warning light MAZDA 6 2002 Suplement Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MAZDA, Model Year: 2002, Model line: 6, Model: MAZDA 6 2002Pages: 909, PDF Size: 17.16 MB
Page 584 of 909

ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
K2–169
K2
DTC P0778A6E577018901226
DTC P0778 2-4 brake solenoid valve circuit malfunction (open/short)
DETECTION
CONDITION•Open or short in 2-4 brake solenoid signal system (while TCM monitors solenoid output voltage, the
voltage that differs from the ON/OFF signal output by CPU in TCM is detected).
Diagnostic support note:
•This is continuous monitor (CCM).
•MIL does not illuminates.
•PENDING CODE is not available.
•FREEZE FRAME DATA is not available.
•AT warning light indication.
•DTC is stored in TCM memory.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Open circuit between 2-4 brake solenoid valve terminal A and TCM terminal 2V
•Short to ground between 2-4 brake solenoid valve terminal A and TCM terminal 2V
•Short to power between 2-4 brake solenoid valve terminal A and TCM terminal 2V
•2-4 brake solenoid valve malfunction
•Damaged connector between 2-4 brake solenoid valve and TCM
•TCM malfunction
CPU
CPU2V
A
D
A
A J 2PB TCM
AT X
TCM
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTORTERMINAL COMPONENT
NO.1(12-PIN)
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
COUPLER COMPONENT
(10-PIN)
PART SIDE CONNECTOR2-4 BRAKE
SOLENOID VALVE
2-4 BRAKE
SOLENOID VALVE
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
Page 587 of 909

K2–172
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
DTC P0791A6E577018901227
DTC P0791 Intermediate sensor circuit malfunction (open/short)
DETECTION
CONDITION•Rotation speed of output gear (intermediate sensor) is low when vehicle speed and engine speed exceed
the preprogrammed value.
Diagnostic support note:
•This is continuous monitor (CCM).
•MIL illuminates if TCM detects the above malfunction condition.
•PENDING CODE is not available.
•FREEZE FRAME DATA is available.
•AT warning light indication.
•DTC is stored in TCM memory.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Intermediate sensor malfunction.
•Short to ground between intermediate sensor terminal B and TCM terminal 1K
•Short to ground between intermediate sensor terminal A and TCM terminal 1X
•Open circuit between intermediate sensor terminal B and TCM terminal 1K
•Open circuit between intermediate sensor terminal A and TCM terminal 1X
•Damaged connectors between intermediate sensor and TCM.
•TCM malfunction.
D
B
AC
1K
1X CDTCM
AT X
TCM
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
TERMINAL COMPONENT
NO.2(8-PIN)
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
COUPLER COMPONENT
(8-PIN)
PART SIDE CONNECTORINTERMEDIATE SENSOR
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR INTERMEDIATE
SENSOR
Page 590 of 909

ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
K2–175
K2
DTC P0798A6E577018901228
DTC P0798 High clutch solenoid valve circuit malfunction (open/short)
DETECTION
CONDITION•Open or short is high clutch solenoid signal system (while TCM monitors solenoid output voltage, the
voltage that differs from the ON/OFF signal output by CPU in TCM is detected).
Diagnostic support note:
•This is continuous monitor (CCM).
•MIL does not illuminate.
•PENDING CODE is not available.
•FREEZE FRAME DATA is not available.
•AT warning light indication.
•DTC is stored in TCM memory.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Open circuit between high clutch solenoid valve terminal A and TCM terminal 2U
•Short to ground between high clutch solenoid valve terminal A and TCM terminal 2U
•Short to power between high clutch solenoid valve terminal A and TCM terminal 2U
•high clutch solenoid valve malfunction
•Damaged connector between high clutch solenoid valve and TCM
•TCM malfunction
C
F
A
A J 2PB 2U TCM
CPU
CPUAT X
TCM
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
TERMINAL COMPONENT
NO.1(12-PIN)
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
COUPLER COMPONENT
(10-PIN)
PART SIDE CONNECTORHIGH CLUTCH
SOLENOID VALVE
HIGH CLUTCH SOLENOID VALVE
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
Page 593 of 909

K2–178
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
DTC P1710A6E577018901229
DTC P1710 GND return circuit malfunction
DETECTION
CONDITION•TCM detects open circuit in GND return signal line from solenoid valve.
