sensor MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 3000GT, Model: MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991Pages: 1146, PDF Size: 76.68 MB
Page 147 of 1146
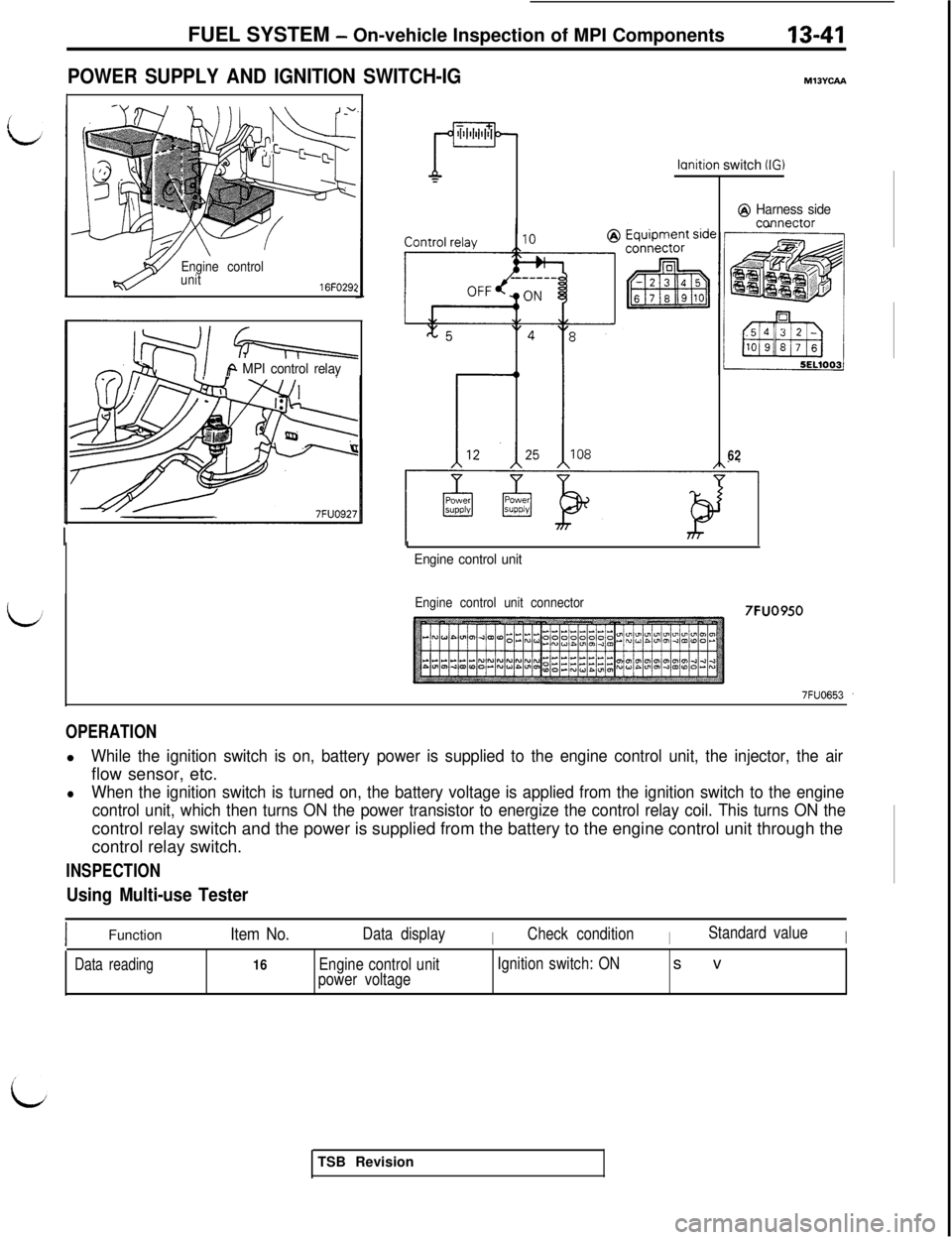
FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components13-41
POWER SUPPLY AND IGNITION SWITCH-IG
Engine control
unit
16FO29:
Q-i=++=
iA MPI control relay
ml3Yuu
lcmition switch (IG)
@ Harness sideccmnector
62
I
Engine control unit
Engine control unit connector7FUO950
OPERATIONl
While the ignition switch is on, battery power is supplied to the engine control unit, the injector, the airflow sensor, etc.
lWhen the ignition switch is turned on, the battery voltage is applied from the ignition switch to the engine
control unit, which then turns ON the power transistor to energize the control relay coil. This turns ON thecontrol relay switch and the power is supplied from the battery to the engine control unit through the
control relay switch.
