front JEEP CHEROKEE 1994 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1994Pages: 1784, PDF Size: 77.09 MB
Page 1416 of 1784
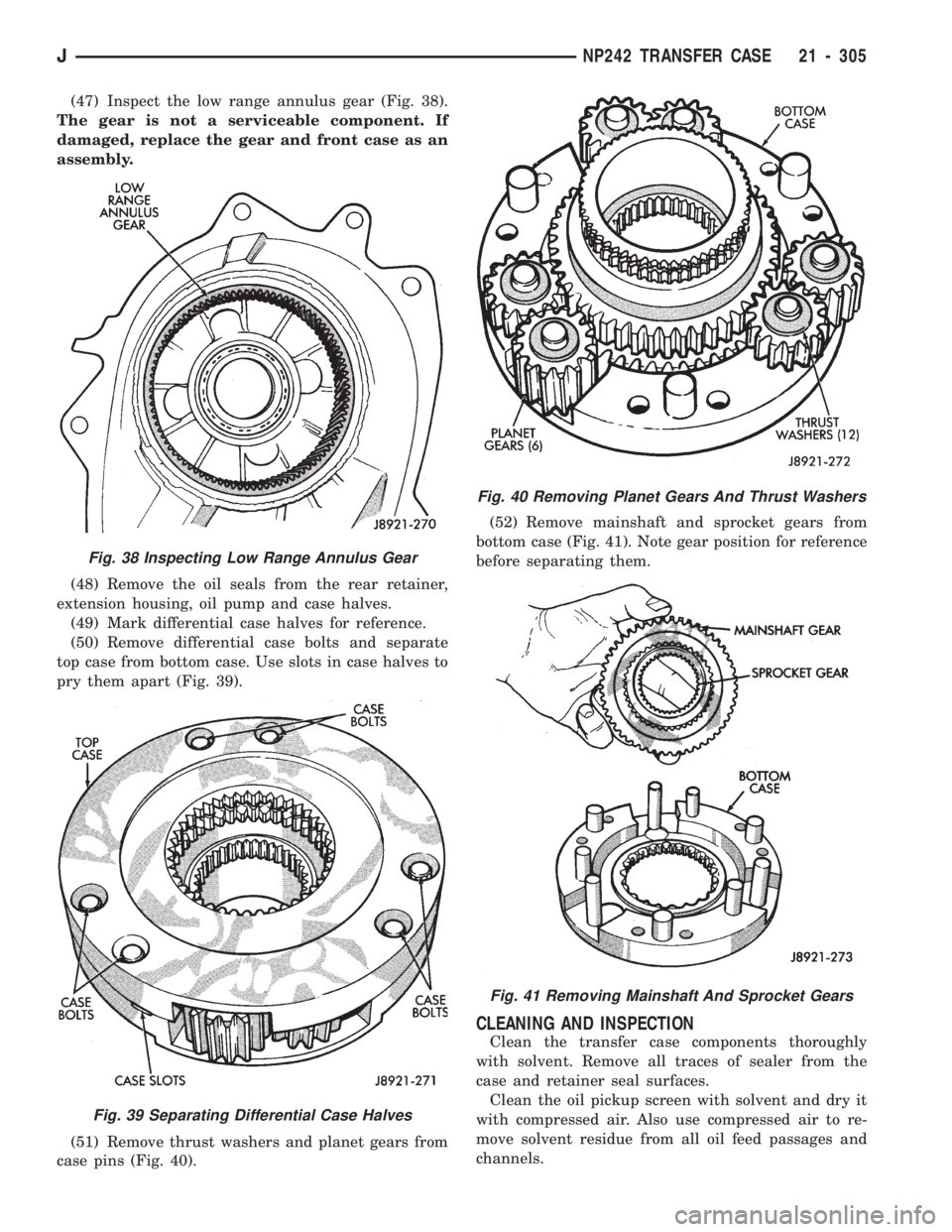
(47) Inspect the low range annulus gear (Fig. 38).
The gear is not a serviceable component. If
damaged, replace the gear and front case as an
assembly.
(48) Remove the oil seals from the rear retainer,
extension housing, oil pump and case halves.
(49) Mark differential case halves for reference.
(50) Remove differential case bolts and separate
top case from bottom case. Use slots in case halves to
pry them apart (Fig. 39).
(51) Remove thrust washers and planet gears from
case pins (Fig. 40).(52) Remove mainshaft and sprocket gears from
bottom case (Fig. 41). Note gear position for reference
before separating them.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
Clean the transfer case components thoroughly
with solvent. Remove all traces of sealer from the
case and retainer seal surfaces.
Clean the oil pickup screen with solvent and dry it
with compressed air. Also use compressed air to re-
move solvent residue from all oil feed passages and
channels.