Diagnostic support note:
•This is a diagnostic support DTC (monitored one per key cycle).
•MIL does not illuminate.
•PENDING CODE is not available.
•FREEZE FRAME DATA is not available.
•AT warning light does not indication.
•DTC is stored in TCM memory.
POSSIBLE
CAUSE•Open circuit between duty type solenoid valves terminal and TCM terminal 2P
•Damaged connector between solenoid valve and TCM
•TCM malfunction
A J 2PB TCM
CPU
CPUAT X
TCM
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR TERMINAL COMPONENT
NO.1(12-PIN)
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
COUPLER COMPONENT
(10-PIN)
PART SIDE CONNECTORSOLENOID VALVE
SOLENOID VALVE
HARNESS SIDE CONNECTOR
Page 631 of 909

M–1
M
MFRONT AND REAR AXLES
OUTLINE............................................................... M-2
OUTLINE OF CONSTRUCTION ........................ M-2
FEATURES ......................................................... M-2
SPECIFICATIONS .............................................. M-2
REAR AXLE.......................................................... M-4
REAR AXLE OUTLINE ....................................... M-4
CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW ............................... M-4
DRIVE SHAFT....................................................... M-5
DRIVE SHAFT OUTLINE.................................... M-5
STRUCTURAL VIEW.......................................... M-5
REAR DRIVE SHAFT ......................................... M-5
REAR DIFFERENTIAL.......................................... M-6
REAR DIFFERENTIAL OUTLINE ....................... M-6
CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW ............................... M-6
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM............ M-7
OUTLINE ............................................................ M-7
ELECTRONIC CONTROL COUPLING .............. M-9
DIFFERENTIAL OIL TEMPERATURE
SENSOR ........................................................ M-12
4WD WARNING LIGHT .................................... M-12
4WD CONTROL MODURE .............................. M-13
4WD SYSTEM CONTROL................................ M-14
CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (CAN) ........ M-15