INSPECTION
Using Multi-use Tester
IFunctionItem No.Data displayICheck conditionIStandard valueI
Data reading16Engine control unit
power voltageIgnition switch: ONsv
TSB Revision
Page 160 of 1146
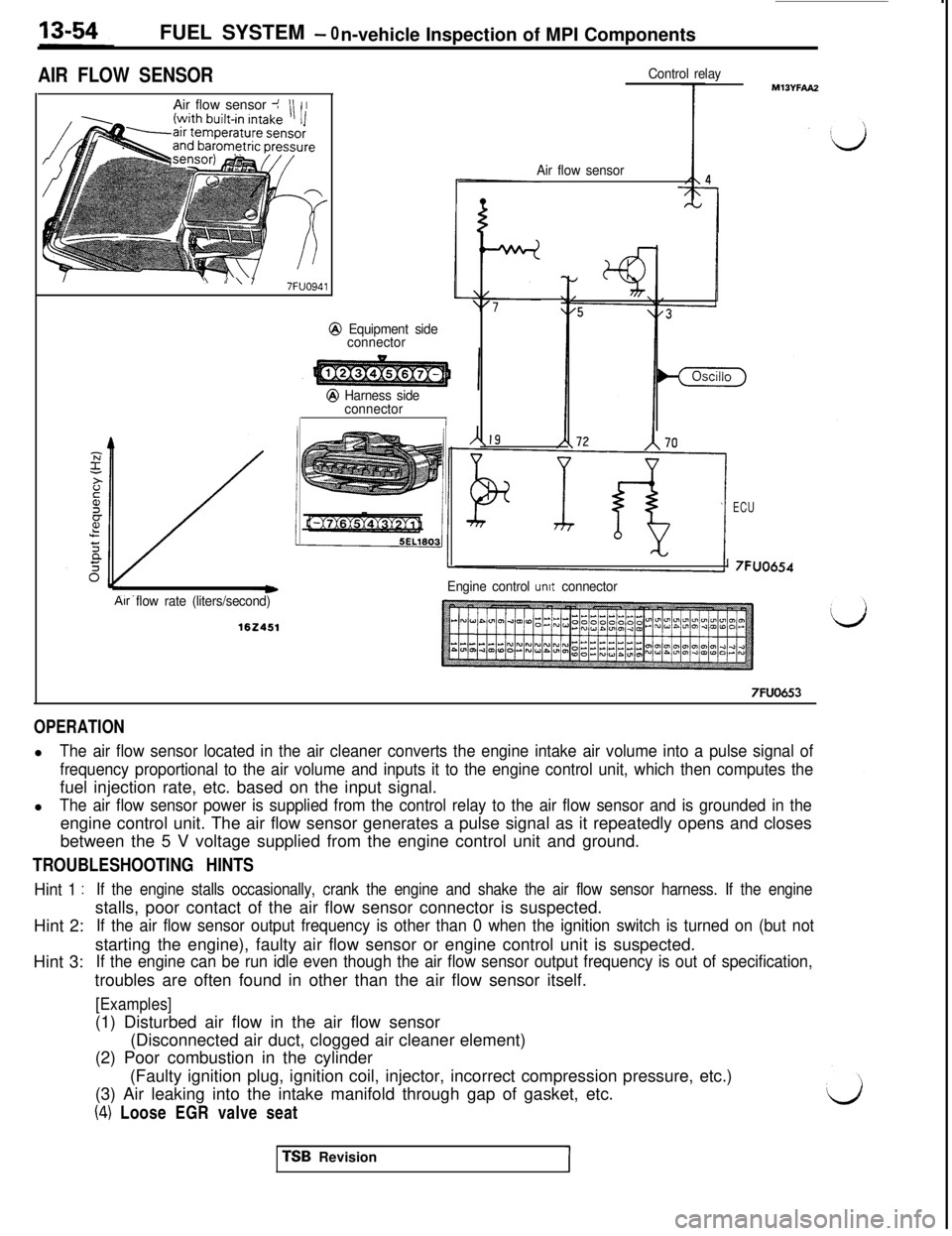
FUEL SYSTEM - 0
n-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
AIR FLOW SENSORAir flow sensor J
III I
\I\Y7FUO941
@ Equipment side
connector
Air flow rate (liters/second)
@ Harness side
connector
I
Control relay
I
Air flow sensor
ECU
’ 7FUO654
Engine control
unit connector
7FUO653
OPERATIONl
The air flow sensor located in the air cleaner converts the engine intake air volume into a pulse signal of
frequency proportional to the air volume and inputs it to the engine control unit, which then computes thefuel injection rate, etc. based on the input signal.
l
The air flow sensor power is supplied from the control relay to the air flow sensor and is grounded in theengine control unit. The air flow sensor generates a pulse signal as it repeatedly opens and closes
between the 5 V voltage supplied from the engine control unit and ground.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
Hint 1 :If the engine stalls occasionally, crank the engine and shake the air flow sensor harness. If the engineHint 2:stalls, poor contact of the air flow sensor connector is suspected.
If the air flow sensor output frequency is other than 0 when the ignition switch is turned on (but notHint 3:starting the engine), faulty air flow sensor or engine control unit is suspected.