Fig. 38 Inspecting Low Range Annulus Gear
Fig. 39 Separating Differential Case Halves
Fig. 40 Removing Planet Gears And Thrust Washers
Fig. 41 Removing Mainshaft And Sprocket Gears
JNP242 TRANSFER CASE 21 - 305
Page 1417 of 1784
Inspect the differential gears, thrust washers and
case halves. Replace the mainshaft gear if the gear
teeth or the brass ring on the underside of the gear
are damaged. Replace the differential as an assembly
if the gears, case halves, or the pins in the lower case
half are damaged.
Inspect the case halves, extension housing and re-
tainers for cracks, porosity, or damaged sealing sur-
faces. Inspect the shafts, gears, chain and shift
components for wear or damage.
Inspect all of the transfer case bearings for wear,
roughness, pitting, or galling. Replace worn or dam-
aged bearings as outlined in the assembly section.
TRANSFER CASE ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate the transfer case components with
automatic transmission fluid or petroleum jelly
(where indicated) during assembly.
CAUTION: The bearing bores in various transfer
case components contain oil feed holes. Be sure re-
placement bearings do not block these feed holes.
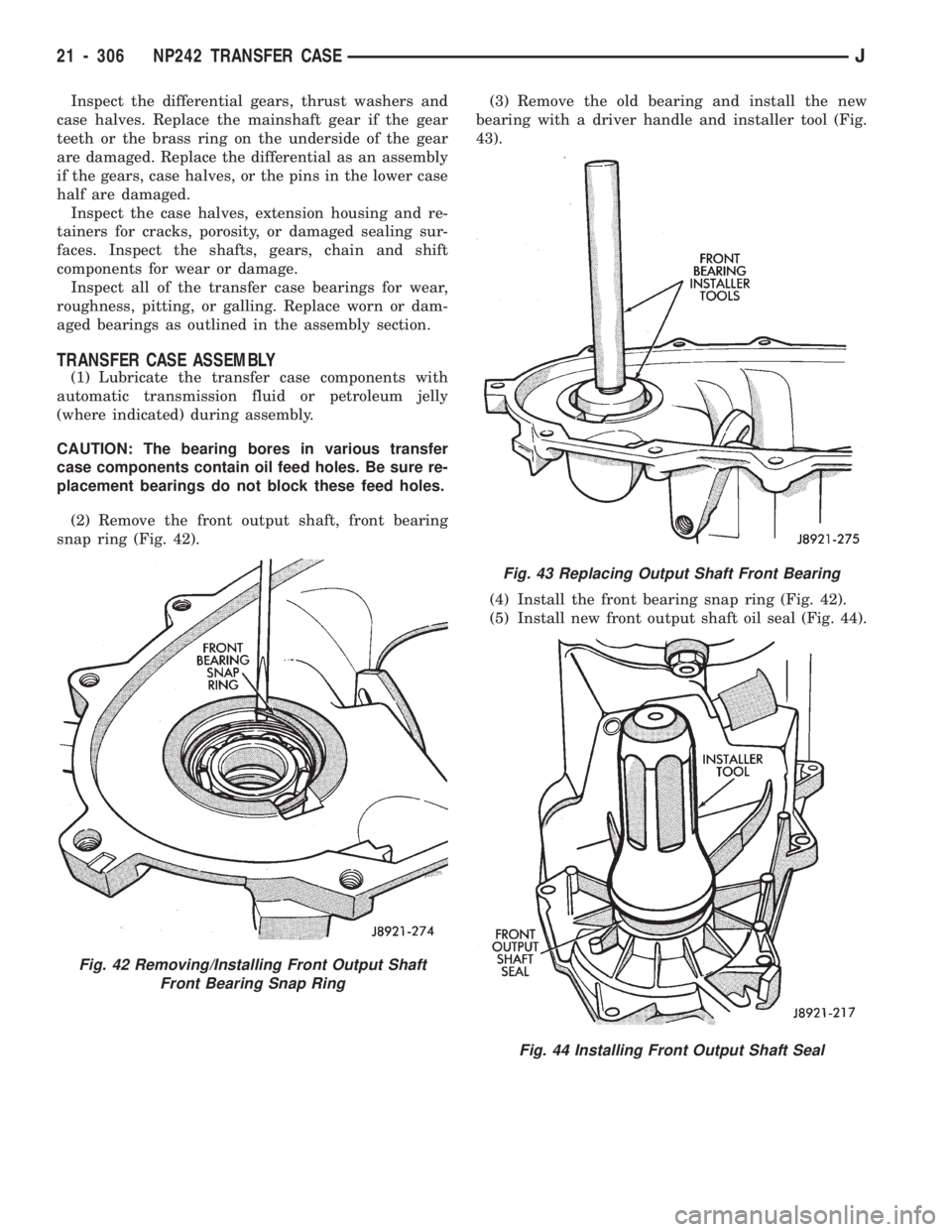
(2) Remove the front output shaft, front bearing
snap ring (Fig. 42).(3) Remove the old bearing and install the new
bearing with a driver handle and installer tool (Fig.
43).
(4) Install the front bearing snap ring (Fig. 42).
