roof MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1900, Model line: DIAMANTE, Model: MITSUBISHI DIAMANTE 1900Pages: 408, PDF Size: 71.03 MB
Page 13 of 408

l
l-14 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
Proper maintenance and tune-up is the key to long
and trouble-free vehicle life, and the work can yield
its own rewards. Studies have shown that a properly
tuned and maintained vehicle can achieve better gas
mileage than an out-of-tune vehicle. As a conscien-
tious owner and driver, set aside a Saturday morning,
say once a month, to check or replace items which
could cause major problems later. Keep your own
personal log to jot down which services you per-
formed, how much the parts cost you, the date, and
the exact odometer reading at the time. Keep all re-
selfer, these receipts are the only proof you have that ceipts for such items as engine oil and filters, so that
they may be referred tp in case of related problems or
to determine operating expenses. As a do-it-your- the required maintenance was performed. In the event
of a warranty problem, these receipts will be invalu-
able.
The literature provided with your vehicle when it
was originally delivered includes the factory recom-
mended maintenance schedule. If you no longer have
this literature, replacement copies are usually avail-
able from the dealer. A maintenance schedule is pro-
vided later in this section, in case you do not have
the factory literature. *
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
Except 2.gL Turbocharged Engine
b See Figures 36 thru 41 9. Place a new air cleaner element inside the
lower housing. Make sure the seal on the element is
fully seated in the groove.
10. Install the upper air cleaner housing and inlet
tube onto the lower housing.
11. Tighten the clamp on the inlet tube at the
throttle body.
12. Attach the breather hose onto the air inlet tube.
13. Plug the connector into the MAF sensor.
14. Attach the air cleaner housing retaining clips.
15. Connect the negative battery cable.
2.DL Turbocharged Engine
b See Figure 42
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Detach the air flow sensor connector.
3. Unfasten the boost hose.
4. Disconnect the solenoid valve with hoses.
93151p50 Fig. 36 Release the retaining clips from the
air cleaner housing
r3151p47 Fig. 37 Unplug the MAF sensor connector
Fig. 49
. . . then remove the air outlet tube
and upper housing from the lower housing 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable. 5. Disconnect the air intake hose.
2. Release the retaining clips from the air 6. Unfasten tie air cleaner retainer bolts and the
cleaner housing. air cleaner assembly.
3. Loosen the clamp on the air outlet tube at the 7. Unclamp the cover and remove from the hous-
throttle body. ing.
4. Detach the breather hose from the air inlet
tube. *Care must be taken when removing the air
cleaner cover. The air flow sensor is at-
5. Unplug the MAF sensor connector.
6. Separate the upper and lower air cleaner tached and could be damaged during cover
removal.
housings and remove the air outlet tube and upper
housing from the lower housing.
7. Remove the air cleaner element from the
housing.
To install:
8. Clean the inside of the air cleaner housing of
any dirt and debris that has collected inside. 8. Remove the air cleaner element. Thoroughly
clean the air cleaner housing prior to replacing the air
filter.
To install:
9. Install the new air cleaner element into the
housing. Install and secure the cover in place.
Fig. 38 Detach the breather hose from the
air tniet tube
Fig. 41 Remove the air cleaner element
from the housing Fig. 39 Loosen the clamp on the air outlet
tube at the throttle body . . .
Fig. 42 Detach the air flow sensor connec-
tor, the boost hose and the solenoid valve
connector
Page 25 of 408

.
1-26 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
TDC of the compression stroke. If this happens, the
piston WIII be at the beginning of the power stroke
just as the compressed and ignited air/fuel mixture
forces the piston down and turns the crankshaft. Be-
cause it takes a fraction of a second for the spark
plug to ignite the mixture in the cylinder, the spark
plug must fire a little before the piston reaches TDC.
Otherwise, the mixture will not be completely ignited
as the piston passes TDC and the full power of the
explosion will not be used by the engine.
The timing measurement is given in degrees of
crankshaft rotation before the piston reaches TDC
(BTDC). If the setting for the ignition timing is 10”
BTDC, each spark plug must fire 10 degrees before
each piston reaches TDC. This only holds true, how-
ever, when the engine is at idle speed. The combus-
tion process must be complete by 23”ATDC to main-
tain proper engine performance, fuel mileage, and
low emissions.
As the engine speed increases, the pistons go
faster. The spark plugs have to ignite the fuel even
sooner if it IS to be completely ignited when the pis-
ton reaches TDC. If the ignition is set too far ad-
vanced (BTDC), the ignition and expansion of the fuel
in the cylinder wtll occur too soon and tend to force
the piston down while it is still traveling up. Thus
causes pre ignition or “knockmg and pinging”. If the
ignition spark is set too far retarded, or after TDC
(ATDC), the piston will have already started on its
way down when the fuel is ignited. The piston will be
forced down for only a portion of its travel, resulting
in poor engine performance and lack of power.
Timing marks or scales can be found on the rim of
the crankshaft pulley and the timing cover. The marks
on the pulley correspond to the posrtion of the piston
in the No. 1 cylinder. A stroboscopic (dynamic) tim-
ing light is hooked onto the No. 1 cylinder spark plug
wrre. Every time the spark plug fires, the timing light
flashes. By aiming the light at the timing marks while
the engine is running, the exact position of the piston
within the cylinder can be easily read (the flash of
light makes the mark on the pulley appear to be
standing still). Proper timing is indicated when the
mark and scale are in specified alignment.
When checking timing with the engine run-
ning, take care not to get the timing light
wires tangled in the tan blades and/or drive
belts.
INSPECTION &ADJUSTMENT
1990-96 Models
e See Figures 113 thru 119
1. Set the parking brake, start and run the engine
until normal operating temperature is obtained. Keep
all lights and accessories OFF and the front wheels
straight-ahead. Place the transaxle in
P for automatic
transaxle or Neutral for manual transaxle.
2. If not at specification, set the idle speed to the
correct level.
3. Turn the engine
OFF. Remove the water-
proof cover from the igmtion timing adjusting con-
nector, and connect a jumper wire from this terminal
Fig. 113 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nector-1990-92 Mirage with 1.5L engine
93151QM Fig. 115 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nectar-Galant with 2.OL engines
93151QO1 Fig. 117 Ignition timing adjustment con.
nectar-1994-96 Galant
to a good ground. Refer to the corresponding illustra-
tions for the correct location of the timing adjustment
connector.
4. Connect a conventional power timing light to
the No. 1 cylinder spark plug wire. Start the engine
and run at idle.