If the engine can be run idle even though the air flow sensor output frequency is out of specification,troubles are often found in other than the air flow sensor itself.
[Examples](1) Disturbed air flow in the air flow sensor
(Disconnected air duct, clogged air cleaner element)
(2) Poor combustion in the cylinder
(Faulty ignition plug, ignition coil, injector, incorrect compression pressure, etc.)
(3) Air leaking into the intake manifold through gap of gasket, etc.
(4) Loose EGR valve seatTSB Revision
Page 161 of 1146
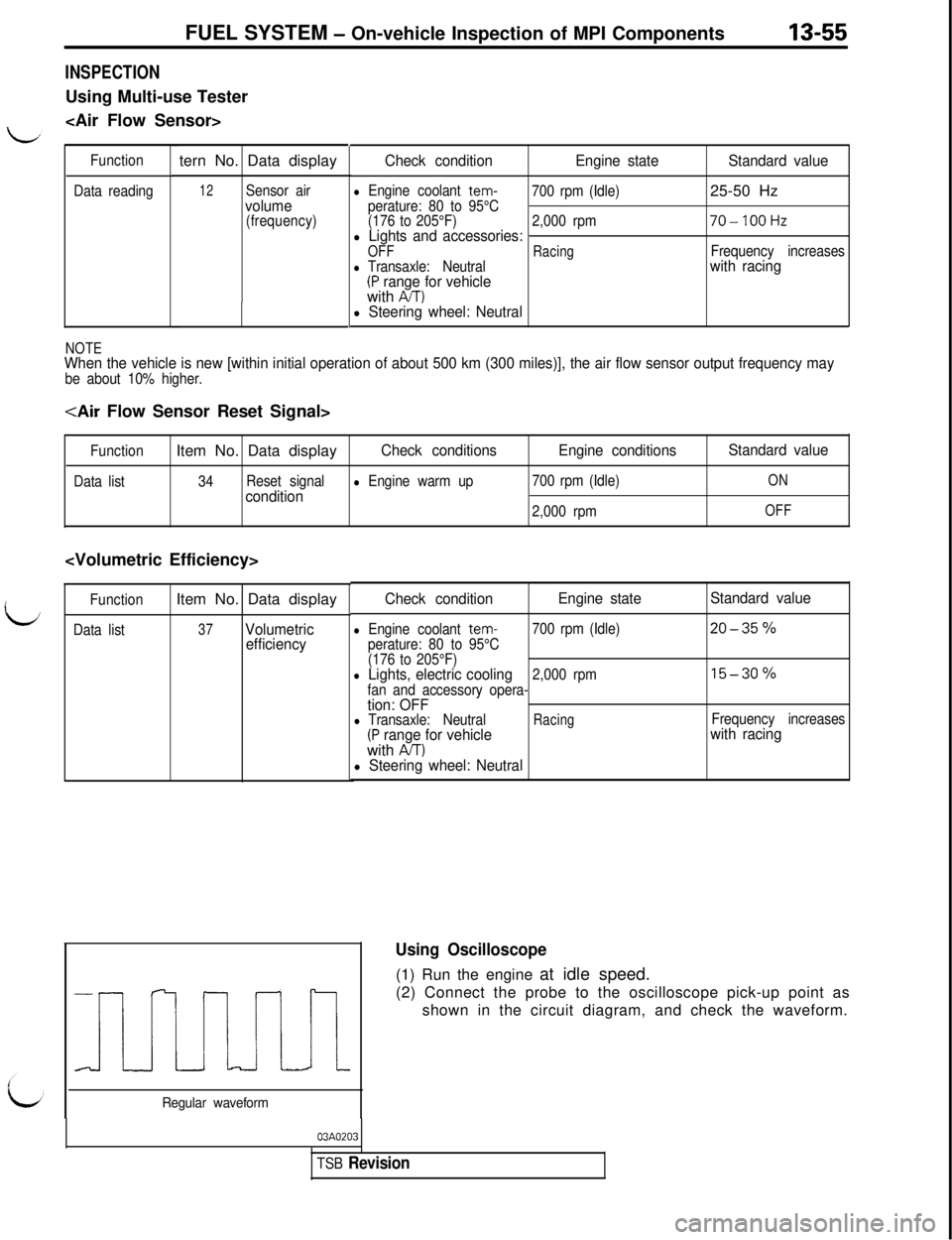
FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components13-55
INSPECTIONUsing Multi-use Tester
Function
Data readingtern No. Data display
12Sensor airvolume(frequency)
Check conditionEngine stateStandard value
l Engine coolant tem-
700 rpm (Idle)25-50 Hzperature: 80 to 95°C
(176 to 205°F)2,000 rpm70-IOOHzl Lights and accessories:OFFRacingFrequency increasesl Transaxle: Neutralwith racing(P range for vehiclewith AIT)l Steering wheel: Neutral
NOTEWhen the vehicle is new [within initial operation of about 500 km (300 miles)], the air flow sensor output frequency maybe about 10% higher.
