check engine MITSUBISHI GALANT 1989 Service Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1989, Model line: GALANT, Model: MITSUBISHI GALANT 1989Pages: 1273, PDF Size: 37.62 MB
Page 223 of 1273
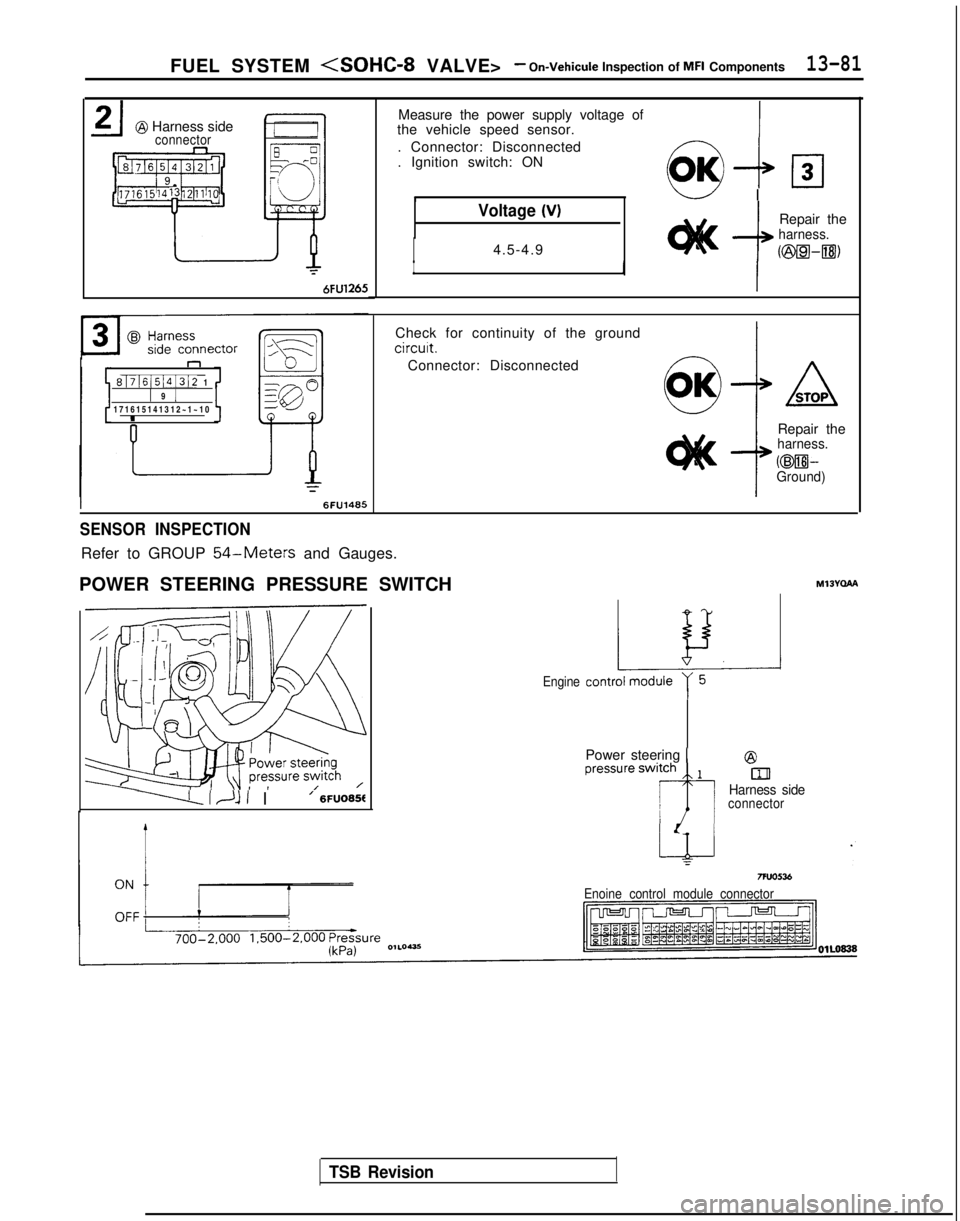
FUEL SYSTEM
@ Harness sideconnector
6FU1265
n
8171615141312 11 9 1171615141312~1~1
0
I
Measure the power supply voltage of
the vehicle speed sensor.
. Connector: Disconnected
. Ignition switch: ON
6&loIw I
Voltage (V)
I4.5-4.9--I
Repair theharness.
II
I
Check for continuity of the ground
circuit.
Connector: Disconnected
Repair the
harness.
@WGround)
SENSOR INSPECTION
Refer to GROUP 54-Meters and Gauges.
