0.004 inch) maximum
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Brake servo mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Caliper bolts (front and rear) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 to 40 23 to 29
Caliper bracket bolts
Front bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102 to 128 75 to 94
Rear bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 to 62 40 to 45
Master cylinder-to-brake servo nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 to 28 16 to 20
Wheel nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1 Specifications Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Brake check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake disc - inspection, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Brake fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Brake hoses and lines - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Brake hydraulic system - bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Brake light switch - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Brake servo - general information, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 7Disc brake caliper - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Disc brake pads - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Handbrake cable - adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Handbrake cables - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Handbrake shoes - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Master cylinder - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
9•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
1 General information
All models covered by this manual are
equipped with hydraulically operated front
and rear disc brake systems. Both front and
rear brakes are self adjusting.
Hydraulic system
The hydraulic system is divided into
two separate circuits. The master cylinder has
separate reservoirs for the two circuits, and, in
the event of a leak or failure in one hydraulic
circuit, the other circuit will remain operative.
All models are equipped with an Anti-lock
Braking System (ABS).
Brake servo
A hydraulic brake servo system is used on
all models covered by this manual. Thissystem uses hydraulic pressure from an
engine-driven pump on models equipped with
a power hydraulic system, and an electric
pump on models without the power hydraulic
system.
Handbrake
The handbrake lever operates the rear
brakes through cable actuation. It’s activated
by a lever mounted in the centre console. The
handbrake assembly uses a pair of brake
shoes located inside the rear hub/brake disc.
Brake pad wear warning system
The brake pad wear warning system turns
on a red light in the instrument cluster when
the brake pads have worn down to the point
at which they must be replaced. Do NOT
ignore this reminder. If you don’t renew the
pads shortly after the brake pad wear warning
light comes on, the brake discs will be
damaged.The wear sensors are attached to the brake
pads. Once the pads wear down to the point
at which they’re flush with the sensor, the disc
grinds away the side of the sensor facing the
disc, the wire inside the sensor is broken, the
circuit is opened and the red light on the
instrument panel comes on.
Always check the sensor(s) when replacing
the pads. If you change the pads before the
warning light comes on, the sensor(s) may still
be good; once the light has come on, renew
the sensor.
Service
After completing any operation involving
dismantling of any part of the brake system,
always test drive the vehicle to check for
proper braking performance before resuming
normal driving. When testing the brakes,
perform the tests on a clean, dry, flat surface.
Conditions other than these can lead to
inaccurate test results.
Page 124 of 227
Test the brakes at various speeds with both
light and heavy pedal pressure. The vehicle
should stop evenly without pulling to one side
or the other. Avoid locking the brakes,
because this slides the tyres and diminishes
braking efficiency and control of the vehicle.
Tyres, vehicle load and wheel alignment are
factors which also affect braking performance.
2 Anti-lock Brake system
(ABS)- general information
The Anti-lock Brake System is designed to
maintain vehicle steerability, directional stability
and optimum deceleration under severe
braking conditions on most road surfaces. It
does so by monitoring the rotational speed of
each wheel and controlling the brake line
pressure to each wheel during braking. This
prevents the wheels from locking up.
The ABS system has three main units - the
wheel speed sensors, the electronic control unit
and the modulator (hydraulic control unit). The
sensors - one at each wheel - send a variable
voltage signal to the electronic control unit,
which monitors these signals, compares them
to its program and determines whether a wheel
is about to lock up. When a wheel is about to
lock up, the control unit signals the hydraulic
unit to reduce hydraulic pressure (or not
increase it further) at that wheel’s brake caliper.
Pressure modulation is handled by three
electrically-operated solenoid valves - one for
each front wheel and one for the rear wheels -
inside the modulator.
If a problem develops within the system, an
“ABS” warning light will glow on the dashboard.
Sometimes, a visual inspection of the ABS
system can help you locate the problem.
Carefully inspect the ABS wiring harness. Pay
particularly close attention to the harness and
connections near each wheel. Look for signs of
chafing and other damage caused by
incorrectly routed wires. If a wheel sensor
harness is damaged, the sensor should be
replaced (the harness and sensor are integral).
Warning: Do NOT try to repair an
ABS wiring harness. The ABS
system is sensitive to even thesmallest changes in resistance. Repairing
the harness could alter resistance values
and cause the system to malfunction. If the
ABS wiring harness is damaged in any way,
it must be replaced.
Caution: Make sure the ignition is turned
off before unplugging or reattaching any
electrical connections.