Function
Data listItem No. Data displayCheck conditionsEngine conditionsStandard value
34Reset signall Engine warm up700 rpm (Idle)ON
condition2,000 rpmOFF
L;
FunctionItem No. Data display
Data list37Volumetric
efficiencyCheck conditionEngine stateStandard valuel Engine coolant tem-700 rpm (Idle)20-35%
perature: 80 to 95°C
(176 to 205°F)
l Lights, electric cooling2,000 rpm15-30%
fan and accessory opera-tion: OFFl Transaxle: NeutralRacingFrequency increases
(P range for vehiclewith racingwith &T)
l Steering wheel: Neutral
Using Oscilloscope(1) Run the engine at idle speed.
(2) Connect the probe to the oscilloscope pick-up point as
shown in the circuit diagram, and check the waveform.
Regular waveform
03A0203
TSB Revision
Page 162 of 1146
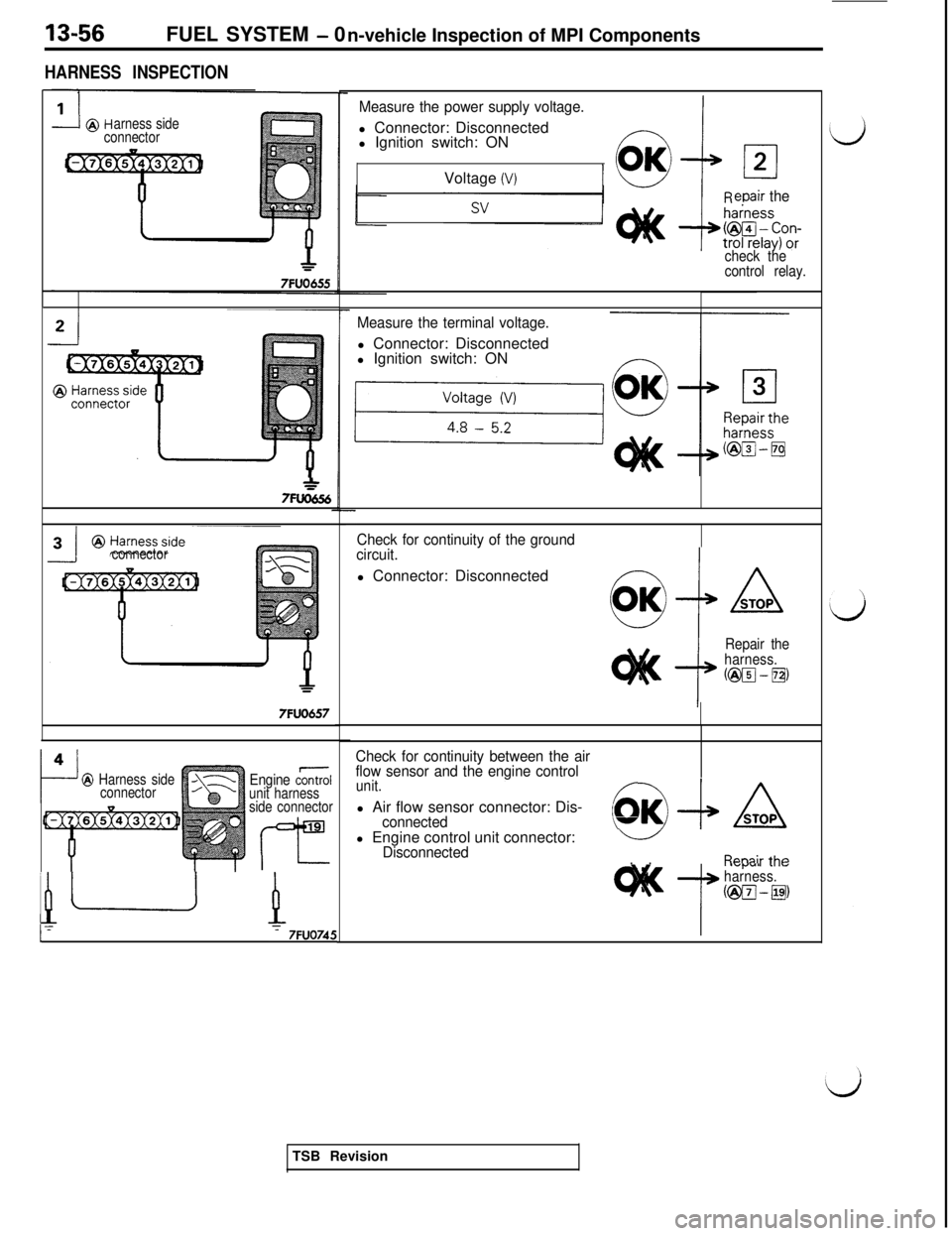
13-56FUEL SYSTEM - 0
n-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
HARNESS INSPECTION
--barness side
connector
*7FUO656
connector
7FUO6574
?
