steering JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1997, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.GPages: 227, PDF Size: 7.2 MB
Page 19 of 227

The maintenance intervals in this manual are provided with the
assumption that you, not the dealer, will be carrying out the work.
These are the minimum maintenance intervals recommended by us for
vehicles driven daily. If you wish to keep your vehicle in peak condition
at all times, you may wish to perform some of these procedures moreoften. We encourage frequent maintenance, because it enhances the
efficiency, performance and resale value of your vehicle.
When the vehicle is new, it should be serviced by a factory-
authorised dealer service department, in order to preserve the factory
warranty.
Maintenance schedule 1•3
1
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Weekly, or every 250 miles (400 km)
m mCarry out all the operations given in “Weekly
checks”at the start of this manual.
m
mRenew the fuel filter (Section 18)
m mCheck the ignition system components (Section 19)
m mCheck the crankcase ventilation system
(Section 20)
m mCheck the condition and tension of the drivebelt(s)
(Section 21)
m mCheck the front wheel bearing adjustment and
repack with grease (Section 22)
m mCheck the propshaft fasteners are tightened to the
specified torque (Section 23)
m mCheck the front wheel alignment (Section 24)
m mCheck the headlight beam alignment (Section 25)
Every 7500 miles (12 000 km)
or 6 months, whichever comes first
In addition to the operations listed previously, carry out the following:
m mRenew the engine oil and filter (Section 3)
m mCheck the spark plugs (Section 4)
m mCheck the power hydraulics fluid level (Section 5)
m mCheck the battery (Section 6)
m mCheck all pipes and hoses for signs of damage or
leakage (Section 7)
m mCheck the automatic transmission fluid level
(Section 8)
m mCheck the differential oil level (Section 9)
m mCheck the condition of the exhaust system
(Section 10)
m mCheck the brake pads and discs for wear and
adjust the handbrake (Section 11)
m mCheck the steering and suspension components
for wear or damage and check the wheel nuts are
tightened to the correct torque (Section 12)
m mCheck the condition of the seat belts (Section 13)
m mLubricate all locks and hinges, and exposed cables
(Section 14)
m mCarry out a road test (Section 15)
Every 2 years, regardless of mileage
m
mRenew the coolant (Section 30)
Every 60 000 miles (96 000 km)
In addition to the operations listed previously, carry out the following:
m
mCheck the handbrake shoes for wear (Section 29)
Every 30 000 miles (48 000 km)
or 2 years, whichever comes first
In addition to the operations listed previously, carry out the following:
m mRenew the automatic transmission fluid and filter
(Section 26)
m mRenew the differential oil (Section 27)
m mRenew the brake fluid (Section 28)
Every 15 000 miles (24 000 km)
or 12 months, whichever comes first
In addition to the operations listed previously, carry out the following:
m mRenew the spark plugs (Section 16)
m mRenew the air cleaner element (Section 17)
Page 20 of 227
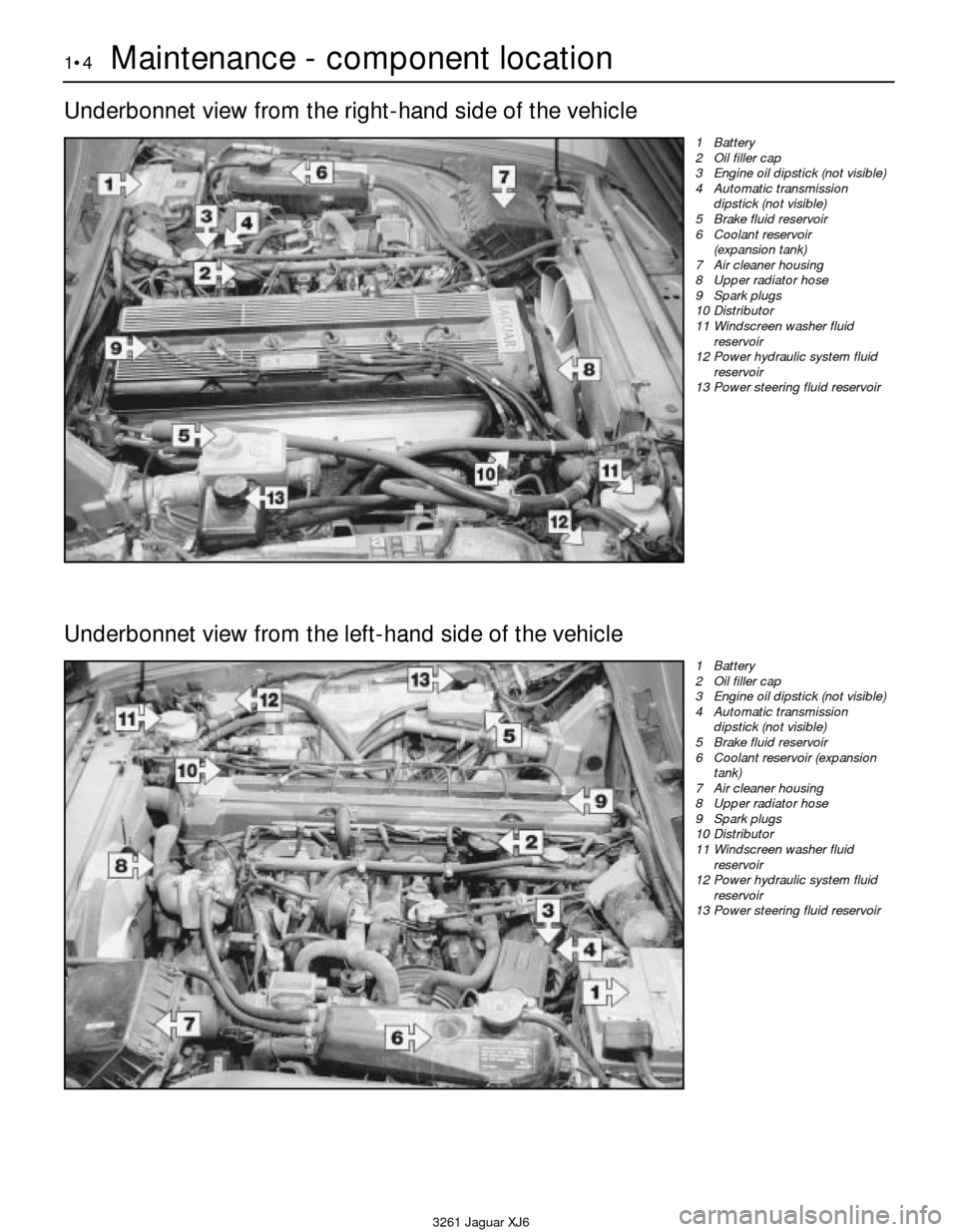
1•4Maintenance - component location
3261 Jaguar XJ6
1 Battery
2 Oil filler cap
3 Engine oil dipstick (not visible)
4 Automatic transmission
dipstick (not visible)
5 Brake fluid reservoir
6 Coolant reservoir
(expansion tank)
7 Air cleaner housing
8 Upper radiator hose
9 Spark plugs
10 Distributor
11 Windscreen washer fluid
reservoir
12 Power hydraulic system fluid
reservoir
13 Power steering fluid reservoir
Underbonnet view from the left-hand side of the vehicle Underbonnet view from the right-hand side of the vehicle
1 Battery
2 Oil filler cap
3 Engine oil dipstick (not visible)
4 Automatic transmission
dipstick (not visible)
5 Brake fluid reservoir
6 Coolant reservoir (expansion
tank)
7 Air cleaner housing
8 Upper radiator hose
9 Spark plugs
10 Distributor
11 Windscreen washer fluid
reservoir
12 Power hydraulic system fluid
reservoir
13 Power steering fluid reservoir
Page 21 of 227
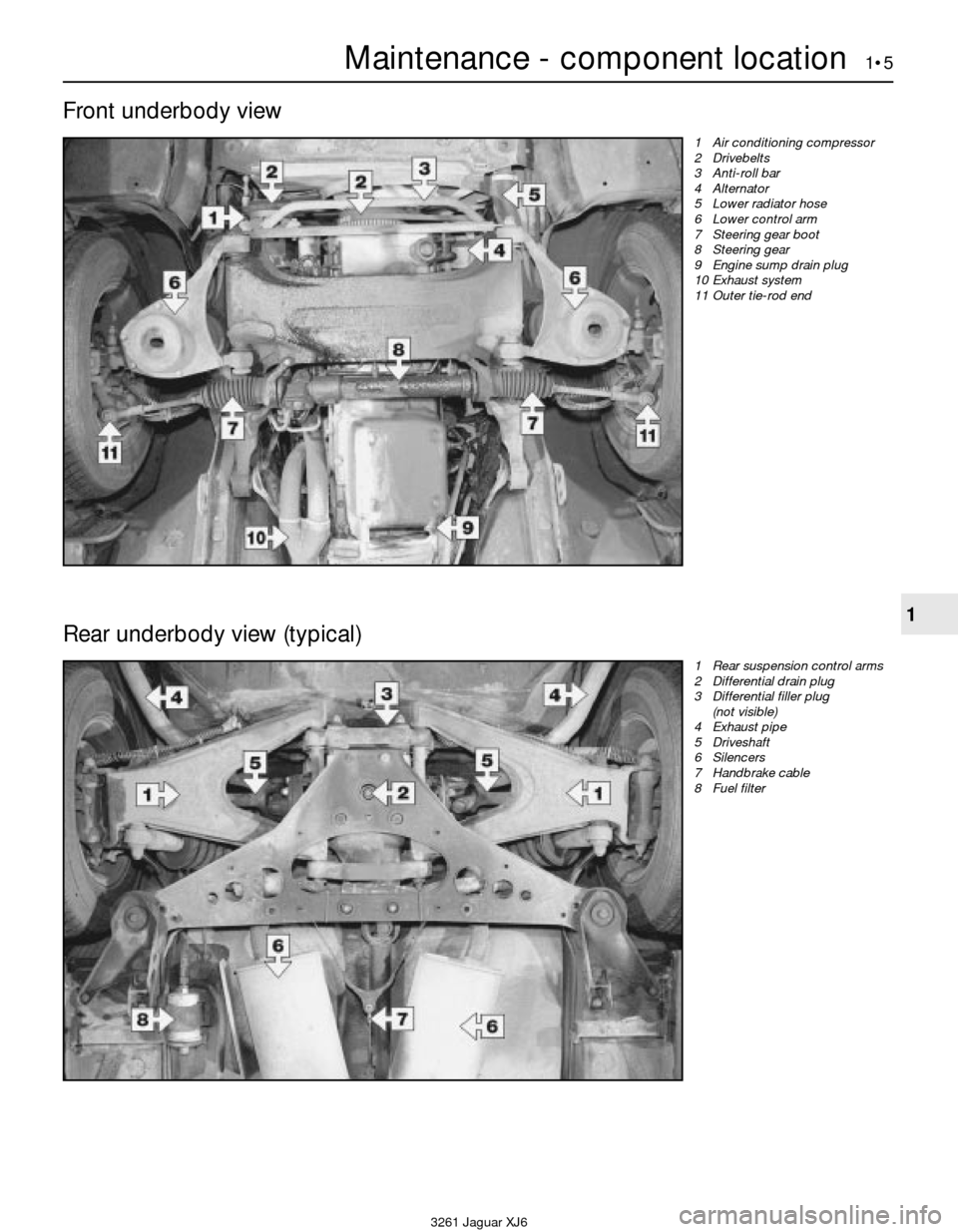
Maintenance - component location 1•5
1
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Front underbody view
1 Air conditioning compressor
2 Drivebelts
3 Anti-roll bar
4 Alternator