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH MI3Yclha
------LI~lI I’ 6FUO65f
TSB Revision
Engine
Power steering 1@
blHarness sideconnector
Enoine control module connector
Page 224 of 1273
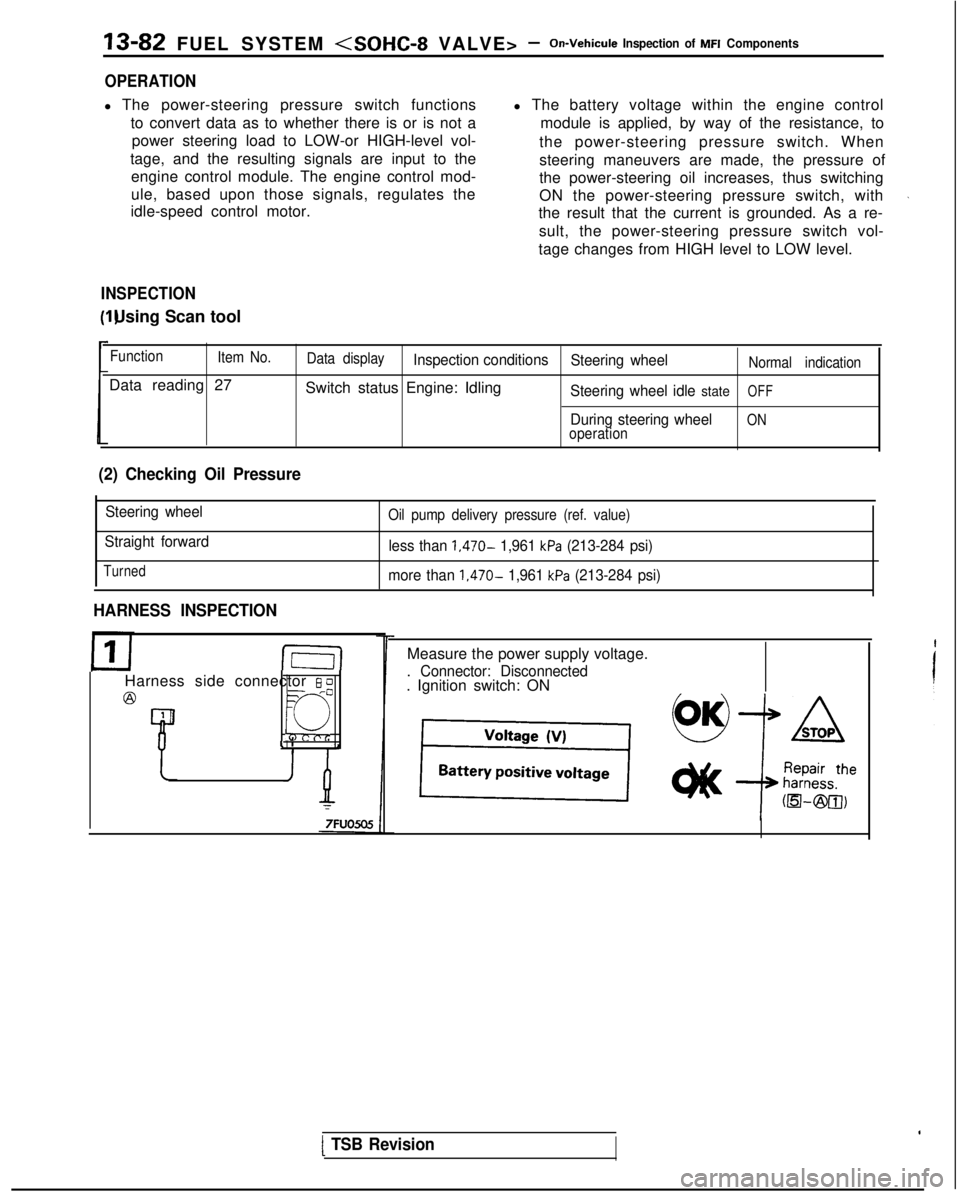
13-82 FUEL SYSTEM
OPERATION
l The power-steering pressure switch functions
to convert data as to whether there is or is not apower steering load to LOW-or HIGH-level vol-
tage, and the resulting signals are input to the engine control module. The engine control mod-
ule, based upon those signals, regulates the
idle-speed control motor. l The battery voltage within the engine control
module is applied, by way of the resistance, to
the power-steering pressure switch. When
steering maneuvers are made, the pressure of
the power-steering oil increases, thus switching
ON the power-steering pressure switch, with
the result that the current is grounded. As a re-
sult, the power-steering pressure switch vol-
tage changes from HIGH level to LOW level.
INSPECTION I) Using Scan tool
Function
Item No.
Data reading 27
Data displayInspection conditions Steering wheelNormal indication
Switch status Engine: IdlingSteering wheel idle stateOFF
During steering wheelONoperation
(2) Checking Oil Pressure
Steering wheel
Straight forward
Turned
Oil pump delivery pressure (ref. value)
less than 1,470- 1,961 kPa (213-284 psi)
more than
1,470- 1,961 kPa (213-284 psi)
HARNESS INSPECTION
I-E-I
Harness side connector 6 0
@=- -0
Q
4 1
Measure the power supply voltage.
. Connector: Disconnected. Ignition switch: ON
[ TSB Revision
Page 226 of 1273
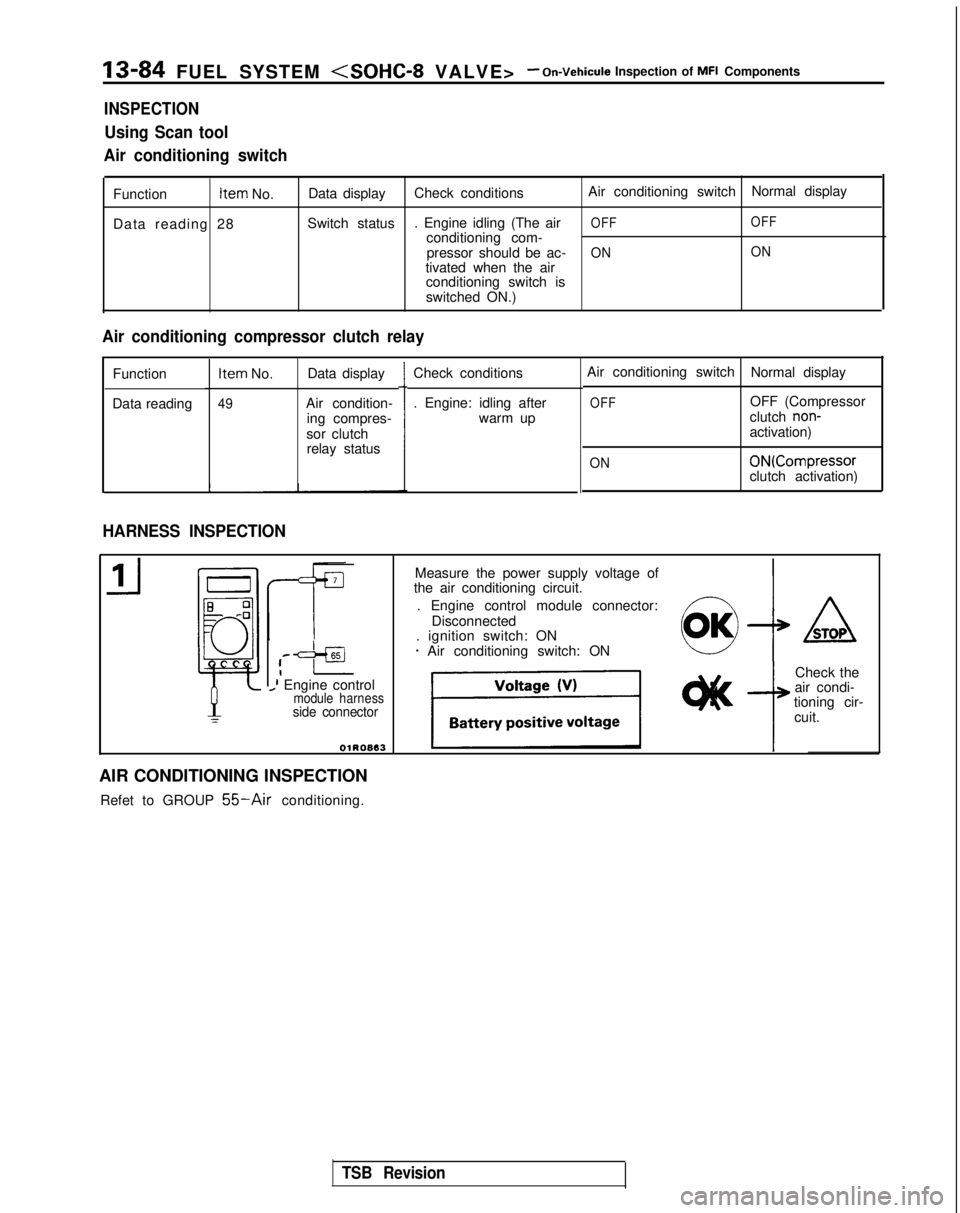
13-84 FUEL SYSTEM
INSPECTION
Using Scan tool
Air conditioning switch
Function Item
No.