5. Aim the timing light at the timing scale lo-
cated near the crankshaft pulley.
6. Loosen the distributor or crank angle sensor
hold-down nut just enough so the housing can be ro-
tated.
7. Turn the housing in the proper direction until
the specified timing is reached. Tighten the hold-
down nut and recheck the timing. Turn the engine
OFF. 8. Remove the jumper wire from the ignition
timing adjusting terminal and install the water-proof
cover.
9. Start the engine and check the actual timing
(the timing without the terminal grounded). This
reading should be approximately 5 degrees more
than the basic timing. Actual timing may increase ac-
cording to altitude. Also, actual timing may fluctuate
because of slight variation accomplished by the ECU.
Fig. 114 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nectar-Miracle with 1.6L enaine
CHECK CONNECTOR 93151QO! Fig. 116 Ignition timing adjustment con.
nectar-1992-96 Oiamante
93151gOB Fig. 116 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nector-1993-96 Mirage with 1.5L engine
Fig. 119 Ignition timing adjustment con-
nector-1993-96 Mirage with 1.6L engine
As long as the basic timing is correct, the engine is
timed correctly.
10. Turn the engine
OFF. 11. Disconnect the timing apparatus and
tachometer.
1997-00 Models
The ignition timing is controlled by the Engine
Control Module (ECM) and is not adjustable. How-
ever it can be inspected using a scan tool.
Page 43 of 408

1-44 GENERALINFORMATIONAND MAINTENANCE
INTERIOR CLEANING
Upholstery
Fabric can usually be cleaned with soapy water or
a proper detergent. For more difficult spots caused by
oil, ice cream, soda, etc., use a fabric cleaner avail-
able at most parts stores. Be sure when purchasing
the cleaner to read the label to ensure it is safe to use
on your type of fabric. A safe method of testing the
cleaner is to apply a small amount to an area usually
unseen, such as under a seat, or other areas. Wart a
while, perhaps even a day to check the spot for fad-
ing, discoloring, etc., as some cleaners will only
cause these problems after they have dried
Leather upholstery requrres special care, it can be
cleaned with a mild soap and a soft cloth. It is recom-
mended that a special leather cleaner be used to
clean but also treat the leather surfaces in your vehi-
cle. Leather surfaces can age quickly and can crack if
not properly taken care of, so it is vital that the leather
surfaces be maintained.
Floor Mats and Carpet
The floor mats and carpet should be vacuumed or
brushed regularly. They can be cleaned with a mild
soap and water. Special cleaners are available to
clean the carpeted surfaces of your vehicle, but take
care in choosing them, and again it is best to test
them in a usually unseen spot.
Dashboard, Console, Door Panels, Etc.
The dashboard, console, door panels, and other
plastic, vinyl, or wood surfaces can be cleaned using
a mild soap and water. Caution must be taken to keep
water out of electronic accessories and controls to
avoid shorts or ruining the components Again spe-
cial cleaners are available to clean these surfaces, as
with other cleaners care must taken in purchasmg
and using such cleaners.
There are protectants available which can treat the
various surfaces in your car giving them a “shiny new
look”, however some of these protectants can cause
more harm than good in the long run. The shine that
is placed on your dashboard attracts sunlight accel-
erating the aging, fading and possibly even cracking
the surfaces. These protectants also attract more dust
to stick to the surfaces they treat, Increasing the cleaning you must do to maintain the appearance of
your vehicle. Personal discretion is advised here.
On most models covered by this manual, the
wheel bearmgs used are sealed units and do not re-
quire routine maintenance. However on some Galant
and Mirage models, the rear wheel bearing do require
periodic repacking. For removal and installation in-
structions, please refer to Section 7 (for rear bear-
ings) or Section 8 (for front bearings).
REPACKING
*Sodium based grease is not compatible
with lithium based grease. Read the package
labels and be careful not to mix the two
types. If there is any doubt as to the type of
grease used, completely clean the old
grease from the bearing and hub before re-
placing.
Before handling the bearings, there are a few
things that you should remember to do and not to do.
DO the following: l Remove all outside dirt from the housing be-
fore exposing the bearing.
l Treat a used bearing as gently as you would a
new one.
l Work with clean tools in clean surroundings. l Use clean, dry gloves, or at least clean, dry
hands.
l Clean solvents and flushing fluids are a must. l Use clean paper when laying out the bearings
to dry.
l Protect drsassembled bearings from rust and
dirt. Cover them up.
l Use clean, lint-free rags to wipe the bearings. l Keep the bearings in oil-proof paper when they
are to be stored or are not in use.
l Clean the inside of the housing before replac-
ing the bearin
Do NOT do he followino: El, l Do not work in dirty sirroundings. l Do not use dirty, chipped or damaged tools. l Do not work on wooden work benches or use
wooden mallets.
l Do not handle bearings with dirty or moist
hands.
l Do not use gasoline for cleaning. Use a safe
solvent.
l Do not spin dry bearings with compressed air.
They will be damaged.
l Do not use cotton waste or dirty cloths to wipe
bearings.
l Do not scratch or nick bearing surfaces. l Do not allow the bearina to come in contact
” with dirt or rust at any time.
The rear wheel bearinas on some Galant and Mi-
rage models require periodic maintenance. A pre-
mium high melting point grease meeting Grade
Multipurpose Grease NLGI Grade #2 or equivalent
must be used. Long fiber type greases must not be
used. This service is recommended every 30,000
miles (48,000 km).
*For information on Wheel Bearing removal
and installation, refer to Section 7 of this
manual.
1. Remove the wheel bearing.
2. Clean all parts in a non-flammable solvent and
let them air dry.
*Only use lint-free rags to dry the bearings.
Never spin-dry a bearing with compressed
air, as this will damage the rollers.
3. Check for excessive wear and damage. Replace
the bearing as necessary.
*Packina wheel bearinos with arease is
best accomplished by u&g a wheel bearing
packer (available at most automotive parts
stores).
4. If a wheel bearing packer is not available, the
bearings may be packed by hand.
a. Place a “healthy’ glob of grease in the
palm of one hand.
b. Force the edge of the bearing into the
grease so that the grease fills the space between
the rollers and the bearing cage.
c. Keep rotating the bearing while continuing
to push the grease through.
d. Continue until the grease is forced out the
other side of the bearing.
5. Place the packed bearing on a clean surface
and cover it until it is time for installation.
6. Install the wheel bearing.
# See Figures 219 and 220
To prevent the bumper from deforming, these vehi-
cles cannot be towed by a wrecker using sling-type
equipment. If these vehicles require towing, use a
wheel lift or flat bed equipment. It is recommended
that the vehicle be towed from the front If a flat bed is
not available.