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC ............................... M-16
OUTLINE............................................................. M-18
SUPPLEMENTAL SERVICE
INFORMATION .............................................. M-18
LOCATION INDEX.............................................. M-19
AXLE/DRIVE SHAFT LOCATION INDEX ......... M-19
REAR DIFFERENTIAL/ELECTRONIC
4WD CONTROL SYSTEM LOCATION
INDEX ............................................................ M-20
GENERAL PROCEDURES................................. M-21
PRECAUTION (FRONT AND REAR AXLE) ..... M-21
REAR AXLE........................................................ M-22
WHEEL HUB BOLT REPL
ACEMENT ..................................................... M-22
WHEEL HUB, KNUCKLE
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................... M-22
FRONT DRIVE SHAFT........................................ M-29
JOINT SHAFT (MZR-CD (RF TURBO))
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ......................... M-29
JOINT SHAFT (4WD)
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ......................... M-31
FRONT DRIVE SHAFT
(MZR-CD (RF TURBO))
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ......................... M-34
FRONT DRIVE SHAFT (4WD)
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ......................... M-39REAR DRIVE SHAFT.......................................... M-42
REAR DRIVE SHAFT PRE-INSPECTION ........ M-42
REAR DRIVE SHAFT
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................... M-43
REAR DRIVE SHAFT
DISASSEMBLY/ASSEMBLY ......................... M-45
REAR DIFFERENTIAL........................................ M-48
DIFFERENTIAL OIL INSPECTION ................... M-48
DIFFERENTIAL OIL REPLACEMENT .............. M-48
OIL SEAL (SIDE GEAR) REPLACEMENT ....... M-49
OIL SEAL (COMPANION FLANGE)
REPLACEMENT ............................................ M-49
REAR DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................... M-51
REAR DIFFERENTIAL DISASSEMBLY ........... M-52
REAR DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY ................. M-56
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM.......... M-65
DIFFERENTIAL OIL TEMPERATURE