Data reading 28 Data display
Check conditions Air conditioning switch
Normal display
Switch status . Engine idling (The air
OFF OFFconditioning com-
pressor should be ac-ON ONtivated when the air
conditioning switch is
switched ON.)
Air conditioning compressor clutch relay
Function
Data reading Item
No. Data display
49Air condition-
ing compres-
sor clutch relay status Check conditions
. Engine: idling after
warm up
HARNESS INSPECTION
Air conditioning switch Normal display
OFFOFF (Compressor
clutch non-activation)
ON ON(Compressor
clutch activation)
,--=+aI_I Engine controlmodule harnessside connector
OlROB13
Measure the power supply voltage of
the air conditioning circuit.
. Engine control module connector: Disconnected
. ignition switch: ON
* Air conditioning switch: ON4
ASTOP
Check the
air condi-
tioning cir-
cuit.
AIR CONDITIONING INSPECTION Refet to GROUP
55-Air conditioning.
TSB Revision
Page 228 of 1273
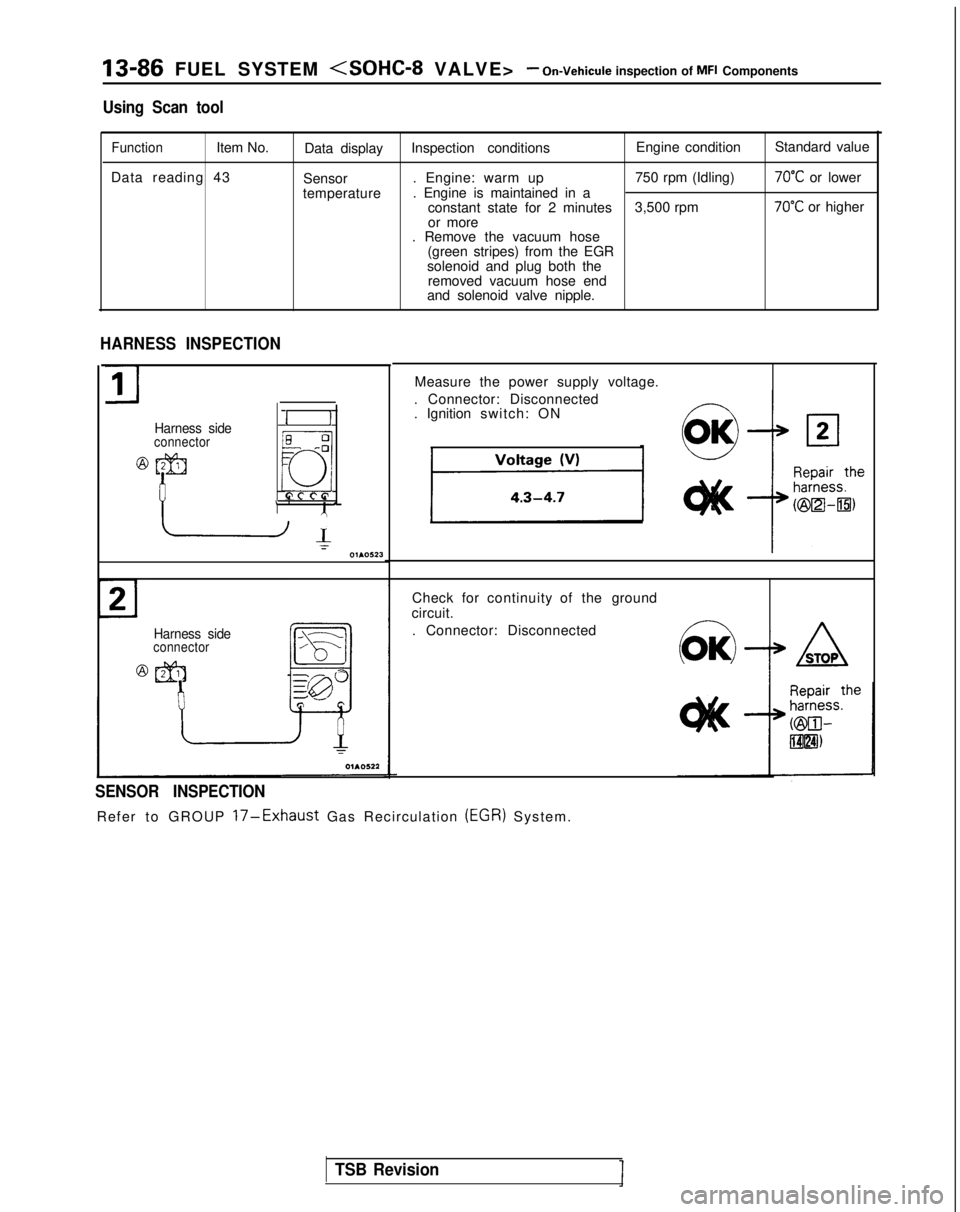
13-86 FUEL SYSTEM
Using Scan tool
FunctionItem No.Data display Inspection conditions Engine condition
Standard value
Data reading 43 Sensor. Engine: warm up
750 rpm (Idling)
70°C or lower
temperature . Engine is maintained in a
constant state for 2 minutes 3,500 rpm
70°C or higher
or more
. Remove the vacuum hose
(green stripes) from the EGR
solenoid and plug both the removed vacuum hose end
and solenoid valve nipple.
HARNESS INSPECTION
Harness sideconnector
@qqJ
I
II
EL -:
f7
Q,
L *A’
-1I01.0523
Measure the power supply voltage.
. Connector: Disconnected
. Ignition switch: ON
Harness sideconnector
Check for continuity of the ground
circuit.
. Connector: Disconnected
SENSOR INSPECTION
Refer to GROUP 17-Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
System.