Manual transaxle vehicles may be towed from the
rear provided that the transaxle is in Neutral and the
driveline has not been damaged. The steering wheel
must be clamped in the straight-ahead positron with a
steering wheel clamping device designed for towing
service use.
Do not use the steering column lock to secure
the front wheel uosition for towina.
Automatic transaxle vehicles may be towed on the
front wheels at speeds not to exceed 30 mph (50
km/h) for a distance not to exceed 18 miles (30 km).
If these limits can not be met, then the front wheels
must be placed on a tow dolly.
# See Figure 221
All Wheel Drive (AWD) vehicles should only be
towed with all 4 wheels on the ground or lifted from
the road surface. This means that the vehicle is to be
towed either with flatbed equipment, with all wheels
on dollies or flat towed. Damage to the viscous cou-
pling may result if the vehicle is towed with only 2
wheels on the ground.
p See Figure 222
Whenever a vehicle is jump started, precautions
must be followed In order to prevent the possibility of
Page 81 of 408

.
3-20 ENGINEANDENGINEOVERHAUL
Never open, service or drain the radiator or
cooling system when hot; serious burns can
occur from the steam and hot coolant. Also,
when draining engine coolant, keep in mind
that cats and dogs are attracted to ethylene
glycol antifreeze and could drink any that is
left in an uncovered container or in puddles
on the ground. This will prove fatal in suffi-
cient quantities. Always drain coolant into a
sealable container. Coolant should be reused
unless it is contaminated or is several years
old.
3. Remove the overflow hose and disconnect
the upper radiator hose.
*It is recommended that each clamp be
matchmarked to the hose. Observe the marks
and reinstall the clamps exactly when rein-
stalling the radiator.
4. If equipped with an automatic transaxle, re-
move and plug the fluid cooler hoses.
5. Unplug the electrical connector(s) from the
coolant fan motor.
6. Remove the mounting bolts, then remove the
fan and shroud assembly from the vehicle.
7. Remove the fan blade retainer nut from the
shaft on the fan motor and separate the fan from the
motor.
8. Remove the motor to shroud attaching
screws and the motor from the shroud.
To tnstall: 9. Install the motor to the shroud and secure
with the mounting bolts.
10. Install the remaining components in the re-
verse order of removal.
11. Fill the coohng system. Connect the negative
battery cable and check the cooling fan for proper op-
eration.
Diamante
# See Figure 94
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable 2. Drain the cooling system only when the radi-
ator and the engine are at safe temperatures. 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable
2. Drain the cooling system.
Never open, service or drain the radiator or
cooling system when hot; serious burns can
occur from the steam and hot coolant. Also,
when draining engine coolant, keep in mind
that cats and dogs are attracted to ethylene
glycol antifreeze and could drink any that is
left in an uncovered container or in puddles
on the ground. This will prove fatal in suffi-
cient quantities. Always drain coolant into a
sealable container. Coolant should be reused
unless it is contaminated or is several years
old.
3. Unplug the cooling fan and radiator sensor
connector(s). Most of these connectors employ a wa-
terproof connector. When disconnecting, make sure
all parts of the connector remain intact.
4. Disconnect the upper radiator hose from the
radiator and remove overflow tank.
5. Remove the fan mounting screws. The radia-
tor and condenser cooling fans are separately remov-
able.
6. Remove the fan assembly and disassemble
Never open, service or drain the radiator or
cooling system when hot; serious burns can
occur from the steam and hot coolant. Also,
when draining engine coolant, keep in mind
that cats and dogs are attracted to ethylene
glycol antifreeze and could drink any that is
left in an uncovered container or in puddles
on the ground. This will prove fatal in suffi-
cient quantities. Always drain coolant into a
sealable container. Coolant should be reused
unless it is contaminated or is several years
old.
3. Remove the engine undercover.
4 Disconnect the clamp bolt from the power
steering hose.
5. Remove the engine drive belts.
6. Support the engine with the appropriate
equipment and remove the engine mount bracket.
7. Remove the timing belt Reier to the timing
belt procedure in this section
8 Remove the power steering pump bracket.
9. Remove the alternator brace.
as required.
To install: 7. Posrtion the fan and install the mounting
screws
*The water pump mounting bolts are differ-
ent in length, note their positioning for re-
assembly.
8 Install the electrical connectors and the upper
radiator hose.
9. Refill the cooling system.
IO. Connect the negative battery cable and check
the fan for orooer ooeration. 10. Remove the water pump, gasket and O-ring
where the water inlet pipe(s) joins the pump.
To install: 11, Thoroughly clean both gasket surfaces of the
water oumo and block.
12. For 1.5L engines, install a new O-ring into
the groove on the front end of the water inlet pipe. Do
not apply oils or grease to the O-ring. Wet the O-ring
with water only
13. For 1.8L engines, apply a 0.09-0.12 in.
(2.5-3 Omm) continuous bead of sealant to water
pump and rnstall the pump assembly. Install the wa-
ter pump within 15 minutes of the applrcation of the
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1.5L and 1.8L Engine
) See Figures 95 and 98
7923PGO :ig. 94 Exploded view of the fan mounting and related components- Fig. 95 Water pump and related components-Mirage with 1.51
liamante (4615) engine
Page 207 of 408

I
6-4 CHASSIS ELECTRICAL
I
printed circuit is sandwiched between two sheets of
plastic for more protection and flexibility. A complete l Weatherproof-these connectors are most the jumper wire is of too small a gauge, it
printed circuit, consisting of conductors, insulating commonly used where the connector is exposed to
may overheat and possibly melt. Never use
material and connectors for lamps or other compo- the elements. Terminals are protected against mois-
nents is called a printed circuit board. Printed cir- ture and dirt by sealing rings which provide a weath- jumpers to bypass high resistance loads in a
et-tight seal. All repairs require the use of a special circuit. Bypassing resistances, in effect, cre-
cuitry is used in place of individual wires or har- ates a short circuit. This may, in turn, cause
nesses in places where space is limited, such as terminal and the tool required to service it. Unlike
behind instrument panels. standard blade type terminals, these weatherproof damage and fire. Jumper wires should only
be used to bypass lengths of wire or to simu-
Since automotive electrical systems are very sen- terminals cannot be straightened once they are bent. late switches.
