MAZDA 323 1992 Workshop Manual Suplement
Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 1992, Model line: 323, Model: MAZDA 323 1992Pages: 279, PDF Size: 24.15 MB
Page 181 of 279

VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBERS (VIN)
(CHASSIS NUMBER)
JMZ 86835200 5OOOOl-
WIRING COLOR CODE
Color Code
I Color Code
Blue I L 1 Natural
I N
Black
1 B I Orange
I 0
Brown BR
Dark Blue DL
Dark Green DG Pink
Red
Purple
Green
Gray
Light Blue
Light Green G
GY
LB Tan
White
Yellow
Violet P
R
PU
T
W
Y
LG
I V
Page 182 of 279

GENERAL INFORMATION
Wiring Diagrams
Contents of wiring diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..*................
Using wiring diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..*............. ............
2
............
2
Reading Wiring Diagrams
Ground points ...........................................................
3
System circuit diagram/connector diagram ..................................
4
Routing diagram ......................................................... fj
“arnesssym~,s.. ...................................................... 7
Symbols .............................................................. ..~
Logic symbols ...........................................................
10
Abbreviations used in this booklet ..........................................
10
Troubleshooting
Precautions to take when servicing an electrical system * - * * * * - * * * * * * - - * * * * * * - * 11
Handling connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12
Using electrical measuring equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13
Measuring voltage . ..~...................................................
14
Measuring continuity/resistance. a e e a a v e s s * e e . e e e a 1 e e . s * e e o s w e e a e e . e * w s a e e a * 1 fj
Findingshortcircuits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..I......... 16
Page 183 of 279

GI Wiring Diagrams
Contents of wiring diagrams
l This document comprises the 8 groups shown below. The main components are summarized in the
components location diagram at the
end of the document.
I I Gi General information A how-to on using and reading wiring diagrams, 1
using test equipment, checking harnesses and
connectors, and findrng trouble spots
Y , Ground points
- Ground routes from and to the battery
W Electrical wiring Shows main fuses and other fuses for each
schematics system
A-U Circuit diagrams for
~ individual systems Shows circuit and connector diagrams and
component and connector location diagrams