SENSOR INSPECTION ................................. M-65
DIFFERENTIAL OIL TEMPERATURE
SENSOR REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........... M-65
4WD SOLENOID INSPECTION........................ M-66
4WD CONTROL MODURE INSPECTION ........ M-66
4WD CONTROL MODURE
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................... M-67
COUPLING COMPONENT
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION ........................... M-68
COUPLING COMPONENT
DISASSEMBLY .............................................. M-69
COUPLING COMPONENT ASSEMBLY........... M-72
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC.................................. M-75
WIRING DIAGRAM ........................................... M-75
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSIS ............................... M-76
DTC P1887 ....................................................... M-77
DTC P1888 ....................................................... M-79
DTC U0100 ....................................................... M-80
DTC U0101 ....................................................... M-80
DTC U0121 ....................................................... M-80
TROUBLESHOOTING......................................... M-81
SYSTEM WIRING DIAGRAM ........................... M-81
FOREWORD ..................................................... M-82
SYMPTOM TROUBLESHOOTING ................... M-82
NO.1 FREQUENT FRONT WHEEL SLIP ......... M-82
NO.2 TIGHT CORNER BRAKING .................... M-83
NO.3 ABNORMAL NOISE AND/OR
VIBRATION FROM COUPLING
COMPONENT ................................................ M-84 FEATURES
SERVICE
Page 637 of 909
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
M–7
M
OUTLINEA6E632227100201Features
Improved off-road mobility, handling stability, operability, fuel economy and marketability
•An electronic 4WD control system, which automatically optimizes traction distribution to the front and rear
wheels, has been adopted.
Improved serviceability
•A self-diagnostic function has been adopted for the electronic 4WD control system.
Electronic 4WD control system outline
•The newly adopted electronic 4WD control system automatically and optimally controls drive torque distribution