sitive to changes in resistance, the selection of prop- ‘Make certain that the connectors are properly seated
erly sized wires is critical when systems are repaired, and all of the sealing rings are in place when con-
netting leads. Jumper wires are simple, yet extremely valuable,
A loose or corroded connection or a replacement wire pieces of test equipment. They are basically test wires
that is too small for the circuit will add extra resis-
l Molded-these connectors require complete which are used to bypass sections of a circuit. Al-
replacement of the connector if found to be defective.
tance and an additional voltage drop to the circuit. though jumper wires can be purchased, they are usu-
The wire gauge number is an expression of the This means splicing a new connector assembly into ally fabricated from lengths of standard automotive
cross-section area of the conductor. Vehicles from the harness. All splices should be soldered to insure
proper contact. Use care when probing the connec- wire and whatever type of connector (alligator clip,
countries that use the metric system will typically de- spade connector or pin connector) that is required for
scribe the wire size as its cross-sectional area in tions or replacing terminals in them, as it is possible
square millimeters. In this method, the larger the to create a short circuit between opposite terminals. If the particular application being tested. In cramped,
hard-to-reach areas, it is advisable to have insulated
wire, the greater the number. Another common sys- this happens to the wrong terminal pair, it is possible
to damage certain components. Always use jumper boots over the jumper wire terminals in order to pre-
tern for expressing wire size is the American Wire vent accidental grounding. It is also advisable to in-
Gauge (AWG) system. As gauge number increases, wires between connectors for circuit checking and
NEVER probe through weatherproof seals. elude a standard automotive fuse in any jumper wire.
area decreases and the wire becomes smaller. An 18
gauge wire is smaller than a 4 gauge wire. A wire
l Hard Shell-unlike molded connectors, the This is commonly referred to as a “fused jumper”. By
inserting an in-line fuse holder between a set of test
terminal contacts in hard-shell connectors can be re-
with a higher gauge number will carry less current
placed. Replacement usually involves the use of a leads, a fused jumper wire can be used for bypassing :
than a wire with a lower gauge number. Gauge wire open circuits. Use a 5 amp fuse to provide protection
size refers to the size of the strands of the conductor, special terminal removal tool that depresses the lock- against voltage spikes.
not the size of the complete wire with insulator. It is ing tangs (barbs) on the connector terminal and al-
lows the connector to be removed from the rear of the Jumper wires are used primarily to locate open
possible, therefore, to have two wires of the same
shell. The connector shell should be replaced if it electrical circuits, on either the ground (-) side of the
gauge with different diameters because one may have
thicker insulation than the other. shows any evidence of burning, melting, cracks, or circuit or on the power (+) side. If an electrical corn-
breaks. Replace individual terminals that are burnt, ponent fails to operate, connect the jumper wire be-
It is essential to understand how a circuit works
corroded, distorted or loose. tween the component and a good ground. If the corn-
before trying to figure out why it doesn’t. An electrical ponent operates only with the jumper installed, the
schematic shows the electrical current paths when a ground circuit is open. If the ground circuit is good,
circuit is operating properly. Schematics break the but the component does not operate, the circuit be-
entire electrical system down into individual circuits. tween the power feed and component may be open. ’
In a schematic, usually no attempt is made to repre- Pinpointing the exact cause of trouble in an elec- By moving the jumper wire successively back from
trical circuit is most times accomplished by the use the component toward the power source, you can
; : sent wiring and components as they physically ap-
pear on the vehicle; switches and other components of special test equipment. The following describes isolate the area of the circuit where the open is lo-
are shown as simply as possible. Face views of har- different types of commonly used test equipment and cated. When the component stops functioning, or the f
j
ness connectors show the cavity or terminal locations briefly explains how to use them in diagnosis. In ad- power is cut off, the open is in the segment of wire j
in all multi-pin connectors to help locate test points. dition to the information covered below, the tool between the jumper and the point previously tested.
! manufacturer’s instructions booklet (provided with You can sometimes connect the jumper wire di-
the tester) should be read and clearly under.$ood be- rectly from the battery to the “hot” terminal of the I
CONNECTORS 1 fore attempting any test procedures. component, but first make sure the component uses 1
# See Figures 5 and 6 JUMPER WIRES 12 volts in operation. Some electrical components, i
such as fuel injectors or sensors, are designed to op-
Three types of connectors are commonly used in erate on about 4 to 5 volts, and running 12 volts di- j
)
automotive applications-weatherproof, molded and rectly to these components will cause damage.
hard shell.
Never use jumper wires made from a thinner TEST LIGHTS I
gauge wire than the circuit being tested. If
# See Figure 7
The test light is used to check circuits and compo-
I nents while electrical current is flowing through
Fig. 5 Hard shell (left) and weatherproof
(right) connectors have replaceable termi- Fig. 7 A 12 volt test light is used to di%
nals
ements 1 the presence of voltage in a circuit
Page 209 of 408

.
6-6 CHASSIS ELECTRICAL
This test already assumes the existence of an open
in the circuit and it is used to help locate the open
portion
1. Isolate the circuit from power and ground.
2. Connect the self-powered test light or ohmme-
ter ground clip to the ground side of the circuit and
probe sections of the circuit sequentially.
3. If the light is out or there is infinite resistance,
the open is between the probe and the circuit ground.
4. If the light is on or the meter shows continuity,
the open is between the probe and the end of the cir-
cuit toward the power source.
SHORT CIRCUITS
*Never use a self-powered test tight to per-
form checks for opens or shorts when power Fig. 10 Checking the resistance of a coolant
temperature sensor with an ohmmeter.
Reading is 1.04 kilohms
is applied to the circuit under test. The test
linht man he dmn~nsrl hu nutnitls nnuva~ if there is more than one load in the circuit, since all m.3.m. “Y.. “1 “ulll”y”” u, ““..7IYG p”“lz’.
1. Isolate the circuit from power and ground.
2. Connect the self-powered ’ .,.*. ,
ted ugnt or onmme-
ter ground clip to a good ground
and probe any easy-
to-reach point in the circuit.
3. If the light comes on or there is continuity,
there is a short somewhere in the circuit.
4. To isolate the short, probe a test point at either
end of the isolated circuit (the light should be on or
the meter should indicate continuity).
5. Leave the test light probe engaged and se- voltage drops are cumulative.
1. Set the voltmeter selector switch to the 20 volt
^,.^X^..
pJbl1IUII.
2. Connect the multimeter negative lead to a
good ground.
3. Operate the circuit and check the voltage prior
.
to the hrst component (load).