@ Harness sideEngine c&lconnector
unit harness
side connector
I -
1
m
!h 4.7Fuo745u
Measure the power supply voltage.l Connector: Disconnected
l Ignition switch: ON
Voltage
(V)
eoair the
check the
control relay.
Measure the terminal voltage.l Connector: Disconnected
l Ignition switch: ON
Check for continuity of the ground
circuit.l Connector: Disconnected
Repair the
harness.
@El - I@)
Check for continuity between the air
flow sensor and the engine control
unit.l Air flow sensor connector: Dis-f
connected10l Engine control unit connector:
‘L-/Disconnected. .Rr.annir th(
t
I ‘“yu’3harness.
TSB Revision
Page 163 of 1146
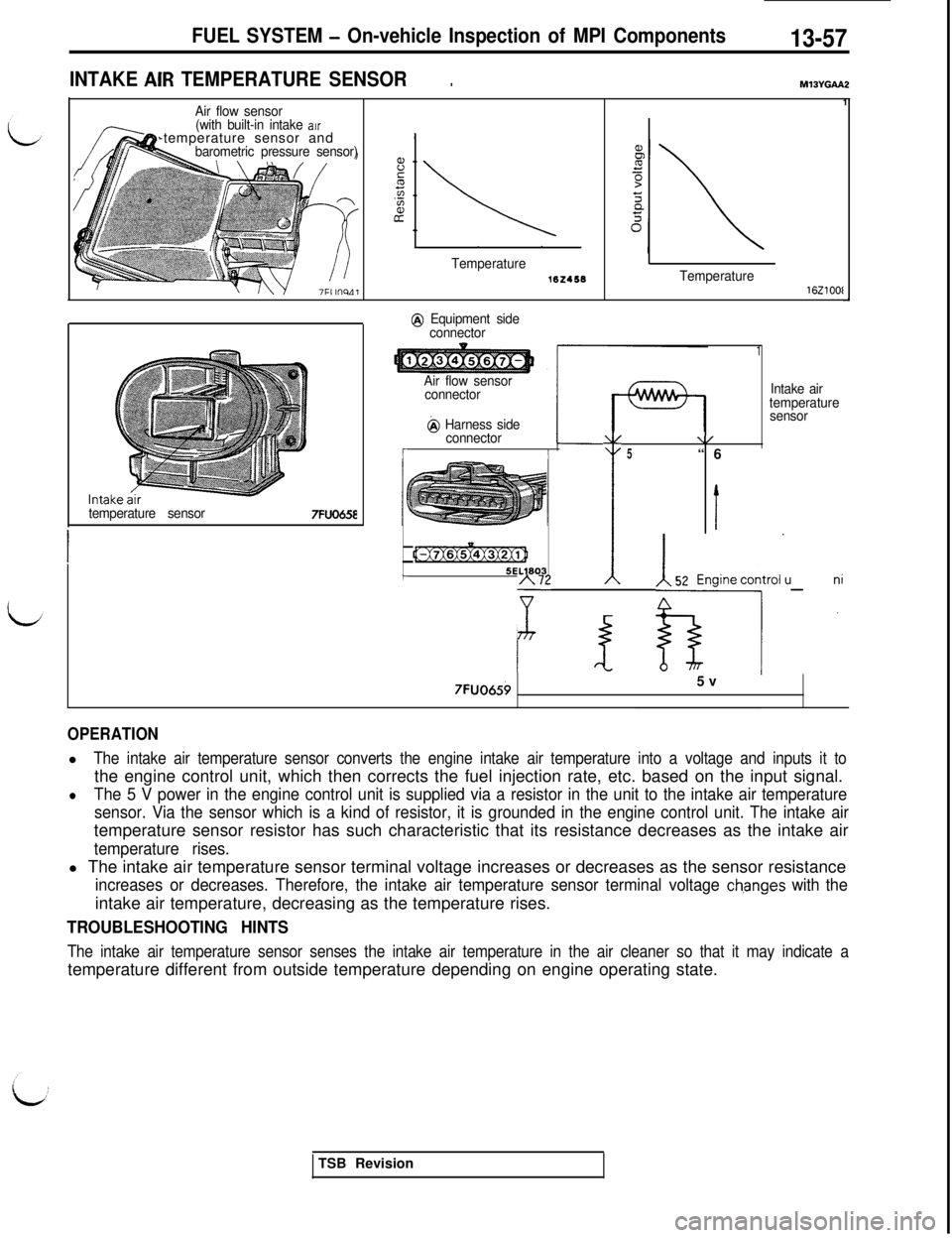
FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components13-57
INTAKE ACR TEMPERATURE SENSOR.MXWGAAZ
Air flow sensor
(with built-in intake arr-temperature sensor and
barometric pressure sensor)
temperature sensor
7FUO658
Temperature162458
@ Equipment side
connector
Air flow sensor
connector
@ Harness side
connector
r/
L
w~7X6x5x4~3x2~1j5ELl803
:
\/5“6
t
~y72 ~ [
1
Intake air
temperature
sensor
7FU065b5v
OPERATIONl
The intake air temperature sensor converts the engine intake air temperature into a voltage and inputs it tothe engine control unit, which then corrects the fuel injection rate, etc. based on the input signal.