for the front and rear wheels. Due to this off-road mobility, driving stability and fuel economy are improved.
•Based on the input signals from each sensor, the 4WD control modure (4WD CM) determines vehicle driving
and road conditions, and controls output current to the electronic control coupling (4WD solenoid) inside the
rear differential. This control allows for optimal distribution of the drive torque from the engine to the rear
wheels.
•Also, the 4WD CM automatically controls the 4WD, greatly reducing the load on the driver and improving
operability.
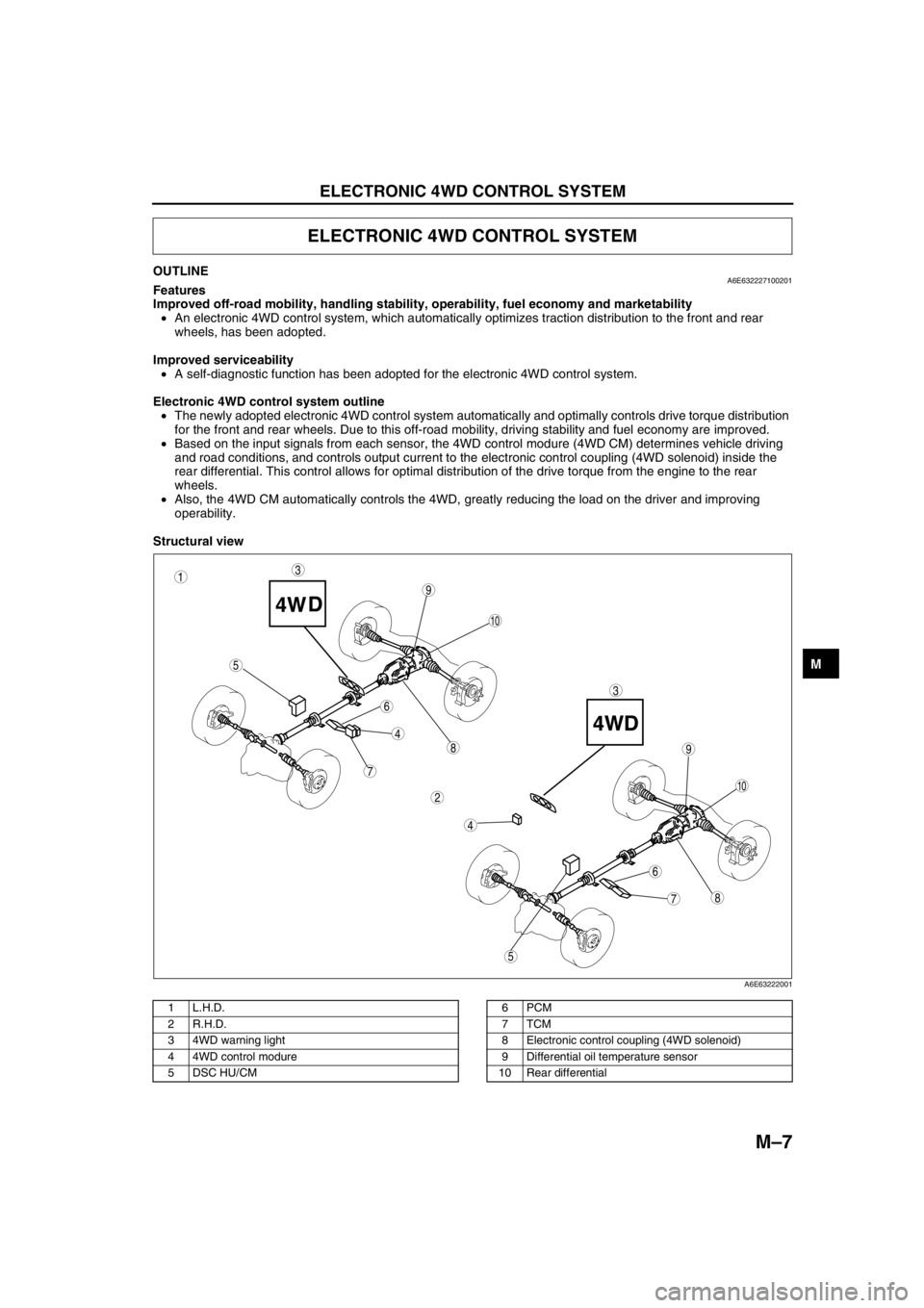
Structural view
.
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
87
5
4
3
6
9
8
7
5
4
3
10
6
1
2
9
10
A6E63222001
1L.H.D.
2 R.H.D.
3 4WD warning light
4 4WD control modure
5 DSC HU/CM6PCM
7TCM
8 Electronic control coupling (4WD solenoid)
9 Differential oil temperature sensor
10 Rear differential
Page 638 of 909
M–8
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
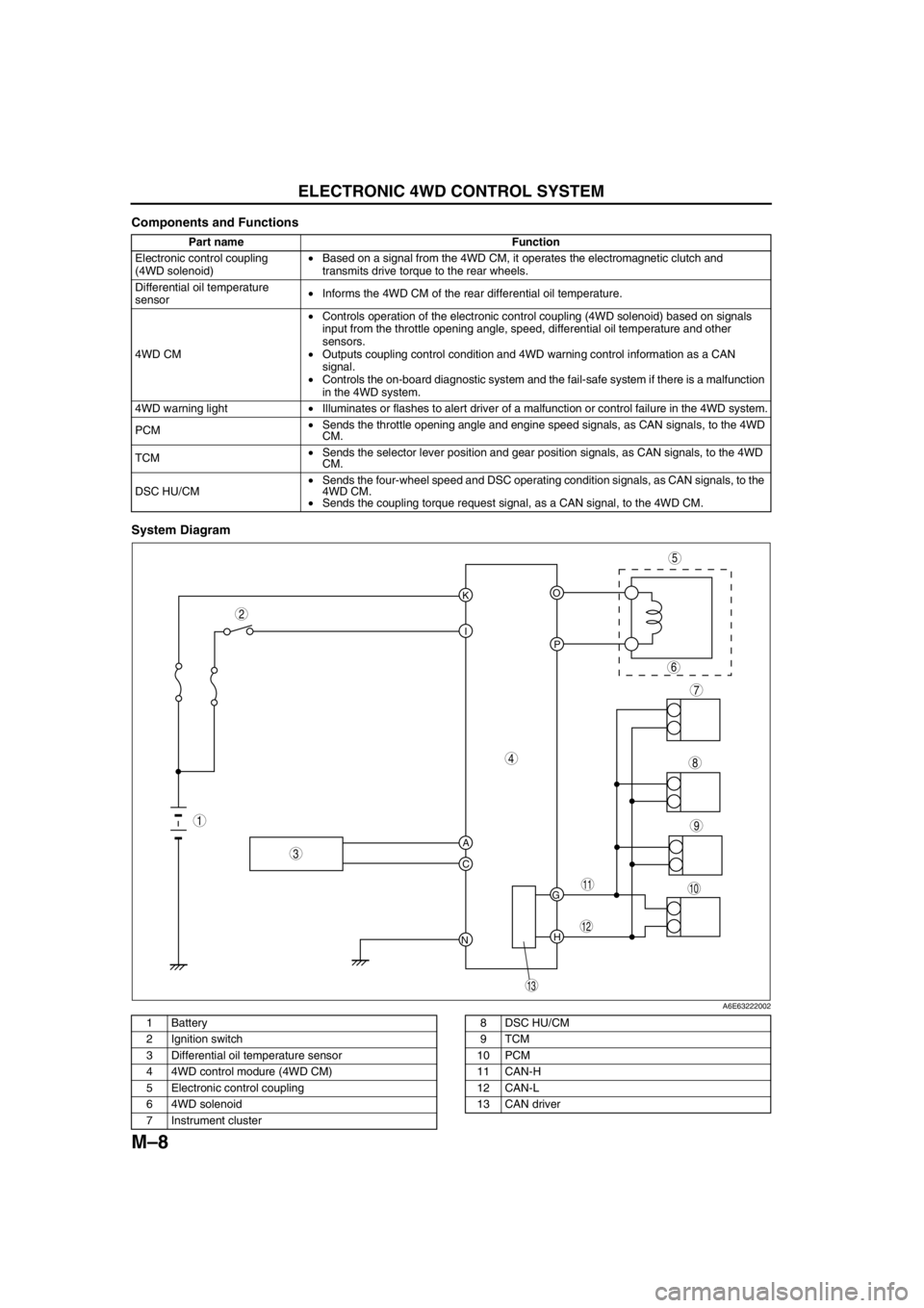
Components and Functions
System Diagram
.
Part name Function
Electronic control coupling
(4WD solenoid)•Based on a signal from the 4WD CM, it operates the electromagnetic clutch and
transmits drive torque to the rear wheels.
Differential oil temperature
sensor•Informs the 4WD CM of the rear differential oil temperature.
4WD CM•Controls operation of the electronic control coupling (4WD solenoid) based on signals
input from the throttle opening angle, speed, differential oil temperature and other
sensors.
•Outputs coupling control condition and 4WD warning control information as a CAN
signal.
•Controls the on-board diagnostic system and the fail-safe system if there is a malfunction
in the 4WD system.
4WD warning light•Illuminates or flashes to alert driver of a malfunction or control failure in the 4WD system.
PCM•Sends the throttle opening angle and engine speed signals, as CAN signals, to the 4WD
CM.
TCM•Sends the selector lever position and gear position signals, as CAN signals, to the 4WD
CM.
DSC HU/CM•Sends the four-wheel speed and DSC operating condition signals, as CAN signals, to the
4WD CM.
•Sends the coupling torque request signal, as a CAN signal, to the 4WD CM.