Diagnosis and repair
If a dashboard warning light comes on and
stays on while the vehicle is in operation, the
ABS system requires attention. Although
special electronic ABS diagnostic testing tools
are necessary to properly diagnose the system,
you can perform a few preliminary checks
before taking the vehicle to a dealer service
department or other qualified repair workshop.
a) Check the brake fluid level in the master
cylinder reservoir.
b) Verify that all ABS system electrical
connectors in the engine compartment
are plugged in.
c) Check the fuses.
d) Follow the wiring harness to each front
wheel and to the differential sensor and
verify that all connections are secure and
that the wiring is undamaged.
If the above preliminary checks do not
rectify the problem, the vehicle should be
diagnosed by a dealer service department.
Due to the complex nature of this system, all
actual repair work must be done by a dealer
service department or other qualified repair
workshop.
3 Disc brake pads- renewal
2
Warning: Disc brake pads must
be replaced on both front wheels
or both rear wheels at the same
time - never renew the pads on
only one wheel. Also, the dust created by
the brake system may contain asbestos,
which is harmful to your health. Never blow
it out with compressed air and don’t inhale
any of it. An approved filtering mask should
be worn when working on the brakes. Do
not, under any circumstances, use
petroleum-based solvents to clean brake
parts. Use brake system cleaner only!
Note:The following procedure applies to both
the front and rear brake pads.
1Remove the cap from the brake fluid
reservoir and siphon off about two-thirds of
the fluid from the reservoir. Failing to do this
could result in fluid overflowing when the
caliper pistons are pressed into their bores.
2Loosen the wheel nuts, raise the front of the
vehicle and support it securely on axle stands.
3Remove the front wheels. Work on one
brake assembly at a time, using the
assembled brake for reference if necessary.
4Inspect the brake disc (see Section 5).
5Follow the accompanying photos,
beginning with illustration 3.5a, for the pad
removal procedure. Be sure to stay in order
and read the caption under each illustration.
9•2 Braking system
3.5a Before starting, wash down the
caliper and disc with brake cleaner
3.5b Attach a hose to the bleed screw,
open the bleed screw slightly and depress
the piston into the caliper. Tighten the
bleed screw when the piston bottoms
3.5c Remove the caliper mounting bolts
(upper bolt arrowed); use another spanner
to hold the flats of the caliper guide pins
while you back out the caliper bolts3.5d Remove the caliper . . .3.5e . . . and suspend it out of the way
with a piece of wire
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 128 of 227
Refitting
8Place the disc on the hub and refit the disc
retaining screw. Tighten the screw securely.
9Refit the caliper mounting bracket, using a
new safety wire on the mounting bolts.
10Refit the brake pads and caliper (see
Section 3). Tighten all fasteners to the torque
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
11Refit the wheel and wheel nuts, then lower
the vehicle to the ground. Tighten the wheel
nuts to the specified torque (see Chapter 1
Specifications). Depress the brake pedal a
few times to bring the brake pads into contact
with the disc.
12Adjust the handbrake shoes, if necessary.
13Check the operation of the brakes
carefully, if possible before driving the vehicle
on public roads.
6 Master cylinder- removal,
overhaul and refitting
3
Note:Although master cylinder parts and
rebuild kits are available for most models, we
recommend replacing the master cylinder with
a new or remanufactured unit, if possible.
Removal
1The master cylinder is connected to the
brake servo, which is attached to the pedal
box, in front of the bulkhead on the driver’s
side of the engine compartment.
2Remove as much fluid as you can from the
reservoir with a syringe.
3Place rags under the line fittings and
prepare caps or plastic bags to cover the
ends of the lines once they are disconnected.
Caution: Brake fluid will damage paint.
Cover all body parts and be careful not to
spill fluid during this procedure.
4Disconnect the electrical connector for the
low fluid level warning light (see illustration).
5Loosen the brake line fittings at the mastercylinder (see illustration). Use a flare-nut
spanner to prevent rounding off the nuts. Pull
the brake lines away from the master cylinder
slightly and plug the ends to prevent
contamination.
6Remove the nuts attaching the master
cylinder to the servo (see illustration). Pull
the master cylinder off the studs and lift it out
of the engine compartment. Again, be careful
not to spill fluid as this is done.