(5) Install new front output shaft oil seal (Fig. 44).
Fig. 42 Removing/Installing Front Output Shaft
Front Bearing Snap Ring
Fig. 43 Replacing Output Shaft Front Bearing
Fig. 44 Installing Front Output Shaft Seal
21 - 306 NP242 TRANSFER CASEJ
Page 1418 of 1784
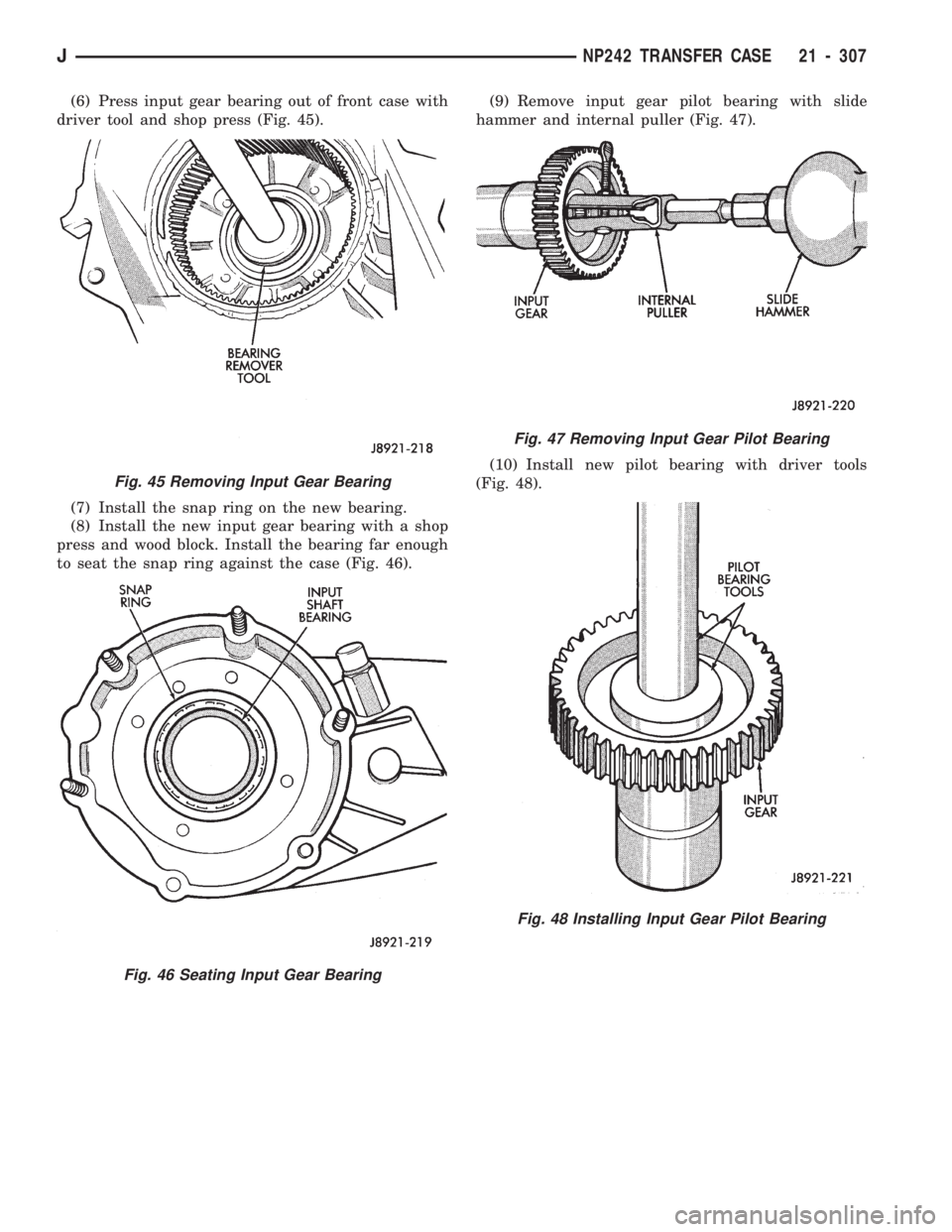
(6) Press input gear bearing out of front case with
driver tool and shop press (Fig. 45).
(7) Install the snap ring on the new bearing.
(8) Install the new input gear bearing with a shop
press and wood block. Install the bearing far enough
to seat the snap ring against the case (Fig. 46).(9) Remove input gear pilot bearing with slide
hammer and internal puller (Fig. 47).
(10) Install new pilot bearing with driver tools
(Fig. 48).