KO
P I
A
C
NH G
9
8
7
5
4
3
10
13
11
12
6
1
2
A6E63222002
1 Battery
2 Ignition switch
3 Differential oil temperature sensor
4 4WD control modure (4WD CM)
5 Electronic control coupling
6 4WD solenoid
7 Instrument cluster8 DSC HU/CM
9TCM
10 PCM
11 CAN-H
12 CAN-L
13 CAN driver
Page 642 of 909
M–12
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
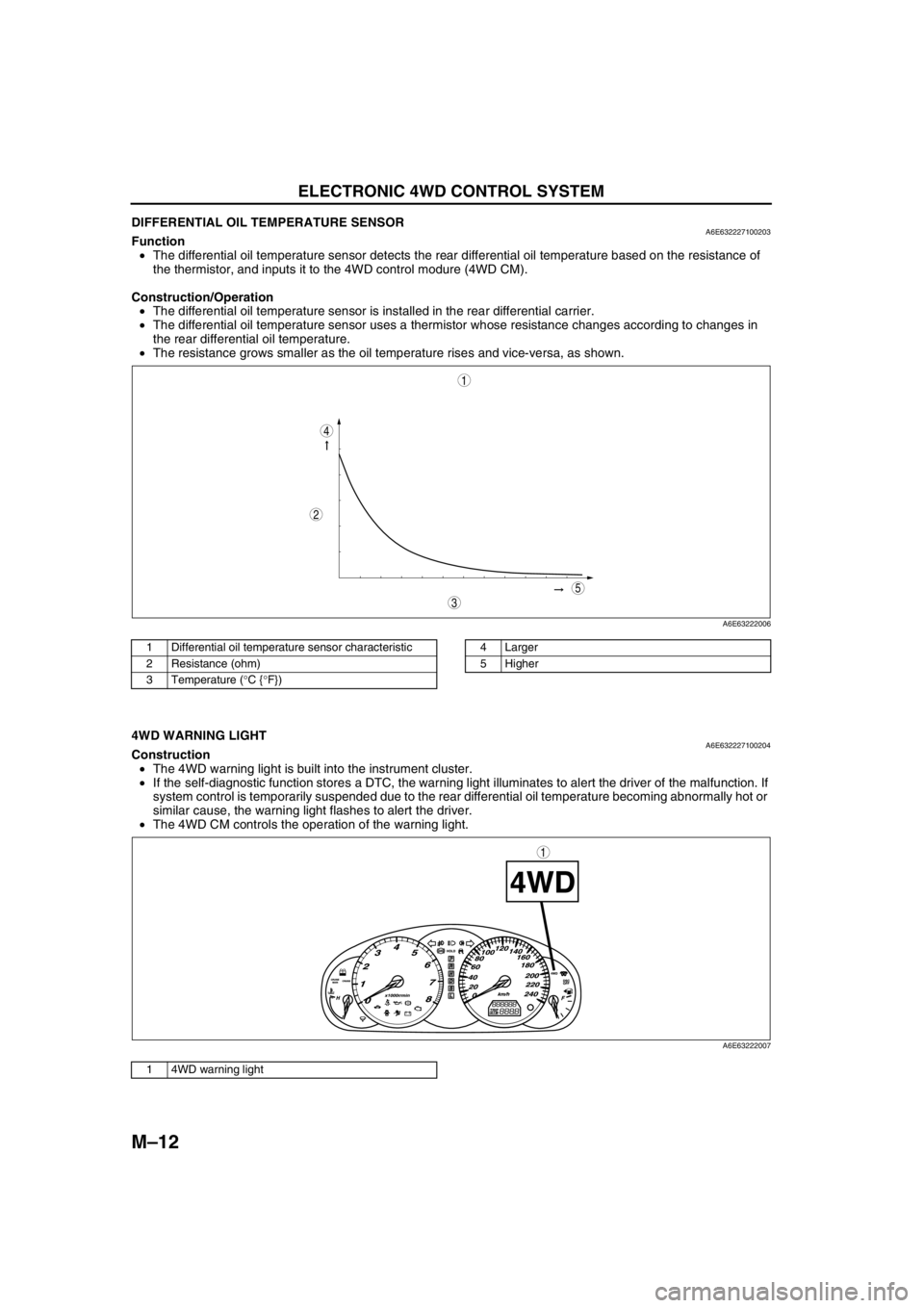
DIFFERENTIAL OIL TEMPERATURE SENSORA6E632227100203Function
•The differential oil temperature sensor detects the rear differential oil temperature based on the resistance of
the thermistor, and inputs it to the 4WD control modure (4WD CM).