X Common connectors Shows connectors common throughout system
~ JB i Joint box complete
wiring system
I Shows internal circuits and connectors
PL Parts location
Pi index Shows location of major electrical parts
Gives page number of circuit diagram for each
component
Using wiring diagrams
l The use of the wiring diagram depends on its application. Application
-or checking
:ircuits of
ndividual
systems
For checking
ground circuit
of individual
systems Use
II Application For checking
fuse
connections
Open to page with circuit diagram and
harness routing to be used and fold out
common connector diagram or joint box
diagram.
II
For finding
page numbers
of systems and
components
Open to page with ground point diagram
and fold out common connector diagram
or joint box diagram. Use
3pen to electrical wiring schematic.
Parts Index System Index
or
Open to parts index or system index.
Page 184 of 279

Reading Wiring Diagrams
Ground points
l This shows ground points of the harness.
#CIGARETTE LIGHTER
BINTERIOR LAMPS
H
3
Page 185 of 279
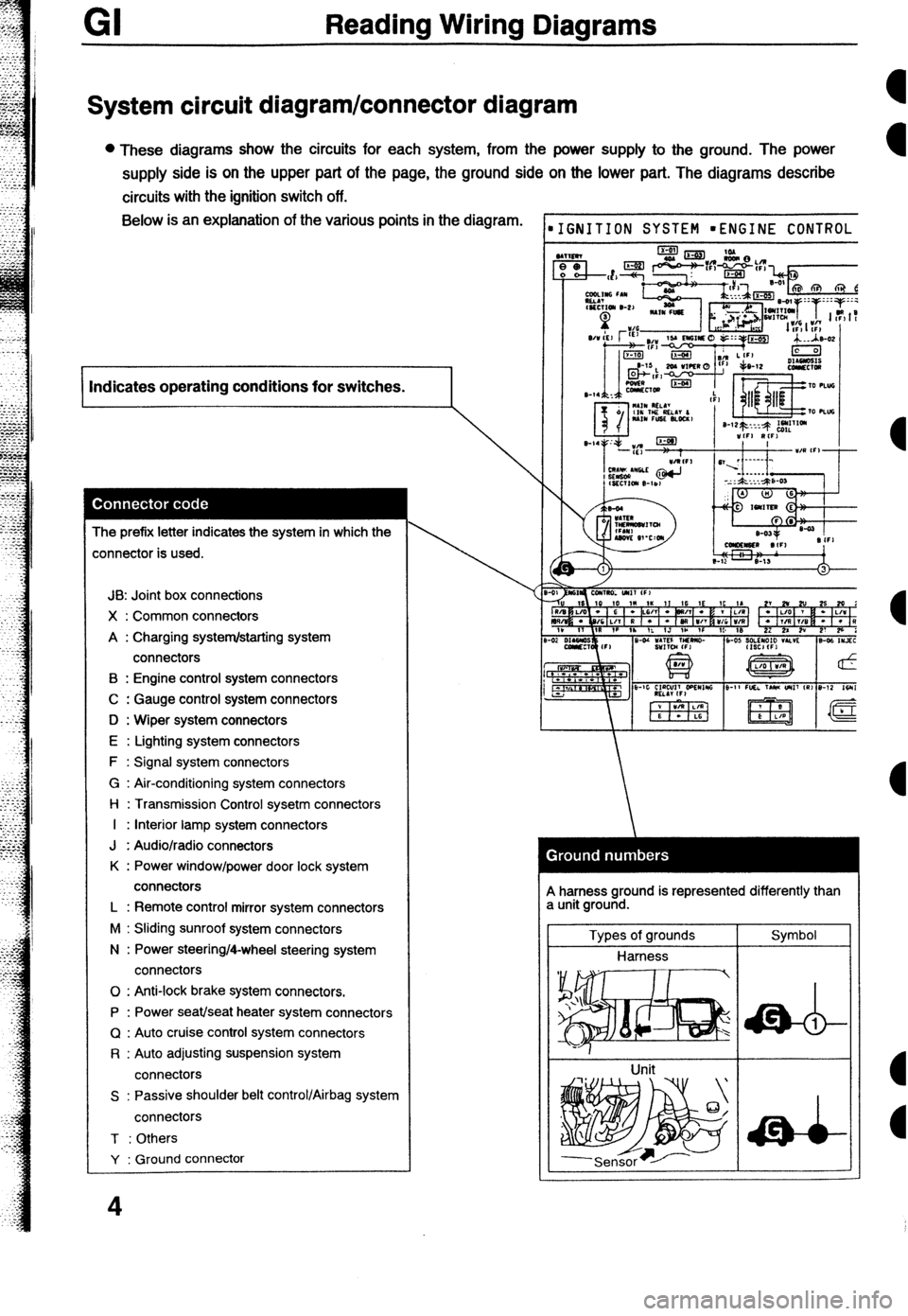
GI Reading Wiring Diagrams
System circuit diagram/connector diagram
l These diagrams show the circuits for each system, from the power supply to the ground. The power
supply side is on the upper part of the page, the ground side on the lower part. The diagrams describe
circuits with the ignition switch off. Below is an explanation of the various points in the diagram.
I Indicates operating conditions for switches.
I
The prefix letter indicates the system in which the
:onnector is used.
JB: Joint box connections
X : Common connectors
A : Charging system/starting system
connectors
B : Engine control system connectors
C : Gauge control system connectors
D : Wiper system connectors
E : Lighting system connectors
F : Signal system connectors
G : Air-conditioning system connectors
l-l : Transmission Control sysetm connectors
I : Interior lamp system connectors
J : Audio/radio connectors
K : Power window/power door lock system
connectors
L : Remote control mirror system connectors
M : Sliding sunroof system connectors
N : Power steering/4-wheel steering system
connectors
0 : Anti-lock brake system connectors.
P : Power seat/seat heater system connectors
Q : Auto cruise control system connectors
R : Auto adjusting suspension system
connectors
S : Passive shoulder belt control/Airbag system
connectors
T : Others
Y : Ground connector
4
IGNITION SYSTEM mENGINE CONTROL
A harness ground is represented differently than
a unit ground.