Fig. 45 Removing Input Gear Bearing
Fig. 46 Seating Input Gear Bearing
Fig. 47 Removing Input Gear Pilot Bearing
Fig. 48 Installing Input Gear Pilot Bearing
JNP242 TRANSFER CASE 21 - 307
Page 1419 of 1784
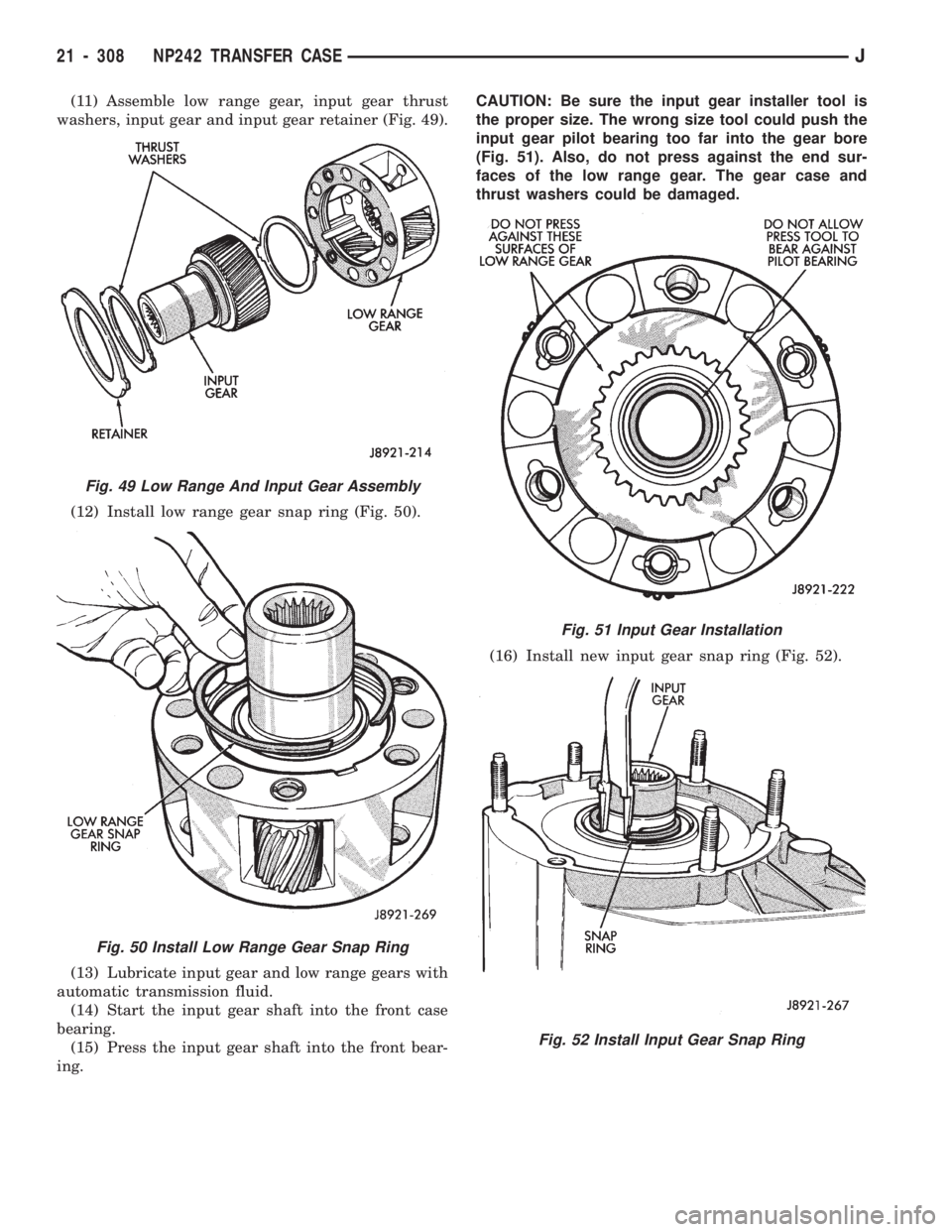
(11) Assemble low range gear, input gear thrust
washers, input gear and input gear retainer (Fig. 49).
(12) Install low range gear snap ring (Fig. 50).
(13) Lubricate input gear and low range gears with
automatic transmission fluid.
(14) Start the input gear shaft into the front case
bearing.
(15) Press the input gear shaft into the front bear-
ing.CAUTION: Be sure the input gear installer tool is
the proper size. The wrong size tool could push the
input gear pilot bearing too far into the gear bore
(Fig. 51). Also, do not press against the end sur-
faces of the low range gear. The gear case and
thrust washers could be damaged.
(16) Install new input gear snap ring (Fig. 52).