4. There should be little or no voltage drop in the
circuit prior to the first component. If a voltage drop
exists, the wire or connectors in the circuit are sus-
WY.+
)JGW 5. While operating the first component in the cir-
.
positive meter lead and observe the voltage readings.
A small voltage drop should be noticed. This voltage
drop is caused by the resistance of the component.
6. Repeat the test for each component (load)
de .-IL- .‘.. .I
uuwn me crrcun. quentially open connectors or switches, remove
parts, etc. until the light goes out or continuity is bro-
ken
6. When the light goes out, the short is between
the last two circuit components which were opened,
nl -r*l?I-
VuLlHbt
This test determines voltage available from the
battery and should be the first step in any electrical
troubleshooting procedure after visual inspection,
Many electrical problems, esoeciallv on comouter
controlled systems, can be caused by a low state of 7. If a large voltage drop is noticed, the preceding
component, wire or connector is suspect.
# See Figures
10 and 11
charge in the battery. Excessive corrosion at the bat-
tery cable terminals can cause poor contact that will
prevent proper charging and full battery current flow,
1. Set the voltmeter selector switch to the 20V
position.
2. Connect the multimeter negative lead to the
h*+tnn,‘n nnn,,,;~,,. , ..^,a ^-L.--:^^l --_I ‘I- ---!I?... Never use an ohmmeter with power applied
to the circuit. The ohmmeter is designed to
operate on its 0 wn power supply. The normal
1^
. . . . . Fig. 11 Spark plug wires can be checke;
MW~ 3 IlG~dllYt: t-1 pUSI UI Lellllllldl allU lilt, pUSlIlVe lead to the battery’s positive (t) post or terminal.
3. Turn the ignition switch ON to provide a load,
4. A well charged battery should register over 12
volts. If the meter reads below 11 5 vnlts tha hq*anr
_ _ .-, . power may be insufficient to operate the eler ii! volt electrical system voltage could dam-
age the meter!
1. Isolate the circuit from the vehicle’s power
CnlOrAn I)““IW. 2. Ensure that the ignition key is OFF when dis- Almost anyone can replace damaged wires, as
long as the proper tools and parts are available. Wire
and terminals are available to fit almost any need.
Even the specialized weatherproof, molded and hard
shell connectors are now cl mdicm available from aftermarket
system properly.
connecting any components or the battery. ““yp,8w’“.
3. Where necessary, also isolate at least one side Be sure the ends of all the wires are fitted with the
VOLTAGEDROP of the circuit to be checked, in order to avoid reading proper terminal hardware and connectors. Wrapping
parallel resistances. Parallel circuit resistances will a wire around a stud is never a permanent solution
# See Figure 9 always give a lower reading than the actual resistance and will only cause trouble later. Replace wires one at
When current flows through a load, the voltage be- of eifhy n< +hn hmnnh-r
GI “I II It: “I a lb1 It?>. a time to avoid confusion. Always route wires exactly
4.
Connect the meter leads to both sides of the the same as the factory.
yond the load drops. This voltage drop is due to the
resistance created by the load and also by small re- circuit (wire or component) and read the actual mea-
sured ohms on the meter scale. Make sure the selec- *If connector repair is necessary, only at-
sistances created by corrosion at the connectors and
tor switch is set to the proper ohm scale for the cir- tempt it if you have the proper tools. Weath-
damaged insulation on the wires. The maximum al- erproof and hard shell connectors require
lowable voltage drop under load is critical, especially cuit being tested, to avoid misreading the ohmmeter
test value. spectal tools to release the pins inside the
connector. Attempting to repair these con-
nectors with conventional hand tools will
damage them.
Page 232 of 408
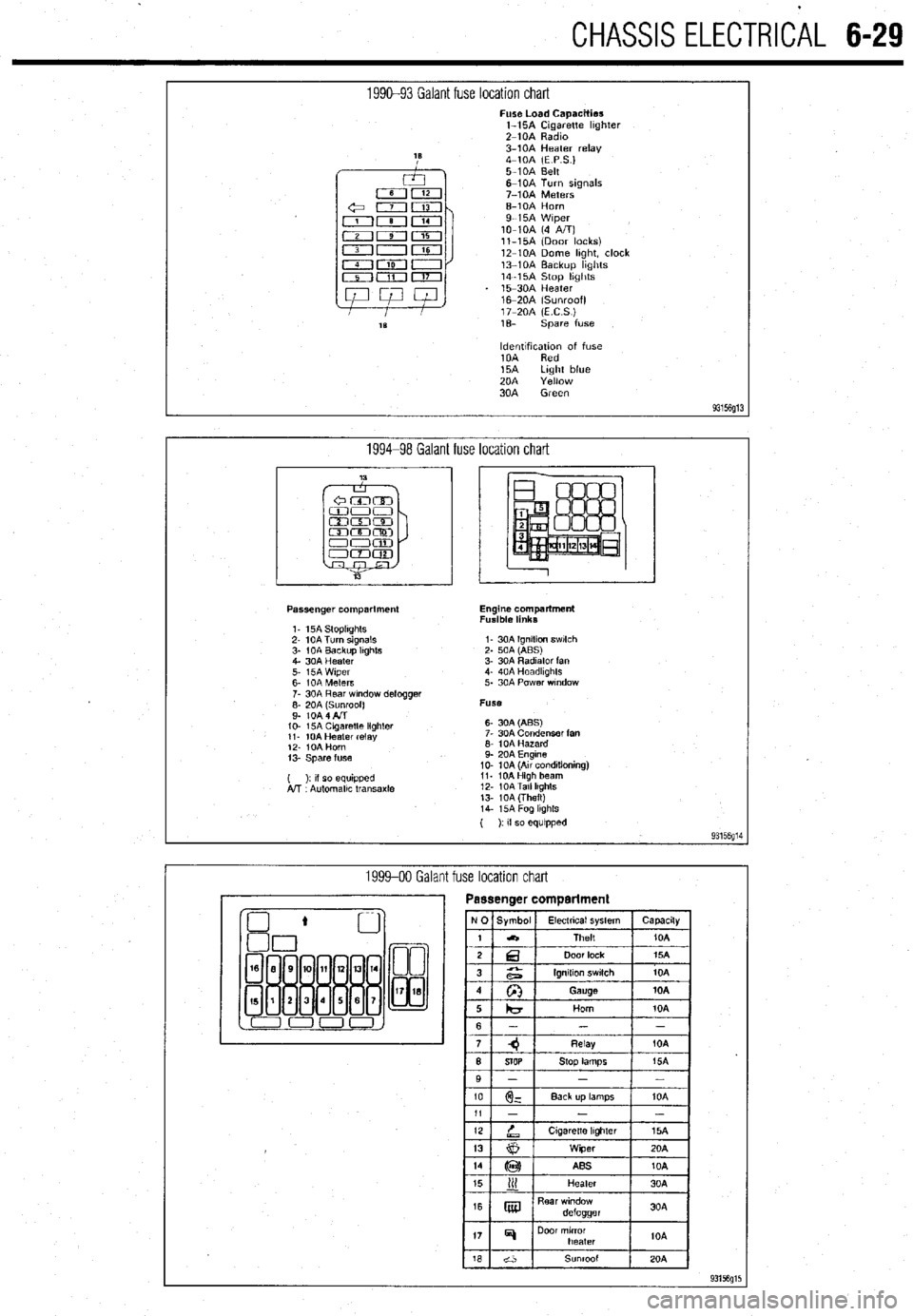
CHASSIS ELECTRlCiL 6-29
1990-93 Galant fuse location chart Fuse Load Capacities
l-15A Cigarette hghter
Z-10A Radm
3-10A Heater relay
4-10A (E P S.)