Types of grounds
Harness
Unit Symbol
Page 186 of 279
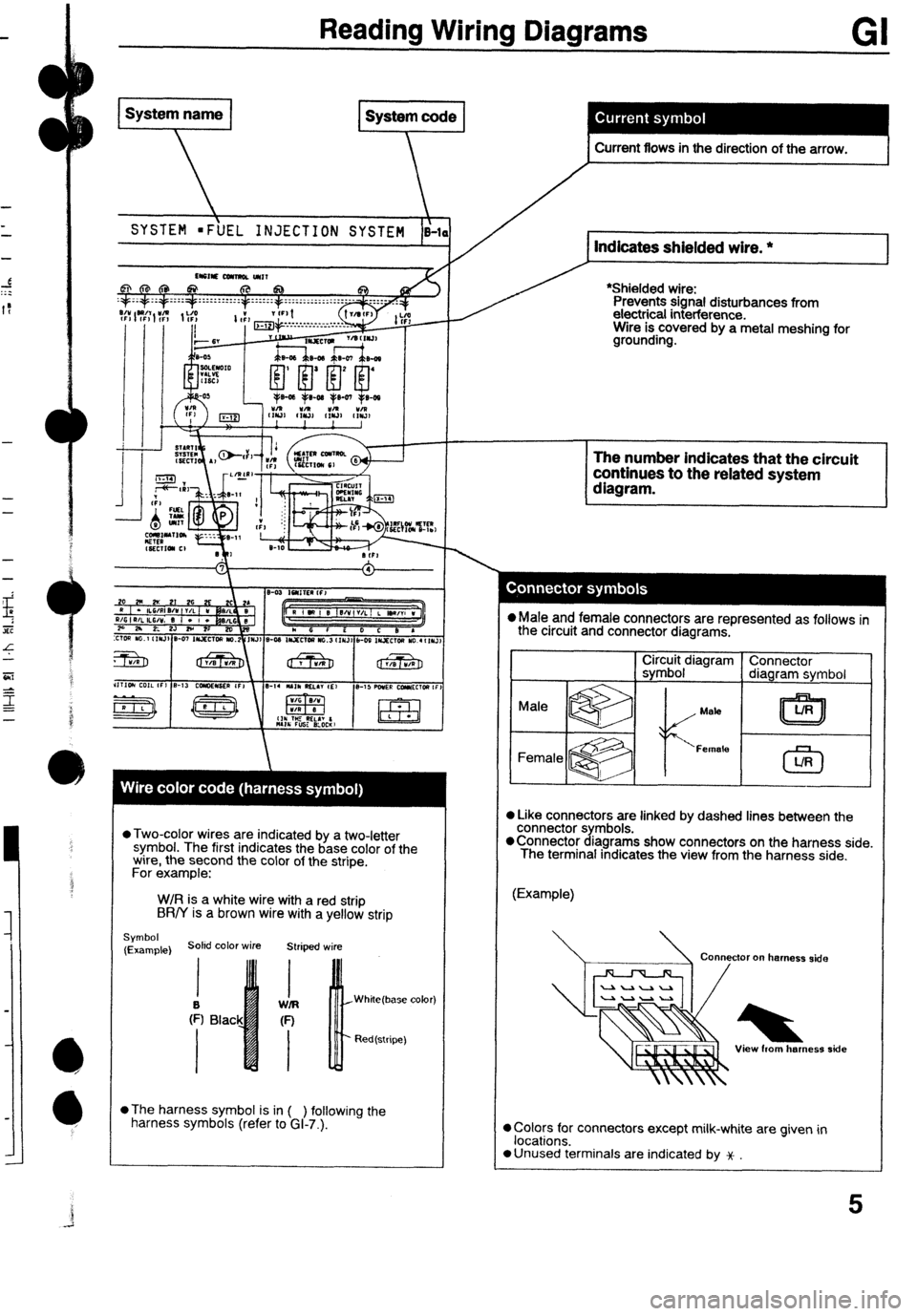
k
Reading Wiring Diagrams GI
SYSTEM =F\UEL INJECTION SYSTEM i-1 Indicates shielded wire. *
I
*Shielded wire:
Prevents signal disturbances from
electrical interference.
Wire is covered by a metal meshing for
grounding. . Current flows in the direction of the arrow. t
l Two-color wires are indicated by a two-letter
symbol. The first indicates the base color of the
wire, the second the color of the stripe.
For example:
W/R is a white wire with a red strip
BR/Y is a brown wire with a yellow strip
Symbol
(Example) Soled color wire Striped wire
White(base color)
Red(stripe)
l
The harness symbol is in ( ) following the
harness symbols (refer to GI-7.).