-w
STOP
TSB Revision
Page 230 of 1273
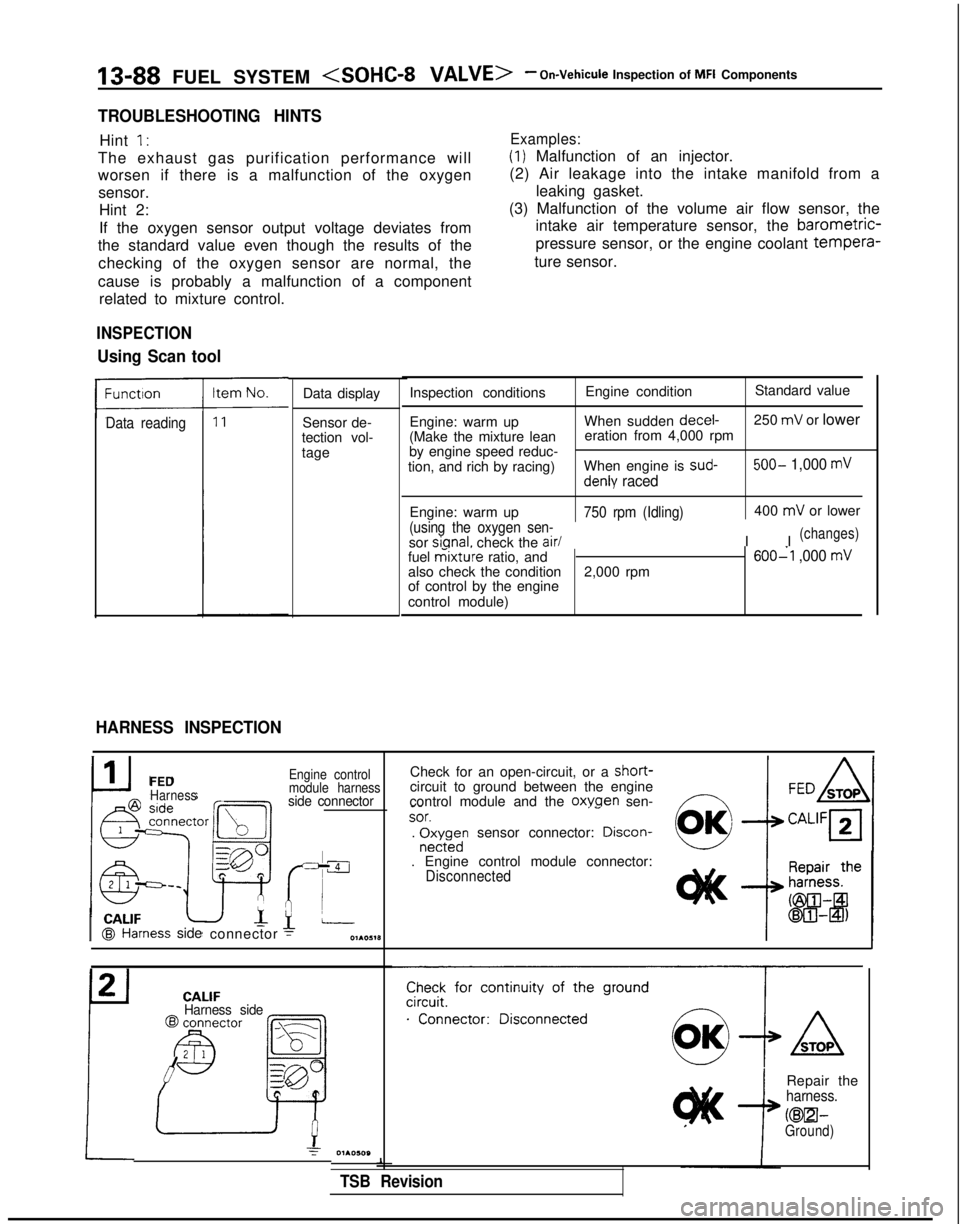
13-88 FUEL SYSTEM
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
Hint I’
The exhaust gas purification performance will
Examples:
(1) Malfunction of an injector.
worsen if there is a malfunction of the oxygen sensor. Hint 2:
If the oxygen sensor output voltage deviates from
the standard value even though the results of the
checking of the oxygen sensor are normal, the
cause is probably a malfunction of a component related to mixture control. (2) Air leakage into the intake manifold from a
leaking gasket.
(3) Malfunction of the volume air flow sensor, the intake air temperature sensor, the barometric-
pressure sensor, or the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor.
Data reading
INSPECTION
Using Scan tool
HARNESS INSPECTION
Data display
Sensor de-
tection vol-
tage Inspection conditions
Engine conditionStandard value
Engine: warm up When sudden decel-
250
mV or lower
(Make the mixture lean eration from 4,000 rpm
by engine speed reduc-
tion, and rich by racing) When engine is sud-
500- 1,000 mV
denly raced
Engine: warm up750 rpm (Idling)
(using the oxygen sen-
sor sianal.
check the air/
400
mV or lower
I I
(changes)
fuel mixture ratio, and600-l ,000 mValso check the condition 2,000 rpm
of control by the engine
control module)
I CALIF@I Hal
FEDHarness
ness
side
connector
Engine control
module harness
side connector
Check for an open-circuit, or a short-circuit to ground between the engine
control module and the oxwen sen-f7 _-
~~SOT.‘-. r$;rdn sensor connector: Drscon-
. Engine control module connector:Disconnected CALIF
Harness side
Check for continuity of the ground
.“‘..“...;;”
Repair theharness.