5-10A Belt
6-10A Turn signals
7-10A Meters
6-10A Horn
9-15A Wiper
lo-10A (4 A/T)
ll-15A (Door locks)
12-10A Dome hght, clock
13-10A Backup hghts
14-15A Stop hghts
15-30A Heater
16m20A (Sunroof)
17-20A (ECS)
1% spare fuse
ldentlfxation of fuse
10A Red
15A Light blue
20A Yellow
30A Green
93156g13
1994-98 Galant fuse location chart
Passenger compartment
1. 15A StoplIghts
2- 10A Turn signals
3- 1 OA Backup Itghts
4. 30A Heater
5. i5A Wiper
6- IOA Meters
7. 30A Rear wndow defogger
;: fo& fl$oof)
IO- 15A Cagaretle lighler
11. 10A Heater relay
12. IOA Horn
13. Spare fuse
( ): II so equipped
A!T Automallc transaxle Engine compartment
Fusible links
I- 30A Ignition swlch
2. 50A (ABS)
3. 30A Radiator fan
4. 40A Headkghts
5. 30A Power wndow
Fuse
6- 30A (ABS)
7. 30A Condenser fan
6. 10A Hazard
9. 20A Engine
10. 10A (Au conditioning)
11. 10AHigh beam
12. 10ATall lkghts
13. 10A (Theft)
14. i5A Fog lkghls
( ): If so equipped
93156g14
1999-00 Galant fuse location chart
Page 233 of 408
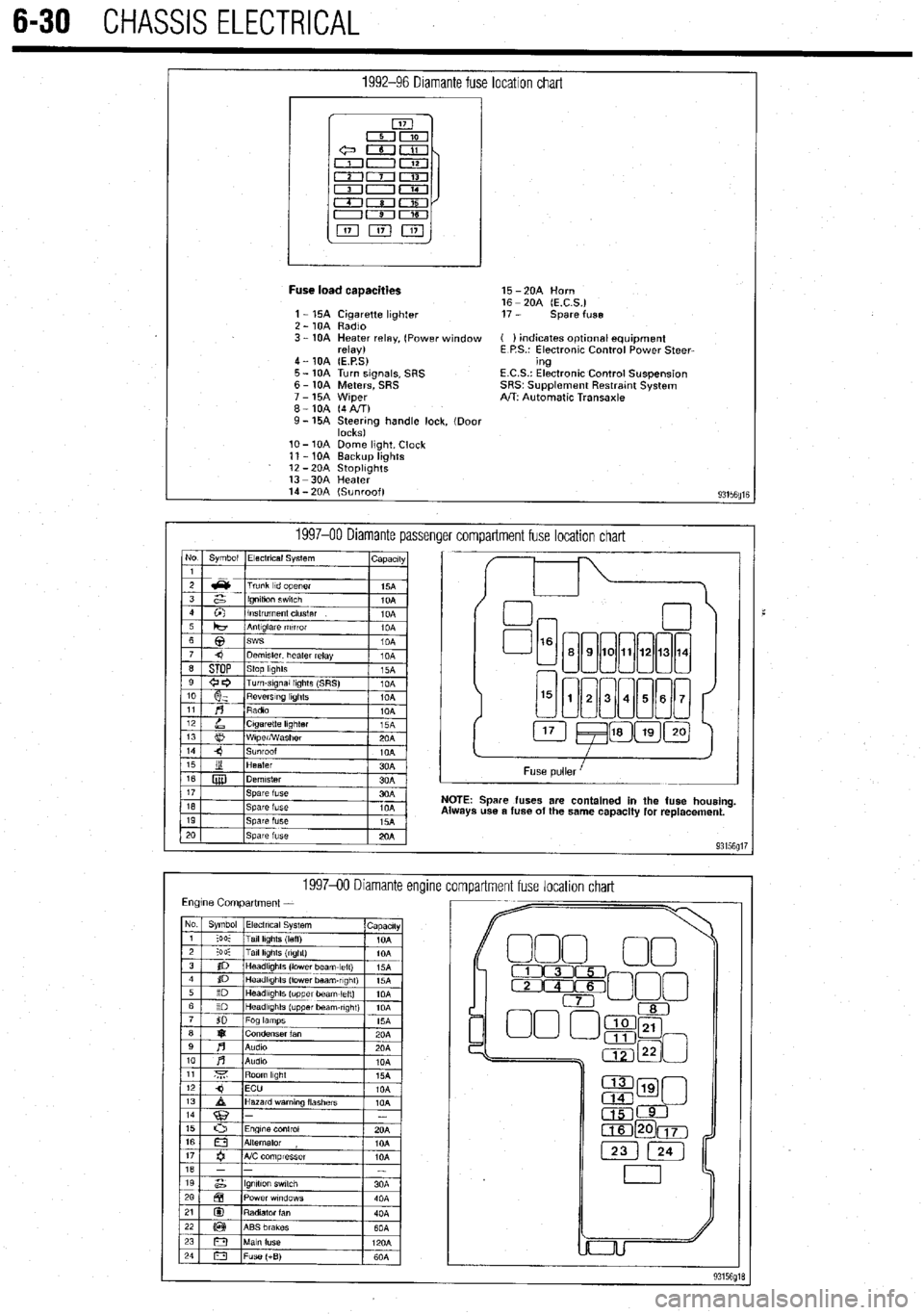
6-30 CHASSIS ELECTRICAL
1992-96 Diamante fuse location chart
I
Fuse load caaacities 15 -2OA Horn
16 - 20A (E.C.S.)