lThe 5 V power in the engine control unit is supplied via a resistor in the unit to the intake air temperature
sensor. Via the sensor which is a kind of resistor, it is grounded in the engine control unit. The intake airtemperature sensor resistor has such characteristic that its resistance decreases as the intake air
temperature rises.l The intake air temperature sensor terminal voltage increases or decreases as the sensor resistance
increases or decreases. Therefore, the intake air temperature sensor terminal voltage ch.anges with theintake air temperature, decreasing as the temperature rises.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
The intake air temperature sensor senses the intake air temperature in the air cleaner so that it may indicate atemperature different from outside temperature depending on engine operating state.
TSB Revision
Page 164 of 1146

13-58FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
INSPECTION
Using Multi-use Tester
FunctionItem No. Data displayCheck conditionIntake air temperatureStandard valued
Data reading13Sensorignition switch: ON orAt -20°C (-4°F)-20°C
temperatureengine running
At 0°C (32°F)0°C
At 20°C (68°F)20°C
At 40°C (104°F)40°C
At 80°C (176°F)80°C
HARNESS INSPECTION7FUO657
I
connector
7FUO6607FUO661
ITSB I
Check for continuity of the groundcircuit.l Connector: Disconnected
Repair the
harness.,
(@I3 - q ,
Measure the power supply voltage.l Connector: Disconnected
l Ignition switch: ON
Voltage
(V)4.5
- 4.9Repair the
harness.
@@J-@)
SENSOR INSPECTION
(1) Disconnect the air flow sensor connectors.
(2) Measure resistance between terminals @ and
@.
ITemperature [“C (“F)]IResistance (kfl)
I0 (32)I6.0
I20 (681I2.7
wisionI
d
Page 165 of 1146
![MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Owners Guide FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components13-59
Intake air
(3) Measure resistance while heating the sensor using a hair
drier.
?
Temperature 1°C (“F)]Resistance (kR)
HigherSmaller
(4) If MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Owners Guide FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components13-59
Intake air
(3) Measure resistance while heating the sensor using a hair
drier.
?
Temperature 1°C (“F)]Resistance (kR)
HigherSmaller
(4) If](/img/19/57085/w960_57085-164.png)
FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components13-59
Intake air
(3) Measure resistance while heating the sensor using a hair
drier.
?
Temperature 1°C (“F)]Resistance (kR)
HigherSmaller
(4) If the value deviates from the standard value or the
resistance remains unchanged, replace the air flow sensor
assembly.
I
1 TSB Revision
Page 166 of 1146
![MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Owners Guide 13-60FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR
Barometric
pressure sensor7FUO66
Output voltage (VI
a---l- 760Barometric pressure [mmHg (in.Hg)] (30) EC1551
@ Equ MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Owners Guide 13-60FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR
Barometric
pressure sensor7FUO66
Output voltage (VI
a---l- 760Barometric pressure [mmHg (in.Hg)] (30) EC1551
@ Equ](/img/19/57085/w960_57085-165.png)
13-60FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR
Barometric
pressure sensor7FUO66
Output voltage (VI
a---l- 760Barometric pressure [mmHg (in.Hg)] (30) EC1551
@ Equipment side
M13YHAA2
d
connecror
Air flow sensor
connector
r
Barometric pressure sensor
@ Harness sideconnector
Engine control unit
A6 IA65A\72
7
7F U0664
Engine control unit connector
7FUO653
OPERATIONl The barometric pressure sensor converts the barometric pressure into a voltage and inputs it to the
engine control unit, which then corrects the fuel injection rate, etc. based on the input signal.
lThe 5 V power in the engine control unit is supplied to the barometric pressure sensor. Through the circuitin the sensor, it is grounded in the engine control unit.1
l
The barometric pressure sensor output voltage which is proportional to the barometric pressure (absolutepressure) is supplied to the engine control unit.