T L The number indicates that the circuit
continues to the related system
l Male and female connectors are represented as follows in
the circuit and connector diagrams.
CirZirb~ldiagram Connector
diagram symbol
Mata
l Like connectors are linked by dashed lines between the
connector symbols.
@Connector diagrams show connectors on the harness side.
The terminal indicates the view from the harness side.
(Example)
Connector on harness side *
View horn herness side
0 Colors for connectors except milk-white are given in
locations.
a Unused terminals are indicated by x
Page 187 of 279
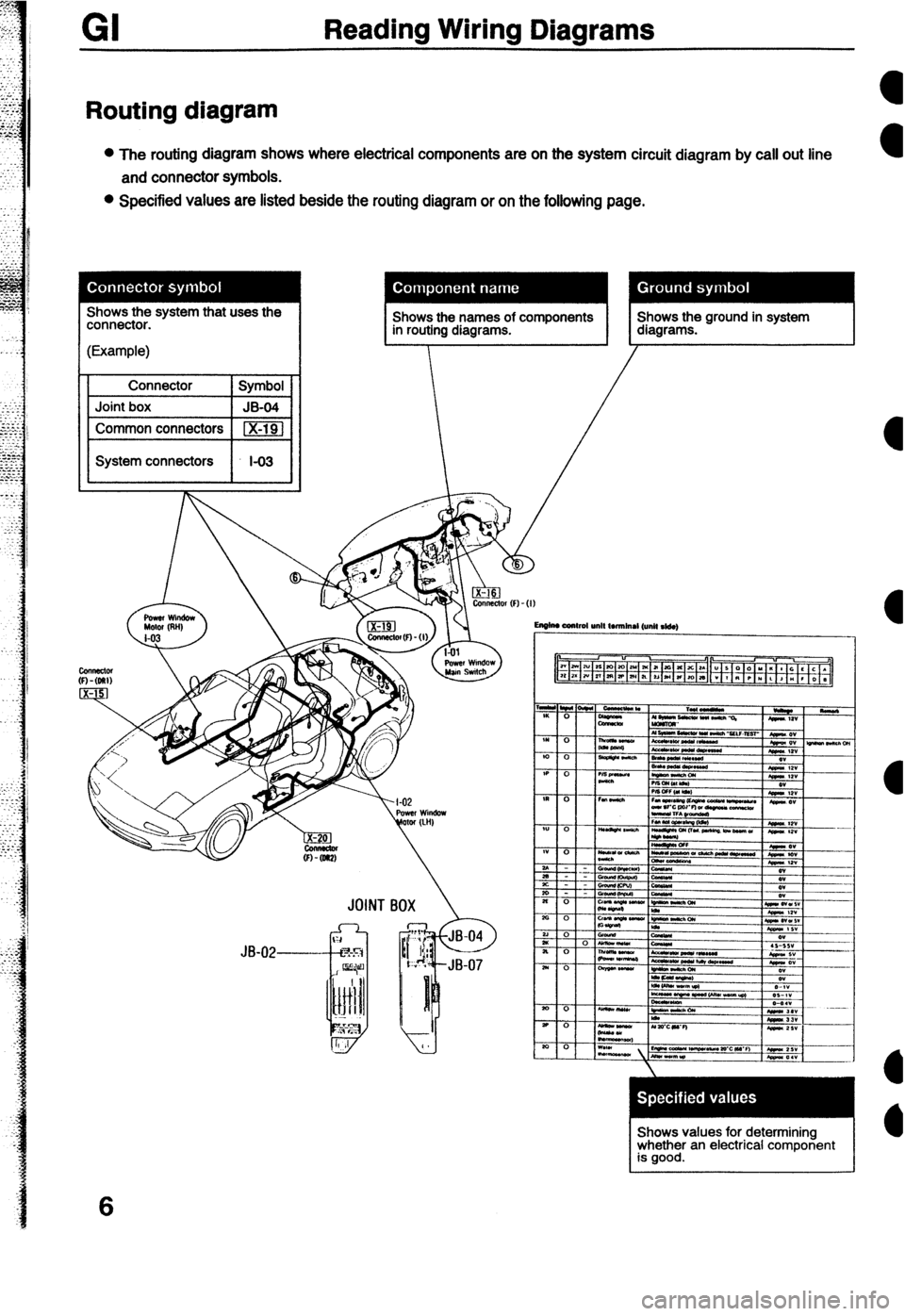
GI Reading Wiring Diagrams
Routing diagram
l The routing diagram shows where electrical components are on the system circuit diagram by call out line
and connector symbols.
l Specified values are listed beside the routing diagram or on the following page.