5 Lower radiator hose
6 Lower control arm
7 Steering gear boot
8 Steering gear
9 Engine sump drain plug
10 Exhaust system
11 Outer tie-rod end
Rear underbody view (typical)
1 Rear suspension control arms
2 Differential drain plug
3 Differential filler plug
(not visible)
4 Exhaust pipe
5 Driveshaft
6 Silencers
7 Handbrake cable
8 Fuel filter
Page 22 of 227
1 General information
1This Chapter is designed to help the home
mechanic maintain his/her vehicle for safety,
economy, long life and peak performance.
2The Chapter contains a master
maintenance schedule, followed by Sections
dealing specifically with each task in the
schedule. Visual checks, adjustments,
component renewal and other helpful items
are included. Refer to the accompanying
illustrations of the engine compartment and
the underside of the vehicle for the locations
of the various components.
3Servicing your vehicle in accordance with
the mileage/time maintenance schedule and
the following Sections will provide a planned
maintenance programme, which should result
in a long and reliable service life. This is a
comprehensive plan, so maintaining some
items but not others at the specified service
intervals, will not produce the same results.
4As you service your vehicle, you will
discover that many of the procedures can -
and should - be grouped together, because of
the particular procedure being performed, or
because of the proximity of two otherwise-
unrelated components to one another. For
example, if the vehicle is raised for any
reason, the exhaust can be inspected at the
same time as the suspension and steering
components.
5The first step in this maintenance
programme is to prepare yourself before the
actual work begins. Read through all theSections relevant to the work to be carried out,
then make a list and gather all the parts and
tools required. If a problem is encountered,
seek advice from a parts specialist, or a dealer
service department.
2 Intensive maintenance
1If, from the time the vehicle is new, the
routine maintenance schedule is followed
closely, and frequent checks are made of fluid
levels and high-wear items, as suggested
throughout this manual, the engine will be
kept in relatively good running condition, and
the need for additional work will be minimised.
2It is possible that there will be times when
the engine is running poorly due to the lack of
regular maintenance. This is even more likely
if a used vehicle, which has not received
regular and frequent maintenance checks, is
purchased. In such cases, additional work
may need to be carried out, outside of the
regular maintenance intervals.
3If engine wear is suspected, a compression
test (refer to Chapter 2) will provide valuable
information regarding the overall performance
of the main internal components. Such a test
can be used as a basis to decide on the extent
of the work to be carried out. If, for example, a
compression test indicates serious internal
engine wear, conventional maintenance as
described in this Chapter will not greatly
improve the performance of the engine, and
may prove a waste of time and money, unless
extensive overhaul work is carried out first.4The following series of operations are those
which are most often required to improve the
performance of a generally poor-running
engine:
Primary operations
a) Clean, inspect and test the battery
(Section 6).
b) Check all the engine-related fluids (refer
to “Weekly checks”).
c) Check the condition and tension of the
auxiliary drivebelt (Section 21).
d) Renew the spark plugs (Section 16).
e) Inspect the distributor cap and rotor arm
(Section 19).
f) Check the condition of the air filter, and
renew if necessary (Section 17).
g) Renew the fuel filter (Section 18).
h) Check the condition of all hoses, and
check for fluid leaks (Section 7).
i) Check the exhaust gas emissions (see
Chapter 6).
5If the above operations do not prove fully
effective, carry out the following secondary
operations:
Secondary operations
All items listed under “Primary operations”,
plus the following:
a) Check the charging system (refer to
Chapter 5).
b) Check the ignition system (refer to
Chapter 5).
c) Check the fuel system (refer to Chapter 4).
d) Renew the distributor cap and rotor arm
(Section 19).
e) Renew the ignition HT leads (Section 19).