Construction/Operation
•The differential oil temperature sensor is installed in the rear differential carrier.
•The differential oil temperature sensor uses a thermistor whose resistance changes according to changes in
the rear differential oil temperature.
•The resistance grows smaller as the oil temperature rises and vice-versa, as shown.
.
End Of Sie
4WD WARNING LIGHTA6E632227100204Construction
•The 4WD warning light is built into the instrument cluster.
•If the self-diagnostic function stores a DTC, the warning light illuminates to alert the driver of the malfunction. If
system control is temporarily suspended due to the rear differential oil temperature becoming abnormally hot or
similar cause, the warning light flashes to alert the driver.
•The 4WD CM controls the operation of the warning light.
.
End Of Sie
5
4
3
1
2
A6E63222006
1 Differential oil temperature sensor characteristic
2 Resistance (ohm)
3 Temperature (°C {°F})4 Larger
5 Higher
1
A6E63222007
1 4WD warning light
Page 643 of 909
ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
M–13
M
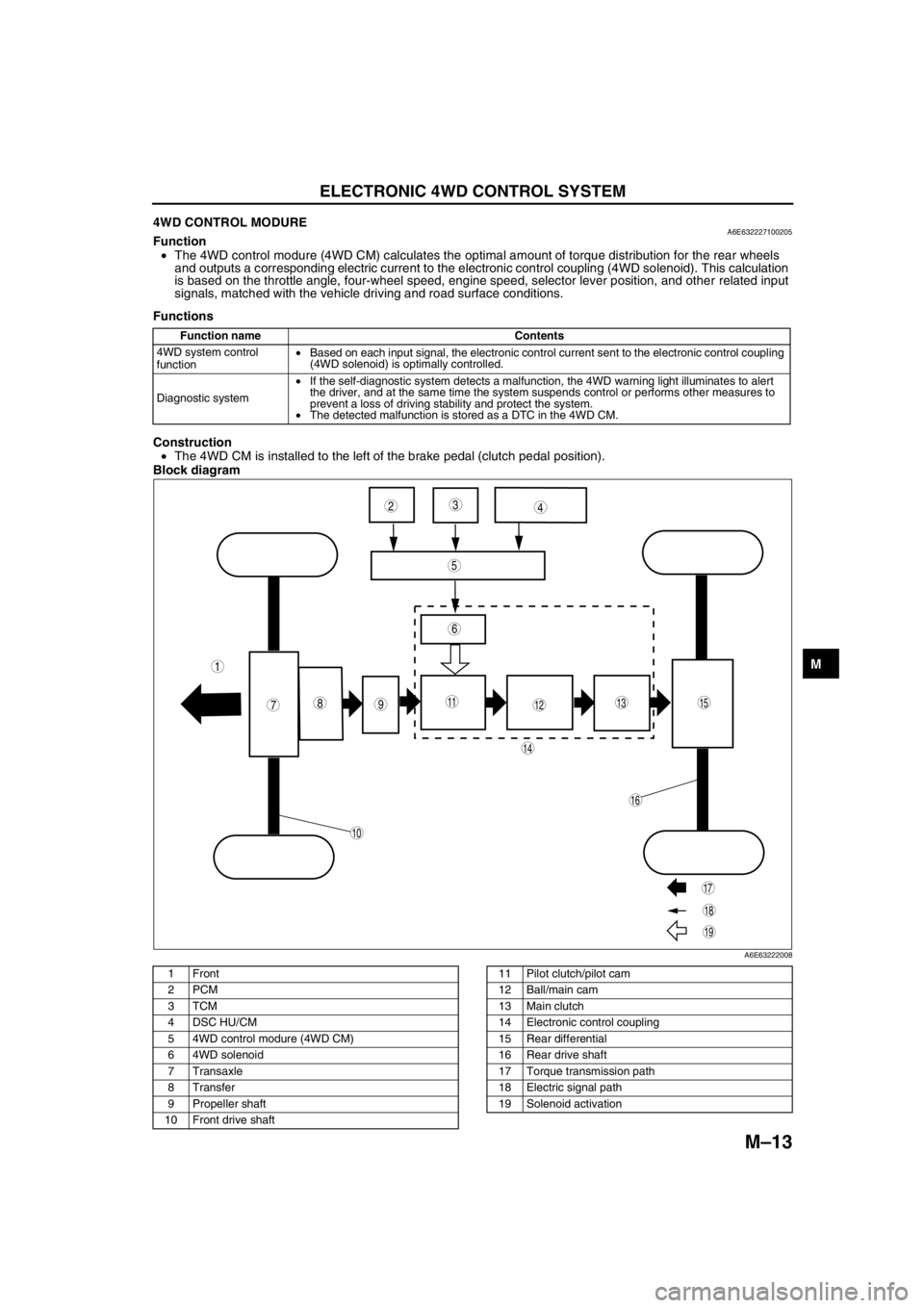
4WD CONTROL MODUREA6E632227100205Function
•The 4WD control modure (4WD CM) calculates the optimal amount of torque distribution for the rear wheels
and outputs a corresponding electric current to the electronic control coupling (4WD solenoid). This calculation
is based on the throttle angle, four-wheel speed, engine speed, selector lever position, and other related input
signals, matched with the vehicle driving and road surface conditions.