1 - 15A Cigarette lighter 17 - spare fuse
2 - 10A Radio
3 - 10A Heater relay, (Power window ( ) indicates optlonal equipment
relay) E P.S.: Electronic Control Power Steer-
4 - 10A (E.P.S) ing
5 - 10A Turn signals, SRS E.C.S.: Electronic Control Suspension
6 - 10A Meters, SRS SRS~ Supplement Restratnt System
7 - 15A Wiper A/T: Automatic Transaxle
8-10A (4AIT)
9- 15A Steering handle lock, (Door
locks)
lo- 10A Dome light, Clock
11 - 10A Backup lights
12 -2OA StoplIghts
13 -3OA Heater
14 - 20A (Sunroof)
93156fllE
1997-00 Diamante passenger compartment fuse location chart No Symbol Electrical System
I capactty
I
Spare fuses are contained in the fuse housing
use a fuse of the same capacity for replacement.
199740 Diamante encline
compartment fuse location chart
Page 372 of 408
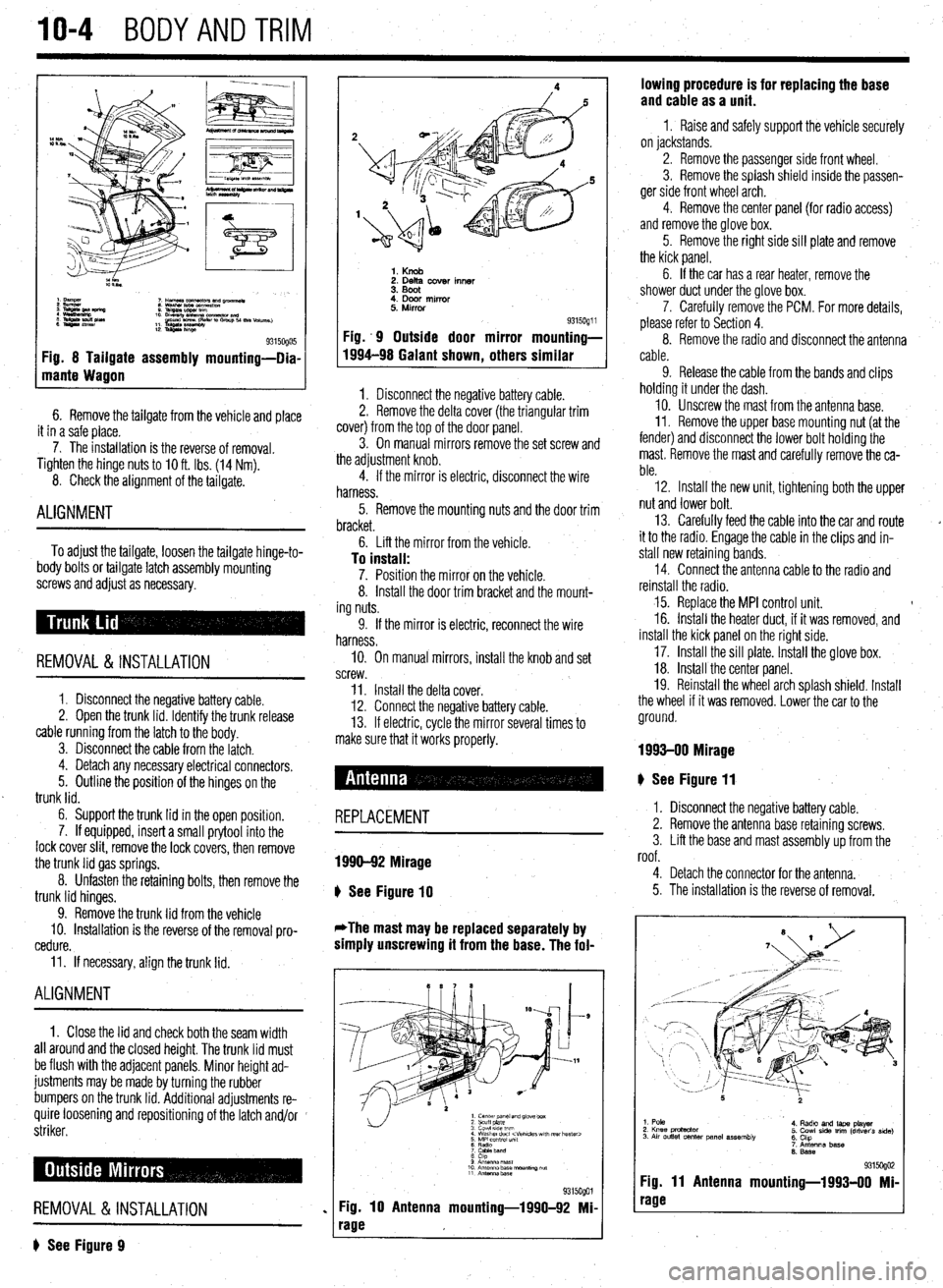
10-4 BODYANDTRIM
Fig. 8 Tailgate assembly mounting-Dia-
mante Wagon
6. Remove the tailgate from the vehicle and place
it in a safe place.
7. The installation is the reverse of removal.
Tighten the hinge
nuts to IO ft. Ibs. (14 Nm).
8. Check the alignment of the tailgate.
ALIGNMENT
To adjust the tailgate, loosen the tailgate hinge-to-
body bolts or tailgate latch assembly mounting
screws and adjust as necessary.
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Open the trunk lid. Identify the trunk release
cable running from the latch to the body.
3. Disconnect the cable from the latch.
4. Detach any necessary electrical connectors.
5. Outline the position of the hinges on the
trunk lid.
6. Support the trunk lid in the open position.
7. If equipped, insert a small prytool into the
lock cover slit, remove the lock covers, then remove
the trunk lid gas springs.
8. Unfasten the retaining bolts, then remove the
trunk lid hinges.
9. Remove the trunk lid from the vehicle
10. Installation is the reverse of the removal pro-
cedure.
11. If necessary, align the trunk lid.
ALIGNMENT
1. Close the lid and check both the seam width
all around and the closed height. The trunk lid must
be flush with the adjacent panels. Minor height ad-
justments may be made by turning the rubber
bumpers on the trunk lid. Additional adjustments re-
quire loosening and repositioning of the latch and/or
striker.
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
? See Figure 9
1. Knob 2. Delta cover inner
3. Boot
4. Door mirror
5. Mirror
Fig. .9 Outside door mirror
1994-98 Galant shown
, others 9315oQ1 i mounting-
similar
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the delta cover (the triangular trim
cover) from the top of the door panel.