1•6Maintenance procedures
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Every 7500 miles (12 000 km) or 6 months
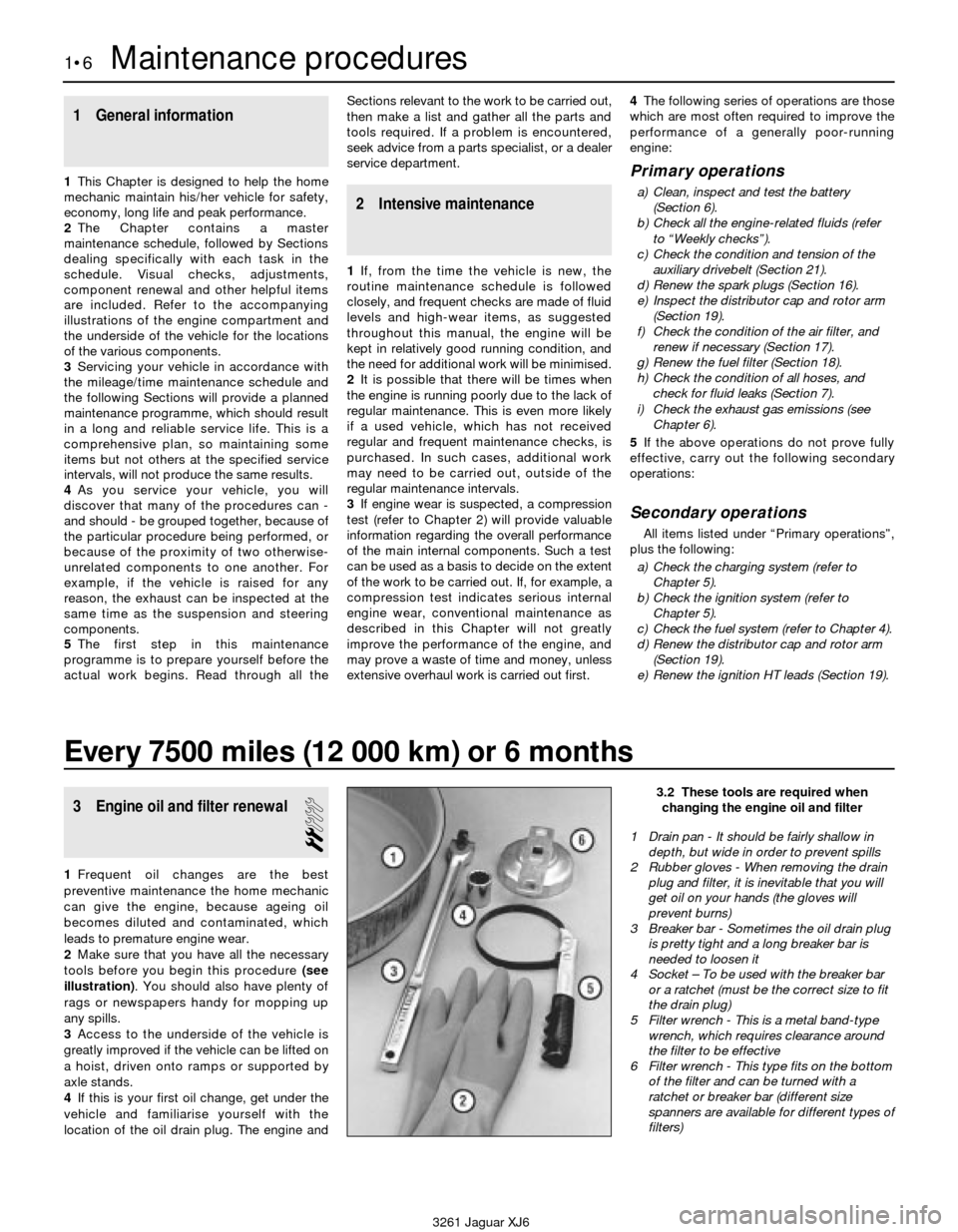
3 Engine oil and filter renewal
2
1Frequent oil changes are the best
preventive maintenance the home mechanic
can give the engine, because ageing oil
becomes diluted and contaminated, which
leads to premature engine wear.
2Make sure that you have all the necessary
tools before you begin this procedure (see
illustration). You should also have plenty of
rags or newspapers handy for mopping up
any spills.
3Access to the underside of the vehicle is
greatly improved if the vehicle can be lifted on
a hoist, driven onto ramps or supported by
axle stands.
4If this is your first oil change, get under the
vehicle and familiarise yourself with the
location of the oil drain plug. The engine and
3.2 These tools are required when
changing the engine oil and filter
1 Drain pan - It should be fairly shallow in
depth, but wide in order to prevent spills
2 Rubber gloves - When removing the drain
plug and filter, it is inevitable that you will
get oil on your hands (the gloves will
prevent burns)
3 Breaker bar - Sometimes the oil drain plug
is pretty tight and a long breaker bar is
needed to loosen it
4 Socket – To be used with the breaker bar
or a ratchet (must be the correct size to fit
the drain plug)
5 Filter wrench - This is a metal band-type
wrench, which requires clearance around
the filter to be effective
6 Filter wrench - This type fits on the bottom
of the filter and can be turned with a
ratchet or breaker bar (different size
spanners are available for different types of
filters)
Page 25 of 227
5 Power hydraulic system
fluid level check
1
Caution: Use only Castrol or Jaguar
hydraulic system mineral oil (HSMO) in the
power hydraulic system (available at
Jaguar dealer service departments).
1The power hydraulic system controls the ride
levelling and the brake servo systems. The
fluid reservoir also supplies the power
steering system on some models. The level
of the fluid should be carefully maintained. Low
fluid levels can adversely affect the riding and
braking capabilities of your vehicle. The power
hydraulic system fluid reservoir is located on
the right inner wing of the engine compartment.
1988 and 1989 models
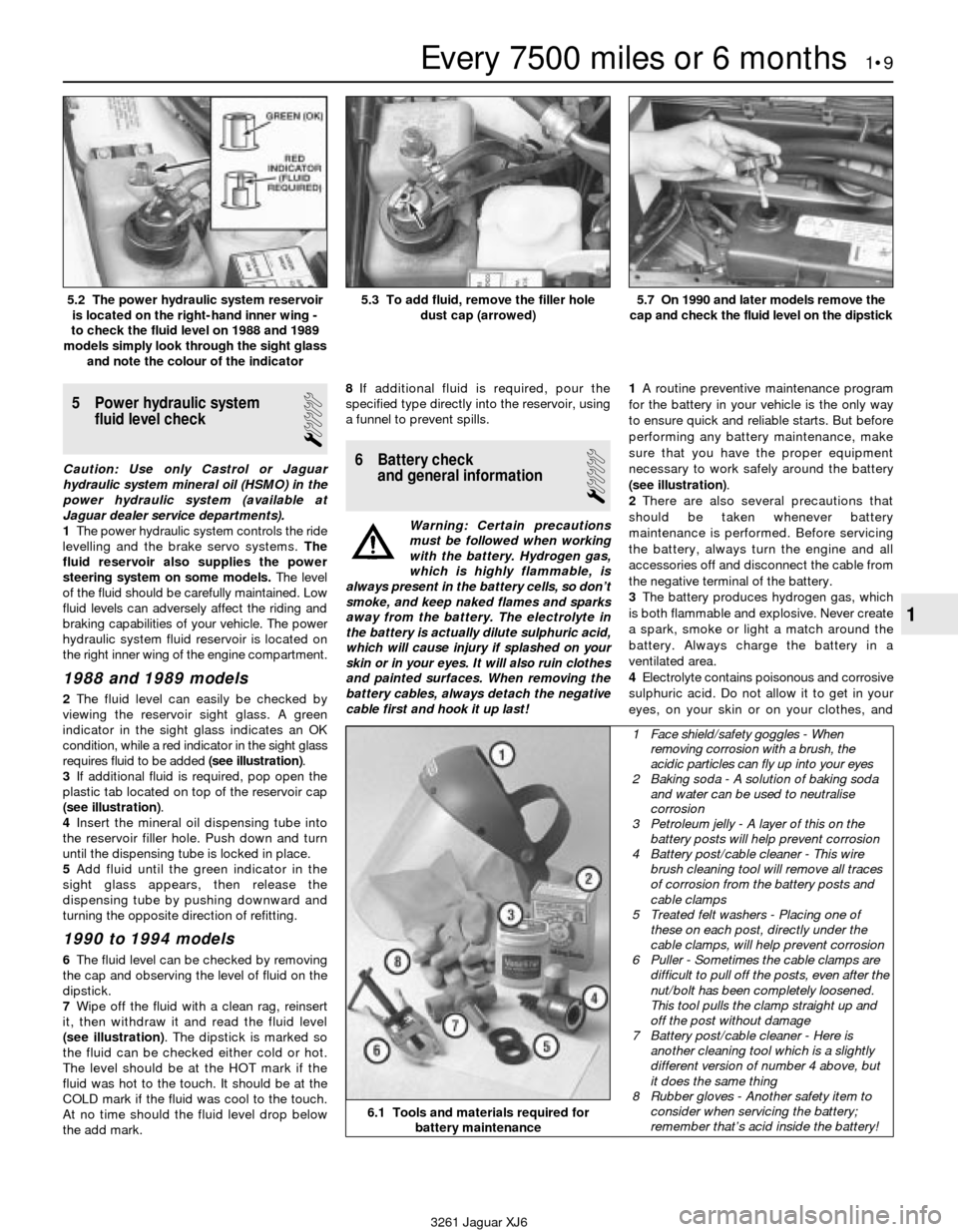
2The fluid level can easily be checked by
viewing the reservoir sight glass. A green
indicator in the sight glass indicates an OK
condition, while a red indicator in the sight glass
requires fluid to be added (see illustration).