Fig. 49 Low Range And Input Gear Assembly
Fig. 50 Install Low Range Gear Snap Ring
Fig. 51 Input Gear Installation
Fig. 52 Install Input Gear Snap Ring
21 - 308 NP242 TRANSFER CASEJ
Page 1420 of 1784
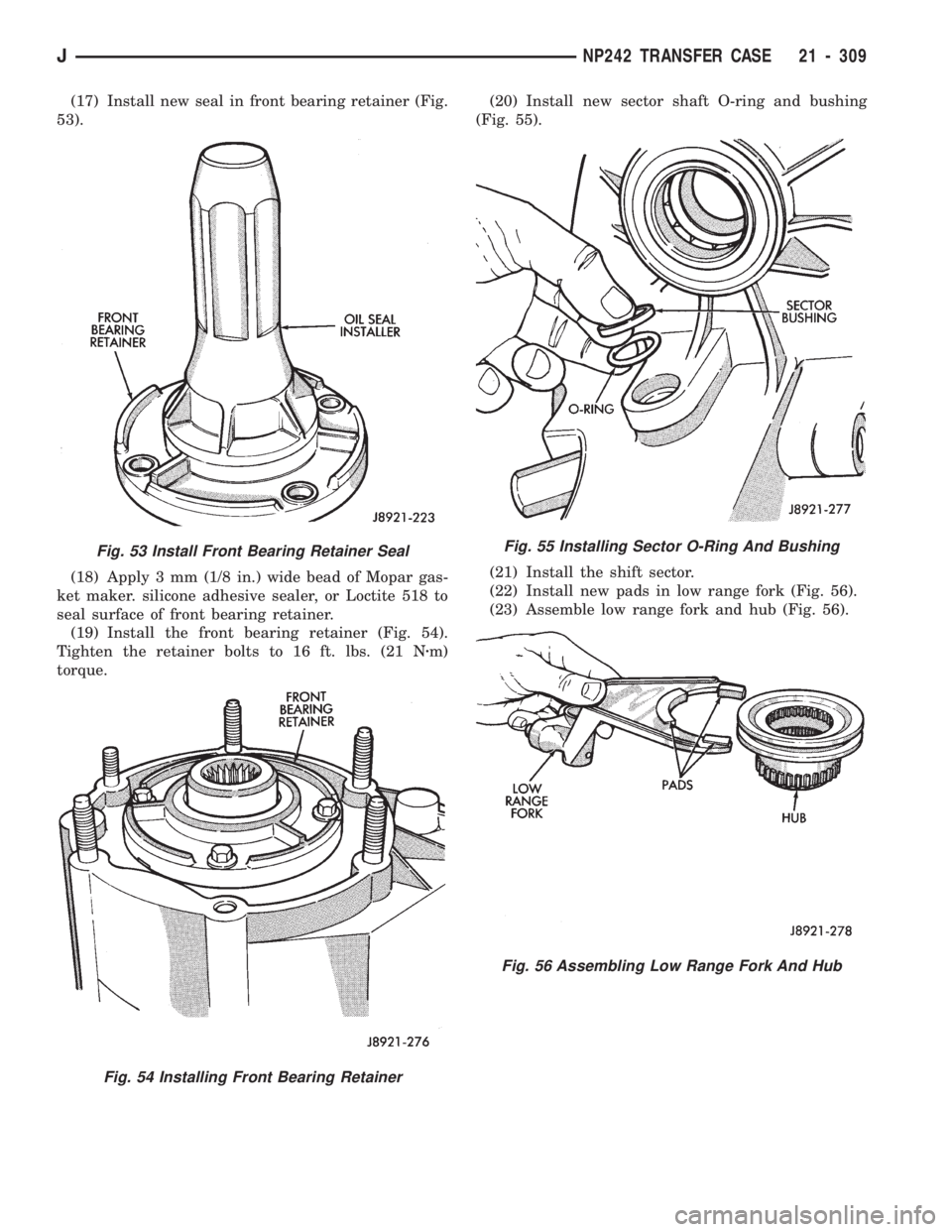
(17) Install new seal in front bearing retainer (Fig.
53).
(18) Apply 3 mm (1/8 in.) wide bead of Mopar gas-
ket maker. silicone adhesive sealer, or Loctite 518 to
seal surface of front bearing retainer.
(19) Install the front bearing retainer (Fig. 54).
Tighten the retainer bolts to 16 ft. lbs. (21 Nzm)
torque.(20) Install new sector shaft O-ring and bushing
(Fig. 55).
(21) Install the shift sector.
(22) Install new pads in low range fork (Fig. 56).
(23) Assemble low range fork and hub (Fig. 56).