d ITSB Revision
Page 167 of 1146
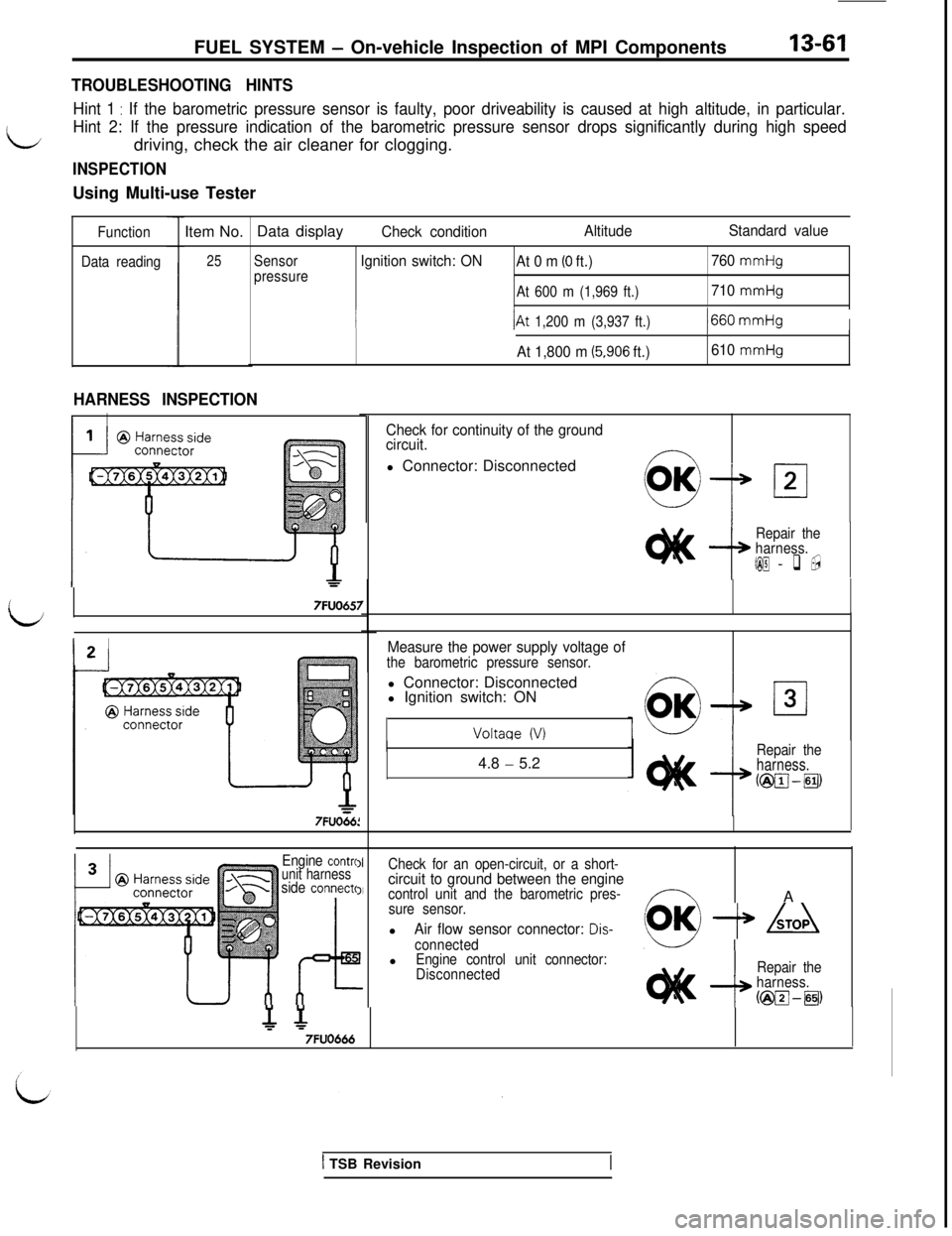
FUEL SYSTEM - On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components13-61
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
Hint 1 : If the barometric pressure sensor is faulty, poor driveability is caused at high altitude, in particular.
L
Hint 2: If the pressure indication of the barometric pressure sensor drops significantly during high speeddriving, check the air cleaner for clogging.
INSPECTIONUsing Multi-use Tester
Function
Data readingItem No.’ Data display
25
Check conditionAltitudeStandard value
Sensor
pressureIgnition switch: ON
At 0 m (0 ft.)760 mmHg
At 600 m (1,969 ft.)
710 mmHg
I/At 1,200 m (3,937 ft.)1660 mmHgI
At 1,800 m (5.906 ft.)610 mmHg
HARNESS INSPECTION
II
L
7FUO657
7FUO66:
Check for continuity of the ground
circuit.l Connector: Disconnected
Repair the
harness.
&@I - q ,
Measure the power supply voltage ofthe barometric pressure sensor.l Connector: Disconnected
l Ignition switch: ON
Voltaqe (V)4.8
- 5.2Repair theharness.
KgpJ-pJ,
Engine contraunit harnessside connects
Check for an open-circuit, or a short-circuit to ground between the enginecontrol unit and the barometric pres-,Y---,A
sure sensor.l
Air flow sensor connector: Dis-(OK) -+ kTOA
connectedlEngine control unit connector:
Disconnected
--I
Repair the
harness.