3If additional fluid is required, pop open the
plastic tab located on top of the reservoir cap
(see illustration).
4Insert the mineral oil dispensing tube into
the reservoir filler hole. Push down and turn
until the dispensing tube is locked in place.
5Add fluid until the green indicator in the
sight glass appears, then release the
dispensing tube by pushing downward and
turning the opposite direction of refitting.
1990 to 1994 models
6The fluid level can be checked by removing
the cap and observing the level of fluid on the
dipstick.
7Wipe off the fluid with a clean rag, reinsert
it, then withdraw it and read the fluid level
(see illustration). The dipstick is marked so
the fluid can be checked either cold or hot.
The level should be at the HOT mark if the
fluid was hot to the touch. It should be at the
COLD mark if the fluid was cool to the touch.
At no time should the fluid level drop below
the add mark.8If additional fluid is required, pour the
specified type directly into the reservoir, using
a funnel to prevent spills.
6 Battery check
and general information
1
Warning: Certain precautions
must be followed when working
with the battery. Hydrogen gas,
which is highly flammable, is
always present in the battery cells, so don’t
smoke, and keep naked flames and sparks
away from the battery. The electrolyte in
the battery is actually dilute sulphuric acid,
which will cause injury if splashed on your
skin or in your eyes. It will also ruin clothes
and painted surfaces. When removing the
battery cables, always detach the negative
cable first and hook it up last!1A routine preventive maintenance program
for the battery in your vehicle is the only way
to ensure quick and reliable starts. But before
performing any battery maintenance, make
sure that you have the proper equipment
necessary to work safely around the battery
(see illustration).
2There are also several precautions that
should be taken whenever battery
maintenance is performed. Before servicing
the battery, always turn the engine and all
accessories off and disconnect the cable from
the negative terminal of the battery.
3The battery produces hydrogen gas, which
is both flammable and explosive. Never create
a spark, smoke or light a match around the
battery. Always charge the battery in a
ventilated area.
4Electrolyte contains poisonous and corrosive
sulphuric acid. Do not allow it to get in your
eyes, on your skin or on your clothes, and
Every 7500 miles or 6 months 1•9
1
5.2 The power hydraulic system reservoir
is located on the right-hand inner wing -
to check the fluid level on 1988 and 1989
models simply look through the sight glass
and note the colour of the indicator5.3 To add fluid, remove the filler hole
dust cap (arrowed)5.7 On 1990 and later models remove the
cap and check the fluid level on the dipstick
6.1 Tools and materials required for
battery maintenance
1 Face shield/safety goggles - When
removing corrosion with a brush, the
acidic particles can fly up into your eyes
2 Baking soda - A solution of baking soda
and water can be used to neutralise
corrosion
3 Petroleum jelly - A layer of this on the
battery posts will help prevent corrosion
4 Battery post/cable cleaner - This wire
brush cleaning tool will remove all traces
of corrosion from the battery posts and
cable clamps
5 Treated felt washers - Placing one of
these on each post, directly under the
cable clamps, will help prevent corrosion
6 Puller - Sometimes the cable clamps are
difficult to pull off the posts, even after the
nut/bolt has been completely loosened.
This tool pulls the clamp straight up and
off the post without damage
7 Battery post/cable cleaner - Here is
another cleaning tool which is a slightly
different version of number 4 above, but
it does the same thing
8 Rubber gloves - Another safety item to
consider when servicing the battery;
remember that’s acid inside the battery!
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 27 of 227
leak be found, renew the offending gasket or
oil seal by referring to the appropriate
Chapters in this manual.
2Also check the security and condition of all
the engine-related pipes and hoses. Ensure
that all cable ties or securing clips are in place
and in good condition. Clips which are broken
or missing can lead to chafing of the hoses,
pipes or wiring, which could cause more
serious problems in the future.
3Carefully check the radiator hoses and
heater hoses along their entire length. Renew
any hose which is cracked, swollen or
deteriorated. Cracks will show up better if
the hose is squeezed. Pay close attention
to the hose clips that secure the hoses to the
cooling system components. Hose clips can
pinch and puncture hoses, resulting in cooling
system leaks.
4Inspect all the cooling system components
(hoses, joint faces etc.) for leaks. A leak in the
cooling system will usually show up as white-
or rust-coloured deposits on the area
adjoining the leak. Where any problems of this
nature are found on system components,
renew the component or gasket with
reference to Chapter 3.
5From within the engine compartment,
check the security of all fuel hose attachments
and pipe unions, and inspect the fuel hoses
and vacuum hoses for kinks, chafing and
deterioration.
6Also check the condition of the power
steering fluid hoses and pipes.
8 Automatic transmission
fluid level check
1
1The level of the automatic transmission fluid
should be carefully maintained. Low fluid level
can lead to slipping or loss of drive, while
overfilling can cause foaming, loss of fluid and
transmission damage.
2The transmission fluid level should only be
checked when the transmission is at its
normal operating temperature.
Caution: If the vehicle has just been driven
for a long time at high speed or in city
traffic in hot weather, or if it has been
pulling a trailer, an accurate fluid level
reading cannot be obtained. Allow the fluid
to cool down for about 30 minutes.
3If the vehicle has not been driven, park the
vehicle on level ground, set the handbrake,
then start the engine and bring it to operating
temperature. While the engine is idling,
depress the brake pedal and move the
selector lever through all the gear ranges,
beginning and ending in Park.
4With the engine still idling, remove the
dipstick from its tube (see illustration). Check
the level of the fluid on the dipstick (see
illustration)and note its condition.
5Wipe the fluid from the dipstick with a clean
rag and reinsert it back into the filler tube until
the cap seats.6Pull the dipstick out again and note the fluid
level. If the transmission is cold, the level
should be in the COLD or COOL range on the
dipstick. If it is hot, the fluid level should be in
the HOT range. If the level is at the low side of
either range, add the specified transmission
fluid through the dipstick tube with a funnel.
7Add just enough of the recommended fluid
to fill the transmission to the proper level. It
takes about one pint to raise the level from the
low mark to the high mark when the fluid is
hot, so add the fluid a little at a time and keep
checking the level until it is correct.