Shows the names of components in routing diagrams. Shows the ground in system
diagrams. JOINT B
Shows values for determining
whether an electrical component
is good.
6
Page 188 of 279

Reading Wiring Diagrams GI
HARNESS SYMBOLS
DESCRIPTION OF HARNESS
FRONT HARNESS
ENGINE HARNESS
INSTRUMENT PANEL HARNESS
REARHARNESS
REAR NO.2 HARNESS
REAR NO.3 HARNESS SYMBOL
F) TTT
E) m
(1) %4l
(W
VW m
(R3) DESCRIPTION OF HARNESS
EMISSION HARNESS
INJECTOR HARNESS
INTERIOR LAMP HARNESS
FLOOR HARNESS
DOOR NO.1 HARNESS
DOOR NO.2 HARNESS
NSTRUMEN\T\PANEL HARNESS (I)
FROM; HARNESS(F) SYMBOL
INTERIOR LAMP HARNESS (IN)
Page 189 of 279

GI Reading Wiring Diagrams
Symbols
Symbol Meaning Symbol Meaning
Battery
l Generates electricity through
Resistance 0 A resistor with a constant value.
chemical reaction. l Mainly used to protect electrical
l Supplies direct current to circuits. components in circuits by maintaining
rated voltage.
l Reading resistance values.
Ground (1)
l Connecting point to vehicle body or No.1 color band other ground wire where current flows No.2 color band
-A-
from positive to negative terminal of No.3 mbr band
battery. No.4 color band
1 l Ground (1) indicates a ground point to
body through wire harness.
Ground (2)
l Gound (2) indicates point where
component is grounded directly to
body.
Remarks
l Current will not flow through a circuit if
ground is faulty.
Fuse (1)
0 Melts when current flow exceeds that
specified for circuit, interrupts current
I__q/y)__ now.
Precautions
(box)
l Do not replace with fuses exceeding
Fuse (2) specified capacity.
(Cartridge)
Main fuse/Fusible
Transistor (1)
l Electrical switching component. l Turns on when voltage is applied to Motor
0 Converts electrical energy into
mechanical energy.
Transistor (2)
0 Reading code. a Pulls in and discharges gases and
liquids.
Number of temtinak
Lamp l Emits light and generates heat when Current flows through filament. Cigarette lighter l Electrical coil that generates heat.
Page 190 of 279

-
Reading Wiring Diagrams GI
Symbol
Horn Meaning l Generates sound when current flows. Symbol Switch (1) Meaning l Allows or breaks current flow by
opening and closing circuits.
Speaker
ccl
Heater l Generates heat when current flows. Normally open (NO)
Switch (2)
I
Normally closed (NC)
Harness l Unconnected intersecting harness.
Speed sensor
+ Movement of magnet in speedometer
turns contact within sensor on and off. (Not connected)
w Connected intersecting harness.
Ignition switch
l Turning ignition key switches circuit to
operate various component.
(Connected)
Relay (1)
l Current flowing through coil produces electromagnetic force causing contact to open or close.
No current to coil Current to coil
Uormally open (NO)
Relay (2) Normally open relay (NO)
lormally closed (NC) [/I jr No flow @jj 1 Flow
Normally closed relay (NC)
Sensor (variable) a Resistance changes with other Diode l Known as a semiconductor rectifier,
components operation. the diode allows current flow in one
IA direction only.
R
CaIhode(K)--++- Anode(A)
- Flow 01 electric C”llO”,
KIIZT)-A K-A K-A
#ensor (thermistor) 0 Resistance changes with temperature. Light-emitting diode l A diode that lights when current flows.
V-ED) l Unlike ordinary bulbs, the diode does
not generate heat when it.
%u
I-
- Cathode(K) -$----- Anode(A)
Capacitor
l Component that temporarily stores
electrical charge.
----it----
Flow of current
Solenoid
l Current flowing through coil generates Reference diode l AIIOWS current to flow in one direction
electromagnetic force to operate (Zener diode) up to a certain voltage; allows current
to flow in the other direction once that
ti
n voltage is exceeded.
9