KEEI-Ground)
1
TSB Revision
Page 231 of 1273
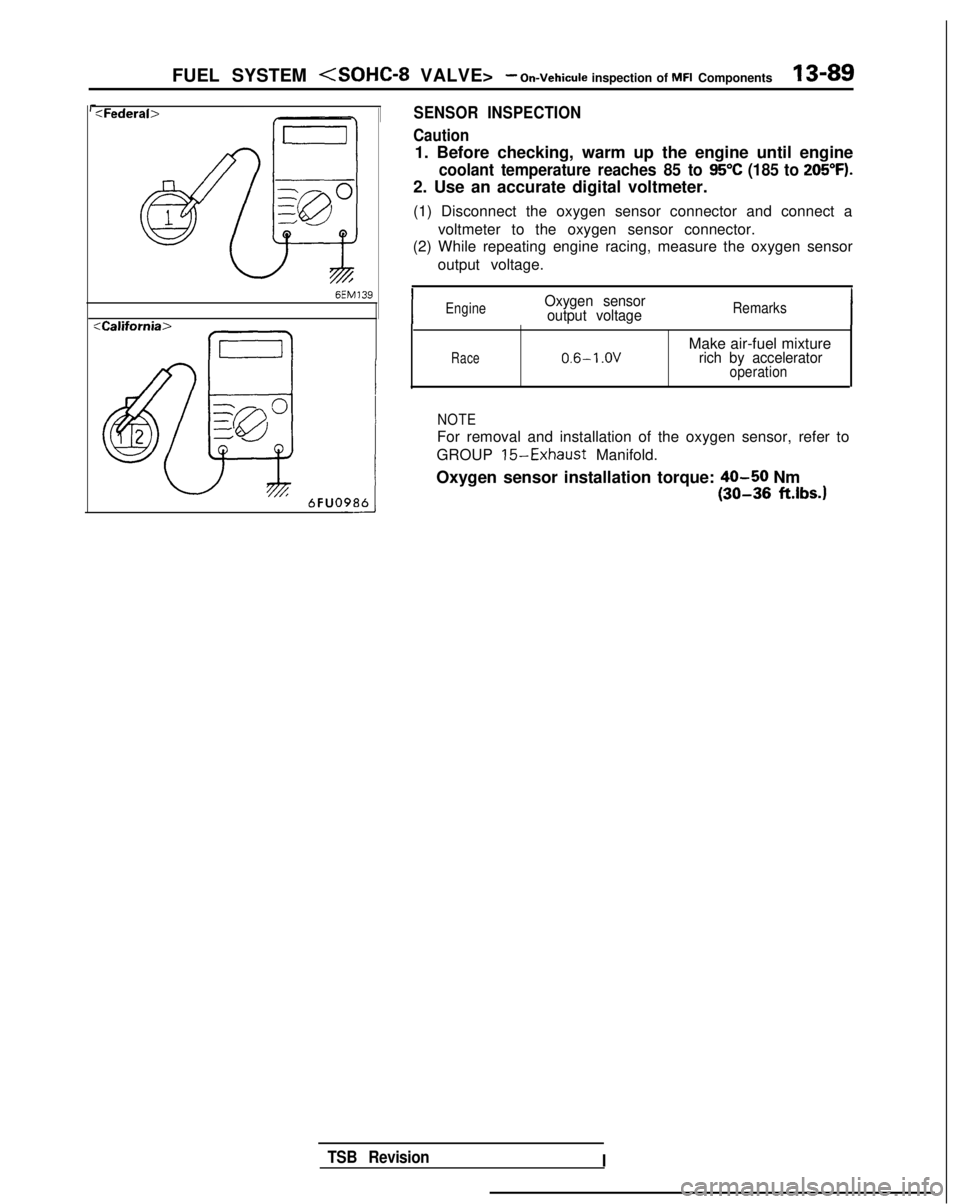
FUEL SYSTEM
:Federab
:California>
Ea
SENSOR INSPECTION
Caution
1. Before checking, warm up the engine until engine
coolant temperature reaches 85 to 95°C (185 to 205°F).
2. Use an accurate digital voltmeter.
(1) Disconnect the oxygen sensor connector and connect a voltmeter to the oxygen sensor connector.
(2) While repeating engine racing, measure the oxygen sensor
output voltage.
,
IEngineOxygen sensoroutput voltageRemarks
Race0.6-l .OVMake air-fuel mixturerich by acceleratoroperation
NOTE
For removal and installation of the oxygen sensor, refer to
GROUP
15-Exhaust Manifold.
Oxygen sensor installation torque:
40-50 Nm
(30-36 ft.lbs.1
TSB Revision I
Page 232 of 1273
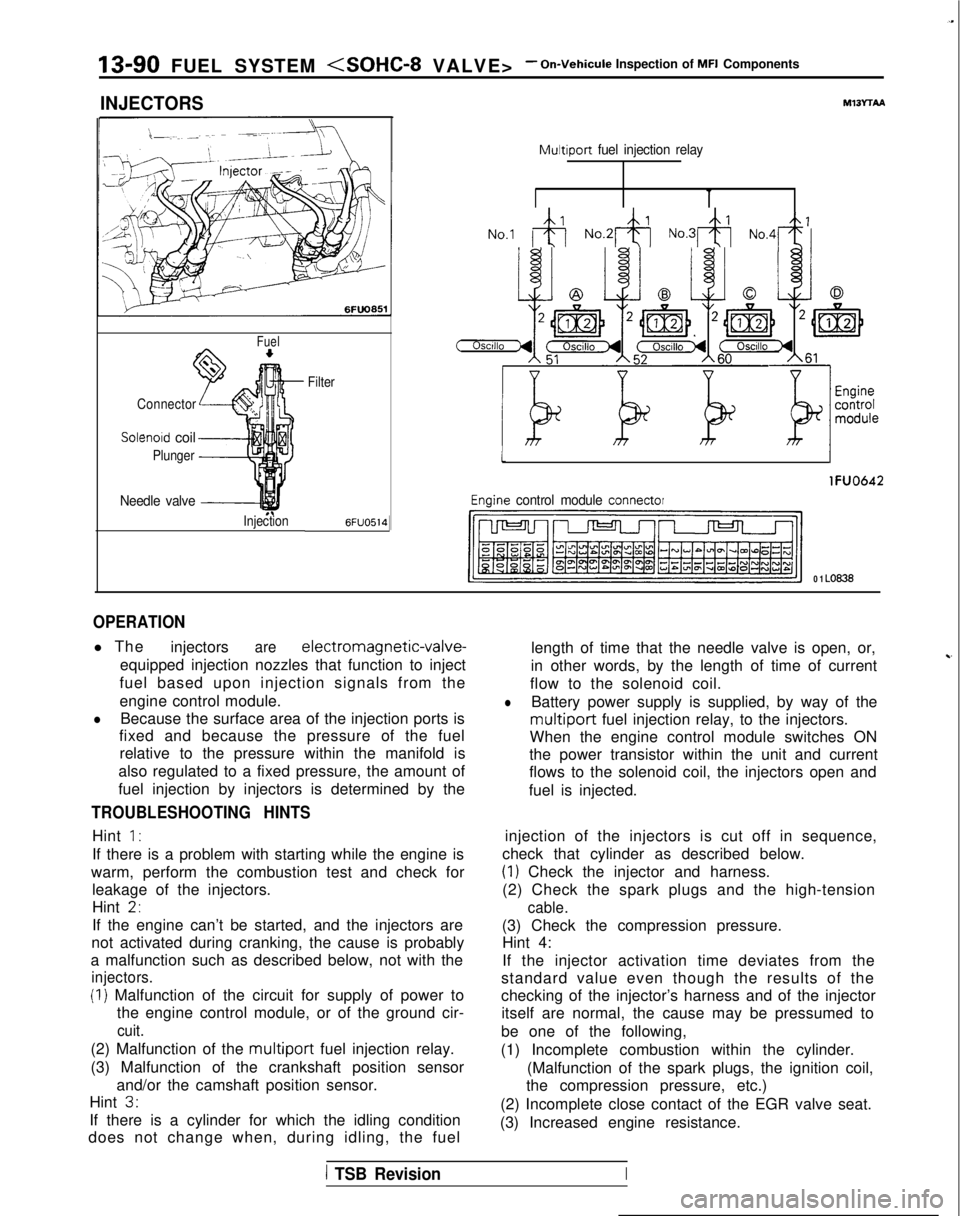
13-90 FUEL SYSTEM
INJECTORS
Fuel
Connector
Solenoid coil
Plunger
Needle valve -----I
InjectionFilter6FUO514
M13rrAA
Multiport
fuel injection relay
No.1 &j No.2& No.3& No,4+
tI
lFUO642
Engine control module connector
CJ=JW=U-I
0 1 LO636
OPERATION
l The
injectorsare electromagnetic-valve-
equipped injection nozzles that function to inject
fuel based upon injection signals from the
engine control module.