8The condition of the fluid should also be
checked along with the level. If the fluid at the
end of the dipstick is black or a dark reddish
brown colour, or if it emits a burned smell, the
fluid should be changed (see Section 26). If
you are in doubt about the condition of the
fluid, purchase some new fluid and compare
the two for colour and smell.9 Differential oil level check
1
1The differential has a check/fill plug which
must be removed to check the lubricant level.
If the vehicle is raised to gain access to the
plug, be sure to support it safely on axle
stands - DO NOT crawl under the vehicle
when it’s supported only by the jack!2Remove the lubricant check/fill plug from
the differential (see illustration).Use a
3/8-inch drive ratchet and a short extension to
unscrew the plug.
3Use your little finger as a dipstick to make
sure the lubricant level is even with the
bottom of the plug hole. If not, use a syringe
or squeeze bottle to add the recommended
lubricant until it just starts to run out of the
opening.
4Refit the plug and tighten it securely.
10 Exhaust system check
1
1With the engine cold (at least three hours
after the vehicle has been driven), check the
complete exhaust system from its starting
point at the engine to the end of the tailpipe.
This should be done on a hoist where
unrestricted access is available.
2Check the pipes and connections for
evidence of leaks, severe corrosion or
damage. Make sure that all brackets and
hangers are in good condition and tight (see
illustration).
3At the same time, inspect the underside of
the body for holes, corrosion, open seams,
etc. which may allow exhaust gases to enter
the passenger compartment. Seal all body
openings with silicone or body putty.
4Rattles and other noises can often be
traced to the exhaust system, especially the
mounts and hangers. Try to move the pipes,
Every 7500 miles or 6 months 1•11
1
9.2 The differential check/fill plug is
located on the rear of the differential
housing - place your finger in the filler plug
hole to make sure the lubricant level is
even with the bottom of the hole
10.2 Check the exhaust system hangers
(arrowed) for damage and cracks
3261 Jaguar XJ6
8.4a The automatic transmission dipstick
(arrowed) is located in a tube which
extends forward from the transmission
8.4b Check the automatic transmission
fluid with the engine idling at operating
temperature and the gear selector in Park,
then add fluid to bring the level to the
upper mark
Page 28 of 227
silencer and catalytic converter. If the
components can come in contact with the
body or suspension parts, secure the exhaust
system with new mounts.
5Check the running condition of the engine
by inspecting inside the end of the tailpipe.
The exhaust deposits here are an indication of
engine state-of-tune. If the pipe is black and
sooty or coated with white deposits, the
engine is in need of a tune-up, including a
thorough fuel system inspection.
11 Braking system - general
check and adjustment
2
Warning: The dust created by
the brake system may contain
asbestos, which is harmful to
your health. Never blow it out
with compressed air and don’t inhale any
of it. An approved filtering mask should be
worn when working on the brakes. Do not,
under any circumstances, use petroleum-
based solvents to clean brake parts. Use
brake system cleaner only! Try to use non-
asbestos replacement parts whenever
possible.
Note: For detailed photographs of the brake
system, refer to Chapter 9.
1In addition to the specified intervals, the
brakes should be inspected every time the
wheels are removed or whenever a defect is
suspected. Any of the following symptoms
could indicate a potential brake system
defect: The vehicle pulls to one side when the
brake pedal is depressed; the brakes make
squealing or dragging noises when applied;
brake pedal travel is excessive; the pedal
pulsates; brake fluid leaks, usually onto the
inside of the tyre or wheel.
2The disc brakes have built-in electrical wear
indicators which cause a warning lamp to
illuminate on the instrument panel when
they’re worn to the renewal point. When the
warning light comes on, replace the pads
immediately or expensive damage to the
discs can result.
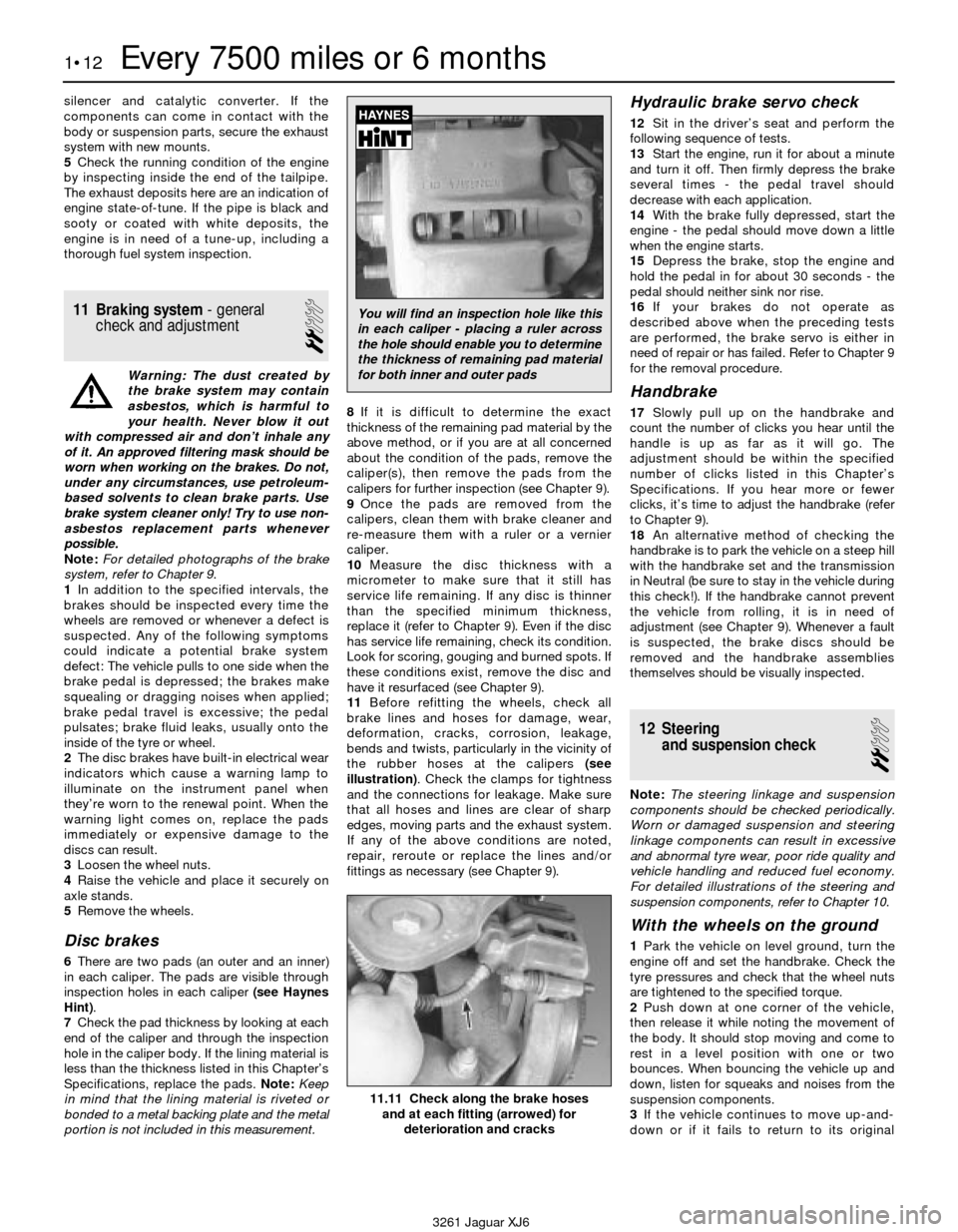
3Loosen the wheel nuts.
4Raise the vehicle and place it securely on
axle stands.
5Remove the wheels.
Disc brakes
6There are two pads (an outer and an inner)
in each caliper. The pads are visible through
inspection holes in each caliper (see Haynes
Hint).