Functions
Construction
•The 4WD CM is installed to the left of the brake pedal (clutch pedal position).
Block diagram
.
Function name Contents
4WD system control
function•Based on each input signal, the electronic control current sent to the electronic control coupling
(4WD solenoid) is optimally controlled.
Diagnostic system•If the self-diagnostic system detects a malfunction, the 4WD warning light illuminates to alert
the driver, and at the same time the system suspends control or performs other measures to
prevent a loss of driving stability and protect the system.
•The detected malfunction is stored as a DTC in the 4WD CM.
987
5
43
10
19
18
17
15
16
14
131112
6
1
2
A6E63222008
1Front
2PCM
3TCM
4 DSC HU/CM
5 4WD control modure (4WD CM)
6 4WD solenoid
7Transaxle
8Transfer
9 Propeller shaft
10 Front drive shaft11 Pilot clutch/pilot cam
12 Ball/main cam
13 Main clutch
14 Electronic control coupling
15 Rear differential
16 Rear drive shaft
17 Torque transmission path
18 Electric signal path
19 Solenoid activation
Page 645 of 909

ELECTRONIC 4WD CONTROL SYSTEM
M–15
M
Operation
Normal control
•When starting off or accelerating during straight-ahead driving, torque transmitted to the rear wheels is
optimally controlled to ensure sufficient acceleration performance. Due to this, standing-start and acceleration
performance is improved.
•Also, in order to improve fuel economy when driving at a stable, consistent speed, torque transmitted to the
rear wheels is damped, and rear-wheel drive is controlled to maintain it close to that of the front wheels.
Tight cornering control
•When the 4WD CM determines, based on the four-wheel speed signal, that the vehicle is in tight cornering, it
reduces the torque transmitted to the rear wheels to avoid tight corner braking characteristics.
Integrated DSC control
•If a signal from the DSC HU/CM input to the 4WD CM indicates that ABS control is activated, the module
controls the torque transmitted to the rear wheels to prevent undue influence on ABS control.
•Also, when a coupling torque request signal is received from the DSC HU/CM, the module controls the torque
transmitted to the rear wheels to match the amount of requested torque.
Other control
•In case the rear differential oil temperature exceeds the specified amount, or when there is an unusually large
variation in the rotation speed of the front and rear wheels (ex. when trying to get unstuck), control is
temporarily suspended in order to protect the 4WD system. When this occurs the 4WD warning light flashes to
indicate the situation to the driver.
End Of Sie
CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (CAN)A6E632227100207Outline
•The 4WD CM transmits/receives information using the CAN system. See Section T for detailed information
regarding the CAN system.
Operation
Transmitted information
•Coupling torque
•4WD system operating condition (warning light information)
Received information
•Four-wheel speed
•Throttle opening angle
•Engine speed
•ABS/DSC operating condition
•Gear position
•Selector lever position
•Coupling torque request
End Of Sie