lBecause the surface area of the injection ports is
fixed and because the pressure of the fuel
relative to the pressure within the manifold is
also regulated to a fixed pressure, the amount of
fuel injection by injectors is determined by the
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
Hint 1:
If there is a problem with starting while the engine is
warm, perform the combustion test and check for leakage of the injectors.
Hint
2,
If the engine can’t be started, and the injectors are
not activated during cranking, the cause is probably
a malfunction such as described below, not with the
injectors.
(I) Malfunction of the circuit for supply of power to the engine control module, or of the ground cir-
cuit.
(2) Malfunction of the multiport fuel injection relay.
(3) Malfunction of the crankshaft position sensor and/or the camshaft position sensor.
Hint
3.
If there is a cylinder for which the idling condition
does not change when, during idling, the fuel length of time that the needle valve is open, or,
in other words, by the length of time of current
~-
flow to the solenoid coil.
lBattery power supply is supplied, by way of the
multiport fuel injection relay, to the injectors.
When the engine control module switches ON
the power transistor within the unit and current
flows to the solenoid coil, the injectors open and
fuel is injected.
injection of the injectors is cut off in sequence,
check that cylinder as described below.
(1) Check the injector and harness.
(2) Check the spark plugs and the high-tension
cable.
(3) Check the compression pressure. Hint 4:
If the injector activation time deviates from the
standard value even though the results of the
checking of the injector’s harness and of the injector itself are normal, the cause may be pressumed to
be one of the following,
(1) Incomplete combustion within the cylinder. (Malfunction of the spark plugs, the ignition coil,
the compression pressure, etc.)
(2) Incomplete close contact of the EGR valve seat.
(3) Increased engine resistance.
1 TSB RevisionI
Page 233 of 1273
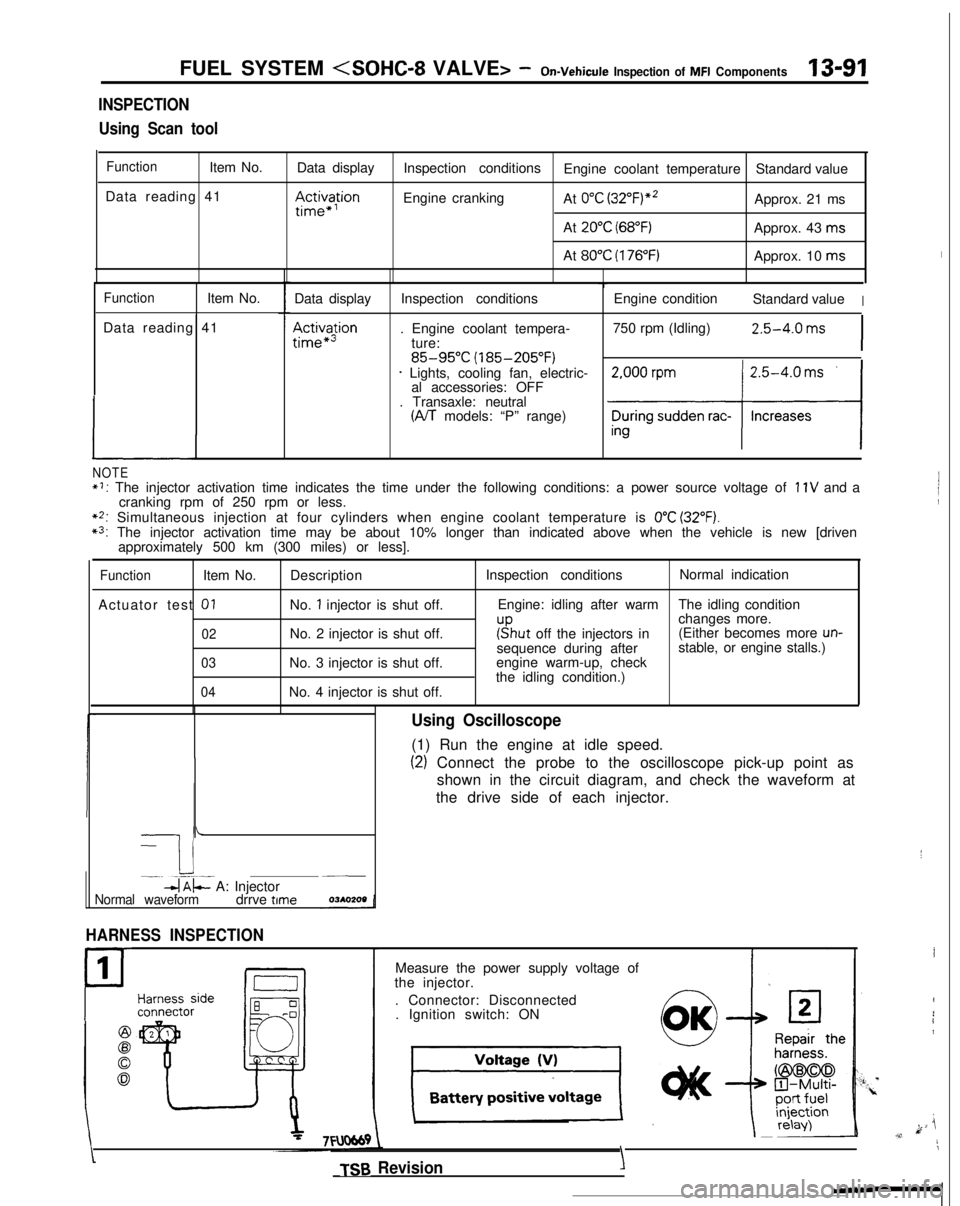
FUEL SYSTEM
Inspection of MFI Components13-91
INSPECTION
Using Scan tool
FunctionItem No. Data display
Data reading 41
III~~~ion
Inspection conditions Engine coolant temperature Standard value
Engine cranking At
0°C (3~2°F)“~Approx. 21 ms
At
20°C (68°F)Approx. 43 ms
At
80°C (176°F)Approx. 10 ms
FunctionItem No.