7Check the pad thickness by looking at each
end of the caliper and through the inspection
hole in the caliper body. If the lining material is
less than the thickness listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications, replace the pads. Note:Keep
in mind that the lining material is riveted or
bonded to a metal backing plate and the metal
portion is not included in this measurement.8If it is difficult to determine the exact
thickness of the remaining pad material by the
above method, or if you are at all concerned
about the condition of the pads, remove the
caliper(s), then remove the pads from the
calipers for further inspection (see Chapter 9).
9Once the pads are removed from the
calipers, clean them with brake cleaner and
re-measure them with a ruler or a vernier
caliper.
10Measure the disc thickness with a
micrometer to make sure that it still has
service life remaining. If any disc is thinner
than the specified minimum thickness,
replace it (refer to Chapter 9). Even if the disc
has service life remaining, check its condition.
Look for scoring, gouging and burned spots. If
these conditions exist, remove the disc and
have it resurfaced (see Chapter 9).
11Before refitting the wheels, check all
brake lines and hoses for damage, wear,
deformation, cracks, corrosion, leakage,
bends and twists, particularly in the vicinity of
the rubber hoses at the calipers (see
illustration). Check the clamps for tightness
and the connections for leakage. Make sure
that all hoses and lines are clear of sharp
edges, moving parts and the exhaust system.
If any of the above conditions are noted,
repair, reroute or replace the lines and/or
fittings as necessary (see Chapter 9).
Hydraulic brake servo check
12Sit in the driver’s seat and perform the
following sequence of tests.
13Start the engine, run it for about a minute
and turn it off. Then firmly depress the brake
several times - the pedal travel should
decrease with each application.
14With the brake fully depressed, start the
engine - the pedal should move down a little
when the engine starts.
15Depress the brake, stop the engine and
hold the pedal in for about 30 seconds - the
pedal should neither sink nor rise.
16If your brakes do not operate as
described above when the preceding tests
are performed, the brake servo is either in
need of repair or has failed. Refer to Chapter 9
for the removal procedure.
Handbrake
17Slowly pull up on the handbrake and
count the number of clicks you hear until the
handle is up as far as it will go. The
adjustment should be within the specified
number of clicks listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications. If you hear more or fewer
clicks, it’s time to adjust the handbrake (refer
to Chapter 9).
18An alternative method of checking the
handbrake is to park the vehicle on a steep hill
with the handbrake set and the transmission
in Neutral (be sure to stay in the vehicle during
this check!). If the handbrake cannot prevent
the vehicle from rolling, it is in need of
adjustment (see Chapter 9). Whenever a fault
is suspected, the brake discs should be
removed and the handbrake assemblies
themselves should be visually inspected.
12 Steering
and suspension check
2
Note: The steering linkage and suspension
components should be checked periodically.
Worn or damaged suspension and steering
linkage components can result in excessive
and abnormal tyre wear, poor ride quality and
vehicle handling and reduced fuel economy.
For detailed illustrations of the steering and
suspension components, refer to Chapter 10.
With the wheels on the ground
1Park the vehicle on level ground, turn the
engine off and set the handbrake. Check the
tyre pressures and check that the wheel nuts
are tightened to the specified torque.
2Push down at one corner of the vehicle,
then release it while noting the movement of
the body. It should stop moving and come to
rest in a level position with one or two
bounces. When bouncing the vehicle up and
down, listen for squeaks and noises from the
suspension components.
3If the vehicle continues to move up-and-
down or if it fails to return to its original
1•12Every 7500 miles or 6 months
11.11 Check along the brake hoses
and at each fitting (arrowed) for
deterioration and cracks
3261 Jaguar XJ6
You will find an inspection hole like this
in each caliper - placing a ruler across
the hole should enable you to determine
the thickness of remaining pad material
for both inner and outer pads
Page 29 of 227
position, a worn or weak shock absorber is
probably the reason.
4Repeat the above check at each of the
three remaining corners of the vehicle.
Under the vehicle
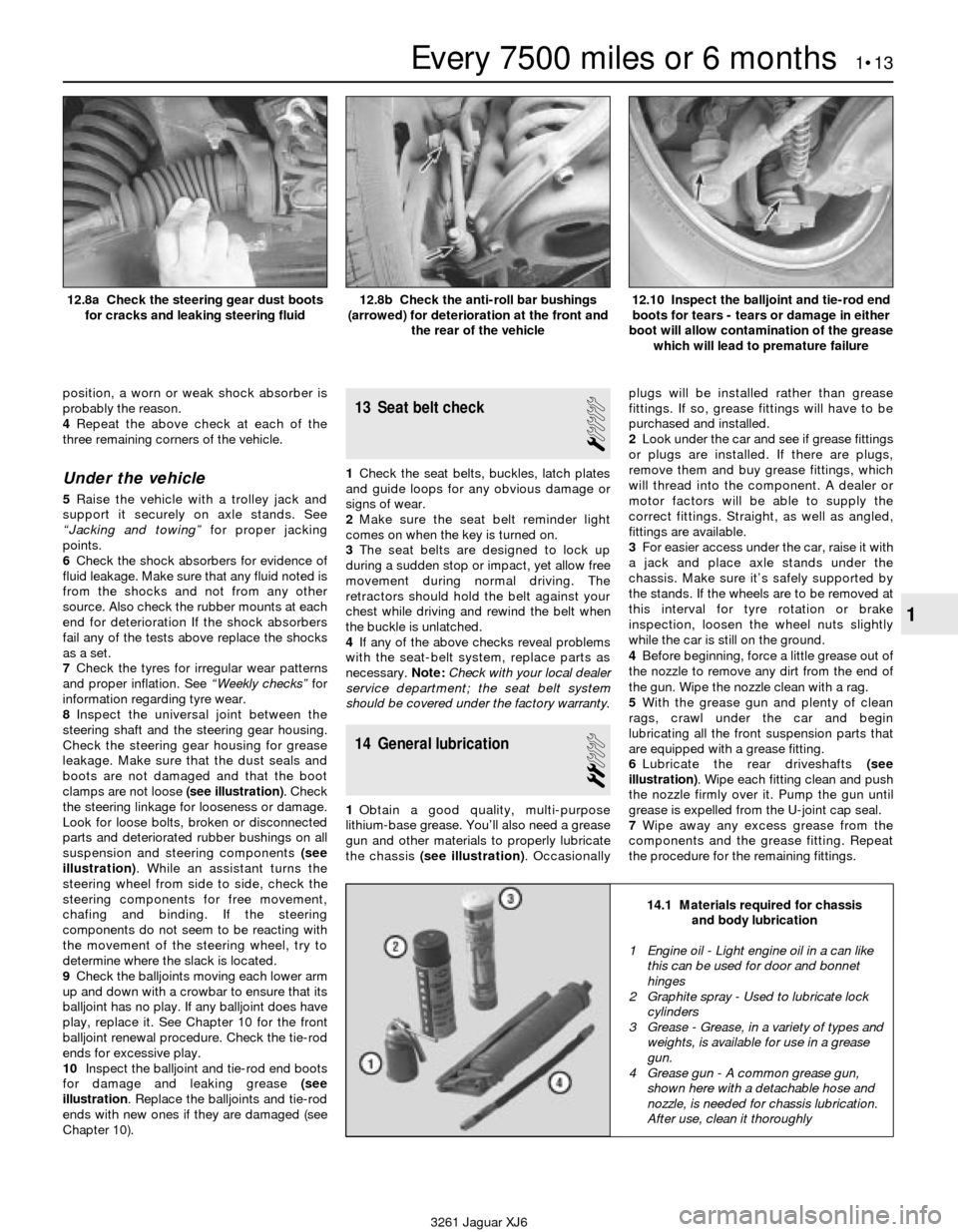
5Raise the vehicle with a trolley jack and
support it securely on axle stands. See
“Jacking and towing”for proper jacking
points.
6Check the shock absorbers for evidence of
fluid leakage. Make sure that any fluid noted is
from the shocks and not from any other
source. Also check the rubber mounts at each
end for deterioration If the shock absorbers
fail any of the tests above replace the shocks
as a set.