Fig. 55 Installing Sector O-Ring And Bushing
Fig. 56 Assembling Low Range Fork And Hub
Fig. 53 Install Front Bearing Retainer Seal
Fig. 54 Installing Front Bearing Retainer
JNP242 TRANSFER CASE 21 - 309
Page 1425 of 1784
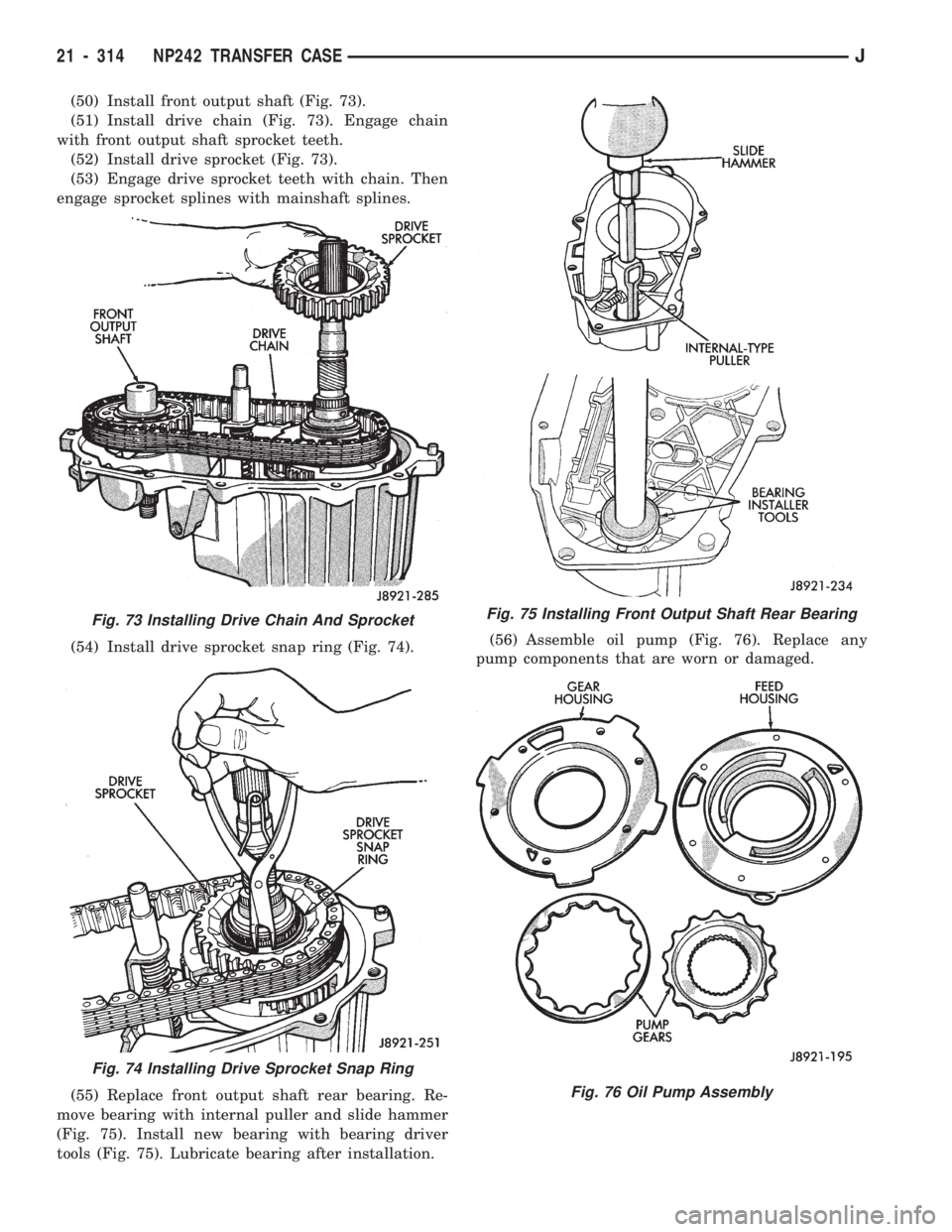
(50) Install front output shaft (Fig. 73).
(51) Install drive chain (Fig. 73). Engage chain
with front output shaft sprocket teeth.
(52) Install drive sprocket (Fig. 73).
(53) Engage drive sprocket teeth with chain. Then
engage sprocket splines with mainshaft splines.
(54) Install drive sprocket snap ring (Fig. 74).
(55) Replace front output shaft rear bearing. Re-
move bearing with internal puller and slide hammer
(Fig. 75). Install new bearing with bearing driver
tools (Fig. 75). Lubricate bearing after installation.(56) Assemble oil pump (Fig. 76). Replace any
pump components that are worn or damaged.