Overhaul
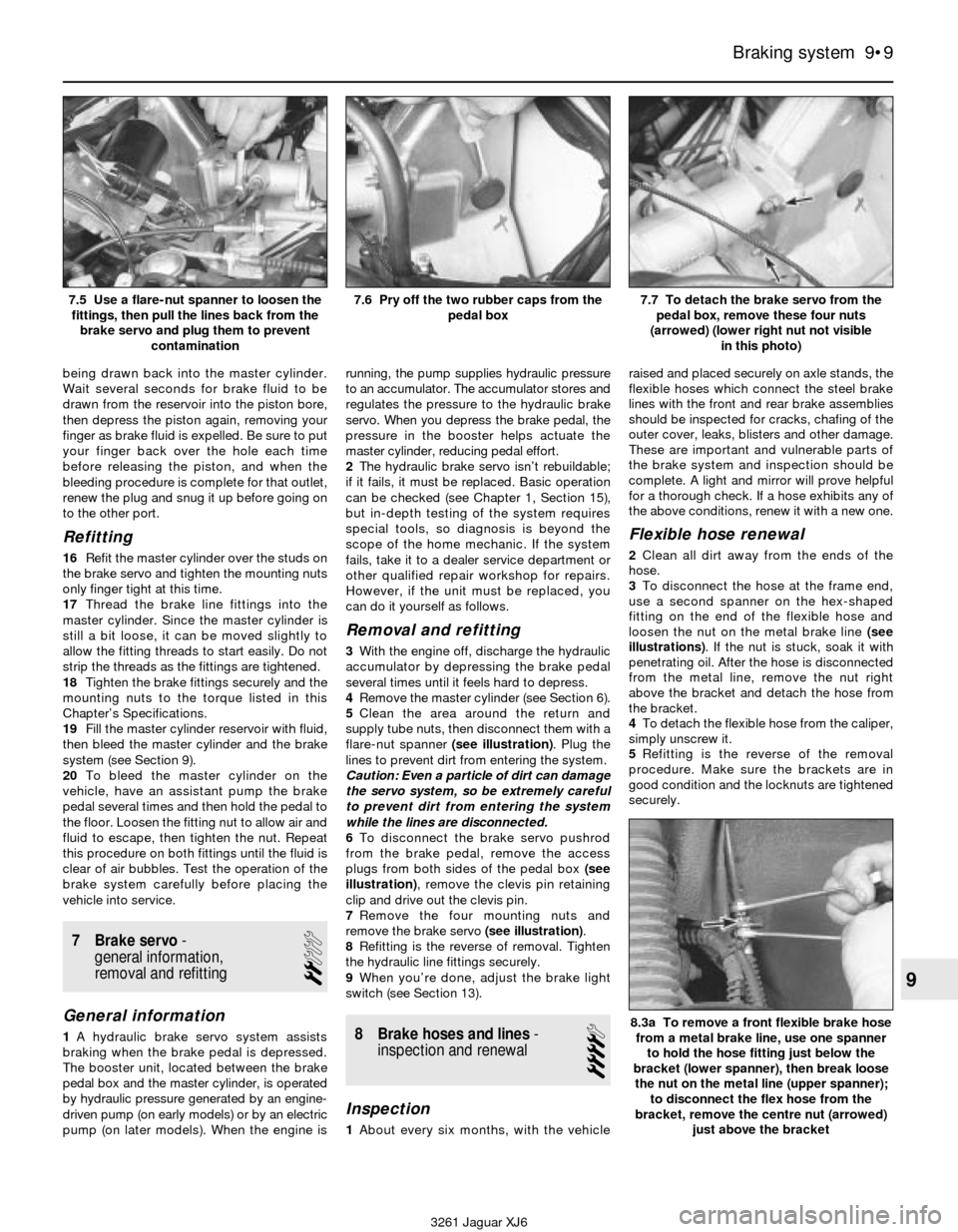
7Follow the accompanying photo sequence,
beginning with illustration 6.7a. Stay in order,don’t skip steps, read each caption and study
the photo carefully.
8Once you have dismantled the master
cylinder, clean everything thoroughly, blow
the parts dry with compressed air and
carefully inspect the secondary piston and the
bore of the master cylinder with a bright light.
If the secondary piston or the master cylinder
bore is damaged or worn, renew the master
cylinder with a new or rebuilt unit.
Bench bleeding procedure
9Before refitting a new or rebuilt master
cylinder it should be bench bled. Because it
9•6 Braking system
6.7a Knock out the roll pin that secures
the reservoir to the master cylinder
6.7b Carefully pry off the reservoir by
inserting a screwdriver between the
reservoir and each grommet; this takes
firm pressure, so don’t slip and damage
the reservoir or the master cylinder
6.7c Remove the grommets, noting the
position of each one
6.6 Remove the two master cylinder
mounting nuts
3261 Jaguar XJ6 6.4 Trace the electrical lead back from the reservoir cap and
disconnect the low fluid level sensor
6.5 Loosen the hydraulic brake line fittings with a flare-nut
spanner to protect the corners of the nuts
Page 131 of 227
being drawn back into the master cylinder.