Data reading 41
L
Data display
Ac&a$ion
Inspection conditions
. Engine coolant tempera- ture:
85-95°C (185-205°F)* Lights, cooling fan, electric-al accessories: OFF
. Transaxle: neutral
(A/T models: “P” range) Engine condition
Standard value
I
750 rpm (Idling)2.5-4.0 ms
I
NOTE*I: The injector activation time indicates the time under the following con\
ditions: a power source voltage of 11V and a
cranking rpm of 250 rpm or less.
**: Simultaneous injection at four cylinders when engine coolant temperatur\
e is 0°C (32°F).*3: The injector activation time may be about 10% longer than indicated abo\
ve when the vehicle is new [driven approximately 500 km (300 miles) or less].
FunctionItem No.
Actuator test
01
02
03
04
Description
No.
1 injector is shut off.
No. 2 injector is shut off.
No. 3 injector is shut off.
No. 4 injector is shut off. Inspection conditions
Normal indication
Engine: idling after warm The idling condition
changes more.
r”sput off the injectors in(Either becomes more un-sequence during after stable, or engine stalls.)
engine warm-up, check
the idling condition.)
-
I i-. --.-~-db$- A: Injector~__
Normal waveformdrrve time
HARNESS INSPECTION
1
P
Using Oscilloscope
(1) Run the engine at idle speed.
(2) Connect the probe to the oscilloscope pick-up point as
shown in the circuit diagram, and check the waveform at
the drive side of each injector.
Measure the power supply voltage of
the injector.
. Connector: Disconnected. Ignition switch: ON
TSB Revision
I
I
4
i1
k ji,v,11
\
YIY’.
Page 234 of 1273
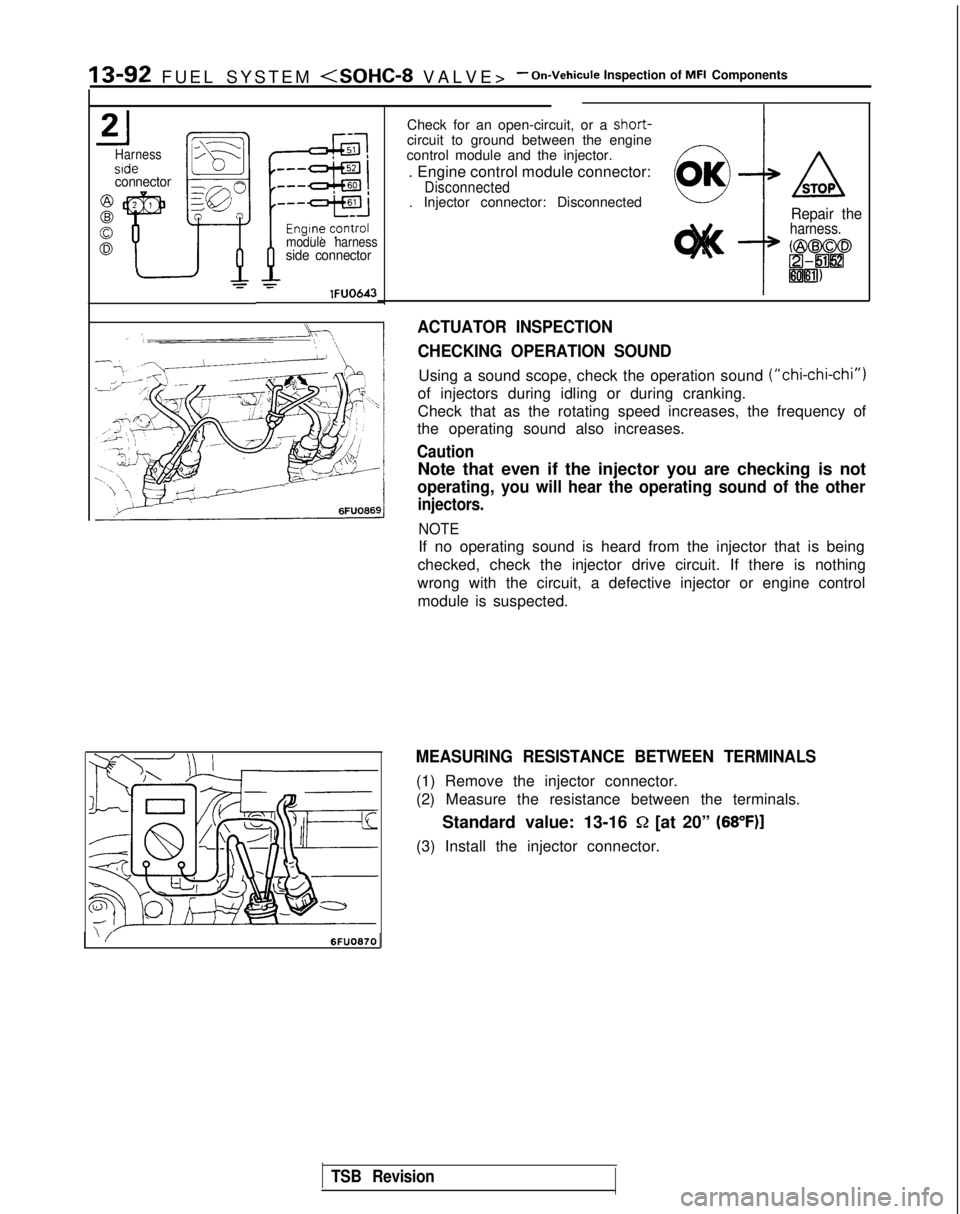
13-92 FUEL SYSTEM
- On-Vehicule Inspection of MFI Components
21Harnesssideconnector
g *’
gr
module harnessside connector
-rlFUO643
‘/6FUO870
Check for an open-circuit, or a short-circuit to ground between the engine
control module and the injector.