Fig. 73 Installing Drive Chain And Sprocket
Fig. 74 Installing Drive Sprocket Snap Ring
Fig. 75 Installing Front Output Shaft Rear Bearing
Fig. 76 Oil Pump Assembly
21 - 314 NP242 TRANSFER CASEJ
Page 1426 of 1784
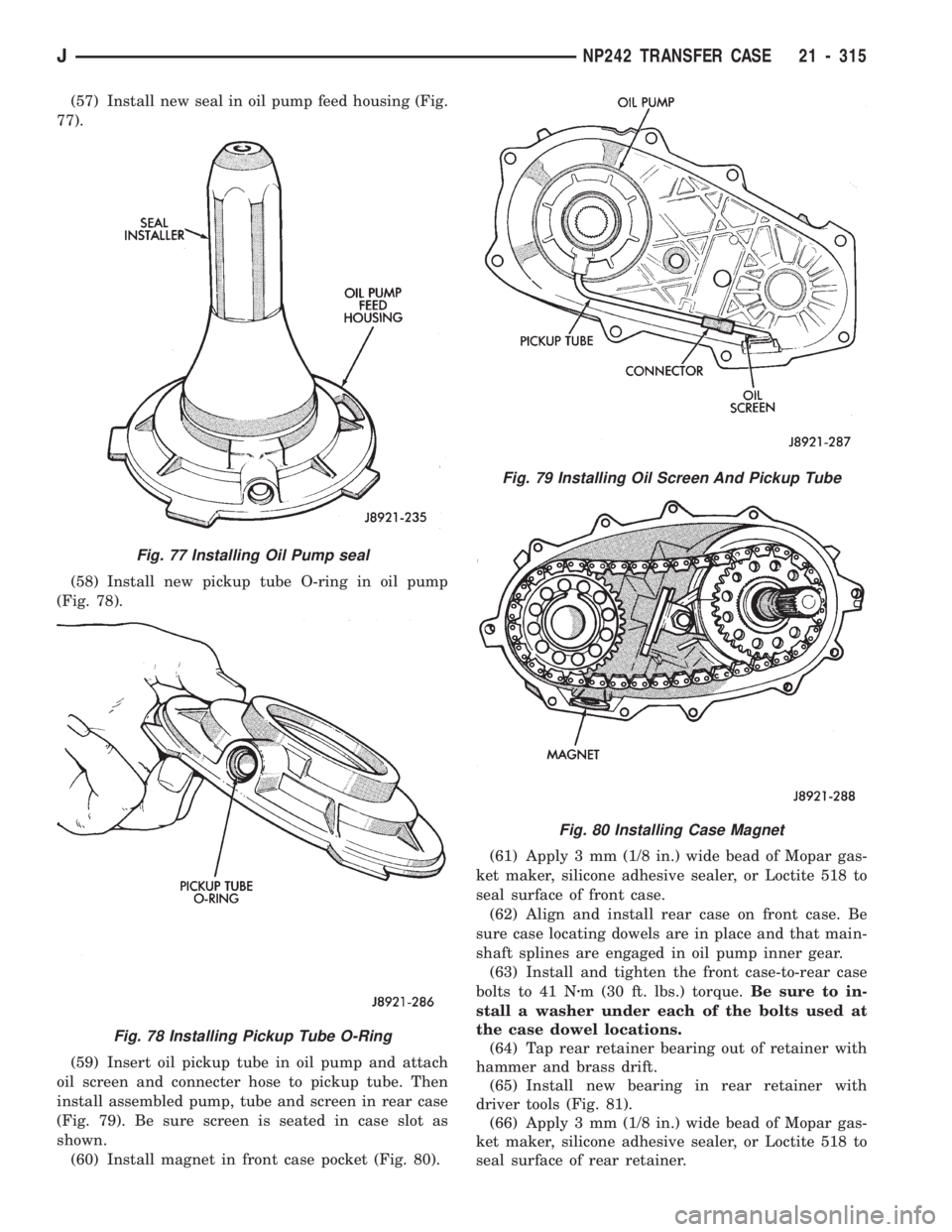
(57) Install new seal in oil pump feed housing (Fig.
77).
(58) Install new pickup tube O-ring in oil pump
(Fig. 78).
(59) Insert oil pickup tube in oil pump and attach
oil screen and connecter hose to pickup tube. Then
install assembled pump, tube and screen in rear case
(Fig. 79). Be sure screen is seated in case slot as
shown.
(60) Install magnet in front case pocket (Fig. 80).(61) Apply 3 mm (1/8 in.) wide bead of Mopar gas-
ket maker, silicone adhesive sealer, or Loctite 518 to
seal surface of front case.
(62) Align and install rear case on front case. Be
sure case locating dowels are in place and that main-
shaft splines are engaged in oil pump inner gear.
(63) Install and tighten the front case-to-rear case
bolts to 41 Nzm (30 ft. lbs.) torque.Be sure to in-
stall a washer under each of the bolts used at
the case dowel locations.
(64) Tap rear retainer bearing out of retainer with
hammer and brass drift.
(65) Install new bearing in rear retainer with
driver tools (Fig. 81).
(66) Apply 3 mm (1/8 in.) wide bead of Mopar gas-
ket maker, silicone adhesive sealer, or Loctite 518 to
seal surface of rear retainer.
Fig. 77 Installing Oil Pump seal
Fig. 78 Installing Pickup Tube O-Ring
Fig. 79 Installing Oil Screen And Pickup Tube
Fig. 80 Installing Case Magnet
JNP242 TRANSFER CASE 21 - 315
Page 1428 of 1784

(72) Apply 3 mm (1/8 in.) wide bead of Mopar gas-
ket maker, silicone adhesive sealer, or Loctite 518 to
seal surface of extension housing.
(73) Install extension housing on case. Tighten
housing bolts to 41 Nzm (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(74) Install front yoke. Secure yoke with new seal
washer and nut. Tighten nut to 149 Nzm (110 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(75) Install new gasket on vacuum switch and in-
stall switch in the case. Tighten switch to 27 Nzm (20
ft. lbs.) torque.