Jg
7FUO666
1 TSB Revision
Page 168 of 1146
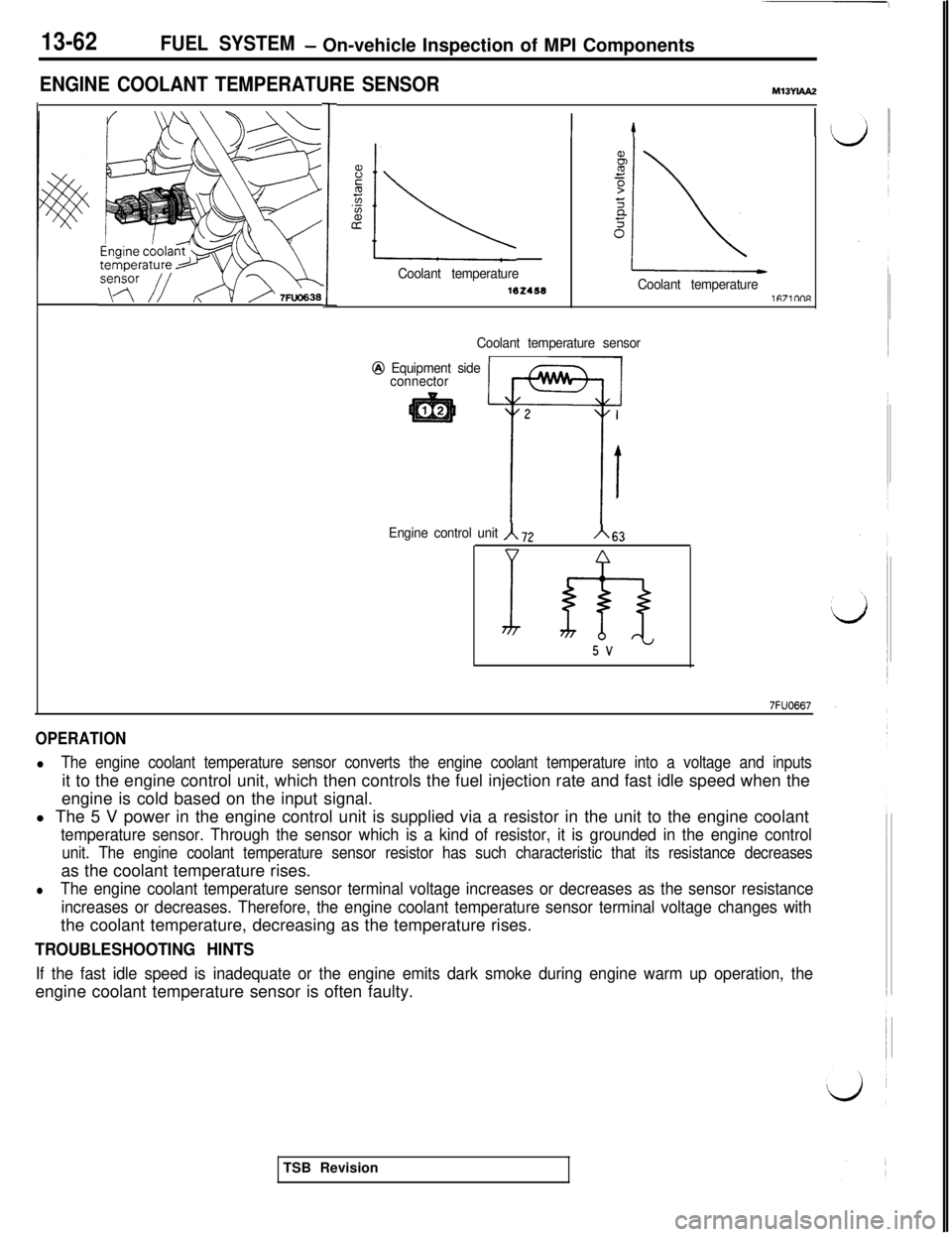
13-62FUEL SYSTEM- On-vehicle Inspection of MPI Components
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORM13Ybu2
1
If
il\__ ;I\*
Coolant temperature
162458Coolant temperaturei67im-m
Coolant temperature sensor
@ Equipment side
connector
2
fi
I
Engine control unit ), 72A63
1 ff35V
7FUO667
OPERATION
lThe engine coolant temperature sensor converts the engine coolant temperature into a voltage and inputsit to the engine control unit, which then controls the fuel injection rate and fast idle speed when the
engine is cold based on the input signal.
l The 5 V power in the engine control unit is supplied via a resistor in the unit to the engine coolant
temperature sensor. Through the sensor which is a kind of resistor, it is grounded in the engine control
unit. The engine coolant temperature sensor resistor has such characteristic that its resistance decreasesas the coolant temperature rises.
lThe engine coolant temperature sensor terminal voltage increases or decreases as the sensor resistance
increases or decreases. Therefore, the engine coolant temperature sensor terminal voltage changes withthe coolant temperature, decreasing as the temperature rises.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
If the fast idle speed is inadequate or the engine emits dark smoke during engine warm up operation, theengine coolant temperature sensor is often faulty.
TSB Revision