. Engine control module connector:
Disconnected. Injector connector: Disconnected
:
ASTOP
Repair theharness.
ACTUATOR INSPECTION
CHECKING OPERATION SOUND
Using a sound scope, check the operation sound (“chi-chi-chi”)
of injectors during idling or during cranking.
Check that as the rotating speed increases, the frequency of
the operating sound also increases.
Caution
Note that even if the injector you are checking is not
operating, you will hear the operating sound of the other
injectors.
NOTE
If no operating sound is heard from the injector that is being
checked, check the injector drive circuit. If there is nothing
wrong with the circuit, a defective injector or engine control module is suspected.
MEASURING RESISTANCE BETWEEN TERMINALS
(1) Remove the injector connector.
(2) Measure the resistance between the terminals.
Standard value: 13-16
Q [at 20” (68”F)]
(3) Install the injector connector.
TSB Revision
Page 235 of 1273
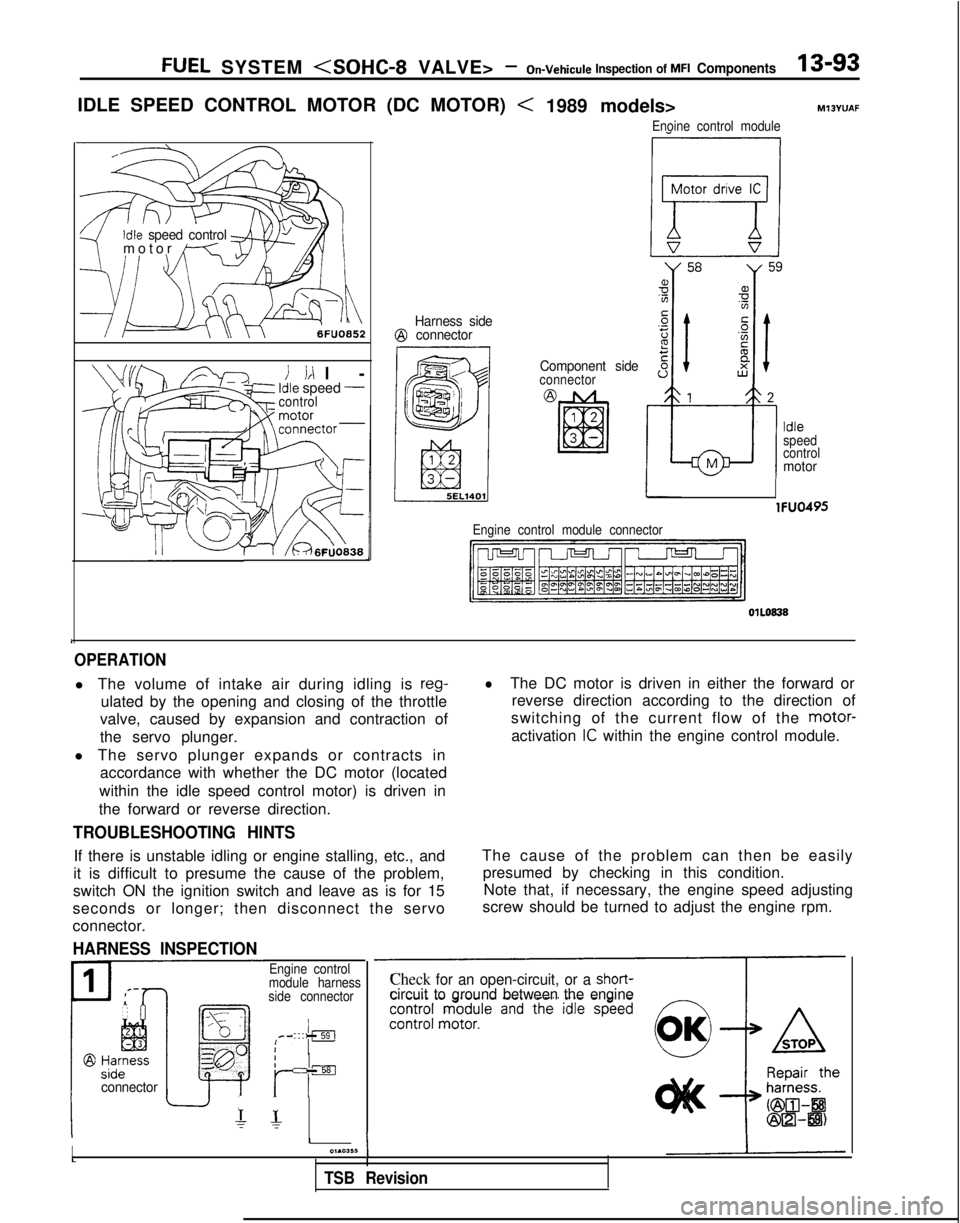
FUEL SYSTEM
IDLE SPEED CONTROL MOTOR (DC MOTOR)
Idle speed control9-/
motor
/---T-,I \
6FUO852
i id l
-
Idle speed -control
r1 /&46~U0838
Harness side@ connector
< 1989 models>
Enoine control module
M13YUAF
Component sideconnector
!
a,Yg
z.-t;Fs 8
B
12
d
Idle
speed
control
Mmotor
lFUO495
Engine control module connector
1
OPERATION
l The volume of intake air during idling is reg-
ulated by the opening and closing of the throttle
valve, caused by expansion and contraction of
the servo plunger.
l The servo plunger expands or contracts in accordance with whether the DC motor (located
within the idle speed control motor) is driven in
the forward or reverse direction.
lThe DC motor is driven in either the forward or reverse direction according to the direction of
switching of the current flow of the motor-
activation
IC within the engine control module.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
If there is unstable idling or engine stalling, etc., and
it is difficult to presume the cause of the problem,
switch ON the ignition switch and leave as is for 15
seconds or longer; then disconnect the servo
connector.
HARNESS INSPECTION
The cause of the problem can then be easily presumed by checking in this condition.Note that, if necessary, the engine speed adjusting
screw should be turned to adjust the engine rpm.
Iconnector
Engine control
module harness
side connector
IIrIsEI
r- r-
II01.03,~I
TSB Revision
Check for an open-circuit, or a short-circuit to ground between the engine