(76) Install speedometer components (Fig. 85).
(77) Install and tighten drain plug to 47 Nzm (35
ft. lbs.) torque.
(78) After installing transfer case, refill with rec-
ommended transmission fluid.
(79) Tighten fill plug to 47 Nzm (35 ft. lbs.) torque.
(80) Adjust transfer case shift linkage.
Fig. 85 Speedometer Components
JNP242 TRANSFER CASE 21 - 317
Page 1444 of 1784

WHEELS AND TIRES
CONTENTS
page page
SPECIFICATIONS....................... 11
TIRES................................. 1VEHICLE VIBRATION..................... 9
WHEELS............................... 6
TIRES
INDEX
page page
Cleaning of Tires.......................... 2
General Information........................ 1
Pressure Gauges......................... 2
Repairing Leaks.......................... 3
Replacement Tires........................ 2Rotation................................ 3
Tire Inflation Pressures..................... 2
Tire Noise or Vibration..................... 4
Tire Wear Patterns........................ 4
Tread Wear Indicators...................... 3
GENERAL INFORMATION
Tires are designed for each specific vehicle. They
provide the best overall performance for normal op-
eration. The ride and handling characteristics match
the vehicle's requirements. With proper care they
will give excellent reliability, traction, skid resis-
tance, and tread life. These tires have specific load
carrying capacities. When correctly inflated, they
will operate properly.
Tires used in cool climates, and with light loads
will have a longer life than tires used in hot climates
with heavy loads. Abrasive road surfaces will accel-
erate tire wear.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain much
greater mileage than careless drivers.
Driving habits that shorten the life of any tire;
²Rapid acceleration and deceleration
²Severe application of brakes
²High-speed driving
²Taking turns at excessive speeds
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
It is very important to follow the tire rotation in-
terval
IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 1).
Performance tires will have a speed rating letter
after the aspect ratio number. The speed rating isnot always printed on the tire sidewall. The letterS
indicates that the tire is speed rated up to 112 mph.
²Qup to 100 mph
²Tup to 118 mph
²Uup to 124 mph
²Hup to 130 mph
²Vup to 149 mph
²Zmore than 149 mph (consult the tire manufac-
turer for the specific speed rating)
An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
&SorMÐS(indicating mud and snow traction) im-
printed on the side wall.
RADIAL-PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life, ride
quality and decrease rolling resistance.
Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary, but reduced speeds are
recommended.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They use
the same recommended inflation pressures.
SPARE TIRE (TEMPORARY)
The compact spare tire is designed for emergency
use only. The original tire should be repaired and re-
installed at the first opportunity. Refer to Owner's
Manual for complete details.
JWHEELS AND TIRES 22 - 1
Page 1446 of 1784

²Noise
²Handling
²Durability
²Tread life
²Traction
²Rolling resistance
²Speed capability
Original equipment tires should be used when re-
placement is needed.
Refer to the placard on the vehicle or the
Owner's Manual for the correct replacement
tire.
Failure to use original or equivalent replacement
tires may adversely affect the handling of the vehi-
cle.
The use of oversize tiresis not recommended.
They may cause interference with vehicle suspension
and steering travel. This can cause tire damage or
failure.
WARNING: FAILURE TO EQUIP THE VEHICLE WITH
TIRES HAVING ADEQUATE LOAD CAPABILITY CAN
RESULT IN SUDDEN TIRE FAILURE.
ROTATION
Tires on the front and rear axles operate at differ-
ent loads and perform different steering, driving, and
braking functions. For these reasons, the tires wear
at unequal rates. They may also develop irregular
wear patterns. These effects can be reduced by rotat-
ing the tires according to the maintenance schedule
in the Owners Manual. This will improve tread life,
traction and maintain a smooth quiet ride.
The suggested method of tire rotation is thesame
side front to rearpattern (Fig. 4). Other rotation
methods can be used, but may not provide the same
tire longevity benefits.
TREAD WEAR INDICATORS
Tread wear indicators are molded into the bottom
of the tread grooves. When tread is 1.6 mm (1/16 in.),
the tread wear indicators will appear as a 13 mm
(1/2 in.) band across the tread width.
Tire replacement is necessary when indicators ap-
pear in two or more grooves Fig. 5).
REPAIRING LEAKS
For proper repairing, a radial tire it must be re-
moved from the wheel. Repairs should only be made
if the puncture is in thetread area(Fig. 6). If out-
side the tread area the tire should be replaced.
Deflate tire completely before dismounting tire
from the wheel. Use lubrication such as a mild soap
solution when dismounting or mounting tire. Use
tools free of burrs or sharp edges.
Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust
scale is removed from the rim. Repaint or seal if nec-
essary.
Fig. 4 Tire Rotation Pattern
Fig. 5 Tread Wear Indicators
Fig. 6 Tire Repair Area
JWHEELS AND TIRES 22 - 3