Wait several seconds for brake fluid to be
drawn from the reservoir into the piston bore,
then depress the piston again, removing your
finger as brake fluid is expelled. Be sure to put
your finger back over the hole each time
before releasing the piston, and when the
bleeding procedure is complete for that outlet,
renew the plug and snug it up before going on
to the other port.
Refitting
16Refit the master cylinder over the studs on
the brake servo and tighten the mounting nuts
only finger tight at this time.
17Thread the brake line fittings into the
master cylinder. Since the master cylinder is
still a bit loose, it can be moved slightly to
allow the fitting threads to start easily. Do not
strip the threads as the fittings are tightened.
18Tighten the brake fittings securely and the
mounting nuts to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications.
19Fill the master cylinder reservoir with fluid,
then bleed the master cylinder and the brake
system (see Section 9).
20To bleed the master cylinder on the
vehicle, have an assistant pump the brake
pedal several times and then hold the pedal to
the floor. Loosen the fitting nut to allow air and
fluid to escape, then tighten the nut. Repeat
this procedure on both fittings until the fluid is
clear of air bubbles. Test the operation of the
brake system carefully before placing the
vehicle into service.
7 Brake servo-
general information,
removal and refitting
2
General information
1A hydraulic brake servo system assists
braking when the brake pedal is depressed.
The booster unit, located between the brake
pedal box and the master cylinder, is operated
by hydraulic pressure generated by an engine-
driven pump (on early models) or by an electric
pump (on later models). When the engine isrunning, the pump supplies hydraulic pressure
to an accumulator. The accumulator stores and
regulates the pressure to the hydraulic brake
servo. When you depress the brake pedal, the
pressure in the booster helps actuate the
master cylinder, reducing pedal effort.
2The hydraulic brake servo isn’t rebuildable;
if it fails, it must be replaced. Basic operation
can be checked (see Chapter 1, Section 15),
but in-depth testing of the system requires
special tools, so diagnosis is beyond the
scope of the home mechanic. If the system
fails, take it to a dealer service department or
other qualified repair workshop for repairs.
However, if the unit must be replaced, you
can do it yourself as follows.
Removal and refitting
3With the engine off, discharge the hydraulic
accumulator by depressing the brake pedal
several times until it feels hard to depress.
4Remove the master cylinder (see Section 6).
5Clean the area around the return and
supply tube nuts, then disconnect them with a
flare-nut spanner (see illustration). Plug the
lines to prevent dirt from entering the system.
Caution: Even a particle of dirt can damage
the servo system, so be extremely careful
to prevent dirt from entering the system
while the lines are disconnected.
6To disconnect the brake servo pushrod
from the brake pedal, remove the access
plugs from both sides of the pedal box (see
illustration), remove the clevis pin retaining
clip and drive out the clevis pin.
7Remove the four mounting nuts and
remove the brake servo (see illustration).
8Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the hydraulic line fittings securely.
9When you’re done, adjust the brake light
switch (see Section 13).
8 Brake hoses and lines-
inspection and renewal
4
Inspection
1About every six months, with the vehicleraised and placed securely on axle stands, the
flexible hoses which connect the steel brake
lines with the front and rear brake assemblies
should be inspected for cracks, chafing of the
outer cover, leaks, blisters and other damage.
These are important and vulnerable parts of
the brake system and inspection should be
complete. A light and mirror will prove helpful
for a thorough check. If a hose exhibits any of
the above conditions, renew it with a new one.
Flexible hose renewal
2Clean all dirt away from the ends of the
hose.
3To disconnect the hose at the frame end,
use a second spanner on the hex-shaped
fitting on the end of the flexible hose and
loosen the nut on the metal brake line (see
illustrations). If the nut is stuck, soak it with
penetrating oil. After the hose is disconnected
from the metal line, remove the nut right
above the bracket and detach the hose from
the bracket.
4To detach the flexible hose from the caliper,
simply unscrew it.
5Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Make sure the brackets are in
good condition and the locknuts are tightened
securely.
Braking system 9•9
9
7.5 Use a flare-nut spanner to loosen the
fittings, then pull the lines back from the
brake servo and plug them to prevent
contamination7.6 Pry off the two rubber caps from the
pedal box7.7 To detach the brake servo from the
pedal box, remove these four nuts
(arrowed) (lower right nut not visible
in this photo)
8.3a To remove a front flexible brake hose
from a metal brake line, use one spanner
to hold the hose fitting just below the
bracket (lower spanner), then break loose
the nut on the metal line (upper spanner);
to disconnect the flex hose from the
bracket, remove the centre nut (arrowed)
just above the bracket
3261 Jaguar XJ6