3. On manual mirrors remove the set screw and
the adjustment knob.
4. If the mirror is electric, disconnect the wire
harness.
5. Remove the mounting nuts and the door trim
bracket.
6. Lift the mirror from the vehicle.
To install: 7. Position the mirror on the vehicle.
8. Install the door trim bracket and the mount-
ing nuts.
9. If the mirror is electric, reconnect the wire
harness.
IO. On manual mirrors, install the knob and set
screw.
11. Install the delta cover.
12. Connect the negative battery cable.
13. If electric, cycle the mirror several times to
make sure that it works properly.
# See Figure 11
REPLACEMENT
1990-92 Mirage
b
See Figure 10
*The mast may be replaced separately by
simply unscrewing it from the base. The fol-
1. center panel and glove box
2 scuff plate
3 cowl 51ae wm
4 Washer duct
7 CaMeband
8 cap
9 Anrsnna mast
10 Antenna base “ourmng ““f
11 Antennz.base
%i%Qol
Fig. 10 Antenna mounting-1990-92 Mi-
rage lowing procedure is for replacing the base
and cable as a unit.
1 I Raise and safely support the vehicle securely
on jackstands.
2. Remove the passenger side front wheel.
3. Remove the splash shield inside the passen-
ger side front wheel arch.
4. Remove the center panel {for radio access)
and remove the glove box.
5. Remove the right side sill plate and remove
the kick panel.
6. If the car has a rear heater, remove the
shower duct under the glove box.
7. Carefully remove the PCM. For more details,
please refer to Section 4.
8. Remove the radio and disconnect the antenna
cable.
9. Release the cable from the bands and clips
holding it under the dash.
10. Unscrew the mast from the antenna base.
II. Remove the upper base mounting nut (at the
fender) and disconnect the lower bolt holding the
mast. Remove the mast and carefully remove the ca-
ble.
12. Install the new unit, tightening both the upper
nut and lower bolt.
13. Carefully feed the cable into the car and route
it to the radio. Engage the cable in the clips and in-
stall new retaining bands.
14. Connect the antenna cable to the radio and
reinstall the radio.
15. Replace the MPI control unit. t
16. Install the heater duct, if it was removed, and
install the kick panel on the right side.
17. Install the sill plate. Install the glove box.
18. Install the center panel.
19. Reinstall the wheel arch splash shield. Install
the wheel if it was removed. Lower the car to the
ground.
1993-00 Mirage
I. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the antenna base retaining screws.
3. Lift the base and mast assembly up from the
roof.
4. Detach the connector for the antenna.
5. The installation is the reverse of removal.
1. Pole
2. Knee protactor
3. Air outlet center panel assembly 4. Radto and laps player
5. Cowl side trim (driver’s side)
6. Chp
7. Antenna base
6. Base
931 !iogo2 Fig. 11 Antenna mounting-1993-00 Mi-
rage
Page 379 of 408

BODYANDTRiVl 1041
8. llnm all mtainar din!: xc! .wnnratmi rmnnve -.*I-_.. .I._. ..I. -..r-~.--“* -.-.- I( .” .I._._ the dot jr panel assembly.
9. Carefully remove any retainer clips that re-
mained in the door during panel removal. If dam-
aaed. reolace the retainer clios.
- 10. if necessary, remove’the waterproof film from
the door.
To install:
11. If removed, install the waterproof film from
. .
tne aoor.
12. Install and missing or damaged retainer clips
into the door panel.
- .- ” - 13. . - Install the door panel onto the vehicle. Push . - -. ” - ret;liners intn the hnlss in the rlnnr until thev lnck intn . - - - -. -. . . . “, - ” . .- position. If any clips do not lock, replace with new 4. Remove the lock cylinder from the trunk lid,
hatch, or tailgate. T- 1-a-11.
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
1. Disconnect the r
negative battery cable.
2. If necessary, ren love any trim in on the under-
side of the trunk lid, hz
Itch, or tailgate.
3. Release locking tab retaining the lock cylinder
to outside handle.
9315opo5 1 Fig. 46 Remove the two front door panel re-
taining screws . , . IU Inrlall; 5. Place the lock cylinder into the opening on the
ones.
14. The remainder of installation is the reverse of
removal. trunk lid, hatch, or tailsate. -
6. Snap the locking tab into place retaining the
lock cylinder to the outside handle.
7. If removed, install any trim in on the underside
of the trunk lid, hatch, or tailgate.
8. Connect the negative battery able:
REMOVAL &INSTALLATION
II See Figurd 50
1‘ &connect the negative battery cable. REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
9315ctpm Fig. 47 . . .
and also the rear retaining
screws from the door panel 2. Remove the door panel.
3. Peel back the weathproofing film from the
door.
4. Remove the retaining clip and the lock rod
from the handle assembly.
5. Remove the retaining hardware and remove the
handle from the door.
6. The installation is the reverse of removal. 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the hatch/tailgate trim cover.
3. Remove the retaining clip and the lock rod
from the handle assembly.
4. Remove the retaining hardware and.remove the
handle from the hatch/tailgate.
5. The installation is the reverse of removal.
I 1. Disconnect the neaative batterv cable. ) See Figures 51, 52, 53/ 54, and 55 REMOVAL&INSTALLATION REMOVAL&INSTALLATION
2. Remove the door ~andle/latchassembly.
3. Release locking tab retaining the lock cylinder
to the outside handle.
4. Remove the lock cylinder from the outside
handle and feed the illumination wire through the
opening in the handle.
To install:
5. Route the illumination wire through the handle
and install the lock cylinder.
6. Snap the locking tab into place retaining the
lock cvlinder to the outside handle.
7. ‘Install the door handle/latch assembly.
8. Connect the negative battery cable. 1. Lower the door glass. ‘1,
2. Remove the door panel and moisture barrier.
3. Using a non-marring tool and a cloth pad,
gently pry the belt molding up and off the door.
4. Remove the inner glass sthbilizers.
5. On front doors only, remove the glass guide
/
slider.
6. Support the bottom of the door glass and re-
move the two mounting bolts holdirtg the glass to the
regulator. If the glass is not supporfed, it will fail into
+I%? Ann. . ..hmn hr. l..4+s are remove&.
9315opa Fig, 49 . . . then remove the door panel from
the vehicle 50 Common door handle/latch mount-
I
, Flg. 51 After the door panel is removed, re-
move the Insulation from the door