7Check the tyres for irregular wear patterns
and proper inflation. See “Weekly checks”for
information regarding tyre wear.
8Inspect the universal joint between the
steering shaft and the steering gear housing.
Check the steering gear housing for grease
leakage. Make sure that the dust seals and
boots are not damaged and that the boot
clamps are not loose (see illustration). Check
the steering linkage for looseness or damage.
Look for loose bolts, broken or disconnected
parts and deteriorated rubber bushings on all
suspension and steering components (see
illustration). While an assistant turns the
steering wheel from side to side, check the
steering components for free movement,
chafing and binding. If the steering
components do not seem to be reacting with
the movement of the steering wheel, try to
determine where the slack is located.
9Check the balljoints moving each lower arm
up and down with a crowbar to ensure that its
balljoint has no play. If any balljoint does have
play, replace it. See Chapter 10 for the front
balljoint renewal procedure. Check the tie-rod
ends for excessive play.
10Inspect the balljoint and tie-rod end boots
for damage and leaking grease (see
illustration. Replace the balljoints and tie-rod
ends with new ones if they are damaged (see
Chapter 10).
13 Seat belt check
1
1Check the seat belts, buckles, latch plates
and guide loops for any obvious damage or
signs of wear.
2Make sure the seat belt reminder light
comes on when the key is turned on.
3The seat belts are designed to lock up
during a sudden stop or impact, yet allow free
movement during normal driving. The
retractors should hold the belt against your
chest while driving and rewind the belt when
the buckle is unlatched.
4If any of the above checks reveal problems
with the seat-belt system, replace parts as
necessary.Note:Check with your local dealer
service department; the seat belt system
should be covered under the factory warranty.
14 General lubrication
2
1Obtain a good quality, multi-purpose
lithium-base grease. You’ll also need a grease
gun and other materials to properly lubricate
the chassis (see illustration). Occasionallyplugs will be installed rather than grease
fittings. If so, grease fittings will have to be
purchased and installed.
2Look under the car and see if grease fittings
or plugs are installed. If there are plugs,
remove them and buy grease fittings, which
will thread into the component. A dealer or
motor factors will be able to supply the
correct fittings. Straight, as well as angled,
fittings are available.
3For easier access under the car, raise it with
a jack and place axle stands under the
chassis. Make sure it’s safely supported by
the stands. If the wheels are to be removed at
this interval for tyre rotation or brake
inspection, loosen the wheel nuts slightly
while the car is still on the ground.
4Before beginning, force a little grease out of
the nozzle to remove any dirt from the end of
the gun. Wipe the nozzle clean with a rag.
5With the grease gun and plenty of clean
rags, crawl under the car and begin
lubricating all the front suspension parts that
are equipped with a grease fitting.
6Lubricate the rear driveshafts (see
illustration). Wipe each fitting clean and push
the nozzle firmly over it. Pump the gun until
grease is expelled from the U-joint cap seal.
7Wipe away any excess grease from the
components and the grease fitting. Repeat
the procedure for the remaining fittings.
Every 7500 miles or 6 months 1•13
1
14.1 Materials required for chassis
and body lubrication
3261 Jaguar XJ6 12.8a Check the steering gear dust boots
for cracks and leaking steering fluid
12.8b Check the anti-roll bar bushings
(arrowed) for deterioration at the front and
the rear of the vehicle12.10 Inspect the balljoint and tie-rod end
boots for tears - tears or damage in either
boot will allow contamination of the grease
which will lead to premature failure
1 Engine oil - Light engine oil in a can like
this can be used for door and bonnet
hinges
2 Graphite spray - Used to lubricate lock
cylinders
3 Grease - Grease, in a variety of types and
weights, is available for use in a grease
gun.
4 Grease gun - A common grease gun,
shown here with a detachable hose and
nozzle, is needed for chassis lubrication.
After use, clean it thoroughly
Page 30 of 227

16 Spark plug renewal
2
Refer to Section 4, renewing the plugs
regardless of their apparent condition.
17 Air cleaner element renewal
1
1The air filter is located inside a housing at
the left side of the engine compartment. To
remove the air filter, release the four spring
clips that secure the two halves of the air
cleaner housing together, then lift the cover
up and remove the air filter element (see
illustration).
Caution: Never drive the car with the air
cleaner removed. Excessive engine wear
could result and backfiring could even
cause a fire under the bonnet.
2Wipe out the inside of the air cleaner
housing.
3Place the new filter into the air cleaner
housing, making sure it seats properly.
4Refitting the cover is the reverse of removal.
18 Fuel filter renewal
2
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system.
Don’t smoke or allow open flames or bare
light bulbs near the work area, and don’t
work in a garage where a natural gas-typeappliance (such as a water heater or
clothes dryer) with a pilot light is present.
Since petrol is carcinogenic, wear latex
gloves when there’s a possibility of being
exposed to fuel, and, if you spill any fuel on
your skin, rinse it off immediately with soap
and water. Mop up any spills immediately
and do not store fuel-soaked rags where
they could ignite. The fuel system is under
constant pressure, so, if any fuel lines are
to be disconnected, the fuel pressure in
the system must be relieved first (see
Chapter 4 for more information). When you
perform any kind of work on the fuel
system, wear safety glasses and have a
Class B type fire extinguisher on hand.
1The canister type filter is mounted
underneath the car on the passenger’s side
frame rail just in front of the left rear tyre.
2Depressurise the fuel system (refer to
Chapter 4), then disconnect the cable from
the negative terminal of the battery.
3On 1988 to 1990 models, detach the banjo
bolt from the outlet side of the filter then
remove the union from the inlet side of the
filter. Unscrew the filter mounting bolt and
remove the filter (see illustration).
4On 1991 to 1994 models, the fuel filter has
quick-disconnect fittings that do not require 8Clean and lubricate the handbrake cable,
along with the cable guides and levers. This
can be done by smearing some of the chassis
grease onto the cable and its related parts
with your fingers.
9Open the bonnet and smear a little chassis
grease on the bonnet latch mechanism. Have
an assistant pull the bonnet release lever from
inside the car as you lubricate the cable at the
latch.
10Lubricate all the hinges (door, bonnet,
etc.) with engine oil to keep them in proper
working order.
11The key lock cylinders can be lubricated
with spray graphite or silicone lubricant, which
is available at motor factors.12Lubricate the door weather-stripping with
silicone spray. This will reduce chafing and
retard wear.
15 Road test
1
Instruments and electrical
equipment
1Check the operation of all instruments and
electrical equipment.
2Make sure that all instruments read
correctly, and switch on all electrical
equipment in turn, to check that it functions
properly.
Steering and suspension
3Check for any abnormalities in the steering,
suspension, handling or road “feel”.
4Drive the car, and check that there are no
unusual vibrations or noises.
5Check that the steering feels positive, with
no excessive “sloppiness”, or roughness, and
check for any suspension noises when
cornering and driving over bumps.
Drivetrain
6Check the performance of the engine and
transmission, listening for any unusual noises.7Make sure that the engine runs smoothly
when idling, and that there is no hesitation
when accelerating.
8Check that the gear changing action of the
transmission is smooth and progressive and
that the drive is taken up smoothly from a
standing start.
Braking system
9Make sure that the car does not pull to one
side when braking, and that the wheels do not
lock prematurely when braking hard.
10Check that there is no vibration through
the steering when braking.
11Check that the handbrake operates
correctly without excessive movement of the
lever, and that it holds the car stationary on a
slope.
12Test the operation of the brake servo unit
as follows. With the engine off, depress the
footbrake four or five times to exhaust the
vacuum. Hold the brake pedal depressed, then
start the engine. As the engine starts, there
should be a noticeable “give” in the brake
pedal as vacuum builds up. Allow the engine to
run for at least two minutes, and then switch it
off. If the brake pedal is depressed now, it
should be possible to detect a hiss from the
servo as the pedal is depressed. After about
four or five depressions, no further hissing
should be heard, and the pedal should feel
considerably harder.
1•14Every 7500 miles or 6 months
17.1 Detach the clips and separate the
cover, then slide the filter element out of
the housing
3261 Jaguar XJ6
14.6 Grease fittings for the rear
driveshafts are located in the centre
on each U-joint
Every 15 000 miles (24 000 km) or 12 months
Page 32 of 227
20 Crankcase ventilation
system check
1
Refer to Chapter 6.
21 Drivebelt check and renewal
2
Check
1The drivebelts, or V-belts as they are
sometimes called, are located at the front of
the engine and play an important role in the
overall operation of the vehicle and its
components. Due to their function and
material make-up, the belts are prone to
failure after a period of time and should be
inspected and adjusted periodically to prevent
major engine damage.
2The number of belts used on a particular
vehicle depends on the accessories installed.
The main belt transmits power from the
crankshaft to the water pump, alternator and
the power steering pump. The second belt
transmits power from the crankshaft to the air
conditioning compressor.
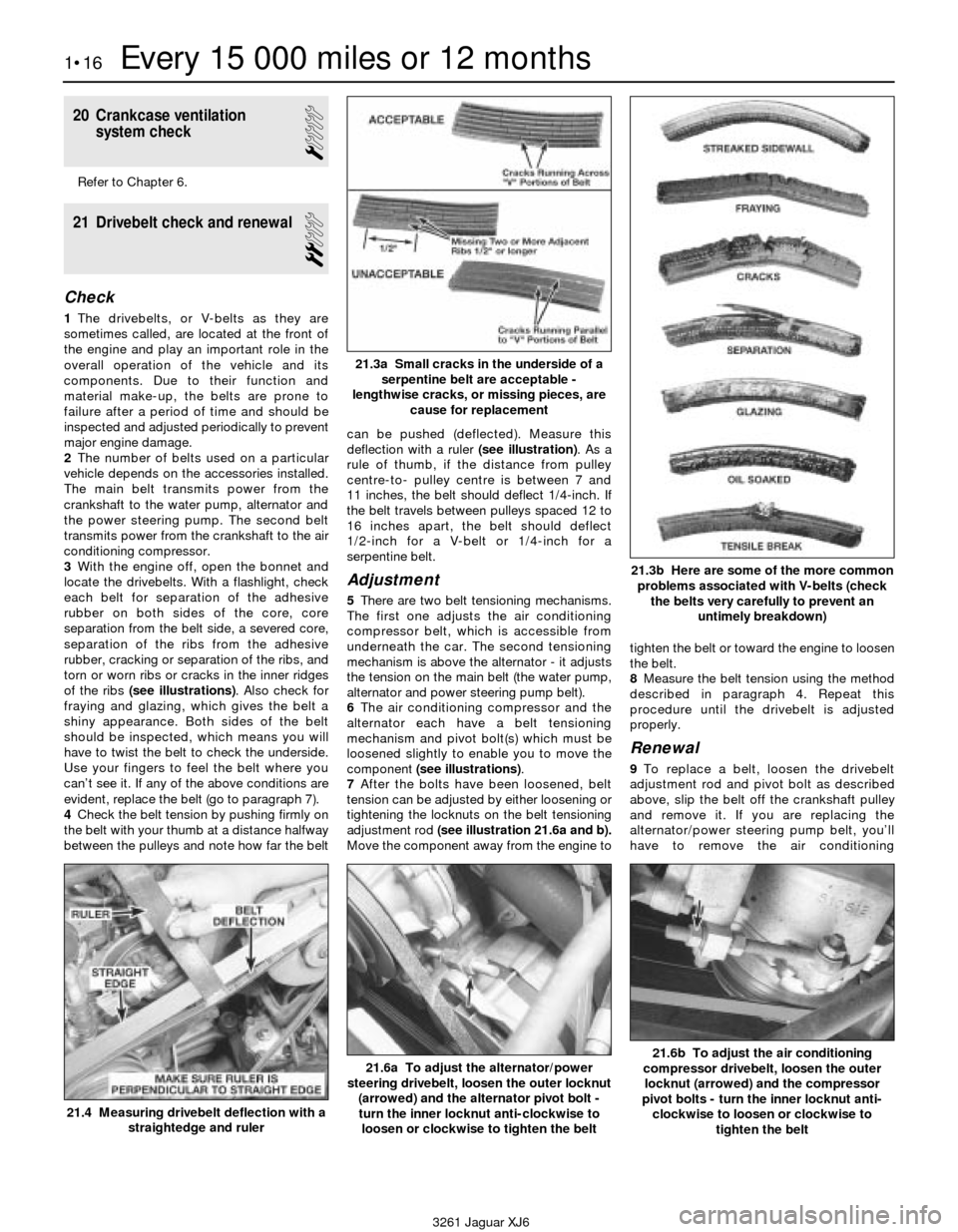
3With the engine off, open the bonnet and
locate the drivebelts. With a flashlight, check
each belt for separation of the adhesive
rubber on both sides of the core, core
separation from the belt side, a severed core,
separation of the ribs from the adhesive
rubber, cracking or separation of the ribs, and
torn or worn ribs or cracks in the inner ridges
of the ribs (see illustrations). Also check for
fraying and glazing, which gives the belt a
shiny appearance. Both sides of the belt
should be inspected, which means you will
have to twist the belt to check the underside.
Use your fingers to feel the belt where you
can’t see it. If any of the above conditions are
evident, replace the belt (go to paragraph 7).
4Check the belt tension by pushing firmly on
the belt with your thumb at a distance halfway
between the pulleys and note how far the beltcan be pushed (deflected). Measure this
deflection with a ruler (see illustration). As a
rule of thumb, if the distance from pulley
centre-to- pulley centre is between 7 and
11 inches, the belt should deflect 1/4-inch. If
the belt travels between pulleys spaced 12 to
16 inches apart, the belt should deflect
1/2-inch for a V-belt or 1/4-inch for a
serpentine belt.
Adjustment
5There are two belt tensioning mechanisms.
The first one adjusts the air conditioning
compressor belt, which is accessible from
underneath the car. The second tensioning
mechanism is above the alternator - it adjusts
the tension on the main belt (the water pump,
alternator and power steering pump belt).
6The air conditioning compressor and the
alternator each have a belt tensioning
mechanism and pivot bolt(s) which must be
loosened slightly to enable you to move the
component (see illustrations).
7After the bolts have been loosened, belt
tension can be adjusted by either loosening or
tightening the locknuts on the belt tensioning
adjustment rod (see illustration 21.6a and b).
Move the component away from the engine totighten the belt or toward the engine to loosen
the belt.
8Measure the belt tension using the method
described in paragraph 4. Repeat this
procedure until the drivebelt is adjusted
properly.
Renewal
9To replace a belt, loosen the drivebelt
adjustment rod and pivot bolt as described
above, slip the belt off the crankshaft pulley
and remove it. If you are replacing the
alternator/power steering pump belt, you’ll
have to remove the air conditioning
1•16Every 15 000 miles or 12 months
21.3a Small cracks in the underside of a
serpentine belt are acceptable -
lengthwise cracks, or missing pieces, are
cause for replacement
21.3b Here are some of the more common
problems associated with V-belts (check
the belts very carefully to prevent an
untimely breakdown)
21.4 Measuring drivebelt deflection with a
straightedge and ruler
21.6a To adjust the alternator/power
steering drivebelt, loosen the outer locknut
(arrowed) and the alternator pivot bolt -
turn the inner locknut anti-clockwise to
loosen or clockwise to tighten the belt21.6b To adjust the air conditioning
compressor drivebelt, loosen the outer
locknut (arrowed) and the compressor
pivot bolts - turn the inner locknut anti-
clockwise to loosen or clockwise to
tighten the belt
3261 Jaguar XJ6